Sepiolite-Based Anisotropic Nanoparticles: A New Player in the Rubber Reinforcement Technology for Tire Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
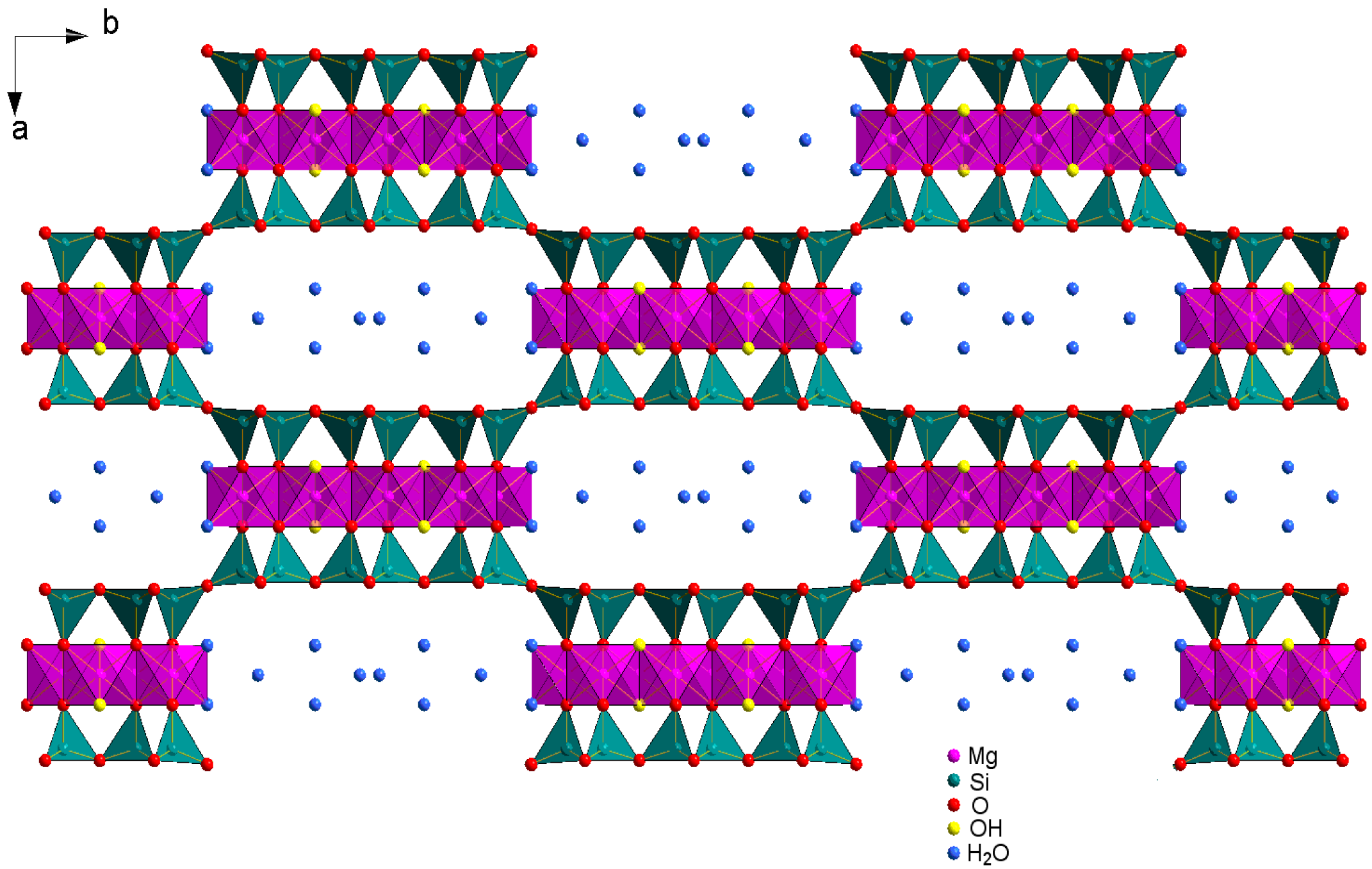
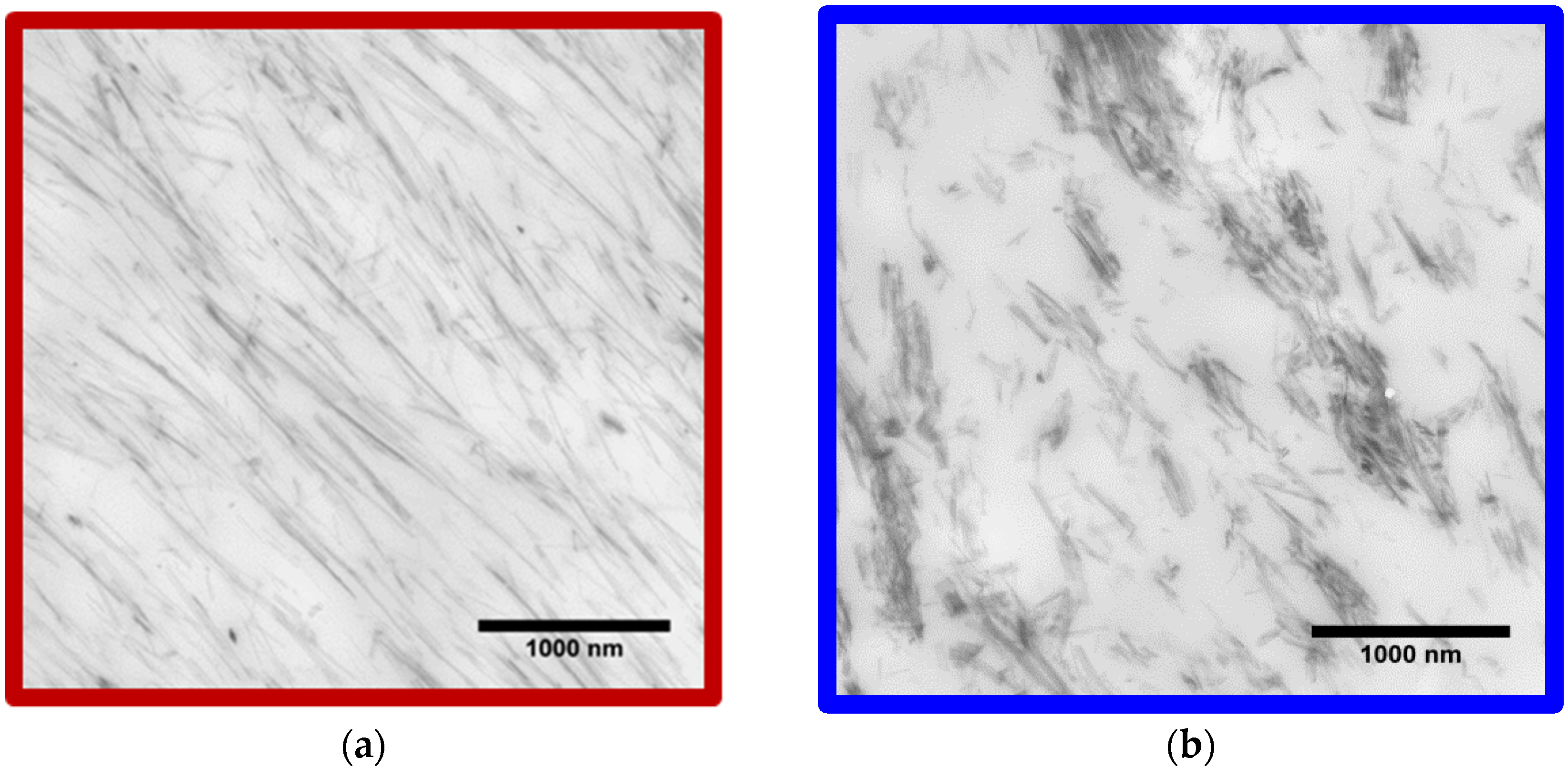
2. Sepiolite as a Reinforcing Filler
3. Sepiolite Hybrid Network Properties
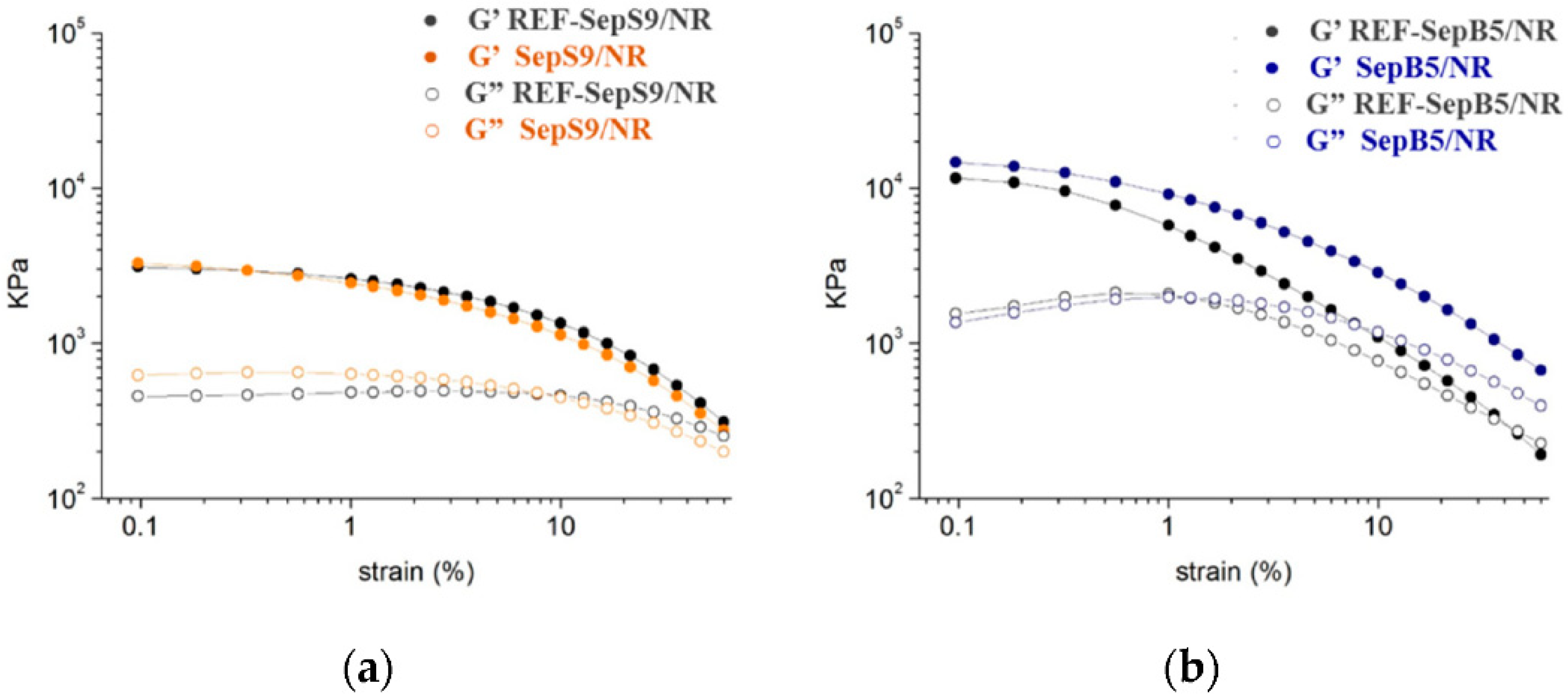
3.1. Filler Network Properties
3.2. The Silica-CB Network
3.3. Filler Networks with Other Nanofillers
4. Hybrid Filler Networks in Compounds for Tire Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Blanc, J.L. Rubber–filler interactions and rheological properties in filled compounds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 627–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brinke, J.W.; Debnath, S.C.; Reuvekamp, L.A.; Noordermeer, J.W. Mechanistic aspects of the role of coupling agents in silica–rubber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, J.; Niedermeier, W.; Luginsland, H.D. The effect of filler–filler and filler–elastomer interaction on rubber reinforcement. Compos. Part A 2005, 36, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, M. Rubber-Clay Nanocomposites: Science, Technology, and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbari, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Tl4CdI6 Nanostructures: Facile Sonochemical Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity for Removal of Organic Dyes. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 11443–11455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi-Derazkola, S.; Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Novel simple solvent-less preparation, characterization and degradation of the cationic dye over holmium oxide ceramic nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 9593–9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; El-Zein, A.; Airey, D.W.; Alonso-Marroquin, F.; Schubel, P.; Manalo, A. Self-healing polymers: Synthesis methods and applications. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2020, 23, 100500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.H. Overview—Clay mineral applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 1991, 5, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Aranda, P.; Álvarez, A.; Santarén, J.; Esteban-Cubillo, A. Advanced materials and new applications of sepiolite and palygorskite. Dev. Clay Sci. 2011, 3, 393–452. [Google Scholar]
- Di Credico, B.; Cobani, E.; Callone, E.; Conzatti, L.; Cristofori, D.; D’Arienzo, M.; Dirè, S.; Giannini, L.; Hanel, T.; Scotti, R.; et al. Size-controlled self-assembly of anisotropic sepiolite fibers in rubber nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 152, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustetto, R.; Seenivasan, K.; Bonino, F.; Ricchiardi, G.; Bordiga, S.; Chierotti, M.R.; Gobetto, R. Host/guest interactions in a sepiolite-based Maya Blue pigment: A spectroscopic study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 34, 16764–16776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, A.; García, N.; Guzmán, J.; Tiemblo, P. Surface modification of sepiolite nanofibers with PEG based compounds to prepare polymer electrolytes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokobza, L.; Chauvin, J.P. Reinforcement of natural rubber: Use of in situ generated silicas and nanofibres of sepiolite. Polymer 2005, 46, 4144–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, M.; Lostritto, A.; Spatola, A.; Guerra, G. Clay delamination in hydrocarbon rubbers. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2495–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, V.; Martín-de León, J.; Laguna-Gutiérrez, E.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.Á. PMMA-sepiolite nanocomposites as new promising materials for the production of nanocellular polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 96, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T.; Darr, J.A. Preparation of polypropylene/sepiolite nanocomposites using supercritical CO2 assisted mixing. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4931–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L.; Leroy, E.; Lalanne, V. Effect of filling mixtures of sepiolite and a surface modified fumed silica on the mechanical and swelling behavior of a styrene–butadiene rubber. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, C.; Aranda, P.; Moreira Martins Fernandes, F.M.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Procedimiento de Preparación de Xerogeles de Sepiolita, Productos Obtenidos y Utilización. WO2014177745A1, 6 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, K.; Tabuani, D.; Camino, G. Nanocomposites of PLA and PCL based on montmorillonite and sepiolite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, M.S.; Peli, G.; Barbera, V.; Locatelli, D.; Cipolletti, V.R.; Luca, G. Sepiolite for rubber nanocomposites with high mechanical reinforcement and low dissipation of energy. Rubber World 2019, 8, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, L.G.; Ibarra Rueda, L.M.; Antón, C.C. Magnesium silicate filler in rubber tread compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1987, 60, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, N. Compounding Precipitated Silica in Elastomers: Theory and Practice; Williams Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Galimberti, M.; Cipolletti, V.; Peli, G.; Barbera, V.; Bernardi, A.; Locatelli, D.; Giannini, L. Nanometric high aspect ratio fillers and chemical reactivity with the polymer matrix. In Proceedings of the 194th Technical Meeting of the Rubber Division of the American Chemical Society, Louisville, KY, USA, 9–11 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://web.mit.edu/ceder/publications/Percolation.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Concepts and conflicts in nanoparticles reinforcement to polymers beyond hydrodynamics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 84, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, J.; Fayolle, B.; Gilormini, P. A review on the Mullins effect. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, A.R. The dynamic properties of carbon black-loaded natural rubber vulcanizates. Part I. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1962, 6, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, S.; Ramezani, M.; Razzaghi-Kashani, M.; Bahramian, A.R. Nonlinear viscoelastic dissipation in vulcanizates containing carbon black and silanized silica hybrid fillers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2018, 91, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohjiya, S.; Kato, A.; Ikeda, Y. Visualization of nanostructure of soft matter by 3D-TEM: Nanoparticles in a natural rubber matrix. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, E. Theory of filler reinforcement. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1945, 18, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, M.; Agnelli, S.; Cipolletti, V. Hybrid filler systems in rubber nanocomposites. In Progress in Rubber Nanocomposites; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; p. 596. [Google Scholar]
- Galimberti, M.; Coombs, M.; Cipolletti, V.; Riccio, P.; Ricco, T.; Pandini, S.; Conzatti, L. Enhancement of mechanical reinforcement due to hybrid filler networking promoted by an organoclay in hydrocarbon based nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 65–66, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, R.; Conzatti, L.; D’Arienzo, M.; Di Credico, B.; Giannini, L.; Hanel, T.; Stagnaro, P.; Susanna, A.; Tadiello, L.; Morazzoni, F. Shape controlled spherical (0D) and rod-like (1D) silica nanoparticles in silica/styrene butadiene rubber nanocomposites: Role of the particle morphology on the filler reinforcing effect. Polymer 2014, 55, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobani, E.; Tagliaro, I.; Geppi, M.; Giannini, L.; Leclère, P.; Martini, F.; Nguyen, T.C.; Lazzaroni, R.; Scotti, R.; Tadiello, L.; et al. Hybrid interface in sepiolite rubber nanocomposites: Role of self-assembled nanostructure in controlling dissipative phenomena. Nanomaterials. 2019, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://velo.pirelli.com/it/it/tecnologia-pirelli-p-zero-velo (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Di Credico, B.; Tagliaro, I.; Cobani, E.; Conzatti, L.; D’Arienzo, M.; Giannini, L.; Mascotto, S.; Scotti, R.; Stagnaro, P.; Tadiello, L. A green approach for preparing high-loaded sepiolite/polymer biocomposites. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanni, M.N.; Giannini, L.; Lostritto, A. High Performance Tyre for Vehicle Wheels. International Patent Application WO2012164433, 6 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giannini, L.; Lostritto, A. Tire for Vehicle Wheels. International Patent Application WO2014068451, 8 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Giannini, L.; Lostritto, A.; Mariani, M. Tire for Vehicle Wheels. International Patent Application WO2014049516, 3 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Giannini, L.; Tadiello, L.; Jorge José, T.H.; Cacho, P.; Julve Sebastián, D.J. Microbeads Comprising Silicate Fibres with Needle-Shaped Morphology of Nanometric Size, Preparation Thereof, Elastomeric Compositions and Tyres for Vehicles Comprising Them. International Patent Application WO2019106562, 6 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brivio, P.; Meni, F.; Giannini, L.; Tadiello, L.; Misani, P. Tyre for Bicycle Wheels. International Patent Application WO2018207068, 15 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giannini, L.; Tadiello, L.; Hanel, T.; Galimberti, M.; Cipolletti, V.; Giulia, P.E.L.I.; Morazzoni, F.; Scotti, R.; Di Credico, B. Vulcanisable Elastomeric Materials for Components of Tyres Comprising Modified Silicate Fibres, and Tyres Thereof. European Patent Application EP3289013, 7 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tadiello, L.; Cipolletti, V.R.; Giannini, L.; Hanel, T.; Galimberti, M.; Scotti, R.; Di Credico, B.; Morazzoni, F.; D′arienzo, M.; Tagliaro, I. Elastomeric Compositions Comprising Silicate Fibres with Needle-Shaped Morphology of Nanometric Size and Tyres for Vehicles That Comprise Them. International patent application WO2018116125, 28 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://corporate.pirelli.com/corporate/en-ww/sustainability/sustainability-targets (accessed on 26 September 2021).

| Reference | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | 100 | 100 |
| Carbon Black | 63 | 56 |
| Sepiolite Pangel B5 | 9 | |
| Tensile modulus at 100% strain (MPa) | 4.5 | 6.5 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 19.5 | 20.1 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 374 | 350 |
| E′ (70 °C, 100 Hz), MPa | 16.9 | 20.6 |
| tanD (70 °C, 100 Hz) | 0.19 | 0.188 |
| Reference | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|
| Polyisoprene Rubber | 100 | 100 |
| Precipitated Silica | 50 | 27 |
| Sepiolite Pangel B5 | 5 | 27 |
| Tensile modulus at 100% strain (MPa) | 4.04 | 4.84 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 21.20 | 21.24 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 518 | 492 |
| E′ (23 °C, 100 Hz), MPa | 15.9 | 19.7 |
| E′ (100 °C, 100 Hz), MPa | 11.0 | 14.4 |
| Delta E′ (23–100 °C), % | 45% | 40% |
| Reference | Sep Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Black | 25 | 25 |
| Silica | 30 | 20 |
| Modified Sepiolite | - | 8.29 |
| E′ [MPa] 23 °C 100 Hz | 8.41 | 8.55 |
| E′ [MPa] 70 °C 100 Hz | 8.44 | 8.65 |
| Tan Delta 23 °C 100 Hz | 0.094 | 0.075 |
| Tan Delta 70 °C 100 Hz | 0.066 | 0.052 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadiello, L.; Guerra, S.; Giannini, L. Sepiolite-Based Anisotropic Nanoparticles: A New Player in the Rubber Reinforcement Technology for Tire Application. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052714
Tadiello L, Guerra S, Giannini L. Sepiolite-Based Anisotropic Nanoparticles: A New Player in the Rubber Reinforcement Technology for Tire Application. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(5):2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052714
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadiello, Luciano, Silvia Guerra, and Luca Giannini. 2022. "Sepiolite-Based Anisotropic Nanoparticles: A New Player in the Rubber Reinforcement Technology for Tire Application" Applied Sciences 12, no. 5: 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052714
APA StyleTadiello, L., Guerra, S., & Giannini, L. (2022). Sepiolite-Based Anisotropic Nanoparticles: A New Player in the Rubber Reinforcement Technology for Tire Application. Applied Sciences, 12(5), 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052714





