Dynamic Analysis of Quasi-Zero Stiffness Pneumatic Vibration Isolator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model of Quasi-Zero Stiffness Pneumatic Vibration Isolator
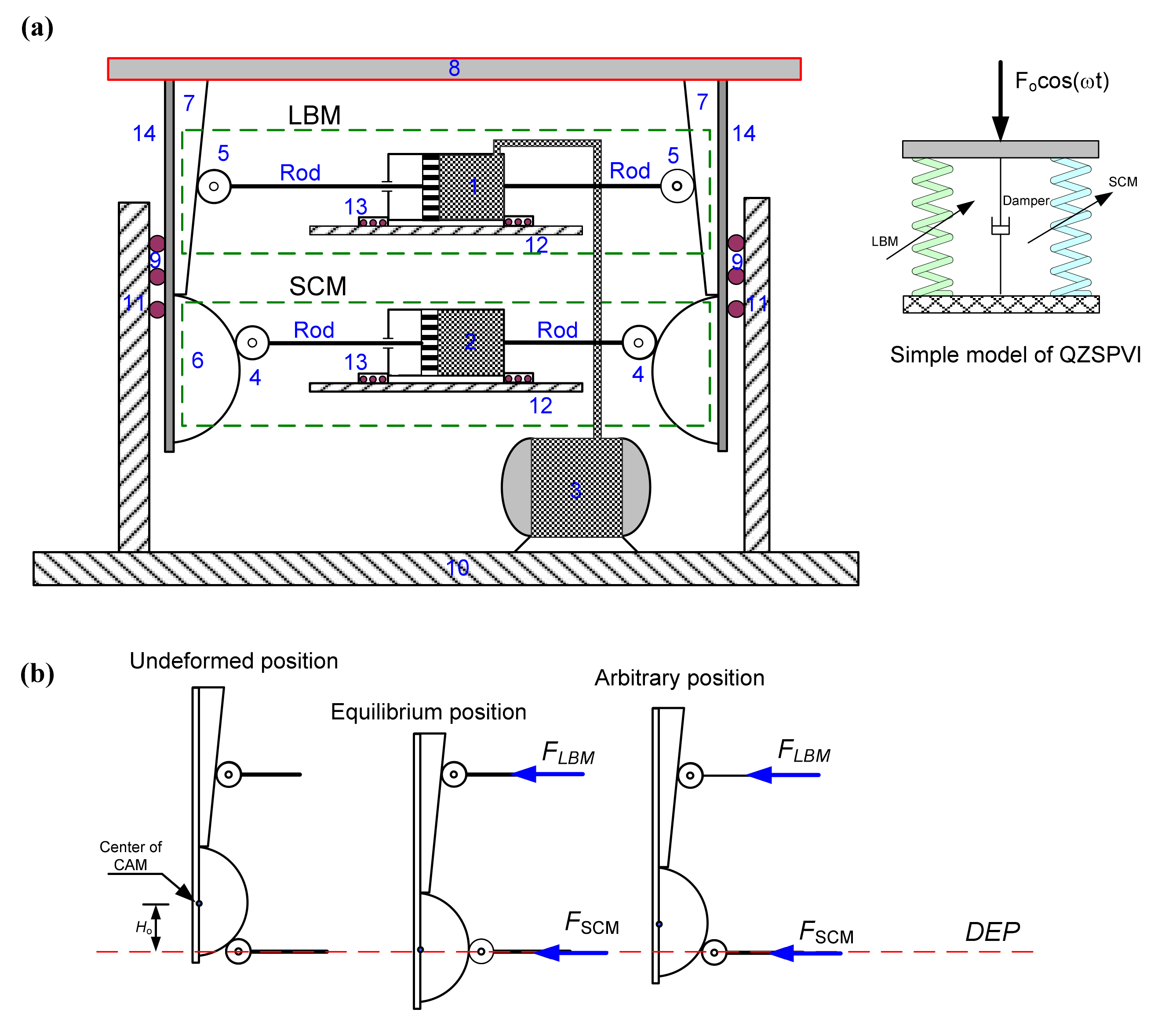
2.1. Description
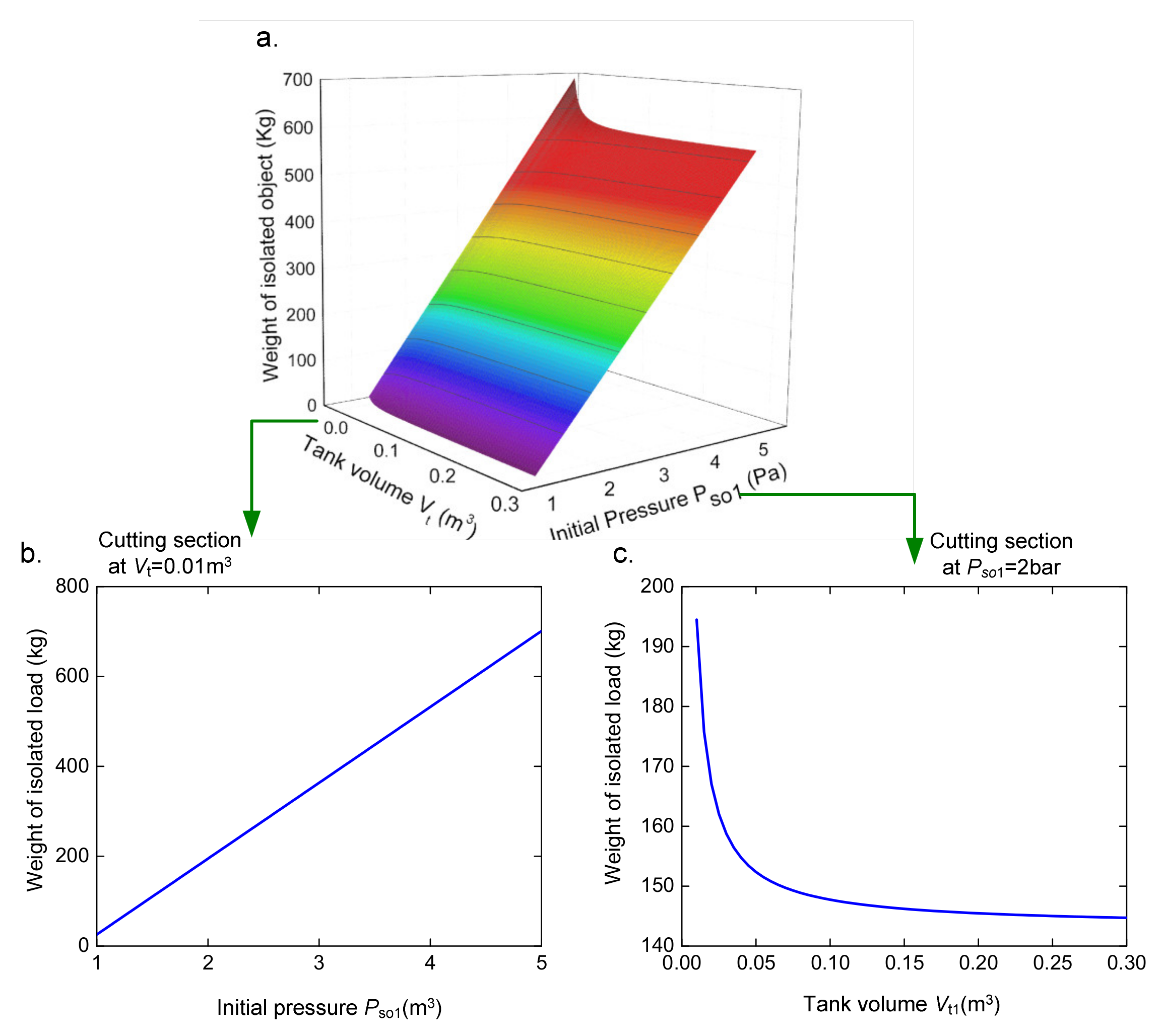
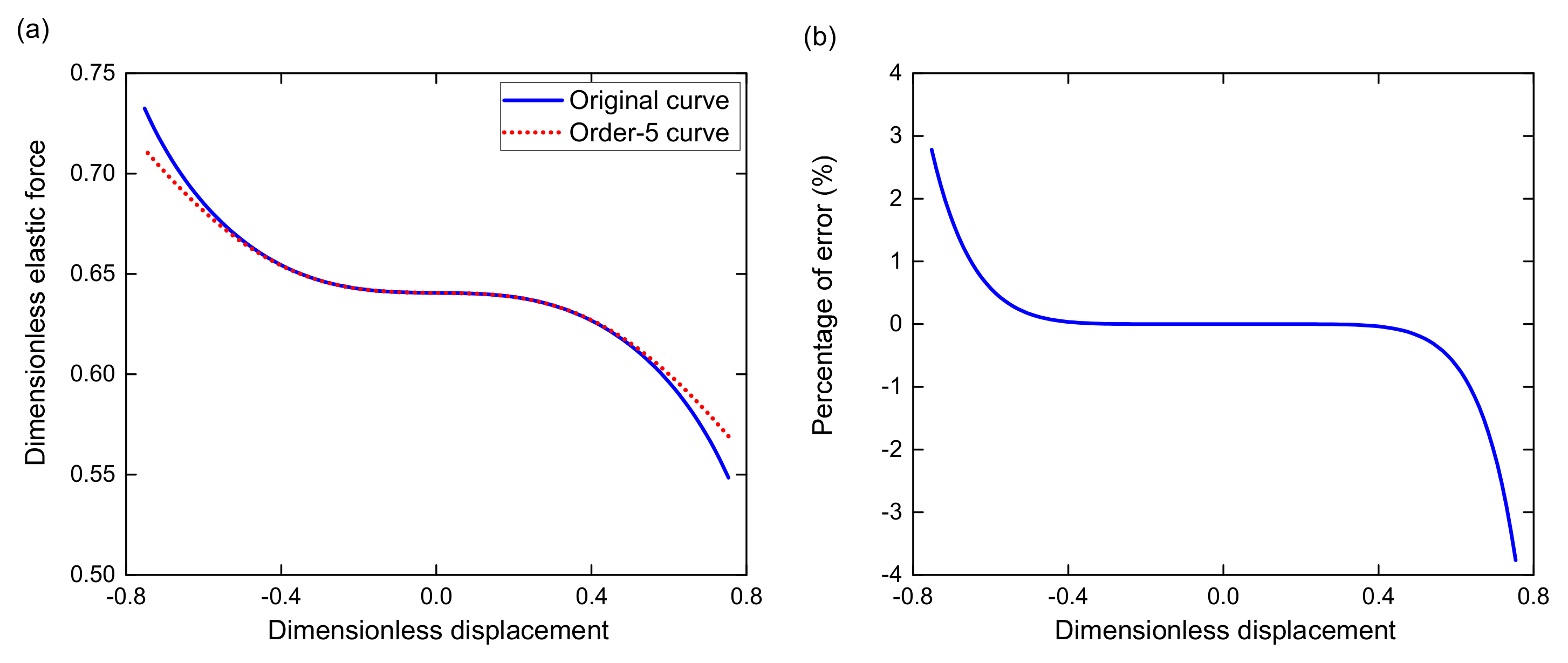
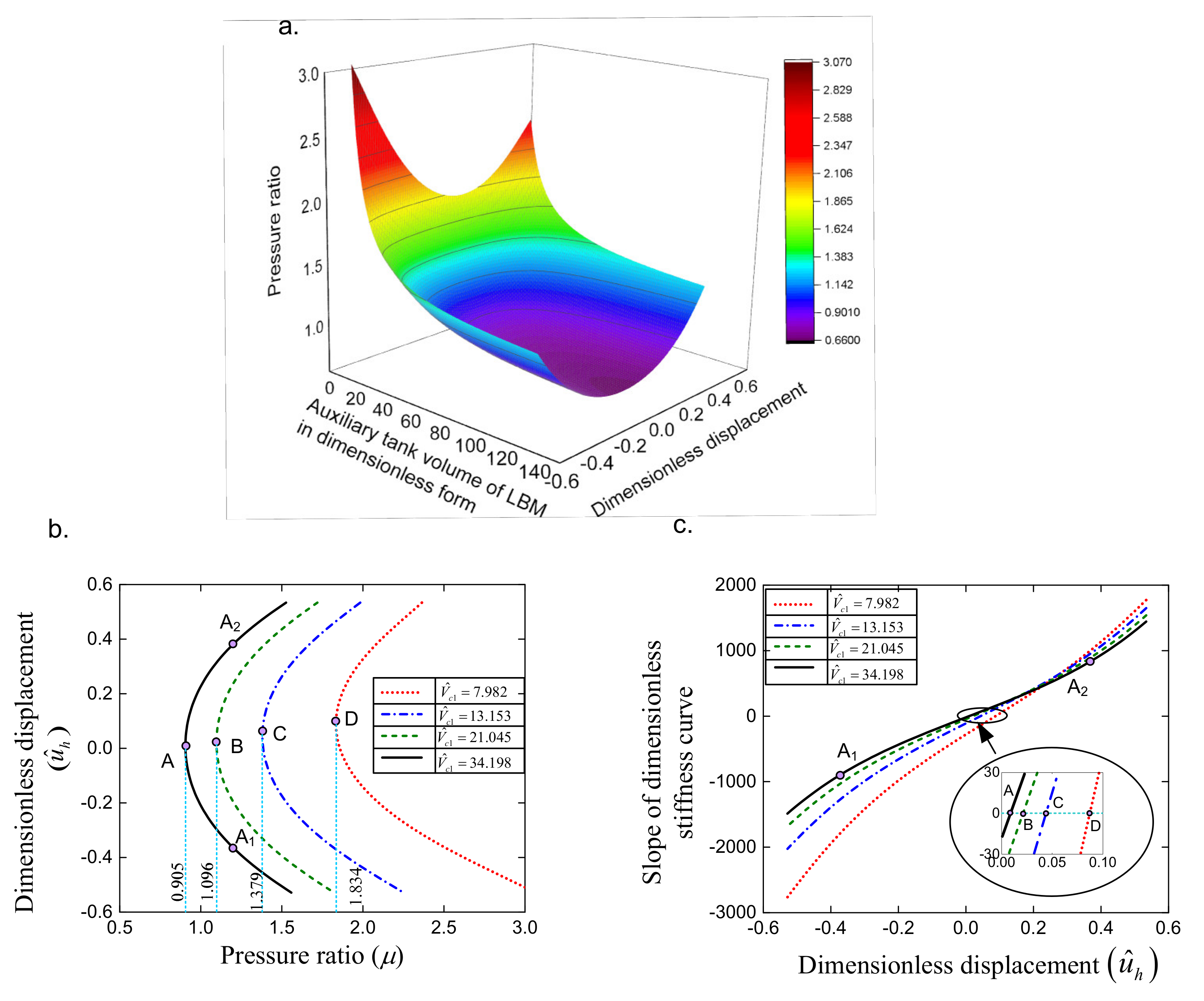
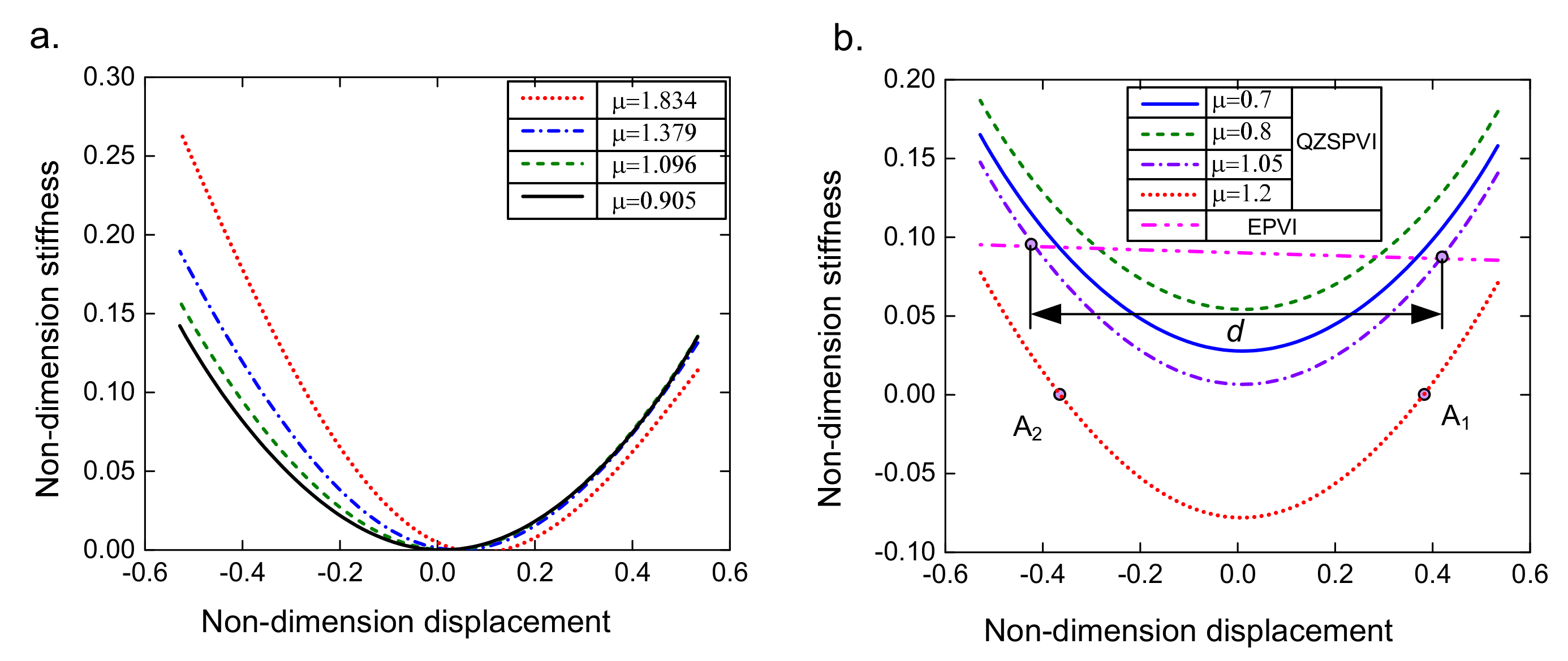
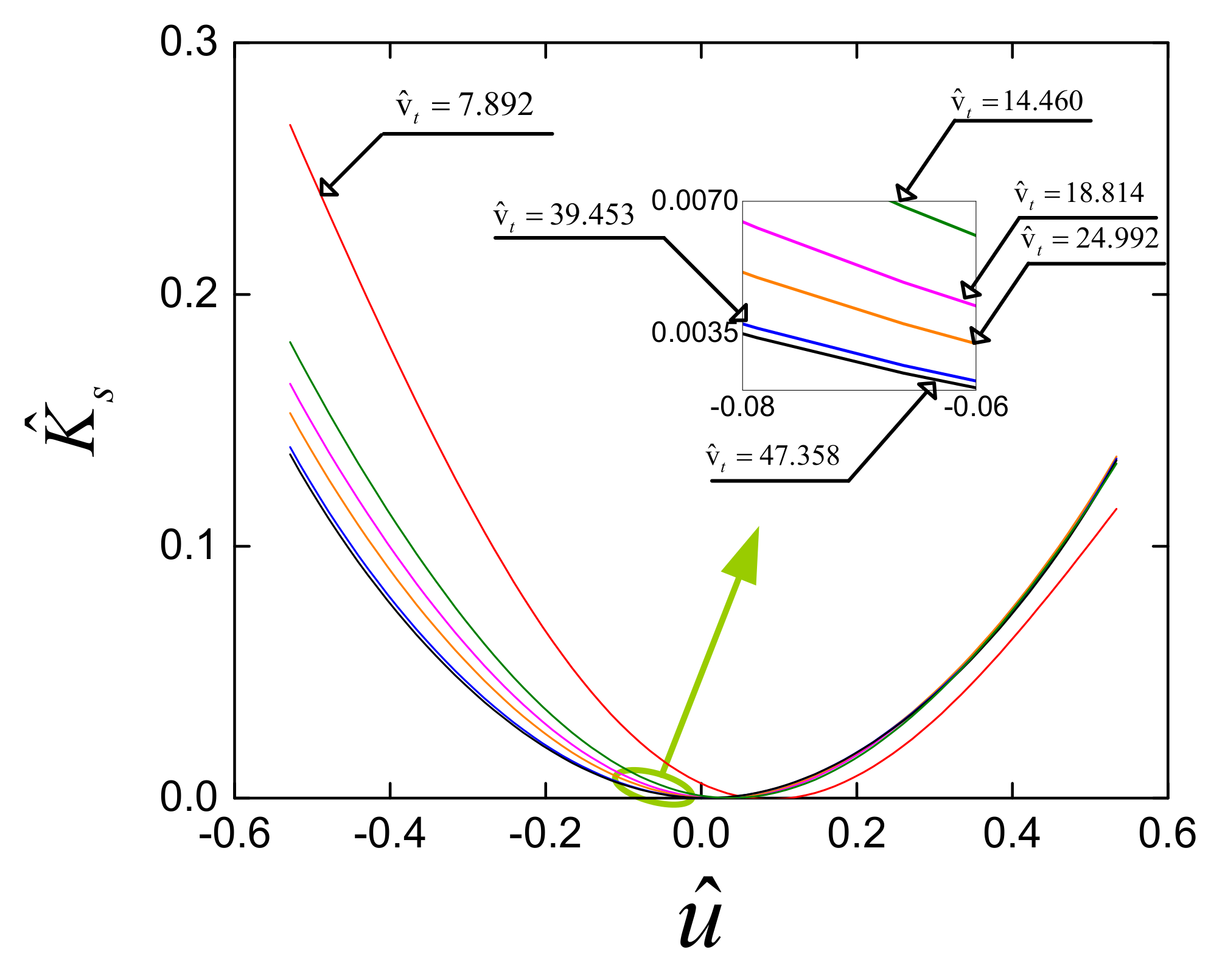
2.2. Stiffness Analysis
3. Dynamic Analysis
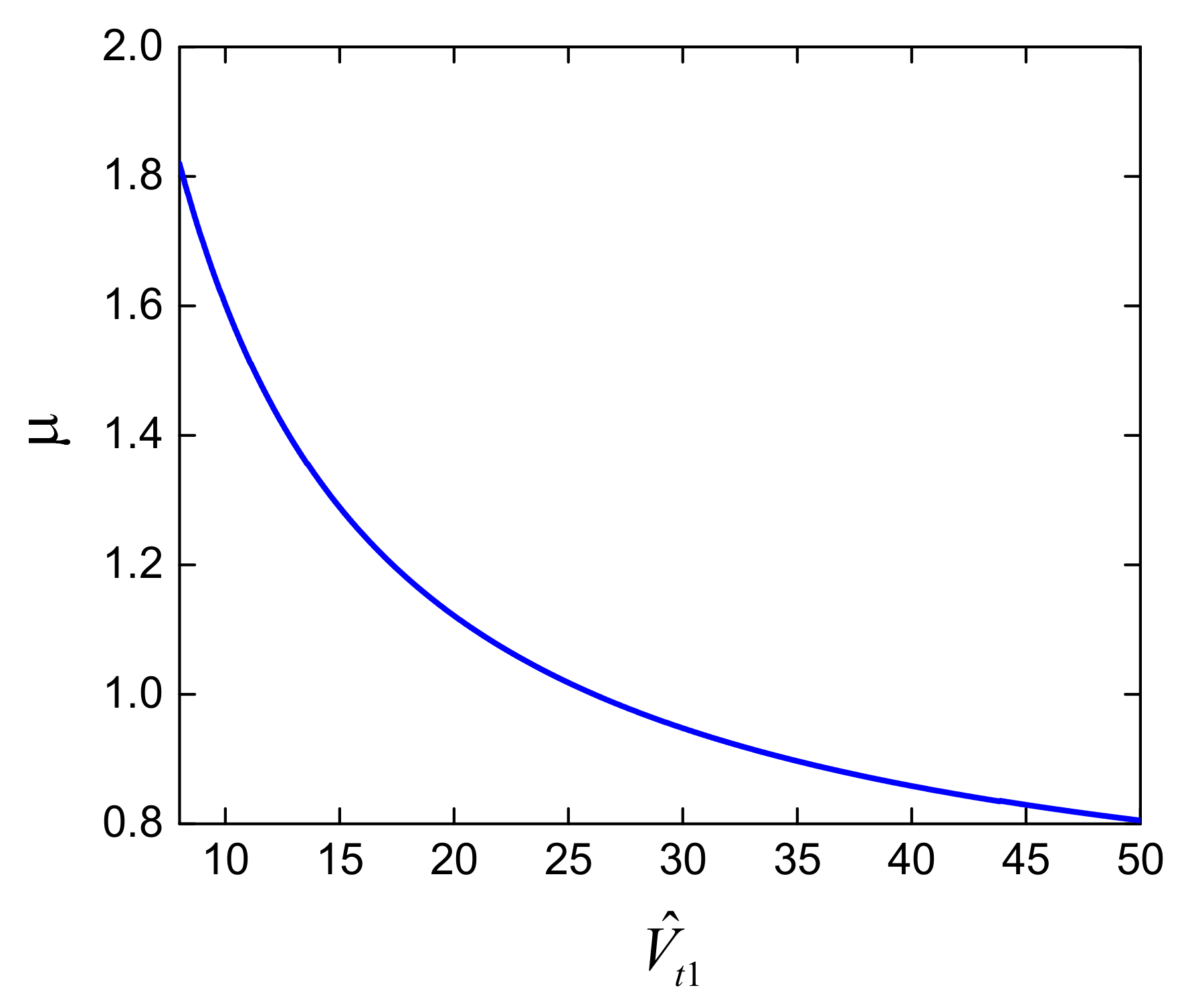
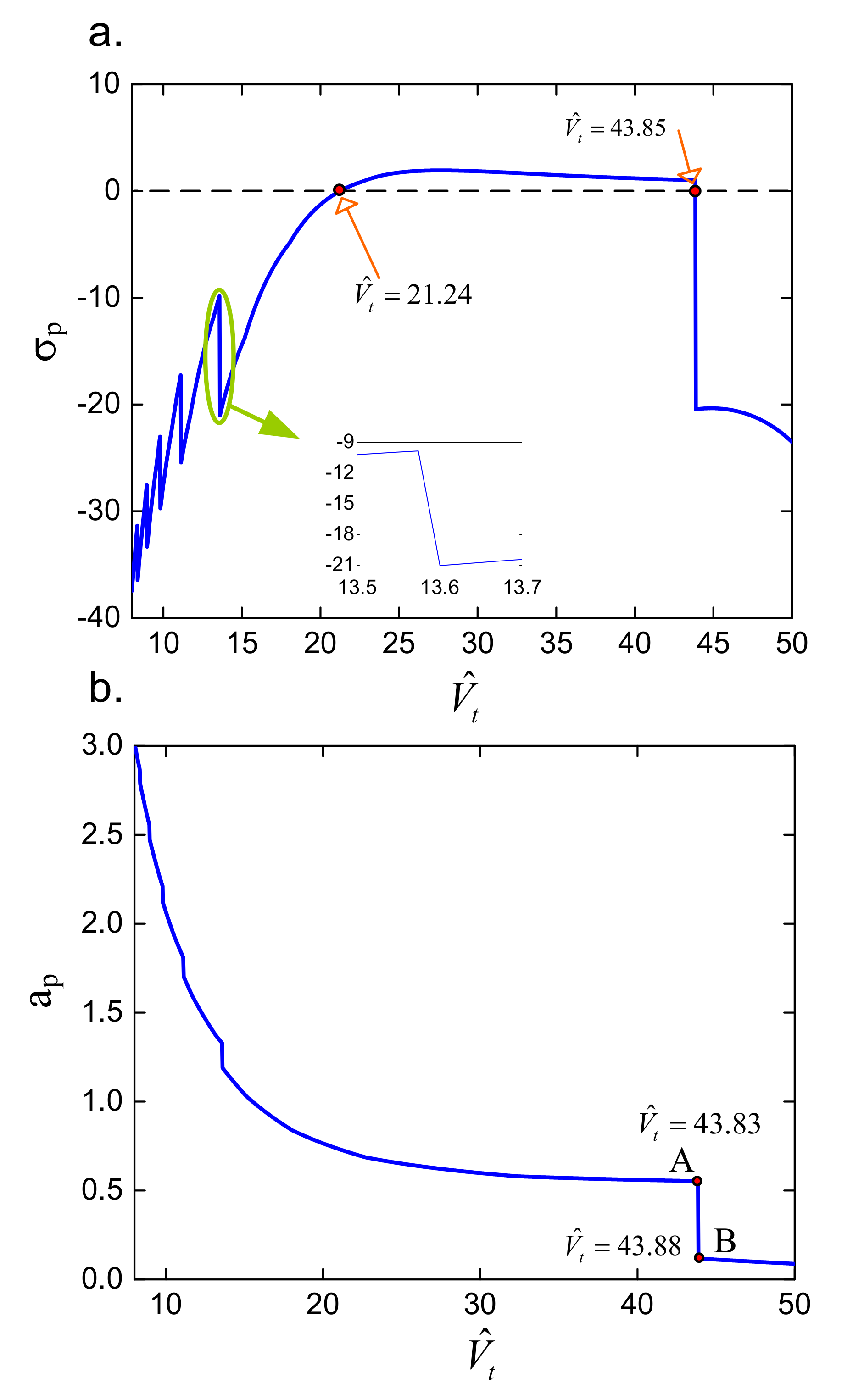
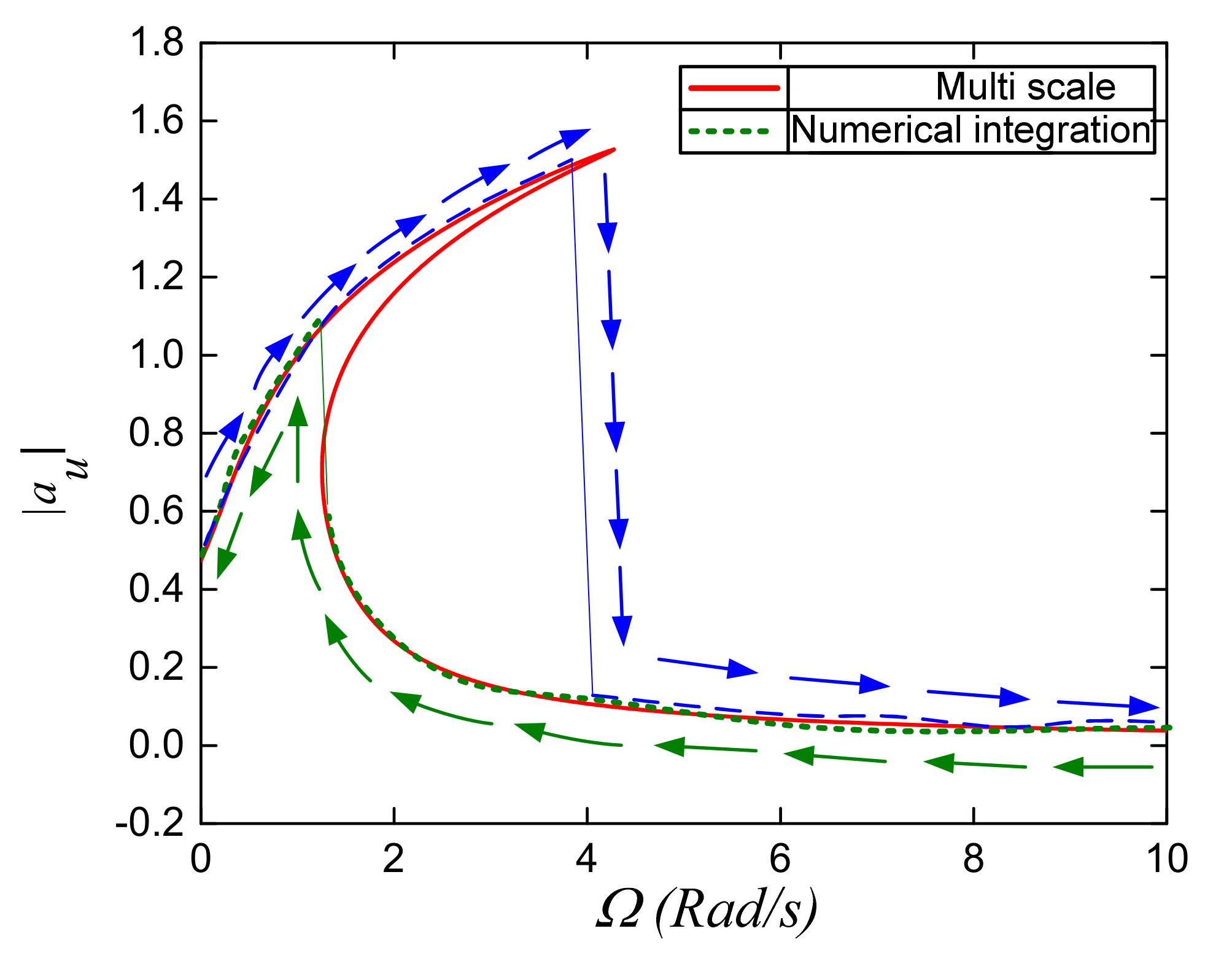
3.1. Primary Frequency—Amplitude Relation
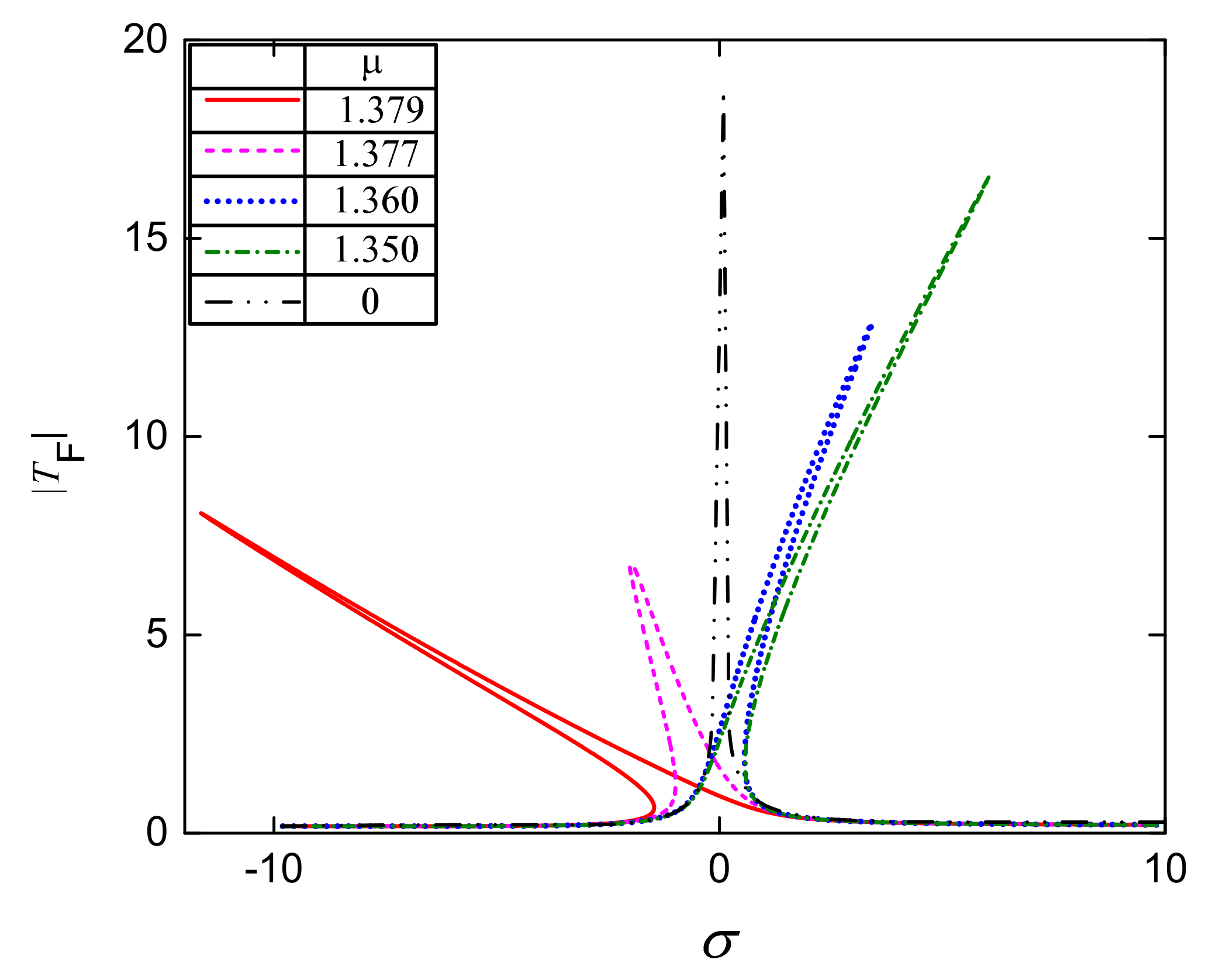
3.2. Transmissibility for Force Excitation
4. Numerical Simulation
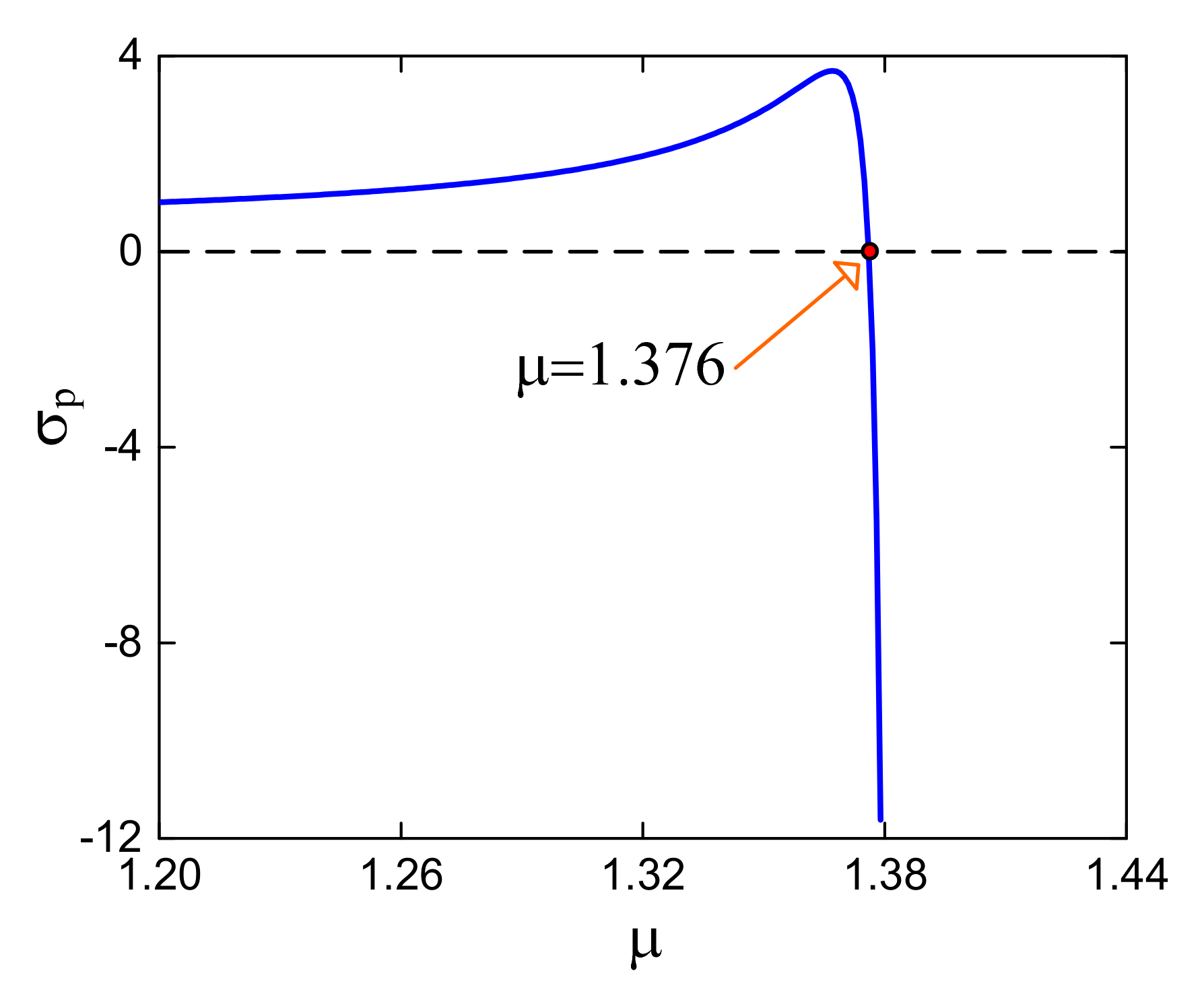
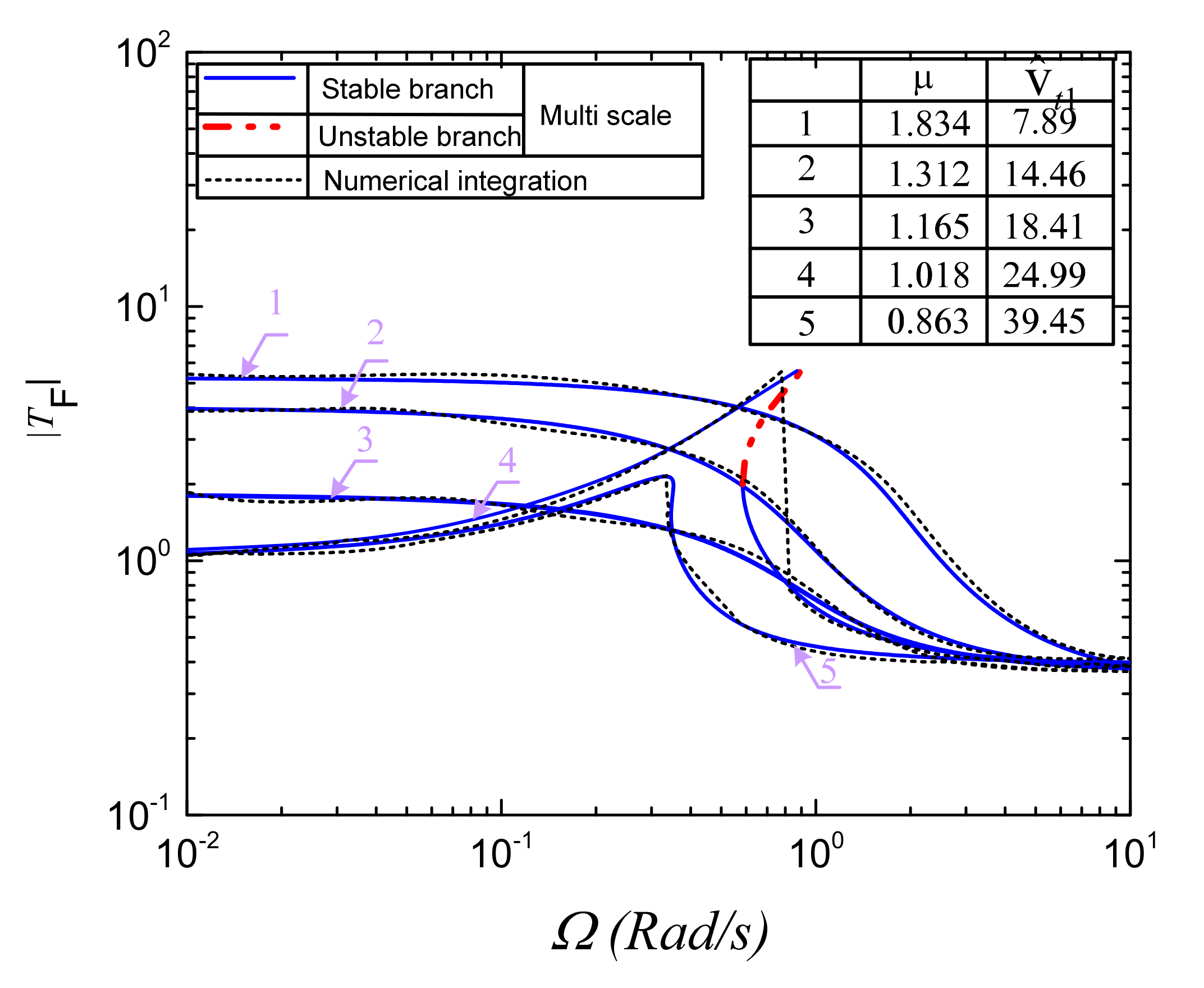
4.1. Influence of Parameters on the Force Transmitted Curve
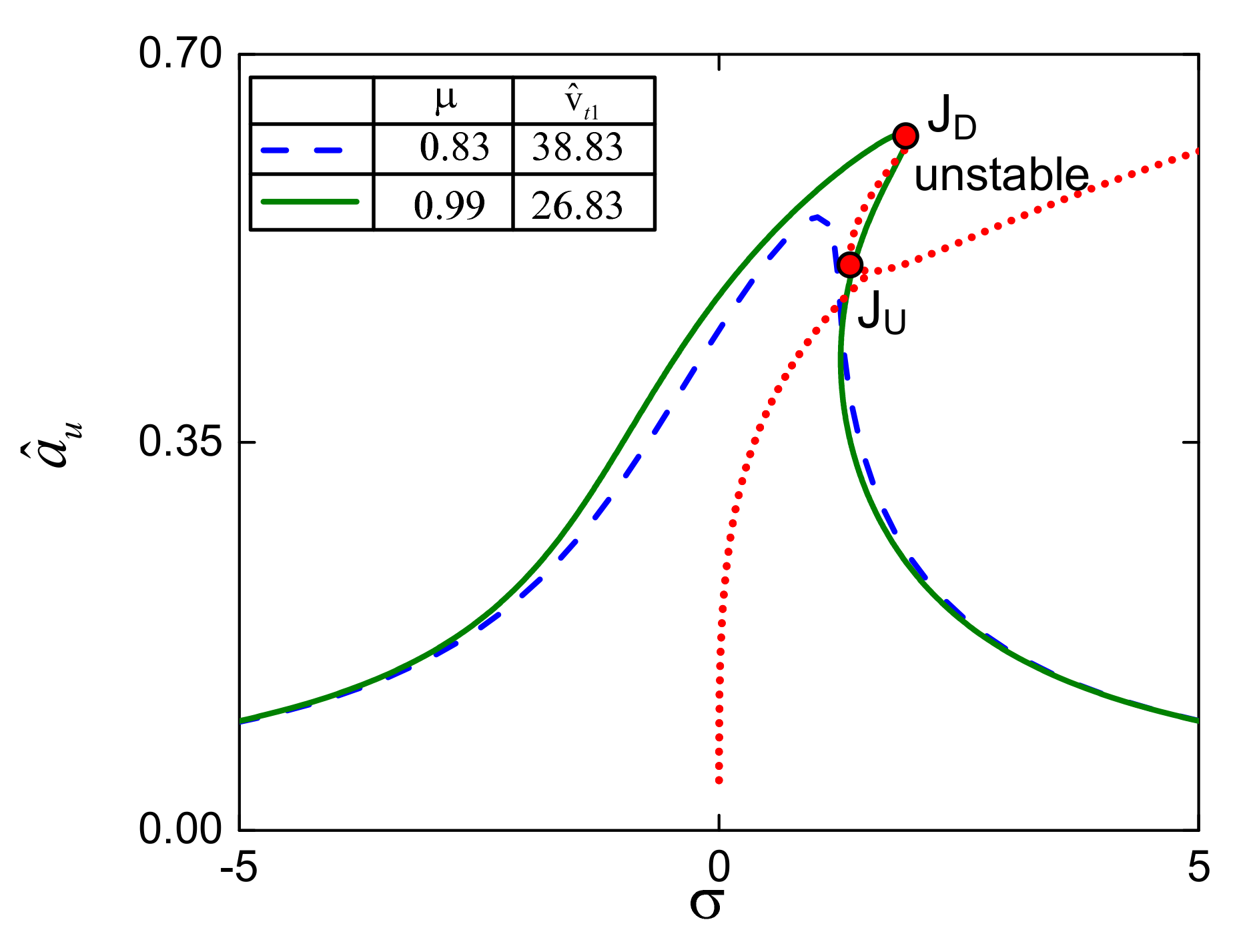
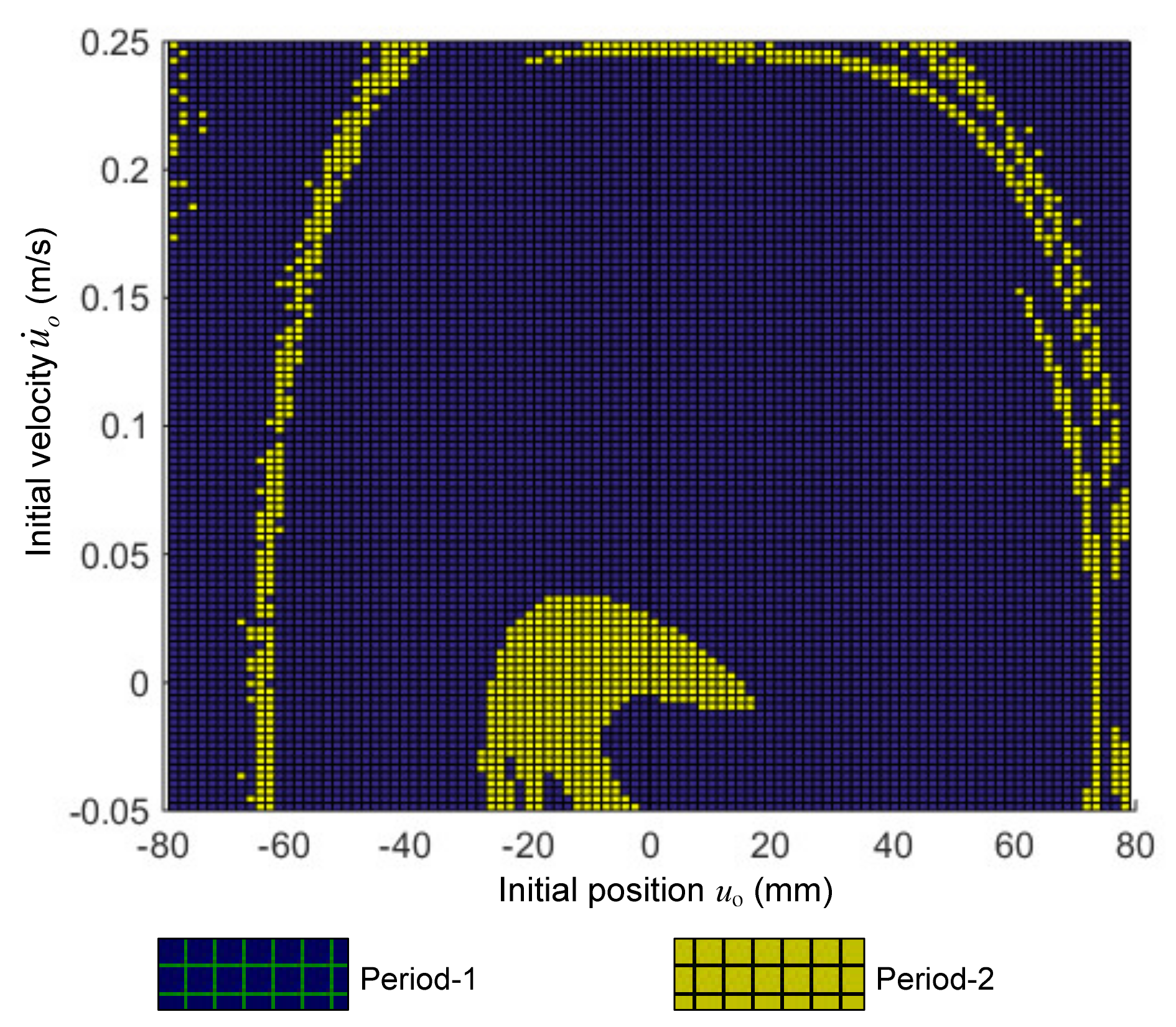
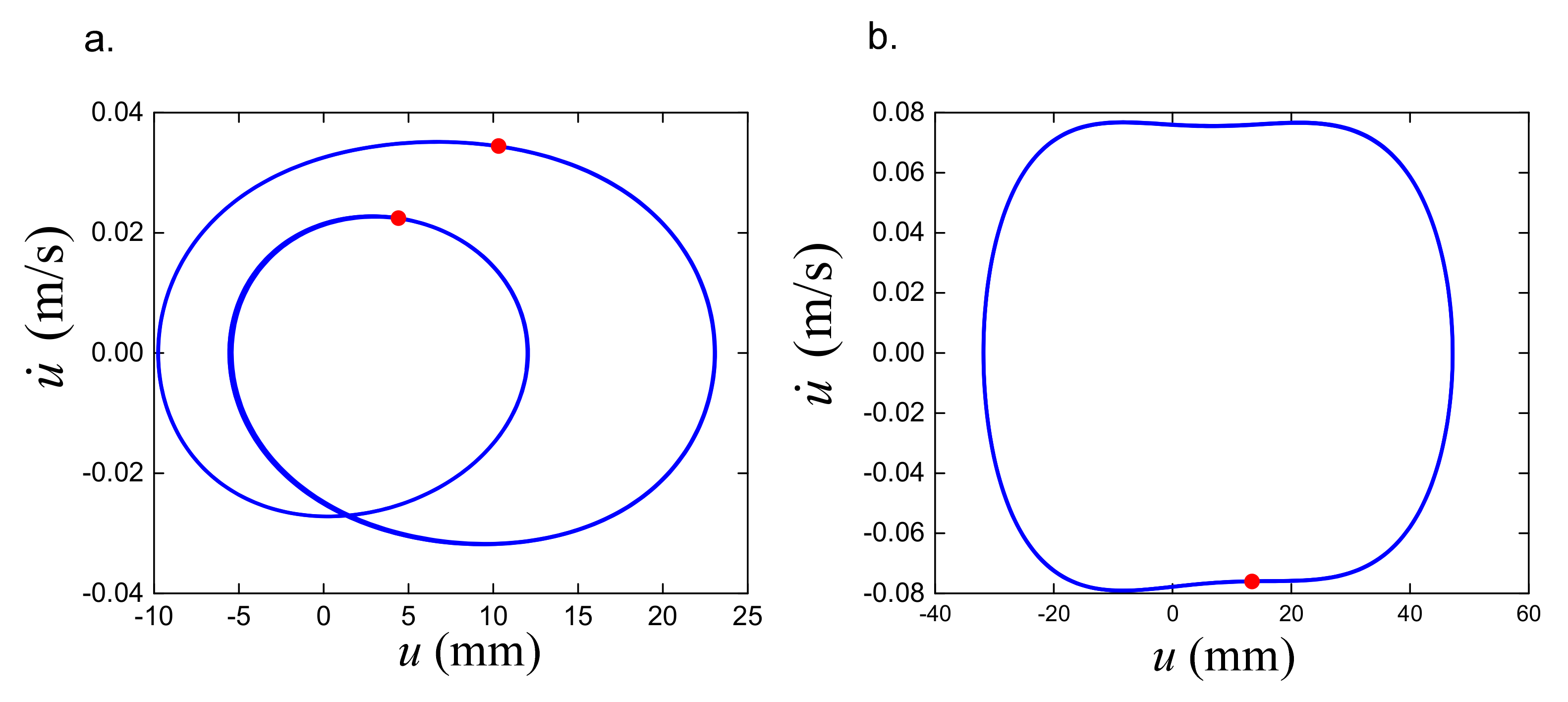
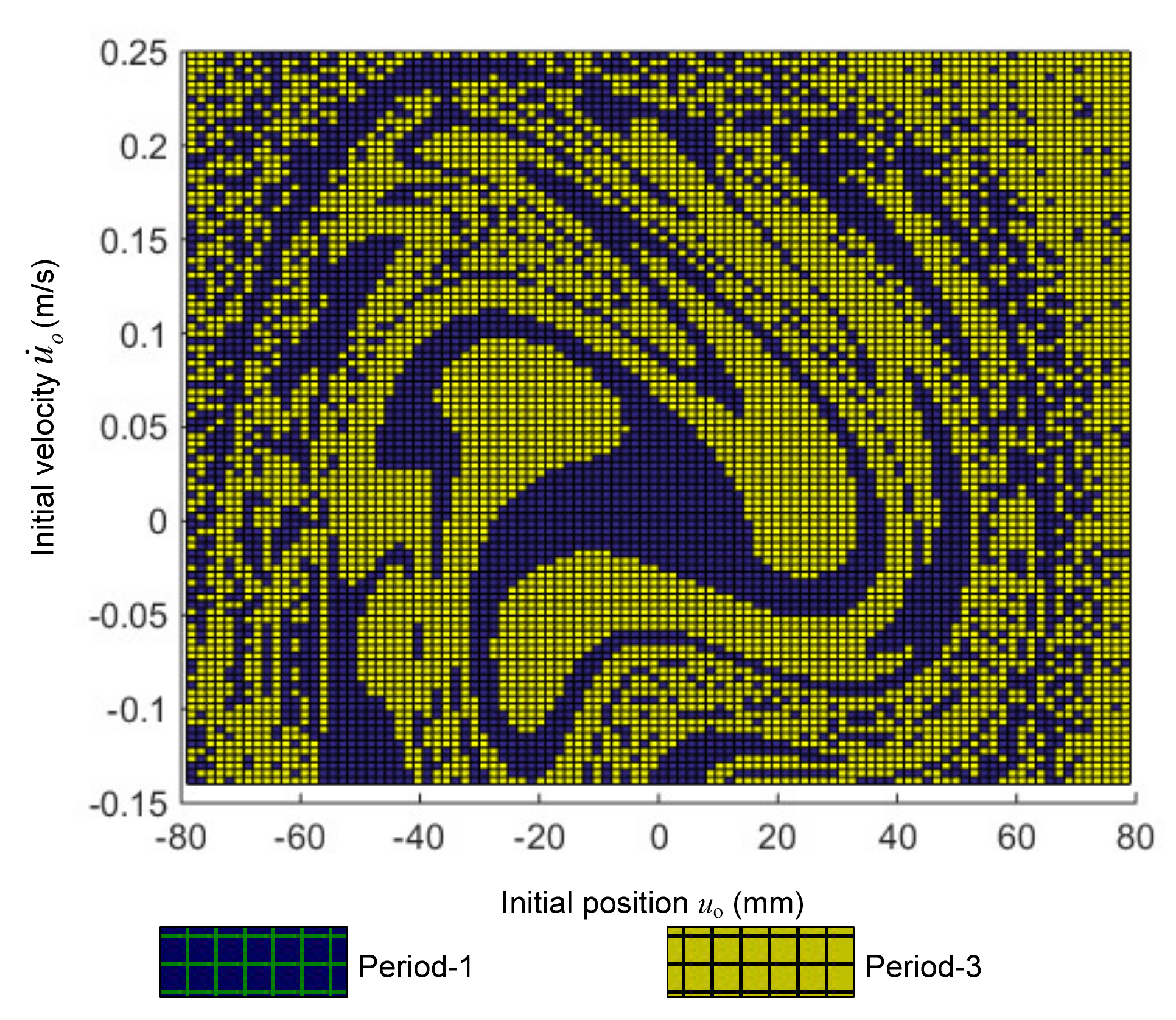
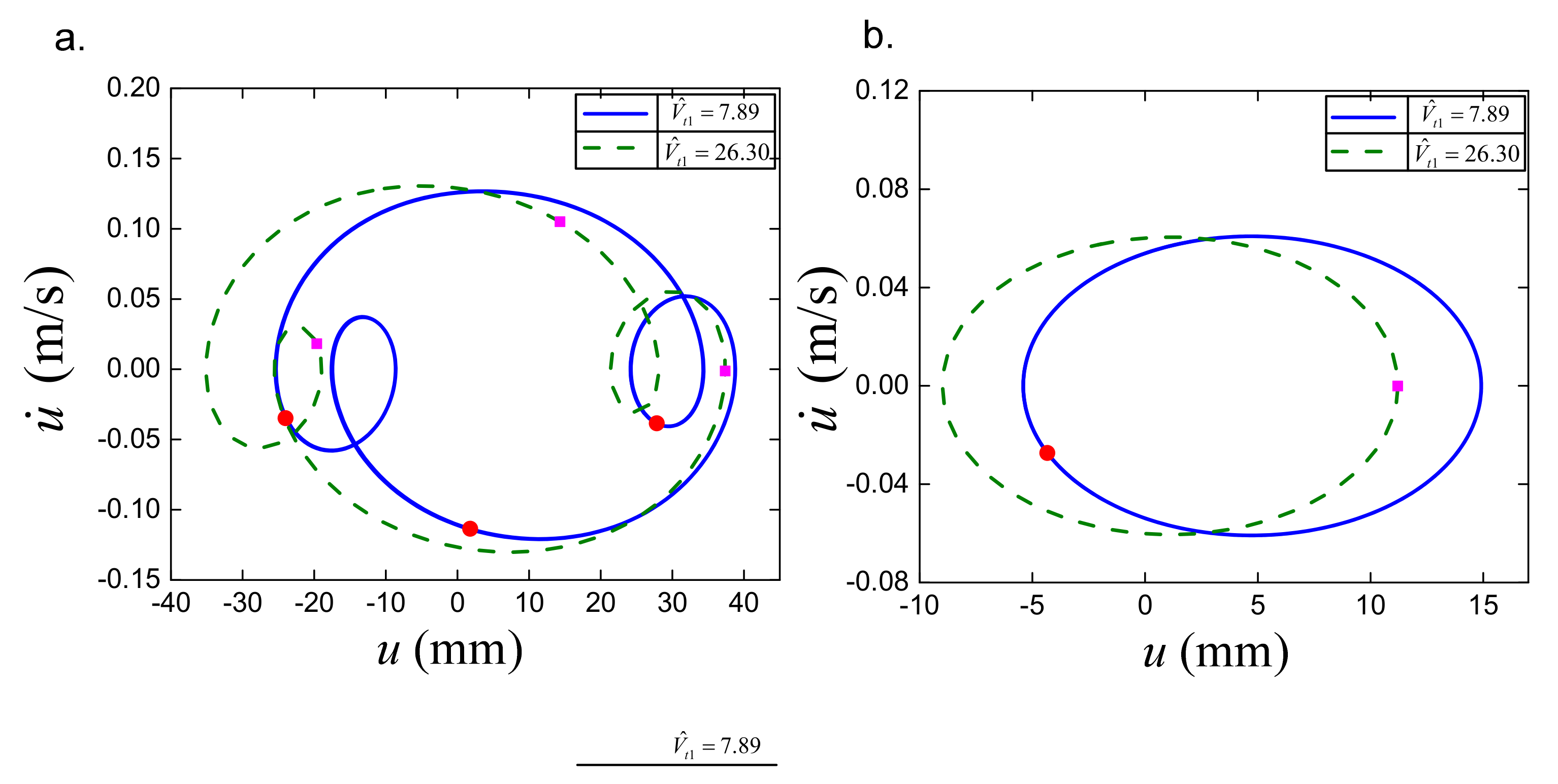
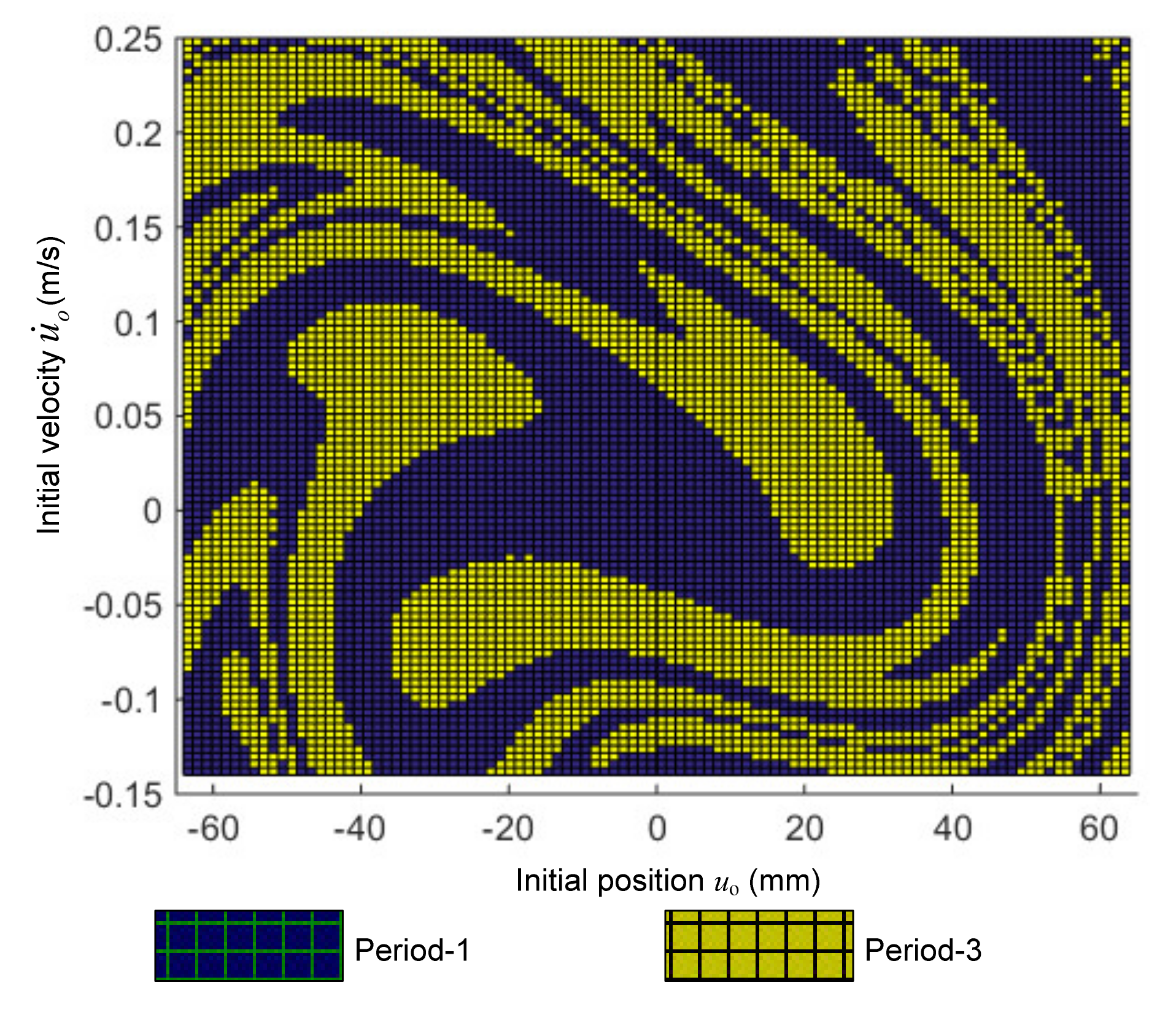
4.2. Complex Dynamic Response
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, H.; Yan, J. Micro-cutting characteristics of EDM fabricated high-precision polycrystalline diamond tools. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 2013, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Pan, W.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Sun, Y. Fabrication of micro-reentrant structures by liquid/gas interface shape-regulated electrochemical deposition. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 2020, 10, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, K. Accurate modeling and analysis of a typical nonlinear vibration isolator with quasi-zero stiffness. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 2141–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, J.; Chang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y. A nonlinear ultra-low-frequency vibration isolator with dual quasi-zero-stiffness mechanism. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 101, 755–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. On the analytical and experimental assessment of the performance of a quasi-zero-stiffness isolator. J. Vib. Control 2013, 20, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.D.; Ahn, K.K. Experimental investigation of a vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structure. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2013, 70, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Bishop, S. Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with cam-roller- spring mechanism. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 346, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.C.; Yang, S.A.; Wu, Y.S. Design and experiment of a compact quasi-zero-stiffness isolator capable of wide range of loads. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 4843–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jing, X. Multi-direction vibration isolation with quasi-zero stiffness by employing geometrical nonlinearity. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 62, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Cao, Q. The isolation characteristics of an archetypal dynamical model with stable-quasi-zero-stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 340, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, K.; Yang, Q.C.; Lou, J.J. Dynamic characteristic analysis of two-stage quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolation system. J. Vibroengineering 2016, 10, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, L.Q. Nonlinear vibration isolation for fluid-conveying pipues using quasi-zero stiffness characteristics. J. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 121, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G. Statics and dynamics of a nonlinear oscillator with quasi-zero stiffness behaviour for large deflections. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2019, 83, 105143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Jing, X. Analysis and design of a novel and compact X-structured vibration isolation mount (X-Mount) with wider quasi-zerostiffness range. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 101, 2195–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G. Optimizing elastic potential energy via geometric nonlinear stiffness. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2021, 103, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Zou, H.X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.M. Bio-inspired vibration isolation: Methodology and design. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2021, 73, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.D.; Nguyen, V.A.D. Low frequency vibration isolator with adjustable configurative parameter. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 134, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Yan, B.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. A Stewart isolator with high-static-low-dynamic stiffness struts based on negative stiffness magnetic springs. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 422, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lue, Y.; Yan, B.; Ma, C. Design and experiment of a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness isolator using a negative stiffness magnetic spring. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 360, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shao, S.; Tian, Z.; Xu, M.; Xie, M. Active passive hybrid vibration isolation with magnetic negative stiffness isolator based on Maxwell normal stress. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 123, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, S. Analytical study of the low frequency multi-direction isolator with high-static-low-dynamic stiffness struts and spatial pendulum. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 110, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhao, J.; Bian, X.; Zou, L. Improving low frequency isolation performance of optical platforms using electromagnetic active-negative-stiffness method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Meng, K.; Wang, W.; Pu, H.; Peng, Y.; Luo, J.; Xie, S. A tunable quasi-zero stiffness isolator based on a linear electromagnetic spring. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 482, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erin, B.; Wilso, B.; Zapfe, J. An improved model of a pneumatic vibration isolator: Theory and experiment. J. Sound Vib. 1998, 218, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.J. Modelling of nonlinear complex stiffness of dual-chamber pneumatic spring for precision vibration isolators. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 301, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankovits, T.; Szabó, T. Finite element analysis of rubber bumper used in air-springs. Procedia Eng. 2012, 48, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danh, L.T.; Ahn, K.K. Active pneumatic vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structures for a vehicle seat. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 1245–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.D.; Bui, M.T.N.; Ahn, K.K. Improvement of vibration isolation performance of isolation system using negative stiffness structure. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, E.; Nieto, A.J.; Morales, A.L.; Chicharro, J.M.; Pintado, P. Numerical and experimental analysis of a vibration isolator equipped with a negative stiffness system. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 414, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Ho, C.M.; Ahn, K.K. An air spring vibration isolator based on a negative stiffness structure for vehicle seat. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.Y.P.; Le, T.D. Static analysis of low frequency isolation model using pneumatic cylinder with auxiliary chamber. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 21, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Sun, B.; Han, F. Self-locking avoidance and stiffness compensation of a three-axis micromachined electrostatically suspended accelerometer. Sensors 2016, 16, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gatt1, G.; Shaw, A.D.; Goncalves, P.J.P.; Brennan, M.J. On the detailed design of a quasi-zero stiffness device to assist in the realisation of a translational Lanchester damper. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.B.; Nguyen, V.L.; Tran, K.D. Effects of friction models on simulation of pneumatic cylinder. Mech. Sci. 2019, 10, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




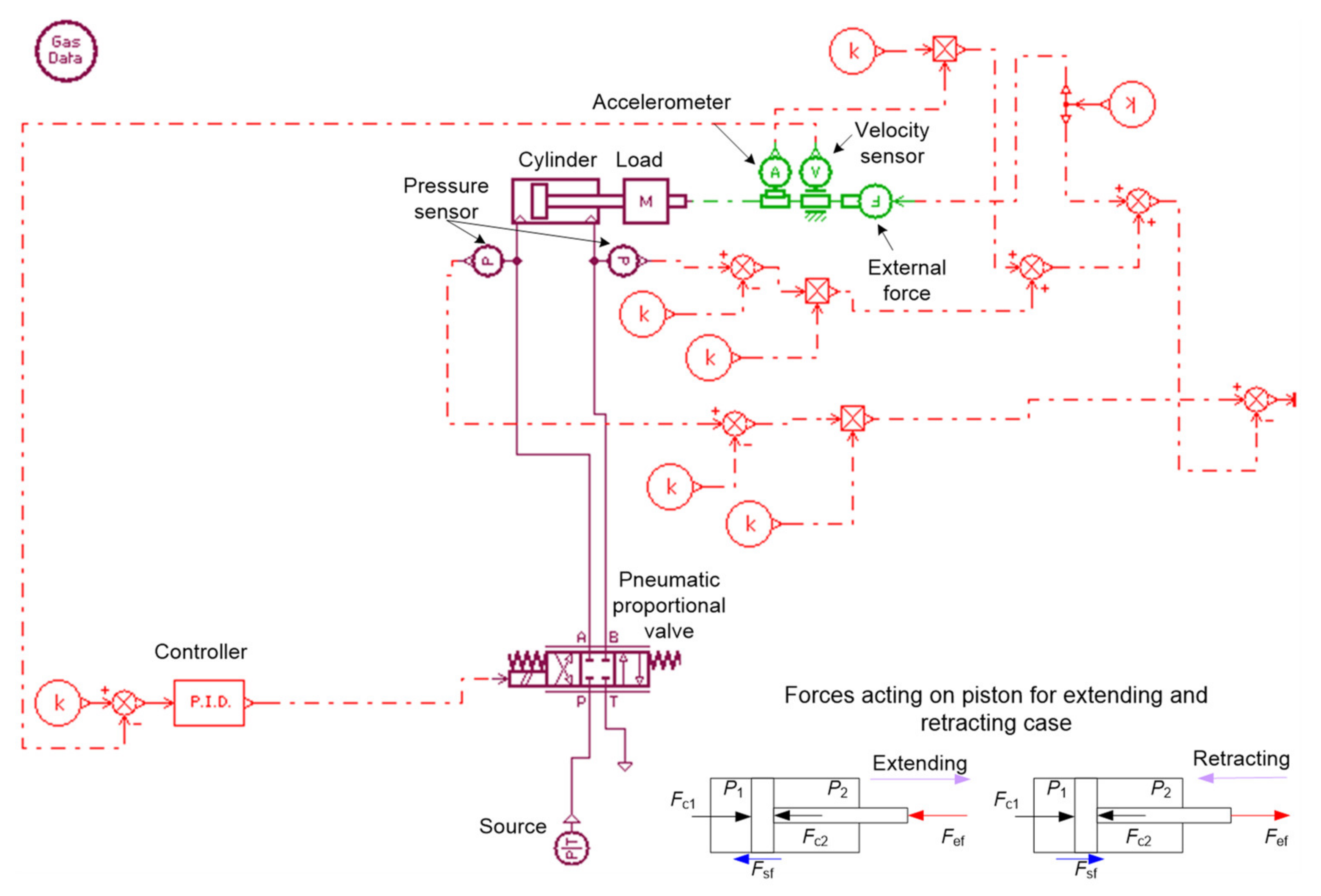
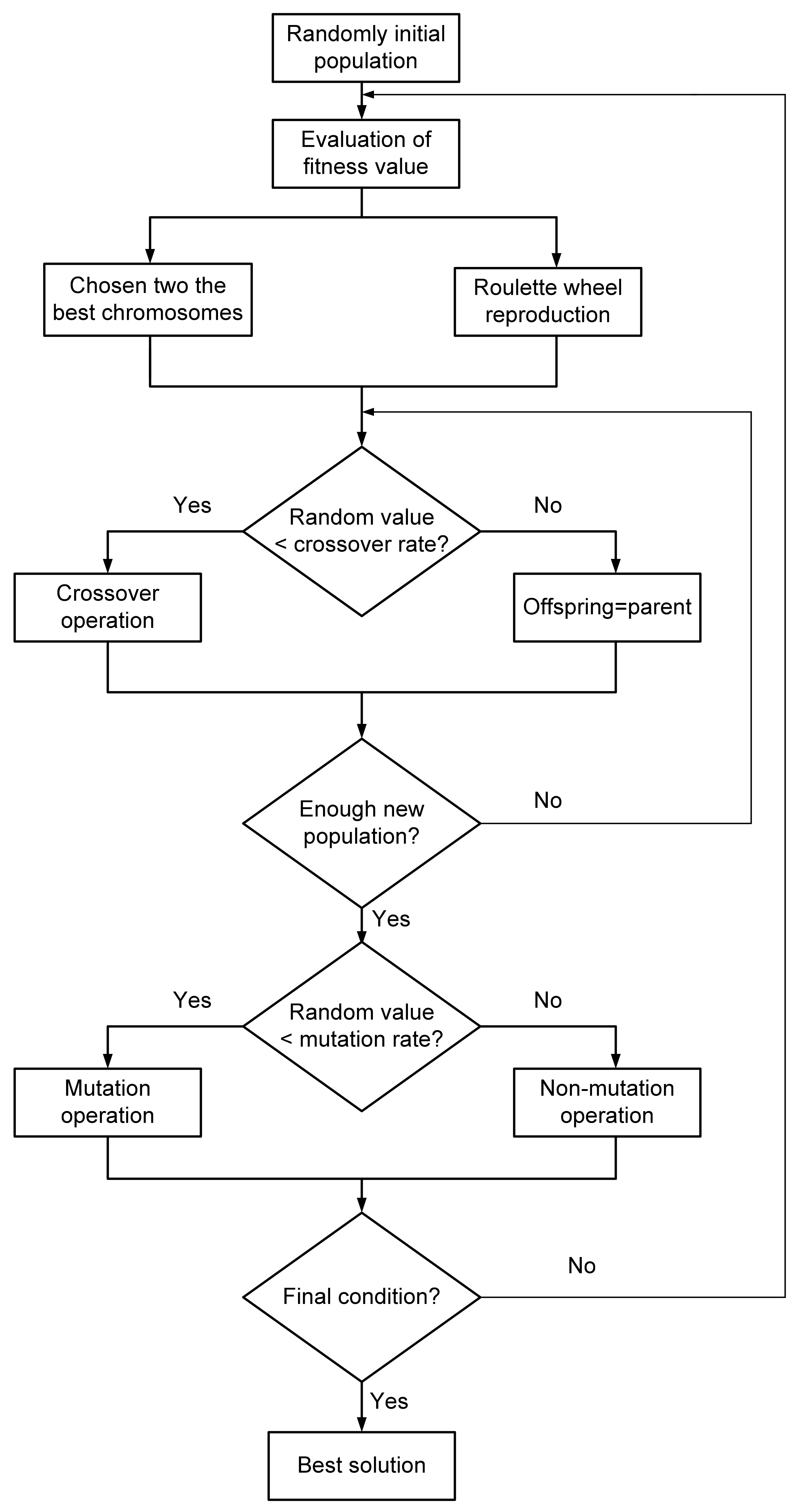
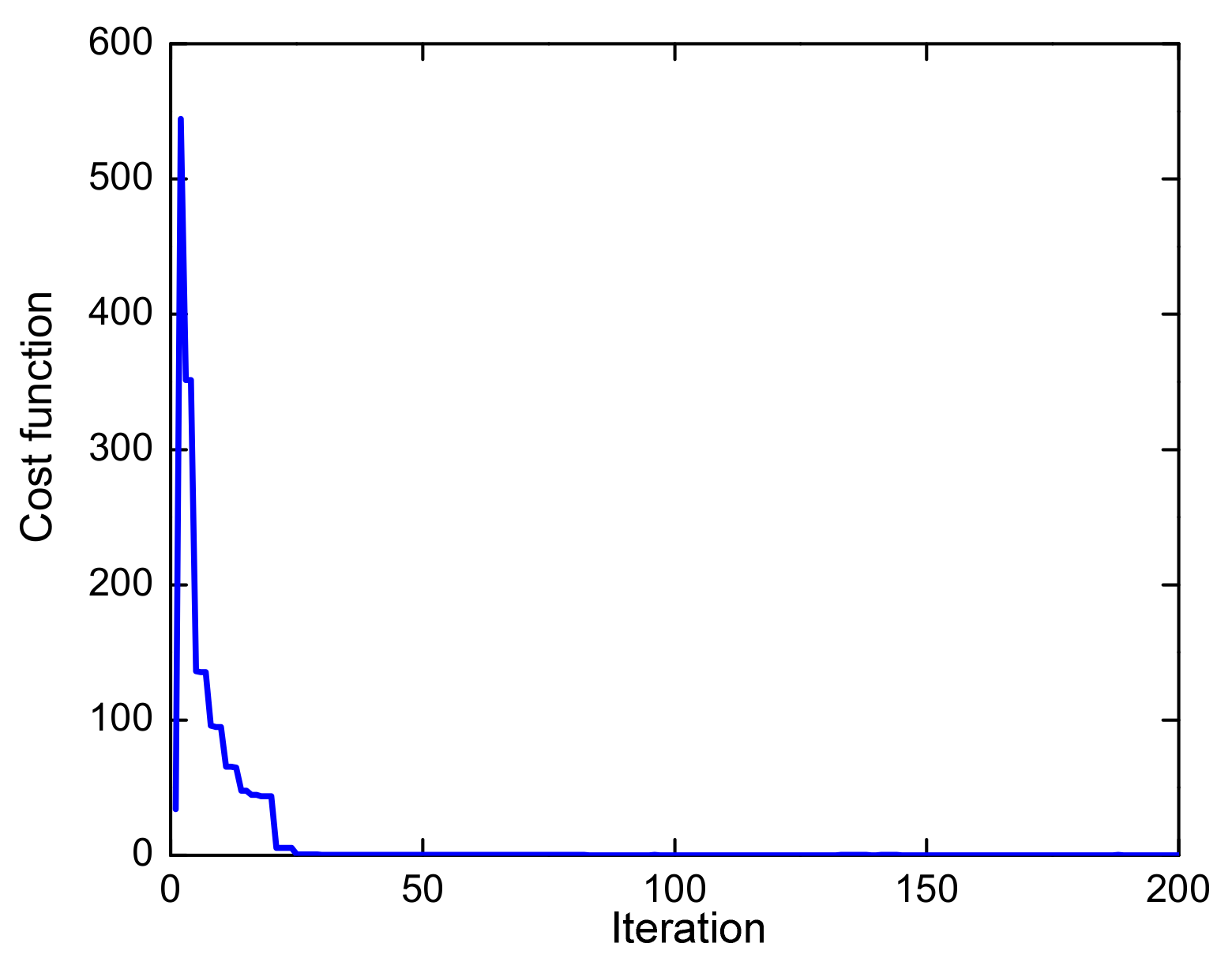
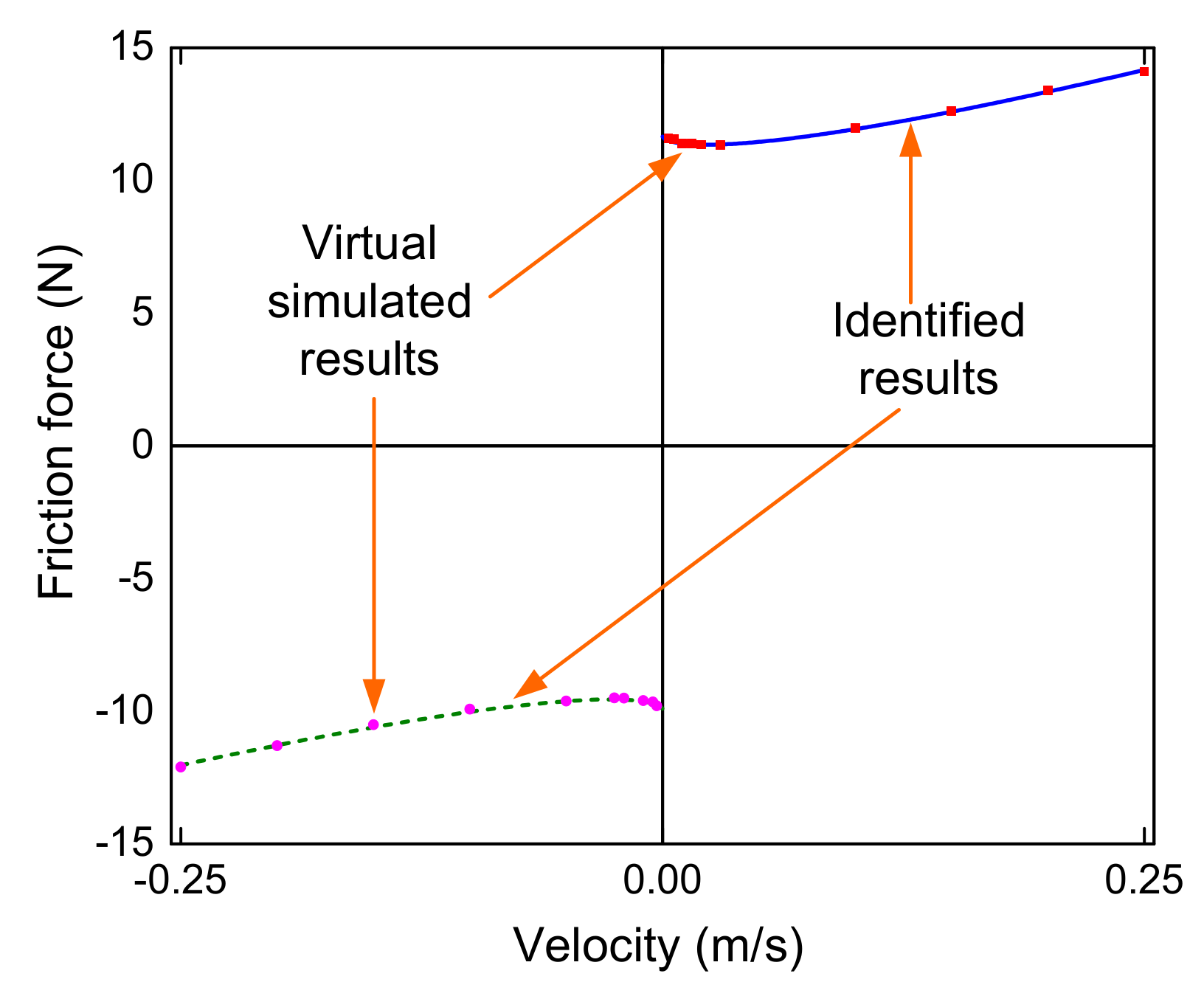

| Parameter | Original Value |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere pressure | 1 bar |
| Specific heat ratio | 1.4 |
| Thermal exchange coefficient | 500 J/mm2/K/s |
| External temperature | 293.15 K |
| External force | 100 N |
| Source pressure | 5 bar |
| Velocity of load | 0.003; 0.006; 0.01; 0.015; 0.02; 0.03; 0.05; 0.1; 0.15; 0.2; 0.25 m/s |
| Parameter | Extending | Retracting |
|---|---|---|
| Fc | 4.338 | −3.904 |
| Fs | 11.655 | −9.906 |
| vs | 0.4961 | −0.372 |
| σ | 23.7 | 23.356 |
| n | 0.681 | 0.681 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vo, N.Y.P.; Le, T.D. Dynamic Analysis of Quasi-Zero Stiffness Pneumatic Vibration Isolator. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052378
Vo NYP, Le TD. Dynamic Analysis of Quasi-Zero Stiffness Pneumatic Vibration Isolator. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(5):2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052378
Chicago/Turabian StyleVo, Ngoc Yen Phuong, and Thanh Danh Le. 2022. "Dynamic Analysis of Quasi-Zero Stiffness Pneumatic Vibration Isolator" Applied Sciences 12, no. 5: 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052378
APA StyleVo, N. Y. P., & Le, T. D. (2022). Dynamic Analysis of Quasi-Zero Stiffness Pneumatic Vibration Isolator. Applied Sciences, 12(5), 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052378





