Differential Expression of Genes Associated with Chromatin Modifications in Skeletal Muscle during Aerobic Training Program
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Differential Gene Expression Quantification
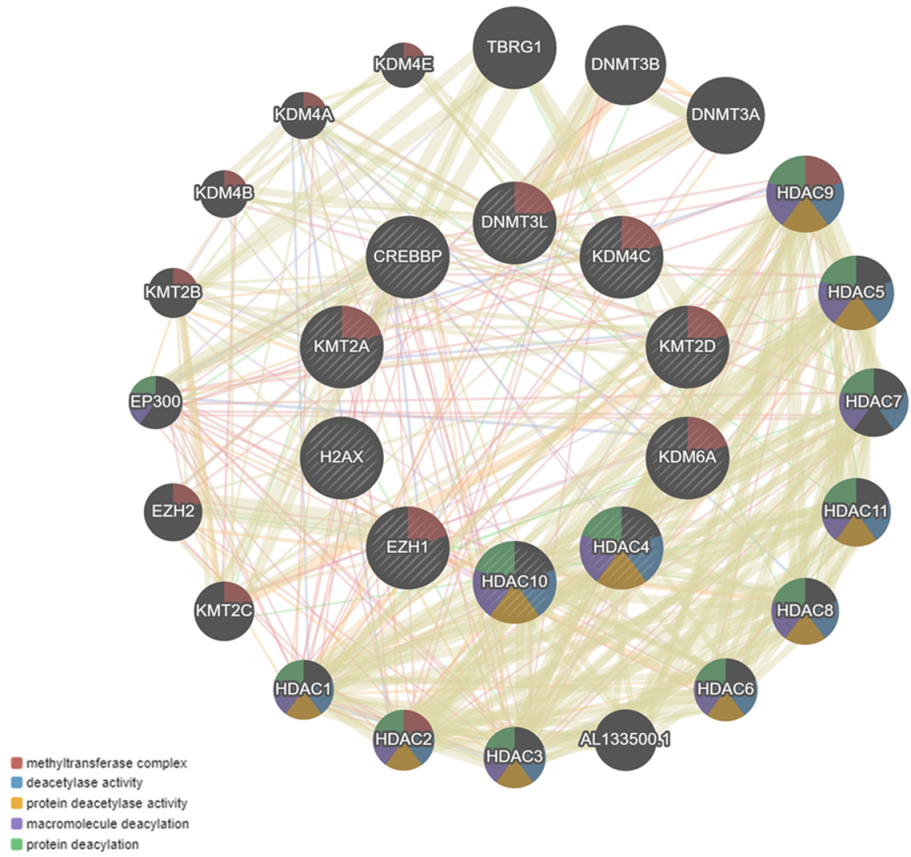
4. Co-Expression Interaction Network
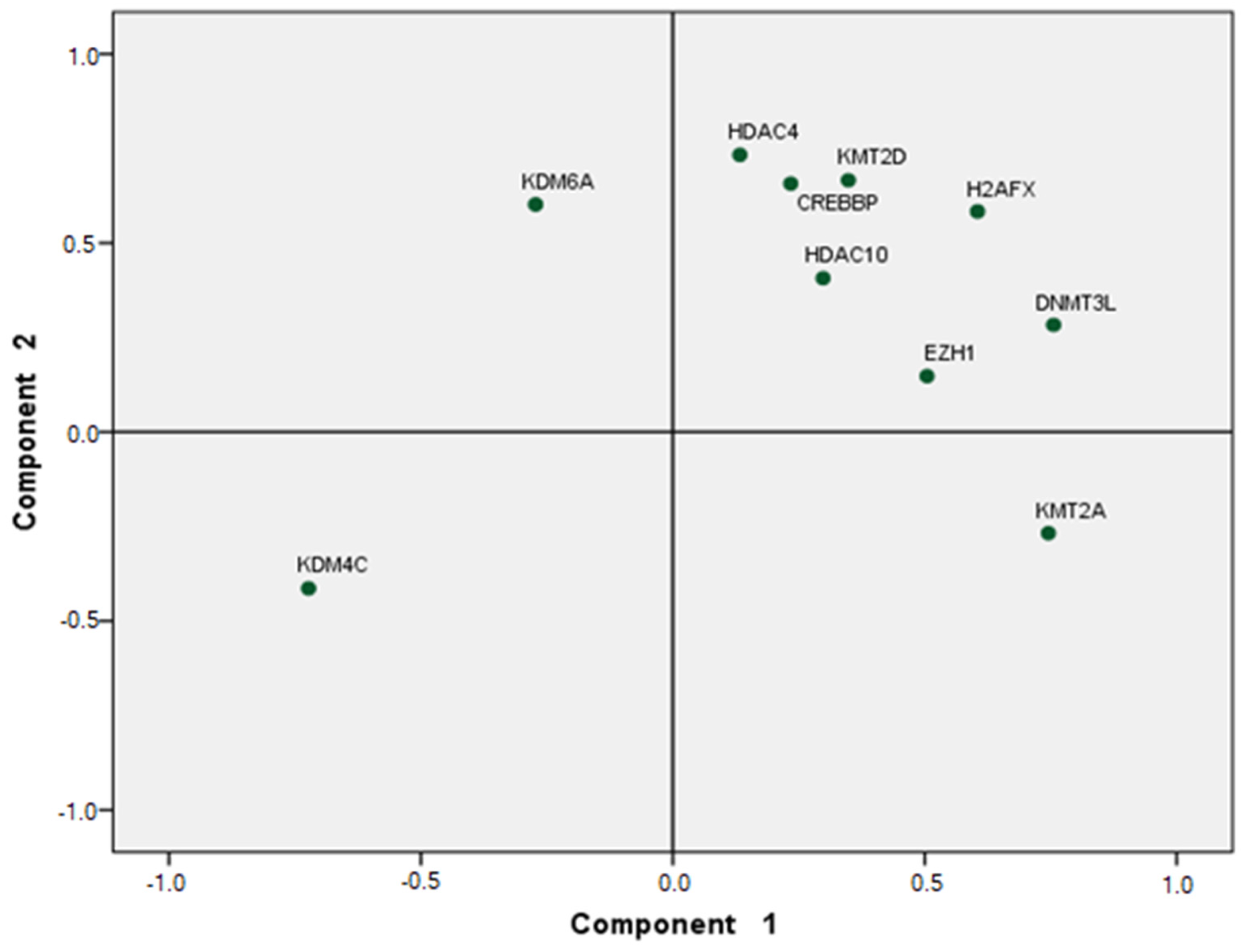
5. Statistical Analysis
6. Results
7. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, F.S.; Lander, E.S.; Rogers, J.; Waterston, R.H.; Conso, I.H. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 2004, 431, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, L.M.; Roth, S.M. Genetic influence on athletic performance. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2013, 25, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malsagova, K.A.; Butkova, T.V.; Kopylov, A.T.; Izotov, A.A.; Rudnev, V.R.; Klyuchnikov, M.S.; Kaysheva, A.L. Molecular Portrait of an Athlete. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, D.S.; Page, R.A.; Sukala, W.R.; Giri, M.; Ghimbovschi, S.D.; Hayat, I.; Cheema, B.S.; Lys, I.; Leikis, M.; Sheard, P.W.; et al. Multi-omic integrated networks connect DNA methylation and miRNA with skeletal muscle plasticity to chronic exercise in Type 2 diabetic obesity. Physiol. Genom. 2014, 46, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, W.S.; Viveiros de Castro, L.; Deane, E.; Magno-França, A.; Bassini, A.; Cameron, L.C. Investigating the Cellular and Metabolic Responses of World-Class Canoeists Training: A Sportomics Approach. Nutrients 2016, 8, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, Y. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in cardiovascular disease and exercise. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2017, 2017, 2049217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antunes-Correa, L.M. Maximal oxygen uptake: New and more accurate predictive equation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 1075–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunwald, E. Control of myocardial oxygen consumption: Physiologic and clinical considerations. Am. J. Cardiol. 1971, 27, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Hernandez, M.A.; Tafur-Tascon, L.J.; Cohen, D.D.; García-Corzo, S.A.; Quiñonez-Sánchez, A.; Povea-Combariza, C.; Tejada-Rojas, C.X. Concordance between the indirect VO2max value estimated through the distance in Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test level 1 and the direct measurement during a treadmill protocol test in elite youth soccer players. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2018, 13, S401–S412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stong, L.; Haile, L.; Beyer, K.; Andreacci, J. Effect of Test Sequence on Maximal Anaerobic and Aerobic Power Achievements in Adults. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 14, 657–665. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Or, O. The Wingate anaerobic test an update on methodology, reliability and validity. Sports Med. 1987, 4, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumalai, T.; Therasa, S.V.; Elumalai, E.K.; David, E. Intense and exhaustive exercise induce oxidative stress in skeletal muscle. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2011, 1, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher-Wellman, K.; Bloomer, R.J. Acute exercise and oxidative stress: A 30 year history. Dyn. Med. 2009, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yucel, N.; Wang, Y.X.; Mai, T.; Porpiglia, E.; Lund, P.J.; Markov, G.; Garcia, B.A.; Bendall, S.C.; Angelo, M.; Blau, H.M. Glucose metabolism drives histone acetylation landscape transitions that dictate muscle stem cell function. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3939–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandel, N.S. Navigating Metabolism; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2015; Chapter 1; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Plowman, S.A.; Smith, D.L. Exercise Physiology for Health, Fitness, and Performance, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, H.; Mishra, S. Effect of BMI, Body Fat Percentage and Fat Free Mass on Maximal Oxygen Consumption in Healthy Young Adults. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, CC17–CC20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacher, D.F.; Leach, R.M. Oxygen Transport—1. Basic principles. BMJ 1998, 317, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.A.; Dai, Z.; Locasale, J.W. The impact of cellular metabolism on chromatin dynamics and epigenetics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenfeld, G.; Groudine, M. Controlling the double helix. Nature 2003, 421, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouchard, C.L. The heritage family study. Aims, design, and measurement protocol. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheadle, C.; Vawter, M.P.; Freed, W.J.; Becker, K.G. Analysis of microarray data using Z score transformation. J. Mol. Diagn. 2003, 5, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, K.; Ricciardi, S.; Pearson, T.; Bharudin, I.; Davidsen, P.K.; Bonomo, M.; Brina, D.; Scagliola, A.; Simpson, D.M.; Beynon, R.J.; et al. The Role of Eif6 in Skeletal Muscle Homeostasis Revealed by Endurance Training Co-expression Networks. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mina-Paz, Y.; Zambrano, D.C.; Matta, A.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Garcia-Vallejo, F. Muscle genomics and aerobic training. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2021, 17. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, S.L.; Fairlie, E.; Garnham, A.P.; Hargreaves, M. Exercise-induced histone modifications in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5951–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.; Shimizu, J.; Kawano, F.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.K. Adaptive responses of histone modifications to resistance exercise in human skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egan, B.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise metabolism and the molecular regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Yuan, H.; Li, H.; Fu, L. Exercise-induced GLUT4 transcription via inactivation of HDAC4/5 in mouse skeletal muscle in an AMPKα2-dependent manner. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2372–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukouris, A.E.; Zervopoulos, S.D.; Michelakis, E.D. Metabolic enzymes moonlighting in the nucleus: Metabolic regulation of gene transcription. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 712–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, T.; Mackay, L.; Sproul, D.; Karim, M.; Culley, J.; Harrison, D.; Hayward, L.; Langridge-Smith, P.; Gilbert, N.; Ramsahoye, B. Lactate, a product of glycolytic metabolism, inhibits histone deacetylase activity and promotes changes in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4794–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertuzzi, R.; Nascimento, E.M.; Urso, R.P.; Damasceno, M.; Lima-Silva, A.E. Energy system contributions during incremental exercise test. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2013, 12, 454–460. [Google Scholar]
- Luka, Z.; Mudd, S.; Wagner, C. Glycine N-methyltransferase and regulation of S-adenosylmethionine levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22507–22511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Gene ID | Symbol | Z-Score Post | Z-Score Pre | Z-Ratio | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2145 | EZH1 | −0.03 | −0.19 | 2.15 | <0.00001 |
| 4297 | KMT2A | −0.85 | −1.08 | 3.03 | <0.00001 |
| 8085 | KMT2D | −0.98 | −1.15 | 2.30 | <0.00001 |
| 23081 | KDM4C | 0.53 | 0.33 | 2.69 | <0.00001 |
| 7403 | KDM6A | −0.84 | −1.11 | 3.64 | <0.00001 |
| 1387 | CREBBP | −0.09 | −0.24 | 2.09 | <0.00001 |
| 83933 | HDAC10 | 0.15 | −0.00 | 2.00 | <0.00001 |
| 9759 | HDAC4 | −0.12 | −0.30 | 2.38 | <0.00001 |
| 29947 | DNMT3L | −0.78 | −0.95 | 2.35 | <0.00001 |
| 3014 | H2AFX | 0.33 | 0.12 | 2.83 | <0.00001 |
| GO_ID | Description | Gene Count | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6325 | Chromatin organization | 9 | 9.04 × 10−9 |
| 16570 | Histone modification | 8 | 9.04 × 10−9 |
| 18205 | Peptidyl-lysine modification | 7 | 1.07 × 10−7 |
| 16571 | Histone methylation | 5 | 2.04 × 10−6 |
| 43414 | Macromolecule methylation | 6 | 2.32 × 10−6 |
| 6996 | Organelle organization | 10 | 4.69 × 10−5 |
| 40029 | Regulation of gene expression, epigenetic | 5 | 4.69 × 10−5 |
| 34968 | Histone lysine methylation | 4 | 5.13 × 10−5 |
| 10604 | Positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process | 10 | 5.25 × 10−5 |
| 45934 | Negative regulation of nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process | 8 | 6.02 × 10−5 |
| 51172 | Negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process | 9 | 6.51 × 10−5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mina-Paz, Y.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, A.; Hernández-Pérez, D.; Montoya-Villegas, J.C.; Sánchez-Gómez, A.; García-Vallejo, F. Differential Expression of Genes Associated with Chromatin Modifications in Skeletal Muscle during Aerobic Training Program. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031159
Mina-Paz Y, Rodríguez-Ortiz A, Hernández-Pérez D, Montoya-Villegas JC, Sánchez-Gómez A, García-Vallejo F. Differential Expression of Genes Associated with Chromatin Modifications in Skeletal Muscle during Aerobic Training Program. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(3):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031159
Chicago/Turabian StyleMina-Paz, Yecid, Alejandra Rodríguez-Ortiz, Daniela Hernández-Pérez, Julio César Montoya-Villegas, Adalberto Sánchez-Gómez, and Felipe García-Vallejo. 2022. "Differential Expression of Genes Associated with Chromatin Modifications in Skeletal Muscle during Aerobic Training Program" Applied Sciences 12, no. 3: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031159
APA StyleMina-Paz, Y., Rodríguez-Ortiz, A., Hernández-Pérez, D., Montoya-Villegas, J. C., Sánchez-Gómez, A., & García-Vallejo, F. (2022). Differential Expression of Genes Associated with Chromatin Modifications in Skeletal Muscle during Aerobic Training Program. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031159






