Emotionally Controllable Talking Face Generation from an Arbitrary Emotional Portrait
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Audio-Driven Talking Face Generation
2.2. Facial Expression Reenactment
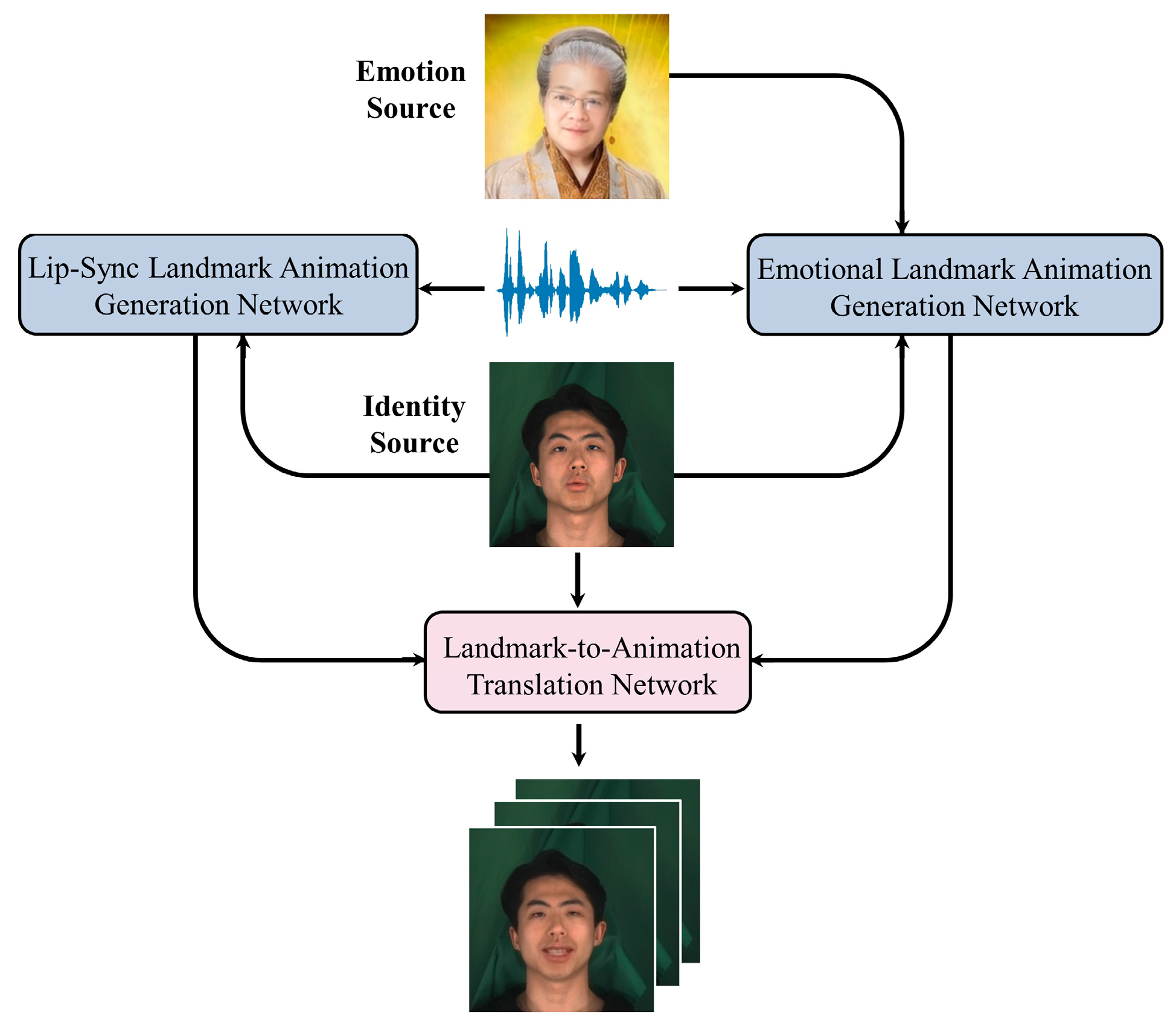
3. Method
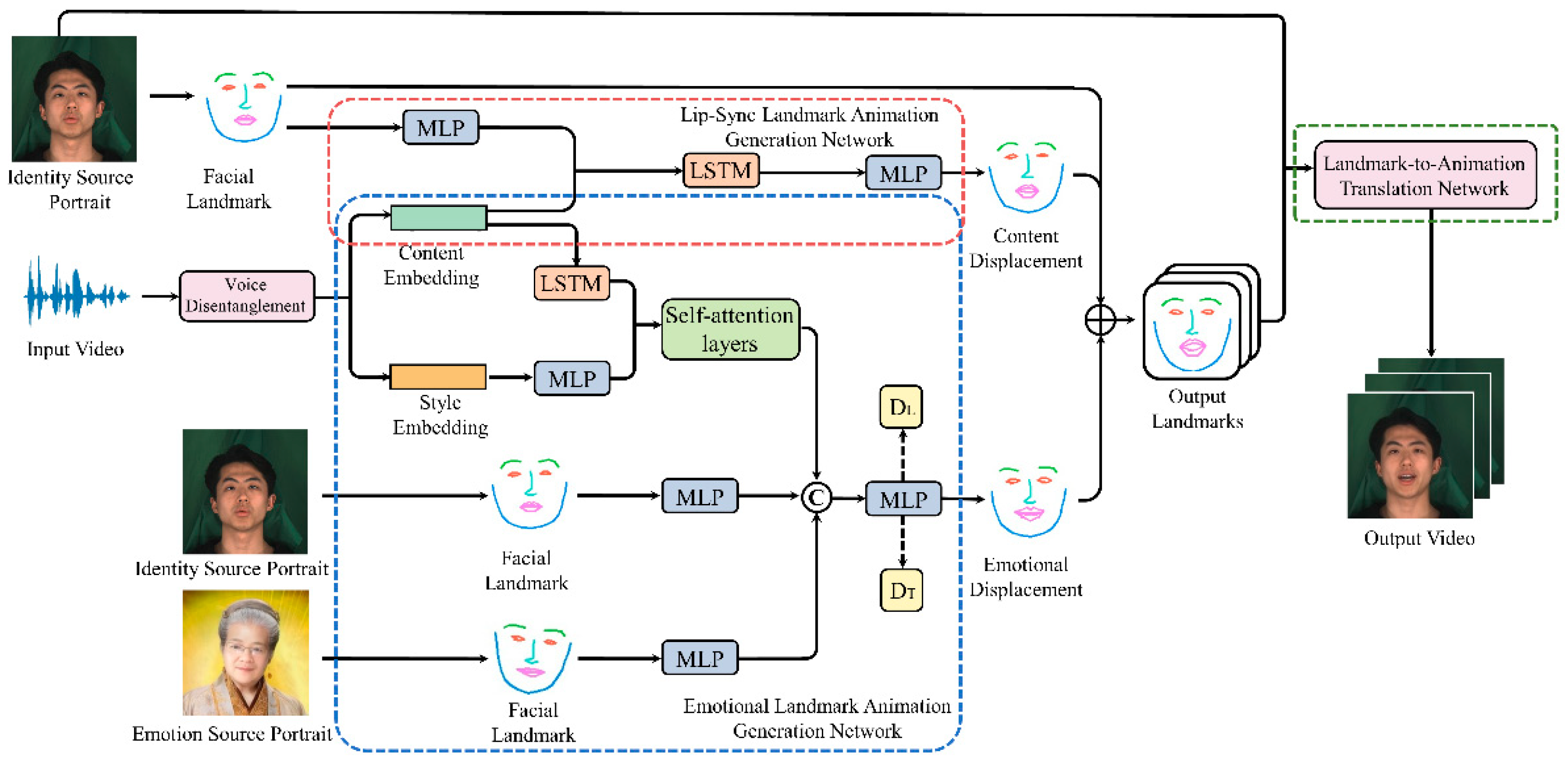
3.1. Overview
3.2. Lip-Sync Landmark Animation Generation Network
3.3. Emotional Landmark Animation Generation Network
3.4. Landmark-To-Animation Translation Network
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Quantitative Evaluation
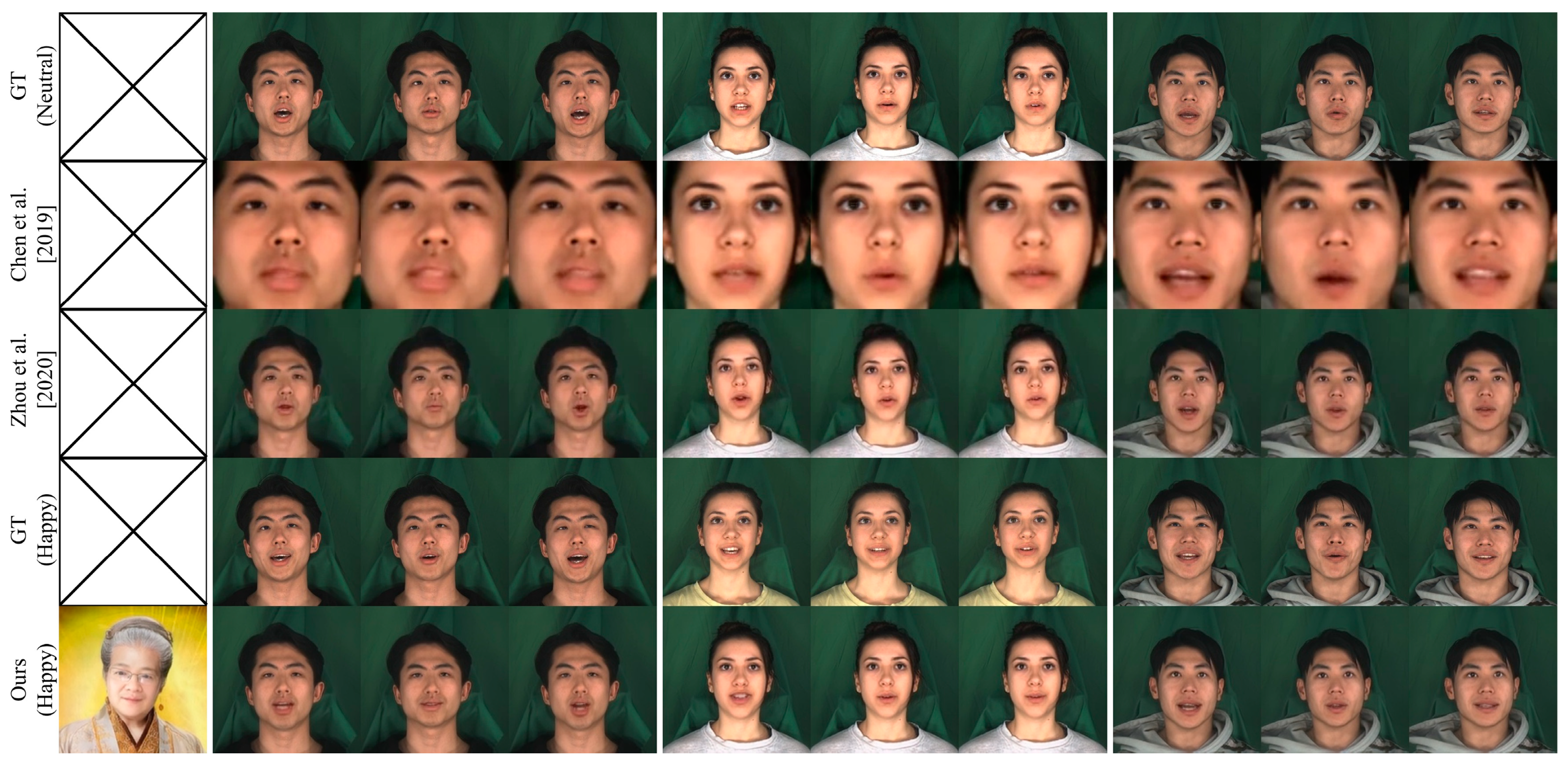
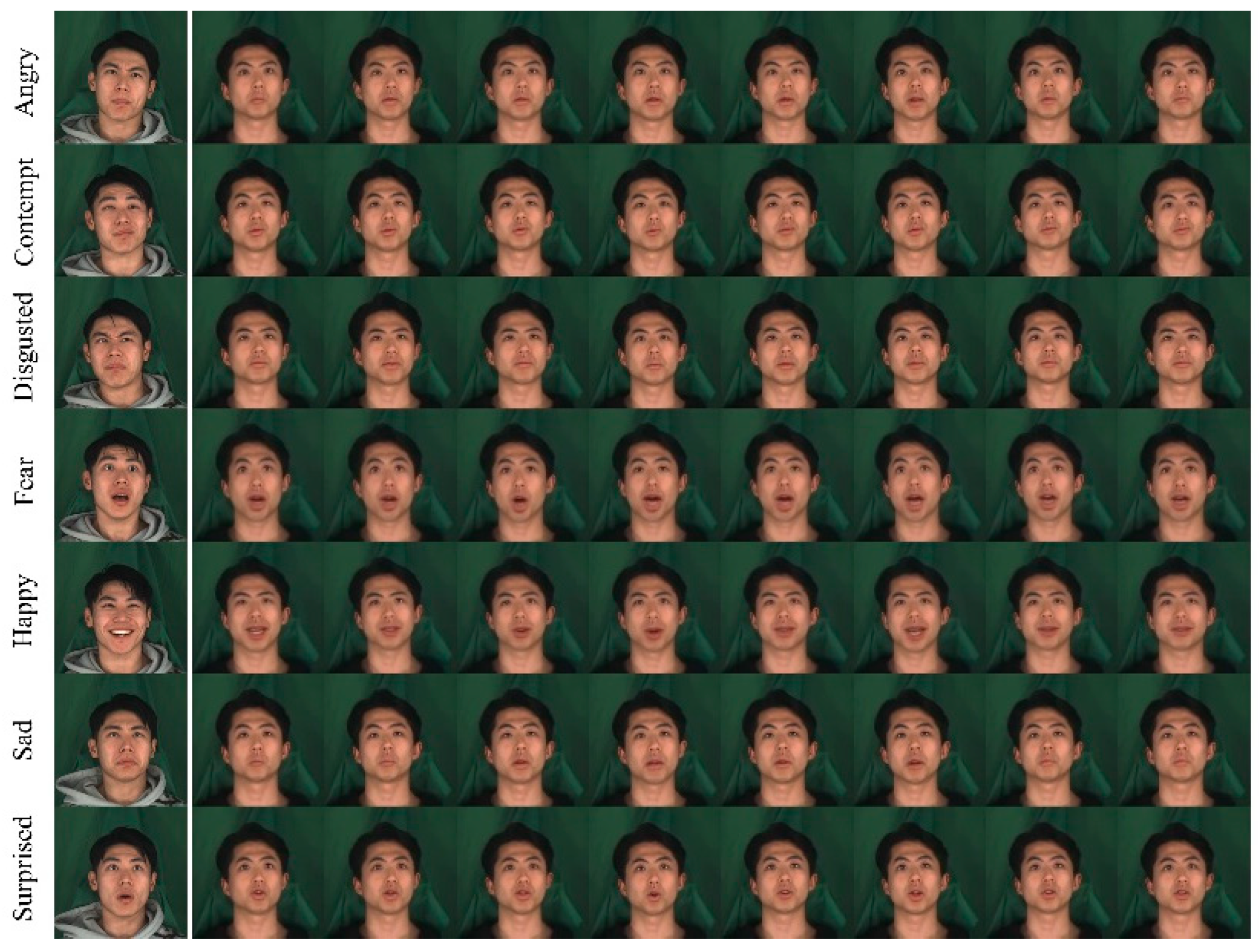
4.3. Qualitative Evaluation
4.4. Ablation Study
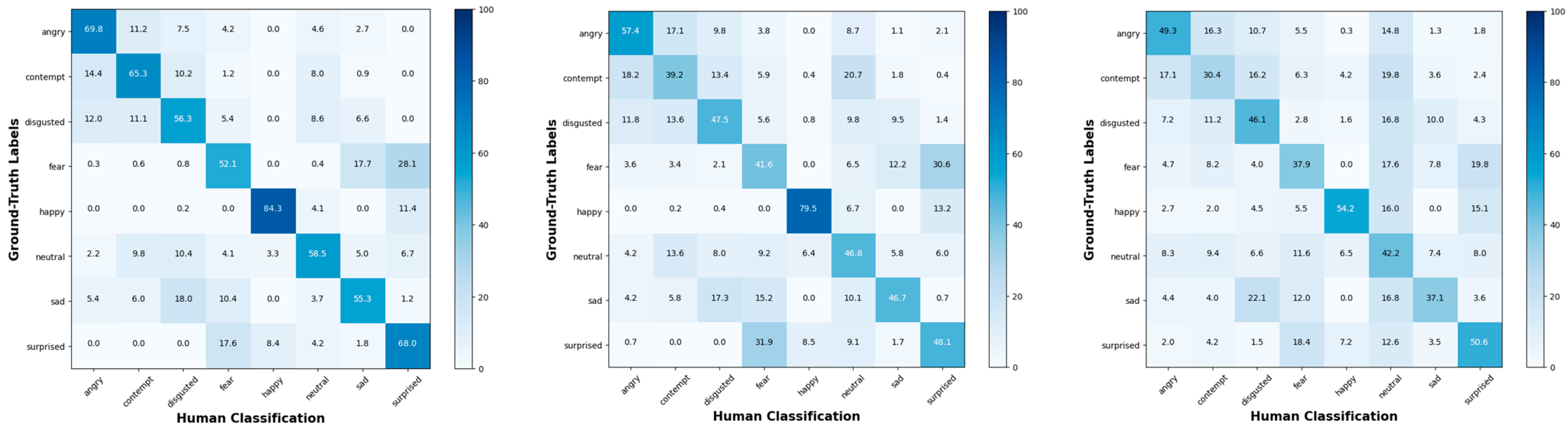
4.5. User Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y.; Qian, R.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, W.; Dai, B.; Zhou, B. Learning Hierarchical Cross-Modal Association for Co-Speech Gesture Generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10462–10472. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wu, W.; Zhou, B. Semantic-aware implicit neural audio-driven video portrait generation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.07786. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, C.; Kuang, G.; Bai, L.; Hou, C.; Guo, Y.; Xu, X.; Pietikäinen, M.; Liu, L. Deep Learning for Visual Speech Analysis: A Survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10839. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, F.-T.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Xu, D. Depth-Aware Generative Adversarial Network for Talking Head Video Generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3397–3406. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Ding, Y.; Yu, X. One-shot talking face generation from single-speaker audio-visual correlation learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtually, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 2531–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Li, W.; Zhu, Z.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Learning Dynamic Facial Radiance Fields for Few-Shot Talking Head Synthesis. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 666–682. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Cui, G.; Kou, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xu, C. What comprises a good talking-head video generation?: A survey and benchmark. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.03201. [Google Scholar]
- Suwajanakorn, S.; Seitz, S.M.; Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. Synthesizing obama: Learning lip sync from audio. ACM Trans. Graph. (ToG) 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Nagrani, A.; Zisserman, A. Voxceleb2: Deep speaker recognition. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.05622. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wu, Q.; Song, L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, W.; Qian, C.; He, R.; Qiao, Y.; Loy, C.C. Mead: A large-scale audio-visual dataset for emotional talking-face generation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2020; pp. 700–717. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.S.; Jamaludin, A.; Zisserman, A. You said that? arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02966. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Qi, H. Talking face generation by conditional recurrent adversarial network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.04786. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Maddox, R.K.; Duan, Z.; Xu, C. Hierarchical cross-modal talking face generation with dynamic pixel-wise loss. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7832–7841. [Google Scholar]
- Prajwal, K.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Namboodiri, V.P.; Jawahar, C. A lip sync expert is all you need for speech to lip generation in the wild. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 484–492. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, X.; Shechtman, E.; Echevarria, J.; Kalogerakis, E.; Li, D. MakeltTalk: Speaker-aware talking-head animation. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2020, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W.; Loy, C.C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Pose-controllable talking face generation by implicitly modularized audio-visual representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4176–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, K.; Wu, W.; Loy, C.C.; Cao, X.; Xu, F. Audio-driven emotional video portraits. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14080–14089. [Google Scholar]
- Sadoughi, N.; Busso, C. Speech-driven expressive talking lips with conditional sequential generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 12, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, T.; Hung, C.-C.; Xiao, J.; Feng, G. Facial expression GAN for voice-driven face generation. Vis. Comput. 2021, 38, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskimez, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Z. Speech driven talking face generation from a single image and an emotion condition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 3480–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Pan, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, H.; Hong, Z.; Han, X.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Ding, E.; Wang, J. Expressive talking head generation with granular audio-visual control. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3387–3396. [Google Scholar]
- Friesen, E.; Ekman, P. Facial action coding system: A technique for the measurement of facial movement. Palo Alto 1978, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, T.; Zhang, W.; Shen, T.; Li, Z.; Mei, T. Deep Person Generation: A Survey from the Perspective of Face, Pose and Cloth Synthesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.02081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, M.; Wang, R.; Zheng, A.H.; He, R. Deep Audio-visual Learning: A Survey. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2021, 18, 351–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Herva, A.; Lehtinen, J. Audio-driven facial animation by joint end-to-end learning of pose and emotion. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2017, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskimez, S.E.; Maddox, R.K.; Xu, C.; Duan, Z. Generating talking face landmarks from speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation, Guildford, UK, 2–6 July 2018; pp. 372–381. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z.; Wang, L. Talking Head Generation with Audio and Speech Related Facial Action Units. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.09951. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, A.B.L.; Sønderby, S.K.; Larochelle, H.; Winther, O. Autoencoding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1558–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-P.; Yu, N.; Fritz, M. Hijack-gan: Unintended-use of pretrained, black-box gans. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 7872–7881. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Shi, W.; Chen, K.; Fu, L.; Dong, C. GCFSR: A Generative and Controllable Face Super Resolution Method Without Facial and GAN Priors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1889–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Sricharan, K.; Chellappa, R. Exprgan: Facial expression editing with controllable expression intensity. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Pumarola, A.; Agudo, A.; Martinez, A.M.; Sanfeliu, A.; Moreno-Noguer, F. Ganimation: One-shot anatomically consistent facial animation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 698–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, G.; Lu, S.; Chen, T. Cascade ef-gan: Progressive facial expression editing with local focuses. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5021–5030. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, F.; Yao, N.; Jiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. Geometry-contrastive gan for facial expression transfer. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.01822. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, X.; Wang, M.; Pan, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Fan, C. Freenet: Multi-identity face reenactment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5326–5335. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Liang, T.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Zou, S.; Dai, J.; Han, J. Li-Net: Large-Pose Identity-Preserving Face Reenactment Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shenzhen, China, 5–9 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Jaitly, N. Towards end-to-end speech recognition with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; pp. 1764–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, S.; Yang, X.; Hasegawa-Johnson, M. Autovc: Zero-shot voice style transfer with only autoencoder loss. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 5210–5219. [Google Scholar]
- Bulat, A.; Tzimiropoulos, G. How far are we from solving the 2d & 3d face alignment problem? (and a dataset of 230,000 3d facial landmarks). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1021–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.; Wang, Q.; Papir, A.; Moreno, I.L. Generalized end-to-end loss for speaker verification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4879–4883. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov, E.; Shysheya, A.; Burkov, E.; Lempitsky, V. Few-shot adversarial learning of realistic neural talking head models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9459–9468. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6629–6640. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.C.; Tao, Y.; Martinez, A.M. Compound facial expressions of emotion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1454–E1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Method | SSIM↑ | PSNR↑ | FID↓ | L-LD↓ | L-LVD↓ | F-LD↓ | F-LVD↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [13] | 0.60 | 28.55 | 67.60 | 3.27 | 2.09 | 3.82 | 1.71 |
| Zhou et al. [15] | 0.62 | 28.94 | 17.33 | 2.49 | 1.66 | 3.55 | 1.64 |
| Wang et al. [10] | 0.68 | 28.61 | 22.52 | 2.52 | 2.28 | 3.16 | 2.01 |
| Ji et al. [17] | 0.71 | 29.53 | 7.99 | 2.45 | 1.78 | 3.01 | 1.56 |
| Ours | 0.62 | 28.92 | 16.80 | 2.52 | 1.68 | 2.98 | 1.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Guo, H.; Li, Y. Emotionally Controllable Talking Face Generation from an Arbitrary Emotional Portrait. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12852. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412852
Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Wu T, Guo H, Li Y. Emotionally Controllable Talking Face Generation from an Arbitrary Emotional Portrait. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12852. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412852
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zikang, Yujia Zhang, Tianjun Wu, Hao Guo, and Yao Li. 2022. "Emotionally Controllable Talking Face Generation from an Arbitrary Emotional Portrait" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12852. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412852
APA StyleZhao, Z., Zhang, Y., Wu, T., Guo, H., & Li, Y. (2022). Emotionally Controllable Talking Face Generation from an Arbitrary Emotional Portrait. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12852. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412852







