Effect of Wood Medium on Dispersion Parameters of Prefabricated Spherical Fragments in Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Comparison of Penetration Experiment and Simulation
3. Fragment Penetration Calculation Based on Forest Environment
- Set the wood diameter and stand density as fixed values, change the horizontal dispersion angle between two adjacent fragments, and compare the average penetration trajectory length of fragments with formula (3). (1°, 3°, 5°)
- Set different wood diameters without changing the stand density and scattering angle, and compare the average penetration trajectory length of fragments with formula (3). (200 mm, 300 mm, 400 mm)
- The average penetration trajectory length of fragments is compared with formula (3) by setting different stand densities without changing the tree diameter and scattering angle. (1/m2, 0.5/m2, 0.25/m2)
4. Simulation Comparison of Different Penetration Modes
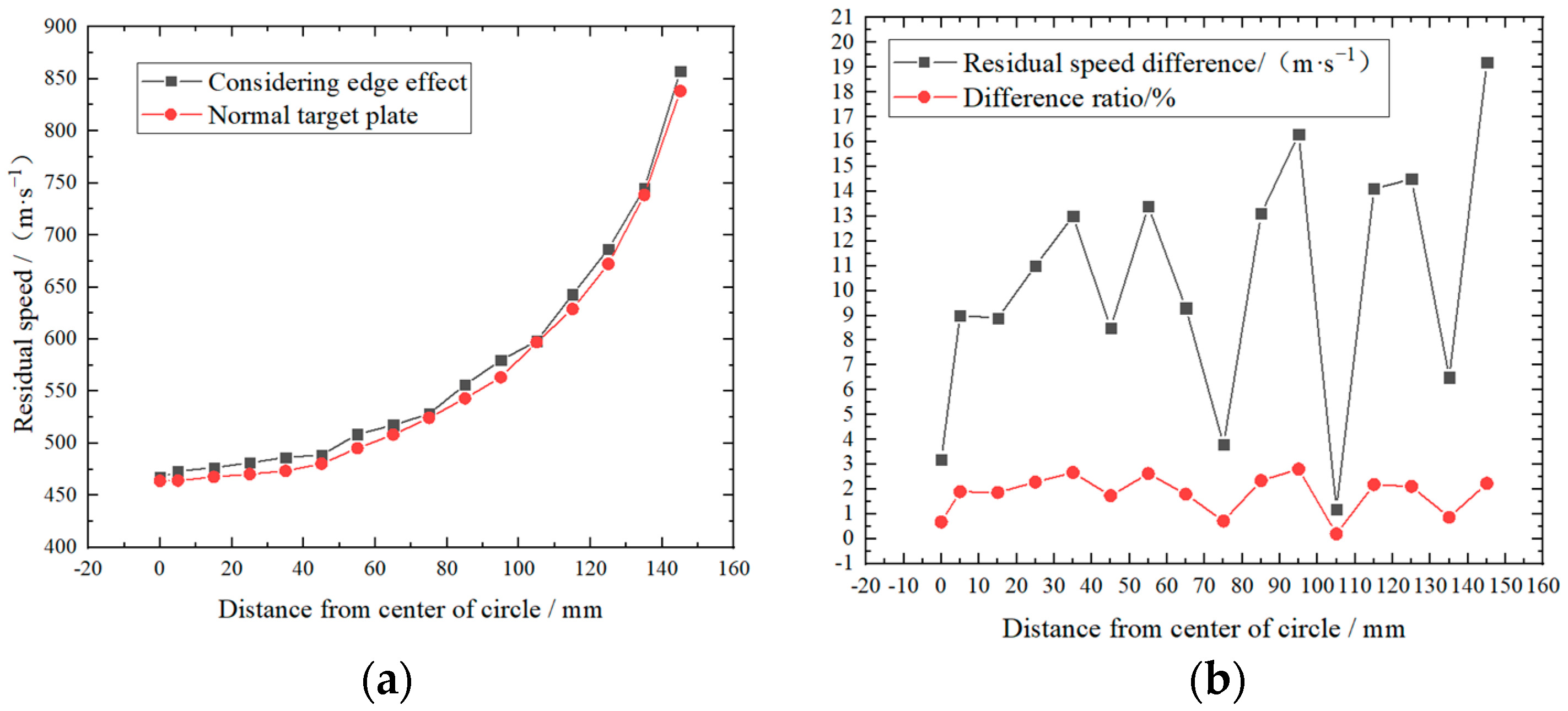
4.1. Edge Effect of Wood Penetration
4.2. Influence of the Number of Target Layers on the Residual Velocity
5. Conclusions
- Based on the Poncelet formula, it is feasible to calculate the residual velocity of the spherical fragment penetrating the wood target, which is verified by the comparison with the experiment.
- Based on the forest parameters such as stand density, tree diameter, and fragment flying angle, a simple calculation model of penetration path length is obtained, which has good applicability when the flying angle is small and the stand density is large.
- The residual velocity increases with the increase in the number of spacer targets on the fragment penetration trajectory, and it changes most obviously when the number of layers is seven. The wood target is less affected by the boundary effect. When the thickness d outside the penetration trajectory decreases continuously, the influence of the wood boundary effect on the residual velocity is relatively stable, and the maximum difference is 2.67%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.X.; Han, X.G.; Zhao, X.X.; Wang, S.S. Experimentation Research on Failure Behavior of Tungsten Alloy Penetrating Low Carbon Steel Plate at High Velocity. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.Q.; Liu, J.X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, S.K.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Cao, J. Comparison of penetration performance and penetration mechanism of w-cu shaped charge liner against three kinds of target: Pure copper, carbon steel and Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 60, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Gao, S.Q.; Jin, L.; Wu, Q.H. Research on the acceleration phenomenon of projectile leaving the target when penetrating thick concrete target. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2022, 164, 104191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.X.; Feng, S.S.; Huang, G.Y.; Liu, C.M.; Xiao, L.X.; Song, Q. Ballistic Impact Characteristics of Flat-nose Projectile Penetrating Concrete and Soil Compound Target. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 13, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, Z.; Pol, M.H.; Alawode, A.O.; Faezipour, M.; Liaghat, G.H.; Via, B.K.; Abdolkhani, A. Performance Comparison of Wood, Plywood, and Oriented Strand Board under High- and Low-Velocity Impact Loadings. For. Prod. J. 2021, 71, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Ramakrishnan, K.R.; Shankar, K. Experimental study of the medium velocity impact response of sandwich panels with different cores. Mater. Des. 2016, 99, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, E.E.; Szpunar, J.A.; Odeshi, A.G. Dynamic and ballistic impact behavior of biocomposite armors made of HDPE reinforced with chonta palm wood (Bactris gasipaes). Def. Technol. 2019, 14, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, M.; Wagih, A.; Melaibari, A.; Lubineau, G.; Abdraboh, A.M.; Eltaher, M.A. Impact and post-impact response of lightweight CFRP/wood sandwich composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhoff, W.; Alberink, I.; Mattijssen, E.J.A.T. An Empirical Study on the Relation Between the Critical Angle for Bullet Ricochet and the Properties of Wood. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 60, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Analysis of Cutting Soil and Wood Based on ANSYS/LS-DYNA; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.J.; Hui, G.Y.; Sun, C.Z. Comparison of different stand density measures. J. Fujian For. Univ. 2011, 31, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, G.Y. Study on the Bark Basic Density and the Timber Basic Density of Acacia mangium and Acacia crassicarpa. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 2993–2994. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.S. Endpoint Effect; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 182–208. [Google Scholar]
- Backman, M.E. Terminal Ballistics; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1981; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Wang, H.; Tan, Z.J. Relevance Between Aspect Ratio of Projectile and Boundary Effect of Concrete Target. J. Weapon Equip. Eng. 2018, 39, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Minak, G.; Ghelli, D. Influence of diameter and boundary conditions on low velocity impact response of CFRP circular laminated plates. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2008, 39, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.N.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.L. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Investigation on Slanting Penetration of Tungsten Alloy Long Rod upon Three-ply Me. J. Sichuan Mil. Eng. 2011, 32, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.M.; Zhai, X.L.; Jiang, H.Z. An investigation on the penetration of multi-layered space plates of aluminum alloy by a tungsten sphere. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 1997, 1, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Feng, S.S.; Pei, S.X. The study of penetration of tungsten spheres at ly12cz spaced layered targets. Acta Armamentarii. 1998, 2, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, G.J.; Yin, J.P.; Wang, Z.J.; Jia, Z.J. Micro Fracture Behavior of Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Structure. Materials 2021, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Dong, L.Y.; Dong, F.D. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Projectile Oblique Impact Target Plate. J. Ordnance Equip. Eng. 2019, 40, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Long, Y.; Yue, X.B. Effects of the yaw on kinetic projectile penetrating into spaced targets in high impact. J. Ballist. 2004, 4, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
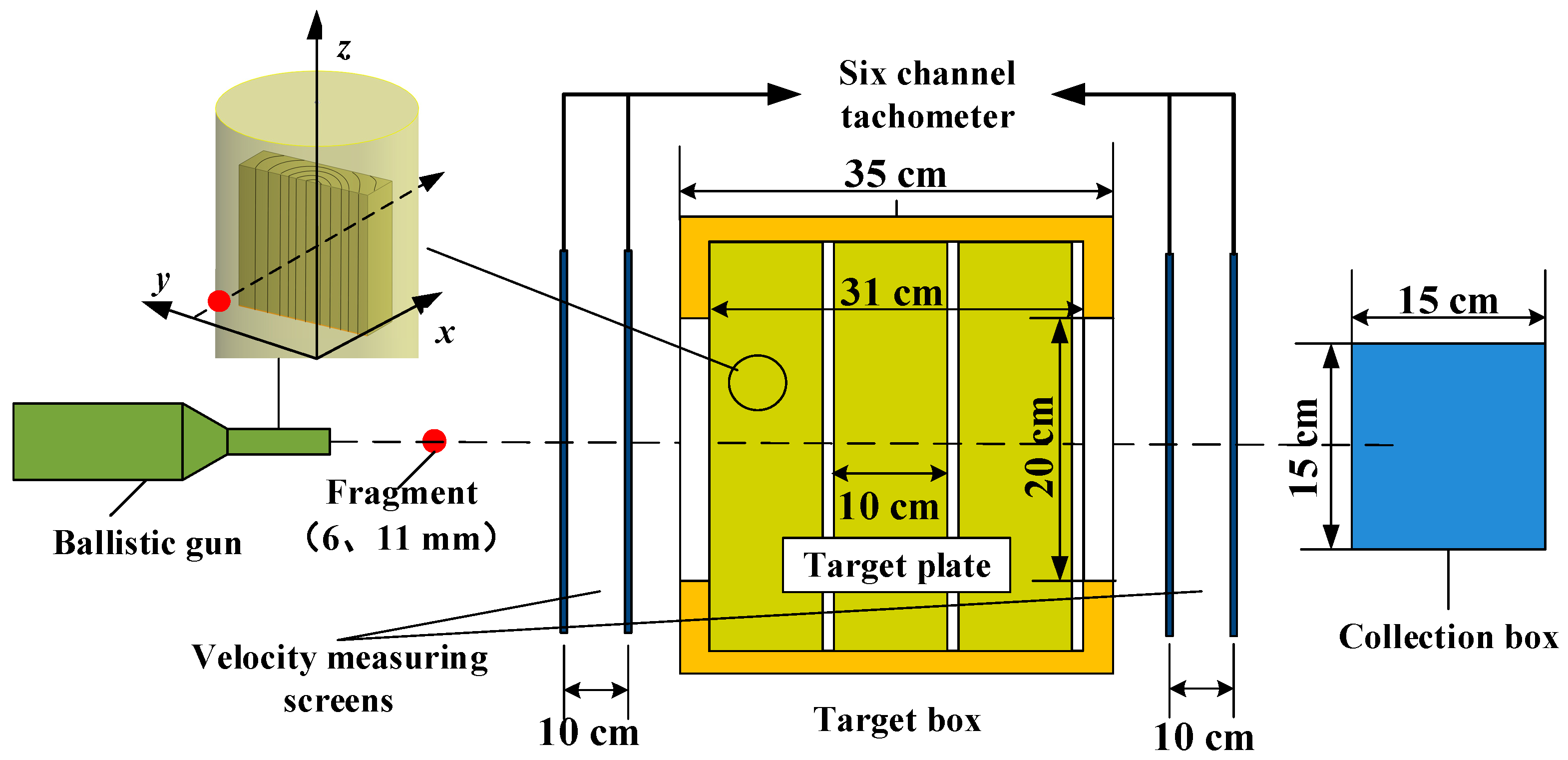
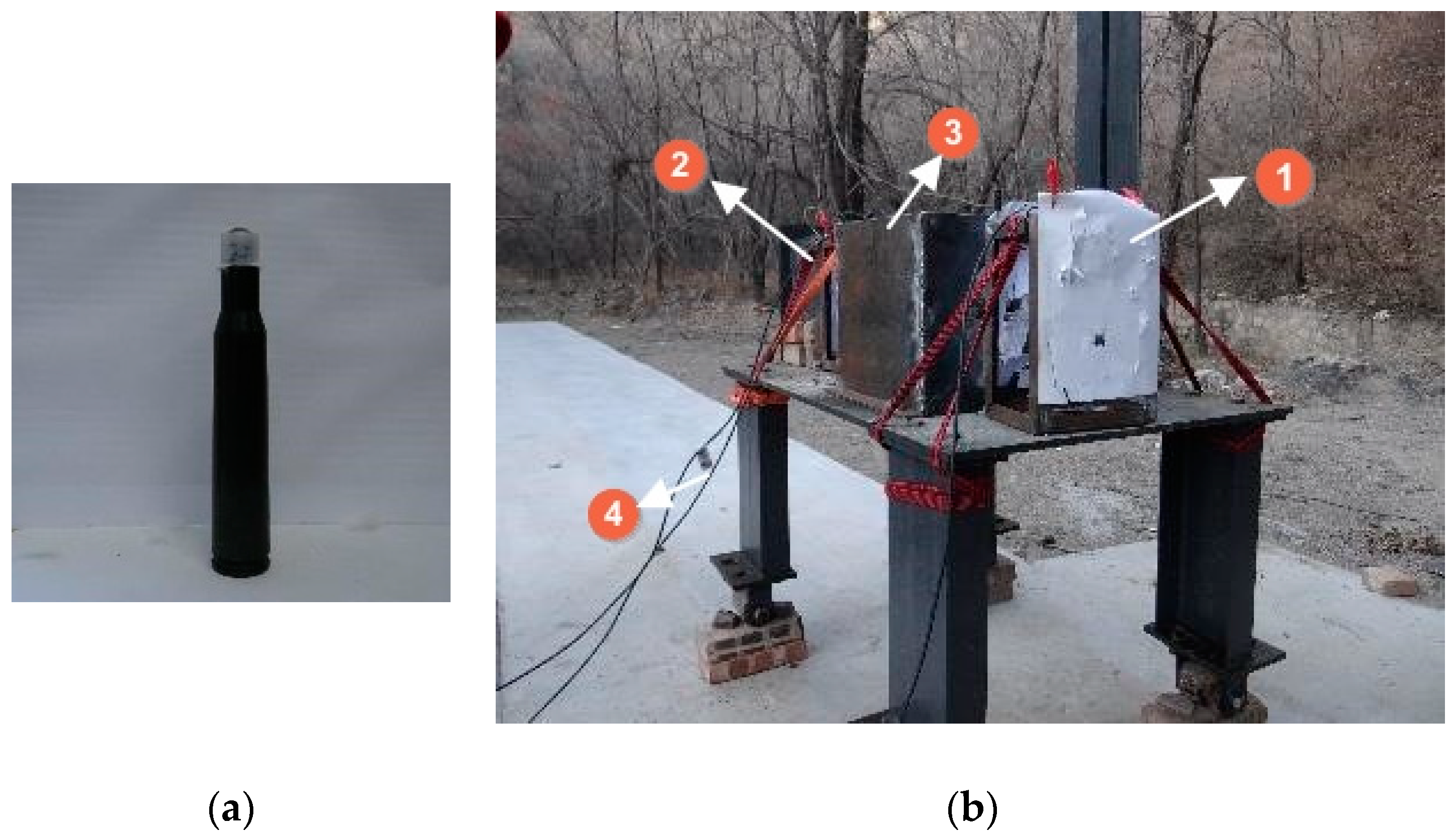
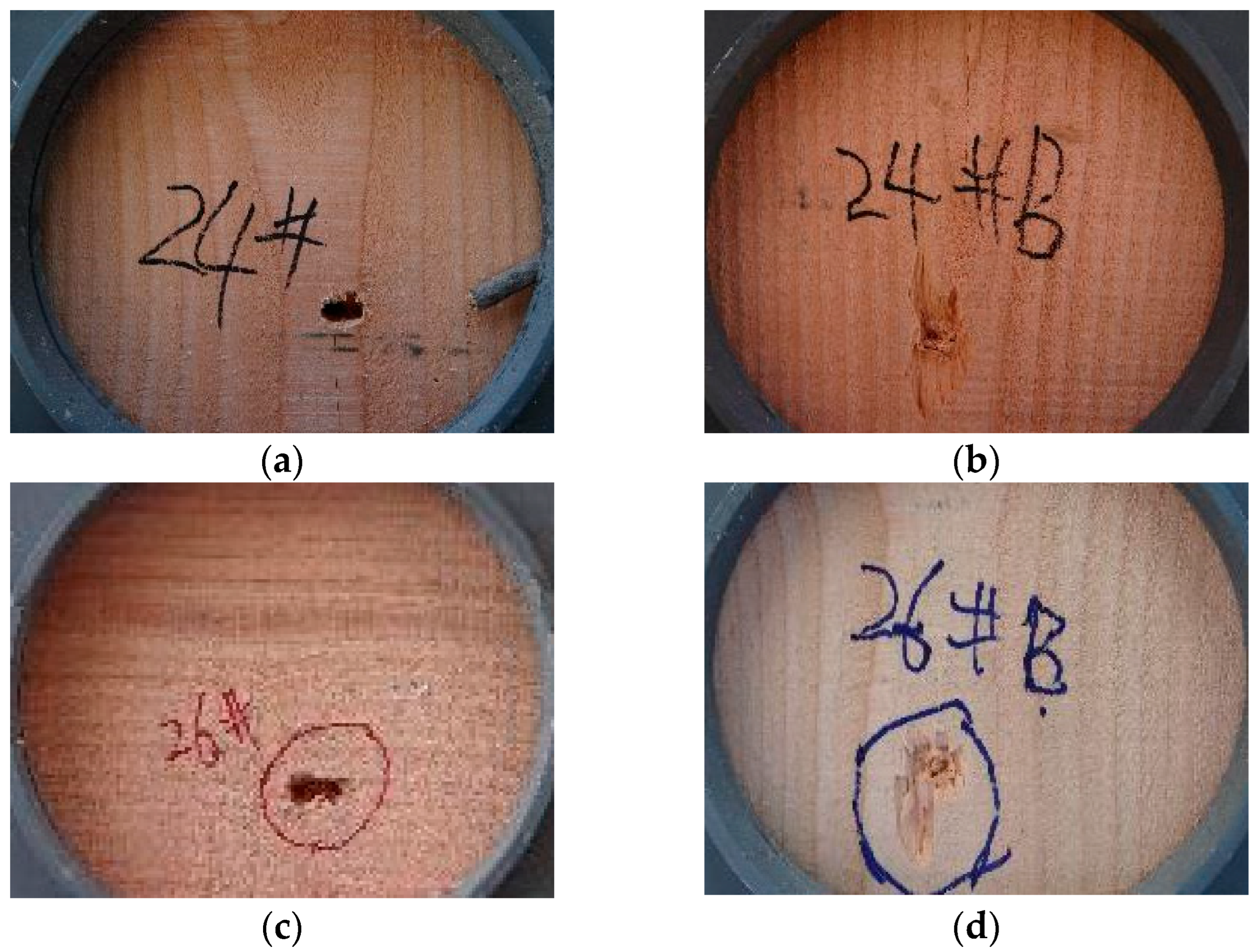
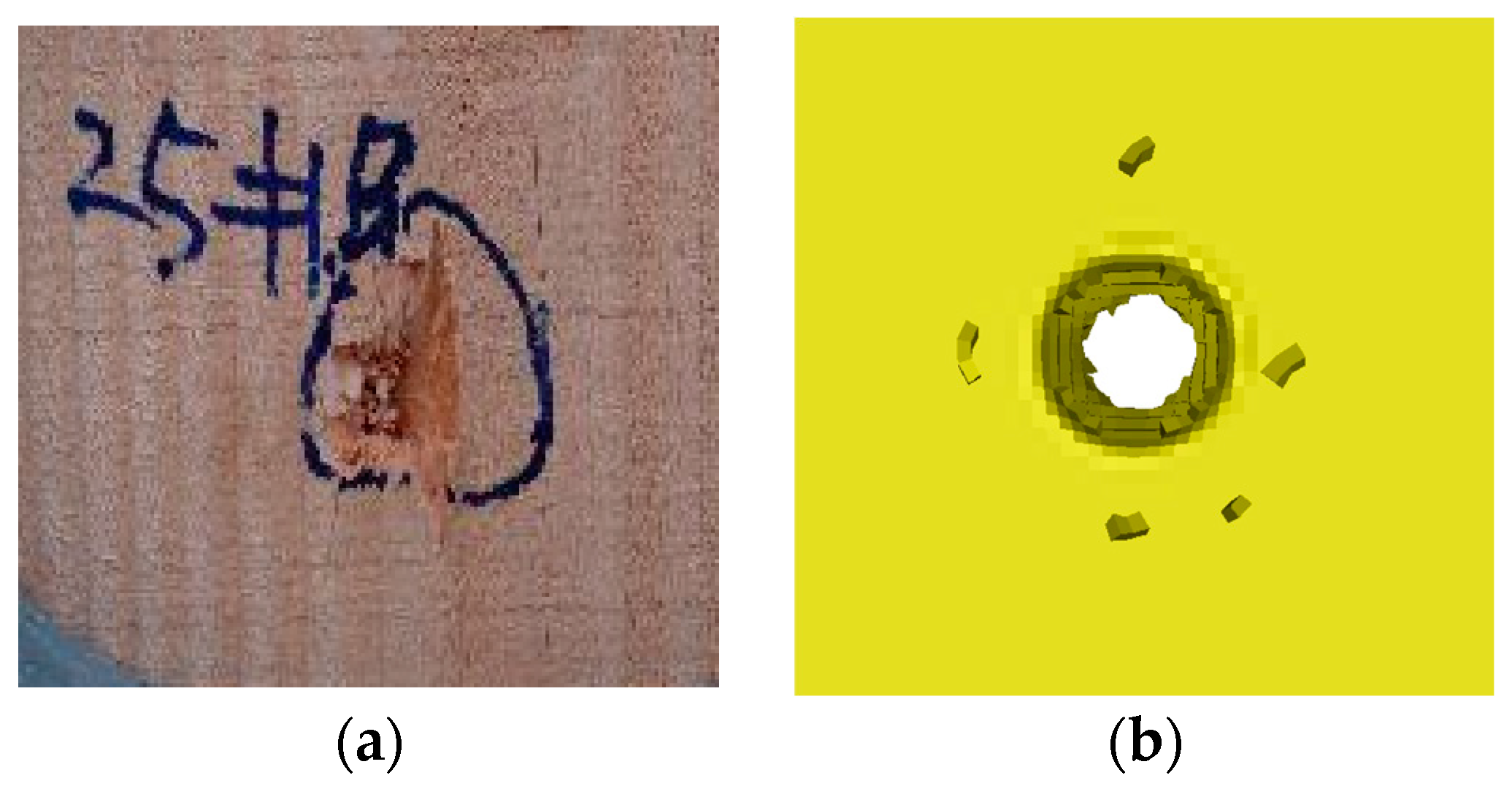



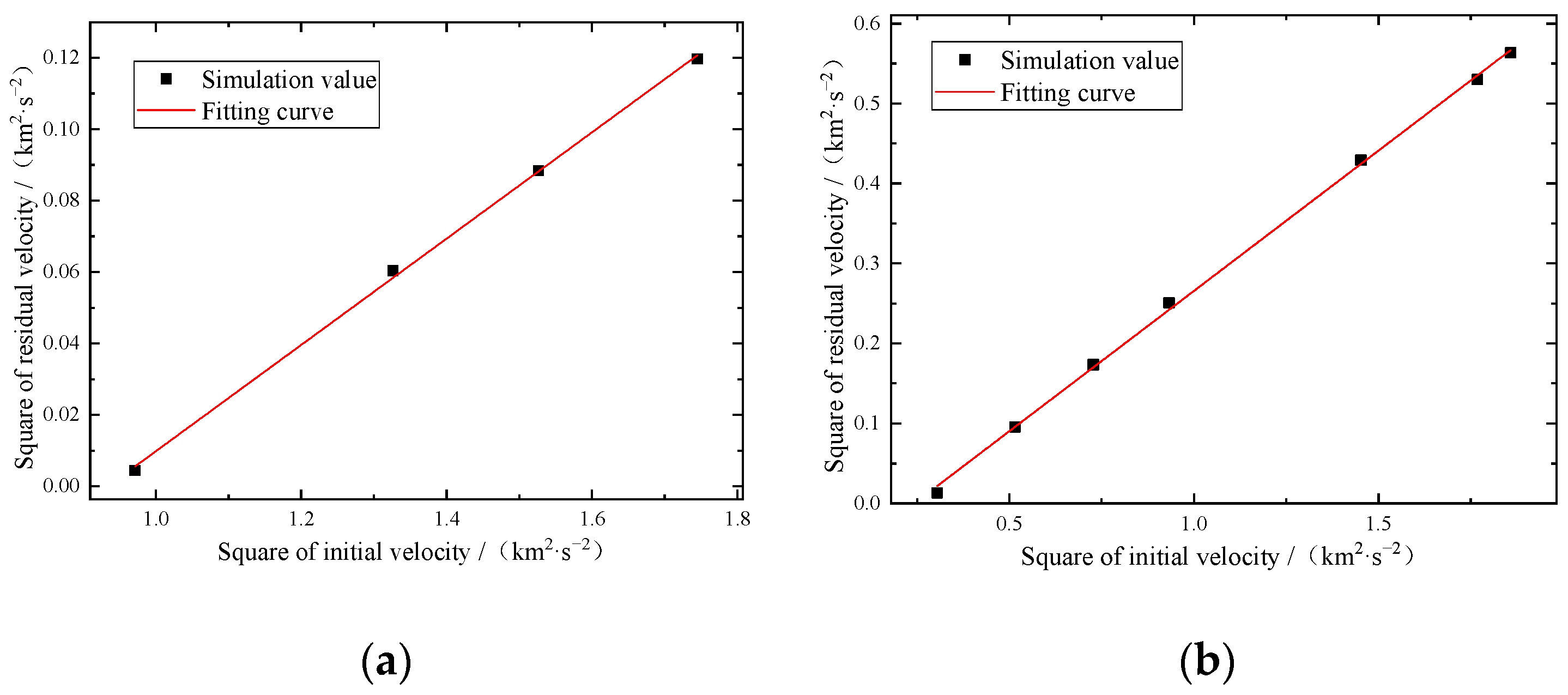
| Number | Fragment Type/mm | Target Plate Type | Initial Speed/(m·s−1) | Residual Speed/(m·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | pine | 985.65 | 115.36 |
| 2 | 6 | pine | 1151.6 | 153.24 |
| 3 | 6 | pine | 854.05 | no penetration |
| 4 | 6 | pine | 1321.07 | 347.36 |
| 5 | 6 | pine | 1235.48 | 172.36 |
| 6 | 6 | pine | 785.44 | no penetration |
| 7 | 6 | pine | 663.28 | no penetration |
| 8 | 6 | pine | 589.55 | no penetration |
| 9 | 11 | pine | 1205.19 | 654.09 |
| 10 | 11 | pine | 853.13 | 426.81 |
| 11 | 11 | pine | 965.77 | 539.42 |
| 12 | 11 | pine | 1363.24 | 708.13 |
| 13 | 11 | pine | 551.48 | 70.84 |
| 14 | 11 | pine | 717.86 | 306.18 |
| 15 | 11 | pine | 435.76 | no penetration |
| 16 | 11 | pine | 1329.6 | 598.68 |
| ρ/(g·cm−3) | E///GPa | E⊥/GPa | σst///GPa | σsc///GPa | σst⊥/GPa | σsc⊥/GPa | μ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.473 | 11.35 | 0.2468 | 0.0852 | 0.0212 | 0.00205 | 0.00408 | 0.157 |
| Number | Fragment Diameter/mm | Initial Speed/(m·s−1) | Experimental Residual Speed/(m·s−1) | Simulation Residual Speed/(m·s−1) | Difference Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 985.65 | 85.36 | 66.43 | 22.18 |
| 2 | 6 | 1151.6 | 223.24 | 245.7 | 10.06 |
| 3 | 6 | 854.05 | no penetration | no penetration | nothing |
| 4 | 6 | 1321.07 | 347.36 | 346.0 | 0.39 |
| 5 | 6 | 1235.48 | 272.36 | 297.3 | 9.16 |
| 6 | 6 | 785.44 | no penetration | no penetration | nothing |
| 7 | 6 | 663.28 | no penetration | no penetration | nothing |
| 8 | 6 | 589.55 | no penetration | no penetration | nothing |
| 9 | 11 | 1205.19 | 654.09 | 655.0 | 0.14 |
| 10 | 11 | 853.13 | 426.81 | 416.3 | 2.46 |
| 11 | 11 | 965.77 | 539.42 | 500.9 | 7.14 |
| 12 | 11 | 1363.24 | 708.13 | 750.7 | 6.01 |
| 13 | 11 | 551.48 | 95.84 | 114.4 | 19.37 |
| 14 | 11 | 717.86 | 306.18 | 308.8 | 0.86 |
| 15 | 11 | 435.76 | no penetration | no penetration | nothing |
| 16 | 11 | 1329.6 | 598.68 | 728.1 | 21.62 |
| Number | Stand Density ρ/(n·m−2) | Tree Diameter D/mm | Scattering Angle α/° | Model Calculation Value/mm | Formula Calculation Value/mm | Error Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 300 | 1 | 336.78 | 353.4 | 4.93 |
| 2 | 1 | 300 | 3 | 335.82 | 353.4 | 5.23 |
| 3 | 1 | 300 | 5 | 270.10 | 353.4 | 30.84 |
| 4 | 1 | 200 | 3 | 138.85 | 157.08 | 13.13 |
| 5 | 1 | 300 | 3 | 335.82 | 353.4 | 5.23 |
| 6 | 1 | 400 | 3 | 596.26 | 628.3 | 5.37 |
| 7 | 1 | 300 | 3 | 335.82 | 353.4 | 5.23 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 300 | 3 | 165.76 | 176.7 | 6.60 |
| 9 | 0.25 | 300 | 3 | 66.05 | 88.4 | 33.84 |
| Number | Thickness/mm | Edge Effect/(m·s−1) | Normal Target Plate/(m·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 467.2 | 464.0 |
| 2 | 5 | 473.3 | 464.3 |
| 3 | 15 | 476.7 | 467.8 |
| 4 | 25 | 481.4 | 470.4 |
| 5 | 35 | 486.6 | 473.6 |
| 6 | 45 | 488.9 | 480.4 |
| 7 | 55 | 508.7 | 495.3 |
| 8 | 65 | 517.6 | 508.3 |
| 9 | 75 | 528.3 | 524.5 |
| 10 | 85 | 556.3 | 543.2 |
| 11 | 95 | 579.7 | 563.4 |
| 12 | 105 | 598.3 | 597.1 |
| 13 | 115 | 643.1 | 629.0 |
| 14 | 125 | 686.8 | 672.3 |
| 15 | 135 | 745.0 | 738.5 |
| 16 | 145 | 857.5 | 838.3 |
| Number | Fragment Diameter/mm | Number of Spacer Layers | Simulation Residual Speed/(m·s−1) | Difference Ratio/%(Compared with 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 112.6 | 0 |
| 2 | 10 | 3 | 109.5 | −2.75 |
| 3 | 10 | 5 | 110.7 | −1.69 |
| 4 | 10 | 7 | 124.0 | 10.12 |
| 5 | 10 | 9 | 129.2 | 14.74 |
| 6 | 10 | 11 | 139.5 | 23.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Yin, J.; Li, X.; Yi, J. Effect of Wood Medium on Dispersion Parameters of Prefabricated Spherical Fragments in Forest. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211333
Wang Z, Yin J, Li X, Yi J. Effect of Wood Medium on Dispersion Parameters of Prefabricated Spherical Fragments in Forest. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(22):11333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211333
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhenning, Jianping Yin, Xudong Li, and Jianya Yi. 2022. "Effect of Wood Medium on Dispersion Parameters of Prefabricated Spherical Fragments in Forest" Applied Sciences 12, no. 22: 11333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211333
APA StyleWang, Z., Yin, J., Li, X., & Yi, J. (2022). Effect of Wood Medium on Dispersion Parameters of Prefabricated Spherical Fragments in Forest. Applied Sciences, 12(22), 11333. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211333






