Research on Initial Model Construction of Seismic Inversion Based on Velocity Spectrum and Siamese Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Velocity Spectrum
2.2. The Triple Structure Siamese Network for Velocity Spectra Lateral Target Tracking
2.2.1. Triple Siamese Network Structure
2.2.2. Weight Coefficients
2.2.3. Loss Function and Network Parameters
2.3. Workflow
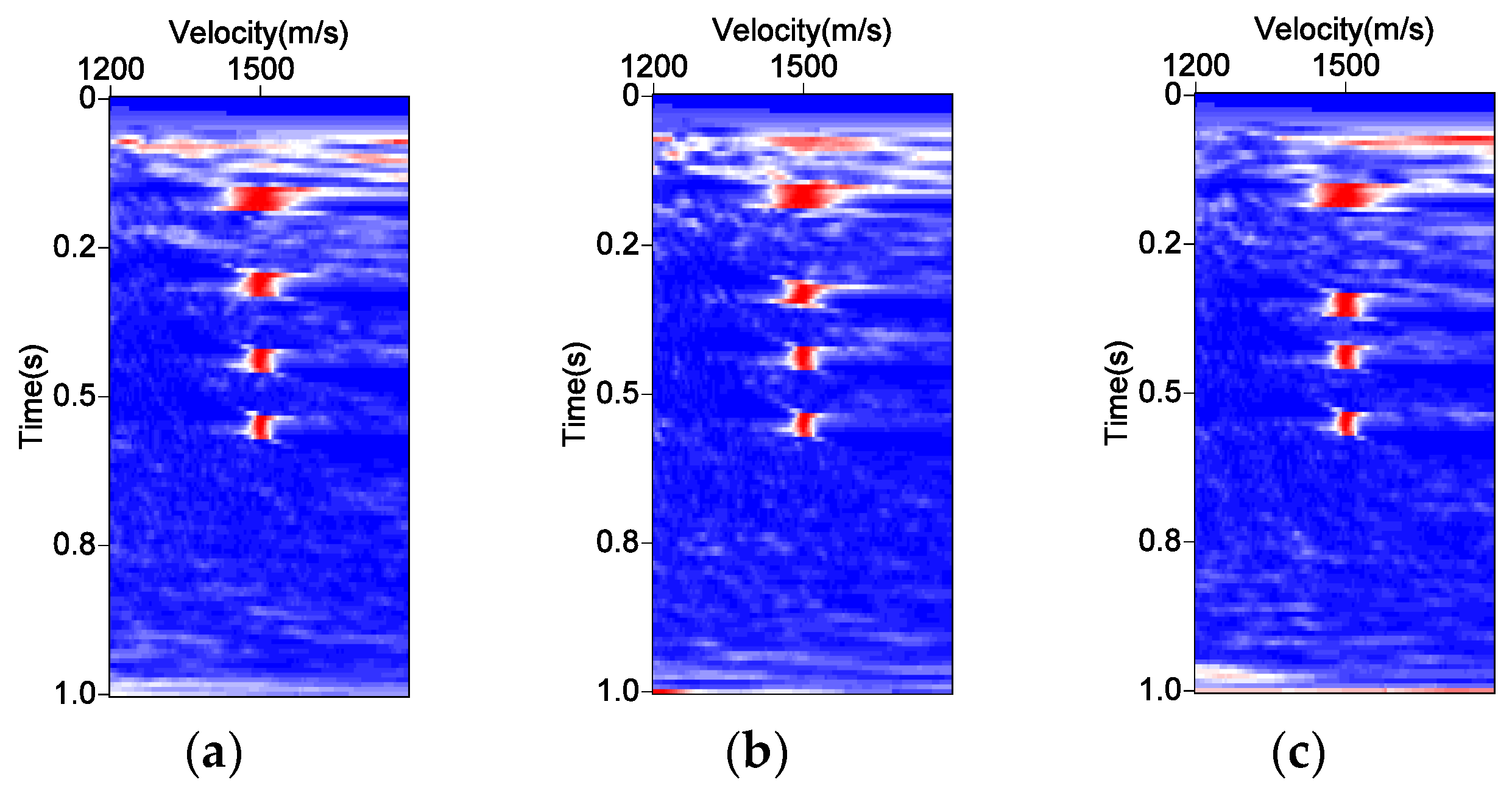
3. Model Test
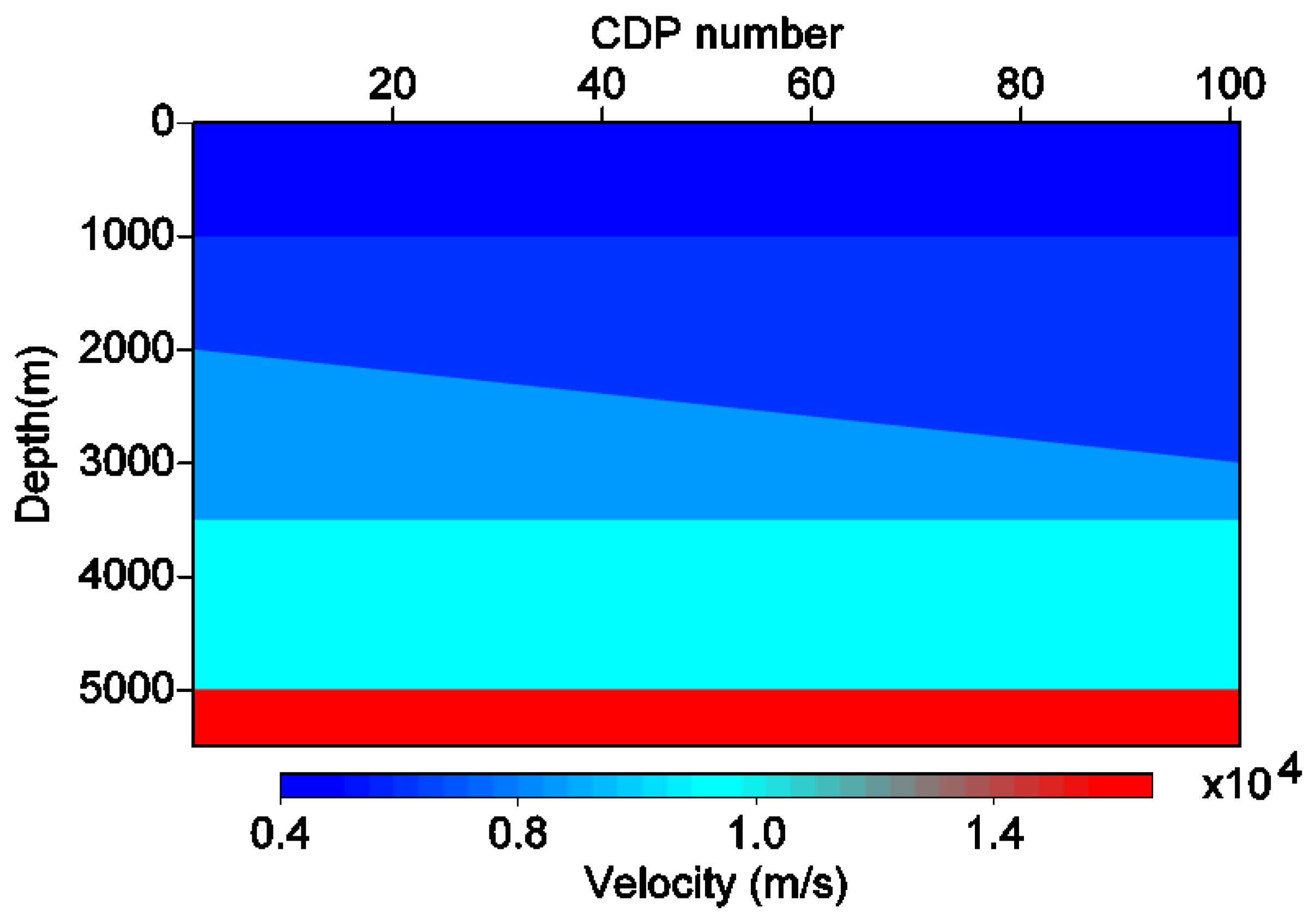
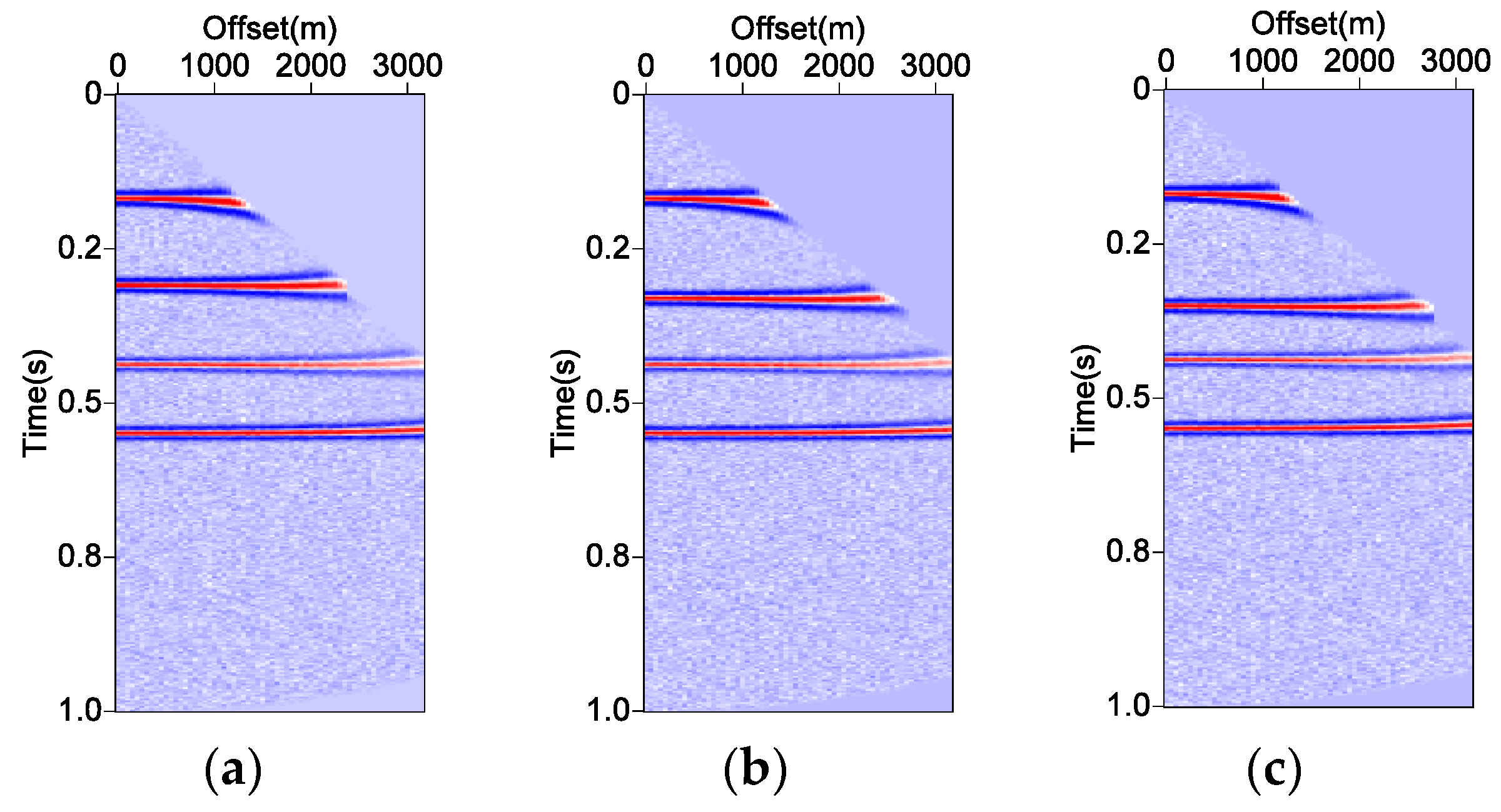
3.1. Theoretical Model
3.2. Model Training
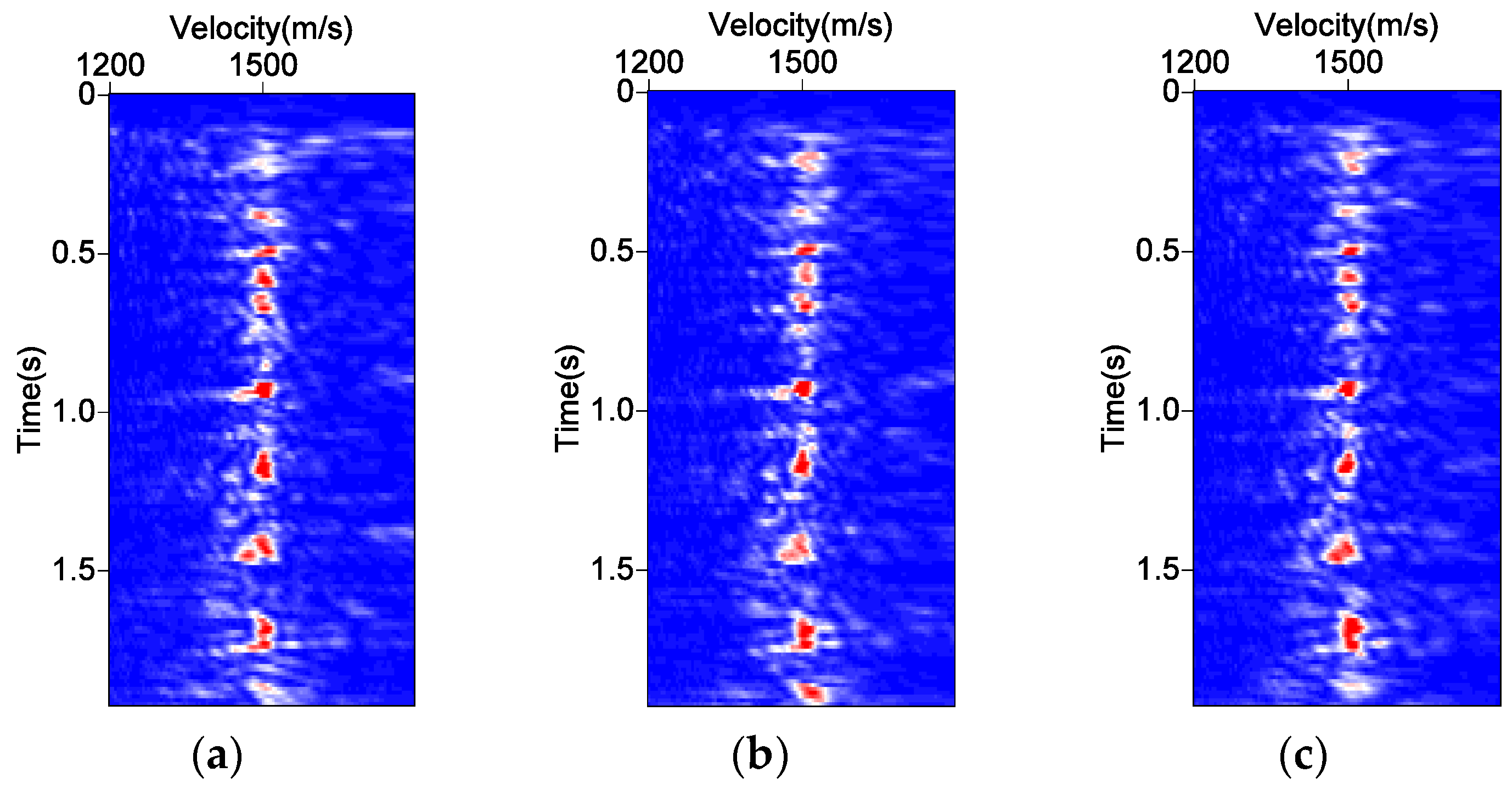
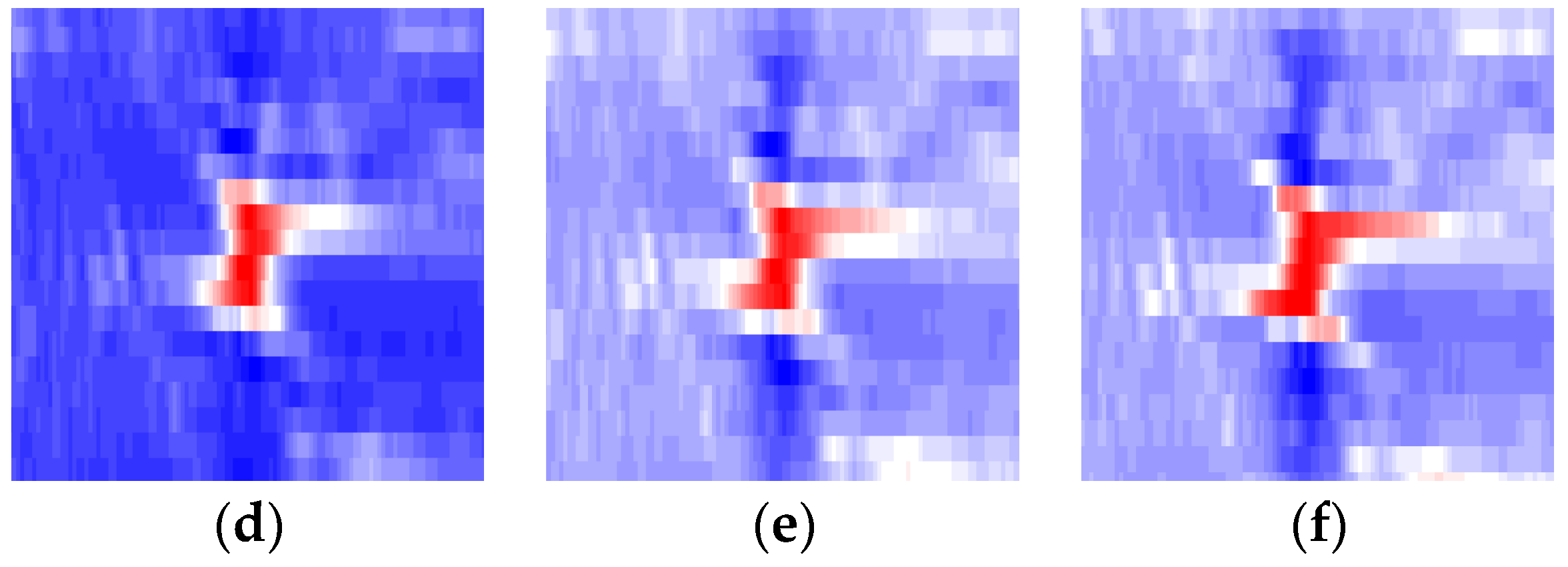
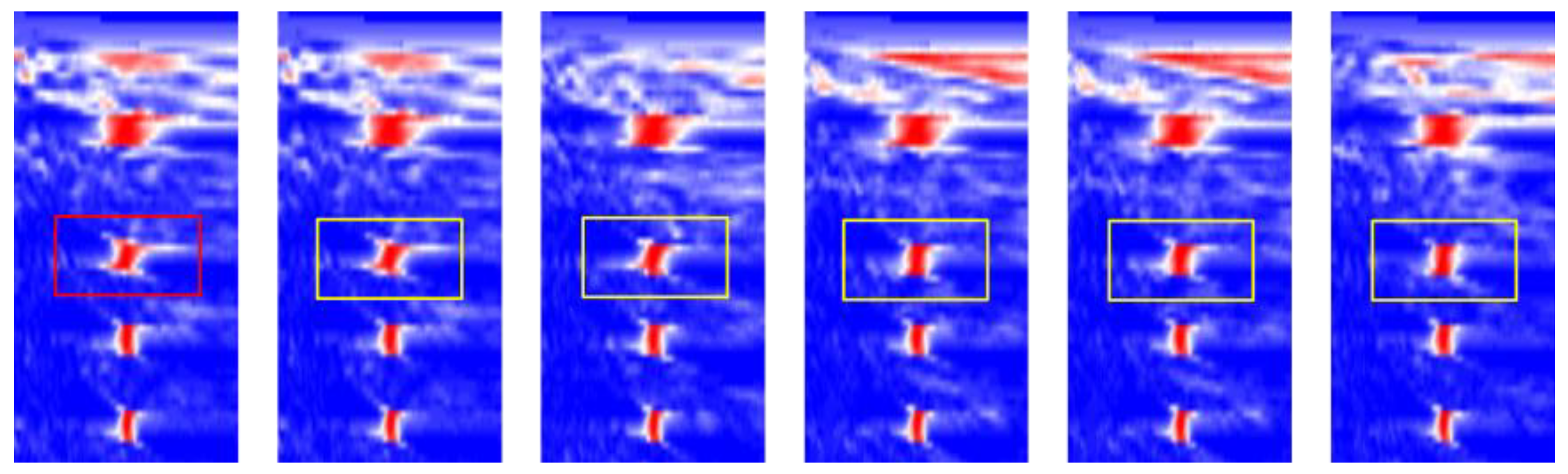
3.3. Tracking Results
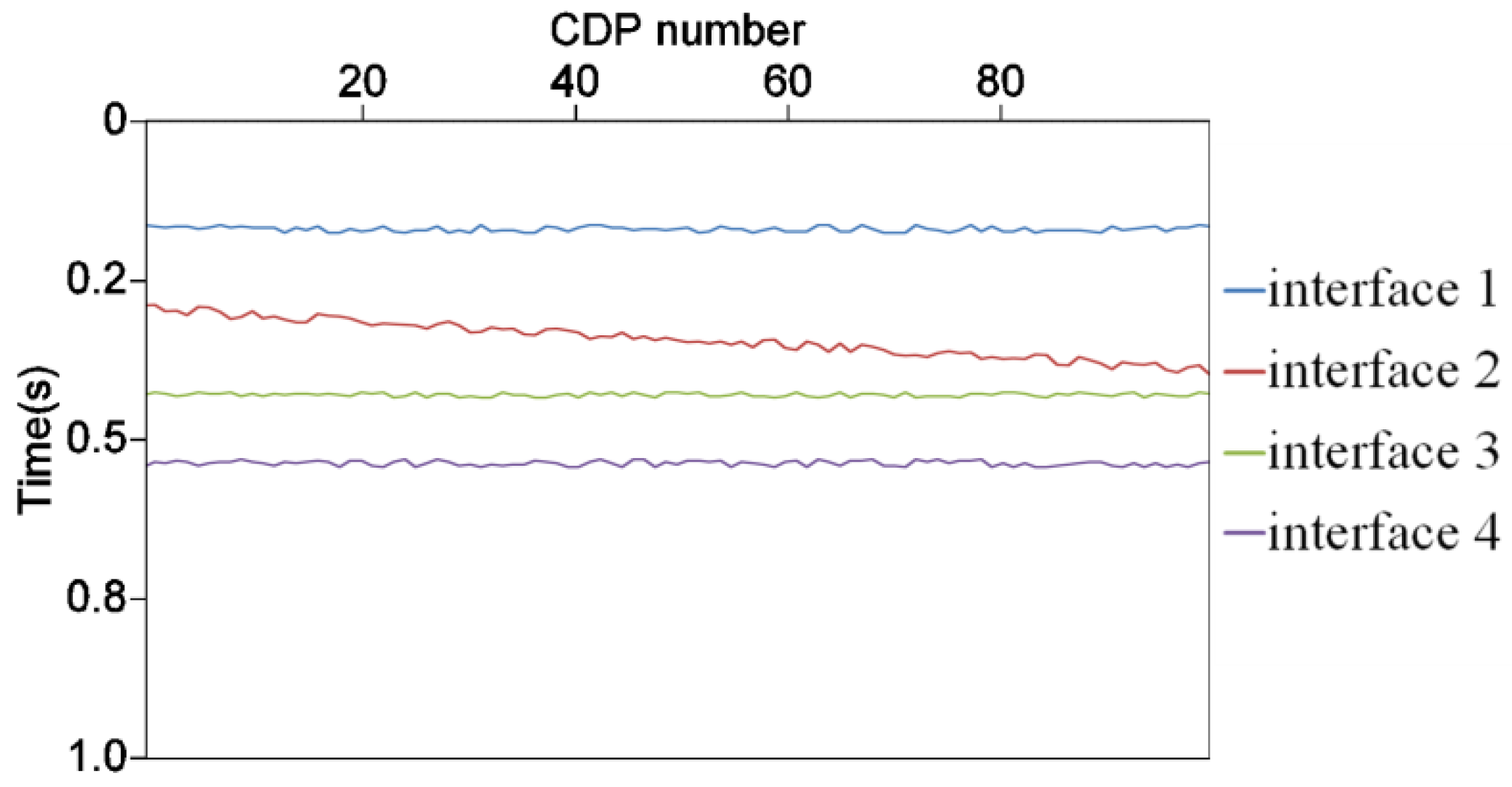
3.4. Initial Velocity Model
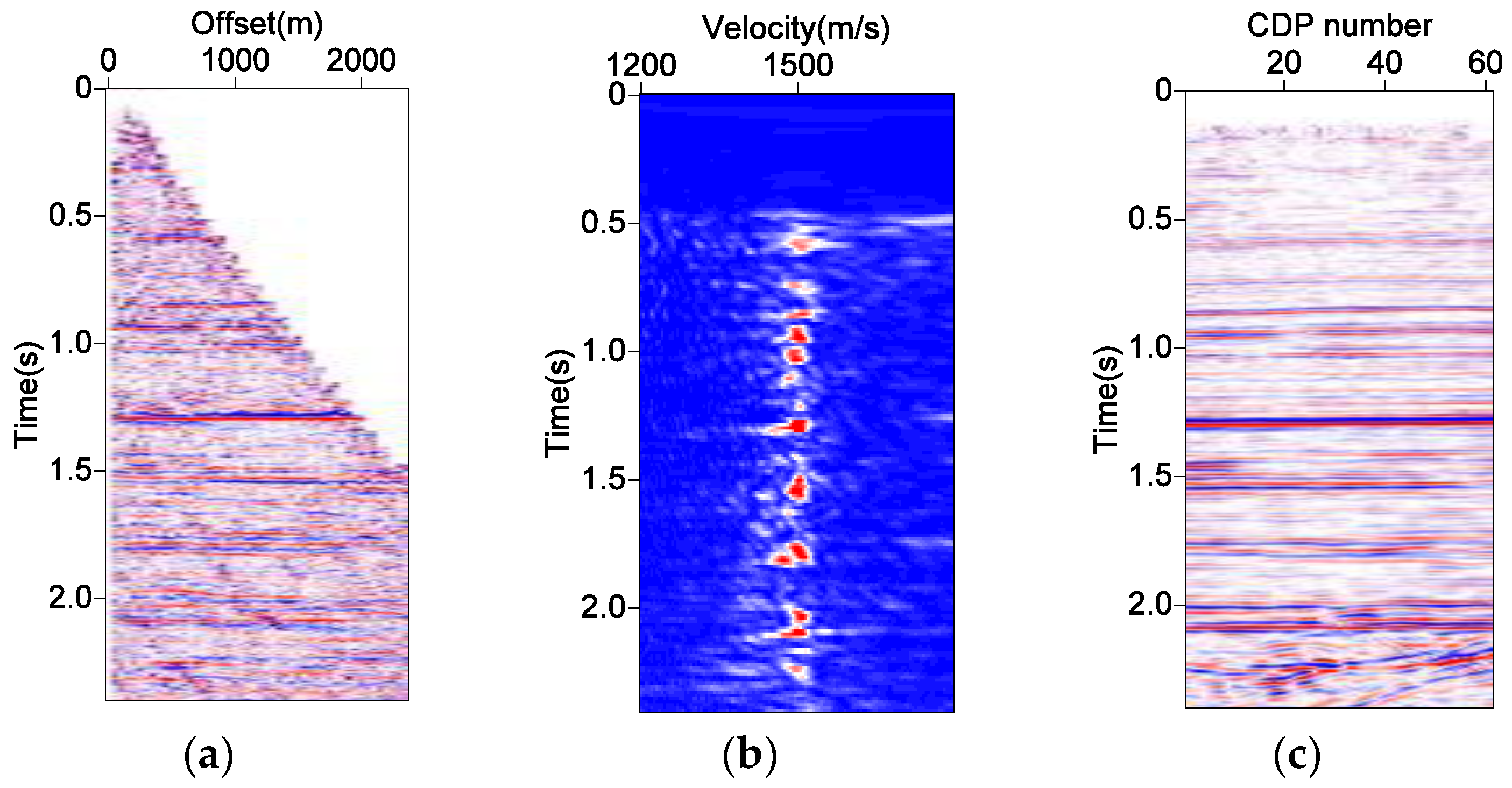
4. Real Data Applications
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mallet, J.L. Geomodeling; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Caumon, G.; Collon-Drouaillet, P.; de Veslud, C.L.C.; Viseur, S.; Sausse, J. Surface-based 3D modeling of geological structures. Math. Geosci. 2009, 41, 927–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, D.; Todorov, T.; Russell, B. Using multi-attribute transforms to predict log properties from seismic data. Explor. Geophys. 2000, 31, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.M.; Mosegaard, K.; Pedersen-Tatalovic, R.; Uldall, A.; Jacobsen, N.L. Attribute-guided well-log interpolation applied to low-frequency impedance estimation. Geophysics 2008, 73, R83–R95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, H. Image-guided 3D Interpolation of Borehole Data. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2010; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 1266–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, D.; Wu, X. Horizon volumes with interpreted constraints. Geophysics 2015, 80, IM21–IM33. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, P.; Fomel, S.; Zhang, R. Creating detailed subsurface models using predictive image-guided well-log interpolation. Interpreatation 2017, 5, T279–T285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyes, J.; Cheret, T. A review of “global” interpretation methods for automated 3D horizon picking. Lead. Edge 2011, 30, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, E.; Kroh, J.; Sandham, W.; Durrani, T. Seismic Horizon Picking Using an Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–26 March 1992; pp. 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Leggett, M.; Sandham, W.A.; Durrani, T.S. 3D horizon tracking using artificial neural networks. First Break 1996, 14, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Di, H. Dip Interpolation for Improved Multitrace Seismic-Attribute Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 29 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fehmers, G.C.; Höcker, C.F. Fast structural interpretation with structure-oriented filtering. Lead. Edge 2002, 21, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y. Automatic Horizon Picking In 3D Seismic Data Using Optical Filters And Minimum Spanning Tree (Patent Pending). In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2011; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 965–969. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Lin, T.; Cao, D.; Lou, Y. Semiautomated seismic horizon interpretation using the encoder-decoder convolutional neural network. Geophysics 2019, 84, B403–B417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidell, N.S.; Taner, M.T. Semblance and Other Coherency Measures for Multichannel Data. Geophysics 1971, 36, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Dai, J.; Ji, X.; Wei, Y. Fully Convolutional Instance-Aware Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2359–2367. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; George, A.M.; Ma, J.; Xie, F. Automatic velocity picking from semblances with a new deep-learning regression strategy: Comparison with a classification approach. Geophysics 2021, 86, 1942–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Polo, M.; Dahlke, T.; Frogner, C.; Zhang, C.; Poggio, T.; Hohl, D. Automated fault detection without seismic processing. Lead. Edge 2017, 36, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley, J.; Guyon, I.; LeCun, Y.; Säckinger, E.; Shah, R. Signature verification using a “siamese” time delay neural network. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 1993, 7, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadsell, R.; Chopra, S.; LeCun, Y. Dimensionality Reduction by Learning an Invariant Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 1735–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Vries, D.D.; Berkhout, A.J. Velocity analysis based on minimum entropy. Geophysics 1984, 49, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B.L.; Kostov, C. High-resolution velocity spectra using eigen structure methods. Geophysics 1989, 54, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, S.C.; Smithson, S.B. New approach to seismic-reflection event detection and velocity determination. Geophysics 1990, 55, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomel, S. Velocity analysis using AB semblance. Geophys. Prospect. 2009, 57, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Hale, D. Velocity analysis using weighted semblance. Geophys. J. Soc. Explor. Geophys. 2012, 77, U15–U22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursin, B.; da Silva, M.G.; Porsani, M.J. Generalized Semblance Coefficients Using Singular Value Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 13th International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society & EXPOGEF, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 26–29 August 2013; pp. 1544–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Kahoo, A.R.; Chen, Y.; Porsani, M. A high-resolution weighted AB semblance for dealing with amplitude-variation-with-offset phenomenon. Geophysics 2017, 82, V85–V93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Polo, M.; Jennings, J.; Adler, A.; Dahlke, T. Deep-learning tomography. Lead. Edge 2018, 37, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ji, X.; Fei, T.W.; Luo, Y. Automatic Velocity Picking with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 14–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, P.; Gu, Y.; Li, X. Automatic Velocity Picking Based on Deep Learning. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2019; pp. 2604–2608. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.; Chang, S.F. A Robust Content Based Digital Signature for Image Authentication. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Lausanne, Switzerland, 19 September 1996; pp. 227–230. [Google Scholar]






| Network Layers | Conv1 | Pool1 | Conv2 | Pool2 | Conv3 | Conv4 | Conv5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convolution kernel | 11 × 11 | 3 × 3 | 7 × 7 | 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 |
| Step size | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Ding, L.; Wang, X. Research on Initial Model Construction of Seismic Inversion Based on Velocity Spectrum and Siamese Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010593
Sun L, Ding L, Wang X. Research on Initial Model Construction of Seismic Inversion Based on Velocity Spectrum and Siamese Network. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010593
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Luping, Ling Ding, and Xiangchun Wang. 2022. "Research on Initial Model Construction of Seismic Inversion Based on Velocity Spectrum and Siamese Network" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010593
APA StyleSun, L., Ding, L., & Wang, X. (2022). Research on Initial Model Construction of Seismic Inversion Based on Velocity Spectrum and Siamese Network. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010593






