Abstract
Carbon dot-based composite materials have been extensively developed for versatile biomedical applications, such as drug delivery, tissue engineering, bioimaging, biosensors, and photothermal cancer therapy, owing to their excellent mechanical properties, electrical and thermal conductivity, large surface-to-volume ratio, and biocompatibility. For instance, the hydrophobicity and delocalized π-electrons of carbon dots enable insoluble drug loading in carbon composite-based drug delivery carriers. In addition, carbon dot-based materials are suitable for optical and electrochemical biosensor applications owing to their intrinsic properties. Thus, this review briefly focuses on the following: (1) general aspects, (2) various sources, and (3) versatile biomedical applications of carbon dots and composite materials. More importantly, we present the emerging applications of carbon dot-based materials, such as in agricultural systems, COVID-19 theranostics, counterfeit, and security.
1. Introduction
Carbon dots (CDs) were found during the attempt to purify single-walled carbon nanotubes using electrophoresis [1]. Based on the term dots, CDs can be defined as tiny, carbonized substances having a size of <10 nm, called carbon quantum dots [2]. Various substances can be processed to yield CDs as a starting source, including natural (i.e., watermelon) and synthetic (i.e., citric acid) substances [3,4]. In addition, the following two main strategies have been employed to synthesize CDs: (1) top-down and (2) bottom-up approaches [5,6,7]. CDs have been gaining popularity since they were first discovered owing to their optical, physiochemical, macroscopic, and microscopic properties, as well as electroconductivity, which enables them for use in versatile applications. CDs have been applied in numerous fields including energy conversion, food quality assessment, and material science [8,9]. More importantly, the low toxicity of CDs renders them highly biocompatible; thus, a plethora of biomedical applications have been addressed, including bioimaging, biosensing, cancer and degenerative disease treatment, ion detection, and coronavirus theranostics [9,10]. In addition, CDs have been utilized to convict criminals because they have been used to make efficient materials for detecting forgery and tracing crime scenes [11,12].
CDs and polymer composite materials have also gained significant attention for biochemical, biological, and biomedical applications owing to their facile preparation, cost-effective processing, and biocompatibility [13]. CDs are readily synthesized from a variety of natural and synthetic sources. CD/polymer composites are readily produced by mixing polymer and CDs with/without further treatments (Figure 1a). Although mixing of polymers and nanomaterials is not a novel synthesis process, developing better CD/polymer composite materials that exhibit favorable biocompatibility and optoelectrical properties is an emerging research topic. Polymers with different architectures, such as homo- and co-polymers, hyperbranched polymers, and various polymeric chains, have been employed to anchor and coat CDs to fabricate biocompatible CD/polymer hybrid composite materials. Recent studies have shown that several methods, including ligand exchange between polymers and CDs, grafting polymers to CDs, grafting polymers from CDs, capping polymers onto CDs, and growing CDs within the polymer template, are generally used for biocompatible CD/polymer composite materials [14,15]. As shown in Figure 1b, the facile preparations and remarkable properties of CDs and cross-linked polymeric properties have inspired the potential applications (i.e., drug delivery system, photodynamic therapy, bioimaging, etc.) in biomedical sciences [16].
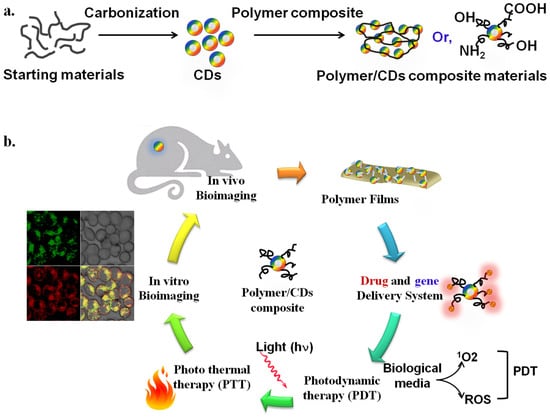
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of the synthesis of CDs from starting materials (first) and fabrications of CD/polymer composite materials (second). (b) The proposed biomedical application of CD/polymer composite materials. The Figure is depicted with slight modification from [16], which is freely accessed, distributed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0 (accessed on 14 August 2022)).
The objective of this study is to provide a brief overview of the sources, methodologies, characterizations, and biomedical applications of CDs. Special emphasis was placed on the emerging uses of CDs and their future prospects in such disciplines. This review was designed in the most straightforward manner to provide a context for non-chemist researchers interested in the study of CDs, such as biomedical professionals.
2. General Aspects of Carbon Dot/Polymer Composites
The sources of CDs for synthesis are easily obtainable natural carbon and synthetic substances including small organic molecules and polymers. CDs are a type of low-dimensional carbon-dominated nanomaterial, which consists of a sp2/sp3 hybridized carbon skeleton and functional groups. A variety of functional groups (carboxyl, hydroxyl, and amine) enable excellent water solubility and convenience for hybridization with other materials without phase separation. Moreover, a variety of functional groups allow CDs to be easily functionalized with various organic or polymeric molecules and promising nanoparticles [17]. For instance, the ‘ease-to-fabricate’ CD-based polymer films are due to their immediate compatibility in water, resulting in a facile wet mixing procedure of the CD/polymer composite materials [13]. Thus, the hydrophilic CDs and polymers intermingle to form a composite film. The CD/polymer composite films have a high contact angle, which indicates the generation of hydrophobic character on the composite film surface. The surface chemistry and topography of any polymeric film largely depend on its wettability, that is, the less hydrophilic CD/polymer composite.
2.1. Synthesis of Carbon Dot/Polymer Composites
Although CD sources and syntheses have been extensively reviewed, it is noteworthy to briefly highlight the sources and preparation as a prelude to the topic. CDs can be derived from the following two main sources: (1) natural sources, such as carrots, lemons, and funnel seeds, and (2) synthetic sources, such as, phenylalanine and citric acid [4,16]. More studies are needed to determine whether the source of CDs affects their effectiveness and properties. Top-down and bottom-up strategies were employed to prepare the CDs (Figure 2). While the top-down approach involves breaking down the carbon material structures (e.g., chemical oxidation process, plasma reactor, microwave, and laser ablation), the bottom-up process involves the carbonizations of tiny molecules to synthesize CDs (e.g., hydrothermal method, solvothermal method, carbonization, and thermal decomposition) [4,18,19,20,21,22]. CD/polymer hybrid composite materials are prepared by several methods such as mixing, crosslinking reactions, polymerizations, and thermal treatments [23,24,25,26,27]. For instance, simple mixing of CD and polymer solutions [24], incorporation of CD into crosslinked polymer networks [25], and interfacial polymerizations with/without the polymers on the thin-film membranes [26,27] are used to prepare CD/polymer hybrid composite materials.
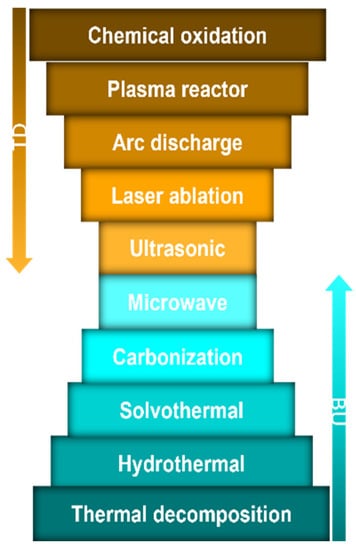
Figure 2.
Synthesis of carbon dots: top-down (TD) and bottom-up (BU) approaches.
2.2. Characteristics of Carbon Dots
CDs are semi-spherical, nanoscale substances in their physical form. In general, the size of CDs is less than 10 nm. Several strategies can be used to adjust the size, including the filter size, temperature, and reducing agent [28,29,30]. The physiochemical characteristics of CDs slightly differ based on their sources, preparation processes and analytical techniques [28]. For instance, the X-ray crystallography (XRD) profile of CDs obtained from dextrose and nano-biomass dots, prepared by ultrasonic-assisted extraction, are reported to be centered at ~2θ = 26° and 21.5°, respectively [31,32]. CDs can carry a negative or positive charge, with a wide range of zeta potential based on the source of the CDs. For example, CDs prepared from Averrhoa carambola fruit using hydrothermal treatment had zeta potential of −15.21 mV [33]. The organic components were found to vary in content as follows: nitrogen, carbon, and hydrogen contents were approximately 0–20%, 7–49%, and 2–9%, respectively, in a study using various starting materials (polyethyleneimine, N,N-dimethylethylene diamine, diethylenetriamine, ethanolamine, N’-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride) and synthesis methods (pyrolysis, microwave, and solvothermal) as reported by Fan et al. [34]. The superficial presence of functional groups (–OH,–COOH, and –NH2), which can be attained by surface passivation techniques, improves the solubility and chemical reactivity of CDs [35].
The absorption spectrum of CDs is very large, covering the entire UV range [2,11,36]. Once excited, CDs display fluorescence, electroluminescence, phosphor-luminescence, and other characteristics [37]. Several explanations of CD photoluminescence have been reported, such as conjugation of the π-domain with a quantum confinement effect originating from the defect/surface state and subdomain state within the graphitic carbon core; the emission may be improved by the surface state, subdomain state, and molecular state crosslink [38]. The understanding of the mechanism behind these luminescent properties remains limited; however, CDs have been utilized in biolabeling and bioimaging owing to their chemiluminescence feature [38].
2.3. Pharmacology of the Carbon Dot—Fate—In the Body
As previously indicated, the majority of CD research has been focused on synthesis, toxicity, and effects. However, pharmacological studies regarding CDs in terms of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PKPD) are scarce. The journey of CDs metabolism begins with administration and ends with elimination. The average dose administered differ by studies. Ding and colleagues found that CDs, prepared from citrate by a hydrothermal method, at a concentration of 25–100 µg/mL, inhibited uveal melanoma growth [39]. Furthermore, Phellodendri Cortex Carbonisatus CDs, fabricated by the solvothermal method, showed excellent hemostatic effects in mice at a dose of 1 mg/kg [40,41]. CDs are biotransformed by enzymatic degradation, notably myeloperoxidase, neutrophil, and eosinophil peroxidase enzymes (in the presence of H2O2), which are mainly involved in the metabolism of CDs, as investigated by Martin et al. [42]. In summary, the smaller the size, the lesser the toxicity and more efficient the processing, which includes metabolism, target interaction, and elimination. Ideal CDs have a high specificity to the target, minimal off-site interaction, high cell uptake, are readily excreted or biodegradable, hydrophilic, and have a hydrodynamic size of 6 nm or less. CDs can be excreted by the kidney depending on their size and charge [43].
Wang et al. investigated the acute toxicity of the CDs prepared from nitric acid [44]. This study concluded that CDs of 5.1 to 51 mg/kg body weight in mice were safe, and no toxic signs or mortality were recorded even after 2 weeks in acute toxicity evaluations. However, subacute doses (0.2 to 20 mg/kg) caused mild changes in liver enzymes and blood lipoprotein profile, indicating a possibility of mild toxic effects; thus, species variation should be considered. In addition, the bioavailability of graphene quantum dots (GQD) in lung tissues has been detected by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) [45]. The intravenously injected GQDs prepared from graphite flakes into the rats showed no significant acute toxicity with 5 and 15 mg/kg body weight, but mild foreign body reactions to the GQD were found. Future studies regarding CDs absorption, distribution, biotransformation, and excretion are essential for understanding the effects of the body on CDs and to enable researchers to design CDs with optimum effects according to the PK characteristics indicated above.
2.4. Carbon Dots and Polymer Hybrid Composite Materials
2.4.1. Features of Carbon Dot/Polymer Composites
CDs and polymer composite materials demonstrate a polymer-carbon hybrid structure rather than a central carbon body structure, contributing to the predominant polymeric surface properties, which is different from the traditional carbonized CDs. Therefore, composite hybrid materials possess superior optical properties compared to conventional carbonized CDs and bare polymers [17,46]. In general, polymers can act as stabilizing agents for high-volume-to-surface nanoparticles such as CDs. Polymer structures tend to diffuse through the nanoparticle surface to compensate for the starving nature of the nanoparticle surface energy. For these CDs, identical phenomena have been encountered in the polymer chains, and desirable synergistic features were presented. The newly formed CD-based hybrid features have higher optical properties, retaining all other polymer features intact. A remarkable advantage of polymer materials is their reliability in the era of functional product development. The durability of polymer materials is sometimes influenced by improper stress depletion, lack of uniformity in reinforcement, and thermal stability. Under these conditions, CDs play a crucial role in remediating inherent demerits. Physical interactions, H-bonding, polar–polar anchoring, polymeric entanglement, and surface passivation allow CDs to achieve better physisorption-aided anchoring of polymer chains onto the surfaces of CDs [13,47]. The polymeric hybridization of CDs mainly includes the following three features: (1) abundant functional groups and attachment of polymer chains, (2) predefined polydispersity in structures and properties influenced by the polymeric conjugation process, and (3) superior optical properties generated by the process of surface passivation. CDs with tunable optical properties have been extensively developed. For example, nitrogen-doped CDs emit bright blue fluorescence when subjected to UV excitation [48]. In addition, CDs showed red fluorescence when rhodamine B was added as a donor molecule, resulting in these unique optical tuning properties to the transfer of nano-radioactive energy from excited donor to acceptor [48]. Furthermore, oxygen-containing CDs obtained from lemon juice via the hydrothermal method showed bright blue-green emissions when excited with UV [49]. CDs (1.8 nm) synthetized from carbon tetrachloride by hydride-reducing agents showed a wide absorption band at 270 nm. By increasing the mean diameter of CDs, a distinct shift was found in wavelength absorption to 304 and 306 nm [29].
Carbon dot/polymer composites are distinguished from a molecular state, where the surface state is the synergistic hybridization of a polymeric backbone. The energy gap of the surface state, where electrons and holes (e/h) pair and recombine to emit fluorescence, corresponds to the extent of the π-electron and surface chemistry. New sub-levels can be created by surface passivation or other effective modification methods, thus roughly controlling the photoluminescence (PL). Moreover, several studies have demonstrated that most of the fluorescence of the CD/polymer composite originates from the surface state and highlights its potential to change the photoluminescence (PL) properties [50,51,52].
Bare CDs usually exhibit light absorption in the UV–vis region, which has an extremely strong UV absorption. In the CD/polymer composite structure, light absorption results from multiple hybrid structures in the polymer/carbon nanoparticles. The π–π* transition is typically attributed to the aromatic carbon structure, and the n–π* transition is assigned to the functional chemical groups with lone pairs of electrons, including the amino-based chromospheres. Molecular state-connected structures possessing a band gap similar to that of organic fluorescent molecules may also generate specific absorption peaks. The absorption in the longer-wavelength region is assigned to the energy level transition from the angstrom (A°)-sized conjugated π-structure. The derivatives of the aforementioned structure connected with various chemical groups (such as –OH,–COOH, and –NH2) can alter the absorption features of the CD/polymer composite structure. The compact structure within the CD/polymer composite materials enhances the interactions among the groups, changing the energy bandgap and resulting in variations in the absorption [17,53].
2.4.2. Photoluminescent Feature of Carbon Dot and Polymer Composites
The photoluminescence (PL) origin of CDs has been extensively studied; the mechanism generally includes intrinsic state emission (quantum size effect) and surface-defect state emission. The fluorescence origin of the CD/polymer composite structure resembles that of certain fluorescent polymer materials. Standard fluorescent polymer materials include conjugated polymers and polymers that are linked to fluorescent molecules [52]. The fluorescence source may be related to the heteroatom-containing bonds (C-O, C-N, N-O), called sub-fluorophores. Although these sub-fluorophore band gaps are not suitable for visible emission, the configuration of the polymer chains enables interactions among the chemical groups. Therefore, the band gap decreases, resulting in the observed fluorescence emission. Moreover, compared to small-molecule precursors, synthesis conditions such as pH, time, and temperature have a lower impact on the emission wavelength and chemical structure of CD/polymer composite materials [35,46,50].
In addition, the polymer chain can stabilize the CDs. Considering their large surface area, CDs are susceptible to coalesce to form larger aggregates, which enables better fluorescence and sensing behaviors. Polymeric materials act as stabilizers that adsorb onto the surfaces of CDs, resulting from CD/polymer nanocomposites. CD-polymer nanocomposites are currently sufficient to be developed in the field of material science. Thus, CD/polymer composites can be utilized for nanocomposite gel fabrications. Previous studies have demonstrated that carbon dot/polymer composites possess superior physio-mechanical properties compared to conventional polymeric gels [13,54]. Furthermore, the hybrid CD/polymer composite film can be used as a highly swellable, rigid, thermally stable, and photo-responsive material.
Typical polymer passivation agents include polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyethyleneimine (PEI), and similar derivatives. Surface-passivated CDs can simultaneously be modified with different chemical functional groups, including hydroxyl, carbonyl, and carboxyl groups, on the surface defect sites. The doping of organic or polymeric compounds has been used in these methods. Different doping methods, such as N-doping, P-doping, S-doping, and Si-doping, have confirmed the effectiveness of these methods [55,56,57]. For example, N-doped CDs demonstrated an average diameter of 2.5 nm in the n high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) image analysis and broad and robust PL spectra over bare CDs [56].
2.4.3. Integrative Feature of Carbon Dot and Polymer Composites
The selection of the polymer and conjugation strategy can retain the required functional groups, such as -COOH and -OH groups, for the secondary loading of bioactive molecules [28]. Integrated CD/polymer composites with bioactive molecules have been demonstrated to possess reliable biocompatibility, bioimaging functions, anticancer effects, and combined drug tracing in vivo. Diverse applications can be achieved with abundant reactive groups, such as drug tracing, optical temperature sensing, magnetic/near-infrared (NIR)-thermally responsive drug delivery, enhanced photosensitivity, and other biomedical sciences, by integrating fluorescent CD/polymer composites with functional compounds. As a result, the major polymeric characteristics of CD/polymer composites result in more changeable properties, promoting their applications in several emerging fields [50].
3. Biomedical Applications of Carbon Dot/Polymer Composite Materials
The low-dimensional nanoscale materials are increasingly studied in the healthcare area. Among them, metallic quantum dots (QDs) received considerable attention compared with carbon-based CDs nanoparticles. However, the CDs have unique physicochemical and photo-physical merits that can be better in different preclinical and clinical research. For instance, PEG-passivated CDs can provide biocompatibility and stealth character in an in vivo environment. Such attempts can be utilized in combination with different organic/inorganic agents for desired biomedical applications. It has been found in different studies that desired CDs/polymeric nanomaterials can be a potential candidate for drug and gene delivery in target areas such as a tumor (Figure 1b). It is one of few relatively less explored areas of CDs/polymeric nanomaterials in biomedical applications [58,59].
The use of CD/polymer composites as a drug delivery system for chemotherapy drugs like doxorubicin, an anticancer drug, or biological molecules such as insulin-smart nanocarriers made by integrating insulin into CD/polymer hydrogels containing phenyl-boronic acid, which demonstrate a self-release pattern, are some of the most notable bio-medical applications [60,61]. This makes it possible for the medicine to be delivered to the target tissue efficiently (Figure 1b). In addition, the developments for advanced drug delivery that can trigger externally are an attractive area of research. Such triggers can be used to control the dose and extend therapeutic outcomes. Recently, several triggerable nanomaterials have been studied that can be triggered such as light, ultrasound, and microwave. In this case, the CD/polymer can work as light trigger drug carriers. The drug release can be regulated through a photo-degradable bond, photo-induced hydrophobic/hydrophilic phase transition, or thermally by photothermal heat [23,62,63]. Additionally, PEG in this CD/polymer system can allow for long-term circulation before degradation and elimination from the body. The composite merit of the CD/polymer can be engineered in such a promising desired light-trigger drug delivery system [23,64].
The nanoscale size and electronic conductivity features of carbon-based CDs exhibited photoluminescent (PL) properties. As a consequence of PL merits, the CDs can be studied in photothermal heat and photosensitize singlet oxygen (ROS, reactive oxygen species) generation for photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT)-based cancer therapy. The morphological and electronical properties of CD/polymer composites are also allowed for covalent and non-covalent conjugation with diagnostic and therapeutic drugs and genes. The prospect of CD/polymer NPs of such easy functionalization causes favorable diagnostic and therapeutic applications [59].
The growing nanotechnology and nanofabrication techniques address sensitive analytes detection up to nano-molar quantity at an affordable cost [58]. It is particularly essential since most existing detection and measurement processes involve sophisticated costly analytical instruments [65]. The sample preparation and conventional limit of detection (LOD) may not be suitable for all analyses. In this case, the optoelectronic, electronic, PL, and surface adsorption properties of the CD/polymeric NPs probe can be given superior strength in medical diagnoses, sensing, and treating different diseases [66]. Although organic fluorescence dyes are widely used in bioimaging, their stability and photo-bleaching are prime drawback features. The stable and biocompatible CD/polymer can be used as an alternative for live cell imaging and in vivo bioimaging materials [67,68]. In addition, carbon dot/polymer composites are used in biosensing, bioimaging, and diagnostic applications to detect drugs and genetic materials (DNA or RNA) due to CDs’ broad UV absorption spectrum and other physical, photothermal, mechanical stability, and chemical aspects [69].
CD/polymer composites have drawn attention due to their comprehensive adsorption, separation, photoelectron, and electrochemical capabilities, which lead to powerful and expeditious analytic detection in this field. However, additional study is required on simple, minimal-cost methods for producing CD/polymer composites that are environmentally friendly for using in drug delivery, biosensors, bioimaging, and other applications (Table 1).

Table 1.
Representative biomedical applications of carbon dot/polymer composites.
The polymer-passivated carbon core structure (CD/polymer) is one of the promising carbon nanomaterials. The nanoscale CD/polymer composites have attracted considerable attention in biological applications. Their optoelectronic properties can be used in biosensors and bioelectronics [79,80,81,82,83]. In addition, their photoluminescence and biocompatibility make it suitable for bioimaging, bio-labeling, drug and gene delivery, and theranostics [64,65,66,67,68,69,70]. Tunable advantages can be used in tissue engineering films and matrix development [70,71,72,73,74,75,76]. The tunable merits can be utilized in tissue engineering film and matrix developments [77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. Furthermore, the photo-responsive nature of CDs originating from polymers makes them an effective candidate for photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT) in cancer treatments [89,90].
4. Emerging Applications of Carbon Dots and Their Composite Materials
CDs and CD/polymer composite materials are widely developed in various fields beyond the existing limited areas. There has been increased recognition of CDs and CD/polymer composites, which is considered a new domain with largely emerging applications due to aforementioned beneficial characteristics as well as the utilization of technology. This section summarizes the role of CDs in agriculture, COVID-19, emerging diseases, anti-counterfeit, and security.
4.1. Agricultural System
CDs have also benefitted the agricultural industry by improving both the pre-harvest (growth, productivity, and disease resistance) and post-harvest (food preservation and safety) processes [93]. The role of CDs in the pre-harvest process refers to the ability of CDs to function as nano-bio-fertilizers by enhancing sunlight-energy conversion by upregulating photosynthetic genes such as PsbP and PsiK [94]. CDs have been reported to potentiate growth regulators, elevate cellulose and protein content, and improve germination rates [95]. Considering post-harvest, CDs have bacterial inhibitory properties. Fan et al. found that stored cucumbers treated with CDs fabricated from kelp demonstrated a substantially lower load of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli [96]. It was also found that covering mango fruits with CDs and chitosan reduced water loss and sugar acid conversion, thereby protecting mango quality throughout storage [97]. Figure 3 presents the benefits of CDs in agricultural systems. Hence, establishing a program for the large-scale usage of CDs in agricultural fertilizers and materials for coating agricultural products, as well as examining their toxicity in the food chain (effects on soil, plants, animals, and humans), would be of considerable interest in future studies. CDs have also been used for genetic therapy in plants. Schwartz and colleagues utilized the solvothermal method to synthesize CDs from polyethyleneimine. CD/siRNA could be successfully delivered into the tomato with gene silencing in the Nicotiana benthamiana 16C line [98].
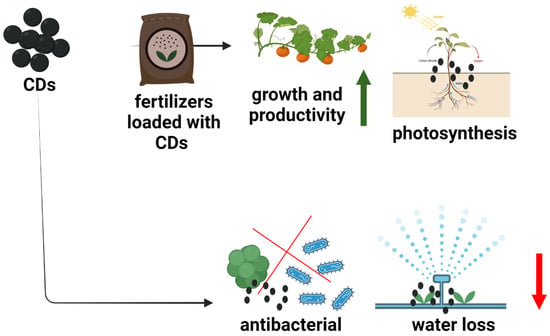
Figure 3.
Application of carbon dots (CDs) on agricultural systems. CDs prevented water loss, agricultural produces storage, and enhanced photosynthesis. The Figure was created with BioRender.com (accessed on 1 September 2022).
4.2. COVID-19 (SARS-2-CoV-2) and Emerging Pandemics
COVID-19 (SARS-2-CoV-2) is a viral disease that mostly affects the lungs and causes severe respiratory distress and fever. A recent outbreak has resulted in massive deaths globally [99,100]. Scientists are continuing to work on a rapid diagnosis and therapy for COVID-19 because once the virus binds to the receptors and penetrates the lung cells, immune cells create mediators such as interleukins and α-defensins, which induce inflammation [100,101]. In addition, they have been motivated to employ CDs in the diagnosis and treatment of the COVID-19 pandemic [102]. CDs generated from herbs are more effective anti-COVID-19 agents than those obtained from medical plants via carbonization. For example, CDs derived from garlic reduced viral attachment and entry while suppressing inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients [103]. Additionally, the bioimaging applications of the CDs may be beneficial for identifying SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections in the lungs by fluorescing the virus inside the lungs [104]. Thus, CDs play a critical role in the fight against COVID-19. Figure 4 summarizes the role of CDs in COVID-19 theranostics. However, the mechanism underlying the antiviral action has yet to be elucidated. Several questions arise, including whether the charge, size, and source of the CDs affect their anti-COVID-19 viral properties. Further studies in animals are required to assess the effects of CDs in vivo. CD/polymer composite materials have also been used to fight the COVID-19 pandemic. Singh et al. fabricated citric acid–CDs/poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) nonporous-membrane face masks [105]. These face masks with a hydrophobic surface are recyclable, allowing for easy breath and holding particles of ≥100 nm diameter [105].
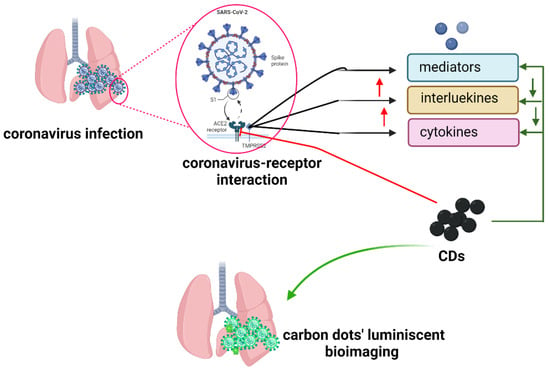
Figure 4.
The theranostics role of carbon dots (CDs) in coronavirus infection. CDs prevents coronavirus receptor attachment and, by its fluorescence property, allow for bioimaging of the infected lung. The Figure was created with BioRender.com (accessed on 1 September 2022).
4.3. Anti-Counterfeit and Security
CDs have been applied in forensic medicine, a science that provides scientific evidence with respect to anti-counterfeits [106,107,108,109]. A previous study reported that scientists were able to use orange-emitting CDs composed of the rhodamine B substance to rapidly and efficiently visualize the latent fingerprints even after four months under ultraviolet (UV) light and in bad environments, such as bent and colored surfaces [72]. In addition, CDs have been employed in anti-counterfeit systems for detecting forgery in banknotes. A CD-based printable ink made from luminescent m-phenylenediamine and poly(vinyl alcohol) allowed for the detection of cheating in banknotes by displaying triple-mode photoluminescence when excited with a 365 nm UV light [108]. Several studies regarding the use of CDs for the detection of drugs, narcotics, and explosive compounds have been performed [109]. Figure 5 demonstrates the possible role of CDs in anti-counterfeit detection. CDs are inevitable in the world of counterfeit detection. Hence, developing portable carbon-dot devices or sensors that are resistant to heat and water will facilitate the role of counterfeit investigators. Colloid photonic crystal (CPC)/CD beads prepared with poly(styrene-butyl acrylate-acrylic acid) (P(St-MMA-AA) microspheres were recently constructed by combining environmentally friendly fluorescent CDs (derived from turtle shell); fluorescent CPC/CD patterned films were then created and used as a multi-signal anti-counterfeiting device [12].
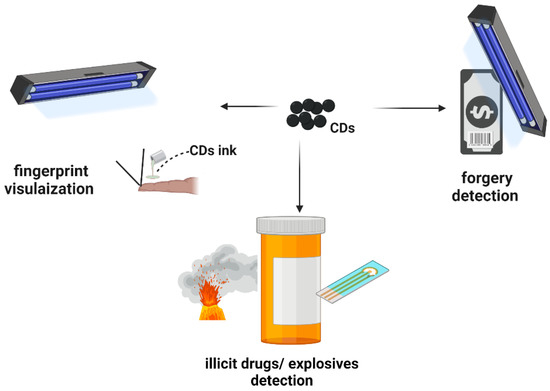
Figure 5.
The possible role of carbon dots (CDs) in counterfeit detection. The Figure was created with BioRender.com (accessed on 1 September 2022).
4.4. Treatments of Neurodegenerative Disease
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) are significant problems that affect movement, coordination, speech, and other organ functions that receive nerve supply [110]. Scientists have extensively studied the pathobiology and diagnosis of NDDs. However, this treatment remains challenging [111]. CDs have recently been employed for the treatment and diagnosis of NDDs. The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a key obstacle in the delivery of drugs to the brain. A group of researchers was able to breach the BBB using CDs synthesized by pyrolysis from D-glucose and L-aspartic acid [112,113]. Fluorescent-glucose CDs produced intriguing findings in vitro and in vivo, indicating a bright future for CDs as drug delivery systems for brain imaging and therapy. In zebrafish and rat models, GluCDs traverse the BBB without the need for conjugation to a specific ligand for receptor-mediated transport. GluCDs can transport cargo to the CNS, as illustrated in Figure 6 [114]. Furthermore, the absorption of GluCDs or glucose is critical in yeast models [114]. CDs derived from sodium citrate have also been utilized to treat Alzheimer’s disease, a disease in which amyloid cells, which play a crucial role in neuronal development and repair, are severely damaged [115]. In addition, high-oxygen-content CDs obtained from L- and D-cysteine are able to suppress the protein fibrillation that may prevent the fibril formation associated with neurodegenerative diseases [116]. CD/polymer composites have also been used to treat neurological problems. For instance, CDs generated from chitosan by carbonization were coupled with chitosan polymers to prepare dopamine-encapsulated CD/chitosan nanoparticles (NPs). CD/chitosan NPs were used as drug depots with sustained release capabilities of dopamine in neurological illness [117].
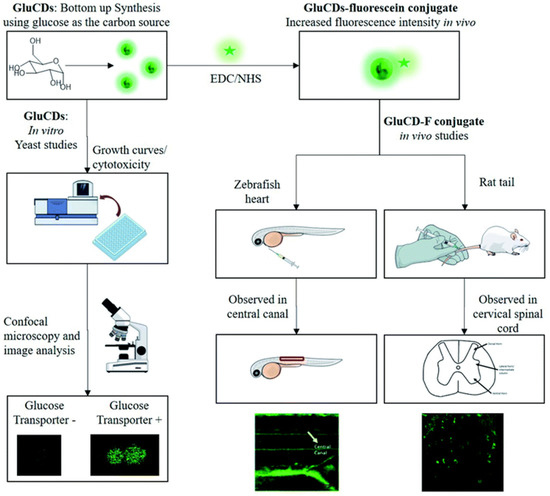
Figure 6.
Diagram of in vivo and in vitro glucose CDs (GluCDs) transport. In zebrafish and rat models, GluCDs cross the BBB without the necessity for conjugation to a targeted ligand for receptor-mediated transport. GluCDs have the ability to convey cargo to the CNS. In a yeast model, the absorption process of GluCDs needs glucose transporter proteins. The figure was depicted from [114], which is unrestrictedly accessed and distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ (accessed on 14 August 2022)).
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
In summary, the sources, characteristics, and synthesis of CDs, as well as their biomedical applications, were highlighted herein with an emphasis on emerging applications. The review was presented in a manner that non-chemists and other professionals may readily comprehend regarding the concept of CDs. CDs as well as carbon-based composite materials have evolved into being used in a variety of biomedical applications owing to their distinct physiochemical, biocompatible, immune quiescent, and other features. The key contribution of this review is the proposed following future framework: (1) whether various sources produce CDs with versatile biomedical applications, (2) comprehending the pharmacology of CDs in the body as well as their ultimate fate in bodily systems, (3) determining how CDs disintegrate the BBB to enter the brain, whether alone or in combination with other chemical substances, (4) creating portable gadgets from carbon dot and composites allows biomedical specialists and environmentalists to undertake more effective work such as medical diagnostics, counterfeit detection, or pollution detection, and (5) establishing a program for the large-scale use of CDs in agricultural systems, such as fertilizers and storage, for the sake of both humans and the environment. Carbon dot-based biomedical applications are emerging, and significantly more is expected from them.
A clear understanding of the fundamental property is required for new class materials of CD/polymer composites. Some state-of-the-art spectroscopic and electronic microscopic techniques could explain the fluorescence mechanism at the single-particle level. The new route of synthesis and modifications by doping and polymer conjugation is expected to play a significant role in biomedical sciences. In the future, the fluorescence off/on mode of CD/polymer composites can be applied to the ratiometric detection of important bioanalytes. It would not be far away from transferring that laboratory-scale knowledge into the commercial and industrial applications of CD-based polymers and CD composite materials. The preclinical study of CD/polymer demonstrates that drug delivery, cancer therapy, and others are very bright in the future. More specifically, the lab-on-a-chip and diagnosis with the naked eye are one of the few examples that could soon become vibrant in the biomedical sciences.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, G.O.A., S.M.S., and J.H.R.; writing—review and editing, G.O.A., S.M.S., and J.H.R.; supervision and funding acquisition, J.H.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Wonkwang University in 2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; Kesse, S.; Opoku-Damoah, Y.; Filli, M.S.; Aquib, M.; Joelle, M.M.B.; Farooq, M.A.; Mavlyanova, R.; Raza, F.; Bavi, R.; et al. Carbon dots: Applications in bioimaging and theranostics. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte-Filho, S.S.; Andrade, S.I.E.; Lima, M.B.; Araujo, M.C.U. Synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon dots from lemon and onion juices for determination of riboflavin in multivitamin/mineral supplements. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.W.; Lee, S.L.; Chang, C.J.; Liu, L. Recent Progress of Carbon Dot Precursors and Photocatalysis Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, A.; Belachew, N.; Hagos, M.; Basavaiah, K. Synthesis of fluorescent nitrogen and phosphorous co-doped carbon quantum dots for sensing of iron, cell imaging and antioxidant activities. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doring, A.; Ushakova, E.; Rogach, A.L. Chiral carbon dots: Synthesis, optical properties, and emerging applications. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.H.; Wei, Q.; Sun, D.W. Carbon dots: Principles and their applications in food quality and safety detection. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2466–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Liang, W.X.; Seilkop, A.; Veca, L.M.; Sun, Y.P.; Bunker, C.E. Carbon dots for energy conversion applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 220903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Wu, H.; Xu, H.M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Li, X.H.; Fan, L.N. Carbon dots: A booming material for biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Gong, T.; Cui, K.; Hou, L.; Yuan, C. B, N co-doped carbon dots based fluorescent test paper and hydrogel for visual and efficient dual ion detection. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Yen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chang, H. Photoluminescent carbon nanomaterials for sensing of illicit drugs: Focus. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, H.; Ling, L.; Li, G.; Cheng, R.; Lu, X.; Xie, A.-Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, S. Green synthesis of carbon dots toward anti-counterfeiting. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C. Advancement in science and technology of carbon dot-polymer hybrid composites: A review. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2019, 1, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foubert, A.; Beloglazova, N.V.; Rajkovic, A.; Sas, B.; Madder, A.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; De Saeger, S. Bioconjugation of quantum dots: Review & impact on future application. Trac-Trends Analyt. Chem. 2016, 83, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Peng, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Polymers in carbon dots: A review. Polymers 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharker, S.M.; Do, M. Nanoscale carbon-polymer dots for theranostics and biomedical exploration. J. Nanotheranostics 2021, 2, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Evolution and Synthesis of Carbon Dots: From Carbon Dots to Carbonized Polymer Dots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, M.; Megarajan, S.; Subramaniyan, S.B.; Kamlekar, R.K.; Anbazhagan, V. A convenient green method to synthesize luminescent carbon dots from edible carrot and its application in bioimaging and preparation of nanocatalyst. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 278, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Sarkar, K.; Devi, P.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, P. Current and future perspectives of carbon and graphene quantum dots: From synthesis to strategy for building optoelectronic and energy devices. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.D.; Lai, G.W.; Huq, M.M. Hydrothermal route to graphene quantum dots: Effects of precursor and temperature. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 79, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.; Wu, R.S.; Wei, S.C.; Ross, G.M.; Chang, H.T. The analytical and biomedical applications of carbon dots and their future theranostic potential: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Das, J. Small molecules derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulfajri, M.; Sudewi, S.; Ismulyati, S.; Rasool, A.; Adlim, M.; Huang, G.G. Carbon dot/polymer composites with various precursors and their sensing applications: A Review. Coatings 2021, 11, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwar, A.; Gogoi, N.; Majumdar, G.; Chowdhury, D. Green chitosan–carbon dots nanocomposite hydrogel film with superior properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Z.-Z.; Weng, Y.; Tan, H. Pyrophosphate ion-responsive alginate hydrogel as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for alkaline phosphatase detection. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11450–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Zhang, R.; Shen, J.; Liu, Y.-N.; He, M.; You, X.; Su, Y.; Jiang, Z. Graphene quantum dots engineered nanofiltration membrane for ultrafast molecular separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Shao, D.D.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, Q.C.; Chen, J.; Cao, X.L.; Zheng, T.; Sun, S.P. Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) nanofiltration membranes towards efficient biogas slurry valorization. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Feng, B.; Zhong, X.; Ostrikov, K.K. Photoluminescence mechanism of carbon dots: Triggering high-color-purity red fluorescence emission through edge amino protonation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, K.; Doyle, H. Size controlled synthesis of carbon quantum dots using hydride reducing agents. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6025–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Pramanick, A.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Ray, M. Amorphous carbon dots and their remarkable ability to detect 2,4,6-trinitrophenol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.B.; Liu, K.K.; Song, S.Y.; Zhou, R.; Shan, C.X. Fluorescent nano-biomass dots: Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and their application as nanoprobe for Fe3+ detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulfajri, M.; Dayalan, S.; Li, W.Y.; Chang, C.J.; Chang, Y.P.; Huang, G.G. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots from averrhoa carambola fruit extract as a fluorescent probe for methyl orange. Sensors 2019, 19, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Claudel, M.; Ronzani, C.; Arezki, Y.; Lebeau, L.; Pons, F. Physicochemical characteristics that affect carbon dot safety: Lessons from a comprehensive study on a nanoparticle library. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Dong, T. Photoluminescence tuning in carbon dots: Surface passivation or/and functionalization, heteroatom doping. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7944–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalache, I.; Radoi, A.; Pascu, R.; Romanitan, C.; Vasile, E.; Kusko, M. Engineering graphene quantum dots for enhanced ultraviolet and visible light p-si nanowire-based photodetector. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29234–29247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Tan, Z. Fluorescent carbon dots: Fantastic electroluminescent materials for light-emitting diodes. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yan, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Solvent-controlled synthesis strategy of multicolor emission carbon dots and its applications in sensing and light-emitting devices. Nano Res. 2021, 15, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Tu, Z.; Shen, G.; Wang, H.; Jia, R.; Ge, S.; Ruan, J.; et al. Dose-dependent carbon-dot-induced ros promote uveal melanoma cell tumorigenicity via activation of mtor signaling and glutamine metabolism. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.K.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Guo, X.H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, J.K.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y. Herbal medicine derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in therapeutics, bioimaging and sensing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Jun, G.; Schurhammer, R.; Reina, G.; Chen, P.; Bianco, A.; Menard-Moyon, C. Enzymatic degradation of graphene quantum dots by human peroxidases. Small 2019, 15, e1905405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truskewycz, A.; Yin, H.; Halberg, N.; Lai, D.T.H.; Ball, A.S.; Truong, V.K.; Rybicka, A.M.; Cole, I. Carbon dot therapeutic platforms: Administration, distribution, metabolism, excretion, toxicity, and therapeutic potential. Small 2022, 18, e2106342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gao, Z.; Gao, G.; Wo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, G.; Cui, D. Systematic safety evaluation on photoluminescent carbon dots. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, T.A.; Lin, L.; Ali, M.; Jabeen, F.; Ali, M.; Iqbal, R.; Horsell, D.W.; Winyard, P.G.; Zhang, S. Investigating the bioavailability of graphene quantum dots in lung tissues via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Interface Focus 2018, 8, 20170054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.B.; Zhu, S.J.; Shao, J.R.; Yang, B. Polymer carbon dots-a highlight reviewing their unique structure, bright emission and probable photoluminescence mechanism. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellani, S.; Bartolotta, A.; Agresti, A.; Calogero, G.; Grancini, G.; Di Carlo, A.; Kymakis, E.; Bonaccorso, F. Solution-processed two-dimensional materials for next-generation photovoltaics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11870–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthurasu, A.; Ganesh, V. Tuning optical properties of nitrogen-doped carbon dots through fluorescence resonance energy transfer using Rhodamine B for the ratiometric sensing of mercury ions. Analyt. Methods 2021, 13, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Kong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, W. Material and optical properties of fluorescent carbon quantum dots fabricated from lemon juice via hydrothermal reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Xia, C.; Song, Y.; Yang, B. The polymeric characteristics and photoluminescence mechanism in polymer carbon dots: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2017, 6, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cui, K.; Gong, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, Z.; Hou, L.; Zaman, F.U.; Yuan, C. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of n-doped, multicolor carbon dots toward fluorescent inks, fluorescence sensors, and logic gate operations. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.J.; Song, Y.B.; Zhao, X.H.; Shao, J.R.; Zhang, J.H.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Phatake, R.S.; Nabha Barnea, S.; Zerby, N.; Zhu, J.J.; Shikler, R.; Lemcoff, N.G.; Jelinek, R. Fluorescent self-healing carbon dot/polymer gels. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Xiong, H.M. Exploring the blue luminescence origin of nitrogen-doped carbon dots by controlling the water amount in synthesis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 66528–66533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Zhang, P.; Tian, F.; Li, W.C.; Li, F.; Liu, W.G. One-step synthesis of surface passivated carbon nanodots by microwave assisted pyrolysis for enhanced multicolor photoluminescence and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 13163–13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharker, S.M. Hexagonal Boron Nitrides (White Graphene): A promising method for cancer drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9983–9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, V. Chemical modifications and bioconjugate reactions of nanomaterials for sensing, imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 744–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.Q.; Ma, Y.; Che, M.X.; Zhang, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.D.; Sang, S.B. Fluorescent carbon dots as carriers for intracellular doxorubicin delivery and track. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, D.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Carbon dots embedded hybrid microgel with phenylboronic acid as monomer for fluorescent glucose sensing and glucose-triggered insulin release at physiological pH. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.F.; Wu, H.C.; Kuan, C.H.; Lin, C.J.; Wang, L.W.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, T.W. Multi-functionalized carbon dots as theranostic nanoagent for gene delivery in lung cancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.; Yi, G.; Yoo, J.; Park, C.; Koo, H.; Choi, H.S. Light-responsive nanomedicine for biophotonic imaging and targeted therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.L.; Liu, H.R.; Lou, Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.K.; Dong, L.; Shan, C.X. Recent progress of carbon dots in targeted bioimaging and cancer therapy. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2860–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L. Synthesis and applications of red-emissive carbon dots. Chem. Rec. 2019, 19, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, X.; Luo, Y.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Hydrothermal treatment of grass: A low-cost, green route to nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, photoluminescent polymer nanodots as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for label-free detection of Cu(II) ions. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Sui, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, A.; Jin, M.; Yang, B. Near-Infrared photoluminescent polymer-carbon nanodots with two-photon fluorescence. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Liu, R.L.; Koynov, K.; Wu, D.Q.; Best, A.; Kumar, R.; Bonoiu, A.; Prasad, P.N. Photoluminescent carbon dots as biocompatible nanoprobes for targeting cancer cells in vitro. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 12062–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Feng, T.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, S.; Yang, B. Carbonized polymer dots: A brand new perspective to recognize luminescent carbon-based nanomaterials. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5182–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; He, B.; Huang, J. Amphibious fluorescent carbon dots: One-step green synthesis and application for light-emitting polymer nanocomposites. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8078–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Zhai, X.; Liu, C.; Dai, L.; Liu, W. A facile and versatile approach to biocompatible “fluorescent polymers” from polymerizable carbon nanodots. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10431–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.Y.; Liu, H.J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yao, Y. Hyperbranched polymer functionalized carbon dots with multistimuli-responsive property. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhai, X.; Tian, F.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. Nano-carrier for gene delivery and bioimaging based on carbon dots with PEI-passivation enhanced fluorescence. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3604–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Singha, K.; Kim, W.J. Transfection and intracellular trafficking properties of carbon dot-gold nanoparticle molecular assembly conjugated with PEI-pDNA. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7168–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, A.; Matai, I.; Gopinath, P. Carbon dots incorporated polymeric hydrogels as multifunctional platform for imaging and induction of apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 141, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mishra, A.; Kumari, R.; Sinha, K.K.; Singh, M.K.; Das, P. Carbon dots assisted formation of DNA hydrogel for sustained release of drug. Carbon 2017, 114, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Gu, X.Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.Y. Low chemically cross-linked PAM/C-dot hydrogel with robustness and superstretchability in both as-prepared and swelling equilibrium states. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3174–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Xue, Y.N.; Li, S.R.; Zhang, X.H.; Fei, H.X.; Wu, X.G.; Sang, S.B.; Li, X.N.; Wei, M.; Chen, W.Y. Nanocomposite carbon dots/PAM fluorescent hydrogels and their mechanical properties. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, J.; Velado, D.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, S. Immobilization of carbon dots in molecularly imprinted microgels for optical sensing of glucose at physiological pH. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15735–15745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Di, J.; Sun, Y.; Fu, J.; Wei, Z.; Matsui, H.; del C. Alonso, A.; Zhou, S. Biocompatible PEG-chitosan@ carbon dots hybrid nanogels for two-photon fluorescence imaging, near-infrared light/pH dual-responsive drug carrier, and synergistic therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5537–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Han, J.; Ma, Z. Polyamidoamine dendrimers-capped carbon dots/Au nanocrystal nanocomposites and its application for electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Hu, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Weng, W.; Ni, J.; Bao, X.; Lin, Y. Carbon dots and chitosan composite film based biosensor for the sensitive and selective determination of dopamine. Analyst 2013, 138, 5417–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, S.; Das, K.; Das, P.K. Label-free fluorimetric detection of histone using quaternized carbon dot–DNA nanobiohybrid. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8851–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, S.; Kumar, M.; Mandal, B.B.; Karak, N. High performance luminescent thermosetting waterborne hyperbranched polyurethane/carbon quantum dot nanocomposite with in vitro cytocompatibility. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, S.; Adolfsson, K.H.; Wu, D.; Hakkarainen, M. Supramolecular assembly of biobased graphene oxide quantum dots controls the morphology of and induces mineralization on poly (ε-caprolactone) films. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Erdal, N.B.; Hakkarainen, M.; Nandan, B.; Srivastava, R.K. Cellulose-derived nanographene oxide reinforced macroporous scaffolds of high internal phase emulsion-templated cross-Linked poly (ε-caprolactone). Biomacromolecules 2019, 21, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Dong, P.; Huang, J. A mini review on carbon quantum dots: Preparation, properties, and electrocatalytic application. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Samanta, A.; Srivastava, R.K.; Hakkarainen, M. Nano-graphene oxide functionalized bioactive poly (lactic acid) and poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibrous scaffolds. Materials 2018, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazrad, Z.A.I.; Phuong, P.T.M.; Choi, C.A.; In, I.; Lee, K.D.; Park, S.Y. pH/redox-triggered photothermal treatment for cancer therapy based on a dual-responsive cationic polymer dot. Chem. Med. Chem. 2018, 13, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardekani, S.M.; Dehghani, A.; Hassan, M.; Kianinia, M.; Aharonovich, I.; Gomes, V.G. Two-photon excitation triggers combined chemo-photothermal therapy via doped carbon nanohybrid dots for effective breast cancer treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, X.; Sun, J.; Gao, F. Dual-emission carbonized polymer dots for ratiometric ph sensing, ph-dependent generation of singlet oxygen, and imaging-guided dynamics monitoring of photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 7663–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajjad, F.; Jin, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Bao, L.; Chen, T.; Yan, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Z.-L. Incorporation of green emission polymer dots into pyropheophorbide-α enhance the PDT effect and biocompatibility. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 37, 102562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnol, L.D.; Neves, R.M.; Maraschin, M.; Moura, S.; Luiz, H.L.; Dias, F.T.G.; Bianchi, O. Green synthesis of Spirulina-based carbon dots for stimulating agricultural plant growth. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 30, e00347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zheng, J. Fluorescent carbon-dots enhance light harvesting and photosynthesis by overexpressing PsbP and PsiK genes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.B.; Zhang, M.L.; Song, Y.X.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Shao, M.W.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.H. Carbon dots promote the growth and photosynthesis of mung bean sprouts. Carbon 2018, 136, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, M.; Fan, D.; Jiang, F. Effect of carbon dots with chitosan coating on microorganisms and storage quality of modified-atmosphere-packaged fresh-cut cucumber. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6032–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.; HongMei, P.; Hao, T.; DeZhi, Y.; YaLing, Y.; Hong, L. Application of carbon dots-chitosan coating in preservation of mango. Food Ferment. Ind. 2019, 45, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.H.; Hendrix, B.; Hoffer, P.; Sanders, R.A.; Zheng, W. carbon dots for efficient small interfering RNA delivery and gene silencing in plants. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wong, L.R.; Li, K.; Verma, A.K.; Ortiz, M.E.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Leidinger, M.R.; Knudson, C.M.; Meyerholz, D.K.; McCray, P.B.; et al. COVID-19 treatments and pathogenesis including anosmia in K18-hACE2 mice. Nature 2021, 589, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Qi, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, S. COVID-19 Pandemic: Advances in diagnosis, treatment, organoid applications and impacts on cancer patient management. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 606755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotta, S.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Md, S.; Nair, A.B.; Deb, P.K. Exploring the potential of carbon dots to combat COVID-19. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 616575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkal, A.; Allawadhi, P.; Pradhan, R.; Khurana, A.; Bharani, K.K.; Packirisamy, G. Allium sativum derived carbon dots as a potential theranostic agent to combat the COVID-19 crisis. Sensors Int. 2021, 2, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belza, J.; Opletalova, A.; Polakova, K. Carbon dots for virus detection and therapy. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Shauloff, N.; Sharma, C.P.; Shimoni, R.; Arnusch, C.J.; Jelinek, R. Carbon dot-polymer nanoporous membrane for recyclable sunlight-sterilized facemasks. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 592, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilia, P.D.I.; Freeman, M.D.; Herkutanto; Zeegers, M.P. A review of the diversity in taxonomy, definitions, scope, and roles in forensic medicine: Implications for evidence-based practice. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2018, 14, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Ren, G.; Zhu, B.; Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Chai, F.; Wu, H.; Wang, C. Facile synthesis of orange emissive carbon dots and their application for mercury ion detection and fast fingerprint development. Analyt. Methods 2019, 11, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, C.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Triple-mode emission of carbon dots: Applications for advanced anti-counterfeiting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7231–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, A.; Kelarakis, A. Carbon dots for forensic applications: A critical review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Oloketuyi, S.F. A future perspective on neurodegenerative diseases: Nasopharyngeal and gut microbiota. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneu, V.; Lax, P.; Cuenca, N. Current and future therapeutic strategies for the treatment of retinal neurodegenerative diseases. Neural. Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Xu, N.; Fan, J.; Sun, W.; Peng, X. Carbon dots for in vivo bioimaging and theranostics. Small 2019, 15, e1805087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Ruan, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, T.; Qu, D.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Gao, H.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. Self-targeting fluorescent carbon dots for diagnosis of brain cancer cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11455–11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seven, E.S.; Seven, Y.B.; Zhou, Y.; Poudel-Sharma, S.; Diaz-Rucco, J.J.; Kirbas Cilingir, E.; Mitchell, G.S.; Van Dyken, J.D.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with carbon dots: Uptake mechanism and in vivo cargo delivery. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 3942–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damian Guerrero, E.; Lopez-Velazquez, A.M.; Ahlawat, J.; Narayan, M. Carbon quantum dots for treatment of amyloid disorders. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, S.L.; Jiang, P.; Jiang, F.L.; Liu, Y. High-oxygen-content carbon dots as a high-efficiency inhibitor of human insulin aggregation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4067–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.A.; Praveena, P.; Dhanavel, S.; Manikandan, R.; Senthilkumar, S.; Stephen, A. Luminescent chitosan/carbon dots as an effective nano-drug carrier for neurodegenerative diseases. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24386–24396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).