Simulation of Intellectual Property Management on Evolution Driving of Regional Economic Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Basis
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Theoretical Basis
3. System Feedback Mechanism Analysis and Model Construction
3.1. System Evolution Process Analysis and Feedback Loop Generation
3.1.1. Analysis of Evolution Driving Process of Intellectual Property Management System
3.1.2. The Driving Mechanism of Technological Innovation on Performance
3.1.3. Subsystem Function Analysis
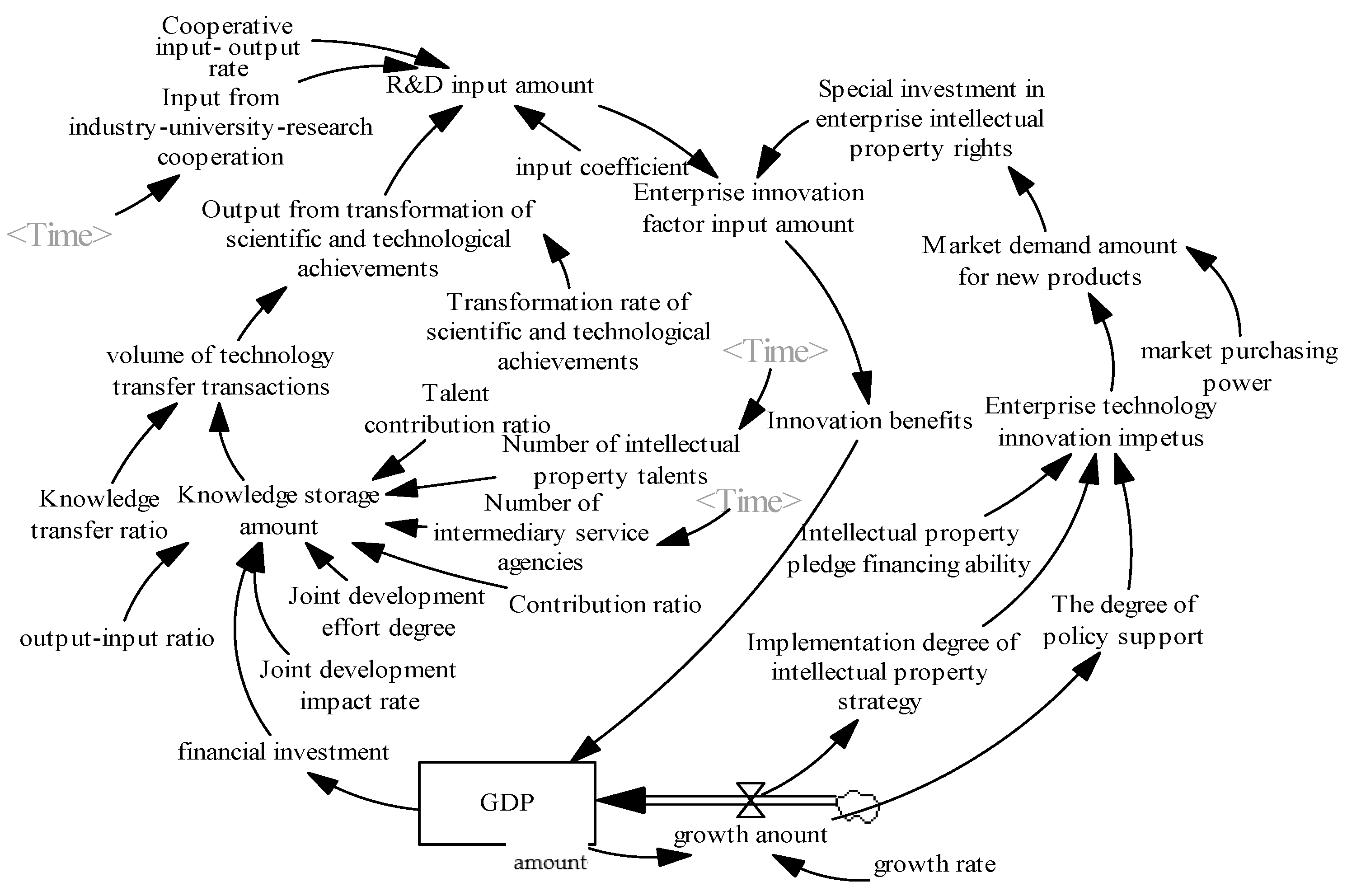
3.2. Generation of System Dynamics Flow Diagram
4. System Dynamics Simulation of Driving Mechanism of Intellectual Property Management to Regional Economic Development
4.1. Basic Assumptions of the Model
4.2. Parameter Estimation and Variable Model Construction
- (1)
- GDP growth = INTEG (growth rate, initial value of regional gross output);
- (2)
- Initial value of regional gross output value = 70,116.4, growth rate = 0.0184;
- (3)
- Knowledge stock = Number of intermediary service agencies * Contribution of intermediary service agencies * 0.25+ Number of intellectual property talents * contribution of intellectual property talents * 0.25 *+ Joint development efforts * Joint development impact factor * 0.25+ Financial input * financial input-output factor * 0.25 + 72.38;
- (4)
- R&D capital input = Input of industry–university–research cooperation * transformation factor of input of industry–university–research cooperation * 0.32+ output of transformation of scientific and technological achievements * input coefficient * 0.25 + 44.56 (The data of input of industry–university–research cooperation came from the internal expenditure of R&D funds in the China Statistical Yearbook of Science and Technology, listed in table function form (see Equation (9)). This Equation was obtained by the regression analysis method);
- (5)
- Enterprise innovation factor investment = “R&D investment” * 0.325+ Enterprise intellectual property special capital investment * 0.511 + 33.51;
- (6)
- Enterprise innovation motivation = policy support * 0.35+ of intellectual property strategy * 0.5+ financing capacity of intellectual property pledge * 0.25;
- (7)
- Innovation revenue = enterprise innovation factor input * 6.5 + 33.38(Above (4)–(7) Equations were obtained from regression analysis);
- (8)
- Output of transformation of scientific and technological achievements = transaction amount of technology market * transformation rate of scientific and technological achievements = 0.218, which is based on the trend of transaction amount of technology market and ratio of patent application from 2015 to 2020;
- (9)
- Input from industry-university-research cooperation = WITH LOOKUP (time, ([(2015, 1801.23)–(2020, 3002.43)], (2015, 1801.23), (2016, 2026.87), (2017, 2260.06), (2018, 2504.43), (2019, 2779.52), (2020, 3002.43)).
4.3. Model Test
4.4. Model Simulation and Analysis
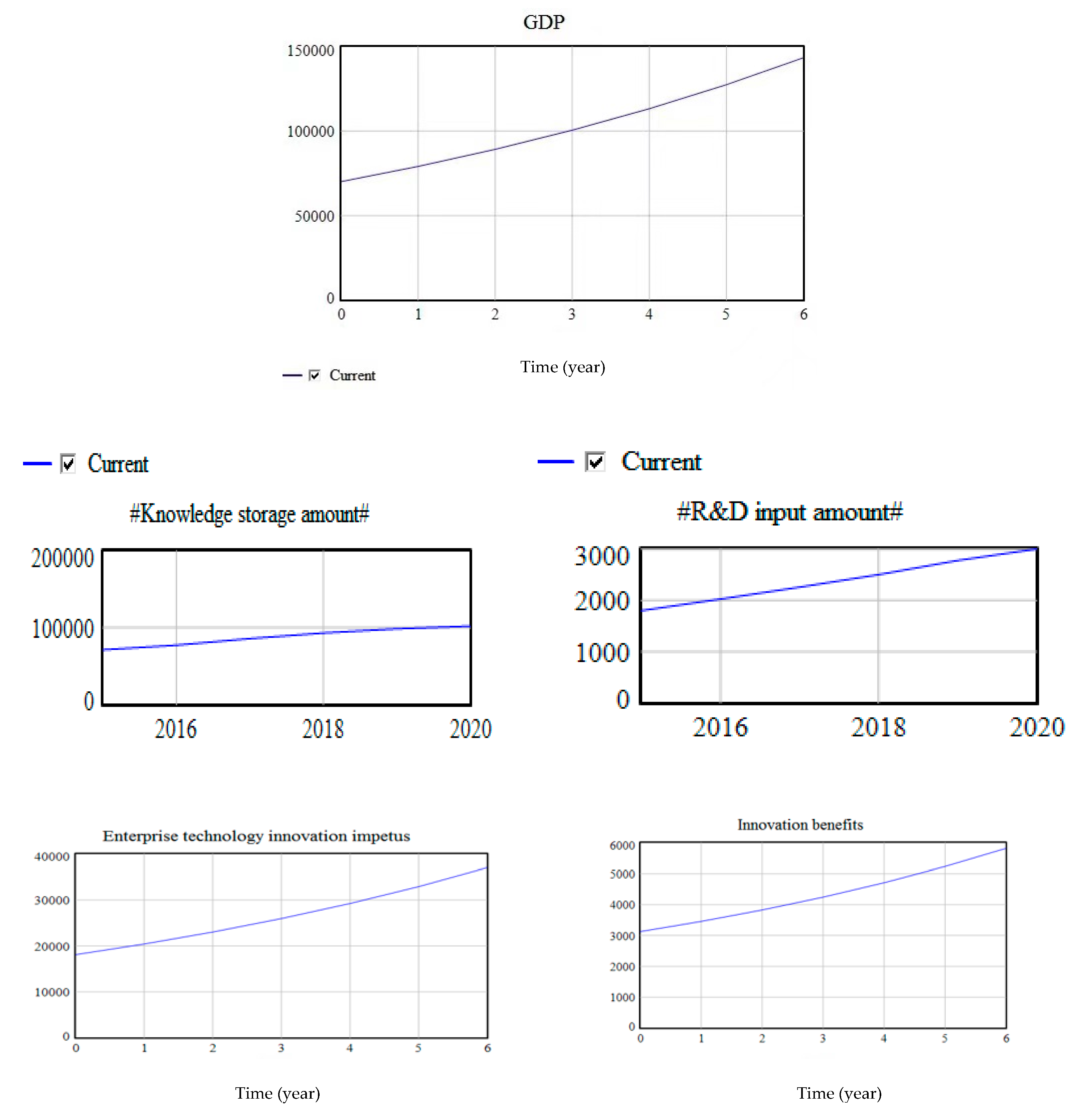
4.4.1. The Data Simulation of Intellectual Property and Technological Innovation in Jiangsu Province
- Several key factors were selected to analyze. The analysis showed that regional economy was in the trend of steady growth. This is inseparable from the implementation of the intellectual property strategy since 2009, the implementation of Jiangsu Provincial government’s plan to strengthen the province of intellectual property, and the promotion of the intellectual property strategy. According to the above figure, compared with other factors, R&D investment contributes more to regional economic growth, showing a steep slope. This shows that, in the management of intellectual property rights to the mature stage, the continuing growth of R&D spending is still the key element of technology innovation. This has to do with Jiang-Hong Zeng [25] and other scholars that believe that high-tech enterprise R&D investment is the basic way to maintain sustained growth and competitive advantage of the view consistently [26]. In addition, the government’s R&D investment is more important. When the government’s R&D investment reaches and stays at a certain level, then enterprises are stimulated to increase the R&D investment in such an innovative atmosphere, and the R&D investment needs an abrupt process of a large scale.
- Looking further at the chain structure in the dynamic flow diagram of the system, it mainly comes from the opening of the intellectual property market. With the promotion of the intellectual property strategy, the intellectual property market of Jiangsu Province was active, and the transfer of intellectual property in the technology market also showed a trend of steady growth. According to statistics, by the end of 2015, there were more than 1800 intellectual property service agencies of all kinds, and 2230 people were qualified as patent agents. The number of trademark agencies reached 685, three times that of the end of the 11th Five-Year Plan. Emerging intellectual property services such as information retrieval, analysis and evaluation, pledge financing, finance and insurance, strategic consulting, and industrial early warning are gradually emerging. At the same time, with the close deepening of industry–university–research cooperation, the transformation of scientific and technological achievements is also strengthened, which makes the government’s investment in research and development continuously increase at the macro level, as well as enterprises’ investment in innovation factors, and enterprises eventually produce innovative products.
- From the perspective of the promotion of the implementation of the intellectual property strategy and the release of various policies, at the end of the decade of the implementation of the intellectual property strategy and according to the new situation, there were new tasks and new requirements during the 13th Five-Year Plan period. The Jiangsu Provincial government has stepped out of the road of building a leading province with strong intellectual property rights that has the characteristics of Jiangsu and meets the requirements of the times. We will guide innovation subjects to strengthen their awareness of an intellectual property operation and implement the strategic application of intellectual property. We will strengthen the construction of operating institutions, establish market-oriented operation mechanisms, innovate operation models, promote the acquisition, storage, development, portfolio, licensing, transaction, and investment of intellectual property, accelerate the flow and utilization of intellectual property, revitalize intellectual property assets, and accelerate the realization of the market value of intellectual property. In the process of market research and data collection, it was found that, in 2017, Jiangsu Province proposed to promote the construction of a high value patent cultivation demonstration carrier, focusing on strategic emerging industries and characteristic advantages industries, to strengthen the patent intelligence analysis and early warning and patent layout of R&D projects, and to cultivate high value patents. At the same time, in order to solve the shortage of funds, we will support enterprises with intellectual property rights to pledge financing loans, so as to broaden the channels for enterprises, especially small and micro private enterprises and “entrepreneurship and innovation” enterprises to obtain loans, and to promote the easing of financing difficulties.
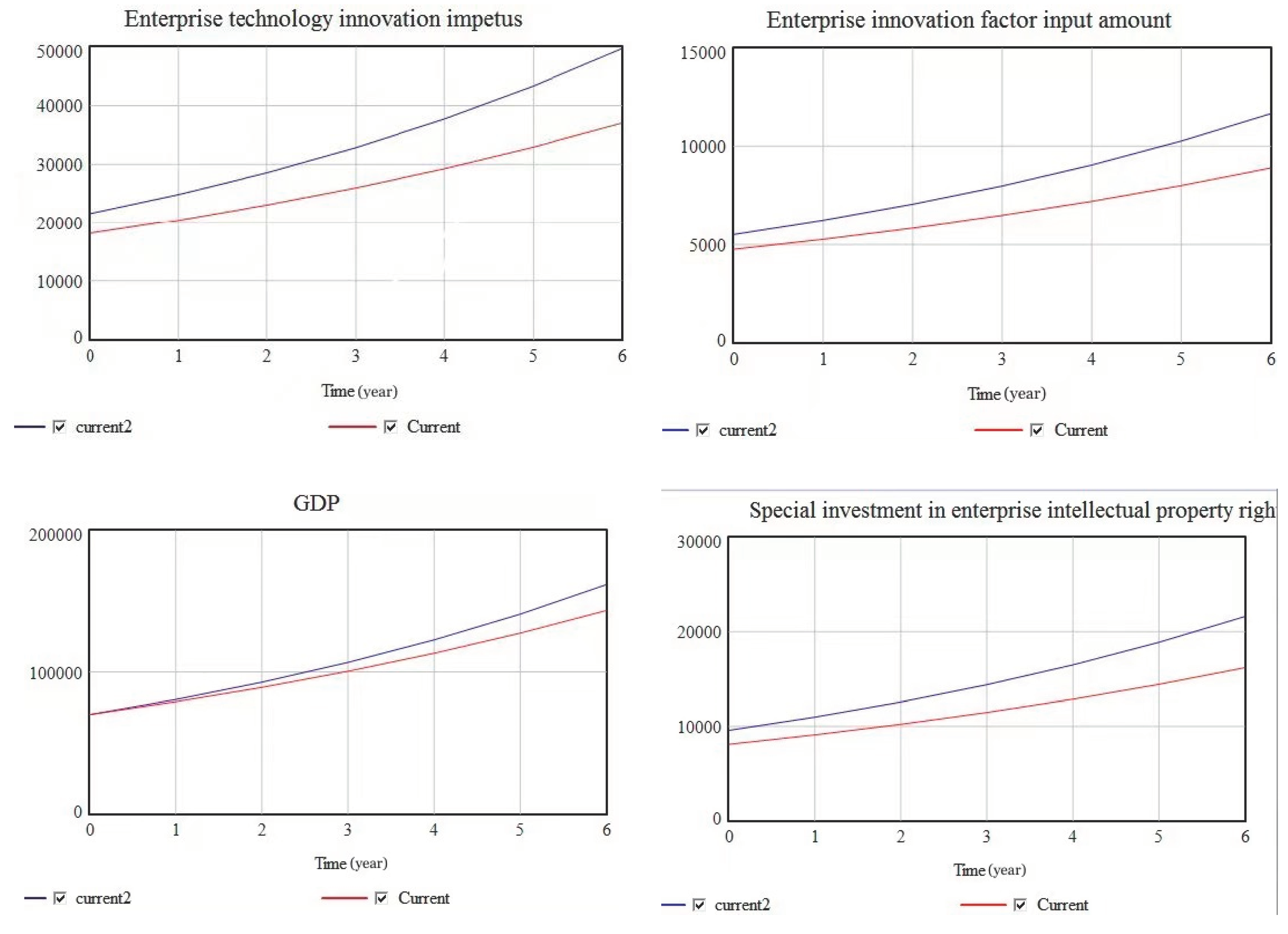
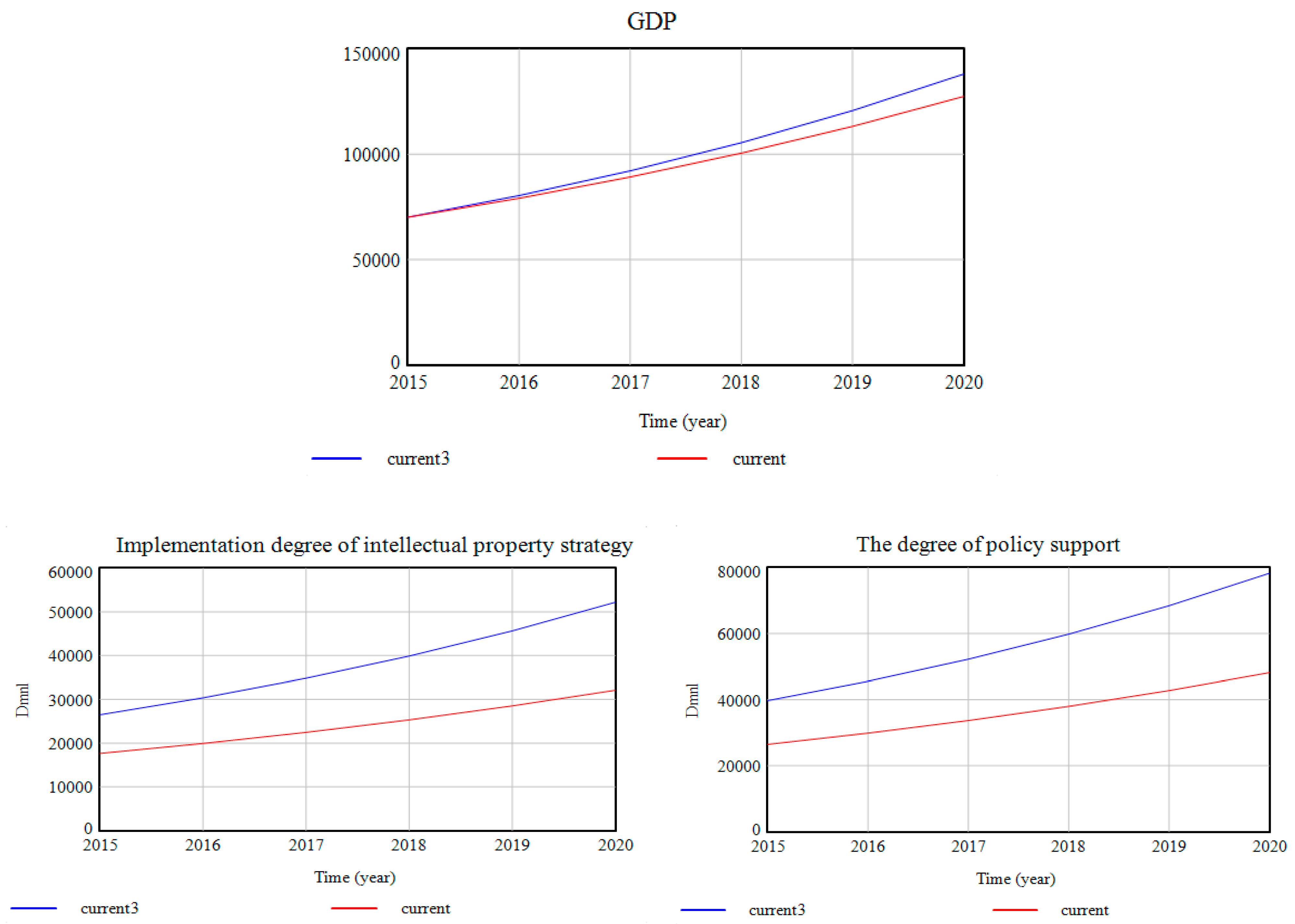
4.4.2. Sensitivity Analysis
- Constant change. By increasing the constant terms by 20% at the same time, it was found that:
5. Conclusions and Enlightenment
5.1. In The Simulation Interval of The System, the Important Variables in the Three Subsystems Show an Increasing Trend
- To increase investment and promote the improvement of intellectual property macro-management capability. The number of invention patents owned by 10,000 people and the proportion of added value of independent brand enterprises in GDP were included in the modern index system. In order to realize the core index system, the government increased the investment of financial funds and strived to create a new pattern of intellectual property. By the end of 2015, the province had 14 national intellectual property pilot cities, 3 national brand strategy implementation demonstration cities, 3 national copyright demonstration cities, 30 strong counties (districts) with national intellectual property pilot demonstration, 23 national intellectual property pilot demonstration parks, and 4 national copyright demonstration gardens (bases), which are the first in the nation.
- The use of intellectual property rights and the growth of output capacity. The government strengthened intellectual property exchange, established trading platforms and centers, and promoted technology transfer and exchange inside and outside the province and at home and abroad. Through provincial patent technology implementation, transformation of scientific and technological achievements, and guidance of key technological innovation projects and other planned projects, it supported the industrialization of 15,000 major patents, achieving a sales revenue of more than CNY 500 billion. In 2015, the transformation and implementation rate of enterprise patents exceeded 70%, the export value of the copyright industry exceeded USD 30 billion, and the added value of the copyright industry exceeded CNY 540 billion, accounting for more than 8% of the GDP. The added value of the core copyright industry exceeded CNY 300 billion, and the added value of independent brand enterprises accounted for 11% of the GDP. The output value of products with independent intellectual property rights accounted for more than 50% of the total output value of industries above designated size.
5.2. The Policy Support and The Promotion of Intellectual Property Strategy Are the Strong Guarantee and Drive of Regional Economic Growth
5.3. Intellectual Property Talent Construction, Intermediary Service Platform Construction and Industry-University-Research Cooperation Are Important Poles for Regional Economic Growth
5.4. Enterprise Technological Innovation Is the Carrier of Intellectual Property Management Activities and the Necessary Path for Regional Economic Growth
6. Future Research Direction
- (1)
- The function and feedback of the intellectual property management system are directional, and the function and driving force are also different. Are there differences in different samples?
- (2)
- With the help of the system dynamics method, the role process of intellectual property management activities on economic growth and the cooperative relationship between subjects are studied. Are the paths explored by other methods, such as the fuzzy set qualitative analysis method, consistent with the paths analyzed in this study?
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, C. An Article commemorating the 10th anniversary of the promulgation and implementation of the Outline of the National Intellectual Property Strategy: A National strategy to Rejuvenate the country and Benefit the People. 2018. Available online: http://www.cnipr.com/sj/zx/201806/t20180606_226713.html (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Iksanova, L.; Kashapov, N. Intellectual property as a factor of increasing innovation activity of economic entities. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 412, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, X. Evaluation and spatial statistical analysis of provincial intellectual property resources in China. Stat. Decis. 2020, 1, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Chao, K.; Chen, X. Reflection on the transformation of intellectual property strategic resources into competitive advantages. Sci. Manag. Res. 2010, 28, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Public Course on Intellectual Property, 1st ed.; China Personnel Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Security-driven distributed platforms for intellectual property resource provision—A case study of TSITE IP. J. Cloud Comput. 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosova, T.; Masych, M.; Afanasyev, A.; Borovskaya, M.; Liabakh, N. Development of Quantitative Methods for Evaluating Intellectual Resources in the Digital Economy. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference Quality Management, St. Petersburg, Russia, 24–28 September; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 629–634. [Google Scholar]
- Markova, M. The Company Digital Competitiveness Focused on Intellectual Property Rights—Concept. Assess. Strategy 2022, 3, 34–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bryan, M. Reconceptualising the debate on intellectual property rights and economic development. Law Dev. Rev. 2010, 3, 65–107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q, Quantitative Research on the Influence of Policy on the Transformation Path of Intellectual Property. Master’s Thesis, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, 2018.
- Dereń, A.; Skonieczny, J. Green Intellectual Property as a Strategic Resource in the Sustainable Development of an Organization. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titu, A.; Pop, A.; Titu, S.; Ceocea, C. Intellectual property policy enhancement in knowledge-based organizations. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2129, p. 020112. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.; Du, C. A Study on the Response Strategies of Intellectual Property by Country in the Era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. KBM J. 2020, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Luo, J. The role of intellectual property in economic development and its contribution to GDP growth. J. Chang. Univ. 2004, 18, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Wu, G. An empirical study on the contribution of intellectual property to regional economy. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2011, 8, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Nie, Y. Empirical study on patent and Economic growth in China. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2008, 7, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J. Differential Study on the Growth Effect of Intellectual Property Protection in Developing Countries. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, China, 13 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X. Intellectual property protection, technology gap and economic growth in underdeveloped regions: An analytical framework. East China Econ. Manag. 2016, 10, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Hou, J. An empirical study on the threshold effect in the relationship between intellectual property protection and economic growth. Stat. Decis. 2016, 24, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, B.; Park, J. Effects of Knowledge Property Utilization on Persistence of Innovation: Comparisons between Manufacturing and Service Industry. J. Res. Ind. Innov. 2020, 36, 27–53. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, R. The Linkage between Intellectual roperty and Innovation in the Global Innovation Ecosystem. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Intangibles and Intellectual Capital (ECIIC), Chieti, Italy, 23–24 May 2019; pp. 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.; Shan, X. Study on the impact of intellectual property management on technological innovation performance. J. Shandong Univ. Adm. 2012, 6, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, K. Innovation-driven system dynamics simulation. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2016, 6, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Pruyt, E. Small System Dynamics Model for Big Issues; TU Delft Library: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 978-94-6186-195-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J. The homogeneity effect of R&D investment in high-tech enterprises. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2019, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Innovation drives the institutional basis of industrial structure upgrading. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Qi, Y. Simulation of Intellectual Property Management on Evolution Driving of Regional Economic Growth. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189011
Yang X, Qi Y. Simulation of Intellectual Property Management on Evolution Driving of Regional Economic Growth. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(18):9011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189011
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiran, and Yong Qi. 2022. "Simulation of Intellectual Property Management on Evolution Driving of Regional Economic Growth" Applied Sciences 12, no. 18: 9011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189011
APA StyleYang, X., & Qi, Y. (2022). Simulation of Intellectual Property Management on Evolution Driving of Regional Economic Growth. Applied Sciences, 12(18), 9011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189011






