NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning Approaches for Age Prediction in Healthy and Parkinson’s Disease Cohorts through Metabolomic Fingerprints
Abstract
:1. Introduction: Background and Objective of the Work
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Ethical Issues
2.3. Metabolomics Analyses
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Serum Metabolite and Lipoprotein Quantification
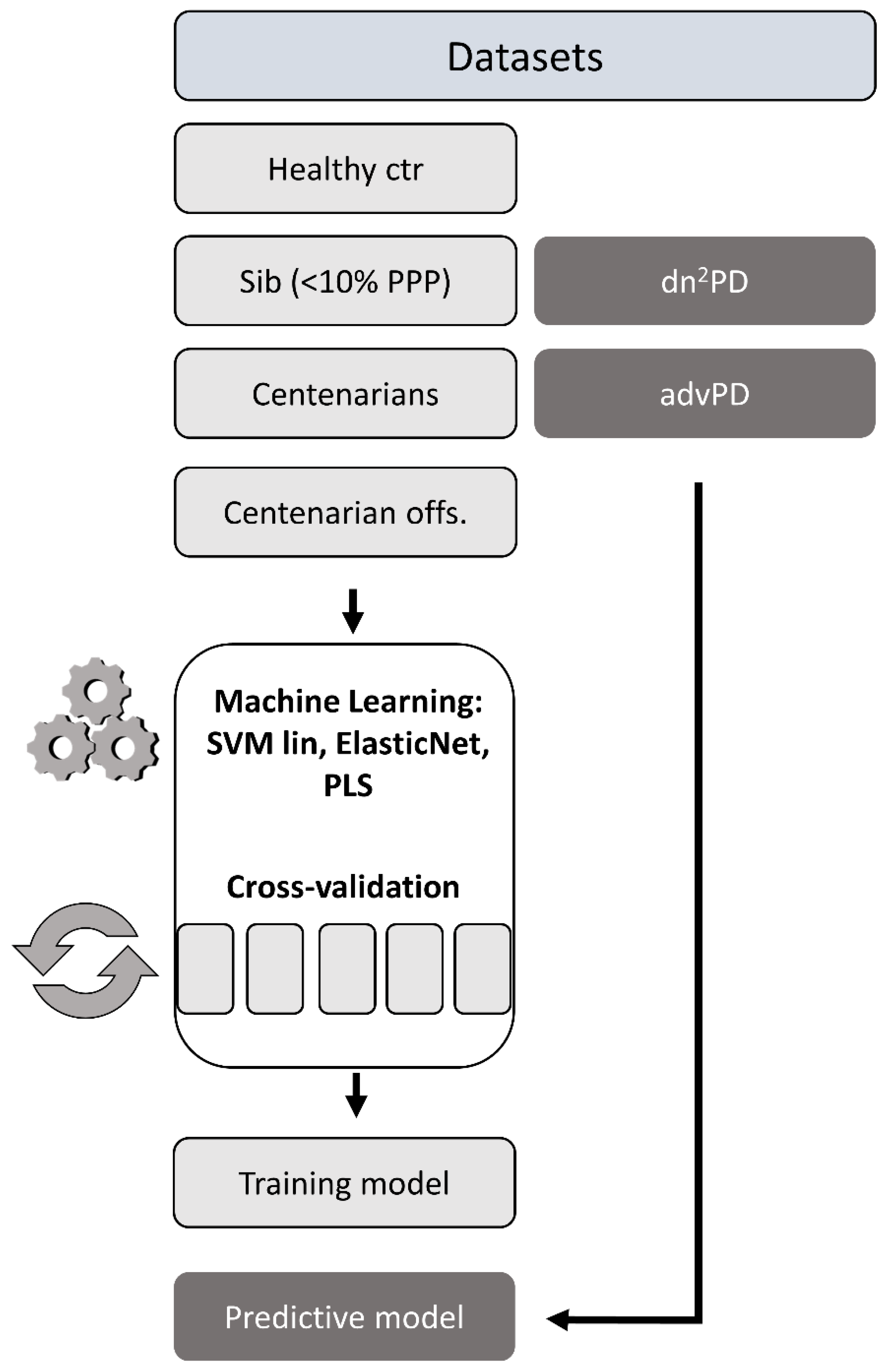
2.6. Age Prediction Using Machine Learning Models
3. Results
3.1. Age Prediction Using Fingerprints and Profiles
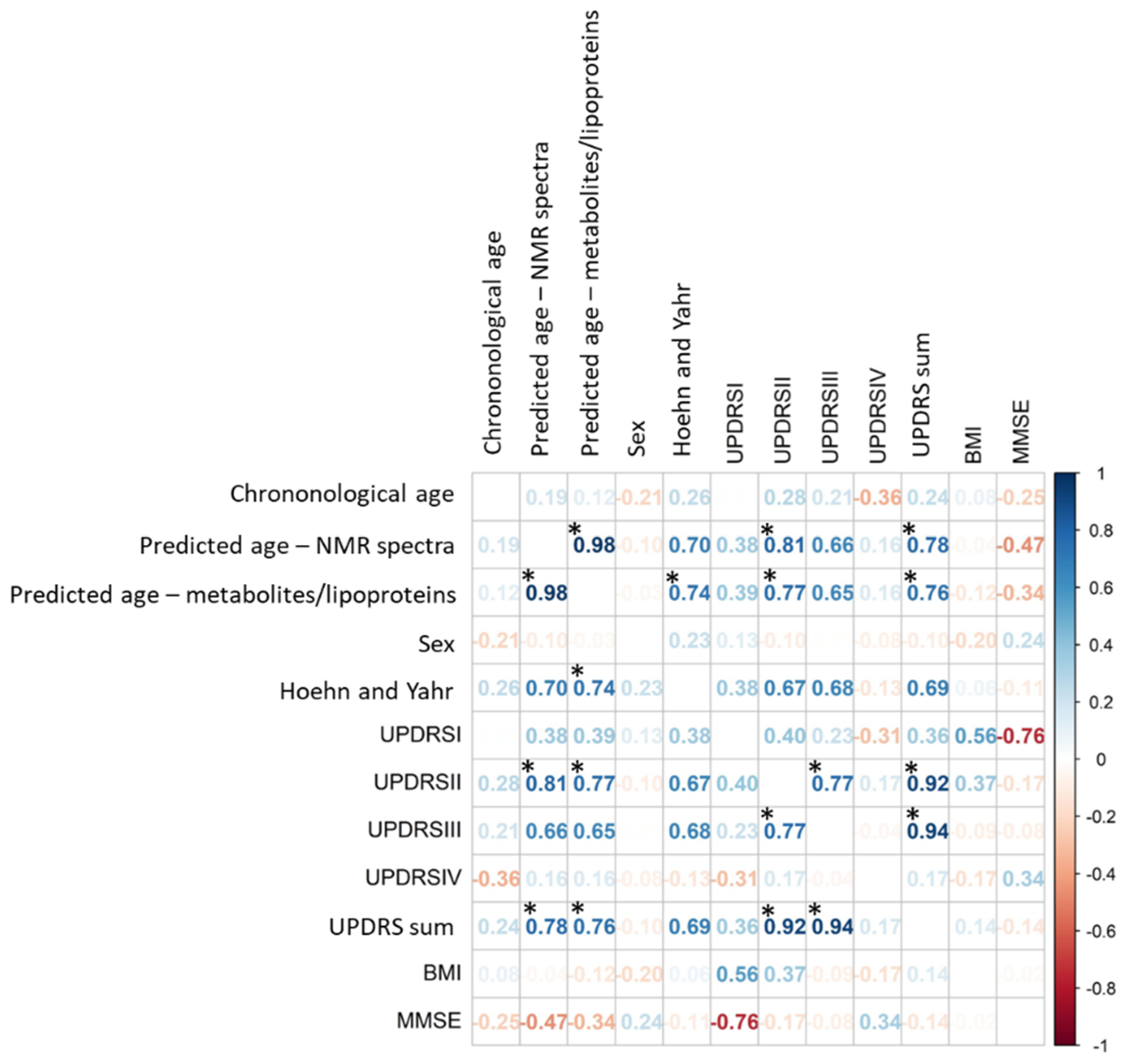
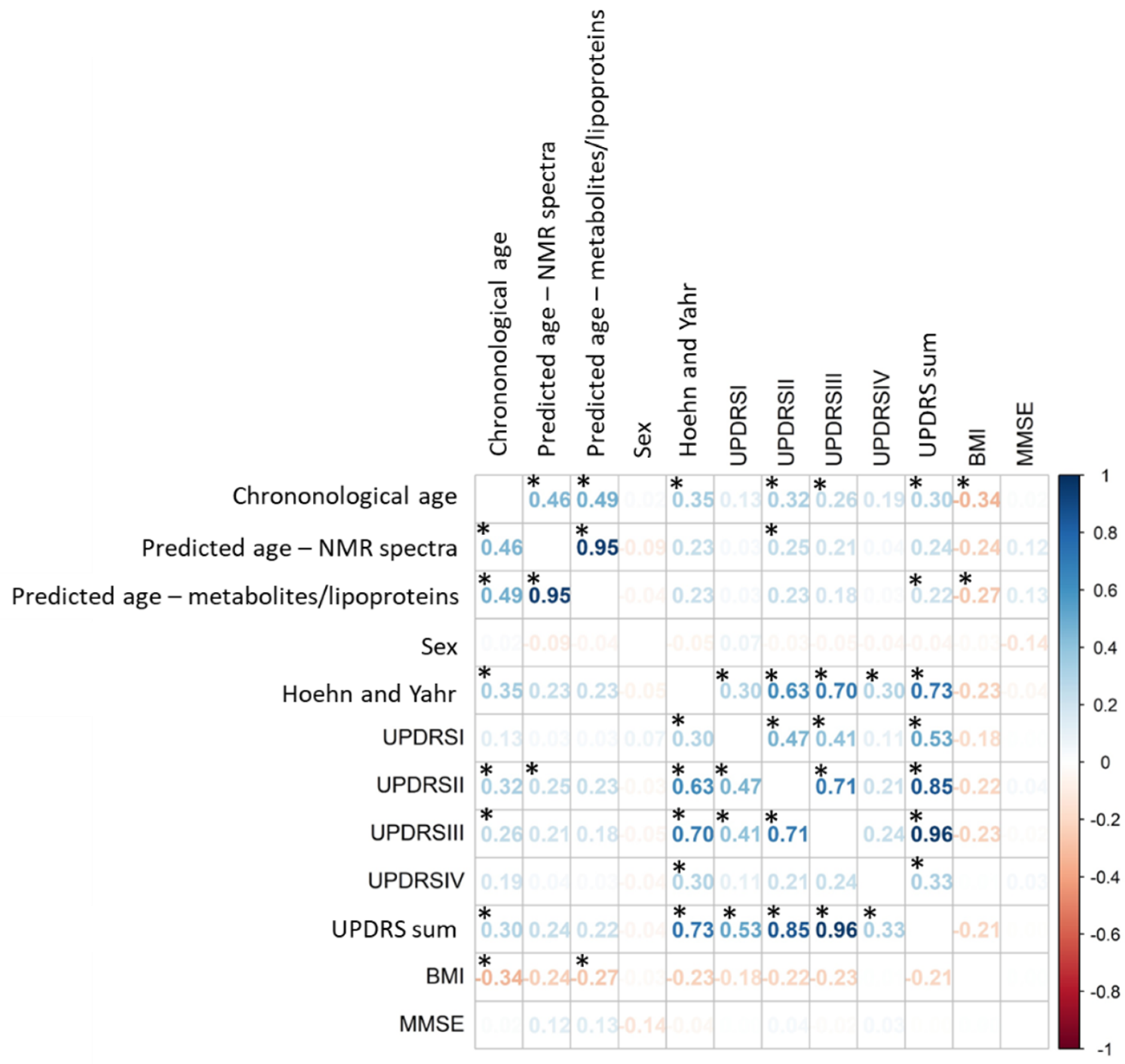
3.2. Correlation between Predicted Ages and Disease Severity
4. Discussion and Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klemera, P.; Doubal, S. A New Approach to the Concept and Computation of Biological Age. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2006, 127, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertel, J.; Friedrich, N.; Wittfeld, K.; Pietzner, M.; Budde, K.; Van der Auwera, S.; Lohmann, T.; Teumer, A.; Völzke, H.; Nauck, M.; et al. Measuring Biological Age via Metabonomics: The Metabolic Age Score. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.H.; Franke, K. Predicting Age Using Neuroimaging: Innovative Brain Ageing Biomarkers. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S.; Raj, K. DNA Methylation-Based Biomarkers and the Epigenetic Clock Theory of Ageing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.E.; Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Chen, B.H.; Assimes, T.L.; Bandinelli, S.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Stewart, J.D.; Li, Y.; et al. An Epigenetic Biomarker of Aging for Lifespan and Healthspan. Aging (Albany NY) 2018, 10, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Wilson, J.G.; Reiner, A.P.; Aviv, A.; Raj, K.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Li, Y.; Stewart, J.D.; et al. DNA Methylation GrimAge Strongly Predicts Lifespan and Healthspan. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auro, K.; Joensuu, A.; Fischer, K.; Kettunen, J.; Salo, P.; Mattsson, H.; Niironen, M.; Kaprio, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Lehtimäki, T.; et al. A Metabolic View on Menopause and Ageing. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, ncomms5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, F.; Tenori, L.; Meoni, G.; Gori, A.M.; Marcucci, R.; Giusti, B.; Saccenti, E. Lipid and Metabolite Correlation Networks Specific to Clinical and Biochemical Covariate Show Differences Associated with Sexual Dimorphism in a Cohort of Nonagenarians. GeroScience 2022, 44, 1109–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Waters, M.J.; Schirra, H.J. Investigating Potential Mechanisms of Obesity by Metabolomics. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 805683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholefield, M.; Unwin, R.D.; Cooper, G.J.S. Shared Perturbations in the Metallome and Metabolome of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A Systematic Review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 63, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Dong, M.-X.; Huang, Y.-L.; Lu, C.-Q.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, C.-C.; Xu, X.-M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.-H.; Wei, Y.-D. Integrated Metabolomics and Proteomics Analysis Reveals Plasma Lipid Metabolic Disturbance in Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Z.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Bennett, D.A.; Zhao, J. Brain and Blood Metabolome for Alzheimer’s Dementia: Findings from a Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 86, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignoli, A.; Paciotti, S.; Tenori, L.; Eusebi, P.; Biscetti, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Scheltens, P.; Turano, P.; Teunissen, C.; Luchinat, C.; et al. Fingerprinting Alzheimer’s Disease by 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhai, G.; Singmann, P.; He, Y.; Xu, T.; Prehn, C.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Lattka, E.; Gieger, C.; Soranzo, N.; et al. Human Serum Metabolic Profiles Are Age Dependent. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Maekawa, K.; Saito, K.; Senoo, Y.; Urata, M.; Murayama, M.; Tajima, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Saito, Y. Plasma and Serum Lipidomics of Healthy White Adults Shows Characteristic Profiles by Subjects’ Gender and Age. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, K.A.; Berger, A.; Mitchell, M.; Milgram, K.E.; Evans, A.M.; Guo, L.; Hanson, R.W.; Kalhan, S.C.; Ryals, J.A.; Milburn, M.V. Analysis of the Adult Human Plasma Metabolome. Pharmacogenomics 2008, 9, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, C.; Kastenmüller, G.; Petersen, A.K.; Bell, J.T.; Psatha, M.; Tsai, P.-C.; Gieger, C.; Schulz, H.; Erte, I.; John, S.; et al. Metabolomic Markers Reveal Novel Pathways of Ageing and Early Development in Human Populations. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collino, S.; Montoliu, I.; Martin, F.-P.J.; Scherer, M.; Mari, D.; Salvioli, S.; Bucci, L.; Ostan, R.; Monti, D.; Biagi, E.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Extreme Longevity in Northern Italian Centenarians Reveal a Complex Remodeling of Lipids, Amino Acids, and Gut Microbiota Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.R.; Spagou, K.; Lewis, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Glei, D.A.; Seeman, T.E.; Coe, C.L.; Goldman, N.; Ryff, C.D.; Weinstein, M.; et al. Microbial-Mammalian Cometabolites Dominate the Age-Associated Urinary Metabolic Phenotype in Taiwanese and American Populations. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3166–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, M.J.; Roth, A.; Frommherz, L.; Weinert, C.H.; Krüger, R.; Merz, B.; Bunzel, D.; Mack, C.; Egert, B.; Bub, A.; et al. Metabolite Patterns Predicting Sex and Age in Participants of the Karlsruhe Metabolomics and Nutrition (KarMeN) Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirazzini, C.; Azevedo, T.; Baldelli, L.; Bartoletti-Stella, A.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; Dal Molin, A.; Dimitri, G.M.; Doykov, I.; Gómez-Garre, P.; Hägg, S.; et al. A Geroscience Approach for Parkinson’s Disease: Conceptual Framework and Design of PROPAG-AGEING Project. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 194, 111426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zago, E.; Dal Molin, A.; Dimitri, G.M.; Xumerle, L.; Pirazzini, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Maturo, M.G.; Azevedo, T.; Spasov, S.; Gómez-Garre, P.; et al. Early Downregulation of Hsa-MiR-144-3p in Serum from Drug-Naïve Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meoni, G.; Tenori, L.; Schade, S.; Licari, C.; Pirazzini, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Garagnani, P.; Turano, P.; PROPAG-AGEING Consortium; Trenkwalder, C.; et al. Metabolite and Lipoprotein Profiles Reveal Sex-Related Oxidative Stress Imbalance in de Novo Drug-Naive Parkinson’s Disease Patients. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignoli, A.; Ghini, V.; Meoni, G.; Licari, C.; Takis, P.G.; Tenori, L.; Turano, P.; Luchinat, C. High-Throughput Metabolomics by 1D NMR. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2019, 58, 968–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoehn, M.M.; Yahr, M.D. Parkinsonism: Onset, Progression and Mortality. Neurology 1967, 17, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebersbach, G.; Baas, H.; Csoti, I.; Müngersdorf, M.; Deuschl, G. Scales in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2006, 253 (Suppl. S4), IV32–IV35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghini, V. NMR for sample quality assessment in metabolomics. New Biotechnol. 2019, 52, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takis, P.G.; Ghini, V.; Tenori, L.; Turano, P.; Luchinat, C. Uniqueness of the NMR Approach to Metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reproducible Metabolite Quantification in Plasma/Serum. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/products/mr/nmr-preclinical-screening/biquant-ps.html (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Lipoprotein Subclass Analysis Enabling Tools on the IVDr Platform. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/products/mr/nmr-preclinical-screening/lipoprotein-subclass-analysis.html (accessed on 2 May 2019).
| Cohort | Tot | N° | F/Tot | Mean Age F (Max; Min) | Mean Age M (Max; Min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hs | 118 | UNIBO (39) UMG-GOE (79) | 54/118 | 66.7 (82.5; 52) | 68.2 (85; 49) |
| Cent | 57 | UNIBO (39) | 39/57 | 105.2 (112.3; 100) | 102.9 (106.3; 100) |
| CentOs | 46 | UNIBO (39) | 29/46 | 70.7 (89; 55) | 71.1 (84; 58) |
| Sib | 199 | AUSL-ISNB (93) SAS (106) | 115/199 | 59.8 (90; 23) | 59.2 (84; 23) |
| dn2PD | 233 | UMG-GOE (228) SAS (5) | 109/233 | 65.1 (84; 29) | 64.8 (87; 39) |
| advPD | 22 | UMG-GOE (22) | 7/22 | 66.7 (77; 52) | 70.0 (84; 59) |
| dn2PD | advPD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | sd | Mean | sd | p-Value | |
| age | 65.24 | 10.09 | 68.95 | 7.33 | 0.11 |
| Hoehn and Yahr Scale | 1.51 | 1.07 | 3.13 | 0.60 | 4.52 × 10−10 |
| UPDRS I | 1.63 | 1.76 | 5.05 | 3.10 | 2.74 × 10−10 |
| UPDRS II | 6.83 | 5.80 | 19.45 | 6.66 | 1.98 × 10−15 |
| UPDRS III | 17.42 | 13.92 | 34.41 | 15.77 | 1.11 × 10−5 |
| UPDRS IV | 0.62 | 1.39 | 5.15 | 4.22 | 2.89 × 10−18 |
| UPDRS sum | 25.57 | 20.28 | 62.10 | 22.08 | 2.75 × 10−11 |
| Duration of the disease (years) | RD | RD | 9.32 | 2.78 | / |
| BMI | 27.18 | 4.79 | 25.95 | 3.72 | 0.28 |
| Model Based on Spectrum | Ctr | dn2PD | advPD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| SVM Linear | 0.865 | 6.273 | 0.208 | 11.209 | 0.037 | 13.057 |
| ElasticNet | 0.811 | 7.466 | 0.255 | 12.488 | 0.049 | 12.789 |
| PLS | 0.825 | 7.126 | 0.219 | 12.963 | 0.129 | 10.348 |
| Klemera–Doubal y.true1 | 0.161 | 38.929 | 0.035 | 25.84 | 0.004 | 25.591 |
| Klemera–Doubal y.true2 | 0.301 | 25.936 | 0.036 | 30.155 | 0.0001 | 29.861 |
| Model Based on Metabolites | Ctr | dn2PD | advPD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| SVM Linear | 0.735 | 8.76 | 0.314 | 12.651 | 0.138 | 10.961 |
| ElasticNet | 0.756 | 8.422 | 0.236 | 11.044 | 0.014 | 13.562 |
| PLS | 0.739 | 8.704 | 0.095 | 15.157 | 0.043 | 10.423 |
| Klemera–Doubal y.true1 | 0.046 | 77.305 | 0.001 | 110.239 | 0.007 | 111.439 |
| Klemera–Doubal y.true2 | 0.318 | 24.903 | 0.039 | 27.304 | 0.0002 | 31.188 |
| Overestimated | Underestimated | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %Subj./Group | RA(m ± SD) | PA(m ± SD) | PA-RA | %Subj./Group | RA(m ± SD) | PA(m ± SD) | RA-PA | |
| advPD | 31.8 | 64.29 ± 7.54 | 79.74 ± 15.49 | 15.45 ± 10.51 | 40.9 | 72.33 ± 6.58 | 60.94 ± 5.09 | 11.39 ± 4.87 |
| dn2PD | 40.8 | 55.84 ± 10.81 | 70.54 ± 9.74 | 14.7 ± 6.40 | 16.7 | 74.23 ± 5.59 | 64.2 ± 6.30 | 10.01 ± 3.24 |
| Ctr | 13.8 | 55.81 ± 15.78 | 66.36 ± 16.17 | 10.55 ± 4.84 | 13.3 | 84.86 ± 16.45 | 74.41 ± 16.2 | 10.44 ± 3.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimitri, G.M.; Meoni, G.; Tenori, L.; Luchinat, C.; Lió, P., on behalf of the PROPAG-AGEING Consortium. NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning Approaches for Age Prediction in Healthy and Parkinson’s Disease Cohorts through Metabolomic Fingerprints. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8954. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12188954
Dimitri GM, Meoni G, Tenori L, Luchinat C, Lió P on behalf of the PROPAG-AGEING Consortium. NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning Approaches for Age Prediction in Healthy and Parkinson’s Disease Cohorts through Metabolomic Fingerprints. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(18):8954. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12188954
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimitri, Giovanna Maria, Gaia Meoni, Leonardo Tenori, Claudio Luchinat, and Pietro Lió on behalf of the PROPAG-AGEING Consortium. 2022. "NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning Approaches for Age Prediction in Healthy and Parkinson’s Disease Cohorts through Metabolomic Fingerprints" Applied Sciences 12, no. 18: 8954. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12188954
APA StyleDimitri, G. M., Meoni, G., Tenori, L., Luchinat, C., & Lió, P., on behalf of the PROPAG-AGEING Consortium. (2022). NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning Approaches for Age Prediction in Healthy and Parkinson’s Disease Cohorts through Metabolomic Fingerprints. Applied Sciences, 12(18), 8954. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12188954









