A Comparison of Pooling Methods for Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
1.2. Pooling
1.3. Selection of Articles for Review
2. Popular Pooling Methods
2.1. Max Pooling Method
2.2. Average Pooling Method
2.3. Mixed Pooling Method
2.4. Tree Pooling
2.5. Stochastic Pooling Method
2.6. Spatial Pyramid Pooling Method
3. Novel Pooling Methods
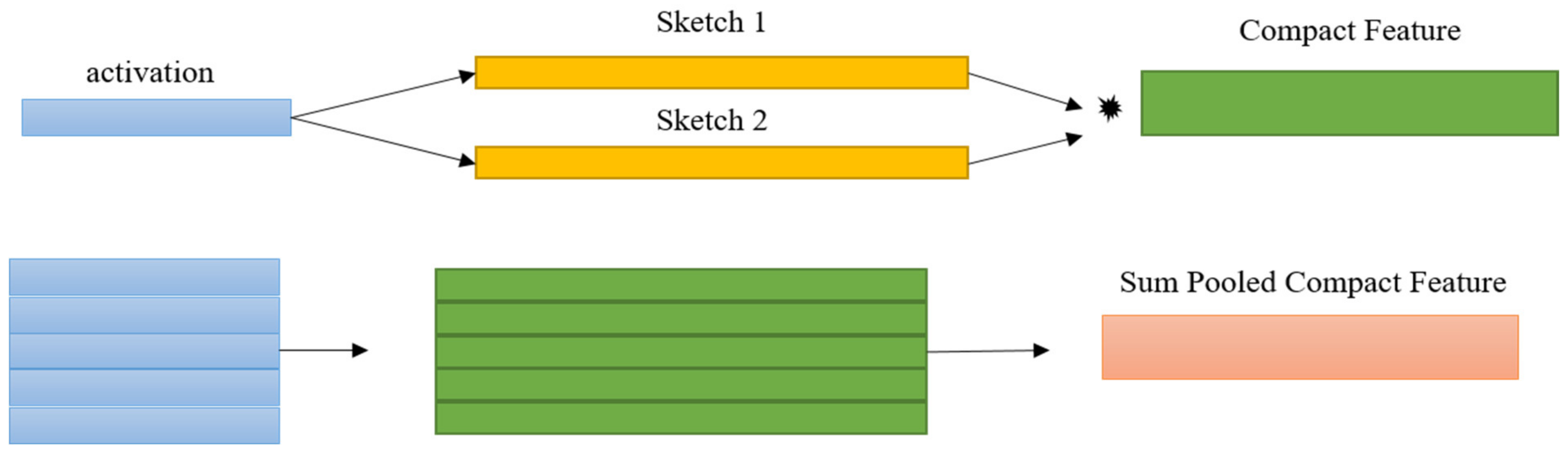
3.1. Compact Bilinear Pooling
3.2. Spectral Pooling
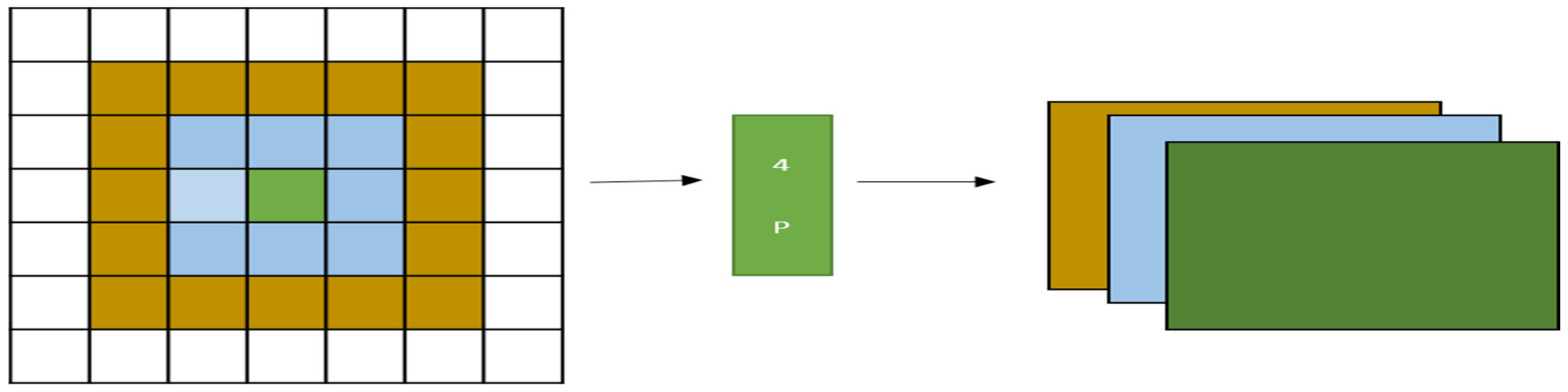
3.3. Per Pixel Pyramid Pooling
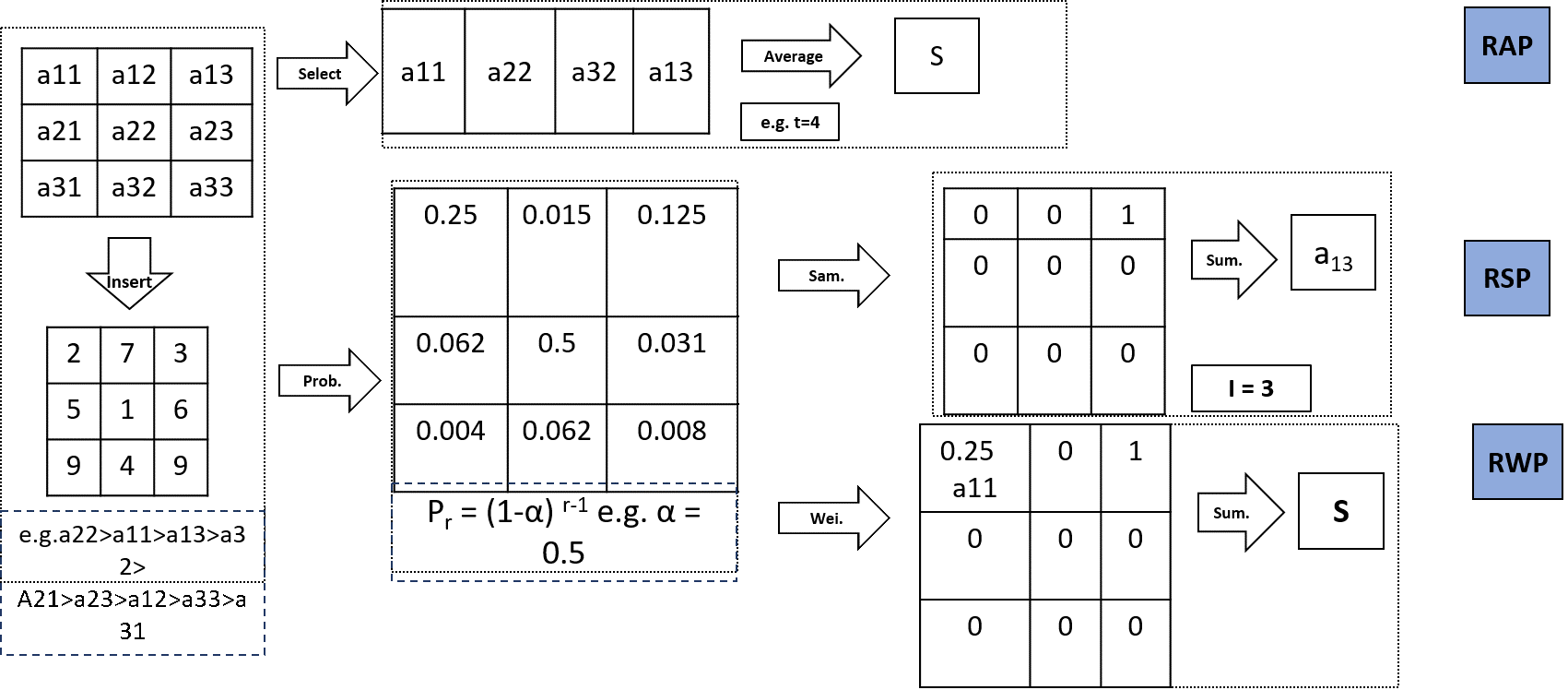
3.4. Rank-Based Average Pooling
3.5. Max-Out Fractional Pooling
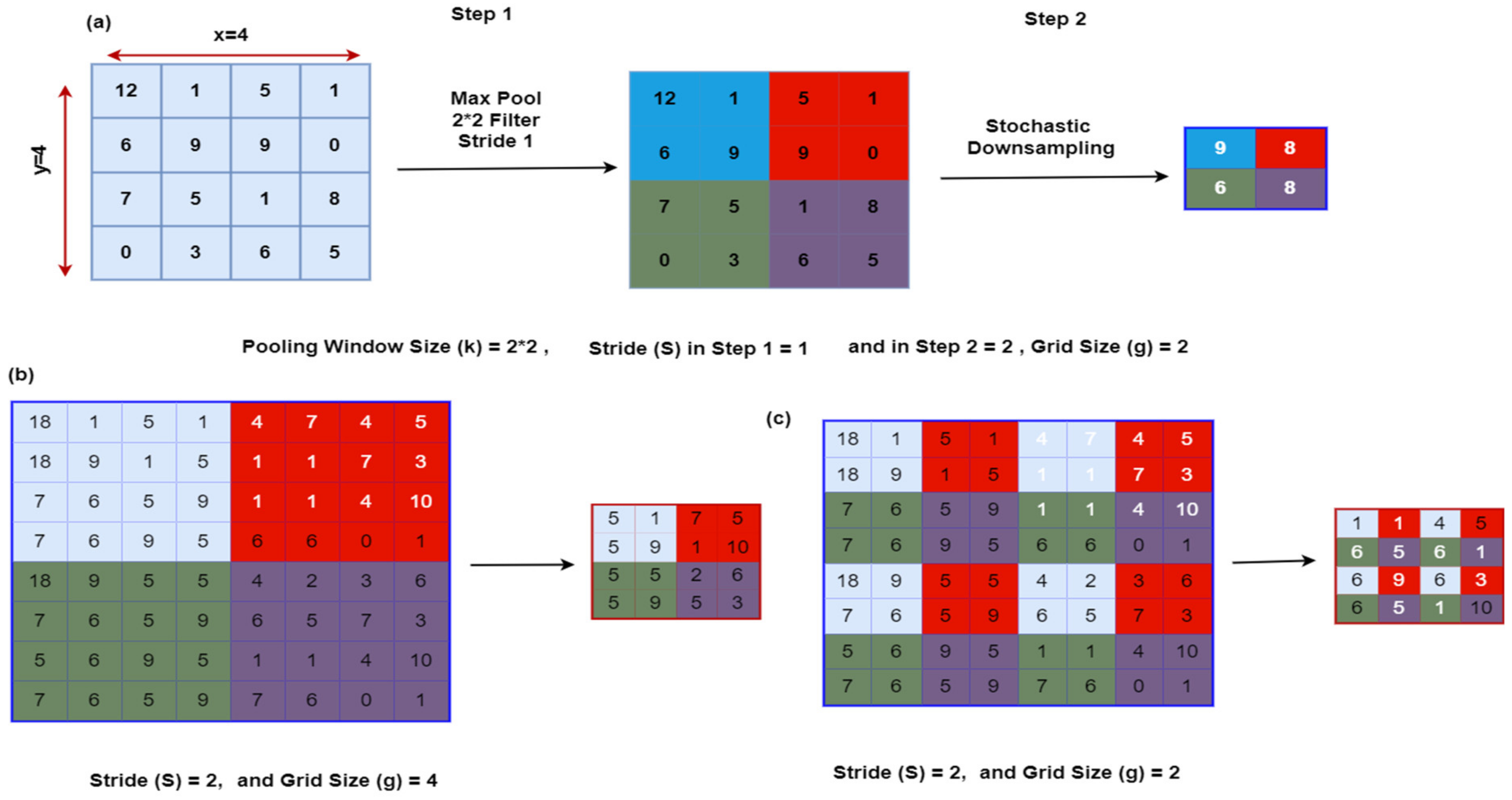
3.6. S3Pooling
3.7. Methods to Preserve Critical Information When Pooling
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Pooling Approaches
Performance Evaluation of Popular Pooling Methods
5. Dataset Description
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.; Li, S.; Knibbs, L.D.; Hamm, N.A.; Cao, W.; Li, T.; Guo, J.; Ren, H.; Abramson, M.J.; Guo, Y. A machine learning method to estimate PM2.5 concentrations across China with remote sensing, meteorological and land use information. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.R.; Lugosi, G.; Venkatesh, S.S. Learning pattern classification-a survey. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1998, 44, 2178–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oja, E. Principal components, minor components, and linear neural networks. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellacott, S.W. An analysis of the delta rule. In Proceedings of the International Neural Network Conference, Paris, France, 9–13 July 1990; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 956–959. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, G.M.; Kemal, E.H. A comprehensive analysis of deep learning based representation for face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal, S.; Singh, M.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. Regularizing deep learning architecture for face recognition with weight variations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 7th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Arlington, VA, USA, 8–11 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, B.B.; Kamsu-Foguem, B.; Tangara, F. Deep convolution neural network for image recognition. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 48, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Foysal, F.A.; Neehal, N.; Karim, E.; Hossain, S.A. InceptB: A CNN based classification approach for recognizing traditional bengali games. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 143, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, F.; Sakib, S.; Siddique, M.A. Recognition of handwritten digit using convolutional neural network in python with tensorflow and comparison of performance for various hidden layers. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 26–28 September 2019; pp. 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Lecun, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning for AI. Commun. ACM 2021, 64, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Wei, Z. Mixed pooling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology, Shanghai, China, 24–26 October 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 364–375. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Gan, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Han, S. Once-for-all: Train one network and specialize it for efficient deployment. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.09791. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, O.; Baloglu, U.B.; Tan, R.S.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. A new approach for arrhythmia classification using deep coded features and LSTM networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 176, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Xing, T.; Lin, J.H.; Srivastava, M.; Gupta, R.; Zhang, Z. Accelerating binarized convolutional neural networks with software-programmable FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, CA, USA, 22–24 February 2017; pp. 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, N.; Perronnin, F. Generalized max pooling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2473–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Gu, X. Towards dropout training for convolutional neural networks. Neural Netw. 2015, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boureau, Y.L.; Ponce, J.; LeCun, Y. A theoretical analysis of feature pooling in visual recognition. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Shao, H.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, X. Ensemble transfer CNNs driven by multi-channel signals for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery cross working conditions. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 207, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Chaudhury, S.; Panigrahi, B.K. Hybrid MPSO-CNN: Multi-level particle swarm optimized hyperparameters of convolutional neural network. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2021, 63, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passricha, V.; Aggarwal, R.K. A comparative analysis of pooling strategies for convolutional neural network based Hindi ASR. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bao, J.; Chen, T.; Yu, A.; Yang, R. Prediction of ball milling performance by a convolutional neural network model and transfer learning. Powder Technol. 2022, 403, 117409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Peng, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. A deep convolutional neural network with new training methods for bearing fault diagnosis under noisy environment and different working load. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 100, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, A.; Poppe, R.; Kalliatakis, G. Refining activation downsampling with SoftPool. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10357–10366. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Qu, Z.; Cao, C. Mixed pooling and richer attention feature fusion for crack detection. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 145, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.R.; Dash, R.; Majhi, B. Automated diagnosis of multi-class brain abnormalities using MRI images: A deep convolutional neural network based method. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliège, A.; Istasse, M.; Kumar, A.; De Vleeschouwer, C.; Van Droogenbroeck, M. Ordinal pooling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.01561. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, T.; Verma, N.K.; Masood, S. Mixed fuzzy pooling in convolutional neural networks for image classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Gallagher, P.W.; Tu, Z. Generalizing pooling functions in convolutional neural networks: Mixed, gated, and tree. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Cadiz, Spain, 9–11 May 2016; pp. 464–472. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Hertel, L.; Maass, M.; Koch, P.; Mazur, R.; Mertins, A. Improved audio scene classification based on label-tree embeddings and convolutional neural networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bello, M.; Nápoles, G.; Sánchez, R.; Bello, R.; Vanhoof, K. Deep neural network to extract high-level features and labels in multi-label classification problems. Neurocomputing 2020, 413, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonder, B.; Both, S.; Jodra, M.; Xu, H.; Fricker, M.; Matos, I.S.; Malhi, Y. Linking functional traits to multiscale statistics of leaf venation networks. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1796–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3557. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Ye, Y.; Wu, Y. Rank-based pooling for deep convolutional neural networks. Neural Netw. 2016, 83, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M.; Qayyum, A.; Awais, M.; Alnowami, M.; Khan, M.K. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: A review. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Goldblum, M.; Sharaf, A.; Kong, K.; Goldstein, T. Data augmentation for meta-learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8152–8161. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Z.; Pan, G. Overfitting remedy by sparsifying regularization on fully-connected layers of CNNs. Neurocomputing 2019, 328, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ming, D.; Lv, X. Superpixel based land cover classification of VHR satellite image combining multi-scale CNN and scale parameter estimation. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, P.; Li, M.; Han, D. A novel stochastic resonance model based on bistable stochastic pooling network and its application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauman, K.; Darrell, T. The pyramid match kernel: Discriminative classification with sets of image features. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05), Beijing, China, 17–21 October 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1458–1465. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekkers, E.J. B-spline cnns on lie groups. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.12057. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2014, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y. Data-driven based tiny-YOLOv3 method for front vehicle detection inducing SPP-net. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 110227–110236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Y. Computer vision-based approach for smart traffic condition assessment at the railroad grade crossing. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 51, 101456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumuni, A.; Mumuni, F. CNN architectures for geometric transformation-invariant feature representation in computer vision: A review. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Hu, B.; Zhou, M. Rapid detection of blind roads and crosswalks by using a lightweight semantic segmentation network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 6188–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, X.; Li, P. Fast and compact bilinear pooling by shifted random Maclaurin. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3243–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelaziz, I.; Chetouani, A.; El Hassouni, M.; Latecki, L.J.; Cherifi, H. No-reference mesh visual quality assessment via ensemble of convolutional neural networks and compact multi-linear pooling. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 100, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippel, O.; Snoek, J.; Adams, R.P. Spectral representations for convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revaud, J.; Leroy, V.; Weinzaepfel, P.; Chidlovskii, B. PUMP: Pyramidal and Uniqueness Matching Priors for Unsupervised Learning of Local Descriptors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–23 June 2022; pp. 3926–3936. [Google Scholar]
- Bera, S.; Shrivastava, V.K. Effect of pooling strategy on convolutional neural network for classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B. Fractional max-pooling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6071. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, S.; Wu, H.; Kumar, A.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feris, R. S3pool: Pooling with stochastic spatial sampling. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July; pp. 4970–4978.
- Pan, X.; Wang, X.; Tian, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Guizani, M. Machine-learning-aided optical fiber communication system. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, R.; Yang, J.; Yue, J.; Wang, Y. A high-precision detection method of hydroponic lettuce seedlings status based on improved Faster RCNN. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedan, F.; Weber, N.; Goesele, M.; Roth, S. Detail-preserving pooling in deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 9108–9116. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, G. Lip: Local importance-based pooling. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3355–3364. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, O.; Kusupati, A.; Simhadri, H.V.; Varma, M.; Jain, P. RNNPool: Efficient non-linear pooling for RAM constrained inference. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 20473–20484. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y. RP-Unet: A Unet-based network with RNNPool enables computation-efficient polyp segmentation. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Workshop on Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 25–28 June 2021; Volume 11913, p. 1191302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Khan, M.A.; Zhang, Y.D. VISPNN: VGG-inspired stochastic pooling neural network. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkaddour, M.K. CNN based features extraction for age estimation and gender classification. Informatica 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Ragavendran, U. Interpretation of intelligence in CNN-pooling processes: A methodological survey. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Yu, H. Learnable dynamic temporal pooling for time series classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 8288–8296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J. Hartley spectral pooling for deep learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04028. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X. Multi-bias non-linear activation in deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning 2016, New York City, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.; Li, R. Wavelet pooling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza Brito, A.; Vieira, M.B.; de Andrade, M.L.S.C.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Giraldi, G.A. Combining max-pooling and wavelet pooling strategies for semantic image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.; Afshar, S.; Tapson, J.; Van Schaik, A. EMNIST: Extending MNIST to handwritten letters. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 2921–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Recht, B.; Roelofs, R.; Schmidt, L.; Shankar, V. Do cifar-10 classifiers generalize to cifar-10? arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00451. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Jain, V.; Mishra, A. An analysis of convolutional neural networks for image classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.L.; Kakarla, J.; Isunuri, B.V.; Singh, M. Multi-class brain tumor classification using residual network and global average pooling. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 13429–13438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Song, K.; Xu, J.; Dong, H.; Yan, Y. An image-level weakly supervised segmentation method for No-service rail surface defect with size prior. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing 2022, 165, 108334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.F.G.D.; Papa, J.P. Avoiding overfitting: A survey on regularization methods for convolutional neural networks. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Z.; Liang, J.; Quan, Y. Encoding spatial distribution of convolutional features for texture representation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 22732–22744. [Google Scholar]




| Type of Pooling | Advantages | Drawbacks | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Pooling |
|
| [38,39] |
| Average Pooling |
|
| [37,38,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] |
| Gated Max Average |
|
| [41] |
| Mixed Max Average |
|
| [42] |
| Pyramid Pooling |
|
| [43] |
| Stochastic Pooling |
|
| [44] |
| Tree Pooling |
|
| [41,66] |
| Fractional Max Pooling |
|
| [36] |
| S3Pool |
|
| [37] |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling |
|
| [45] |
| Pooling Methods | Architecture | Activation Function | Error Rate of Different Datasets | Accuracy | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | CIFAR-10 | CIFAR-100 | |||||
| Gated Method | 6 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.29 | 7.90 | 33.22 | 88% (Rotation Angle) | [32] |
| Mixed Pooling | 6 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.30 | 8.01 | 33.35 | 90% (Translation Angle) | |
| Max Pooling | 6 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.32 | 7.68 | 32.41 | 93.75% (Scale Multiplier) | |
| Max + Tree Pooling | 6 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.39 | 9.28 | 34.75 | ||
| Mixed Pooling | 6 Convolutional Layers (Without data Augmentation) | RELU | 10.41 | 12.61 | 37.20 | 91.5% | [34] |
| Stochastic Pooling | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.47 | 15.26 | 42.58 | --------- | [36] |
| Average Pooling | 6 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.83 | 19.38 | 47.18 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling (RAP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.56 | 18.28 | 46.24 | --------- | [37] |
| Rank-Based Weighted Pooling (RWP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.56 | 19.28 | 48.54 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Stochastic Pooling (RSP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.59 | 17.85 | 45.48 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling (RAP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU (Parametric) | 0.56 | 18.58 | 45.86 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Weighted Pooling (RWP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU (Parametric) | 0.53 | 18.96 | 47.09 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Stochastic pooling (RSP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU (Parametric) | 0.42 | 14.26 | 44.97 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling (RAP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | Leaky RELU | 0.58 | 17.97 | 45.64 | ||
| Rank-Based Weighted Pooling (RWP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | Leaky RELU | 0.56 | 19.86 | 48.26 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Stochastic Pooling (RSP) | 3 Convolutional Layers | Leaky RELU | 0.47 | 13.48 | 43.39 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling (RAP) | Network in Network (NIN) | Leaky RELU | --------- | 9.48 | 32.18 | --------- | [37] |
| Rank-Based Weighted Pooling (RWP) | Network in Network (NIN) | Leaky RELU | --------- | 9.34 | 32.47 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Stochastic Pooling (RSP) | Network in Network (NIN) | Leaky RELU | --------- | 9.84 | 32.16 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling (RAP) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU | --------- | 9.84 | 34.85 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Weighted Pooling (RWP) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU | --------- | 10.62 | 35.62 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Stochastic Pooling (RSP) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU | --------- | 9.48 | 36.18 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling (RAP) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU (Parametric) | --------- | 8.75 | 34.86 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Weighted Pooling (RWP) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU (Parametric) | --------- | 8.94 | 37.48 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Stochastic Pooling (RSP) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU (Parametric) | --------- | 8.62 | 34.36 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Average Pooling (RAP) (Includes Data Augmentation) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU | --------- | 8.67 | 30.48 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Weighted Pooling (RWP) (Includes Data Augmentation) | Network in Network (NIN) | Leaky RELU | --------- | 8.58 | 30.41 | --------- | |
| Rank-Based Stochastic Pooling (RSP) (Includes Data Augmentation) | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU (Parametric) | --------- | 7.74 | 33.67 | --------- | |
| --------- | Network in Network | RELU | 0.49 | 10.74 | 35.86 | --------- | |
| --------- | Supervised Network | RELU | --------- | 9.55 | 34.24 | --------- | |
| --------- | Max out Network | RELU | 0.47 | 11.48 | --------- | --------- | |
| Mixed Pooling | Network in Network (NIN) | RELU | 16.01 | 8.80 | 35.68 | 92.5% | [39] |
| VGG (GOFs Learned Filter) | RELU | 10.08 | 6.23 | 28.64 | |||
| Fused Random Pooling | 10 Convolutional Layers | RELU | --------- | 4.15 | 17.96 | 87.3% | [52] |
| Fractional Max Pooling | 11 Convolutional Layers | Leaky RELU | 0.50 | --------- | 26.49 | [53] | |
| Fractional Max Pooling | Convolutional Layer Network (Sparse) | Leaky RELU | 0.23 | 3.48 | 26.89 | ||
| S3pooling | Network in Network (NIN) (Addition to Dropout) | RELU | --------- | 7.70 | 30.98 | 92.3% | [58] |
| S3pooling | Network in Network (NIN) (Addition to Dropout) | RELU | --------- | 9.84 | 32.48 | ||
| S3pooling | ResNet | RELU | --------- | 7.08 | 29.38 | 84.5% | [66] |
| S3pooling (Flip + Crop) | ResNet | RELU | --------- | 7.74 | 30.86 | ||
| S3pooling (Flip + Crop) | CNN With Data Augmentation | RELU | --------- | 7.35 | --------- | ||
| S3pooling (Flip + Crop) | CNN in Absence of Data Augmenting | RELU | --------- | 9.80 | 32.71 | ||
| Wavelet Pooling | Network in Network | RELU | --------- | 10.41 | 35.70 | 81.04% (CIFAR-100) | [67] |
| ALL-CNN | --------- | 9.09 | --------- | ||||
| ResNet | --------- | 13.76 | 27.30 | 96.87% (CIFAR-10) | |||
| Dense Net | --------- | 7.00 | 27.95 | ||||
| AlphaMaxDenseNet | --------- | 6.56 | 27.45 | ||||
| Temporal Pooling | Global Pooling Layer | Softmax | --------- | --------- | --------- | 91.5% | [68] |
| Spectral Pooling | Attention-Based CNN 2 Convolutional Layers | RELU | 0.605 | 8.87 | --------- | They mentioned improved accuracy but did not mentioned percentage. | [69] |
| Mixed Pooling | 3 Convolutional Layers (Without Data Augmentation) | MBA (Multi Bias Nonlinear Activation) | ------ | 6.75 | 26.14 | [70] | |
| Mixed Pooling | 3 Convolutional Layers (With Data Augmentation) | ------ | 5.37 | 24.2 | |||
| Wavelet Pooling | 3 Convolutional Layers | RELU | ------ | ------ | ------ | 99% (MNIST)74.42 (CIFAR-10)80.28 (CIFAR-100) | [71] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zafar, A.; Aamir, M.; Mohd Nawi, N.; Arshad, A.; Riaz, S.; Alruban, A.; Dutta, A.K.; Almotairi, S. A Comparison of Pooling Methods for Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178643
Zafar A, Aamir M, Mohd Nawi N, Arshad A, Riaz S, Alruban A, Dutta AK, Almotairi S. A Comparison of Pooling Methods for Convolutional Neural Networks. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(17):8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178643
Chicago/Turabian StyleZafar, Afia, Muhammad Aamir, Nazri Mohd Nawi, Ali Arshad, Saman Riaz, Abdulrahman Alruban, Ashit Kumar Dutta, and Sultan Almotairi. 2022. "A Comparison of Pooling Methods for Convolutional Neural Networks" Applied Sciences 12, no. 17: 8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178643
APA StyleZafar, A., Aamir, M., Mohd Nawi, N., Arshad, A., Riaz, S., Alruban, A., Dutta, A. K., & Almotairi, S. (2022). A Comparison of Pooling Methods for Convolutional Neural Networks. Applied Sciences, 12(17), 8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178643






