GPU-Accelerated Target Strength Prediction Based on Multiresolution Shooting and Bouncing Ray Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sonar Target Strength Prediction Method Based on the Multiresolution SBR
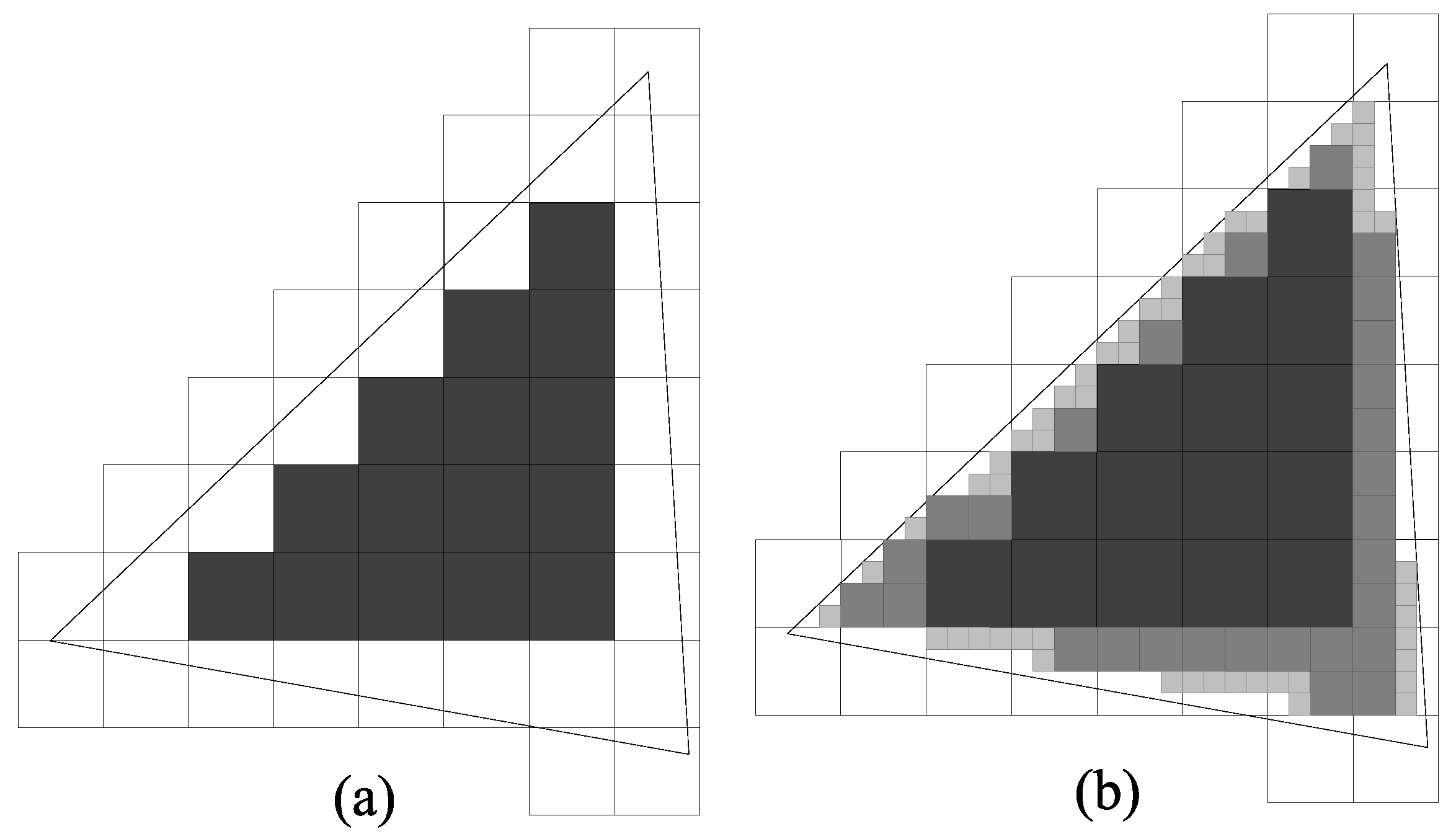
2.1. Multiresolution Grid Algorithm
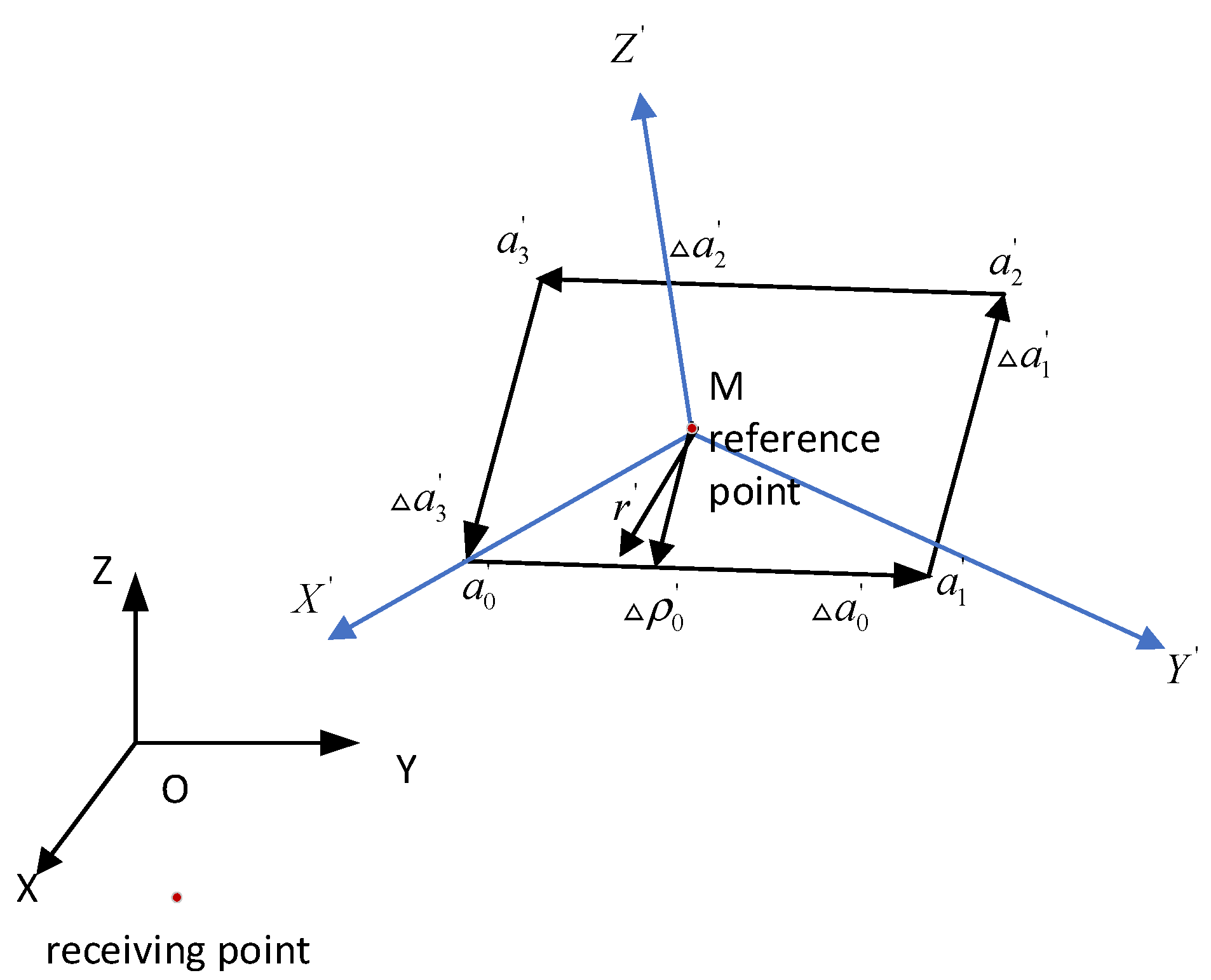
2.2. The Scattered Sound Field Integral Algorithm
3. GPU-Accelerated Implementation for Multiresolution Grid Algorithm in SBR
| Algorithm 1 The GPU-accelerated target strength prediction based on multiresolution SBR |
| Begin Input: the dissected simulation target stackless KD-tree construction; __global__ void create_virtualface_gpu(…);//Generate virtual aperture surface, output ray tube and ray information; while (i < totalraysnum) then//Search all rays in global memory; __global__ void raytracekernel_gpu(…);//ray tracing if(valid ray tubes) then Scattered sound field integral calculation else if(unvalid ray tubes) then discard the ray; else then if(number of splits > threshold) then discard the ray; else then Sound tube bundle split; Store split sound ray bundles in global memory d_ChildRayTube _global__ void reduce_add_sre(float* d_sum_re, float* integralConstRe, int raysBeamNum)//Summation of scattered sound fields using CUDA parallel reduction algorithm Calculate target strength TS end |
4. Results
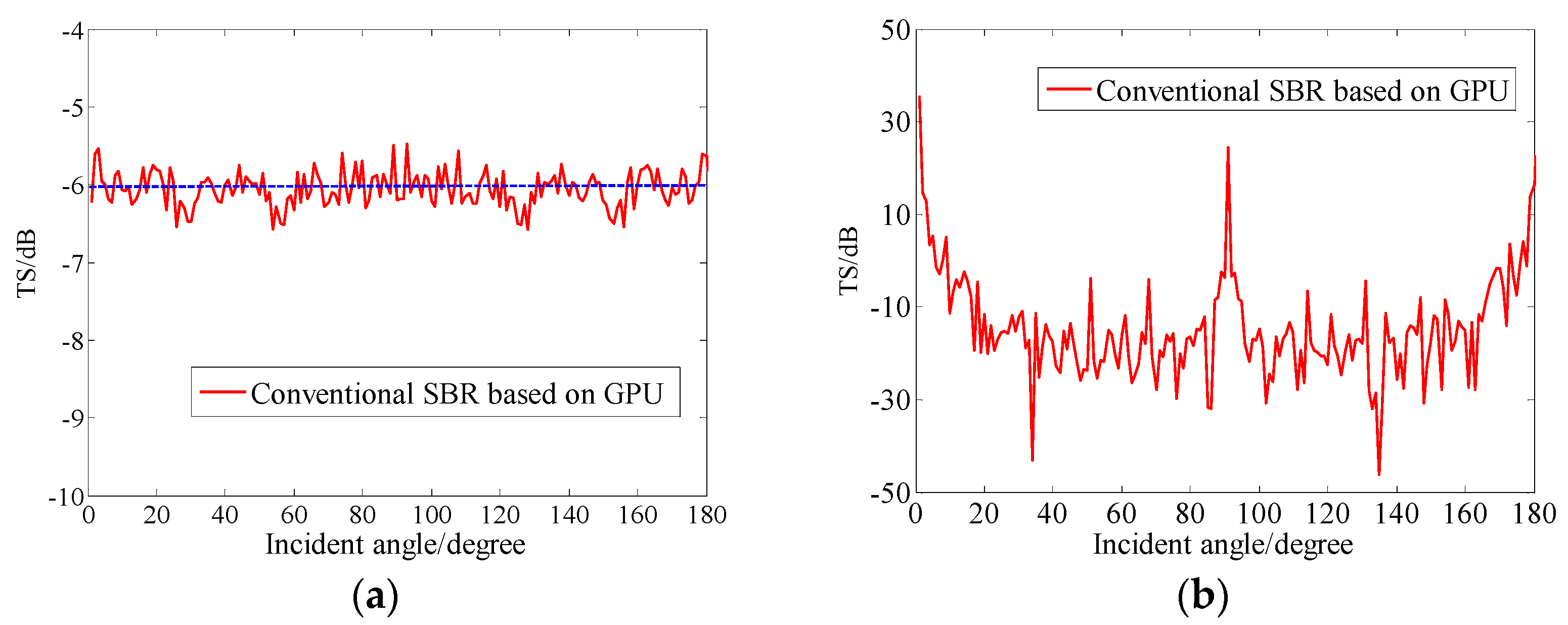
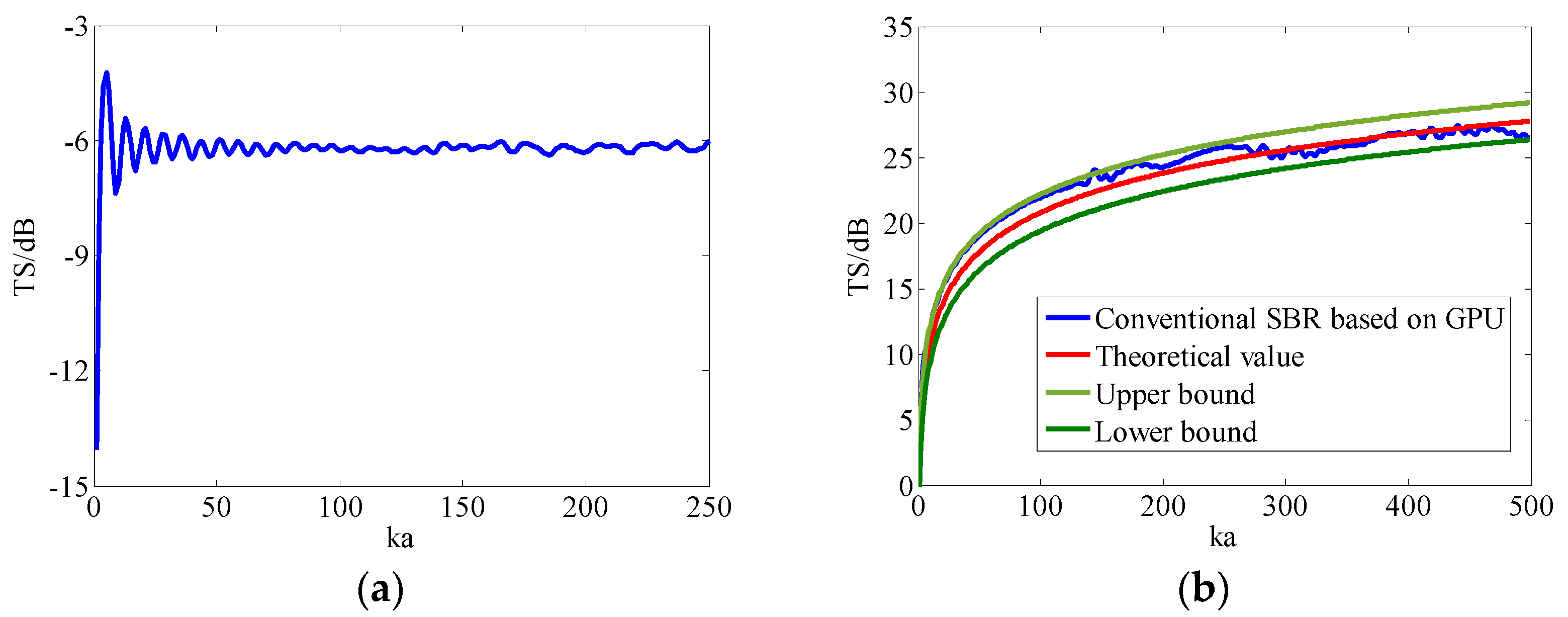
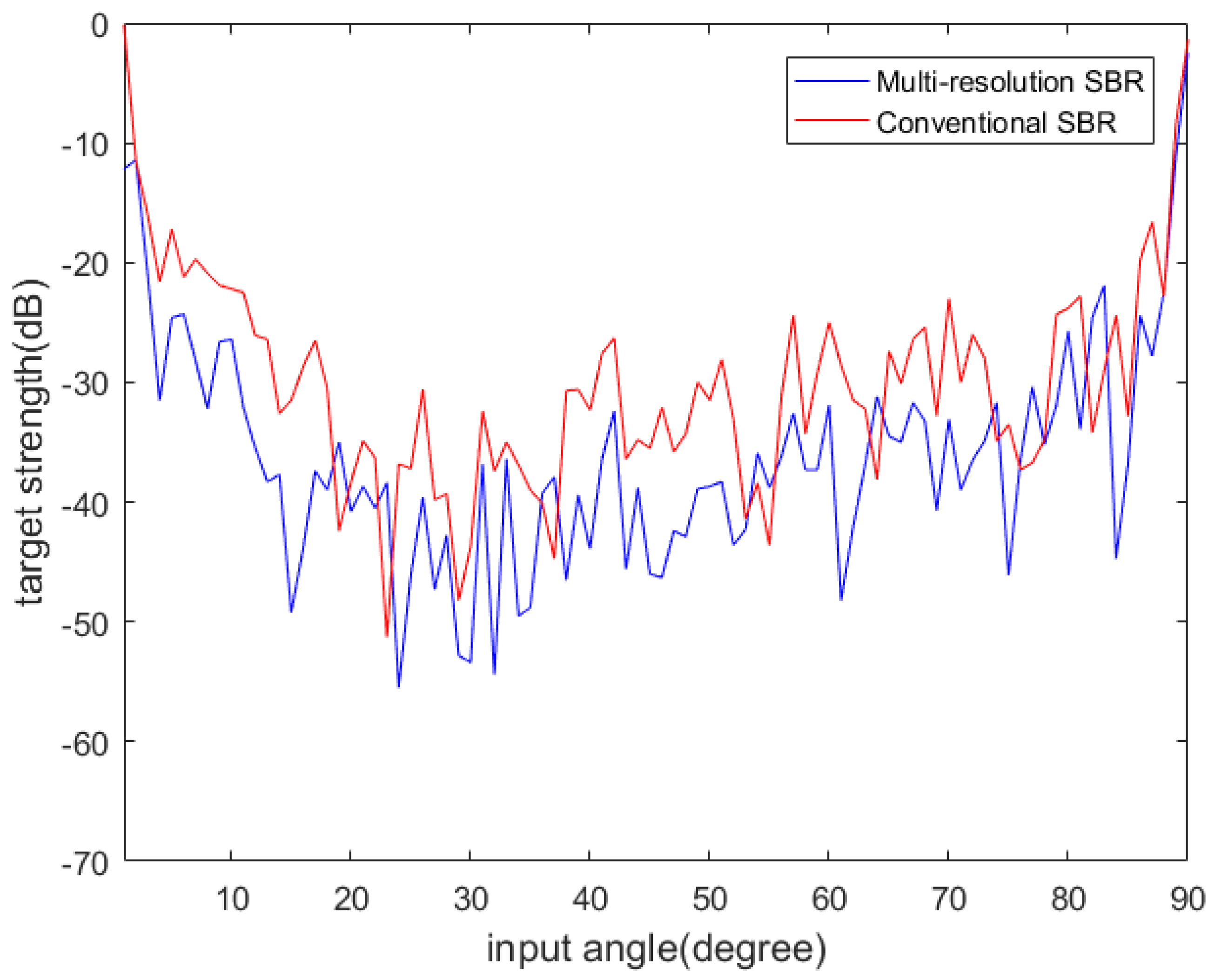
4.1. Algorithm Accuracy Verification
4.2. Algorithm Runtime Evaluation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Odom, R.I. An Introduction to Underwater Acoustics: Principles and Applications. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2003, 84, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fang, Y.Y.; Cheng, K.A.; Sung, P.J.; Chao, C.H.; Chen, C.F. Study of target strength of underwater vehicle. In Proceedings of the Underwater Technology IEEE, Busan, Korea, 21–24 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W. Calculation of acoustic scattering of a nonrigid surface using physical acoustic method. Chin. J. Acoust. 1993, 3, 226–234. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W. Calculation of acoustic scattering from object near an interface using physical acoustic method. Acta Acust. 1999, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, J. Underwater acoustic scattering of a Bessel beam by rigid objects with arbitrary shapes using the T-matrix method. In Proceedings of the 2012 Oceans, Hampton Roads, VA, USA, 14–19 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Yuan, B.C.; Zhou, S.; Wen, G. Graphical Acoustics Computing Method for Highlight Characteristics Calculation of Underwater Targets Echoes. J. Syst. Simul. 2009, 21, 3898–3901. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Tang, W.L.; Zhuo, L.K. Planar elements method for forecasting the echo characteristics from sonar targets. J. Ship Mech. 2012, 16, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, W. Study on calculation method of target strength in waveguide. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 9–11 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Naiwei, S.; Jianchen, L.; Yamin, W. Simulation of Submarine Target Strength Forecast Based on Improved Planar Element Method. Torpedo Technol. 2016, 24, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, M.M.; Cheng, G.L.; Xu, G.J. Improved planar element method for computing target echo. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2008, 20, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, H.; Chou, R.C.; Lee, S.W. Shooting and bouncing rays: Calculating the RCS of an arbitrarily shaped cavity. Antennas Propag. IEEE Trans. 1989, 37, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Chou, R.; Lee, S. Shooting and bouncing rays: Calculating RCS of an arbitrary cavity. In Proceedings of the 1986 Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 8–13 June 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Lin, H.; Bao, H. GPU-Based Shooting and Bouncing Ray Method for Fast RCS Prediction. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, C.Y.; Wang, C.F. Efficient GPU Implementation of the High-Frequency SBR-PO Method. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.B.; Lin, H.; Bao, H. KD-Tree Based Fast Ray Tracing for RCS Prediction. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2008, 81, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, S.; Seo, T.I.; Park, H.S.; Kim, H.T. Multiresolution grid algorithm in the SBR and its application to the RCS calculation. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2001, 29, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.K.; Kim, B.C.; Suk, S.H.; Jin, K.S.; Kim, H.T. Time Consumption Reduction of Ray Tracing for Rcs Prediction using Efficient Grid Division and Space Division Algorithms. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2007, 21, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.C.; Tao, Y.B.; Lin, H. Fast RCS Prediction Using Multiresolution Shooting and Bouncing Ray Method on the Gpu. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2010, 107, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Harris, M.; Zhang, Y.; Owens, J.D. Scan Primitives for GPU Computing. In Proceedings of the Acm Siggraph/eurographics Symposium on Graphics Hardware Eurographics Association, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–5 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
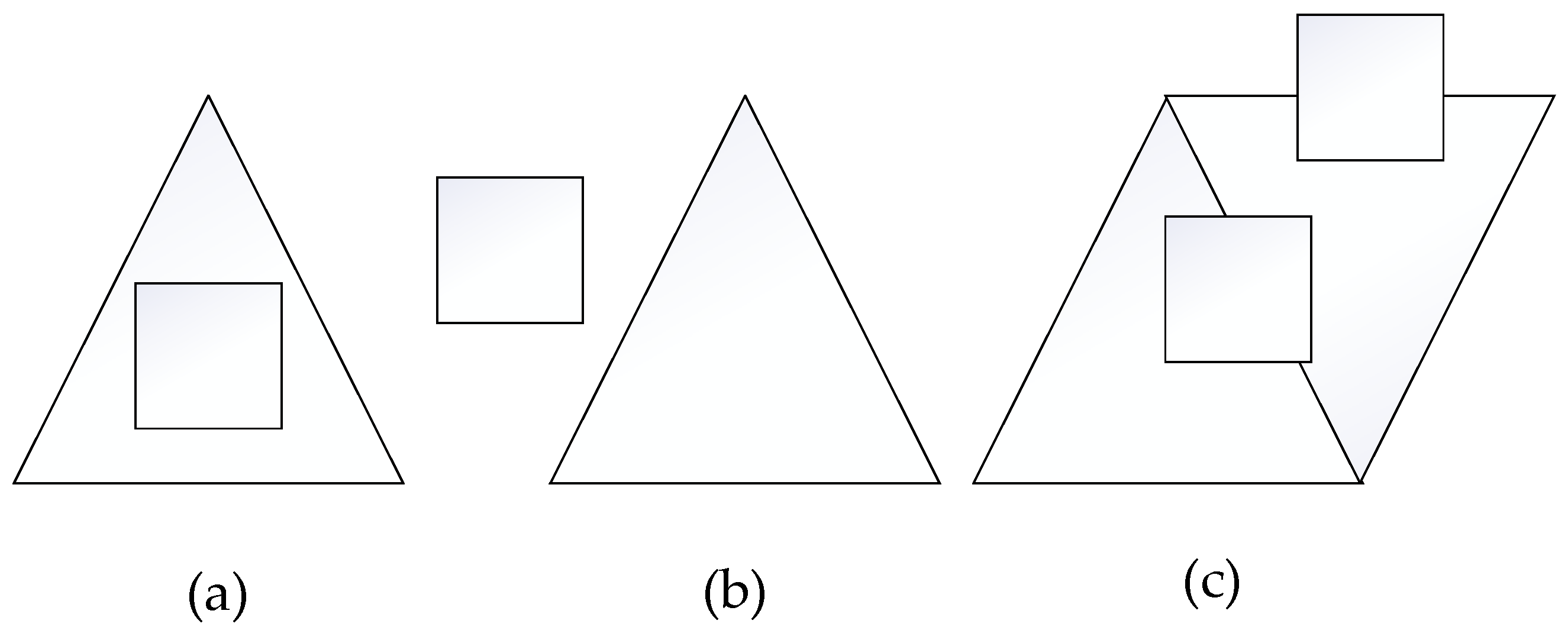
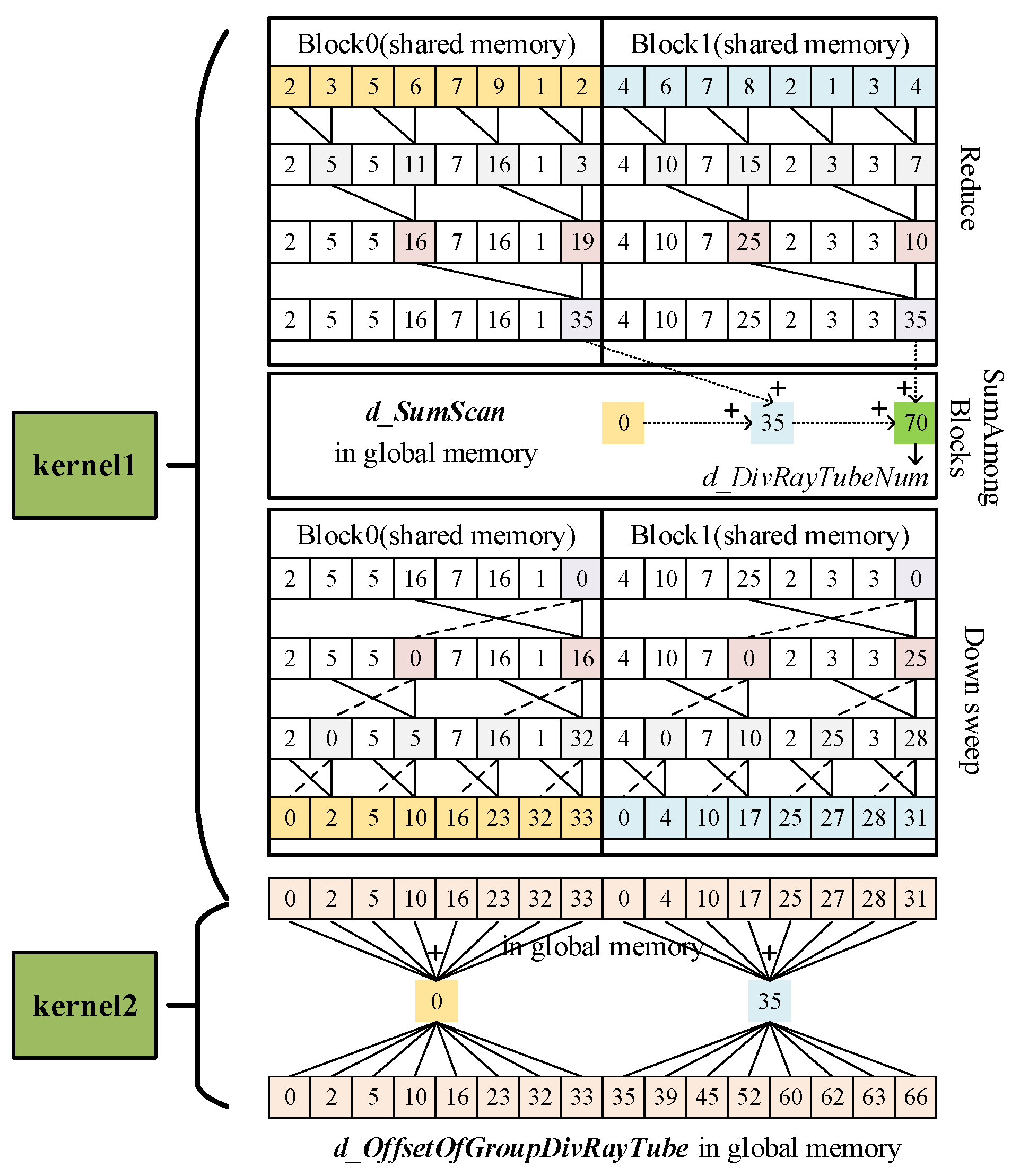



| IsDivRayTube (Bool) | T | F | F | T | T | F | T | F | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step1: Predicate | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Step2: Exclusive Sum Scan | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Target | Size (m) | Maximum Mesh Size | Triangle Number | Node Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphere | 11,000 | 5628 | ||
| Cylinder | 32,328 | 16,445 | ||
| Corner reflector | 294,850 | 147,427 |
| Sphere | Cylinder | Corner Reflector | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angle | |||
| 0° | 13,327 × 13,327 | 3999 × 3999 | 3667 × 2500 |
| 3999 × 14,469 | 3667 × 18,431 | ||
| 3999 × 14,399 | 3667 × 20,500 |
| Targets | CPU-Based SBR | GPU-Based SBR | GPU-Based MSBR | Speedup Ratio (CPU) | Speedup Ratio (GPU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphere | 4336.35 s | 4.45 s | 418.65 ms | 974.68 | 10.65 |
| Cylinder | 1390.06 s | 1.46 s | 389.28 ms | 897.97 | 3.75 |
| Corner reflector | 924.41 s | 1.20 s | 499.44 ms | 768.42 | 2.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, G.; Sun, N.; Shen, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, L. GPU-Accelerated Target Strength Prediction Based on Multiresolution Shooting and Bouncing Ray Method. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126119
Zhao G, Sun N, Shen S, Wu X, Wang L. GPU-Accelerated Target Strength Prediction Based on Multiresolution Shooting and Bouncing Ray Method. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):6119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126119
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Gang, Naiwei Sun, Shen Shen, Xianyun Wu, and Li Wang. 2022. "GPU-Accelerated Target Strength Prediction Based on Multiresolution Shooting and Bouncing Ray Method" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 6119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126119
APA StyleZhao, G., Sun, N., Shen, S., Wu, X., & Wang, L. (2022). GPU-Accelerated Target Strength Prediction Based on Multiresolution Shooting and Bouncing Ray Method. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 6119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126119






