Roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon Alleviated Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis and IgE-triggered Degranulation of RBL-2H3 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of LE
2.2. Animals
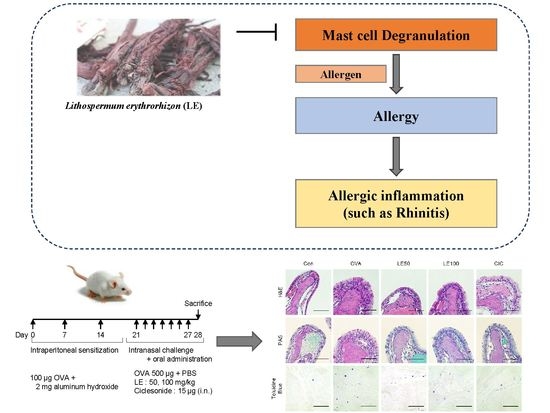
2.3. The OVA-Induced AR Mice Model
2.4. Evaluation of Nasal Symptoms following Last Allergen Exposure
2.5. Collection and Analysis of NALF
2.6. Quantification and Collection of Serum OVA-Specific Immunoglobulins
2.7. Histopathological Assessment of Nasal Mucosa
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
2.10. β-Exosaminidase and Histamine Release Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LE Significantly Ameliorated Nasal Allergy Symptoms and Reduced NALFcytokine Levels in Mice with OVA- Induced AR
3.2. LE Significantly Reduced Nasal Mucosal Thickness and the Accumulation of Eosinophils, Goblet Cells, and Mast Cells in OVA-Induced AR Mice Nasal Tissues
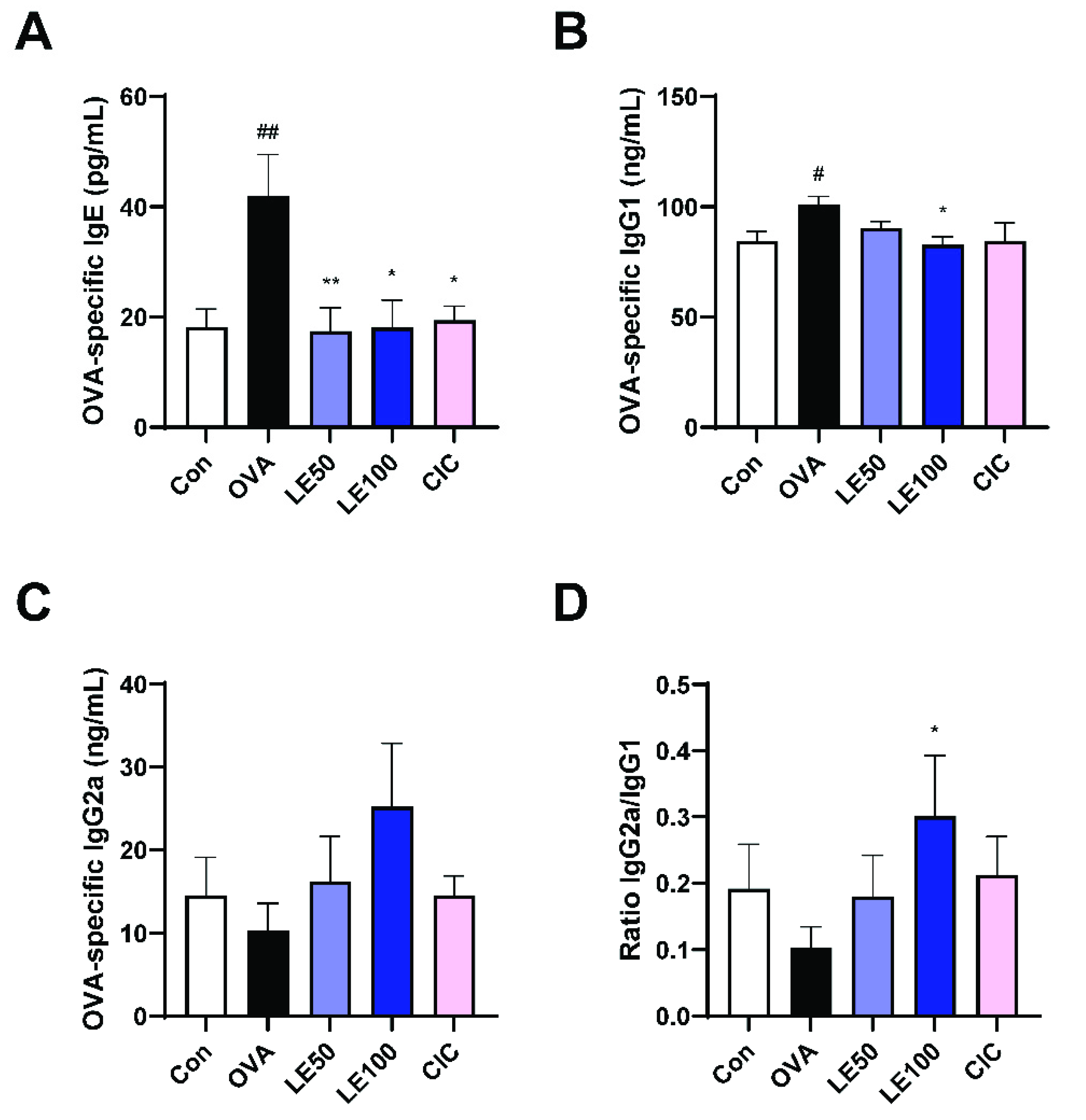
3.3. LE Significantly Suppressed Allergic Responses by Modulating OVA-Specific Immunoglobulins in the Serum of OVA-Induced AR Mice
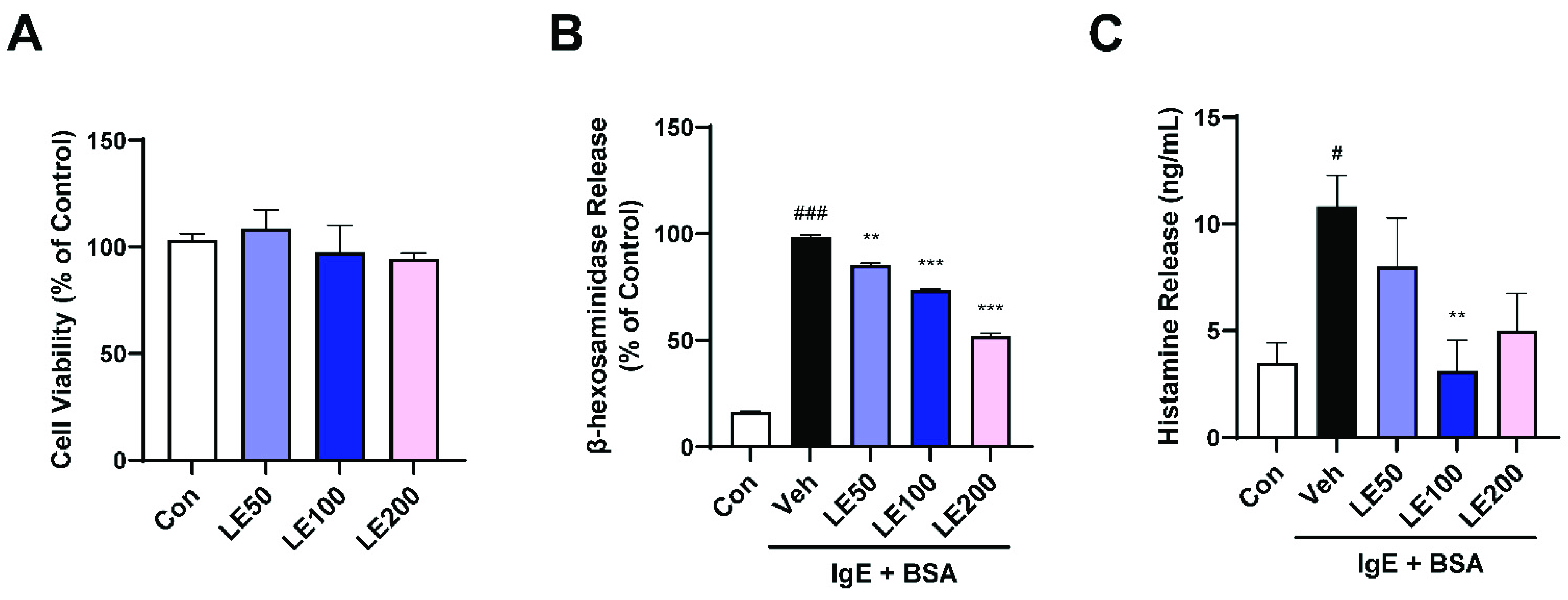
3.4. LE Inhibited IgE-Stimulated Degranulation and Histamine Release by RBL-2H3 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LE | ethanol extract of Lithospermum erythrorhizon |
| OVA | ovalbumin |
| AR | allergic rhinitis |
| DNP-IgE | anti-2,4,6-dinitrophenyl-IgE |
| DNP-BSA | anti-2,4,6-dinitrophenyl-bovine serum albumin |
| NALF | nasal lavage fluid |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| PAS | periodic acid–Schiff |
References
- Tohidinik, H.R.; Mallah, N.; Takkouche, B. History of allergic rhinitis and risk of asthma; a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Allergy Organ J. 2019, 12, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawankar, R.; Mori, S.; Ozu, C.; Kimura, S. Overview on the pathomechanisms of allergic rhinitis. Asia Pac. Allergy 2011, 1, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smolensky, M.H.; Lemmer, B.; Reinberg, A.E. Chronobiology and chronotherapy of allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 852–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuberbier, T.; Lotvall, J.; Simoens, S.; Subramanian, S.V.; Church, M.K. Economic burden of inadequate management of allergic diseases in the European Union: A GA(2) LEN review. Allergy 2014, 69, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakli, H.A.; Riley, T.D. Allergic Rhinitis. Prim. Care 2016, 43, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.K.; Le, T.T.; Kim, K.A.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, W.B.; Jung, S.H. Roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon promotes retinal cell survival in optic nerve crush-induced retinal degeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 203, 108419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, L.A.; Michaels, P.J.; Flores, H.E. Cell-specific production and antimicrobial activity of naphthoquinones in roots of lithospermum erythrorhizon. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberg, A.I.; Yassin, K.; Csikasz, R.I.; Dehvari, N.; Shabalina, I.G.; Hutchinson, D.S.; Wilcke, M.; Ostenson, C.G.; Bengtsson, T. Shikonin increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells and improves plasma glucose levels in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Qu, Z.Y.; Wei, F.X.; Wang, S.Q.; Chen, G.; Qin, L.; Jiang, F.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Shang, L.; et al. Anti-adenovirus activities of shikonin, a component of Chinese herbal medicine in vitro. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, G.Z.; Yu, H.T.; Ni, Y.F.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, Z.P.; Su, K.; Lei, J.; Liu, B.Y.; Ke, C.K.; Zhong, D.X.; et al. Shikonin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. J. Surg Res. 2013, 182, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hayashi, S.; Umezaki, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kageyama-Yahara, N.; Kondo, T.; Kadowaki, M. Shikonin, a constituent of Lithospermum erythrorhizon exhibits anti-allergic effects by suppressing orphan nuclear receptor Nr4a family gene expression as a new prototype of calcineurin inhibitors in mast cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.H.; Cheng, L.; Yan, A.H. Ameliorative effect of acetylshikonin on ovalbumin (OVA)-induced allergic rhinitis in mice through the inhibition of Th2 cytokine production and mast cell histamine release. APMIS 2019, 127, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, J.R.; Romero, F.A., Jr.; Allan, R.J.; Phillips, P.G.; Hackman, F.; Misfeldt, J.; Casale, T.B. The effects of an H3 receptor antagonist (PF-03654746) with fexofenadine on reducing allergic rhinitis symptoms. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Won, S.; Lee, E.K.; Chun, Y.H.; Yoon, J.S.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.H. Effect of Proparacaine in a Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 10, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Patel, D.; Kunjibettu, S.; Hall, N.; Wingertzahn, M.A. Onset of action of ciclesonide once daily in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2008, 87, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, K.D.; Prussin, C.; Metcalfe, D.D. IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S73–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grun, J.L.; Maurer, P.H. Different T-Helper Cell Subsets Elicited in Mice Utilizing 2 Different Adjuvant Vehicles—The Role of Endogenous Interleukin-1 in Proliferative Responses. Cell Immunol. 1989, 121, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Yoshino, S. Enhancement of ovalbumin-specific Th1, Th2, and Th17 immune responses by amorphous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendez-Enriquez, E.; Salomonsson, M.; Eriksson, J.; Janson, C.; Malinovschi, A.; Sellin, M.E.; Hallgren, J. IgE cross-linking induces activation of human and mouse mast cell progenitors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 149, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siraganian, R.P. Mast cell signal transduction from the high-affinity IgE receptor. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aswar, U.; Shintre, S.; Chepurwar, S.; Aswar, M. Antiallergic effect of piperine on ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Jia, J.; He, M. Anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin on mast cell-mediated allergic responses in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis mouse. Cell Immunol. 2015, 298, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almansouri, H.M.; Yamamoto, S.; Kulkarni, A.D.; Ariizumi, M.; Adjei, A.A.; Yamauchi, K. Effect of dietary nucleosides and nucleotides on murine allergic rhinitis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1996, 312, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minai-Fleminger, Y.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Mast cells and eosinophils: The two key effector cells in allergic inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsu, K.; Nakajima, H. IL-5 and eosinophilia. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M.K.; Levi-Schaffer, F. The human mast cell. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowich, I.P.; Rempel, J.D.; HayGlass, K.T. Antigen-specific versus total immunoglobulin synthesis: Total IgE and IgG1, but not IgG2a levels predict murine antigen-specific responses. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 133, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Joo, K.H.; Chung, M.S. Changes of cytokine mRNA expression and IgG responses in rats infected with Capillaria hepatica. Korean J. Parasitol. 2007, 45, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mountford, A.P.; Fisher, A.; Wilson, R.A. The profile of IgG1 and IgG2a antibody responses in mice exposed to Schistosoma mansoni. Parasite Immunol. 1994, 16, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamian, M.; Sohrabi, S.; Kavosifard, H.; Niknam, H.M. Lower levels of IgG1 in comparison with IgG2a are associated with protective immunity against Leishmania tropica infection in BALB/c mice. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deo, S.S.; Mistry, K.J.; Kakade, A.M.; Niphadkar, P.V. Role played by Th2 type cytokines in IgE mediated allergy and asthma. Lung India 2010, 27, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, R.L.; Seymour, B.W.; Hudak, S.; Jackson, J.; Rennick, D. Antibody to interleukin-5 inhibits helminth-induced eosinophilia in mice. Science 1989, 245, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunig, G.; Warnock, M.; Wakil, A.E.; Venkayya, R.; Brombacher, F.; Rennick, D.M.; Sheppard, D.; Mohrs, M.; Donaldson, D.D.; Locksley, R.M.; et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 1998, 282, 2261–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passante, E.; Ehrhardt, C.; Sheridan, H.; Frankish, N. RBL-2H3 cells are an imprecise model for mast cell mediator release. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Kang, J.J.; Chiang, B.L.; Wang, C.N.; Cheng, Y.W. Shikonin inhibited mitogen-activated IL-4 and IL-5 production on EL-4 cells through downregulation of GATA-3 and c-Maf induction. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Zhou, Q.L.; Li, M.; Shang, Y.X. Shikonin alleviates allergic airway remodeling by inhibiting the ERK-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 48, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.Y.; Im, D.S. Anti-allergic effects of salvianolic acid A and tanshinone IIA from Salvia miltiorrhiza determined using in vivo and in vitro experiments. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, T.K.; Le, T.T.; Choi, S.-Y.; Song, H.-W.; Lee, W.-B.; Jung, S.H. Roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon Alleviated Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis and IgE-triggered Degranulation of RBL-2H3 Cells. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126116
Kang TK, Le TT, Choi S-Y, Song H-W, Lee W-B, Jung SH. Roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon Alleviated Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis and IgE-triggered Degranulation of RBL-2H3 Cells. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126116
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Tae Kyeom, Tam Thi Le, Su-Young Choi, Hee-Won Song, Wook-Bin Lee, and Sang Hoon Jung. 2022. "Roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon Alleviated Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis and IgE-triggered Degranulation of RBL-2H3 Cells" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126116
APA StyleKang, T. K., Le, T. T., Choi, S.-Y., Song, H.-W., Lee, W.-B., & Jung, S. H. (2022). Roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon Alleviated Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis and IgE-triggered Degranulation of RBL-2H3 Cells. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126116