Harmonic Extrapolation of Seismic Reflectivity Spectrum for Resolution Enhancement: An Insight from Inas Field, Offshore Malay Basin
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
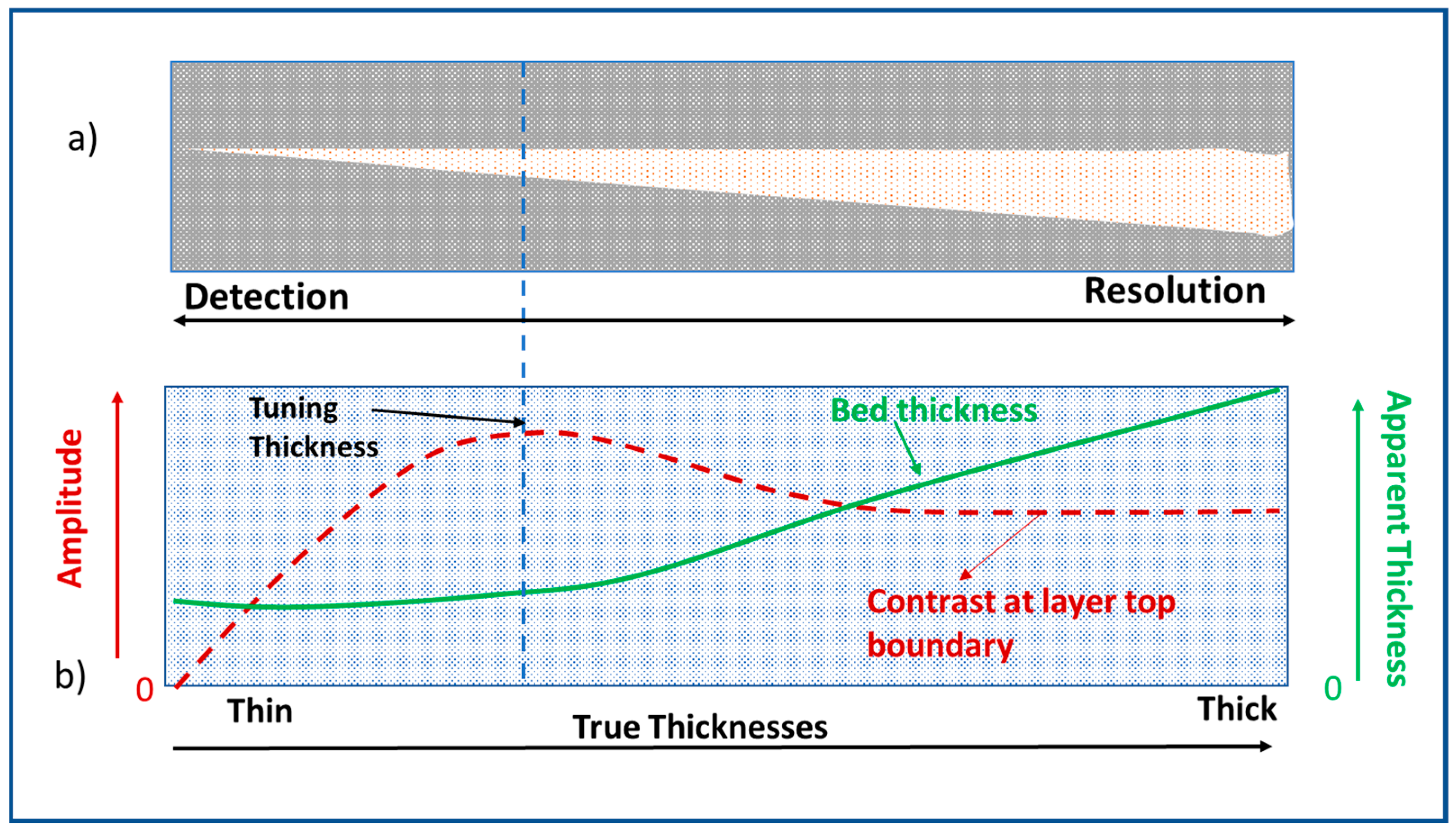
1. Introduction
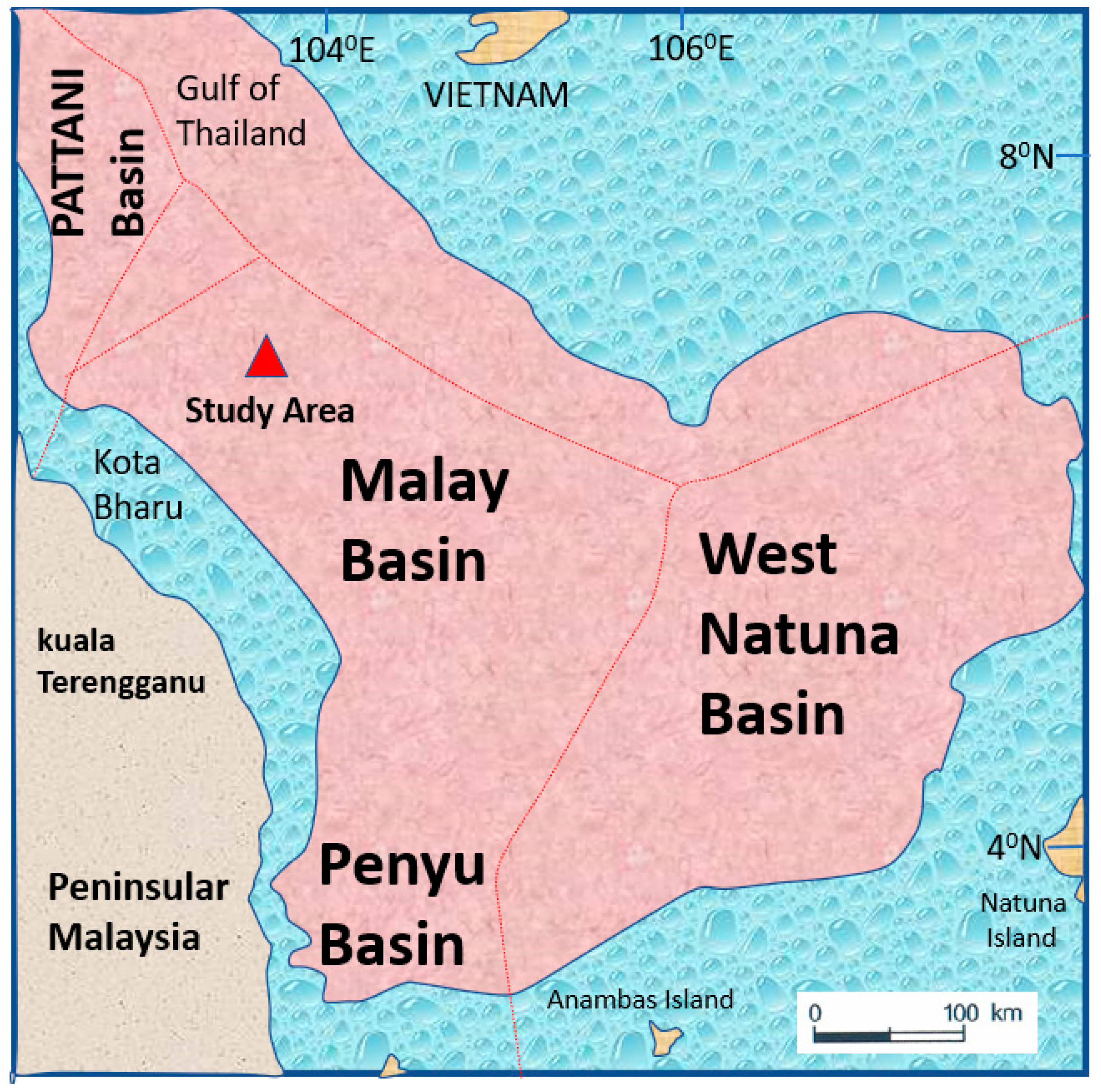
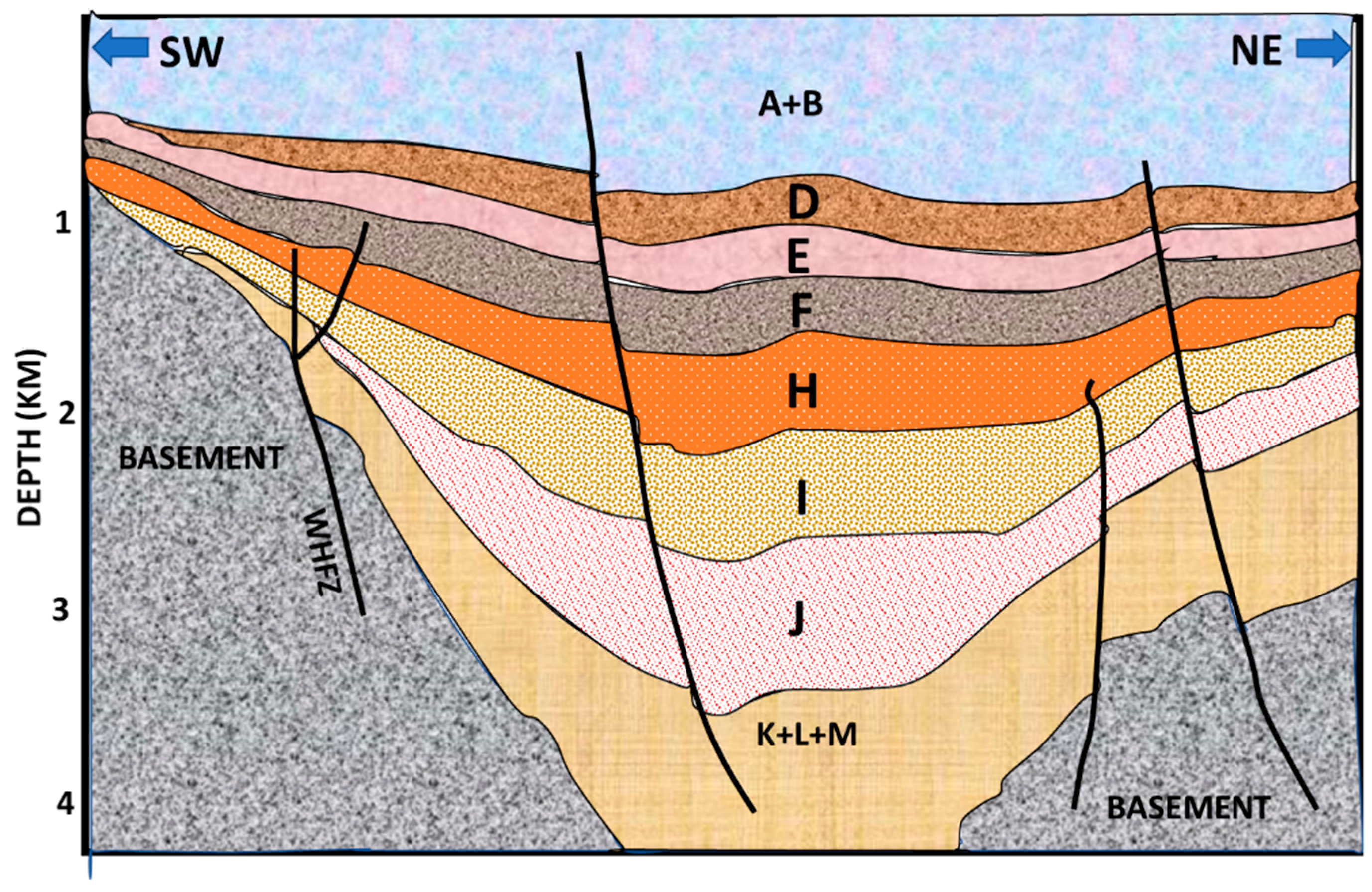
Brief Geologic Background of the Study Area
2. Materials and Methods
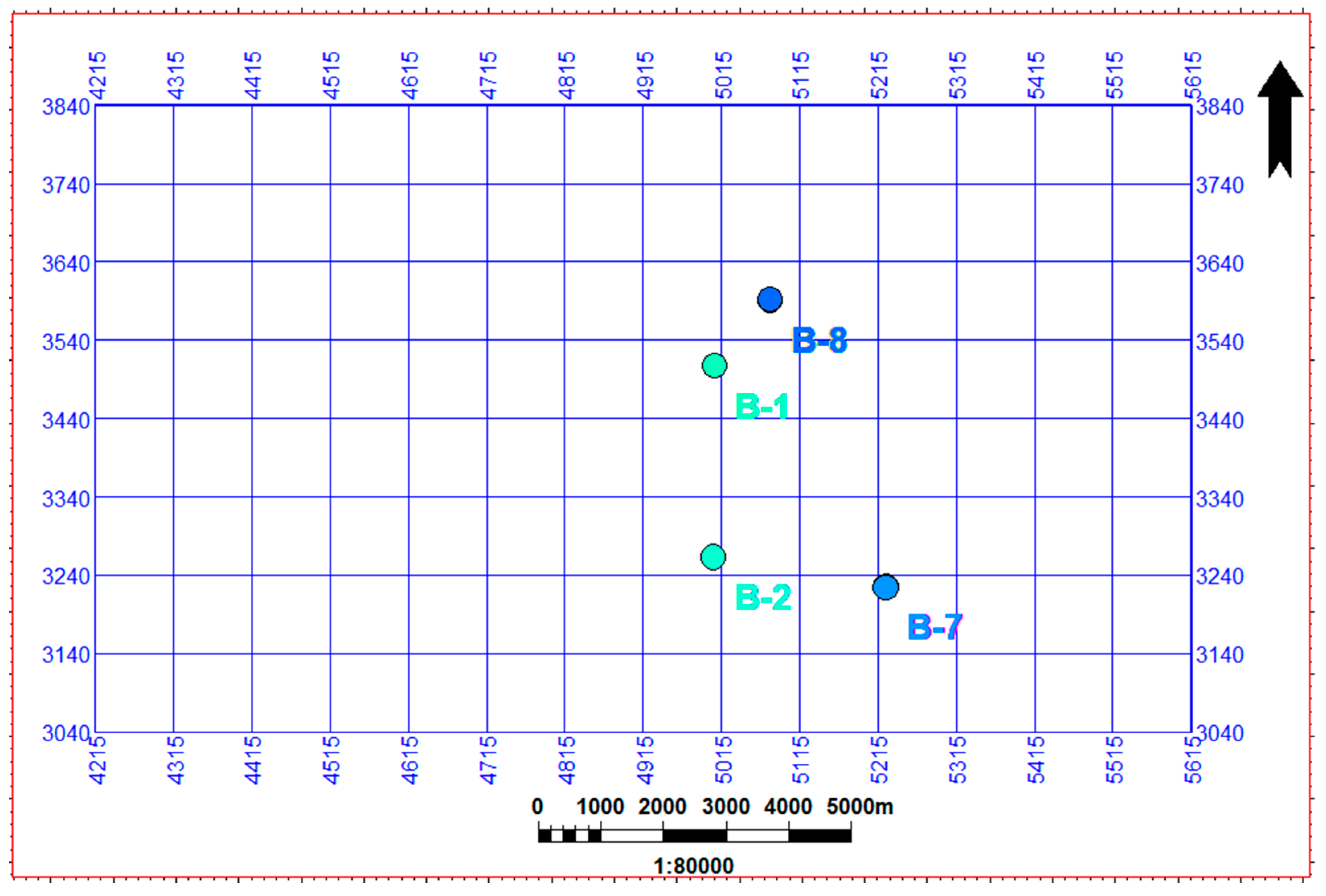
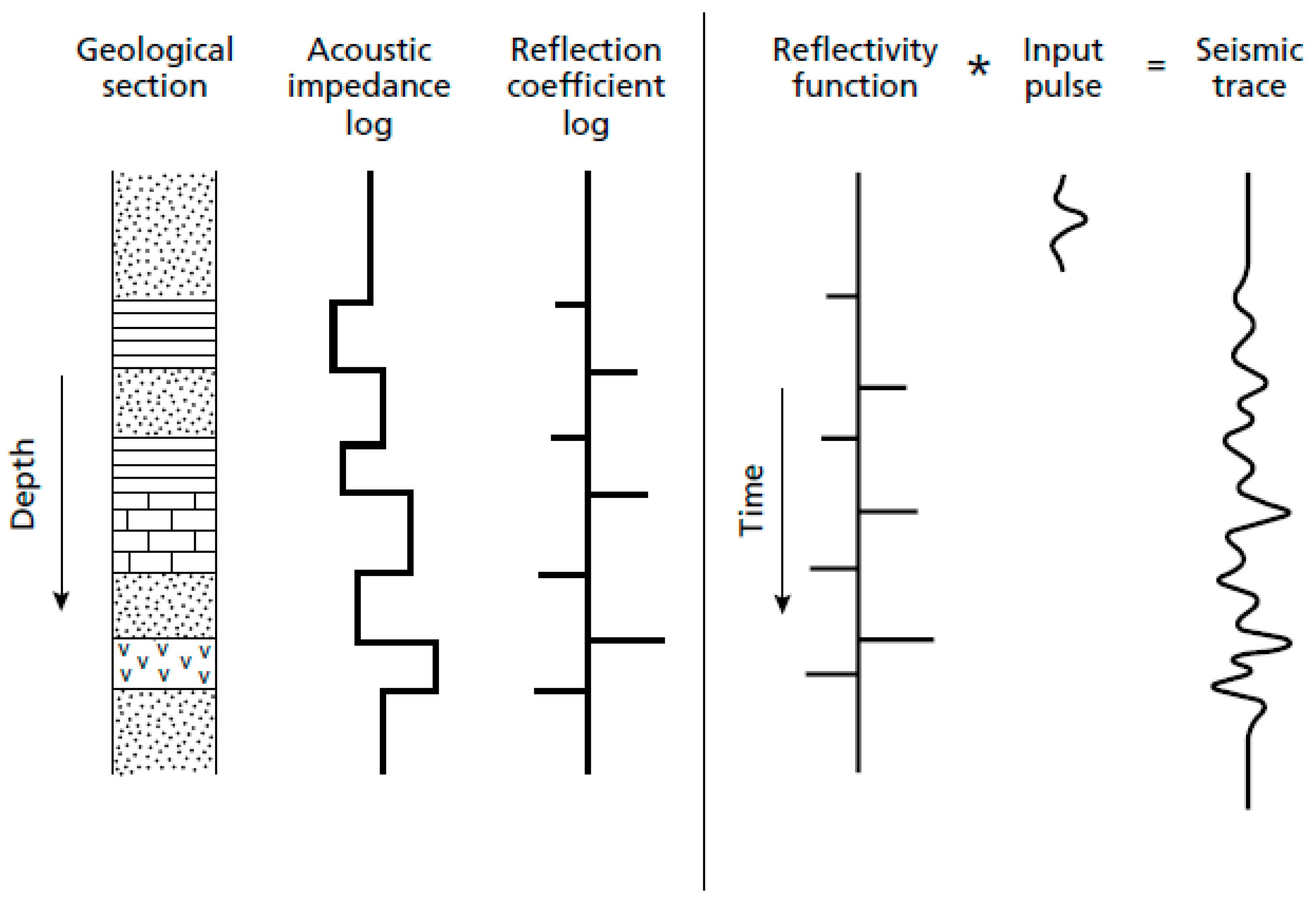
2.1. Data Presentation
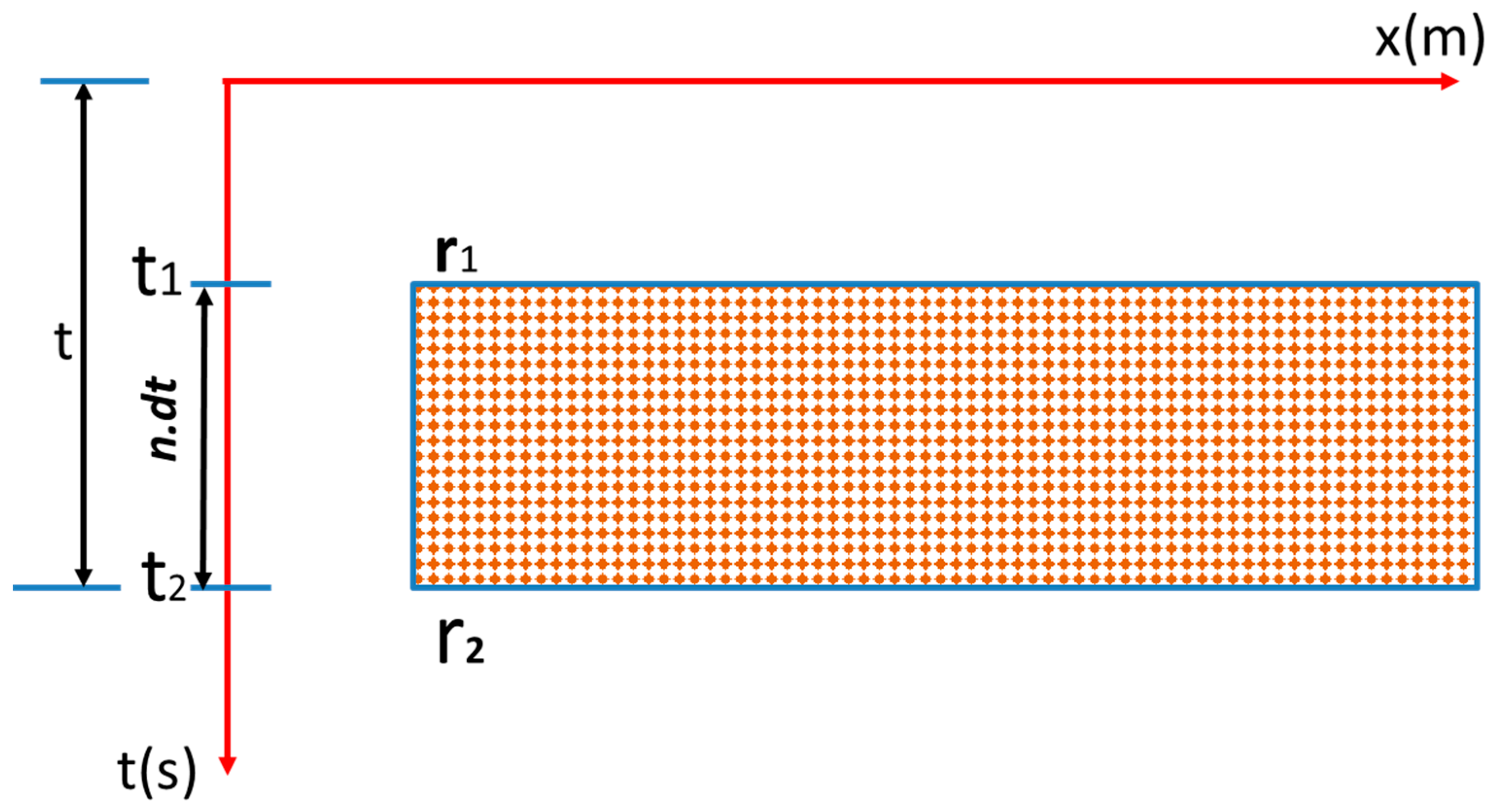
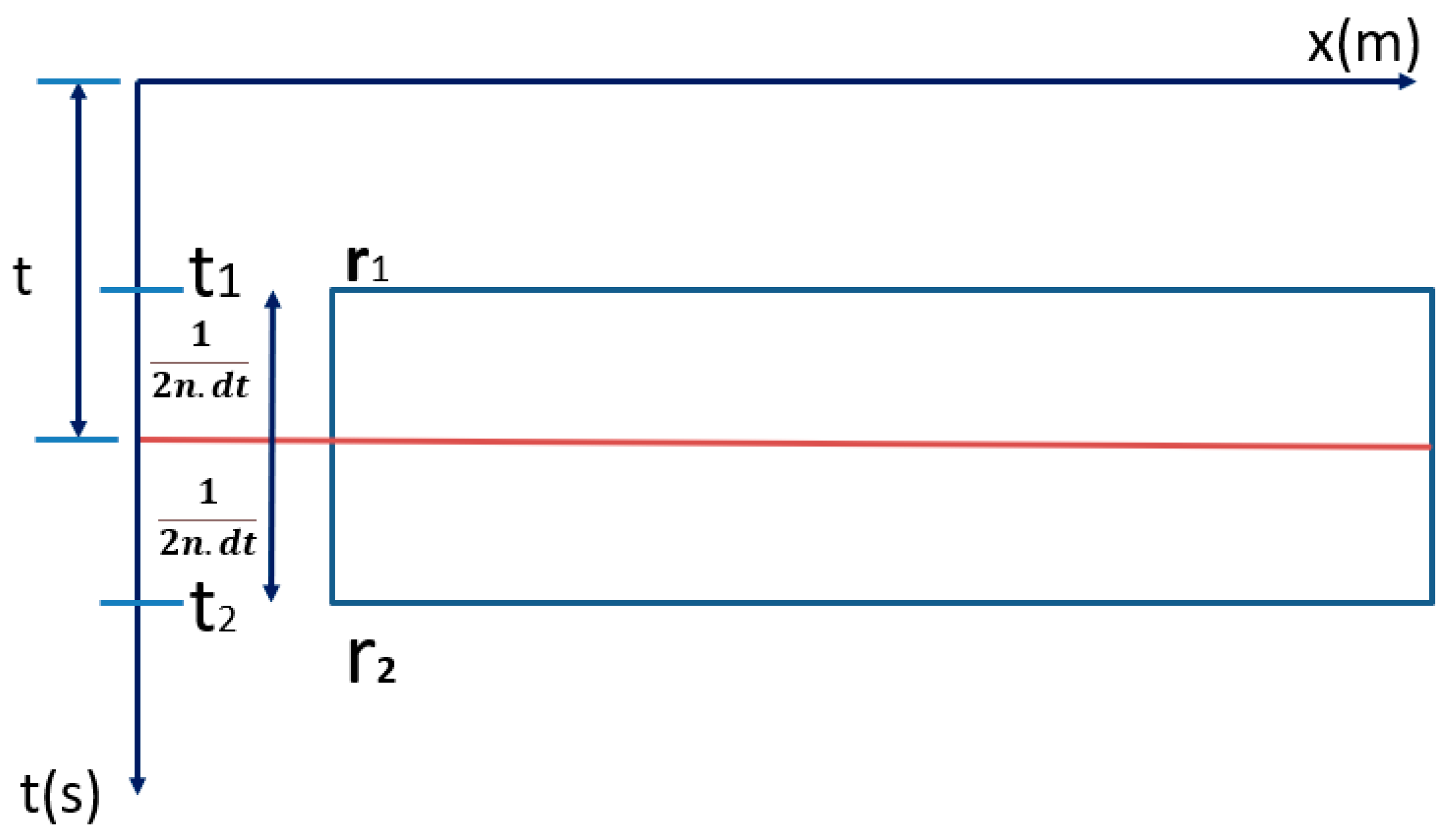
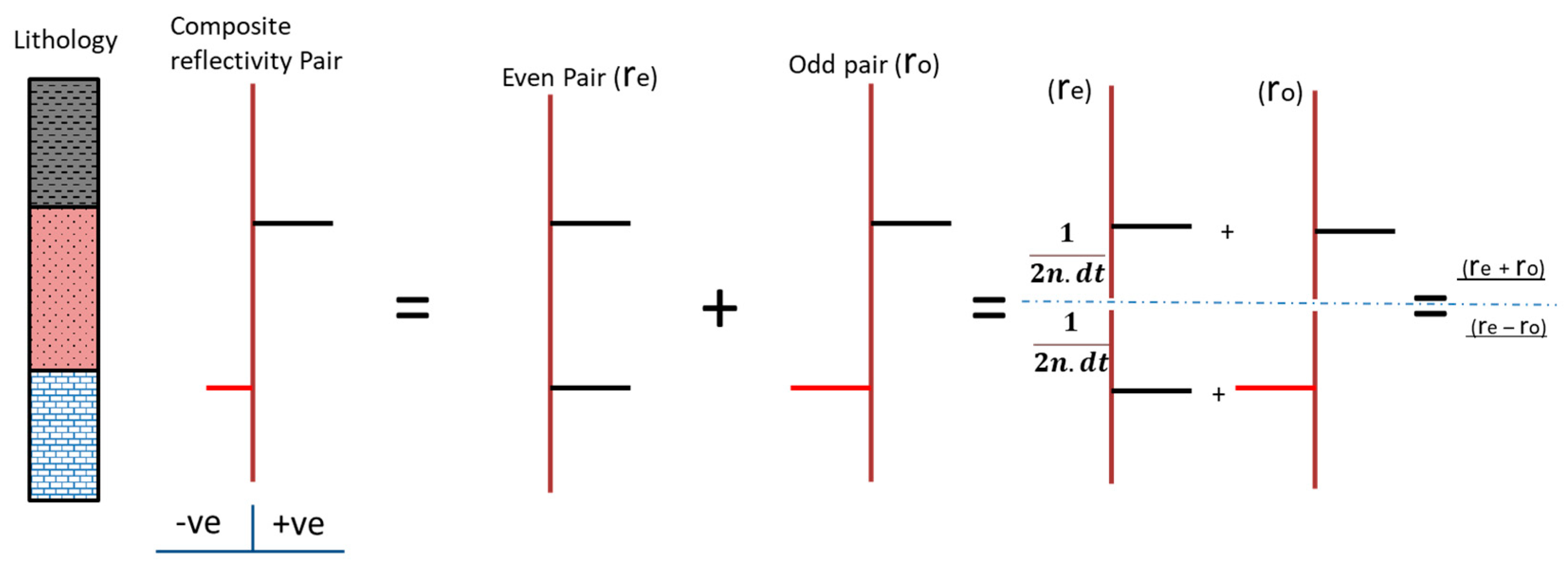
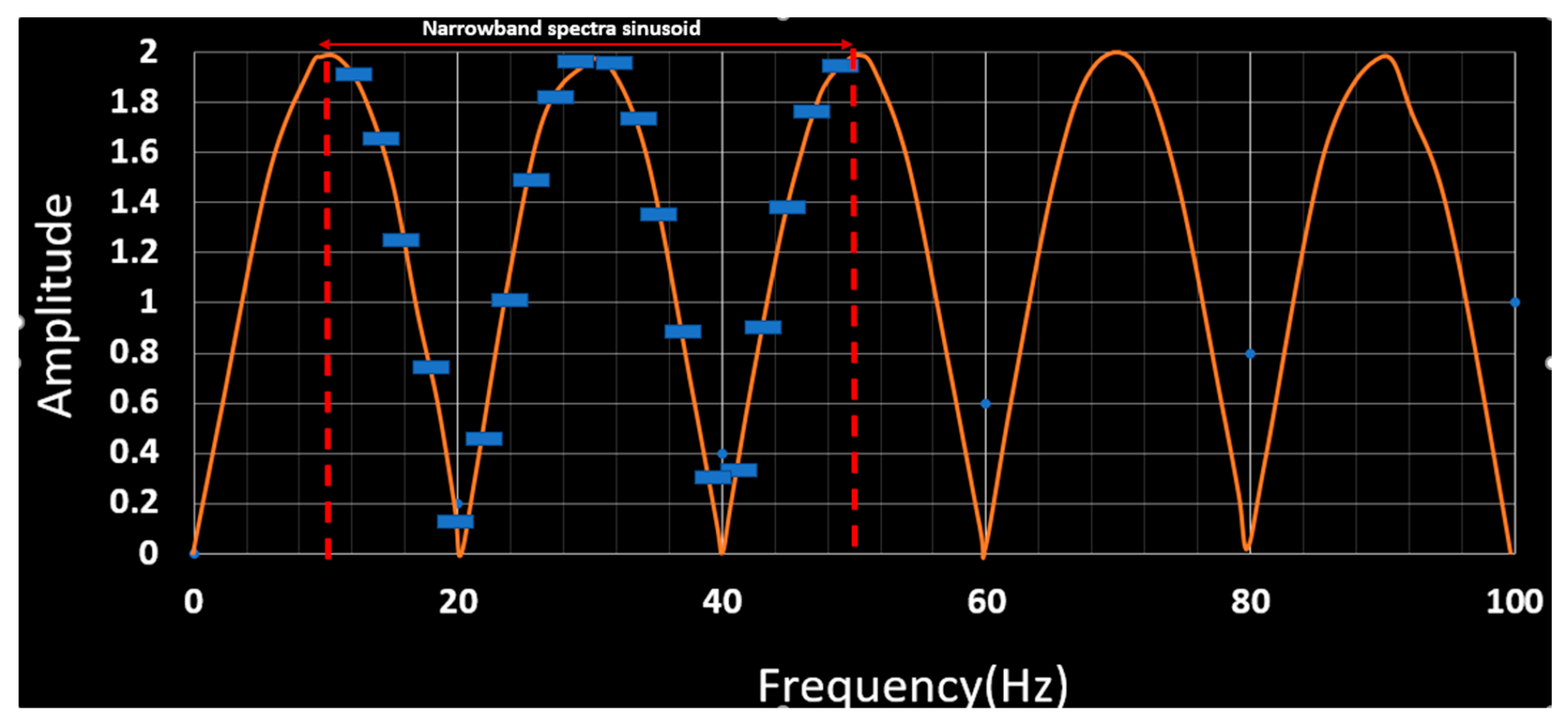
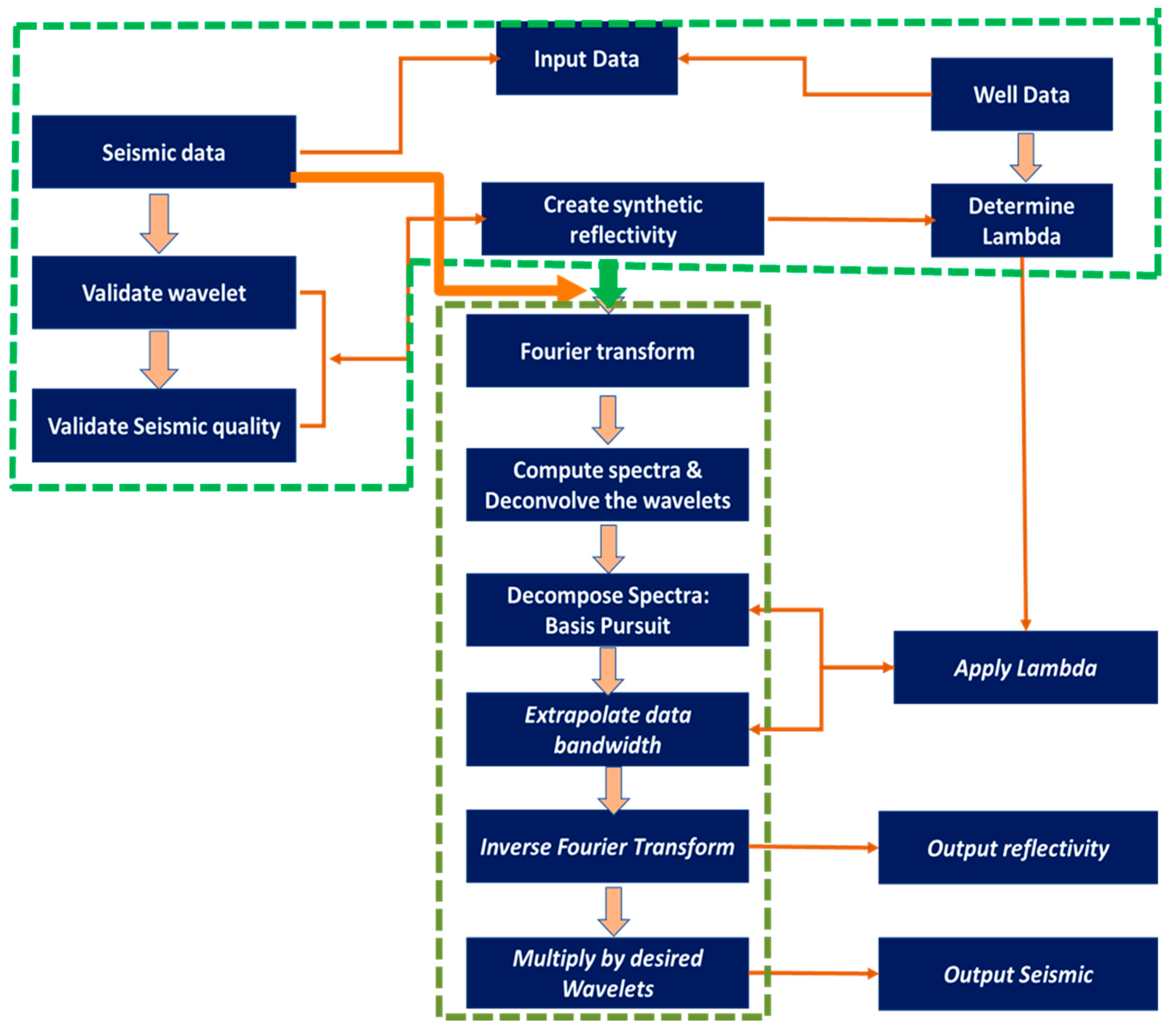
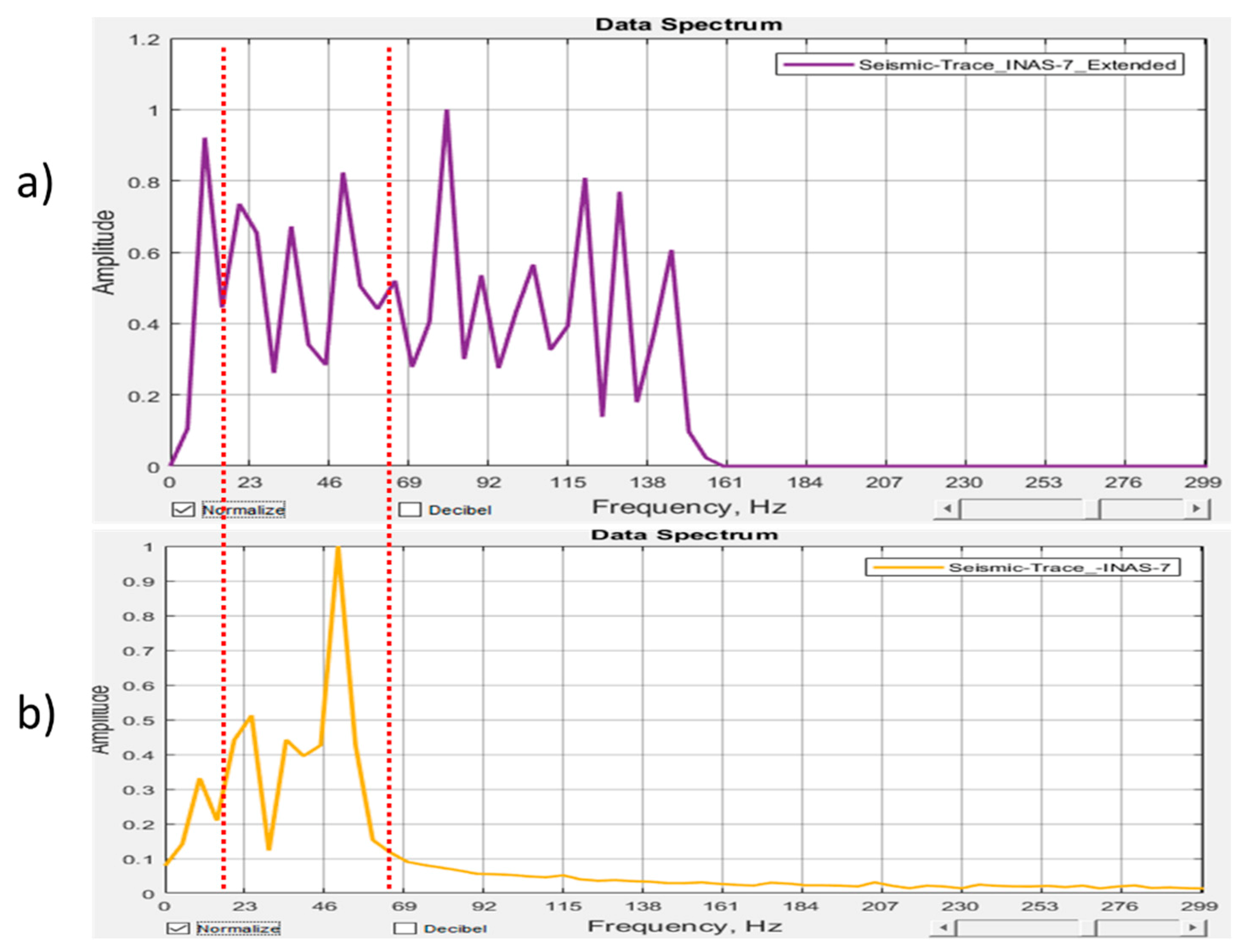
2.2. Reflectivity Spectrum Extrapolation Method
2.3. Summary of the Adopted Method
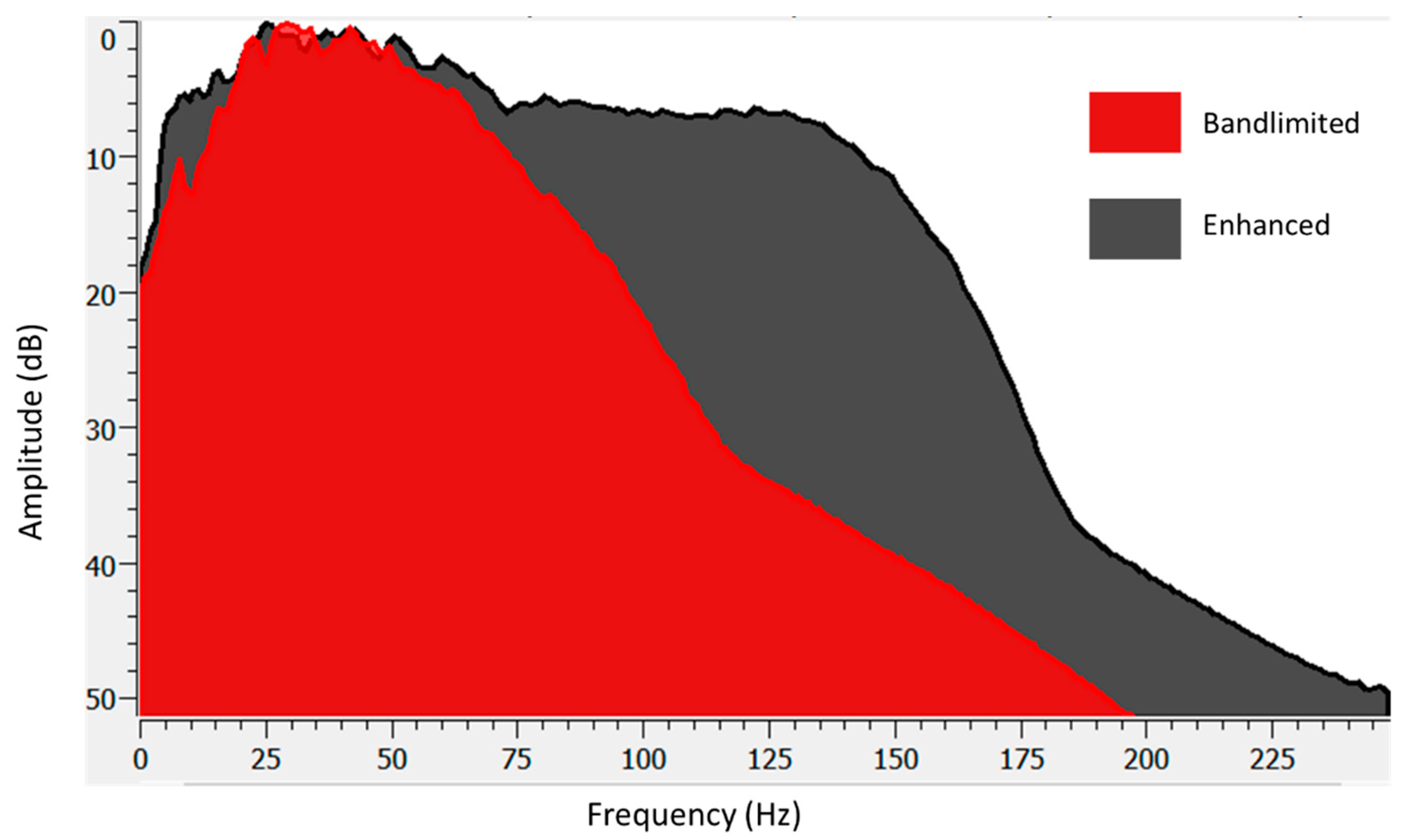
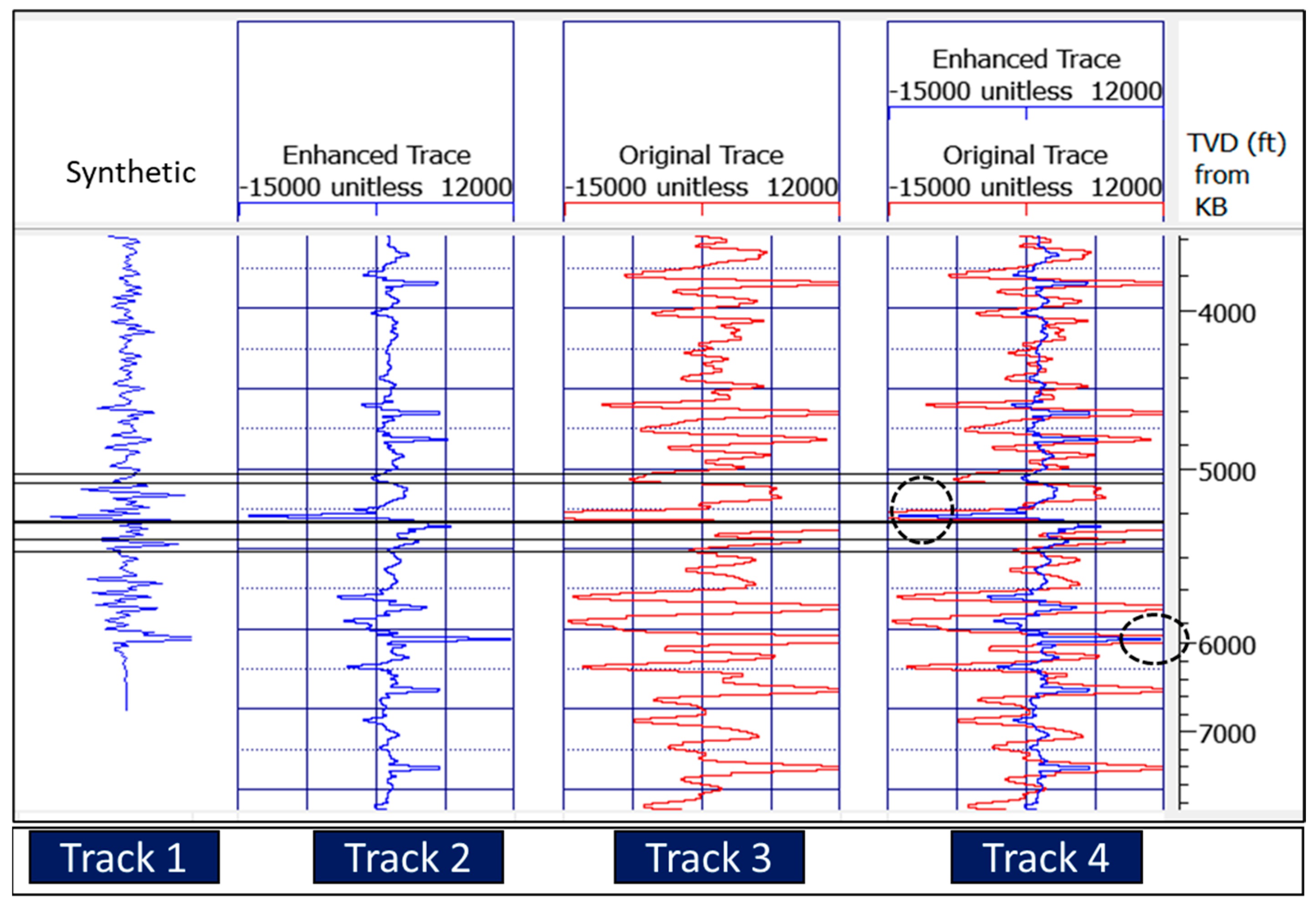
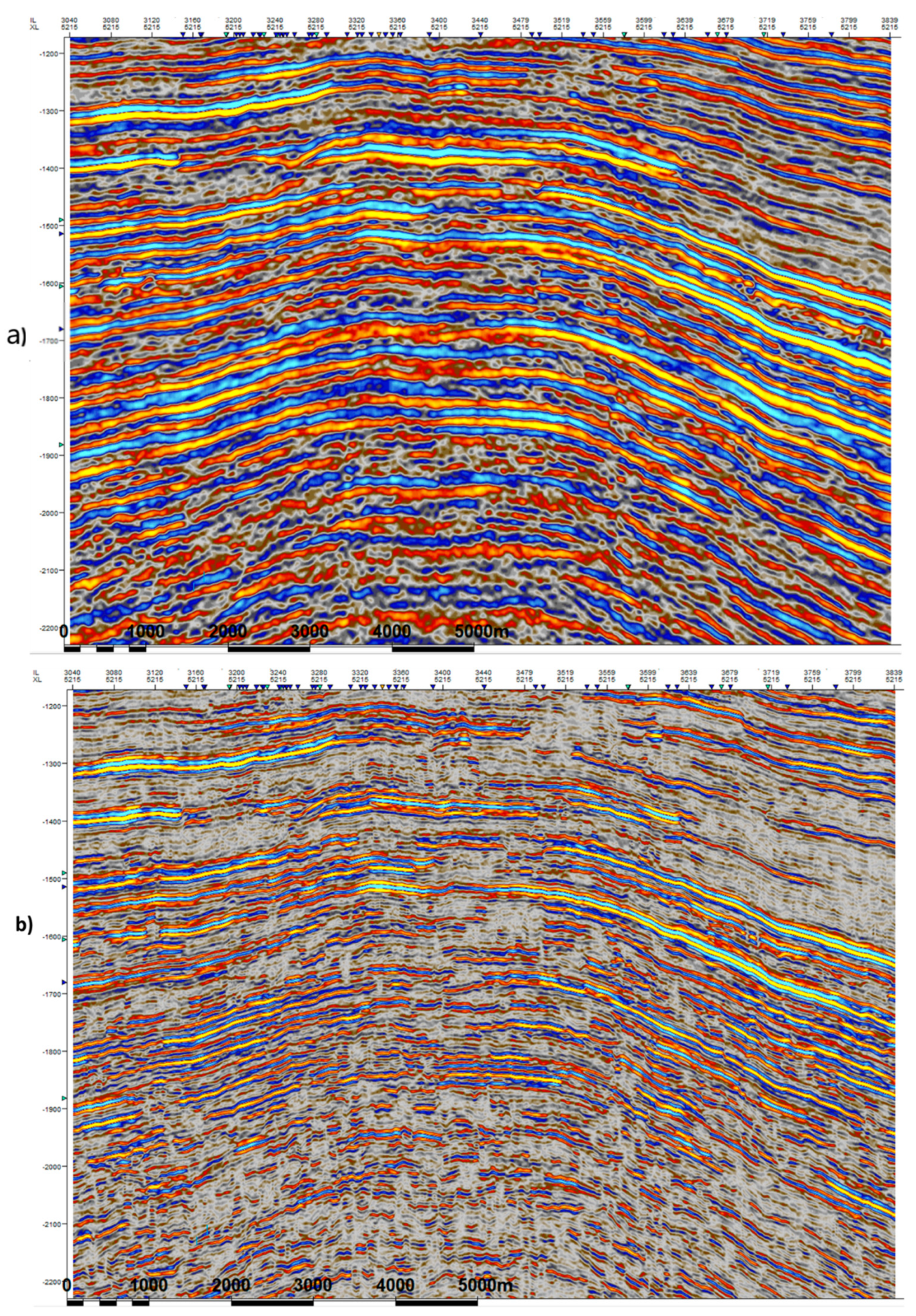
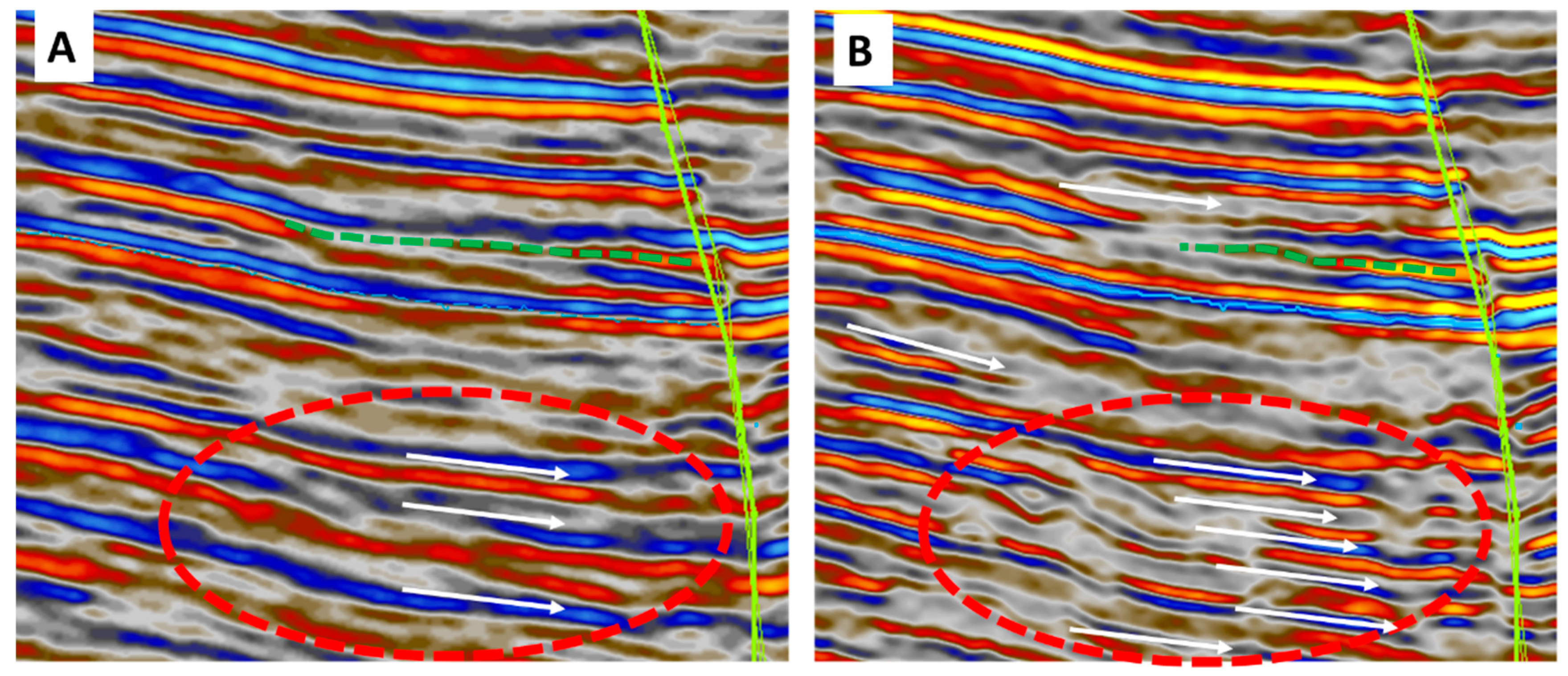
3. Results
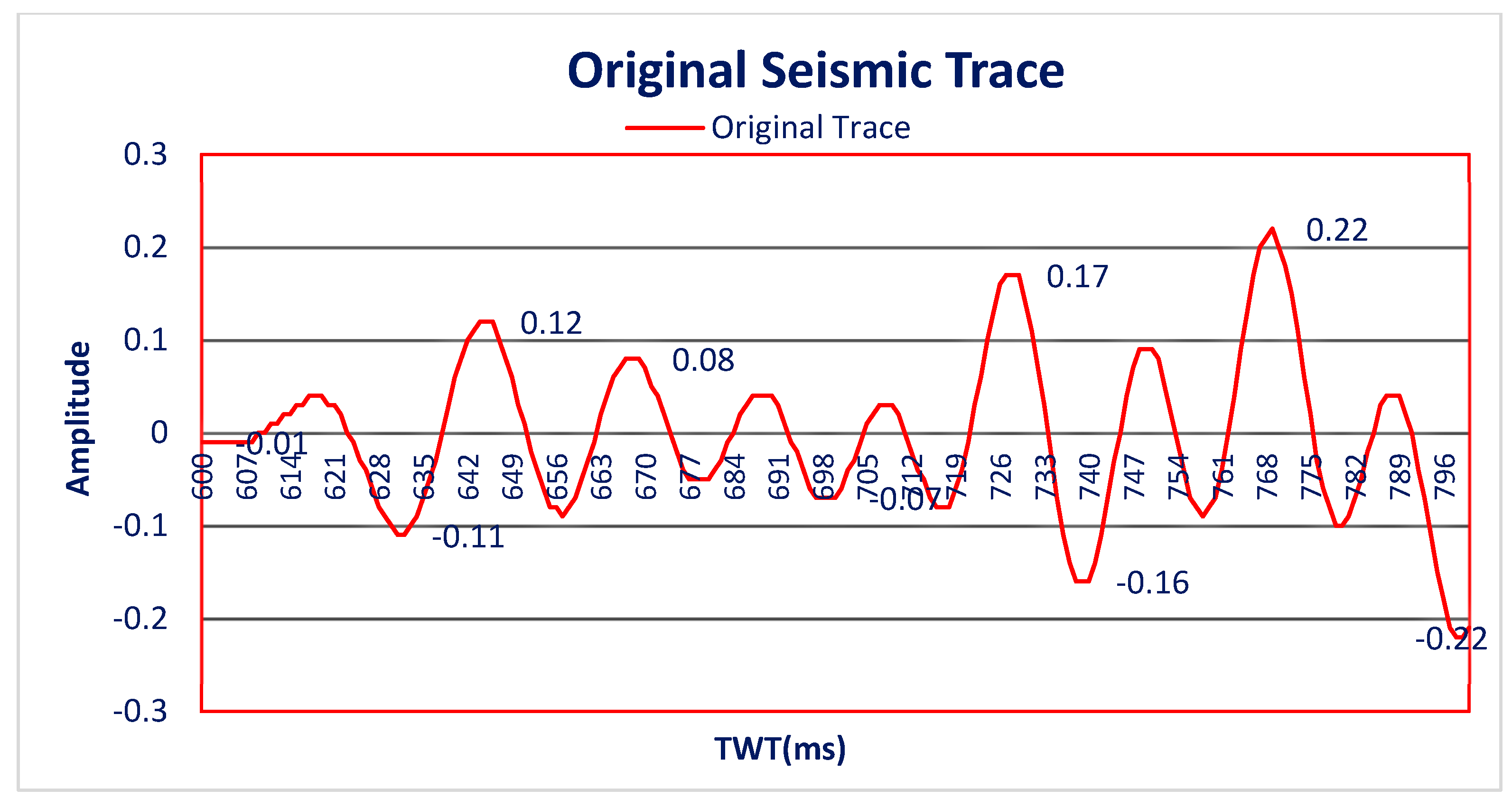
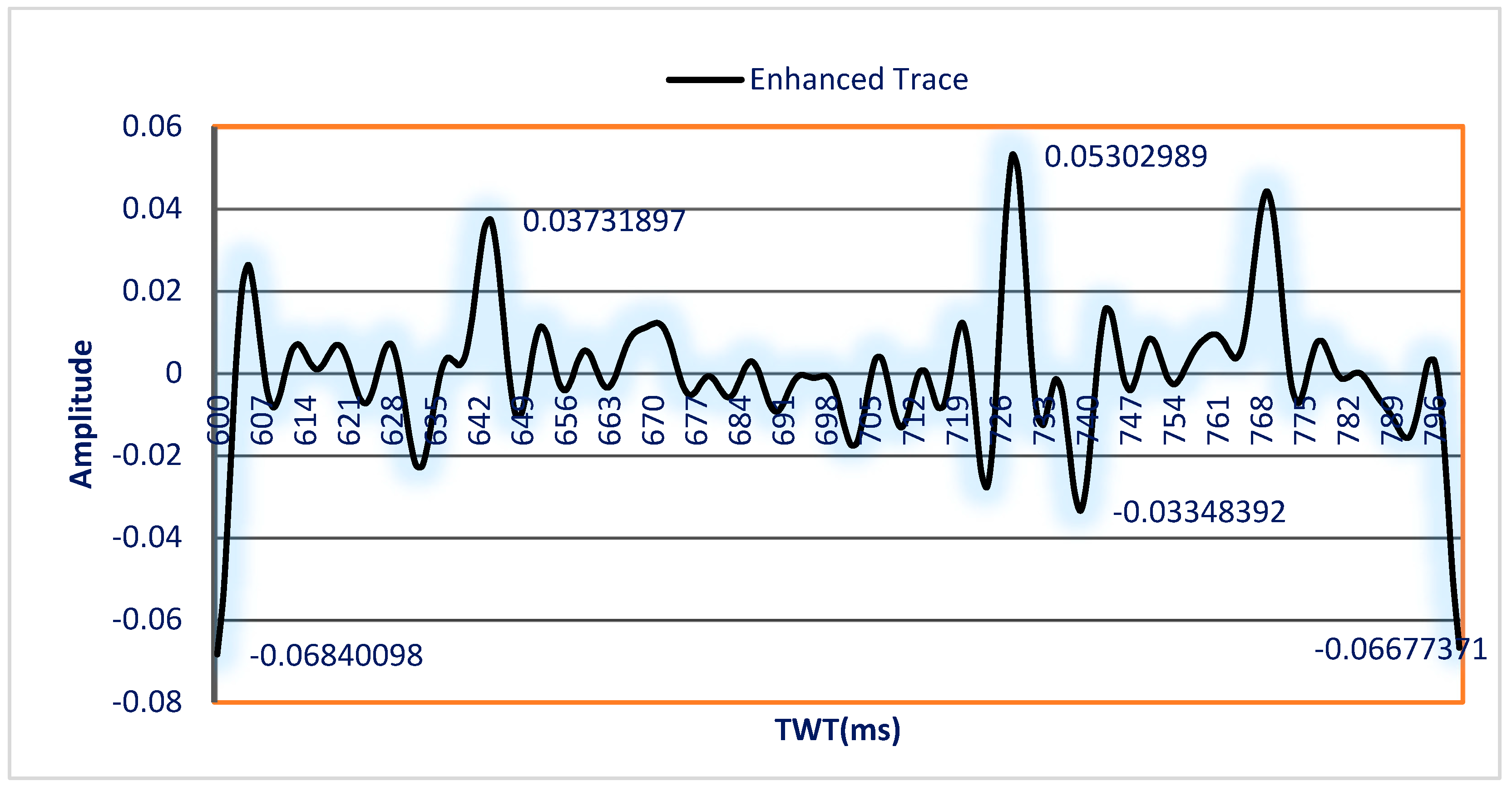
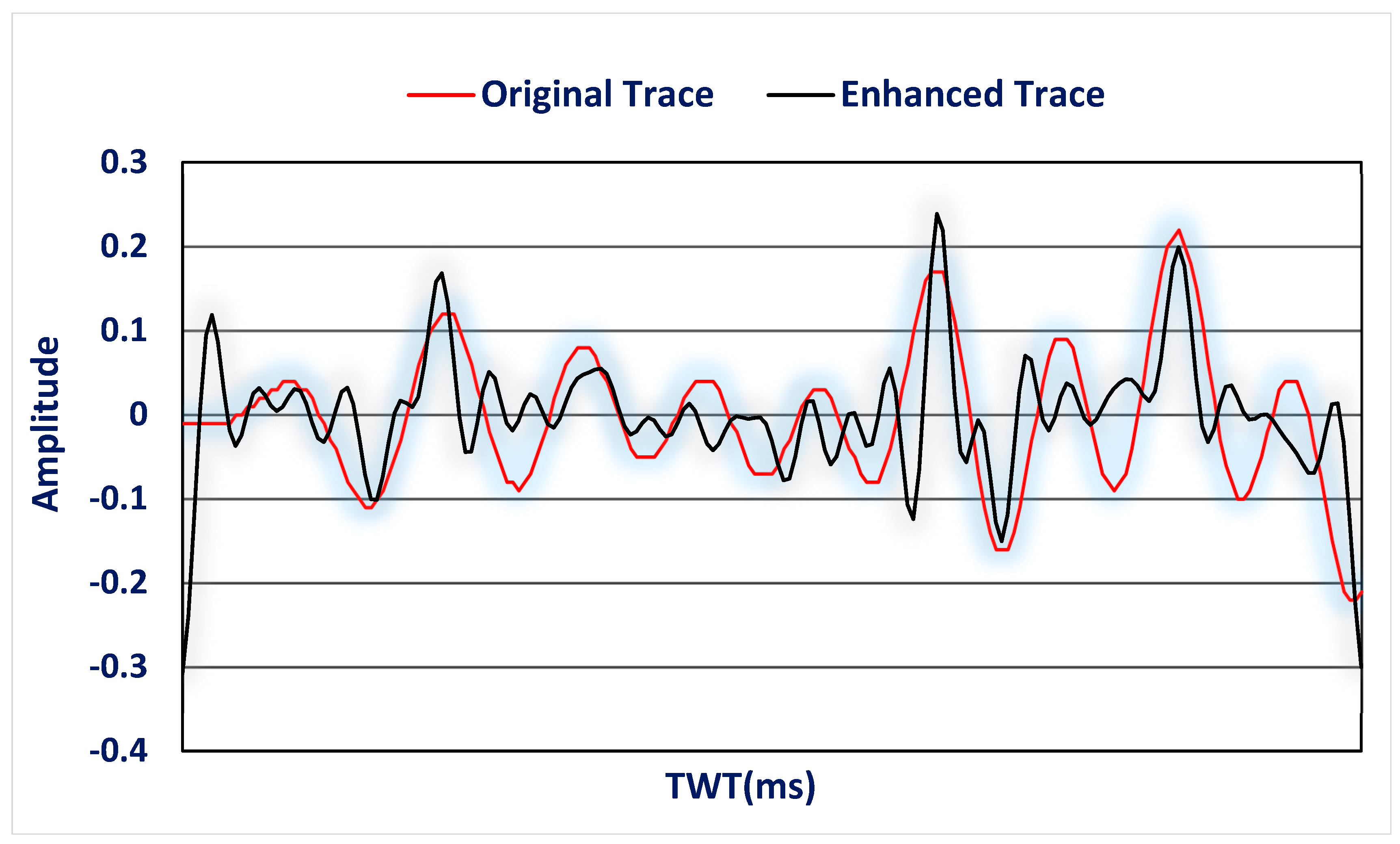
3.1. Test of the Algorithm on the Seismic Trace Model
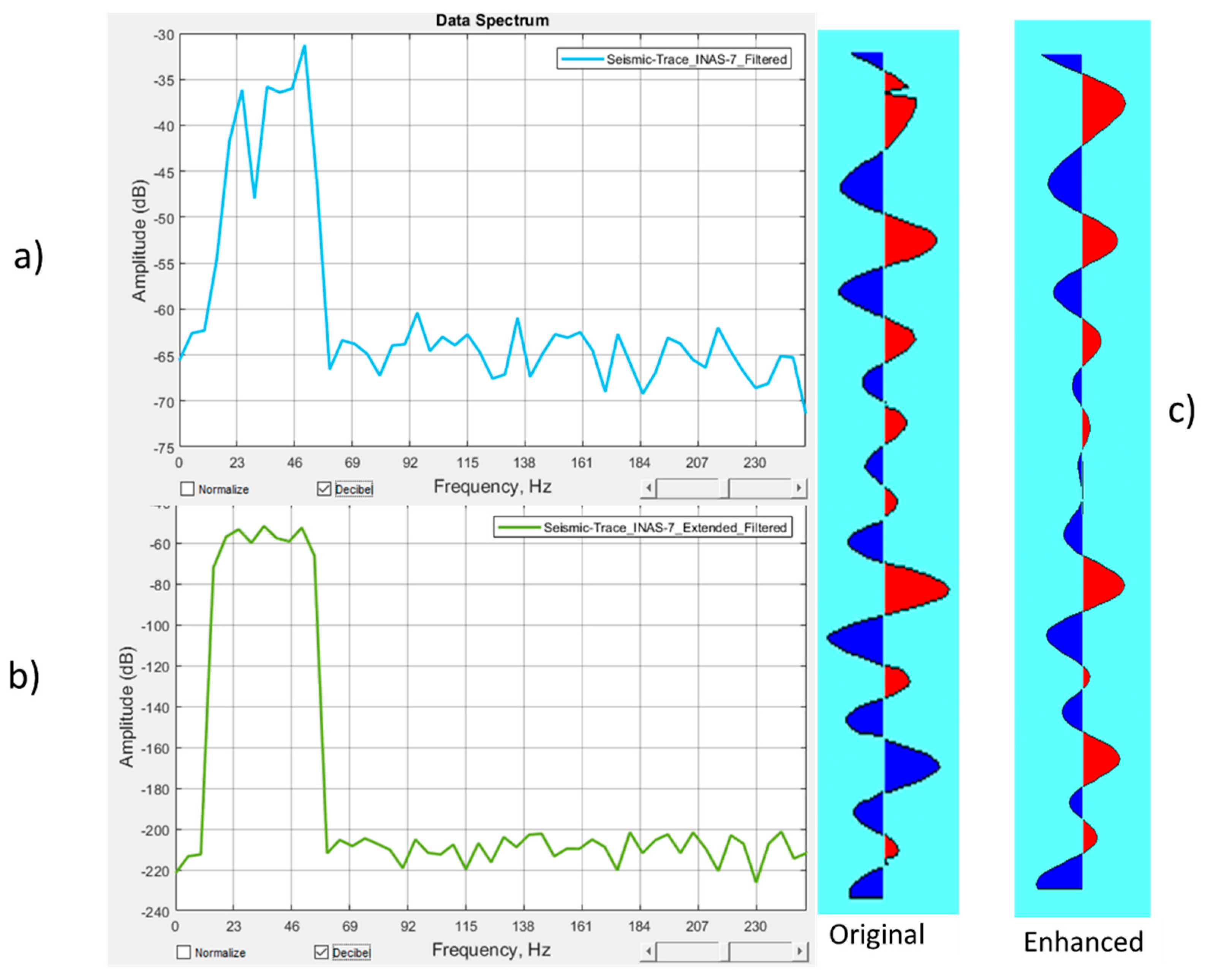
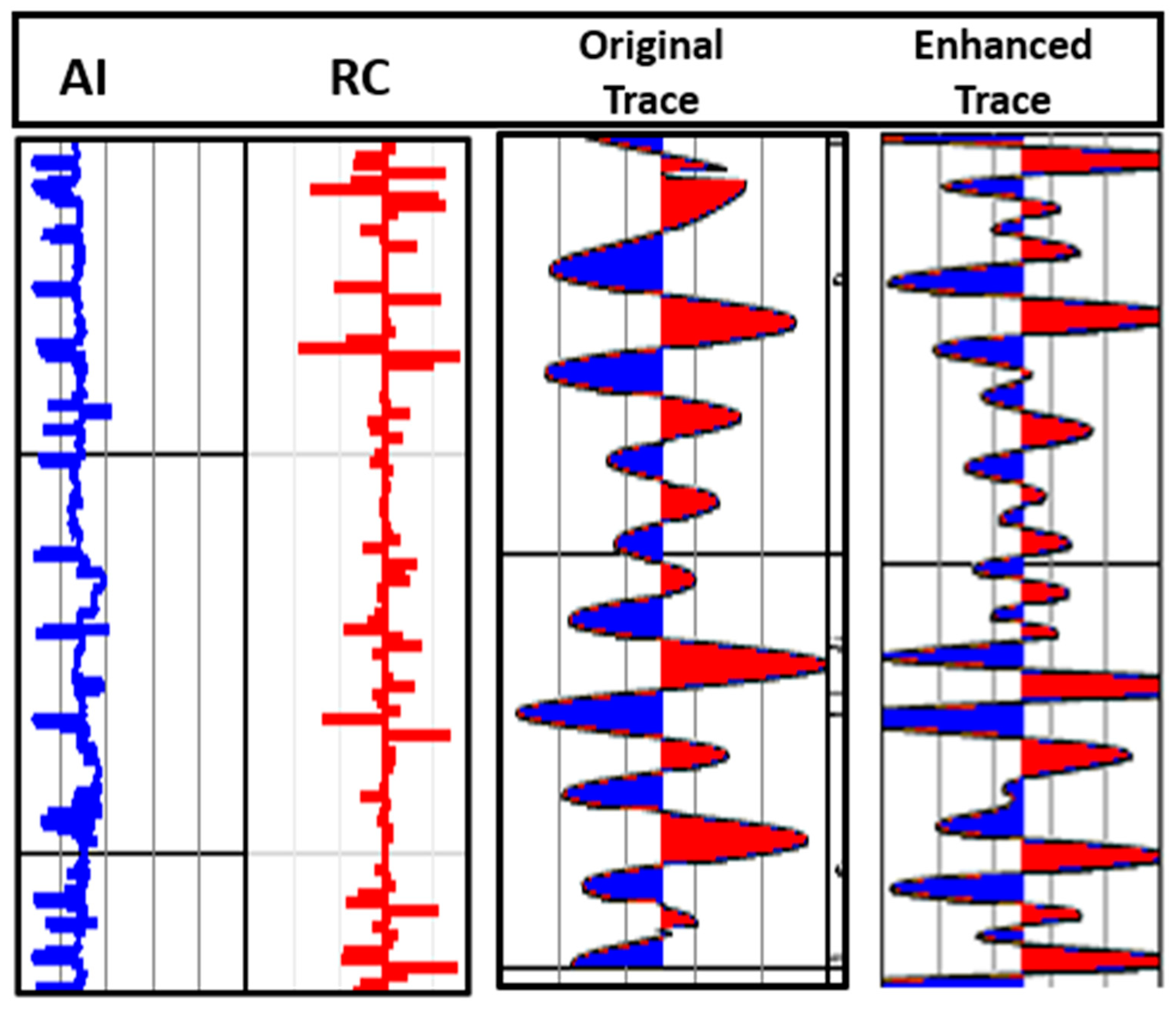
3.2. Test of the Algorithm on Real Seismic Data
3.3. Spectral Decomposition of the High and Low-Frequency Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- it is possible to recover the earth’s reflectivity spectrum from the seismic data by harmonically extending the bandwidth of the data spectrum, because wavelet deconvolution allows the retention of local transient signal characteristics beyond the capabilities of the infinite harmonic basis functions;
- to correctly resolve the thin geologic features, the amplitude magnitude is diminished according to the thinness of the feature., thereby removing the effects of destructive interference that projects incorrect amplitudes;
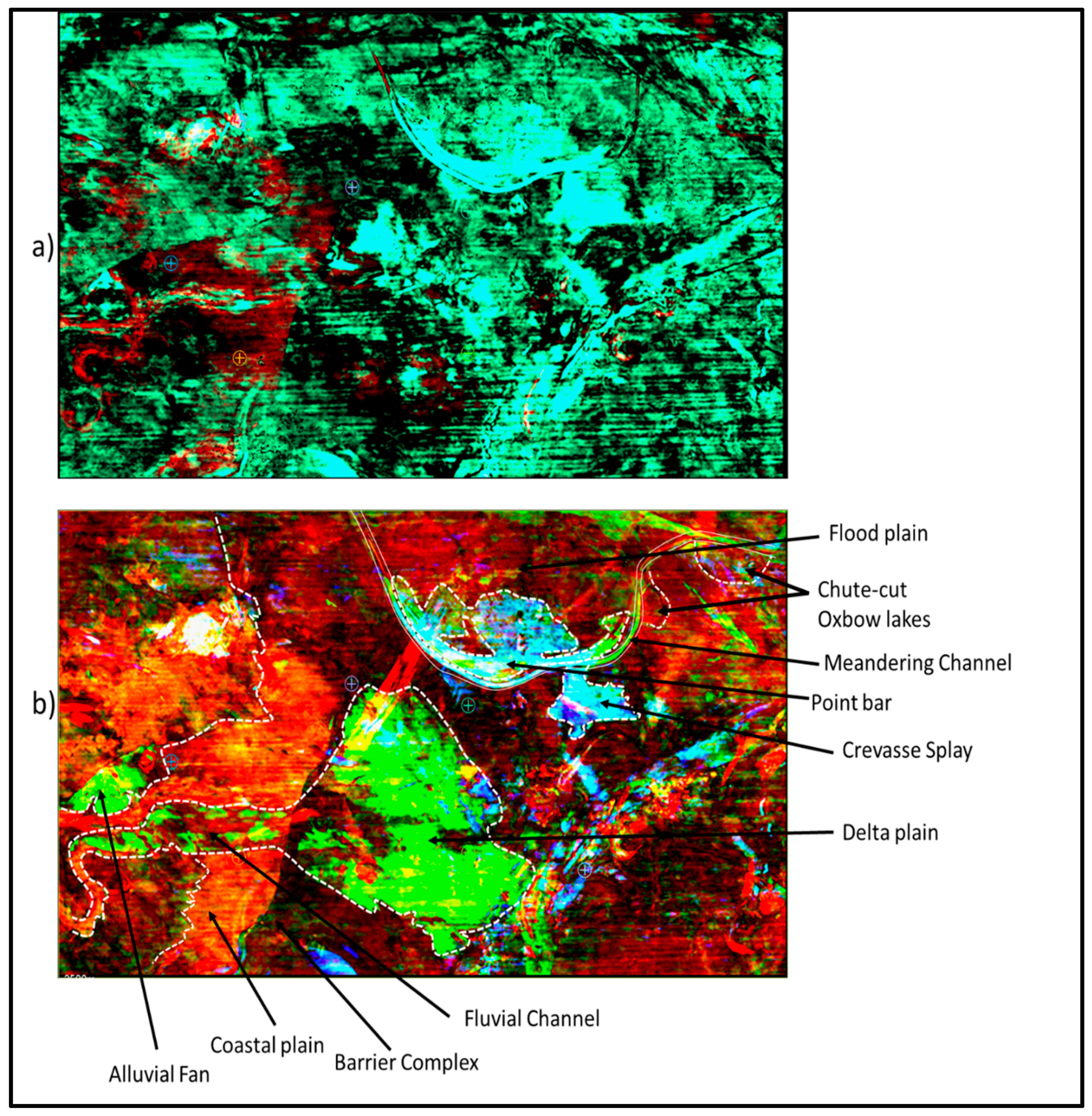
- the harmonic bandwidth extension technique significantly improved the resolutions of the input seismic data and revealed subtle geologic features such as meandering channels, crevasse splay, oxbow lakes, chute-cut, point bars, barrier bar, alluvial fan, and other lagoon elements, thereby suggesting the applicability of this method for detailed stratigraphic studies.
- (1)
- This technique can be applied to investigate the connectivity, continuity, and individuality of reservoir facies, since it enables the imaging of subtle geologic details [39].
- (2)
- The authors of [39] demonstrated that the geostatistical inversion of broadband seismic data can give an accurate prediction of facies extent in a hydrocarbon reservoir. The findings of [62] also revealed that the amount of CO2 storage and enhanced oil recovery is dependent on the pore size distribution, which is indirectly dependent on the reservoir rock facies. Hence, a broadband seismic obtained through the techniques presented in this research can be applied to predict the extent of reservoir rock facies, in an unconventional CO2 storage [63,64,65].
- (1)
- It is unclear whether reducing amplitude magnitudes influences the response of thick beds, or whether this technique affects how amplitude varies with offset (AVO) and other attributes, especially in hydrocarbon reservoirs. Therefore, the authors suggest that more research be done to see how this technique impacts seismic attributes.
- (2)
- The fact that this technique requires a lot of time, space, and processor speed to run is a disadvantage; however, future research can work on lowering the processing needs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, H. Seismic Imaging for Seismic Geomorphology beyond the Seabed: Potentials and Challenges; Special Publications; Geological Society: London, UK, 2007; Volume 277, pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Castagna, J.; Portniaguine, O. Seismic Resolution and Thin-Bed Reflectivity Inversion, Arcis Corporation, Calgary; Fusion Petroleum Technologies, Inc.: Houston, TX, USA; University of Houston: Houston, TX, USA, 2006; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Herron, A.D. First Steps in Seismic Interpretation; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Gurley, K.; Kareem, A. Applications of wavelet transforms in earthquake, wind and ocean engineering. Eng. Struct. 1999, 21, 149–167. [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff, R.E. Encyclopedic Dictionary of Applied Geophysics, 4th ed.; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, R.W. Vertical resolution of thick beds, thin beds, and thin-bed cyclothems. Geophysics 1990, 55, 1942–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simm, R.; Bacon, M. Seismic Amplitude, an Interpreter’s Handbook; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Widess, M.B. How thin is a thin bed? Geophysics 1973, 38, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A. A Simple Guide to Seismic Amplitudes and Detuning. Geo ExPro Mag. 2015, 12, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Roden, R.; Smith, T.A.; Santogrossi, P.; Sacrey, D.; Jones, G. Seismic interpretation below tuning with multiattribute analysis. Lead. Edge 2017, 36, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternoster, B.; Cauquil, E.; Saint-André, C. How good seismic resolution needs to be for detecting thin beds? In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 2 May 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Koefoed, O. Aspects of vertical seismic resolution. Geophys. Prospect. 1981, 29, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi Naeini, E.; Sams, M.S. Accuracy of Wavelets, Seismic Inversion, and Thin-Bed Resolution, Society of Exploration Geophysicists and American Association of Petroleum Geologists. Interpretation 2017, 5, T523–T530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kirchberger, L. Enhancing vertical seismic resolution by spectral inversion. Soc. Pet. Eng. 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, N.; Calvert, A. Inverse Q filtering by Fourier transform. Geophysics 1991, 56, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, G.B.; Neep, J. Increasing seismic resolution using spectral blueing and colored inversion: Cannonball field, Trinidad. In Proceedings of the 74th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, Denver, CO, USA, 10–15 October 2004; pp. 1794–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Castagna, J.P. Seismic sparse-layer reflectivity inversion using basis pursuit decomposition. Geophysics 2011, 76, R147–R158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.; Wild, A. Cosmetic enhancement of seismic data by loop re-convolution. In Proceedings of the CSEG Convention, Expanded Abstracts, Calgary, AB, Canada, 16–19 May 2005; pp. 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Castagna, J.P.; Zavala, R.T. Tutorial: Spectral bandwidth extension—Invention versus harmonic extrapolation. Geophysics 2017, 82, W1–W16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumari, K.; Biswal, A. Frequency Enhancement of Seismic Data—A comparative study. CSEG Rec. 2008, 33, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.S.; Donoho, D.L.; Saunders, M.A. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. Rev. 2001, 43, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A.E. A tutorial on complex seismic trace analysis. Geophysics 2007, 72, W33–W43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu, E.; Jarrah, F.; Aboro, O.; Aziz, A.S. The use of spectral decomposition to QC seismic data. In Proceedings of the SEG international Exposition and 87th Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 24–27 September 2017; pp. 2169–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Partyka, G.; Gridley, J.; Lopez, J. Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Partyka, G.A.; Bush, M.D.; Garossino, P.G.A.; Gutowski, P.R. Spectral decomposition. In Interpretation of Three-Dimensional Seismic Data, 7th ed.; Brown, A.R., Ed.; AAPG Memoir 42 and Society of Exploration Geophysicists Investigations in Geophysics 9; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, K.J.; Kirlin, R.L. Narrow-band spectral analysis and thin-bed tuning. Geophysics 2001, 66, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloshubin, G.M.; Korneev, V.A.; Vingalov, V.M. Seismic low-frequency effects from oil-saturated reservoir zones. In Proceedings of the 72nd Annual International Meeting of the Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 6–11 October 2002; pp. 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, J.; Sun, S.; Siegfried, R.W. Instantaneous spectral analysis: Detection of low-frequency shadows associated with hydrocarbons. Lead. Edge 2003, 22, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Routh, P.S.; Anno, P.D.; Castagna, J.P. Spectral decomposition of seismic data with continuous-wavelet transform. Geophysics 2005, 70, P19–P25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, A.; Brouwer, F.G.C.; Wever, A.; Flierman, W. Spectral decomposition of seismic reflection data to detect gas-related frequency anomalies. In Proceedings of the 70th European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers Conference and Exhibition, Rome, Italy, 9–12 June 2008; pp. 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, E.; Kendall, C.; Kellogg, J.; De Keyser, T.; Hafiz, I.; Albesher, Z.; Martinez, J.A. A depositional model for the Carbonera Formation, Llanos Foothills, Colombia, from workflow of a sequence stratigraphic framework and interpretation from well-log stacking patterns, well cuttings, and three-dimensional seismic spectral decomposition. AAPG Bull. 2022, 106, 321–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Marfurt, K.J. Choice of mother wavelets in CWT spectral decomposition. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2015; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2015; pp. 2957–2961. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, D.; Castagna, J.; Meza, R.; Chen, S.; Jiang, R. Case study: Seismic resolution and reservoir characterization of thin sands using multiattribute analysis and bandwidth extension in the Daqing field, China. Interpretation 2020, 8, T89–T102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado, S. Sand Thickness Estimation Using Spectral Decomposition. Master’s Thesis, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA, 2004; 63p. [Google Scholar]
- Castagna, J.P. Spectral decomposition and high-resolution reflectivity inversion. In Proceedings of the CSEG National Convention, Calgary, AB, Canada, 16–19 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Portniaguine, O.; Castagna, J.P. Spectral inversion: Lessons from modelling and Boonesville case study. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2005; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2005; pp. 1638–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Puryear, C.; Castagna, J.P. Layer-thickness determination and stratigraphic interpretation using spectral inversion: Theory and application. Geophysics 2008, 73, R37–R48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madon, M.B.H. Depositional setting and origin of berthierine oolitic ironstones in the lower Miocene Terengganu shale, Tenggol Arch, offshore peninsular Malaysia. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1992, 65, 899–916. [Google Scholar]
- Nwafor, B.O.; Hermana, M.; Elsaadany, M. Geostatistical inversion of spectrally broadened seismic data for re-evaluation of oil reservoir continuity in Inas field, offshore Malay Basin. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madon, M.; Abolins, P.; Hassan, R.A.; Yakzan, A.M.; Yang, J.S.; Zainal, S.B. Petroleum systems of the Northern Malay Basin. Pet. Geol. Conf. Exhib. Bull. 2004, 49, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.A. Seismic time-invariant convolutional model. Geophysics 1985, 50, 2297–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, K.; Frisch, W.; Meschede, M.; Blakey, R.C. Plate tectonics—Continental drift and mountain building. Bull. Volcanol. 2012, 74, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, C.N. Seismic Data Interpretation and Evaluation for Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production; AOGEP Book Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 25–45. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, S.P.; Singh, N.P.; Singh, K.H. Seismic Inversion Methods: A Practical Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.Q.; Ming, J.; Wei, T.G.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, J.K. Application of the Matching Pursuit Based on Dipole Decomposition to Thin Reservoir of Bohai Bay Basin. In Proceedings of the 80th EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2018, Copenhagen, Denmark, 11–14 June 2018; Volume 2018, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, V. Application of Spectral Inversion to Enhance Seismic Resolution in Nam Con Son Basin, Offshore Vietnam. Master’s Thesis, University of Houston, Houston, TX, USA, 2014. Available online: https://uh-ir.tdl.org/bitstream/handle/10657/1674/HA-THESIS2014.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Chakraborty, A.; Okaya, D. Frequency-time decomposition of seismic data using wavelet-based methods. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, J.; Sun, S. Comparison of spectral decomposition methods. First Break 2006, 24, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puryear, C.I.; Portniaguine, O.N.; Cobos, C.M.; Castagna, J.P. Constrained least-squares spectral analysis: Application to seismic data. Geophysics 2012, 77, V143–V167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeye, H.W.J.; van Riel, P. Lp-Norm Deconvolution. Geophys. Prospect. 1990, 38, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Jenamani, M.; Routray, A.; KumarSingh, S.; Tondon, R.; Bahuguna, C. PySLI: A software for Sparse Layer Inversion using Python. In Proceedings of the 13th Biennial International Concerence and Exhibition, Kochi, Japan, 23–25 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Margrave, G.F.; Lamoureux, M.P.; Henley, D.C. Gabor deconvolution: Estimating reflectivity by nonstationary deconvolution of seismic data. Geophysics 2011, 76, W15–W30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, L.L. Random Noise Reduction. SEG Ext. Abstr. 1984, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.K.; Deb, G.K. Proterozoic rifting in the Pranhita–Godavari Valley: Implication on India–Antarctica linkage. Gondwana Res. 2004, 7, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abma, R.; Claerbout, J. Lateral prediction for noise attenuation by t-x and F-X techniques. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O. Seismic Data Analysis: Processing, Inversion, and Interpretation of Seismic Data; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-1-56080-099-6. [Google Scholar]
- Karsli, H. Further improvement of temporal resolution of seismic data by autoregressive (AR) spectral extrapolation. J. Appl. Geophys. 2006, 59, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekapalli, R.; Tiwari, R.K.; Dhanam, K.; Seshunarayana, T. T-x frequency filtering of high resolution seismic reflection data using singular spectral analysis. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 105, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, N.A.; Philip, R. Application of spectral decomposition and seismic attributes to understand the structure and distribution of sand reservoirs within Tertiary rift basins of the Gulf of Thailand: Interpreter’s Corner. Lead. Edge 2012, 31, 630–634. [Google Scholar]
- Butorin, A.V.; Krasnov, F.V.; GazpromneftScience & Technology Centre LLC. Spectral inversion methods and its application for wave field analysis. In Proceedings of the SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference, Moscow, Russia, 16–18 October 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taner, M.T.; Koehler, F.; Sheriff, R.E. Complex seismic trace analysis. Geophysics 1979, 44, 1041–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.; Trusler, M.; Maitland, G.; Piane, C.D.; Pini, R. The gas-in-place and CO2 storage capacity of shale reservoirs at subsurface conditions. In Proceedings of the 15th Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies Conference, Online, 15–18 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ridwan, T.K.; Hermana, M.; Lubis, L.A.; Riyadi, Z.A. New avo attributes and their applications for facies and hydrocarbon prediction: A case study from the northern malay basin. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngui, J.Q.; Hermana, M.; Ghosh, D.; Yusof, W.I.W. Integrated study of lithofacies identification—A case study in X field, Sabah, Malaysia. Geosciences 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermana, M.; Sani, M.N.M.; Harith, Z.Z.T.; Sum, C.W. Lithology Discrimination in Elastic Impedance Domain Using Artificial Neural Network. J. Eng. Technol. 2012, 2, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nwafor, B.O.; Hermana, M. Harmonic Extrapolation of Seismic Reflectivity Spectrum for Resolution Enhancement: An Insight from Inas Field, Offshore Malay Basin. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115453
Nwafor BO, Hermana M. Harmonic Extrapolation of Seismic Reflectivity Spectrum for Resolution Enhancement: An Insight from Inas Field, Offshore Malay Basin. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(11):5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115453
Chicago/Turabian StyleNwafor, Basil Onyekayahweh, and Maman Hermana. 2022. "Harmonic Extrapolation of Seismic Reflectivity Spectrum for Resolution Enhancement: An Insight from Inas Field, Offshore Malay Basin" Applied Sciences 12, no. 11: 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115453
APA StyleNwafor, B. O., & Hermana, M. (2022). Harmonic Extrapolation of Seismic Reflectivity Spectrum for Resolution Enhancement: An Insight from Inas Field, Offshore Malay Basin. Applied Sciences, 12(11), 5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115453





