MSC-Net: Multitask Learning Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation and Centerline Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
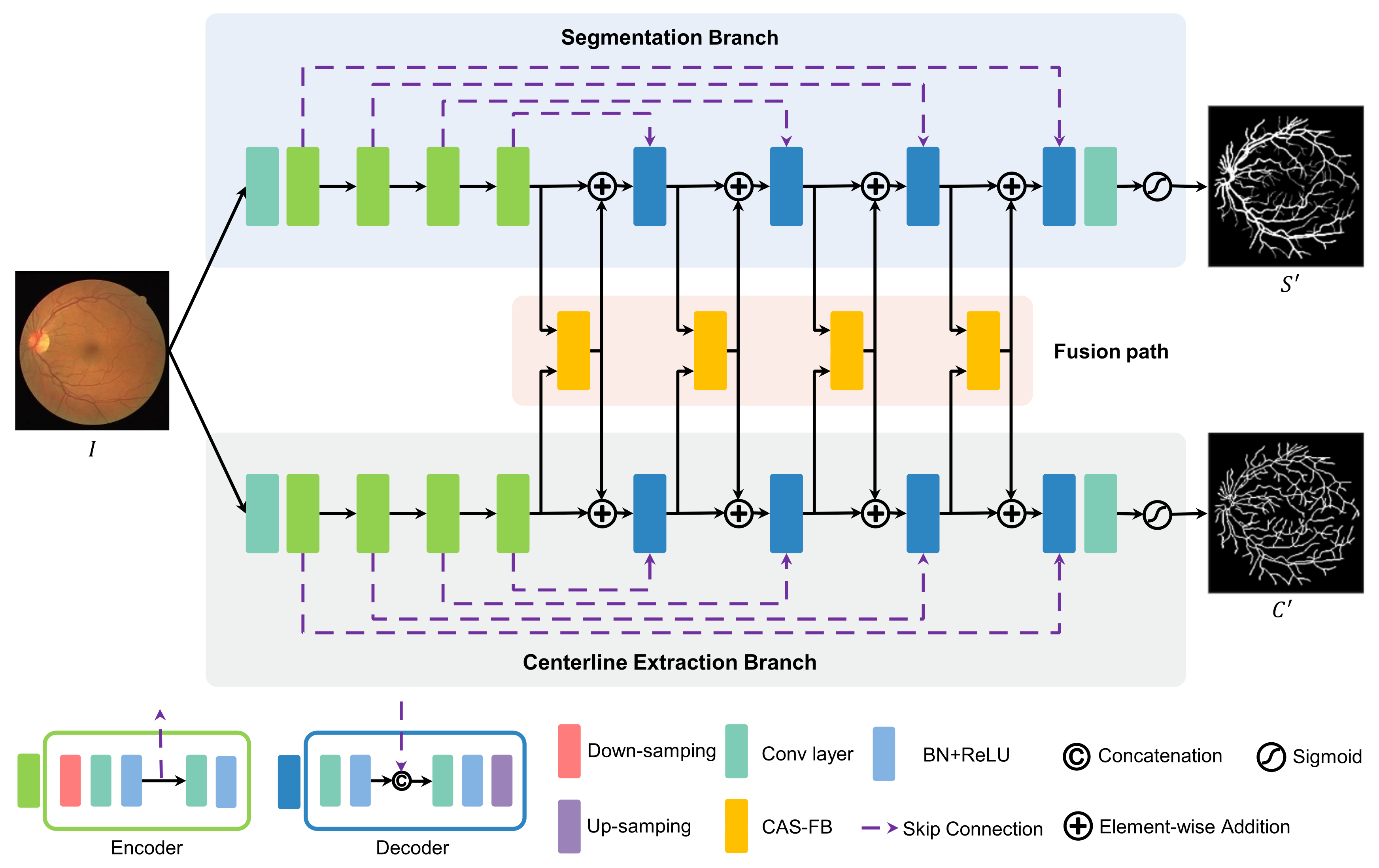
- We propose a multitask learning network for retinal vessel segmentation and centerline extraction, named MSC-Net. The multitask learning with the dual-branch design can complete two tasks at the same time, and the fusion path can effectively aggregate features.
- We design a channel and atrous spatial fusion block (CAS-FB) to solve the feature calibration and fusion of different tasks in different sizes in the fusion path. The channel attention module can effectively calibrate the features of different tasks, and the spatial attention module can aggregate the features of different scales of blood vessels.
- Unlike the original clDice loss, which is only applied to the optimization of segmentation tasks, we apply clDice to segmentation and centerline extraction at the same time. Therefore, the vessel segmentation and centerline result can be mutually constrained to ensure the consistency of the topology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Multitask Learning Network
2.3. Channel and Atrous Spatial Fusion Block
2.4. Loss Function
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Implementation Details
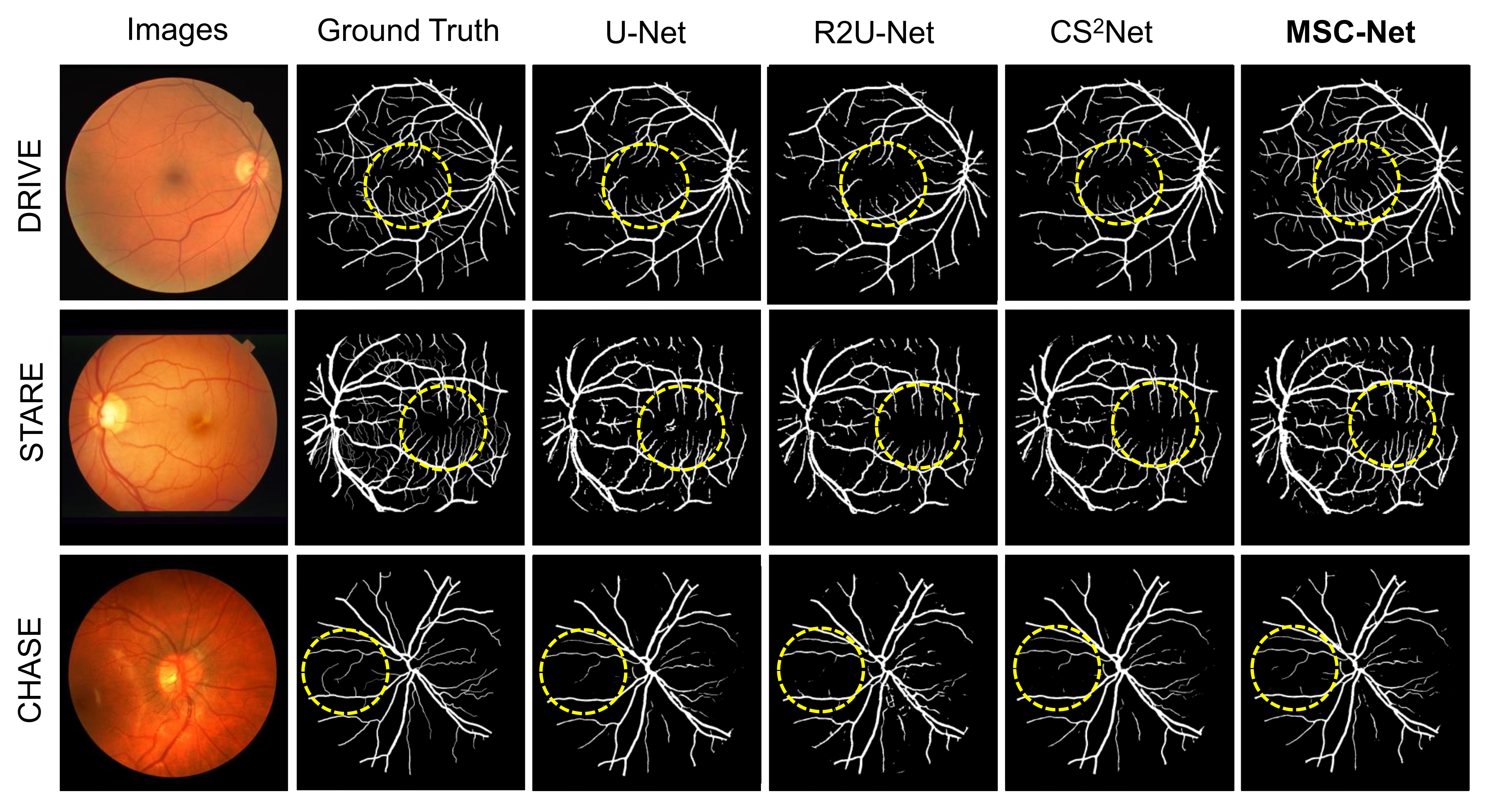
3.3. Results
4. Discussion
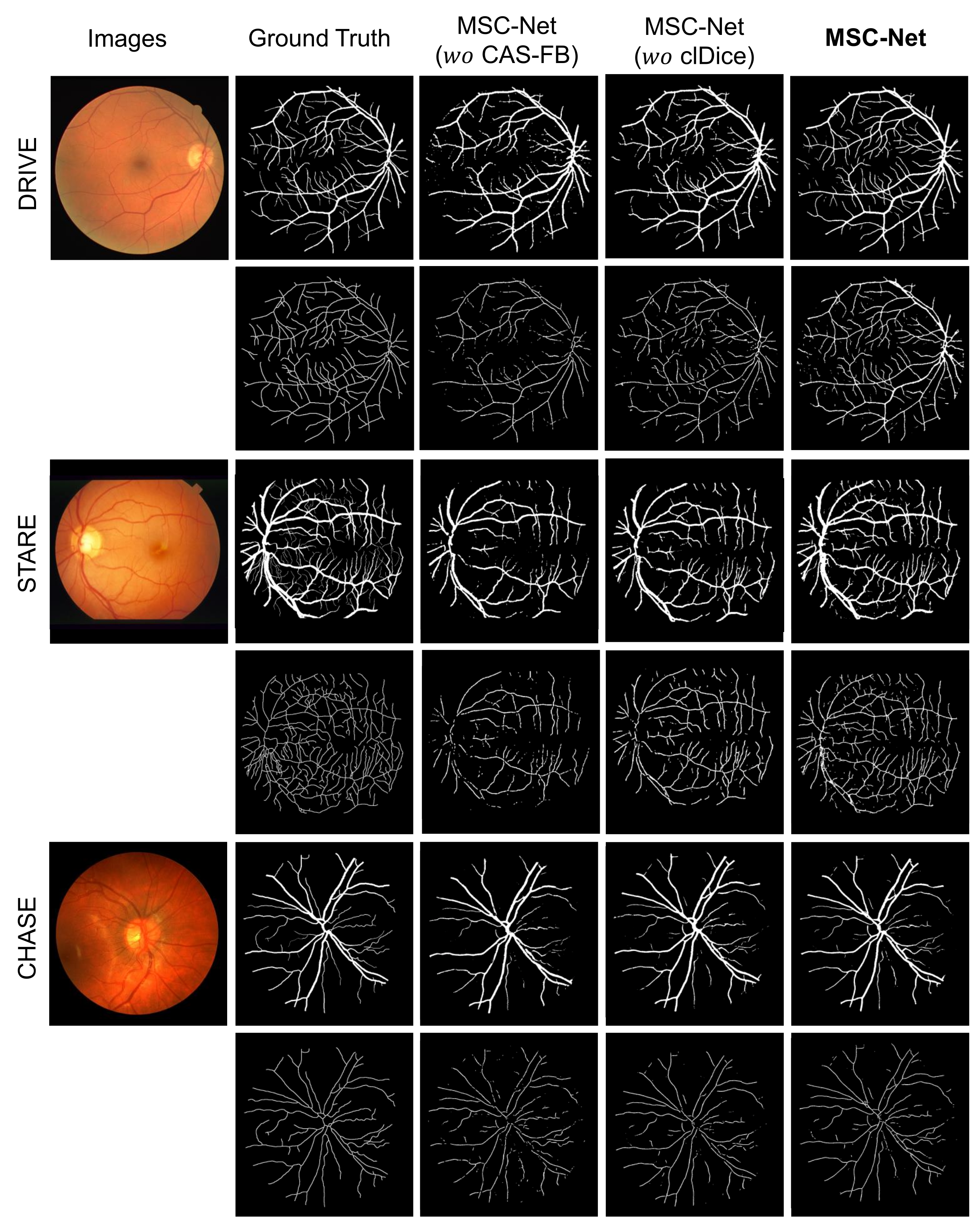
- S-Branch/C-Branch: The segmentation (S)/centerline (C) branch in MSC-Net is trained separately. This method is equivalent to performing only one task to achieve blood vessel segmentation or centerline extraction.
- MSC-Net ( CAS-FB): The CAS-FB module in MSC-Net is replaced with a fusion block. The fusion block only concatenates the features of the two branches and uses a convolutional layer, BN, and ReLU layer for feature fusion.
- MSC-Net ( clDice): When training MSC-Net, the clDice loss function is not added to the loss function (equivalent to the = 0 in Equation (14)).
- MSC-Net: The result of training on our proposed MSC-Net.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Annunziata, R.; Kheirkhah, A.; Aggarwal, S.; Hamrah, P.; Trucco, E. A fully automated tortuosity quantification system with application to corneal nerve fibres in confocal microscopy images. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 32, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franklin, S.W.; Rajan, S.E. Computerized screening of diabetic retinopathy employing blood vessel segmentation in retinal images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 34, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.K.; Ong, Y.T.; Cheung, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Retinal vascular caliber measurements: Clinical significance, current knowledge and future perspectives. Ophthalmologica 2013, 229, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; McCarty, C.A.; Taylor, H.R.; Keeffe, J.E. Costs of mobile screening for diabetic retinopathy: A practical framework for rural populations. Aust. J. Rural Health 2001, 9, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromm, C.; Rohr, K. Inception capsule network for retinal blood vessel segmentation and centerline extraction. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 1223–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Azzopardi, G.; Strisciuglio, N.; Vento, M.; Petkov, N. Trainable COSFIRE filters for vessel delineation with application to retinal images. Med. Image Anal. 2015, 19, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, S.; Na, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Automatic 2-D/3-D vessel enhancement in multiple modality images using a weighted symmetry filter. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 37, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niemeijer, M.; Staal, J.; van Ginneken, B.; Loog, M.; Abramoff, M.D. Comparative study of retinal vessel segmentation methods on a new publicly available database. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2004: Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–19 February 2004; Volume 5370, pp. 648–656. [Google Scholar]
- Saha Tchinda, B.; Tchiotsop, D.; Tchinda, R.; Kenne, G. Automated extraction of the intestinal parasite in the microscopic images using active contours and the Hough transform. Curr. Med. Imaging 2015, 11, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Rada, L.; Chen, K.; Harding, S.P.; Zheng, Y. Automated vessel segmentation using infinite perimeter active contour model with hybrid region information with application to retinal images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, P.; Luo, H.; Sheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Suzuki, K. A new approach to segment both main and peripheral retinal vessels based on gray-voting and gaussian mixture model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127748. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, N.; Roy, A.B.; Pal, M.; Das, A. FCM based blood vessel segmentation method for retinal images. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1209.1181. [Google Scholar]
- Saffarzadeh, V.M.; Osareh, A.; Shadgar, B. Vessel segmentation in retinal images using multi-scale line operator and K-means clustering. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2014, 4, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, J.I.; Prokofyeva, E.; Blaschko, M.B. A discriminatively trained fully connected conditional random field model for blood vessel segmentation in fundus images. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 64, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraz, M.M.; Remagnino, P.; Hoppe, A.; Uyyanonvara, B.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Owen, C.G.; Barman, S.A. An ensemble classification-based approach applied to retinal blood vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Sharif, M.; Akram, M.U.; Saba, T.; Mahmood, T.; Kolivand, M. Automated techniques for blood vessels segmentation through fundus retinal images: A review. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2019, 82, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Hasan, M.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Yi, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Fan, C. Sa-unet: Spatial attention u-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 1236–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Su, P.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Frangi, A.F.; et al. CS2-Net: Deep learning segmentation of curvilinear structures in medical imaging. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, D.; Bui, D.T.; Thung, K.H.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Lin, W.; Li, G.; Shen, D.; et al. CNS: CycleGAN-Assisted Neonatal Segmentation Model for Cross-Datasets. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Graph Learning in Medical Imaging, Shenzhen, China, 17 October 2019; pp. 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.B.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.Y. M-gan: Retinal blood vessel segmentation by balancing losses through stacked deep fully convolutional networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 146308–146322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, M.; Pellino, S. Fighting together against the pandemic: Learning multiple models on tomography images for COVID-19 diagnosis. AI 2021, 2, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ko, S.B. Retinal blood vessel segmentation using fully convolutional network with transfer learning. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yu, S.; Ma, K.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Zheng, Y. Multi-task neural networks with spatial activation for retinal vessel segmentation and artery/vein classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Liu, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, F.; Lin, L.; Li, L.; Tanaka, S.; Chen, Y.W. Joint Extraction of Retinal Vessels and Centerlines Based on Deep Semantics and Multi-Scaled Cross-Task Aggregation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 2020, 25, 2722–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Y.; He, X. Segmentation of blood vessels using rule-based and machine-learning-based methods: A review. Multimed. Syst. 2019, 25, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedri, H.; Abdallah, M.B.; Nasri, F.; Belmabrouk, H. Computer method for tracking the centerline curve of the human retinal blood vessel. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering & MIS (ICEMIS), Monastir, Tunisia, 8–10 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, S.; Naranjo, V.; Angulo, J.; Legaz-Aparicio, A.G.; Verdú-Monedero, R. Retinal network characterization through fundus image processing: Significant point identification on vessel centerline. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2017, 59, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shit, S.; Paetzold, J.C.; Sekuboyina, A.; Ezhov, I.; Unger, A.; Zhylka, A.; Pluim, J.P.; Bauer, U.; Menze, B.H. clDice-a Novel Topology-Preserving Loss Function for Tubular Structure Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 16560–16569. [Google Scholar]
- Tetteh, G.; Rempfler, M.; Zimmer, C.; Menze, B.H. Deep-FExt: Deep feature extraction for vessel segmentation and centerline prediction. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 10 September 2017; pp. 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Hoover, A.; Kouznetsova, V.; Goldbaum, M. Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2000, 19, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Ding, W.; Wang, S.; Pei, C.; Yang, M.; Huang, L. Multi-modality Pathology Segmentation Framework: Application to Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images. In Proceedings of the Myocardial Pathology Segmentation Combining Multi-Sequence CMR Challenge, Lima, Peru, 4 October 2020; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Ding, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Pei, C.; Huang, L.; Zhuang, X. Brain Tumor Segmentation Network Using Attention-based Fusion and Spatial Relationship Constraint. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.15647. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dataset | Quantity | Resolution | Train/Test | Cross Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVE | 40 | 20/20 | No | |
| STARE | 20 | 15/5 | Yes | |
| CHASE | 28 | 21/7 | Yes |
| Hyper-Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| , , and | , , and |
| batchsize | 8 |
| learning rate | 1 × 10 |
| epochs | 100 |
| Dataset | Method | SE | SP | ACC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVE | B-COSFIRE [6] | 0.7526 | 0.9707 | 0.9427 | 0.9514 |
| WSF [7] | 0.7740 | 0.9790 | 0.9580 | 0.9750 | |
| U-Net [17] | 0.7817 | 0.9759 | 0.9531 | 0.9622 | |
| R2U-Net [18] | 0.7992 | 0.9712 | 0.9556 | 0.9681 | |
| CS-Net [20] | 0.8259 | 0.9850 | 0.9622 | 0.9763 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8423 | 0.9783 | 0.9663 | 0.9862 | |
| STARE | B-COSFIRE [6] | 0.7543 | 0.9689 | 0.9467 | 0.9487 |
| WSF [7] | 0.7880 | 0.9760 | 0.9570 | 0.9590 | |
| U-Net [17] | 0.7956 | 0.9764 | 0.9578 | 0.9617 | |
| R2U-Net [18] | 0.8488 | 0.9754 | 0.9618 | 0.9659 | |
| CS-Net [20] | 0.8516 | 0.9748 | 0.9651 | 0.9727 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8763 | 0.9835 | 0.9713 | 0.9786 | |
| CHASE | B-COSFIRE [6] | 0.7257 | 0.9651 | 0.9411 | 0.9434 |
| WSF [7] | - | - | - | - | |
| U-Net [17] | 0.7931 | 0.9793 | 0.9480 | 0.9464 | |
| R2U-Net [18] | 0.8062 | 0.9779 | 0.9457 | 0.9530 | |
| CS-Net [20] | 0.7841 | 0.9831 | 0.9522 | 0.9628 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8056 | 0.9869 | 0.9686 | 0.9714 |
| Dataset | Method | SE | SP | ACC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
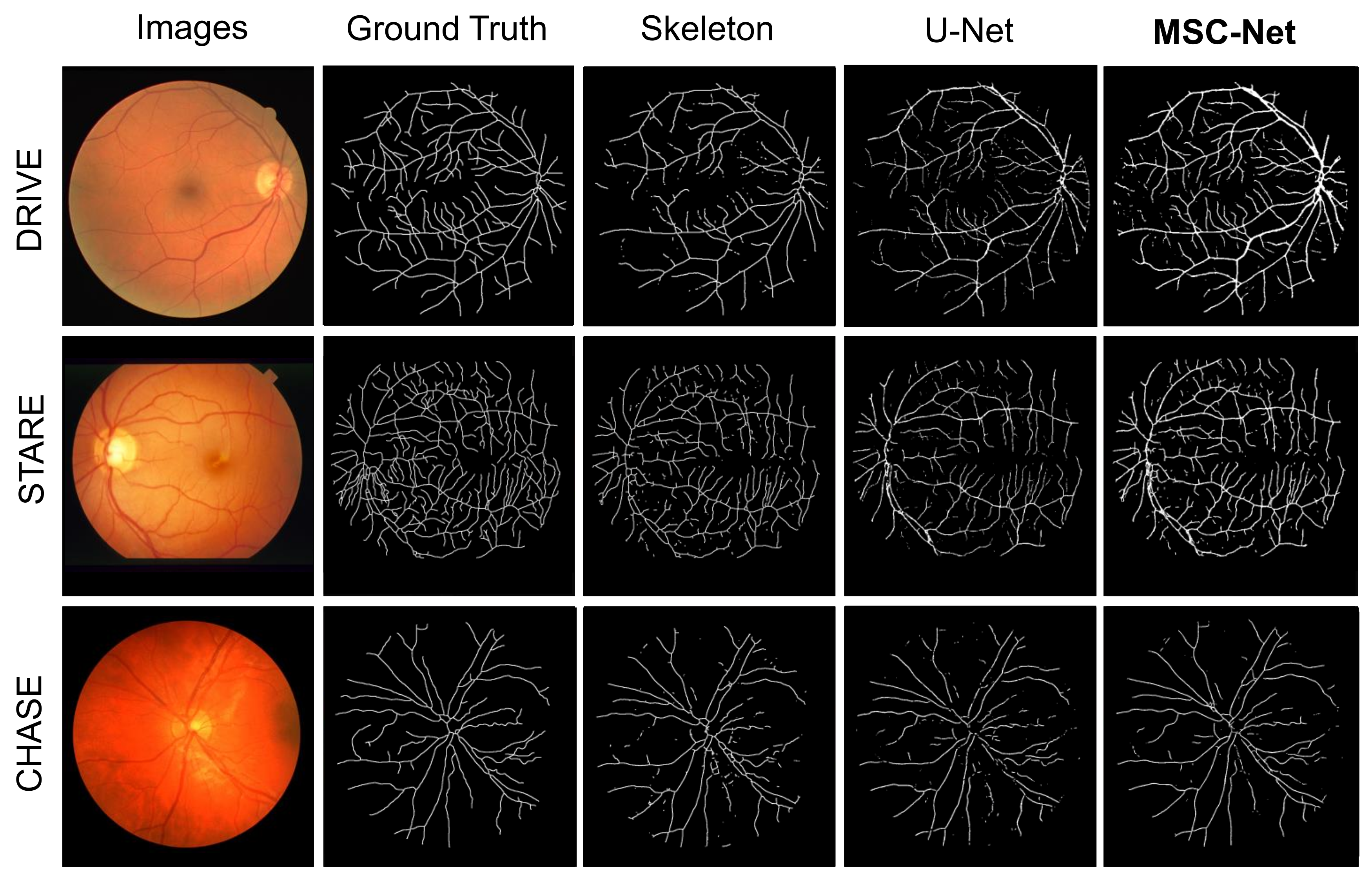
| DRIVE | Skeleton [28] | 0.7224 | 0.8993 | 0.9352 | - |
| U-Net [17] | 0.7403 | 0.9313 | 0.9310 | 0.9045 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.7905 | 0.9552 | 0.9510 | 0.9583 | |
| STARE | Skeleton [28] | 0.7565 | 0.9156 | 0.9148 | - |
| U-Net [17] | 0.7836 | 0.9463 | 0.9589 | 0.9467 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8546 | 0.9625 | 0.9423 | 0.9683 | |
| CHASE | Skeleton [28] | 0.6785 | 0.7636 | 0.9048 | - |
| U-Net [17] | 0.7560 | 0.8581 | 0.8902 | 0.9186 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8144 | 0.8865 | 0.9267 | 0.9541 |
| Dataset | Method | SE | SP | ACC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVE | S-Branch | 0.7917 | 0.9362 | 0.9414 | 0.9422 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 0.7917 | 0.9362 | 0.9587 | 0.9682 | |
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 0.8268 | 0.9533 | 0.9528 | 0.9647 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8423 | 0.9783 | 0.9663 | 0.9862 | |
| STARE | S-Branch | 0.8348 | 0.9684 | 0.9508 | 0.9674 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 0.8684 | 0.9751 | 0.9654 | 0.9681 | |
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 0.8578 | 0.9814 | 0.9477 | 0.9751 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8763 | 0.9835 | 0.9713 | 0.9786 | |
| CHASE | S-Branch | 0.7817 | 0.9701 | 0.9503 | 0.9511 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 0.7941 | 0.9681 | 0.9571 | 0.9582 | |
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 0.8145 | 0.9735 | 0.9583 | 0.9628. | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8056 | 0.9869 | 0.9686 | 0.9714 |
| Dataset | Method | SE | SP | ACC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVE | C-Branch | 0.7861 | 0.9431 | 0.9345 | 0.9353 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 0.7894 | 0.9443 | 0.9358 | 0.9397 | |
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 0.7806 | 0.9389 | 0.9483 | 0.9464 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.7905 | 0.9552 | 0.9510 | 0.9583 | |
| STARE | C-Branch | 0.8038 | 0.9545 | 0.9303 | 0.9455 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 0.8214 | 0.9581 | 0.9358 | 0.9527 | |
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 0.8467 | 0.9424 | 0.9321 | 0.9607 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8546 | 0.9625 | 0.9423 | 0.9683 | |
| CHASE | C-Branch | 0.7675 | 0.8451 | 0.8905 | 0.9412 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 0.7781 | 0.8661 | 0.9183 | 0.9508 | |
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 0.8047 | 0.8538 | 0.9178 | 0.9468 | |
| MSC-Net | 0.8144 | 0.8865 | 0.9267 | 0.9541 |
| Dataset | Resize | Method | Parameters (M) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVE | 576 × 576 | S-Branch/C-Branch | 1.7682 | 0.0147 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 4.2960 | 0.0197 | ||
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 9.5251 | 0.0312 | ||
| MSC-Net | 9.5251 | 0.0326 | ||
| STARE | 624 × 624 | S-Branch/C-Branch | 1.7682 | 0.0163 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 4.2960 | 0.0211 | ||
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 9.5251 | 0.0387 | ||
| MSC-Net | 9.5251 | 0.0362 | ||
| CHASE | 960 × 960 | S-Branch/C-Branch | 1.7682 | 0.0367 |
| MSC-Net ( CAS-FB) | 4.2960 | 0.0434 | ||
| MSC-Net ( clDice) | 9.5251 | 0.0717 | ||
| MSC-Net | 9.5251 | 0.0739 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Huang, L. MSC-Net: Multitask Learning Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation and Centerline Extraction. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010403
Pan L, Zhang Z, Zheng S, Huang L. MSC-Net: Multitask Learning Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation and Centerline Extraction. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(1):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010403
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Lin, Zhen Zhang, Shaohua Zheng, and Liqin Huang. 2022. "MSC-Net: Multitask Learning Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation and Centerline Extraction" Applied Sciences 12, no. 1: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010403
APA StylePan, L., Zhang, Z., Zheng, S., & Huang, L. (2022). MSC-Net: Multitask Learning Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation and Centerline Extraction. Applied Sciences, 12(1), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010403






