Multi-View Attention Network for Visual Dialog
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
Visual Dialog
3. Model
3.1. Multimodal Representation
3.1.1. Visual Features
3.1.2. Language Features
3.2. Multi-View Attention Network
3.2.1. Context Matching Module
3.2.2. Topic Aggregation Module
3.2.3. Modality Alignment Module
3.3. Answer Decoder
3.3.1. Discriminative Decoder
3.3.2. Generative Decoder
3.3.3. Multi-Task Learning
3.3.4. Fine-Tuning on Dense Annotations
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.3. Training Details
4.2. Quantitative Results
4.2.1. Discriminative Setting
4.2.2. Multi-Task Learning
4.2.3. Fine-Tuning on Dense Annotations
4.2.4. Number of Dialog History
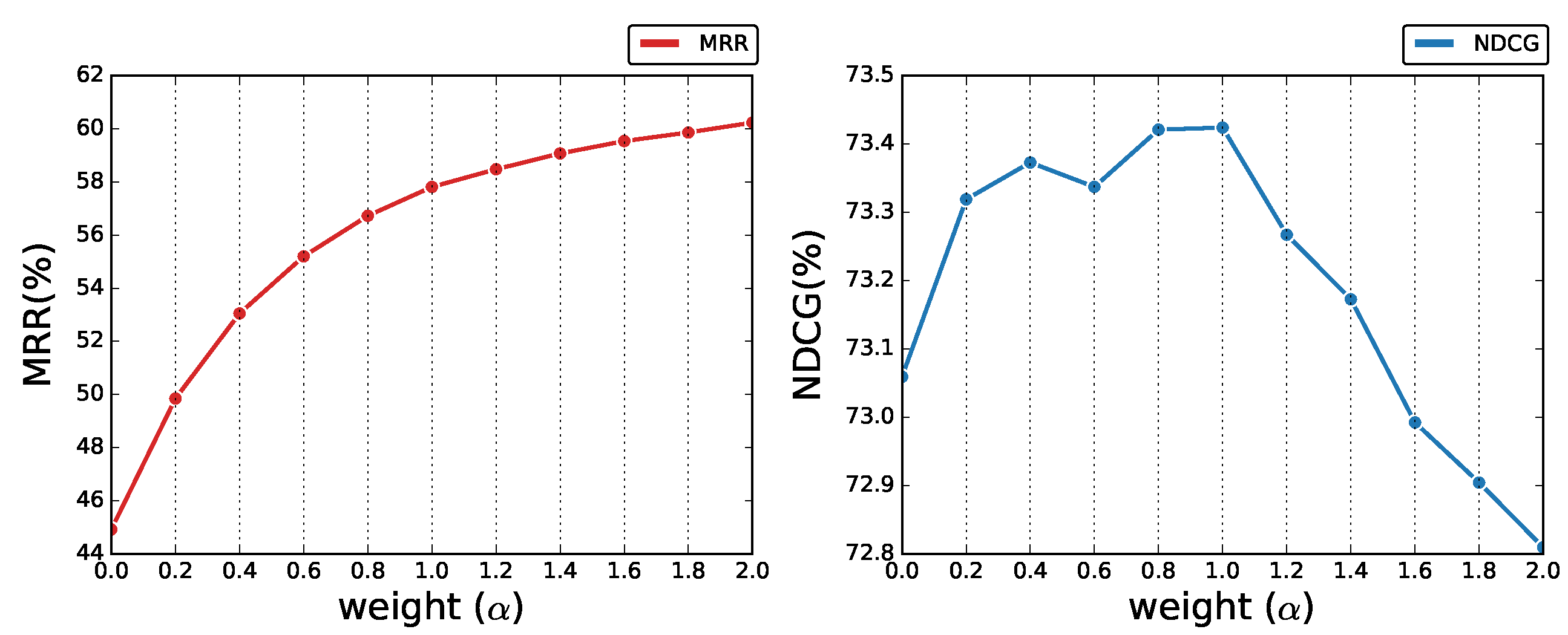
4.3. Ablation Study
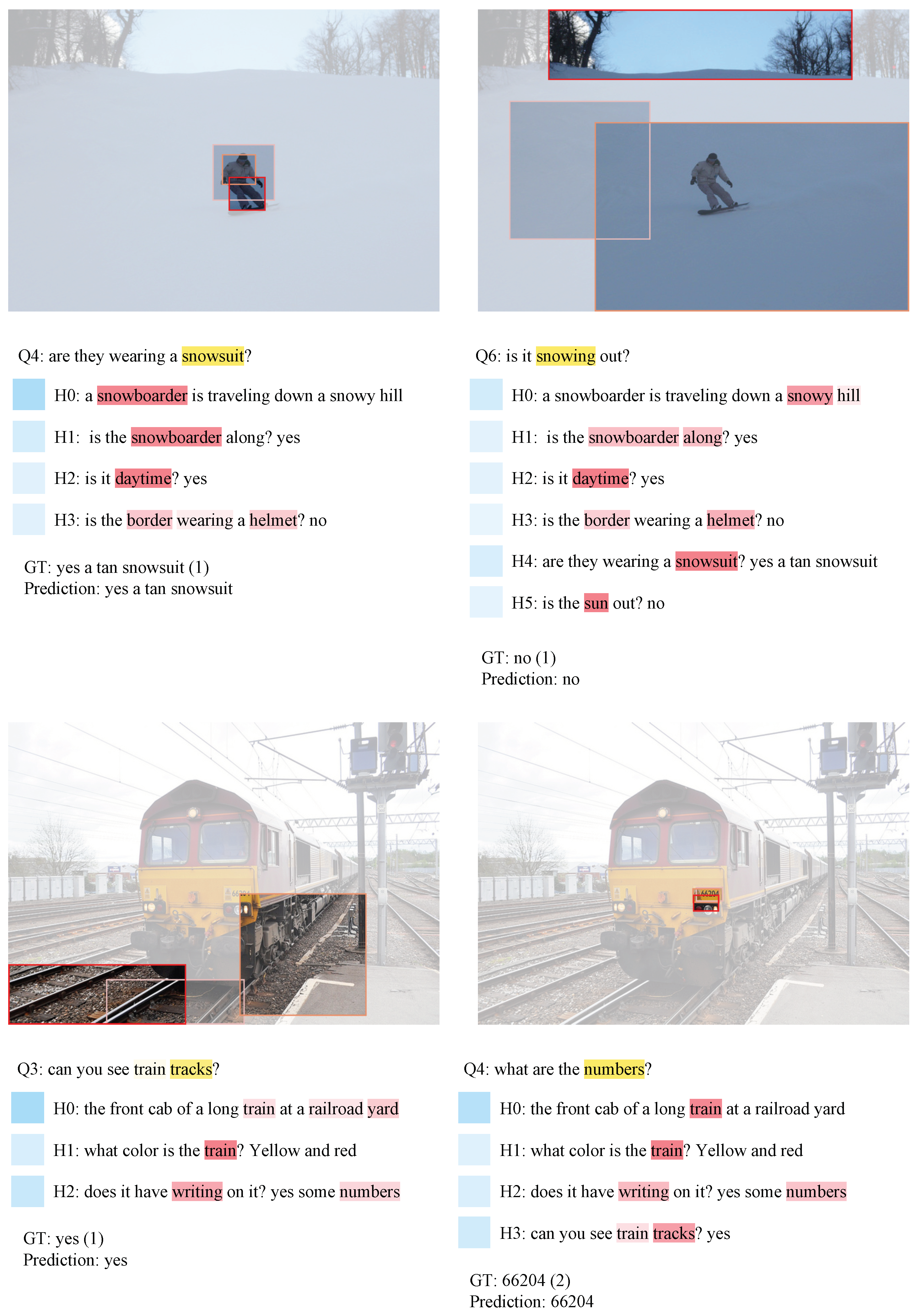
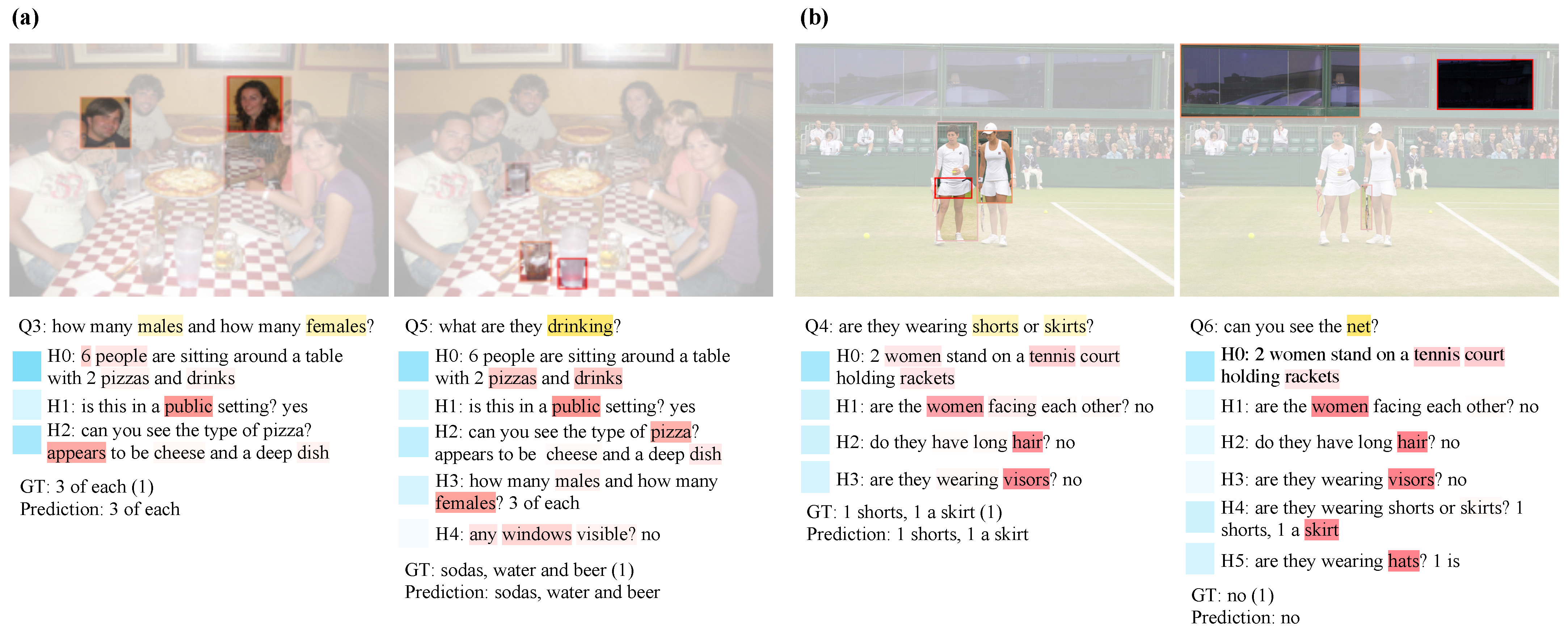
4.4. Qualitative Analysis
4.5. Error Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. More Qualitative Results

References
- Hudson, D.A.; Manning, C.D. Gqa: A new dataset for real-world visual reasoning and compositional question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6700–6709. [Google Scholar]
- Zellers, R.; Bisk, Y.; Farhadi, A.; Choi, Y. From recognition to cognition: Visual commonsense reasoning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6720–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, P.H.; Lehrmann, A.; Han, B.; Sigal, L. Visual reference resolution using attention memory for visual dialog. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 3719–3729. [Google Scholar]
- Kottur, S.; Moura, J.M.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D.; Rohrbach, M. Visual coreference resolution in visual dialog using neural module networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 153–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, G.C.; Lim, J.; Zhang, B.T. Dual Attention Networks for Visual Reference Resolution in Visual Dialog. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 2024–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wen, J.R. Recursive visual attention in visual dialog. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6679–6688. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Kottur, S.; Gupta, K.; Singh, A.; Yadav, D.; Moura, J.M.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Visual dialog. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 326–335. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, P.; Shen, C.; Reid, I.; Van Den Hengel, A. Are you talking to me? Reasoned visual dialog generation through adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6106–6115. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Xu, C.; Tao, D. Image-question-answer synergistic network for visual dialog. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10434–10443. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Kholy, A.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, J. Multi-step Reasoning via Recurrent Dual Attention for Visual Dialog. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 6463–6474. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Tan, H.; Bansal, M. Modality-balanced models for visual dialogue. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, W.; Qi, S.; Zhu, S.C. Reasoning visual dialogs with structural and partial observations. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6669–6678. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, I.; Yu, S.; Hazan, T.; Schwing, A.G. Factor graph attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 2039–2048. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zha, Z.J.; Wang, M. Iterative Context-Aware Graph Inference for Visual Dialog. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–18 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, J.; Rohrbach, M.; Darrell, T.; Klein, D. Neural module networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Murahari, V.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Das, A. Large-scale Pretraining for Visual Dialog: A Simple State-of-the-Art Baseline. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Joty, S.; Lyu, M.R.; King, I.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S.C. Vd-bert: A unified vision and dialog transformer with bert. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.13278. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Niu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H. Two Causal Principles for Improving Visual Dialog. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–18 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Bui, T.; Lee, J.Y.; Konstas, I.; Rieser, V. History for Visual Dialog: Do we really need it? In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Louradour, J.; Collobert, R.; Weston, J. Curriculum learning. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–18 June 2009; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.Q.; Suganuma, M.; Okatani, T. Efficient Attention Mechanism for Visual Dialog that can Handle All the Interactions between Multiple Inputs. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; He, X.; Buehler, C.; Teney, D.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S.; Zhang, L. Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6077–6086. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, R.; Zhu, Y.; Groth, O.; Johnson, J.; Hata, K.; Kravitz, J.; Chen, S.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, L.J.; Shamma, D.A.; et al. Visual genome: Connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 123, 32–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees, E.M. The TREC-8 Question Answering Track Report. In Proceedings of the TREC, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 7–19 November 1999; Volume 99, pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Yu, J.; Qin, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Q. DualVD: An Adaptive Dual Encoding Model for Deep Visual Understanding in Visual Dialogue. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Zha, Z.J.; Zhang, H. Making History Matter: History-Advantage Sequence Training for Visual Dialog. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 2561–2569. [Google Scholar]




| Model | AVG ↓ | NDCG ↑ | MRR ↑ | R@1 ↑ | R@5 ↑ | R@10 ↑ | Mean ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LF [7] | 12 | 45.31 (13) | 55.42 (12) | 40.95 | 72.45 | 82.83 | 5.95 |
| HRE [7] | 12 | 45.46 (12) | 54.16 (13) | 39.93 | 70.45 | 81.50 | 6.41 |
| MN [7] | 11 | 47.50 (11) | 55.49 (11) | 40.98 | 72.30 | 83.30 | 5.92 |
| GNN [12] | 10 | 52.82 (10) | 61.37 (10) | 47.33 | 77.98 | 87.83 | 4.57 |
| CorefNMN [4] | 9 | 54.70 (9) | 61.50 (9) | 47.55 | 78.10 | 88.80 | 4.40 |
| RVA [6] | 8 | 55.59 (8) | 63.03 (7) | 49.03 | 80.40 | 89.83 | 4.18 |
| DualVD [33] | 7 | 56.32 (7) | 63.23 (5) | 49.25 | 80.23 | 89.70 | 4.11 |
| Synergistic [9] | 6 | 57.32 (3) | 62.20 (8) | 47.90 | 80.43 | 89.95 | 4.17 |
| CAG [14] | 5 | 56.64 (6) | 63.49 (4) | 49.85 | 80.63 | 90.15 | 4.11 |
| DAN [5] | 4 | 57.59 (2) | 63.20 (6) | 49.63 | 79.75 | 89.35 | 4.30 |
| HACAN [34] | 3 | 57.17 (4) | 64.22 (3) | 50.88 | 80.63 | 89.45 | 4.20 |
| FGA [13] | 2 | 56.90 (5) | 66.20 (1) | 52.75 | 82.92 | 91.07 | 3.80 |
| MVAN (ours) | 1 | 59.37 (1) | 64.84 (2) | 51.45 | 81.12 | 90.65 | 3.97 |
| Synergistic [9] | 5 | 57.88 (4) | 63.42 (5) | 49.30 | 80.77 | 90.68 | 3.97 |
| CDF [11] | 2 | 59.49 (2) | 64.40 (4) | 50.90 | 81.18 | 90.40 | 3.99 |
| DAN [5] | 2 | 59.36 (3) | 64.92 (3) | 51.28 | 81.60 | 90.88 | 3.92 |
| FGA [13] | 2 | 57.20 (5) | 69.30 (1) | 55.65 | 86.73 | 94.05 | 3.14 |
| MVAN (ours) | 1 | 60.92 (1) | 66.38 (2) | 53.20 | 82.45 | 91.85 | 3.68 |
| Model | AVG ↓ | NDCG ↑ | MRR ↑ | R@1 ↑ | R@5 ↑ | R@10 ↑ | Mean ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReDAN [10] | 2 | 61.86 (2) | 53.13 (3) | 41.38 | 66.07 | 74.50 | 8.91 |
| LTMI * [24] | 2 | 60.92 (3) | 60.65 (2) | 47.00 | 77.03 | 87.75 | 4.90 |
| MVAN * (ours) | 1 | 63.15 (1) | 63.02 (1) | 49.43 | 79.48 | 89.40 | 4.38 |
| ReDAN+ [10] | 3 | 64.47 (2) | 53.74 (3) | 42.45 | 64.68 | 75.68 | 6.64 |
| LTMI * [24] | 1 | 66.53 (1) | 63.19 (2) | 49.18 | 80.45 | 89.75 | 4.14 |
| MVAN * (ours) | 2 | 63.22 (3) | 66.28 (1) | 53.87 | 82.08 | 89.65 | 4.61 |
| Model | AVG ↓ | NDCG ↑ | MRR ↑ | R@1 ↑ | R@5 ↑ | R@10 ↑ | Mean ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCA [22] | 4 | 72.47 (4) | 37.68 (4) | 20.67 | 56.67 | 72.12 | 8.89 |
| Visdial-BERT [17] | 1 | 74.47 (2) | 50.74 (2) | 37.95 | 64.13 | 80.00 | 6.28 |
| VD-BERT [18] | 1 | 74.54 (1) | 46.72 (3) | 33.15 | 61.58 | 77.15 | 7.18 |
| MVAN (ours) | 1 | 73.07 (3) | 56.06 (1) | 44.38 | 68.50 | 81.18 | 5.98 |
| P1_P2 [21] | 4 | 74.91 (2) | 49.13 (5) | 36.68 | 62.96 | 78.55 | 7.03 |
| LTMI [24] | 4 | 74.88 (3) | 52.14 (4) | 38.93 | 66.60 | 80.65 | 66.53 |
| MReal-BDAI [21] | 2 | 74.02 (4) | 52.62 (2) | 40.03 | 68.85 | 79.15 | 6.76 |
| VD-BERT [18] | 1 | 75.35 (1) | 51.17 (4) | 38.90 | 62.82 | 77.98 | 6.69 |
| MVAN (ours) | 2 | 71.40 (5) | 65.16 (1) | 52.88 | 79.50 | 88.55 | 4.27 |
| Model | Context-Level History | Topic-Level History | NDCG ↑ | MRR ↑ | R@1 ↑ | R@5 ↑ | R@10 ↑ | Mean ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVAN | ✓ | ✓ | 60.17 | 65.33 | 51.86 | 82.40 | 90.90 | 3.88 |
| ✗ | ✗ | 62.33 | 61.79 | 47.61 | 79.30 | 88.81 | 4.42 | |
| w/o Topic Aggregation | ✓ | N/A | 58.50 | 64.63 | 50.84 | 81.64 | 90.50 | 3.97 |
| ✗ | N/A | 60.57 | 61.32 | 47.19 | 78.59 | 88.40 | 4.55 | |
| w/o Context Matching | N/A | ✓ | 57.06 | 64.15 | 50.51 | 81.15 | 89.83 | 4.12 |
| N/A | ✗ | 58.60 | 60.36 | 46.09 | 77.71 | 87.64 | 4.73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Whang, T.; Yoon, Y.; Lim, H. Multi-View Attention Network for Visual Dialog. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073009
Park S, Whang T, Yoon Y, Lim H. Multi-View Attention Network for Visual Dialog. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073009
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sungjin, Taesun Whang, Yeochan Yoon, and Heuiseok Lim. 2021. "Multi-View Attention Network for Visual Dialog" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073009
APA StylePark, S., Whang, T., Yoon, Y., & Lim, H. (2021). Multi-View Attention Network for Visual Dialog. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073009






