Chaotic Evolutionary Programming for an Engineering Optimization Problem
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Introduction of the chaotic sequence based population initialization process.
- A chaotic mutation operator is proposed and employed.
- A chaos guided tournament selection operator is considered to select better candidates.
- The Powell’s pattern search is applied to enhance the exploitation of the proposed algorithm.
2. Economic Load Dispatch Problem
- (i)
- The power balance equality constraint:
- (ii)
- The generator operating limits:
- (iii)
- The ramp rate limit.
- As generation increases:
- As generation decreases:
- (iv)
- Prohibited operating zone constraint:
3. Evolutionary Programming
4. Proposed Algorithm
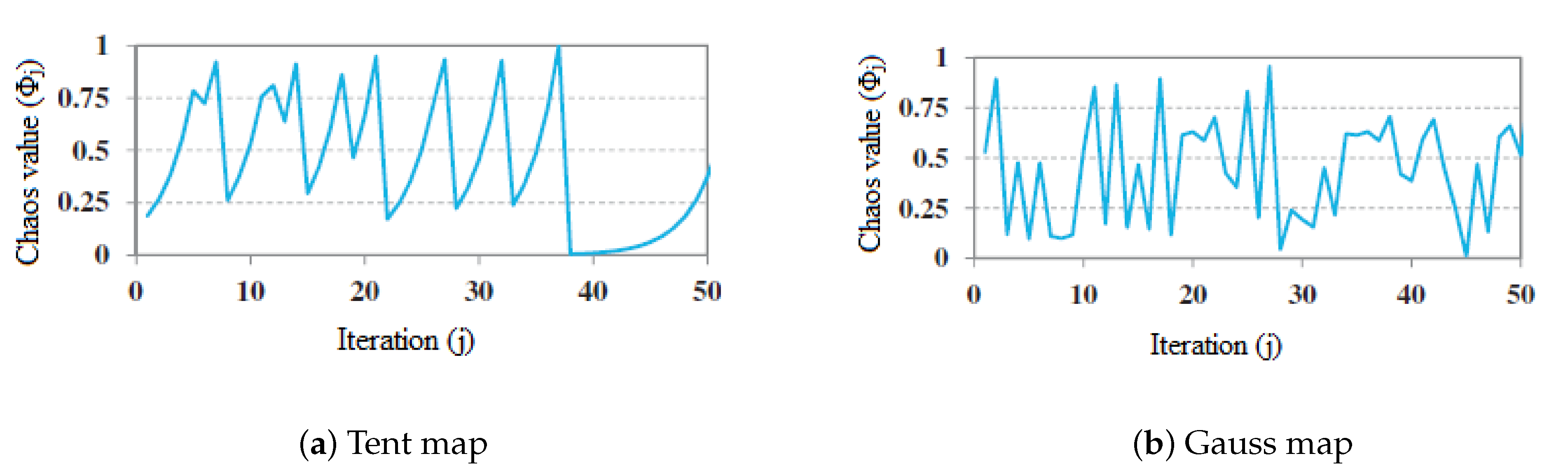
4.1. Chaotic Evolutionary Programming
4.2. Powell’s Pattern Search Method
5. Simulation Test Problems
5.1. Generalized Test Functions
- 1.
- Griewank function: This is described mathematically as:subject to .
- 2.
- Rastrigin’s function: This is described mathematically as:subject to .
- 3.
- Rosenbrock’s function: This is described mathematically as:subject to .
- 4.
- Schwefel 2.22 function: This is described mathematically as:subject to .
- 5.
- Sphere function: This is one of the simplest of De Jong’s functions. It is described mathematically as:subject to .
- 6.
- Step function: This is described mathematically as:subject to .
- 7.
- Step 2 function: This is described mathematically as:subject to
5.2. Multi-Fuel Economic Load Dispatch Problem
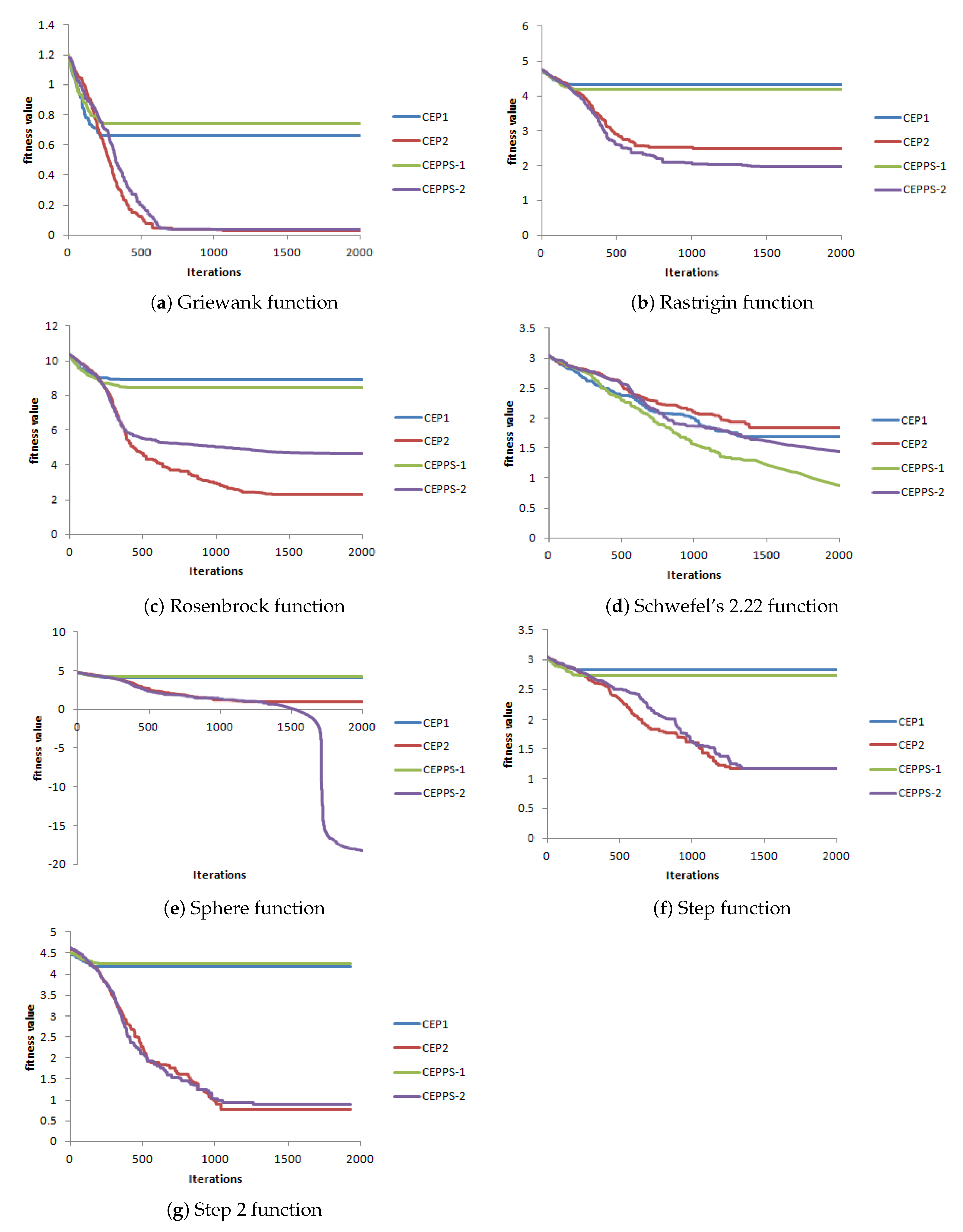
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhillon, J.; Kothari, D. Power System Optimization; PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.J.; Dhillon, J.; Kothari, D. Synergic predator-prey optimization for economic thermal power dispatch problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 43, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.J.; Dhillon, J.; Kothari, D. Surrogate worth trade-off method for multi-objective thermal power load dispatch. Energy 2017, 138, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabarathi, T.; Jayaprakash, K.; Jeyakumar, D.; Raghunathan, T. Evolutionary programming techniques for different kinds of economic dispatch problems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2005, 73, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaing, Z.-L. Particle swarm optimization to solving the economic dispatch considering the generator constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H.; Chang, H.-C. Large-scale economic dispatch by genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power syst. 1995, 10, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellapilla, K.; Fogel, D.B. Two new mutation operators for enhanced search and optimization in evolutionary programming. In Optical Science, Engineering and Instrumentation; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1997; pp. 260–269. [Google Scholar]
- Fogel, L.J.; Fogel, D.B. A preliminary investigation on extending evolutionary programming to include self-adaptation on finite state. Informatica 1994, 18, 387–398. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Liu, Y. Fast evolutionary programming. Evol. Program. 1996, 3, 451–460. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.-T.; Yang, P.-C.; Huang, C.-L. Evolutionary programming based economic dispatch for units with non-smooth fuel cost functions. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1996, 11, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, T.; Schwefel, H.P. An overview of evolutionary algorithms for parameter optimization. Evolu. Comput. 1993, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, G. Evolutionary programming made faster. IEEE Trans. Evolu. Comput. 1999, 3, 82–102. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Higuchi, T. Scaling up fast evolutionary programming with cooperative co evolution. In Proceedings of the Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Seoul, Korea, 27–30 May 2001; Volume 2, pp. 1101–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Yao, X. Evolutionary programming using mutations based on the levy probability distribution. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2004, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, R.; Pant, M.; Chelliah, T.R.; Abraham, A. Opposition based chaotic differential evolution algorithm for solving global optimization problems. In Proceedings of the Fourth World Congress on Nature and Biologically Inspired Computing, Mexico City, Mexico, 5–9 November 2012; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos Coelho, L.; Mariani, V.C. Combining of chaotic differential evolution and quadratic programming for economic dispatch optimization with valve-point effect. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Dong, G.; Wang, F.; Mao, Z. Optimization of dynamic economic dispatch with valve-point effect using chaotic sequence based differential evolution algorithms. Energy Conver. Manag. 2011, 52, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, K.K.; Singh, P.K. Chaotic gradient artificial bee colony for text clustering. Soft Comput. 2016, 20, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Liu, X. Melt index prediction by aggregated rbf neural networks trained with chaotic theory. Neuro Comput. 2014, 131, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, A.H.; Yang, X.-S. Chaotic bat algroithm. J. Compt. Sci. 2014, 5, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, L.-Y.; Hsiao, C.-J.; Yang, C.-H. Chaotic particle swarm optimization for data clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mandal, K.K.; Chakraborty, N. Optimal DG placement by multi-objective opposition based chaotic differential evolution for techno-economic analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 78, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Dhillon, J.S.; Kothari, D.P. Crisscross differential evolution algorithm for constrained hydro thermal scheduling. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2020, 93, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Fei, Z.; Qiu, M. The Effects of Using Chaotic Map on Improving the Performance of Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithms. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 924652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutueva, A.V.; Nepomuceno, E.G.; Karimov, A.I.; Andreev, V.S.; Butusov, D.N. Adaptive chaotic maps and their application to pseudo-random numbers generation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 133, 109615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno, E.G.; Lima, A.M.; Arias-García, J.; Perc, M.; Repnik, R. Minimal digital chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 120, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, G.; Fan, Y.; Liao, R. A nonlinear fractional programming approach for environmental economic power dispatch. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 78, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, D.B. Applying evolutionary programming to selected traveling salesman problems. Cybern. Syst. 1993, 24, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Yang, X.-S. A literature survey of benchmark functions for global optimisation problems. Int. J. Math Model. Numer. Optim. 2013, 4, 150–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-L. Improved genetic algorithm for power economic dispatch of units with valve-point effects and multiple fuels. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Solving complex economic load dispatch problems using bio geography-based optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 3605–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-B.; Jeong, Y.-W.; Shin, J.-R.; Lee, K.Y. An improved particle swarm optimization for non convex economic dispatch problems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisal, A. Dynamic search space squeezing strategy based intelligent algorithm solutions to economic dispatch with multiple fuels. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 45, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Hybrid differential evolution with bio geography-based optimization for solution of economic load dispatch. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, D.N.; Ongsakul, W. Economic dispatch with multiple fuel types by enhanced augmented Lagrange Hopfield network. Appl. Energy 2012, 91, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.; Roy, P.K.; Mandal, S. Economic load dispatch using krill herd algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieu, V.N.; Schegner, P. Augmented lagrange hopfeld network initialized by quadratic programming for economic dispatch with piece wise quadratic cost functions and prohibited zones. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Case | Valve Point Loading | Ramp Rate | Prohibited Operating Zone | Transmission Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | × | × | × | × |
| 2 | ✓ | × | × | × |
| 3 | × | × | ✓ | × |
| 4 | × | × | × | ✓ |
| 5 | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| 6 | × | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| Test Function | Fitness | CEP-1 | CEP-2 | CEPPS-1 | CEPPS-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Worst | 4.61 | 1.08 | 11.05 | 9.29 × | |
| Griewank function | Average | 4.61 | 1.08 | 11.05 | 9.29 × |
| Best | 4.61 | 1.08 | 5.48 | 0.01 × | |
| Worst | 21,893.57 | 305.44 | 40,041.02 | 97.11 | |
| Rastrigin function | Average | 21,893.57 | 305.44 | 40,041.02 | 61.70 |
| Best | 21,893.57 | 305.44 | 15,691.13 | 61.70 | |
| Worst | 7.54 × | 222.46 | 1.00 × | 43,304.03 | |
| Rosenbrock function | Average | 7.54 × | 22.36 | 1.00 × | 7300.95 |
| Best | 7.54 × | 22.36 | 2.91 × | 7300.95 | |
| Worst | 48.16 | 68.45 | 7.57 | 27.71 | |
| Schwefel’s 2.22 function | Average | 48.16 | 68.45 | 7.57 | 27.71 |
| Best | 48.16 | 68.45 | 7.57 | 27.71 | |
| Worst | 13,094.38 | 8.23 | 50,471.00 | 4.79 × | |
| Sphere function | Average | 13,094.38 | 8.23 | 50471.00 | 9.40 × |
| Best | 13,094.38 | 8.23 | 18,642.14 | 9.40 × | |
| Worst | 670.00 | 37.00 | 969.00 | 28.00 | |
| Step function | Average | 670.00 | 37.00 | 969.00 | 28.00 |
| Best | 670.00 | 15.00 | 532.00 | 15.00 | |
| Worst | 15,349.00 | 6.00 | 39,277.00 | 8.00 | |
| Step 2 function | Average | 15,349.00 | 6.00 | 39,277.00 | 5.00 |
| Best | 15,349.00 | 6.00 | 17,381.00 | 5.00 |
| Algorithm | Cost ($/h) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 | |
| BBO [31] | 624.51 | – | – | – | – | – |
| CPSO [32] | – | 623.82 | – | – | – | – |
| CGA-MU [33] | 623.80 | 624.71 | – | – | – | – |
| DE [33] | 623.80 | 624.46 | – | – | – | – |
| DEBBO [34] | 624.51 | – | – | – | – | – |
| ELHN [35] | 624.51 | – | – | – | – | – |
| IGA [30] | 624.51 | – | – | – | – | – |
| IGA-MU [30] | 623.80 | 624.51 | – | – | – | – |
| KHA [36] | 624.51 | – | – | – | – | – |
| PSO [33] | 623.80 | 624.24 | – | – | – | – |
| QP-ALHN [37] | 623.80 | – | 624.32 | – | – | – |
| SPPO | 623.80 | 623.82 | 624.32 | 700.29 | 700.77 | 700.48 |
| CEPPS-1 | 623.75 | 623.87 | 623.76 | 699.70 | 699.54 | 704.94 |
| CEPPS-2 | 623.75 | 623.88 | 623.77 | 699.77 | 699.73 | 700.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, N.J.; Singh, S.; Chopra, V.; Aftab, M.A.; Hussain, S.M.S.; Ustun, T.S. Chaotic Evolutionary Programming for an Engineering Optimization Problem. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062717
Singh NJ, Singh S, Chopra V, Aftab MA, Hussain SMS, Ustun TS. Chaotic Evolutionary Programming for an Engineering Optimization Problem. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(6):2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062717
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Nirbhow Jap, Shakti Singh, Vikram Chopra, Mohd Asim Aftab, S. M. Suhail Hussain, and Taha Selim Ustun. 2021. "Chaotic Evolutionary Programming for an Engineering Optimization Problem" Applied Sciences 11, no. 6: 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062717
APA StyleSingh, N. J., Singh, S., Chopra, V., Aftab, M. A., Hussain, S. M. S., & Ustun, T. S. (2021). Chaotic Evolutionary Programming for an Engineering Optimization Problem. Applied Sciences, 11(6), 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062717








