1. Introduction
A cerebral aneurysm is an abnormal dilation of the artery caused by a weakness on the wall and is located on the subarachnoid space at the base of the brain. A reduction of the tunica media and middle muscular layer on the artery wall, combined with hemodynamic factors, lead to this process [
1]. Wall shear stress (WSS), oscillatory shear index (OSI), and relative residence time (RRT) have been proposed as indicators of aneurysm rupture risk [
2,
3,
4,
5].
Fluid–structural simulations (FSI) using image-based models of cerebral aneurysms can help to better understand the vascular remodeling processes associated with aneurysm growth and its subsequent stabilization or rupture [
6,
7].
Risk factors include hypertensive states [
8,
9]. Regarding these, FSI simulations performed under normal blood and high blood pressure conditions showed that WSS and mechanical stresses in the aneurysm wall were strongly affected by hypertension [
10]. Within these states, a very important one corresponds to isolated systolic hypertension (ISH), which is the most common form of hypertension in elderly people (>65 years old) [
11]. Moreover, the prevalence in young adults has been increasing over the past decade, due to the epidemic of overweight and obesity [
12,
13,
14,
15]. No records of studies about ISH in cerebral aneurysms were found, using computational simulations, CFD, FSI or similar techniques, so, investigate about the effect of this type of condition on the hemodynamics of an aneurysm would represent an advance in the understanding of the pathology.
Therefore, the objective of this research is to report and study the hemodynamic effects of an isolated systolic hypertension condition on image-based cerebral aneurysms models from real patients, comparing it with a “traditional” hypertensive condition and a normal or normotensive pressure condition by carrying out FSI simulations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Models and Properties
In this study, a total of 6 aneurysms models were selected from the database created by Dr. Alvaro Valencia and his research group at Universidad de Chile. For this database, patient-specific cerebral aneurysm images were provided by the Instituto de Neurocirugía Asenjo (INCA), and were obtained using a Phillips Integri Allura 3D Rotational Angiograph. Next, they reconstructed the medical image from a Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML) format to a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model, following the procedure described by Valencia et al. [
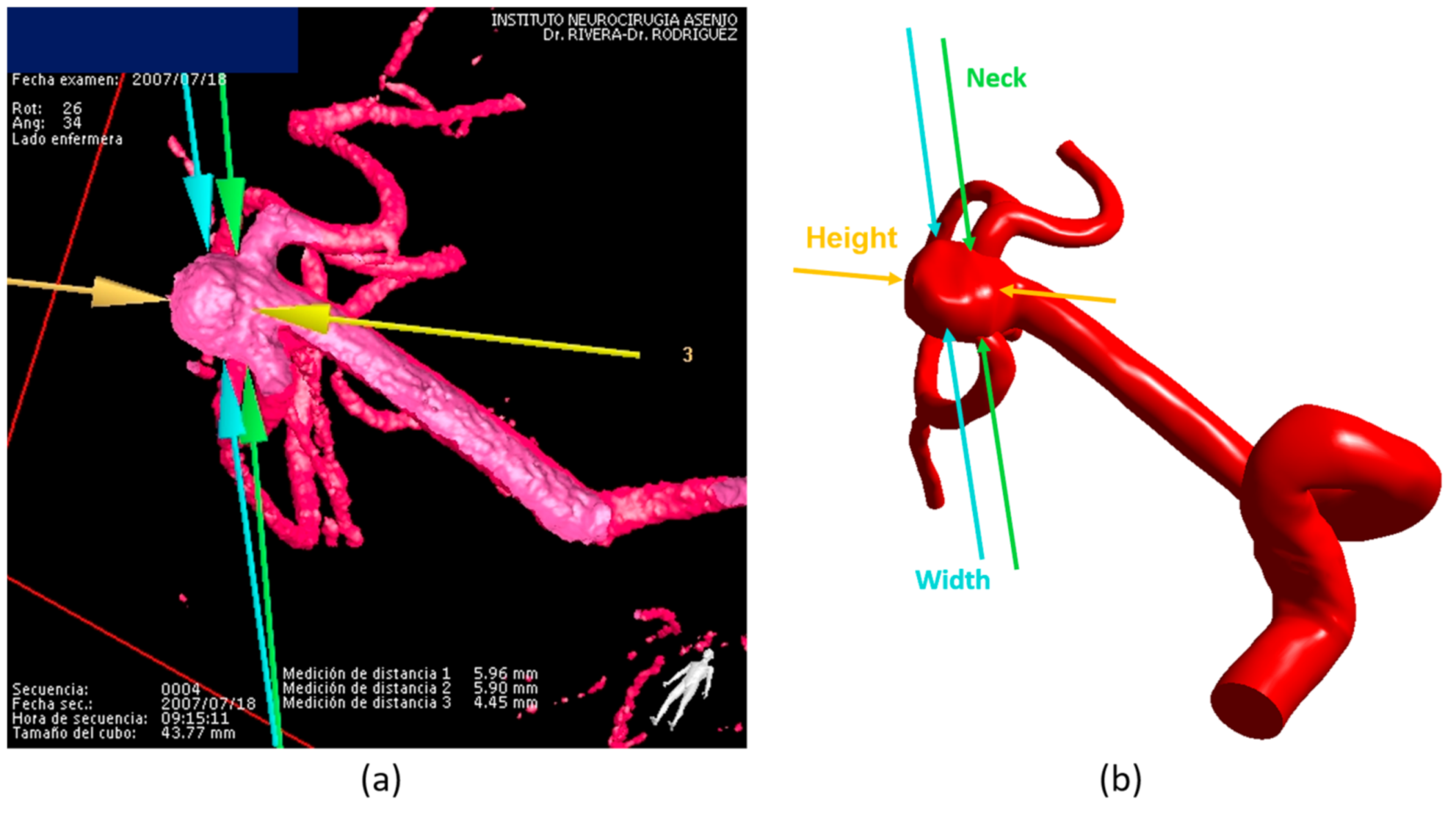
16]. It is important to note that, with the aim of simulation, in the reconstruction process the domain is limited by cutting the blood vessels. The aneurysms were located at different cerebral locations: vertebrobasilar arteries (VBA), the internal carotid artery (ICA) and the middle cerebral artery (MCA). Moreover, the aneurysms were classified accordingly to their type (lateral, terminal, and lateral with bifurcation) and rupture status (unruptured or ruptured). The geometric dimensions of an aneurysm (height in yellow, neck diameter in green, and width in cyan) are shown in
Figure 1a, corresponding to the medical image, and in
Figure 1b, corresponding to the reconstructed model.
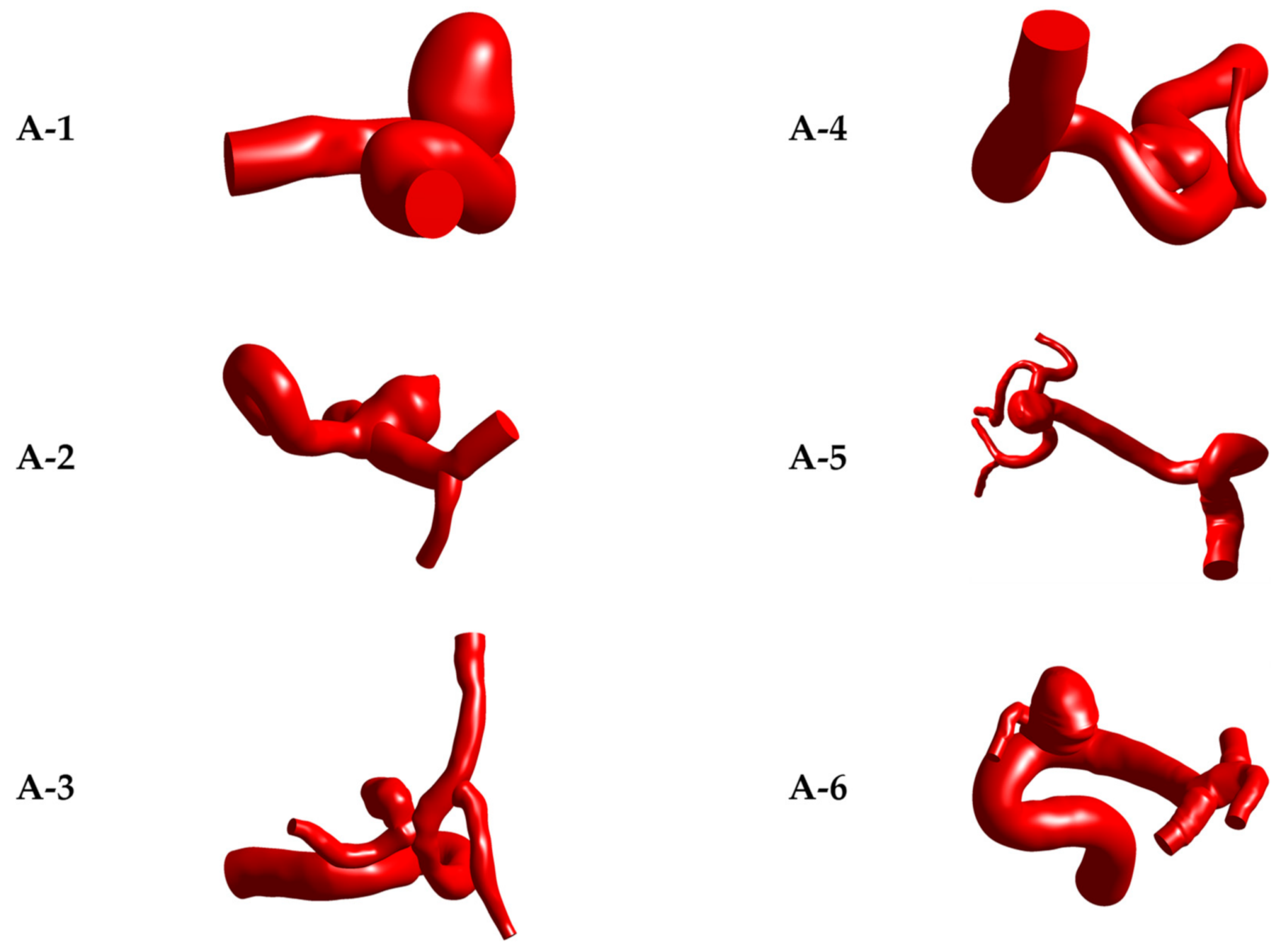
Of the 6 selected aneurysms, 3 were unruptured and 3 were ruptured. In addition, the models were labeled as A-N, where A corresponds to the aneurysm and N to the patient number. Each of the 6 models are shown in
Figure 2.
Table 1 shows the rupture status, location, type, and age of the patient in each model and
Table 2 shows the geometric dimension values. The reason for selecting aneurysms from different locations, types and sizes was to obtain differentiable results. Given the low number of models under study (6 models), the objective was never to produce a statistical analysis between models or similar. Therefore, the morphological parameters usually used for comparisons in a greater number of models are not included in this study.
The blood flow inside the small cerebral arteries was considered as transient, laminar, incompressible, and the Casson non-Newtonian model was implemented (Equation (1)), with a blood density of 1065 kg/m
3 [
17,
18].
where
is the newtonian viscosity given as 0.0036 Pa·s and
is the yield stress.
For the arterial wall, we considered a density of 1125 kg/m
3 [
19] and a hyperelastic material, with the five parameter Mooney-Rivlin model (Equation (2)), following the results measured by Valencia et al. and similar to those of Perrini et al. [
20,
21]. For the thickness of each aneurysm model, we considered a constant value of 0.35 mm [
22].
where
are the strain invariants, and with the hyperelastic constant values as
,
,
,
,
.
2.2. Boundary Conditions
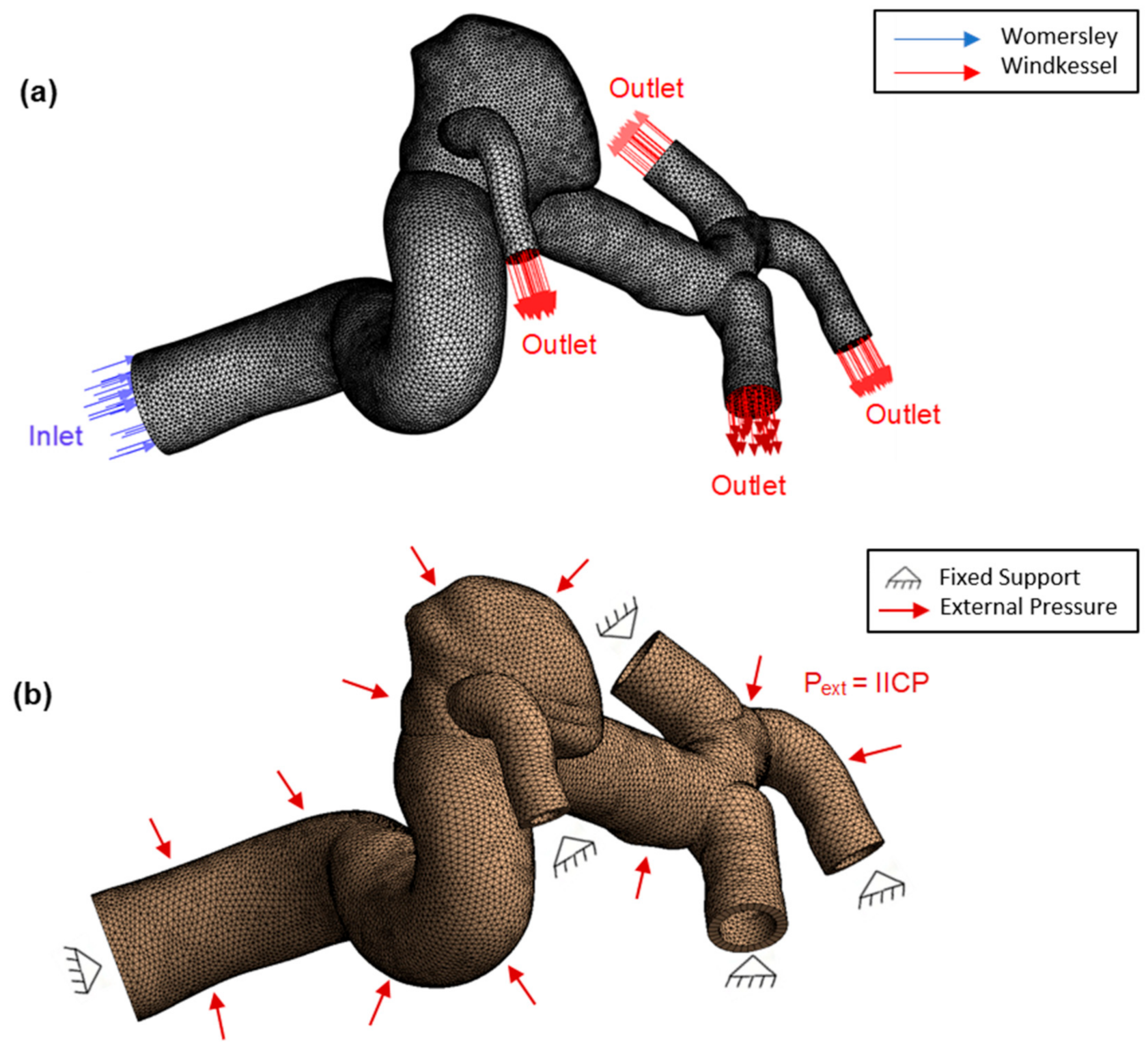
The fluid boundary conditions simulate the internal cardiovascular system of the brain, so these should be adjusted as closely as possible to real conditions. In this case, the inlet condition is represented by a velocity profile, and the outlet condition by the blood flow pressure.
Assuming that the flow is periodic over time, the Womersley velocity profile was used to obtain the physiological conditions at the artery inlet (Equation (3)),
with
, where
is the
Womersley number,
is the inlet artery radius,
is the number of modes, and
is the angular frequency. In our study, there are 8 modes and an angular frequency of 7.703 s
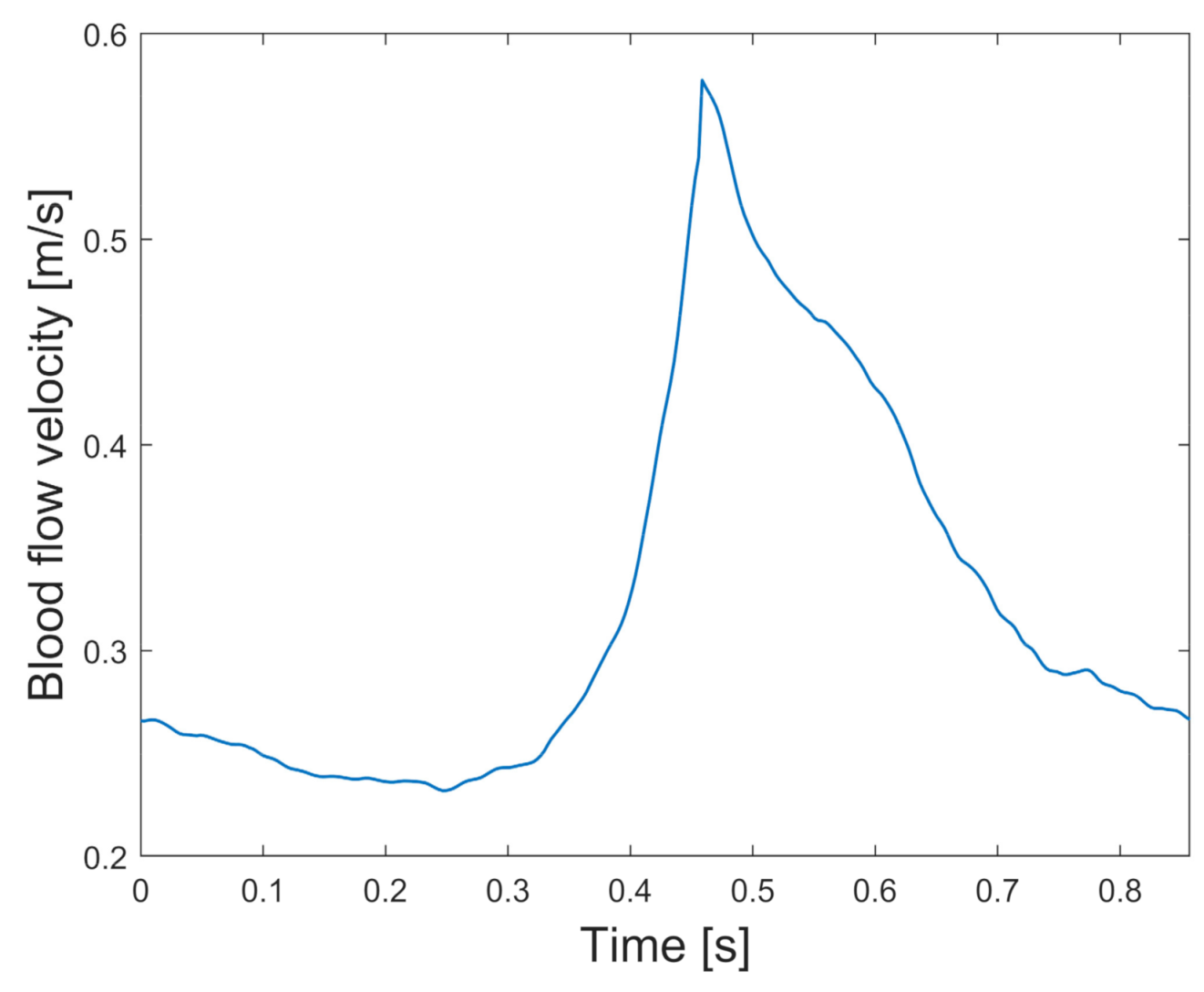
−1 (the period of the cardiac cycle was 0.857 s). For this, a previously averaged blood pulse V(t) of 70 patients from Valencia’s database was used, measured at the internal carotid artery using the Doppler ultrasound technique, and then the blood flow Q (t) for each case was calculated with its corresponding model input area. This averaged blood pulse is shown in
Figure 3. More details about the patient’s measurement and implementation can be found in Amigo’s work [
23].
From this, at time t = 0 s the blood velocity was v(t) = 0.278 m/s. We considered this velocity value as the initial condition at the artery inlet.
To obtain the pulsatile pressure conditions
at the outlet, the RCR Windkessel model (Equation (4)) was used,
where
is the proximal resistance,
is the distal resistance and
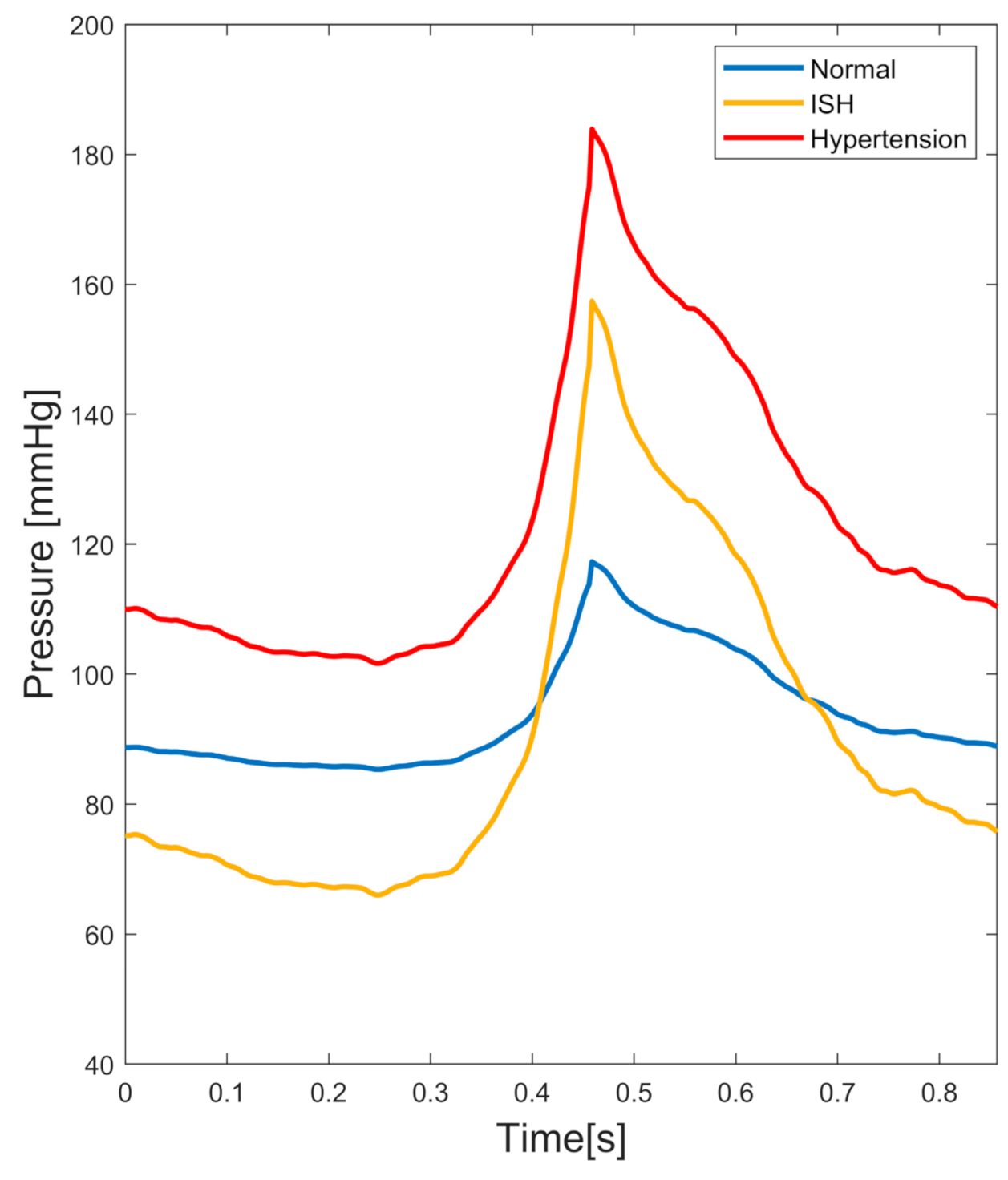
is the capacitance. These constant values were adjusted and calibrated manually. In the present work 3 different pressure conditions were considered: (1st) a normal condition representative of a healthy patient at rest, also called “normotensive” and approximately between 120/80 mmHg; (2nd) a condition representative of a grade 2 hypertension or “hypertensive” between 180/100 mmHg [
24]; (3rd) and a condition representative of a grade 1 isolated systolic hypertension (ISH) between 160/70 mmHg [
11], which are shown in
Figure 4. These hypertensive conditions should not be confused with one another since, while hypertension corresponds to high blood pressure at the entire cardiac cycle, isolated systolic hypertension implies an increase in pressure only at the systolic phase. Therefore, for the sake of clarity, we refer to the latter solely as ‘ISH’.
Table 3 shows the constant values for each pressure condition.
Our study prioritized the effects of the pressure conditions on blood flow dynamics. As it can be observed in the figure, we emphasized that, while the hypertensive condition was the one with the highest pressure of the entire cardiac cycle, the ISH condition has the particularity that at diastole it was the lowest pressure, while at systole it was between normal (blue) and hypertension (red), thus having a quite different shape from the other two conditions.
In addition to this, the previous fluid dynamic conditions, the non-slip condition, was applied to the vessel walls of each model. In regard to the solid or structural boundary conditions, the condition of fixed support was assumed at inlet and outlets, and a constant external pressure of 35 mmHg was considered, representing a high intracranial pressure (IICP) condition of the cerebrospinal fluid, as well as possible surrounding tissue [
25,
26,
27].
2.3. Numerical Methods and Setup
In this study, the 3 pressure conditions described before were simulated in each of the 6 brain aneurysm models, and all with the same velocity condition at inlet, thus totaling 18 FSI simulations. During initial conditions, at the inlet of each model we used the corresponding velocity inlet value at time t = 0, V(t) = 0.278 m/s and an initial gauge pressure P(t) = 0 Pa.
We configured a quadratic order unstructured tetrahedral mesh for the fluid domain and an unstructured triangles mesh using shell elements for the structural domain. During this step we used ANSYS
® Meshing software. For the mesh size, we carried out a mesh or grid convergence study using the smallest aneurysm model (A-4): for the fluid domain, wall shear stress (WSS) at aneurysm surface was chosen for analysis because it is one of the main indicators on hemodynamics studies, and the parameters at study were based on it. Additionally, the static pressure at aneurysm surface was chosen, but we focused on WSS since it is more sensitive to changes in mesh size. Six element sizes were chosen: 0.50, 0.40, 0.30, 0.20, 0.10, and 0.05 mm, with differences in WSS of 2% between sizes 0.05 and 0.10 and below 1% in pressure, thus determining an optimal element size of 0.10 mm at the aneurysm area. For the structural or solid domain, von Mises Stress and displacement at the aneurysm were chosen. Four element sizes were chosen: 0.25, 0.20, 0.15 and 0.10 mm, with differences in von Mises stresses of 8% between the sizes 0.10 and 0.15 and below 1% in displacement. Although our study is FSI, we only analyzed the hemodynamics effects (fluid), thus we determined an optimal element size of 0.15 mm. The described results for the fluid and solid domain, along with the selected element size are shown in
Figure 5a,b. It is important to note that an important factor in this selection was the available computational resources. The configured mesh for A-6 model is shown in
Figure 6a (fluid domain) and 6b (solid domain), along with its boundary conditions.
Simultaneously to the convergence study, we performed a mesh quality analysis for the fluid domain in every model, and we evaluated the maximum or minimum values of the following parameters: maximum skewness, minimum orthogonal quality, and maximum aspect ratio.
Table 4 shows these parameters for the mesh with the selected element size. As it can be observed, the values meet the requirements and recommendations for tetrahedral elements of the ANSYS
® Fluent Theory Guide.
The implementation of each fluid-structural simulation was carried out by a two-way coupling between ANSYS
® Fluent (CFD) and ANSYS
® Mechanical (FEA), solving the transient Navier-Stokes equations coupled with the structural equations through System Coupling component. For the fluid domain, the finite volume method (FVM) was used, with a dynamic meshing and a smoothing method (constant spring factor equal to 0.1). For the structural domain, the finite element method (FEM) was used and considering large deflections. On the other hand, for the fluid domain, the Pressure-Implicit with Splitting of Operators (PISO) algorithm was used to solve Navier-Stokes equations, with a spatial discretization using a least squares cell based on the gradient, second-order for pressure, and second-order upwind for momentum. For the transient formulation, the time was discretized by a first-order implicit formulation. The residuals of the momentum and continuity equations were kept below 0.001. The time step chosen was 0.0005 s in order to adequately capture the phenomenon as it was also used in previous works [
18]. The simulation time was 1.8 s (slightly longer than two cardiac cycles), and the results were obtained from the second cycle. All simulations were parallelized using double precision in an Intel i7-6700K with 8 physical cores and 64Gb of RAM.
Five hemodynamic parameters were calculated for each aneurysm model: diastolic wall shear stress (DWSS), systolic wall shear stress (SWSS), time-averaged wall shear stress (TAWSS), oscillatory shear index (OSI) and relative residence time (RRT). It is important to emphasize that, although the simulations considered fluid–solid interaction, the aim of this study was only to analyze the effects on the hemodynamic behavior (fluid), and hence, we analyzed the mentioned parameters. We mainly focused on TAWSS, OSI and RRT.
3. Results and Discussion
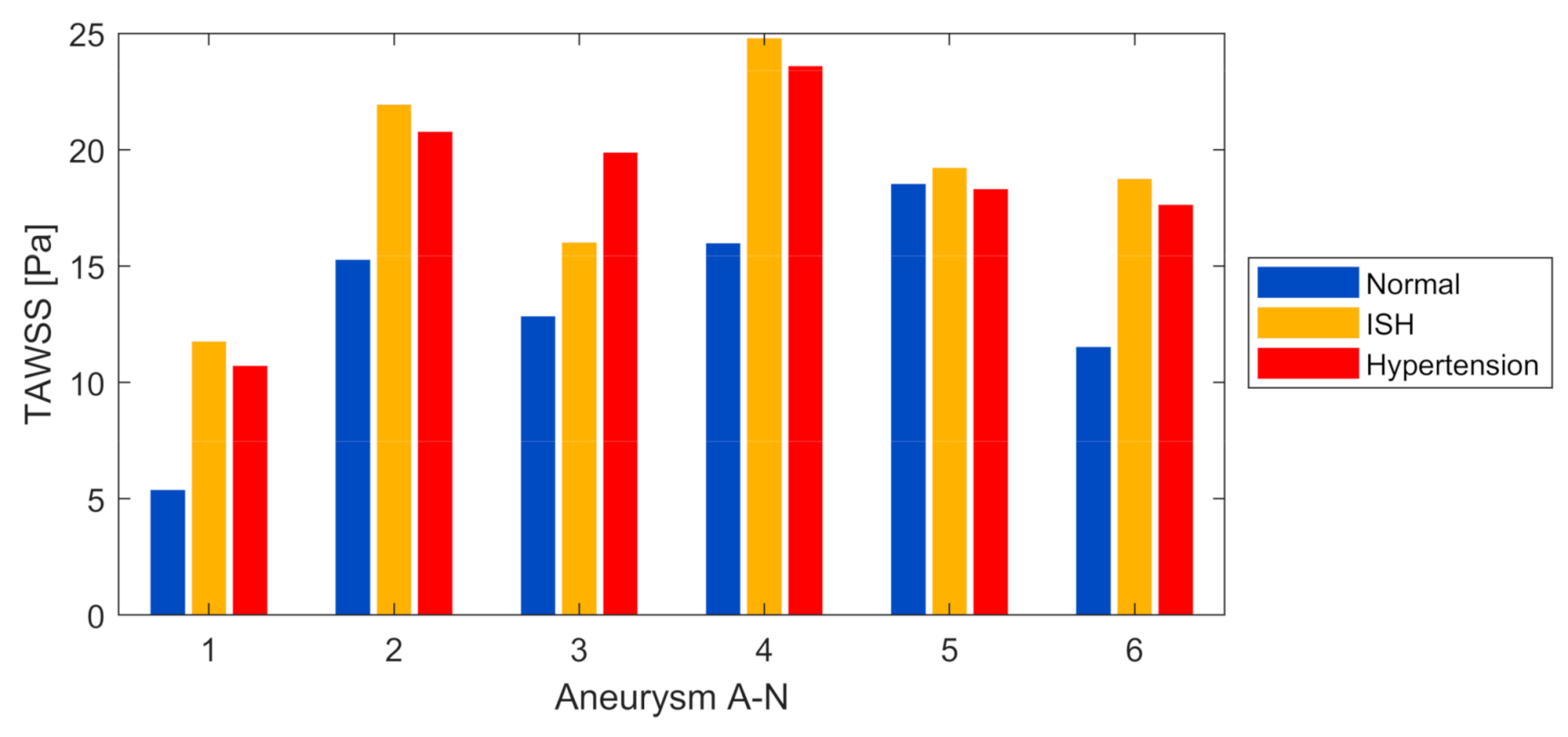
Figure 7 shows the TAWSS magnitude on the aneurysm surface of each model, as well as for each pressure condition under study. As can be seen, in 5 of 6 models, the ISH condition presented the highest values, up to almost 120% higher than in the normal condition. This is curious and interesting since, intuitively, it could be expected that the highest TAWSS presented the condition with highest pressures (hypertension), a situation that did not occur. This exception occurred in the A-3 model, where the hypertension condition presented the highest magnitude, followed by ISH. Moreover, in A-5 there were only minor changes between the three different pressure conditions, and with hypertension presenting a slightly decrease in contrast to a normal condition. This behavior for A-3 and A-5 model showed that fluid–solid interaction phenomena and so the hemodynamics effects and magnitudes on the arterial wall were strongly dependent on the aneurysm type and geometry. Nevertheless, that in 5 of 6 models the ISH presented the highest wall shear stress magnitude could be an important result that should be validated through analysis of a higher number of cerebral aneurysm models, and thus, establish a possible trend in the hemodynamic behavior.
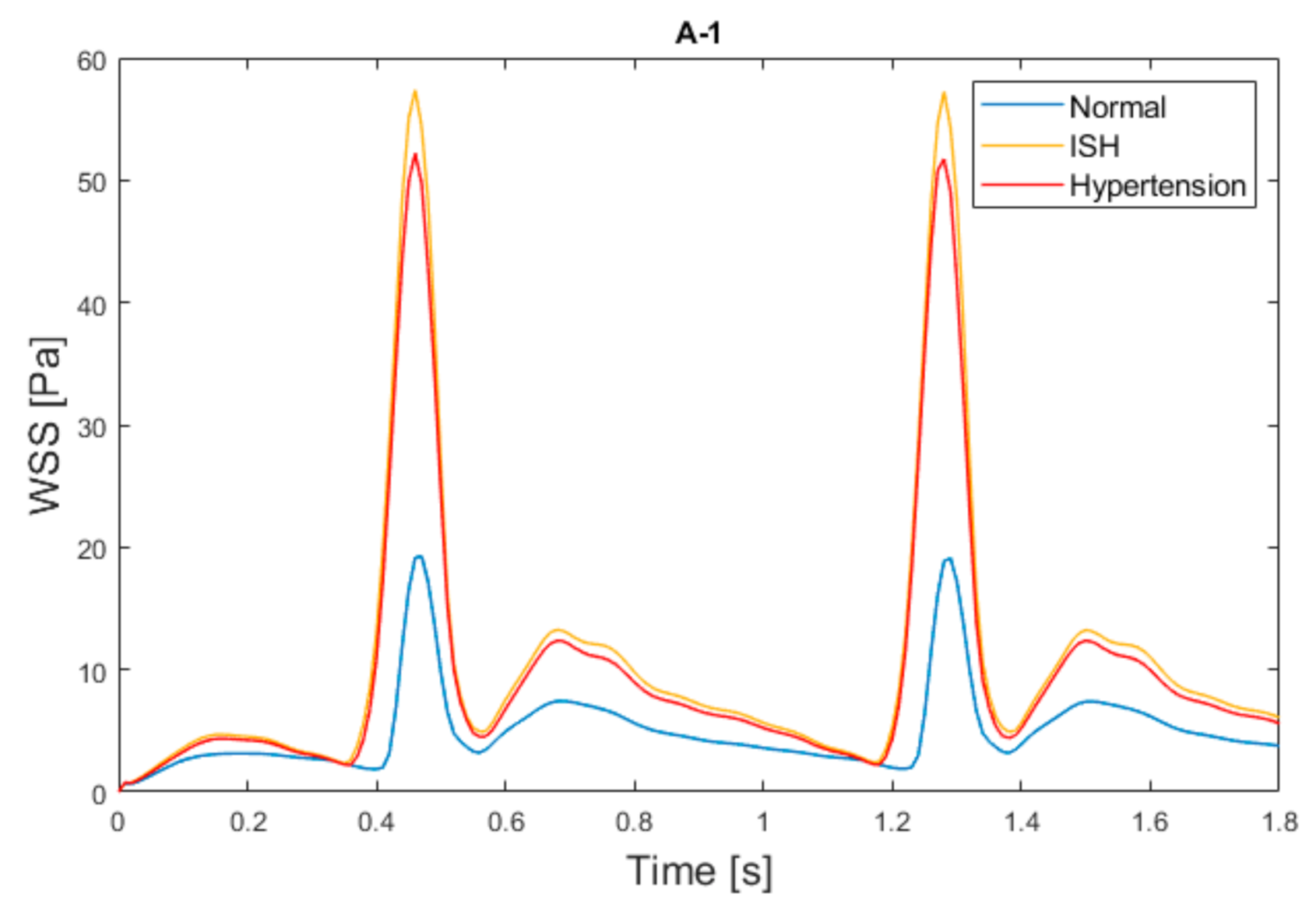
Figure 8 shows the magnitude of the WSS for the A-1 model at the two cardiac cycles of the simulation, where it is clearly observable how the wall shear stresses increased drastically at systole time when passing from the normal condition to a hypertension condition, and even more when passing to a ISH condition.
More specifically,
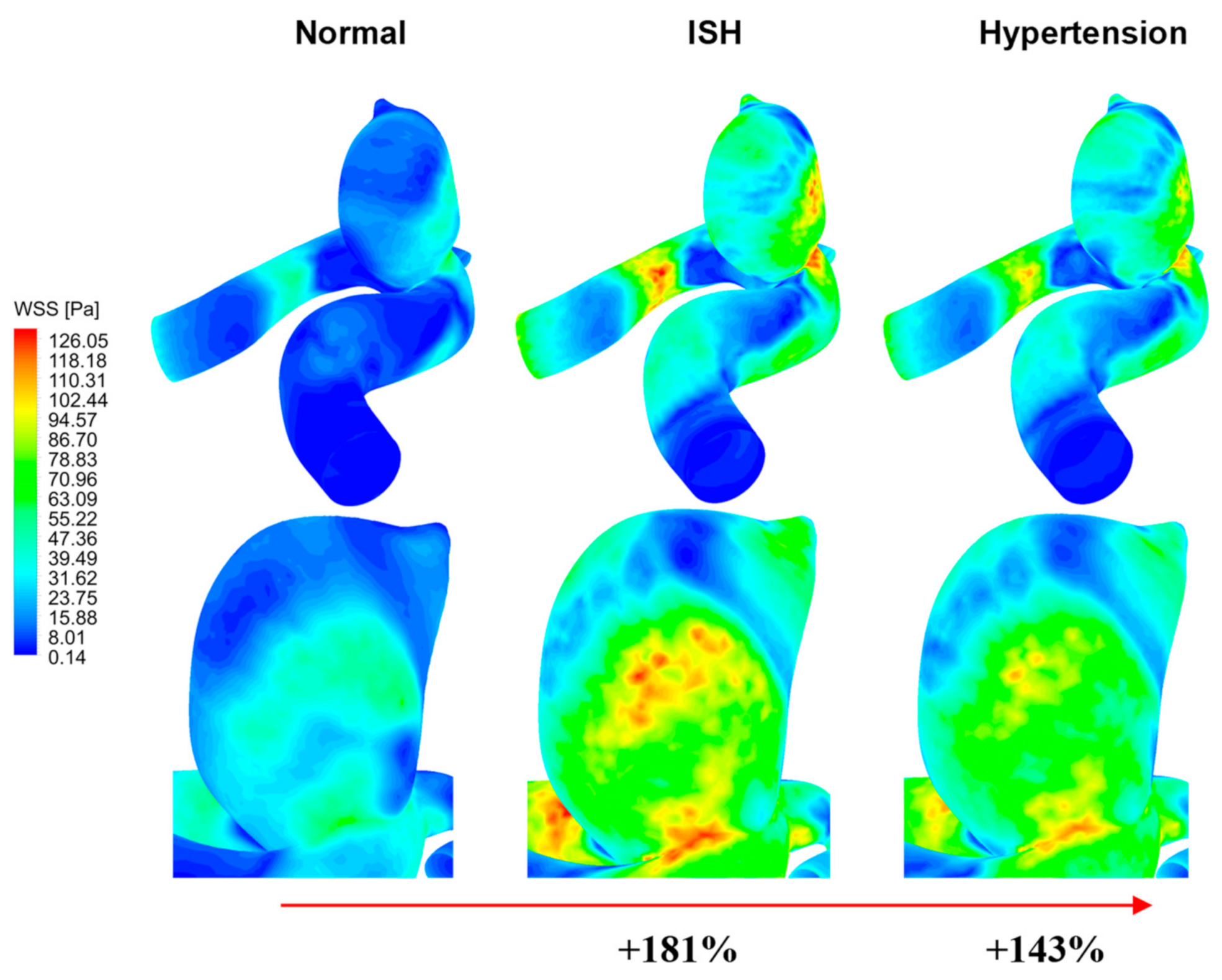
Figure 9 shows the magnitude and wall surface distribution of the WSS at systole of the cardiac cycle (SWSS) for the A-1 model, where it is possible to appreciate how the wall shear stresses increased drastically when passing from the normal condition to a ISH or hypertension condition. At this stage of the cardiac cycle, the ISH condition presented averaged shear stresses up to 180% higher than in the normal condition, and ~40% higher than the hypertension condition.
Analogous to the previous parameter, in
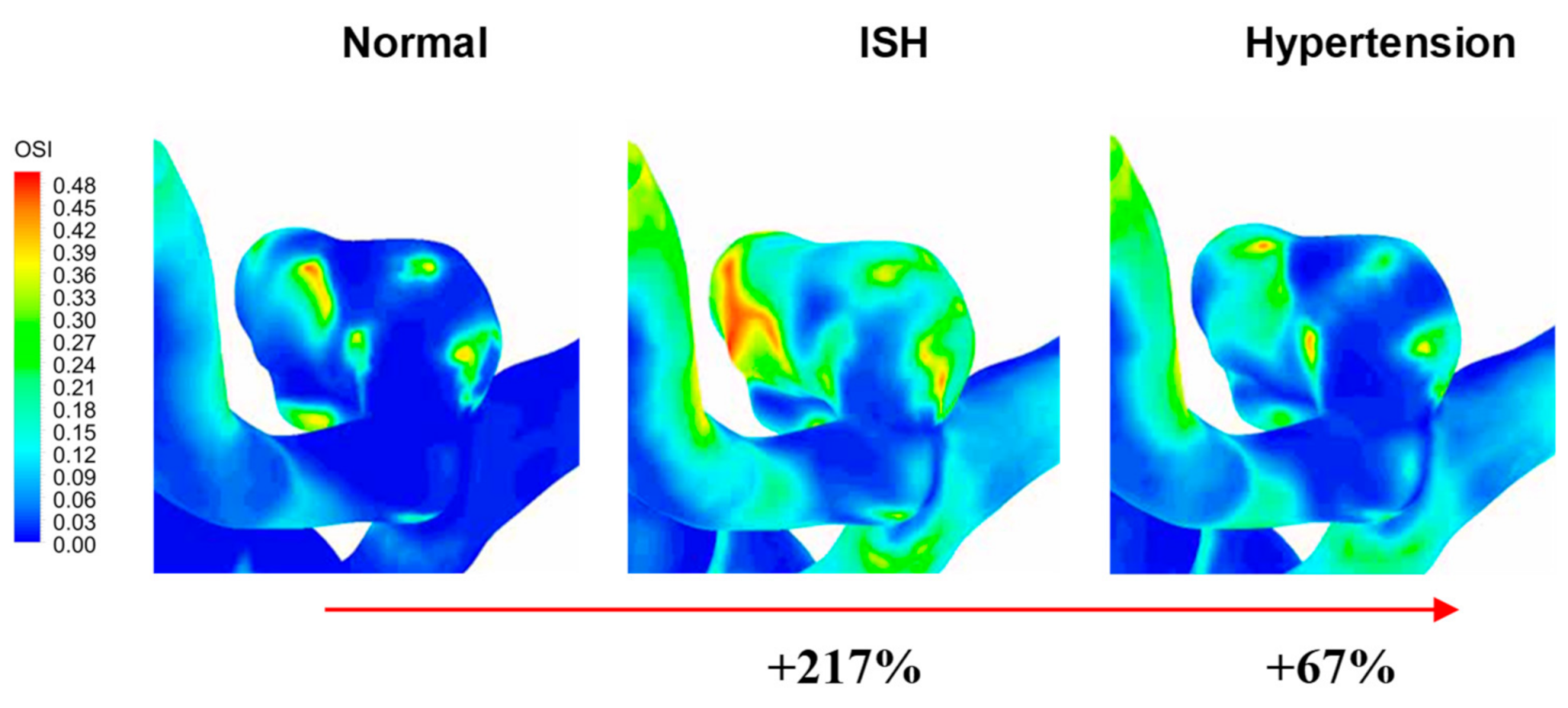
Figure 10, the OSI magnitude is presented, where it is possible to observe how there was a considerable increase when passing to an ISH condition and hypertension, except for the A-1 model (ruptured) where there were minor changes. At the same time, it is once again interesting to notice that in 5 of the 6 models the ISH condition presented the highest magnitudes, with increases in the OSI of up to 300% compared to a normal condition. As an example, in
Figure 11 the magnitude and distribution of the OSI for the A-3 model is presented, and it is clearly observable how the ISH condition presented a drastic increase with respect to the normal condition, as well as when compared to the hypertensive condition. Likewise, as TAWSS, this variable result showed that abrupt hemodynamic changes may occur, depending on the type of aneurysm and its geometry. Furthermore, it is possible to appreciate the complex changes in the OSI distribution on aneurysm surface, such as, for example, in the location where the maximum OSI occurred in the normal condition (0.48), as it turned to be lower in ISH (0.12) and in hypertension (0.25).
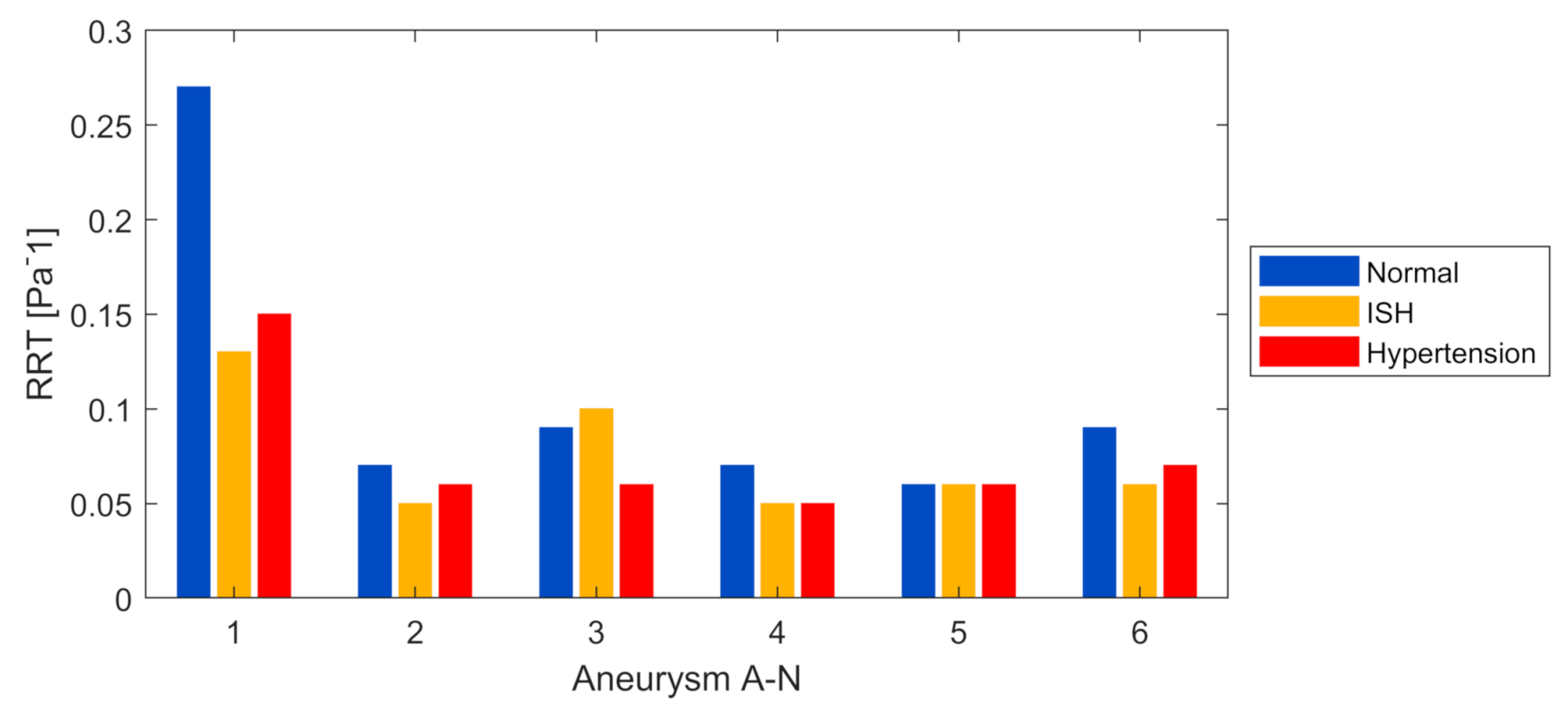
Moreover, in
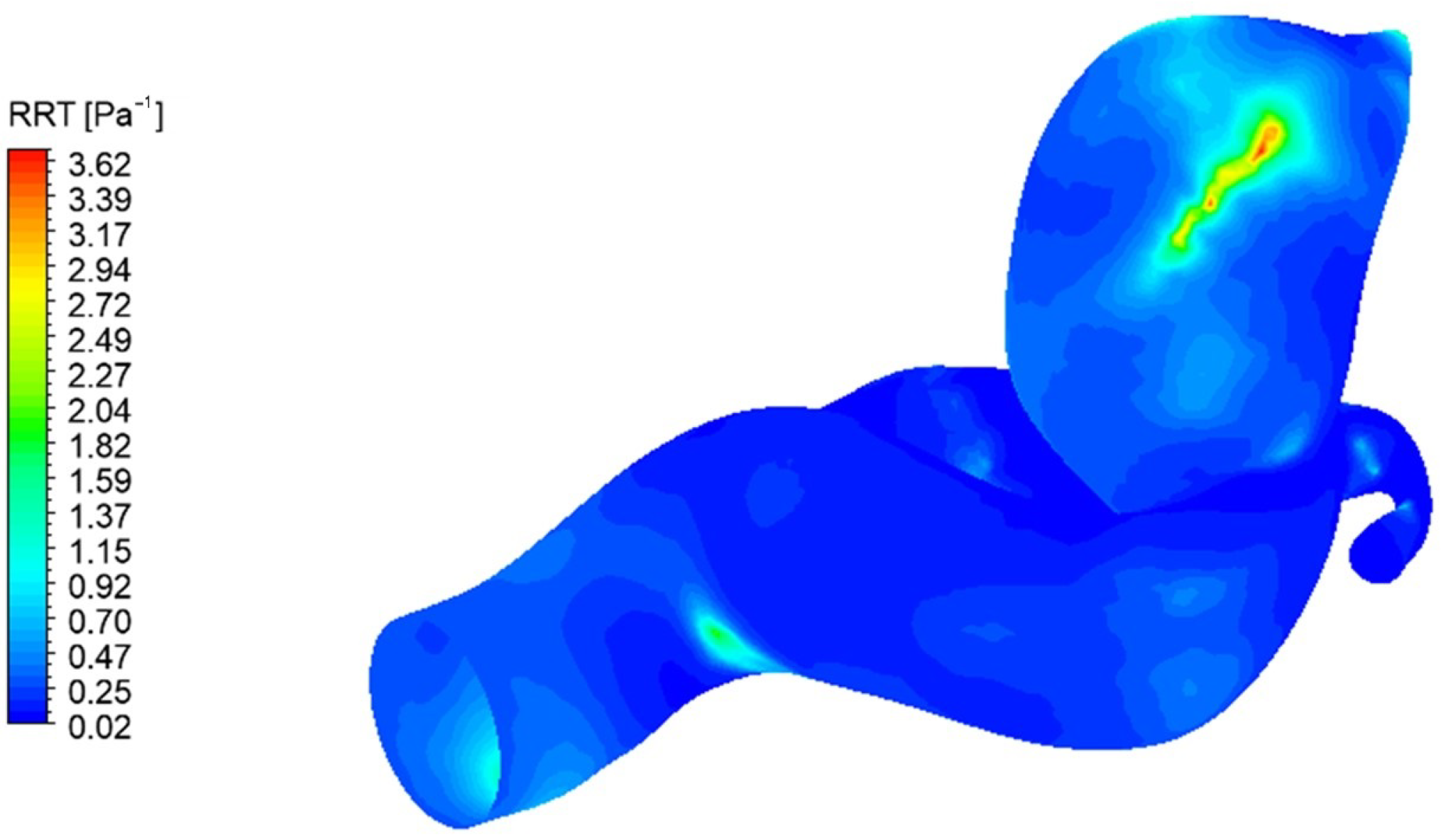
Figure 12 the RRT magnitude is shown, and it is possible to observe that a decrease occurred when passing to an ISH condition and hypertension, with differences of up to almost 52% in ISH. These results aim to determine in future studies what is the implication of this parameter decrease and its effects on the remodeling of the endothelial wall. It should be noted that, for the normal condition, the A-1 model (ruptured) clearly presents the highest RRT of all models. Analyzing this in more detail,
Figure 13 showed the magnitude and distribution of the RRT at normal condition for A-1. Here, it can be observed that, in general, the model presents low RRT, concentrating the greater magnitudes in a very specific and small area at the aneurysm location. Previous studies have related this parameter to possible thin-walled areas, in conjunction with a weakening and increased rupture risk [
28,
29].
The reason for these interesting behaviors could be explained by the fact that the ISH condition, despite not being the highest pressure condition, is the condition that presents the greatest pressure range between diastole and systole of the cardiac cycle (range approximately 90 mmHg). As a result, it is also the condition with the greatest range of displacements and deformations of the arterial wall, which implies a bigger expansion in the fluid domain that would promote more and smoother movement of the blood flow with less deceleration. Having higher velocities inside the domain and, thus, higher shear stresses, is reflected in the WSS, TAWSS, OSI and RRT, which could result in adverse changes from a hemodynamic point of view and its interaction with the endothelium wall. This should not be treated as a general behavior, but it does lead to question at which point this expansion causes this effect and not the opposite, i.e., that too much increase in area due to arterial expansion would actually lead to a decrease in blood flow velocity. It should be noted that in this study a high intracranial pressure (IICP) was used. Therefore, in conditions with lower intracranial pressure, greater displacements could be expected, and, therefore, even more adverse changes.
On the other hand, this study has some limitations and considerations. Only six aneurysm models were studied and, as noted before, in order to validate the behavior exhibited here, a higher number of cases will be needed for future studies. In regard to the conditions, we used the same boundary conditions for all models and a constant external pressure. For the aneurysm thickness we considered it as a constant value at the entire geometry, being this an important simplification because is known that thickness is variable, with thin-walled regions at the aneurysm location. This thickness consideration was used for two reasons: the challenge that implies modelling a variable thickness, and the lack of enough patient data from bibliography and measurements. Concerning the mechanical boundary conditions, the fixed support at inlet and outlets faces is an important consideration that might influence the results, but there is no alternative condition to be imposed.
In regard to the results validation, computational modeling of an intracranial aneurysm can determine its hemodynamic parameters by means of declaring subject-specific boundary conditions, geometry-image reconstruction, the accuracy of spatial and temporal discretization and flow parameters. An important stage in the numerical simulations is the validation of them with either in vitro or in vivo measurements techniques. Berg et al. establishes that, in general, a good agreement between well-conducted numerical study and experimental measurements can be achieved, but quantitative discrepancies still remain [
30]. Many validation studies are limited to the restricted flow conditions of a single case [
31,
32,
33,
34]. However, they showed a good agreement with experimental data obtained through different methods: 4R-MRI, PIV, computer rotational angiography, MR velocimetry measurements. These techniques possess limitations as well and might not be able to capture some flow structures that can be visualized by numerical simulation.
According to the above, it is not yet possible to come to a conclusion for the global validity of hemodynamics simulations. The limitations in regard to an appropriate validation still remain at the moment, and this is the reason why in vitro and in vivo measurement techniques must be improved.