A Risk Assessment for Ozone Regulation Based on Statistical Rollback
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Statistical Rollback Approach
2.1. Quantile Matching Approach
- Based on current ozone levels , estimate parameters (i.e., ).
- Compute , the quantile of such thatfor .
- Estimate parameters under new scenario (i.e., ).
- Determine the corresponding satisfyingfor .
- are adjusted (rollback) values of .
2.2. Weibull Approach in Rollback
2.3. Log-Normal Approach in Rollback
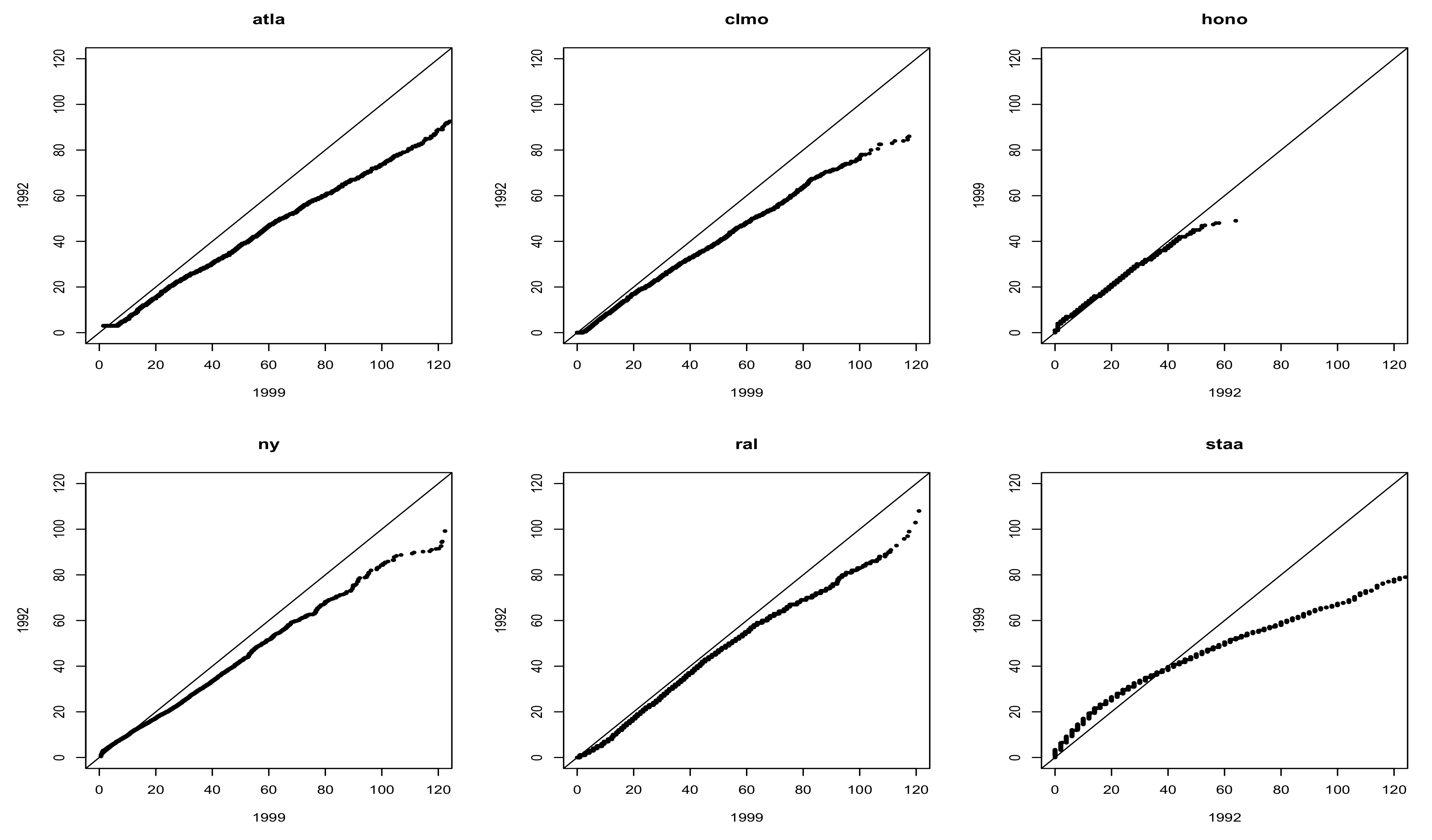
3. Application to NMMAPS Data
3.1. Statistical Modeling
3.2. Inferences
4. Results
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- US Environmental Protection Agency. National Ambient Air Quality Standards for ozone, final rule. Fed. Regist. 1997, 62, 38855–38896. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Z. Ozone pollution: A major health hazard worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samet, J.M. Ozone and respiratory health. The story continues. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 272–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A.; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostro, B.; Chestnut, L. Assessing the health benefits of reducing particulate matter air pollution in the United States. Environ. Res. 1998, 76, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.I.; Carrothers, T.J.; Tuomisto, J.T.; Hammitt, J.K.; Evans, J.S. Assessing the public health benefits of reduced ozone concentrations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F. Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 292, 2372–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; Peng, R.D.; Dominici, F. The Exposure-Response Curve for Ozone and Risk of Mortality and the Adequacy of Current Ozone Regulations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T. A Guide to Selected Algorithms, Distributions, and Databases Used in Exposure Models Developed by the Office Air Quality Planning and Standards; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- National Morbidity Mortality and Air Pollution Study (NMMAPS) Database. Available online: http://www.ihapss.jhsph.edu/ (accessed on 28 October 2004).
- Samet, J.M.; Zeger, S.L.; Dominici, F.; Curriero, F.; Coursac, I.; Dockery, D.W.; Schwartz, J.; Zanobetti, A. The National Morbidity, Mortality, and Air Pollution Study. Part II: Morbidity and mortality from air pollution in the United States. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2000, 94, 5–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J.A. Generalized Linear Models; Chapman & Hall/CRC: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Everson, P.J.; Morris, C.N. Inference for multivariate normal hierarchical models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2000, 62, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
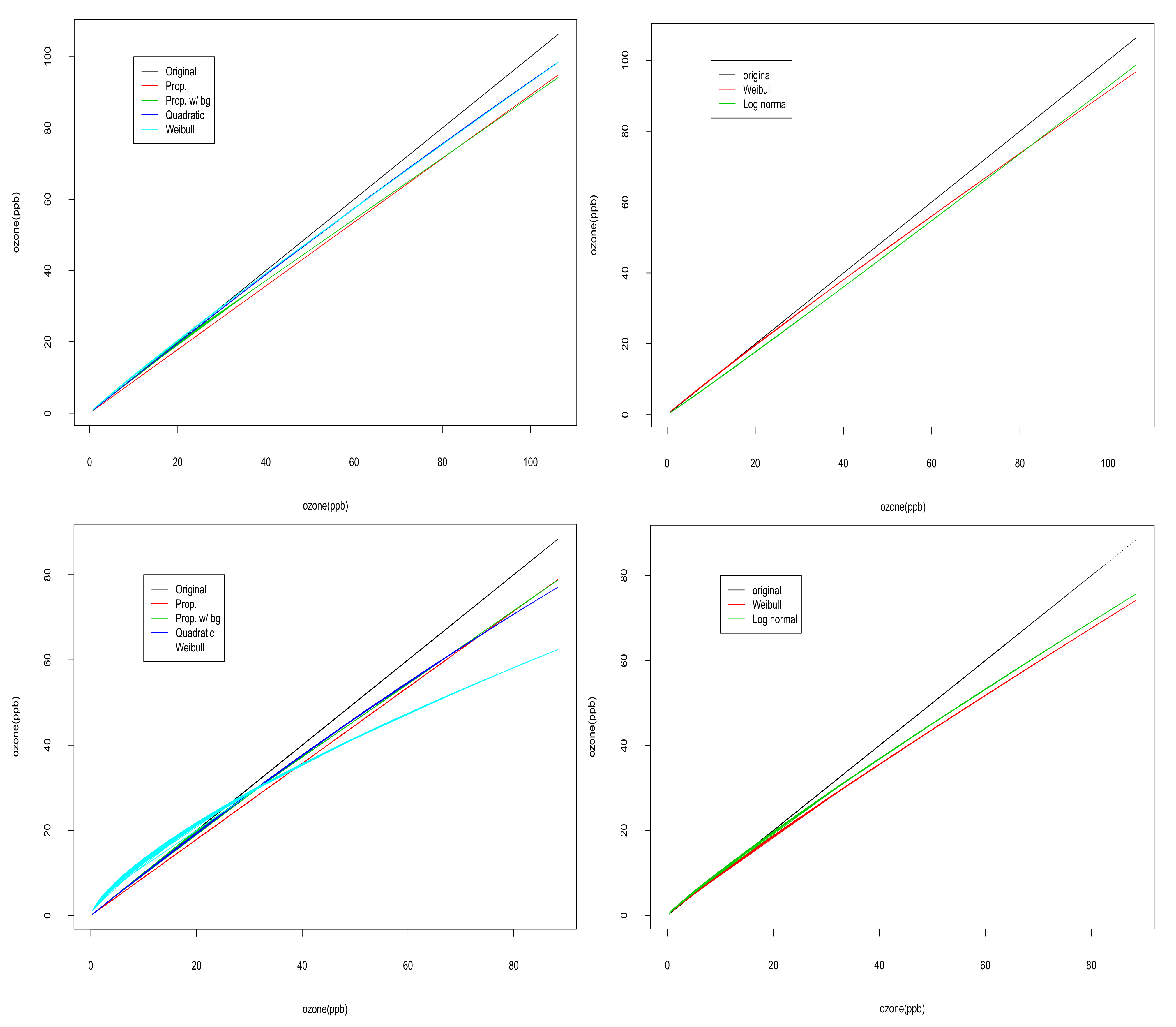
| Model | Reg. | Prop. | Prop. w/ BG | Quadratic | Weibull | Stat.W | Stat.LN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| level 75 | 1.87 | 1.09 | 0.95 | –0.62 | 0.98 | 0.94 | |
| (1.07, 2.62) | (0.62, 1.53) | (0.54, 1.35) | (–1.18, –0.11) | (0.52, 1.37) | (0.49, 1.33) | ||
| CDL | level 70 | 2.86 | 1.66 | 1.46 | 0.60 | 1.51 | 1.47 |
| (1.65, 4.09) | (0.95, 2.39) | (0.84, 2.08) | (0.10, 1.09) | (0.88, 2.14) | (0.83, 2.10) | ||
| level 60 | 4.92 | 2.86 | 2.51 | 2.98 | 2.61 | 2.54 | |
| (2.84, 7.02) | (1.64, 4.09) | (1.43, 3.61) | (1.53, 4.30) | (1.48, 3.75) | (1.46, 3.65) | ||
| level 75 | 1.91 | 1.11 | 0.98 | –0.62 | 1.03 | 0.98 | |
| (1.15, 2.72) | (0.66, 1.59) | (0.58, 1.39) | (–1.17, –0.07) | (0.63, 1.44) | (0.59, 1.40) | ||
| UDL | level 70 | 2.92 | 1.70 | 1.49 | 0.59 | 1.58 | 1.52 |
| (1.66, 4.14) | (0.97, 2.41) | (0.84, 2.10) | (0.10, 1.09) | (0.92, 2.18) | (0.85, 2.13) | ||
| level 60 | 5.01 | 2.92 | 2.56 | 3.05 | 2.79 | 2.60 | |
| (2.93, 7.19) | (1.66, 4.23) | (1.49, 3.70) | (1.73, 4.38) | (1.72, 3.93) | (1.56, 3.78) |
| Model | Reg. | Prop. | Prop. w/ BG | Quadratic | Weibull | Stat.W | Stat.LN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| level 75 | 1.96 | 1.20 | 0.98 | –0.52 | 1.02 | 0.99 | |
| (1.06, 2.92) | (0.61, 1.79) | (0.51, 1.46) | (–1.33, 0.25) | (0.54, 1.51) | (0.50, 1.48) | ||
| CDL | level 70 | 2.75 | 1.66 | 1.38 | 0.44 | 1.42 | 1.39 |
| (1.47, 4.02) | (0.87, 2.46) | (0.74, 2.03) | (–0.36, 1.26) | (0.78, 2.09) | (0.75, 2.05) | ||
| level 60 | 4.62 | 2.76 | 2.40 | 2.67 | 2.56 | 2.49 | |
| (2.64, 6.69) | (1.58, 4.06) | (1.36, 3.52) | (1.38, 3.99) | (1.52, 3.70) | (1.45, 3.62) | ||
| level 75 | 1.96 | 1.19 | 0.98 | –0.51 | 1.01 | 0.99 | |
| (0.93, 2.91) | (0.52, 1.79) | (0.45, 1.46) | (–1.36, 0.36) | (0.49, 1.49) | (0.50, 1.48) | ||
| UDL | level 70 | 2.78 | 1.69 | 1.40 | 0.45 | 1.44 | 1.41 |
| (1.50, 3.96) | (0.88, 2.42) | (0.74, 1.99) | (–0.42, 1.23) | (0.79, 2.08) | (0.74, 2.03) | ||
| level 60 | 4.81 | 2.88 | 2.50 | 2.79 | 2.62 | 2.58 | |
| (2.66, 7.05) | (1.55, 4.26) | (1.36, 3.70) | (1.41, 4.31) | (1.49, 3.84) | (1.44, 3.79) |
| Covariate | Reg. | Prop. | Prop. w/ BG | Quadratic | Weibull | Stat.W | Stat.LN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | level 75 | 1.96 | 1.20 | 0.98 | –0.52 | 1.02 | 0.99 |
| Ave | (1.06, 2.92) | (0.61, 1.79) | (0.51, 1.46) | (–1.33, 0.25) | (0.54, 1.51) | (0.50, 1.48) | |
| level 60 | 4.62 | 2.76 | 2.40 | 2.67 | 2.56 | 2.49 | |
| (2.64, 6.69) | (1.58, 4.06) | (1.36, 3.52) | (1.38, 3.99) | (1.52, 3.70) | (1.45, 3.62) | ||
| Daily | level 75 | 2.32 | 1.91 | 1.66 | 2.48 | 2.12 | 2.09 |
| Max | (1.54, 3.14) | (1.26, 2.59) | (1.09, 2.27) | (1.62, 3.40) | (1.59, 2.79) | (1.55, 2.73) | |
| level 60 | 6.19 | 5.10 | 4.25 | 5.13 | 4.87 | 4.59 | |
| (4.11, 8.31) | (3.33, 6.87) | (2.79, 5.75) | (3.41, 6.91) | (3.38, 6.35) | (3.09, 6.06) | ||
| Daily | level 75 | 2.10 | 1.61 | 1.36 | 1.90 | 1.56 | 1.52 |
| 8 h Max | (1.26, 2.92) | (0.96, 2.23) | (0.79, 1.94) | (1.13, 2.67) | (0.96, 2.15) | (0.94, 2.12) | |
| level 60 | 5.53 | 4.23 | 3.43 | 4.34 | 3.67 | 3.55 | |
| (3.37, 7.50) | (2.52, 5.76) | (1.99, 4.69) | (2.52, 5.91) | (2.26, 4.94) | (2.14, 4.81) |
| Covariate | Reg. | Prop. | Prop. w/ BG | Quadratic | Weibull | Stat.W | Stat.LN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bayesian | level 75 | 1.96 | 1.20 | 0.98 | –0.52 | 1.02 | 0.99 |
| (1.06, 2.92) | (0.61, 1.79) | (0.51, 1.46) | (–1.33, 0.25) | (0.54, 1.51) | (0.50, 1.48) | ||
| level 60 | 4.62 | 2.76 | 2.40 | 2.67 | 2.56 | 2.49 | |
| (2.64, 6.69) | (1.58, 4.06) | (1.36, 3.52) | (1.38, 3.99) | (1.52, 3.70) | (1.45, 3.62) | ||
| MLE | level 75 | 2.23 | 1.31 | 1.09 | –0.30 | 1.21 | 1.19 |
| (1.14, 3.21) | (0.62, 1.91) | (0.54, 1.58) | (–1.15, 0.48) | (0.66, 1.70) | (0.64, 1.69) | ||
| level 60 | 5.07 | 2.93 | 2.52 | 3.03 | 2.56 | 2.52 | |
| (3.00, 7.28) | (1.65, 4.29) | (1.42, 3.68) | (1.69, 4.37) | (1.49, 3.73) | (1.39, 3.69) | ||
| Pooled | level 75 | 1.92 | 1.16 | 0.95 | –0.50 | 1.15 | 1.10 |
| MLE | (1.79, 2.05) | (1.09, 1.24) | (0.89, 1.02) | (–0.61, –0.38) | (1.08, 1.22) | (1.04, 1.18) | |
| level 60 | 4.65 | 2.78 | 2.40 | 2.69 | 2.49 | 2.44 | |
| (4.37, 4.92) | (2.62, 2.93) | (2.27, 2.54) | (2.48, 2.88) | (2.38, 2.62) | (2.32, 2.59) |
| Prop. | Prop. w/ BG | Quadratic | Weibull | Stat.W | Stat.LN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With High Temp | 1.96 | 1.20 | 0.98 | –0.52 | 1.02 | 0.99 |
| (1.06, 2.92) | (0.61, 1.79) | (0.51, 1.46) | (–1.33, 0.25) | (0.54, 1.51) | (0.50, 1.48) | |
| Without High Temp | 1.39 | 0.83 | 0.67 | –0.47 | 0.75 | 0.71 |
| (0.33, 2.41) | (0.15, 1.46) | (0.15, 1.17) | (–1.36, 0.45) | (0.22, 1.26) | (0.18, 1.22) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Lee, J. A Risk Assessment for Ozone Regulation Based on Statistical Rollback. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052388
Kim Y, Lee J. A Risk Assessment for Ozone Regulation Based on Statistical Rollback. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052388
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yongku, and Jeongjin Lee. 2021. "A Risk Assessment for Ozone Regulation Based on Statistical Rollback" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052388
APA StyleKim, Y., & Lee, J. (2021). A Risk Assessment for Ozone Regulation Based on Statistical Rollback. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052388





