Abstract
There are many parameters that could affect the properties of asphalt mixtures, such as the fiber additive, gradation type, nominal maximum aggregate size (NMAS), and asphalt. To evaluate the influence of these factors on the crack resistance of asphalt mixture, 10 different types of asphalt mixtures were prepared. The indirect tensile asphalt cracking test (IDEAL-CT) and semi-circle bending test (SCB) were adopted to test the anti-cracking ability of the test samples. The parameters of these two test results were also used to conduct the correlation analysis to find the correlation between different parameters, and scanning electron microscope (SEM) test was also used to analyze the micro cracks of asphalt mixture. The results showed that basalt fiber could further enhance the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixture. Stone matrix asphalt (SMA) showed better anti-cracking performance than Superpave (SUP) asphalt mixtures. The increase in the nominal maximum aggregate size could decrease the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene (SBS) modified asphalt could better reinforce the anti-cracking ability than pure asphalt. The CTindex of IDEAL-CT test and Flexibility index (FI) value of SCB test results showed better correlation. This paper has certain significance in guiding the design of asphalt mixtures having good crack resistance.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of modern economy, the infrastructures such as highways are being paid more and more attention. There are now more and more highways being built all over the world and most of the highways are flexible roads which are made of asphalt mixtures [1,2,3]. The rising of the traffic volume and the traffic load, etc., are making the asphalt pavement suffer from various distresses such as cracking, raveling, and rutting [4,5,6], etc. The initial distresses of the asphalt pavement are often in the form of cracking which might be induced from the thermal stress [7,8] and the accumulation of traffic load or heavy traffic load [9], etc. The cracking on the road will make the asphalt materials structure suffer from stress concentration [10,11,12], which could make the road being more vulnerable and could further induce more distresses. Therefore, it is very essential and necessary for us to pay more attention to the enhancement of the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures.
Asphalt mixtures consist of different components such as aggregate, asphalt, additives, and have different characteristics such as gradation type, nominal maximum aggregate size. The components and the characteristics of asphalt mixtures could greatly affect the crack resistance of asphalt mixtures. Therefore, the factors such as fiber additive [13], gradation type [14], nominal maximum aggregate size [15], and asphalt [16] were chosen to systematically evaluate their impacts on the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. The comprehensive study of the effect of these factors on the anti-cracking property of asphalt mixtures are very important in guiding the future design of asphalt pavement that could have good anti-cracking ability.
Nowadays, many researchers have been using different fiber additives such as polymer fiber [17], plant fiber [18], and mineral fiber [19] to enhance the properties of asphalt mixtures. Mineral fiber is more eco-friendly than the polymer fibers because the production process of mineral fiber have less by-products than the polymer fibers. In the meantime, mineral fiber also has better strength than plant fiber [20]. Therefore, mineral fiber is being paid more attention nowadays in the enhancement of asphalt mixtures because the use of mineral fiber could meet the requirement of sustainable economy and development. Basalt fiber is a kind of mineral fiber and it has excellent strength, good acid and alkali resistance and temperature stability [21,22,23], etc. Recently, it has been attracting more and more attention. Therefore, this paper adopted basalt fiber to study the enhancement effect of it on the anti-cracking ability of different asphalt mixtures and to conclude the enhance pattern of it on these mixtures. Different gradations could result in different inner stress inside the asphalt mixtures when the other parameters are the same, because the inner structure of asphalt mixtures are different when the gradation types are different. The inner stress differences of the asphalt mixtures could result in different anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. Therefore, this paper chose the commonly used gradation types (SMA and SUP asphalt mixtures) to study the effect of gradation type on the properties of asphalt mixtures. Even when the gradations are the same, the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures could also be influenced by the nominal maximum aggregate size which is a very important index in the asphalt mixture. Because the NMAS could greatly influence the overall distribution of the aggregates in the asphalt mixtures, which could affect the stress dispersion characteristics inside the asphalt mixtures and further affect the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. Furthermore, as a very essential component of the asphalt mixtures, the asphalt type also could influence the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures because the role of the asphalt inside the asphalt mixtures is the binder. It helps to bond the aggregates together and helps to transfer stress inside the asphalt mixtures. These are the reasons why this paper chose to study the effect of these factors on the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures.
When it comes to the testing method of anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. There are now two modern ways to reveal the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. The first one is called IDEAL test [24] and the second test is called Semi-Circle Bending (SCB test) [25]. Some researchers have compared the IDEAL test indexes and the SCB test indexes with the test indexes of other normal test methods such as the four-point trabecular bending test, overlay test, and indirect tensile test, etc., and found that some of the IDEAL test index and SCB test index have a good correlation with the test indexes of other test [26,27]. However, the study about the correlation between the indexes of IDEAL and SCB test are very limited. The correlation analysis between the test indexes of IDEAL and SCB test could make it more clear when using these two methods together to comprehensively evaluate the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures.
Therefore, in this paper, in order to study the effect of basalt fiber on the anti-crack ability of several common used asphalt mixtures, the common used gradations such as SMA-13, SUP-13, SUP-20, and SUP-25 were adopted to study the enhancement effect of basalt fiber on the anti-cracking ability of these asphalt mixtures. With the aim to find the impact of the gradations on the anti-crack ability of asphalt mixtures, two different asphalt mixtures (SMA-13 and SUP-13) without basalt fiber and with the same content of basalt fiber were used to study the effect of gradation type on the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. Meanwhile, in order to conclude the effect of maximum nominal bonding stress on the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures, the SUP-13, SUP-20 with SBS modified asphalt and SUP-20, SUP-25 with pure asphalt (non-modified asphalt) were compared separately. SUP-20 mixtures and basalt fiber reinforced SUP-20 mixtures using SBS modified asphalt and pure asphalt were used to study the effect of asphalt type on the cracking resistance. Additionally, the correlation analysis between the test indexes of IDEAL test and SCB test were adopted to find the most relevant test indexes in these two tests. The findings of this work provide a significant reference for the design of asphalt mixtures having good crack resistance.
2. Experimental Study
2.1. Materials and Mixture Design
2.1.1. Asphalt
In this paper, the pure asphalt was provided by the Nanjing Jinling Asphalt Industry Co., Ltd., Nanjing, Jiangsu, China. SBS modified asphalt was provided by Jiangsu Baoli asphalt Co., Ltd., Wuxi, Jiangsu, China. The properties of the pure asphalt and SBS modified asphalt provided by the manufacturers were listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Properties of pure asphalt and SBS modified asphalt.
2.1.2. Basalt Fiber
Basalt fiber (BF) used in this paper was provided by Jiangsu Tianlong Basalt Continuous Fiber Co., Ltd., Yizheng, Jiangsu, China. The properties of BF provided by the manufacturer were shown in Table 2. The macro image and the micro image of BF is shown in Figure 1a,b. Figure 1 shows that basalt fiber has a hard texture and the basalt fibers are very uniform.

Table 2.
Properties of basalt fiber.
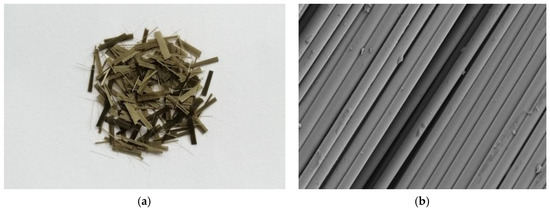
Figure 1.
Image of basalt fiber: (a) Macro image; (b) Micro image.
2.1.3. Lignin Fiber
Lignin fiber (LF) adopted in this paper was provided by the JRS company of Germany. The properties of it was shown in Table 3. As can be seen from Figure 2 that the texture of LF is very soft and the lignin fibers could curl with each other.

Table 3.
Properties of lignin fiber.

Figure 2.
Image of lignin fiber: (a) Macro image; (b) Micro image.
2.1.4. Mixture Design
The gradations used in this paper were some commonly used gradations used in the upper layer (SMA-13 and SUP-13), middle layer (SUP-20), and lower layer (SUP-25) [28,29]. The gradation curves of SMA-13, SUP-13, SUP-20, and SUP-25 were shown in Figure 3. Figure 3a shows the gradation curve of SMA-13 asphalt mixtures, and the three red lines are the upper, middle, and lower limit of the SMA-13 mixtures, the blue line is the synthetic gradation curve. Figure 3b–d is the gradation curve of SUP-13, SUP-20, and SUP-25 asphalt mixtures, and the red points in these graphs are the control point of the limit of the content of certain aggregate with different sizes. The asphalt mixtures with and without basalt fiber were all designed. According to the former researches, the mass content of basalt fiber was chosen as 0.3% and the optimum basalt fiber length of SUP-13, SUP-20, and SUP-25 were 6, 9, and 12 mm, respectively [30]. Therefore, the basalt fiber length adopted in this study for SUP-13 and SMA-13 was chosen as 6 mm, the basalt fiber length chosen for SUP-20 were 9 mm and the fiber length used in SUP-25 were 12 mm. The mixture design results were listed in Table 4. The mixture design of SMA-13 is in accordance with the Technical Specification for Construction of Highway asphalt pavement (JTG F40-2004) [31], and the design of SUP-13, SUP-20, and SUP-25 asphalt mixtures are in consistence with Superpave guidelines [32]. The optimum asphalt content of SMA-13 asphalt mixtures was determined using the Marshall design method and the optimum asphalt content of SUP-13, SUP-20, and SUP-25 was decided when the air void ratio of the asphalt mixture was 4.0% (using the Superpave guidelines).
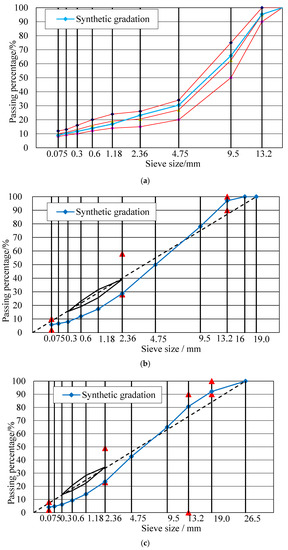
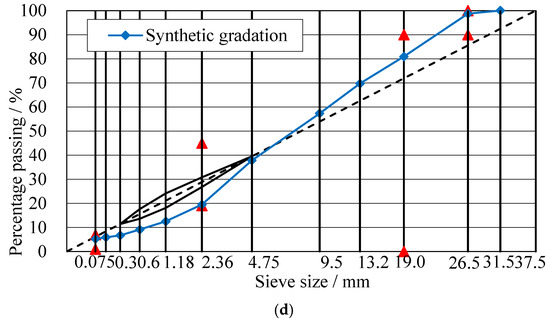
Figure 3.
Gradation curves: (a) SMA-13; (b) SUP-13; (c) SUP-20; (d) SUP-25.

Table 4.
Mixture design results.
2.2. Test Method
2.2.1. IDEAL Test
IDEAL test was a modern method to test the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. The samples did not go through any kind of preparing process before the test (no cutting and drilling, etc.). Thus, the test process could be divided into two phases. As is shown in Figure 4a, P100 is the point when the load is the highest, and P100 represents the load at this point. The left part of the P100 is called the crack initiation stage. The right part of the test was called the crack propagation stage. The specimen thickness is 62 mm and the specimen diameter is 150 mm. The test index adopted in this paper to reveal the anti-cracking ability of the sample in the crack initiation stage is called Ginitial and it is the quotient of integral area of the left part of the load-displacement curve (on the left side of the P100 point) and the product of specimen thickness and diameter (t × D). The integral area of the left part is called Winitial. The index used to reflect the cracking resistance in the crack propagation stage is called CTindex and it is an index revealing the crack propagation rate of the sample. CTindex is an index proposed by American Society of Testing Materials (ASTM) and was defined in Equation (2). It is negatively correlated with the crack propagation rate of asphalt mixture. The equation of the Ginitial and CTindex were shown in Equations (1) and (2). The l75 index in Equation (2) is the displacement when the load in the crack propagation phase is 75% that of the P100. In the equations, Gf is the fracture energy of the whole testing process, |m75| is the value of the slope between PPP85 and PPP65, D is the diameter of the specimen and t is the thickness of the specimen. All the test samples were tested three times and the average value is adopted as the final test result. If the difference between the average value and the single test result is bigger than 10% that of the average value, the whole tests would be re-conducted. The test temperature was 25 °C and the test photo was shown in Figure 4b.
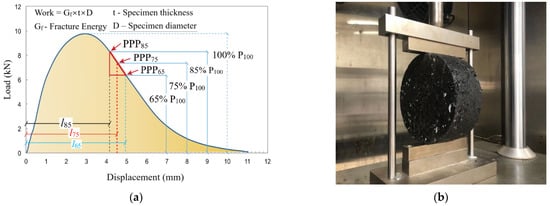
Figure 4.
IDEAL test: (a) Testing curve; (b) Test photo.
2.2.2. SCB Test
Semi-Circle Bending (SCB) test was also a new test method to reveal the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. The shape of the test sample is a semi-circle of which the diameter is 150 mm. The thickness of the sample is 50 mm, the test sample was pre-cut to get an initial crack. The pre-cut length was called the Pre-cut length and the difference between radius and the pre-cut length is called the ligament length. The ligament length area was left for the initial crack to expand. The load-displacement curve of SCB test was shown in Figure 5a and the test photo was shown in Figure 5b. The test indexes used in this test were the fracture energy (Gf) and the FI index. Gf is calculated according to Equation (3). FI is calculated using Equation (4). Wf is the fracture work during the test and is the integral area of the load-displacement curve. Arealig is the product of the ligament length and the thickness (the unit is mm). The index |m| is the slope at the inflection point. A is a unit conversion value and is equal to 0.01. Overall, three parallel tests were conducted and the average value was used as the test result. When the difference between each test results of the same sample and the average value was bigger than 10% that of the average value, the tests would be tested again. Test temperature of SCB test was set as 25 °C and the test photo was illustrated in Figure 5b.
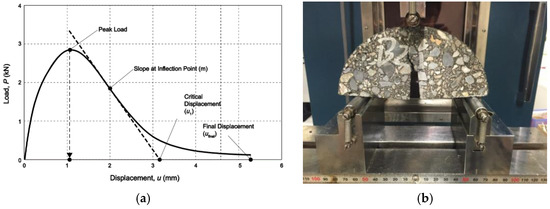
Figure 5.
SCB test: (a) Testing curve; (b) Test photo.
2.2.3. SEM Test
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) test was used in this paper to observe the micro distribution of basalt fibers inside the asphalt mixtures. The Scanning electron microscope used in this study is made by the Philips company Amsterdam, the Netherlands. The cracks of asphalt mixtures with and without basalt fiber was taken to reveal the distribution of basalt fibers between the cracks of mixtures. The asphalt mixture samples after the anti-crack ability test were frozen at −10 °C, and were cut using the precise cutting machine. The crack of the mixture samples and the fiber samples were then being put onto an observation tablet and were plated by gold powder using the vacuum coating machine. After the preparation process, the tablet was put into the observation chamber of the SEM. The micro images of the cracks and the fibers were acquired through the computer connected with the SEM.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. IDEAL Test
3.1.1. Effect of Basalt Fiber on the IDEAL Test Result
As it can be seen from Table 4, there are 10 kinds of different mixtures and the mixtures can be further divided into five kinds of different mixtures using a larger classification method (SMA-13 using SBS modified asphalt, SUP-13 using SBS modified asphalt, SUP-20 using pure asphalt, SUP-20 using SBS modified asphalt and SUP-25 using pure asphalt), and each kind of these mixtures have two types (with and without basalt fiber). IDEAL cracking test results and standard deviation are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. It can be concluded from Figure 6 that the Ginitial index increased after adding basalt fibers. The increasing extent of the sample 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 are 15.4, 11.9, 19.6, 9.3, and 13.6%, respectively. Thus, the basalt fiber can well enhance the initial-cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. This is mainly because basalt fiber has a very good mechanical property and it could help disperse the stress inside the asphalt mixtures during the crack forming process [20]. The added energy appeared in the test result is caused by the adhesion between basalt fiber and asphalt and the basalt fiber itself. It can also be seen from Figure 7 that the basalt fiber could help slow down the crack propagation rate. Figure 8 illustrates the cracks of asphalt mixtures with and without fiber, respectively, as shown in Figure 8, basalt fiber could act as a bridge to bond the crack and slow down the development of the crack when there was a minor crack occurred. Basalt fiber could bear some stress [20] inside the asphalt mixtures and could enhance the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. The bonding between the basalt fiber and the asphalt also contribute to the delaying of the propagation rate. Because in the crack propagation process, the viscous asphalt could bond with the basalt fiber, and it could also transfer the stress to the fiber.
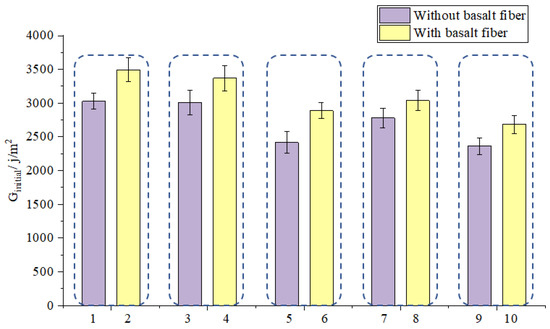
Figure 6.
Effect of basalt fiber on Ginitial.
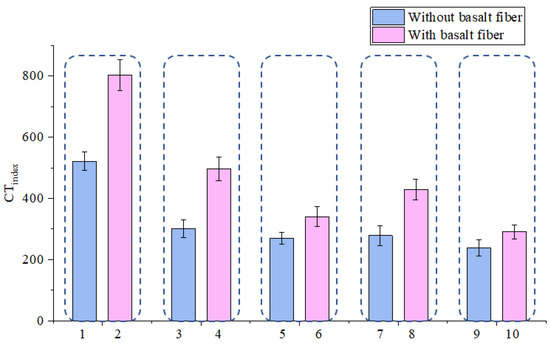
Figure 7.
Effect of basalt fiber on CTindex.
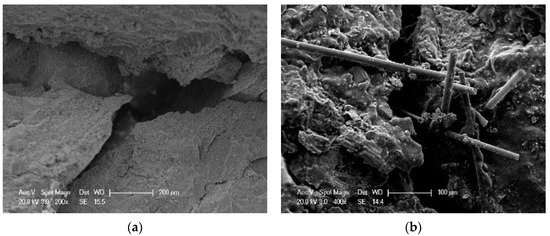
Figure 8.
Cracks of mixtures: (a) without basalt fiber; (b) with basalt fiber.
3.1.2. Effect of Gradation Type on the IDEAL Test Result
As shown in Figure 9, the Ginitial value of sample1 is bigger than that of sample 3 and also the increasing extent of sample 1 after adding basalt fiber are also bigger than that of sample 3 (marked as sample 3 and sample 4) which means that the initial-cracking resistance of SMA-13 mixture is better than that of SUP-13 mixture. As shown in Figure 10, the CTindex of sample 1 is bigger than that of sample 3 which means that SMA-13 mixture has slower crack propagation rate than the SUP-13 mixture. The reason for this phenomenon is because the SMA asphalt mixture is a kind of mixture that has a dense skeleton structure [33] and the coarse aggregates inside the SMA mixtures are more than the fine aggregate. The coarse aggregate could form a solid skeleton to disperse the stress when there is a force being added on the SMA asphalt mixtures. The lignin fiber is usually used in the SMA mixtures to absorb the asphalt inside the SMA asphalt mixtures [34] which could help to enhance the asphalt mortar inside the asphalt mixtures. The lignin fiber helps to absorb the redundant asphalt inside the asphalt mixture and could make the structural asphalt on the surface of the aggregate connect with each other tighter. Because the lignin fibers randomly distribute inside the asphalt binders, which could help to enhance the stress transferring ability of the asphalt binder inside the asphalt mixture and contribute to the connection between the asphalt binder and the structural asphalt on the surface of the aggregates. The solid skeleton structure of it and the asphalt mortar enhanced by lignin fiber helps it to make the anti-crack ability of the SMA mixtures better. Meanwhile, the SUP asphalt mixture is a kind of mixture with suspended dense structure [35]. The gradation curve of it is very uniform and consistent and we could see from Figure 3 that the gradation curve of SUP-13 mixture is more smooth than SMA-13 mixtures. Therefore, the SMA-13 asphalt mixtures have better anti-cracking ability than the SUP-13 asphalt mixtures.
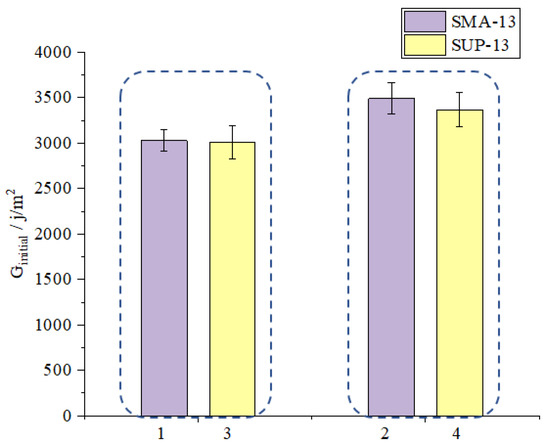
Figure 9.
Effect of gradation type on Ginitial.
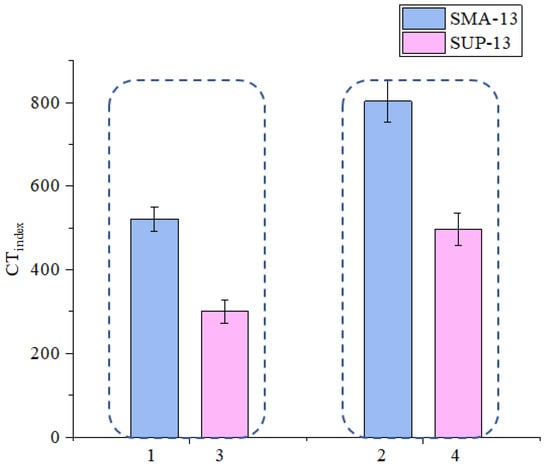
Figure 10.
Effect of gradation type on CTindex.
3.1.3. Effect of NMAS on the IDEAL Test Result
As it can be seen from Figure 11, the Ginitial value of sample 3 is bigger than that of sample 7, and the Ginitial value of sample 5 is bigger than that of sample 9 which indicates that the nominal maximum aggregate size is negatively correlated with the initial-cracking resistance of mixtures. As it can be seen from Figure 12, the CTindex of sample 3 is bigger than that of sample 7, and the CTindex value of sample 5 is bigger than that of sample 9 which means that the nominal maximum aggregate size is positively related with the crack propagation rate of asphalt mixtures. This is mainly because the asphalt mixtures with larger NMAS have lower optimum asphalt content, which is not conducive to crack resistance. The asphalt content is very essential in the crack resistance of asphalt mixtures because asphalt act as a binder inside the asphalt mixtures. The asphalt helps to enhance the crack resistance because it is a kind of viscous material. Therefore, asphalt mixtures having larger NMAS have lower anti-cracking ability.
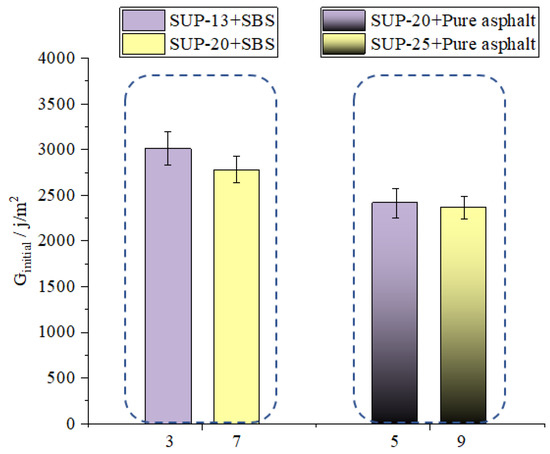
Figure 11.
Effect of NMAS on Ginitial.
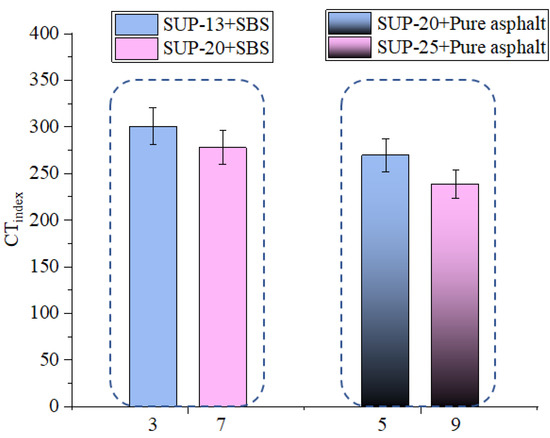
Figure 12.
Effect of NMAS on CTindex.
3.1.4. Effect of Asphalt Type on the IDEAL Test Result
As shown in Figure 13, the Ginitial value of sample 5 is less than that of sample 7 and the increasing extent of sample 5 is also less than that of sample 7 which shows that SBS modified asphalt can better reinforce the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. As shown in Figure 14, the CTindex value of sample 5 is less than that of sample 7 which shows that SBS modified asphalt can better decrease the crack propagation rate of asphalt mixtures. The reason for this result is that the SBS modified asphalt is produced using the pure asphalt and SBS modifier and the SBS modifier is a kind of polymer modifier [36] and could disperse evenly inside the pure asphalt. The chemical bonding of the SBS modifier and the asphalt itself could help to better enhance the property of SBS modified asphalt. The SBS modified asphalt have better mechanical property than the pure asphalt which could help to better transfer the inner stress inside the asphalt mixture. Generally, asphalt with better property could better enhance the anti-crack ability of asphalt mixtures.
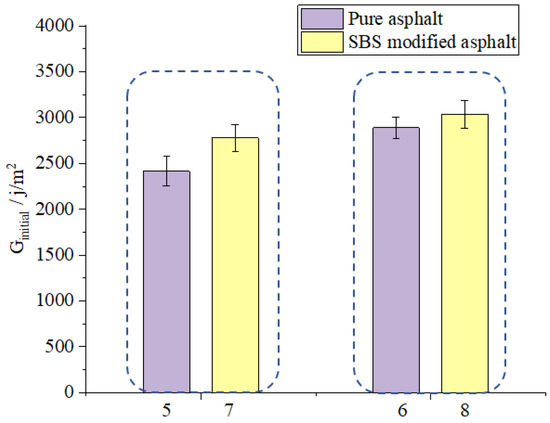
Figure 13.
Effect of asphalt type on Ginitial.
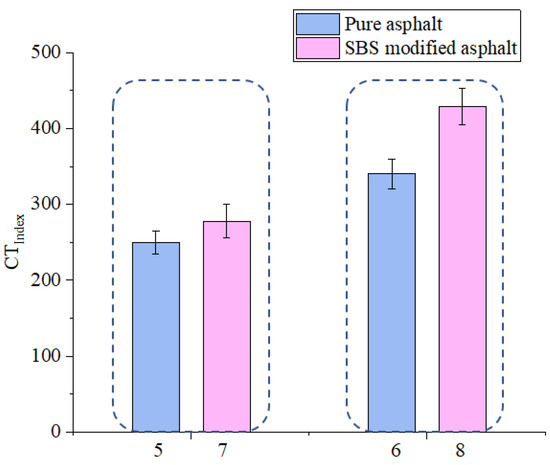
Figure 14.
Effect of asphalt type on CTindex.
3.2. SCB Test
3.2.1. Effect of Basalt Fiber on the SCB Test Result
SCB test results and standard deviation are shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16. It can be concluded from Figure 15 that the Gf value increased after adding basalt fibers. Therefore, basalt fiber can well enhance the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. It can be inferred from Figure 16 that the basalt fiber could help decrease the crack propagation rate of asphalt mixtures because the FI value increase after adding basalt fibers. This test result is in consistence with the IDEAL test results and it help verify the fact that basalt fiber could help enhance the crack resistance of asphalt mixture. Overall, the results show that basalt fiber could well delaying the crack forming and propagation rate of different kinds of asphalt mixtures. The bridge effect formed by the basalt fibers in the micro cracks and the excellent mechanical properties of basalt fiber help to contribute to the enhancement effect on the crack resistance of asphalt mixtures.
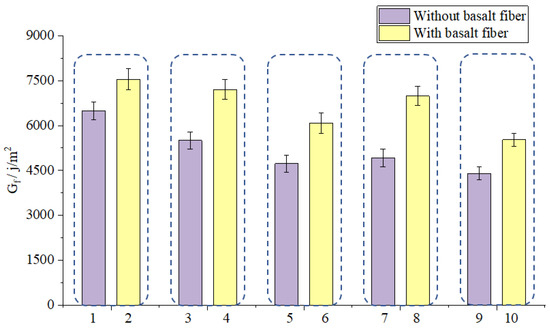
Figure 15.
Effect of basalt fiber on Gf.
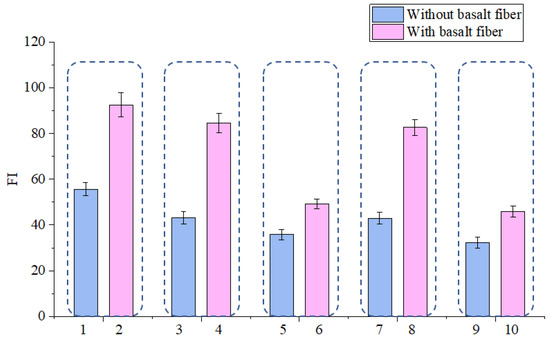
Figure 16.
Effect of basalt fiber on FI value.
3.2.2. Effect of Gradation Type on the SCB Test Result
As shown in Figure 17, the Gf value of sample 1 is bigger than that of sample 3 which means that the cracking resistance of SMA-13 mixture is better than that of SUP-13 mixture. As shown in Figure 18, the FI value of sample 1 is bigger than that of sample 3 which indicates that SMA-13 asphalt mixture has slower crack propagation speed than the SUP-13 mixture. Therefore, it could conclude that the crack resistance of asphalt mixtures could be affected by the gradation type and the asphalt mixtures having better skeleton structures show better anti-crack ability. The test characteristics of SCB test is similar to that of the IDEAL-CT test, therefore, the test result and the conclusions of these two test are also very similar. The cracks are mainly caused by the tensile stress inside the asphalt mixtures during the test loading process. The structure of SMA is a kind of dense skeleton structure while the structure of SUP is a kind of suspended dense structure. The dense skeleton structure could have a more solid structure than the SUP mixtures because the coarse aggregate inside the SMA asphalt mixtures could form a solid skeleton and the consistent structure of SUP does not have a similar solid skeleton structure as the SMA asphalt mixtures.
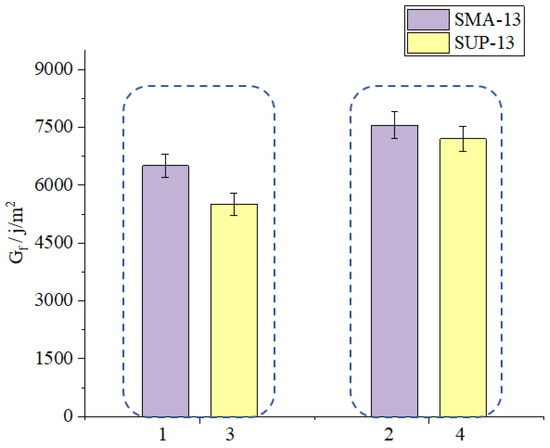
Figure 17.
Effect of gradation type on Gf.
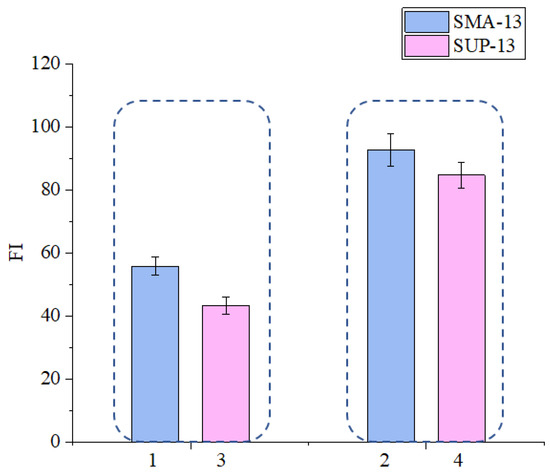
Figure 18.
Effect of gradation type on FI value.
3.2.3. Effect of NMAS on the SCB Test Result
As it can be seen from Figure 19, the Gf value of sample 3 is bigger than that of sample 7, and the Gf value of sample 5 is bigger than that of sample 9 which indicates that the nominal maximum aggregate size is negatively correlated with the cracking resistance of mixtures. As it can be seen from Figure 20, the FI value of sample 3 is bigger than that of sample 7, and the FI value of sample 5 is bigger than that of sample 9, which shows that the nominal maximum aggregate size is positively correlated with the crack propagation speed of asphalt mixtures. Thus, the asphalt mixtures having smaller NMAS could get better anti-crack ability. It can be seen, from Table 4, that in the design of asphalt mixtures, the asphalt mixtures having bigger NMAS have lower optimum asphalt content. When the asphalt content is lower inside the asphalt mixtures, the stress transferring ability of the asphalt inside the asphalt mixtures will be weaker, which could make the asphalt mixtures having smaller NMAS have better anti-cracking ability.
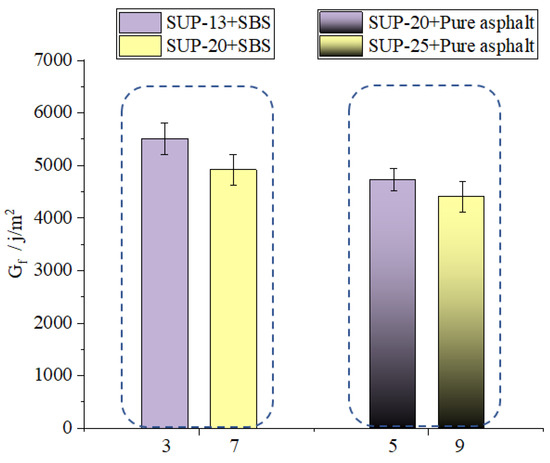
Figure 19.
Effect of NMAS on Gf.
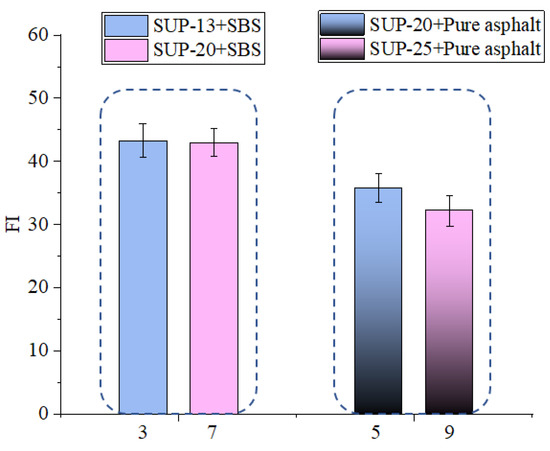
Figure 20.
Effect of NMAS on FI value.
3.2.4. Effect of Asphalt Type on the SCB Test Result
As shown in Figure 21, the Gf value of sample 5 is less than that of sample 7 and the Gf value of sample 6 is less than that of sample 8, which means that SBS modified asphalt has better reinforcing effect on the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. As shown in Figure 22, the FI value of sample 5 is less than that of sample 7 and the FI value of sample 6 is less than that of sample 8, which means that the SBS modified asphalt can better help decrease the crack propagation rate of asphalt mixtures. The SBS modified asphalt could both help enhance the crack resistance of asphalt mixtures with and without basalt fibers. This is mainly because SBS modified asphalt has better mechanical properties than the pure asphalt which could help to better enhance the property of asphalt binder inside the asphalt mixtures. It can be inferred from the mechanics of composite materials theory that the properties of the composite material could enhance when the property of its component are strengthened. Therefore, the asphalt mixtures using SBS modified could have better crack resistance than the pure asphalt.
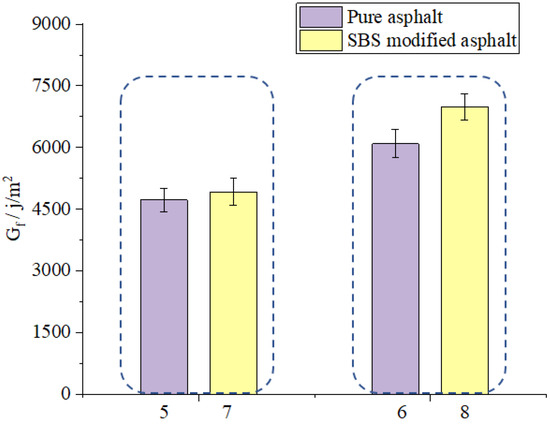
Figure 21.
Effect of asphalt type on Gf.
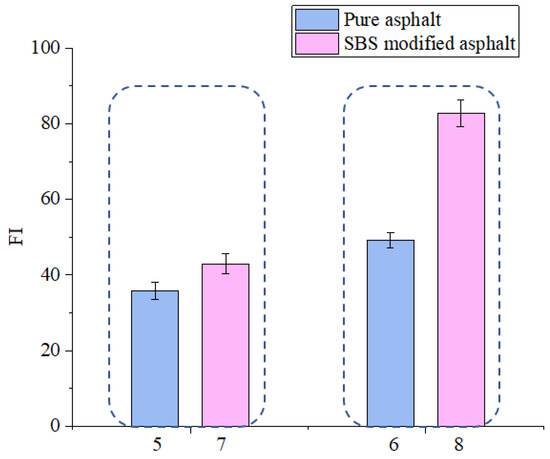
Figure 22.
Effect of asphalt type on FI value.
3.3. Correlation Analysis between the Test Result Indexes of SCB and IDEAL Tests
Generally, the test results of the IDEAL test and the SCB test showed similar change patterns. However, the specific relationship of the test result indexes of IDEAL test and the SCB test could make it more clear when we use these two test methods to comprehensively evaluate the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. To evaluate the sensitivity and correlation of different indexes, Ginitial, CTindex, Gf, and FI of asphalt mixture with and without basalt fiber were selected. As is shown in Figure 23, the test result of sample 1 was selected as the comparison data (the test results of sample 1 were marked as 1.00), the test results of other samples were being normalized according to the test results of sample 1 (the test results of other samples were marked as the quotient of the original test results of the corresponding sample and sample 1). The final normalized test results were shown in Figure 23. It could be concluded that the overall change pattern of all these indexes are very similar, however, the CTindex and the FI value showed similar changing range, and the Ginitial and Gf showed similar changing range. Meanwhile, the FI value and the CTindex were more sensitive to the change of the test samples because the changing range of the FI value and CTindex were bigger than that of the Ginitial and Gf, which means that it would be more clear to see the difference of the anti-cracking ability of different kinds of asphalt mixtures. Therefore, it is more reasonable to use the FI value and CTindex to evaluate the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures. Furthermore, as it can be seen from Figure 24, the correlation between the FI value and the CTindex is also good. The coefficient of determination (R2) is 0.72427.
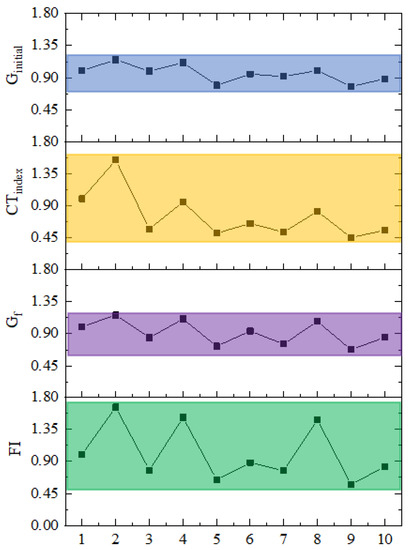
Figure 23.
Increase extent of different test indexes after adding basalt fiber.
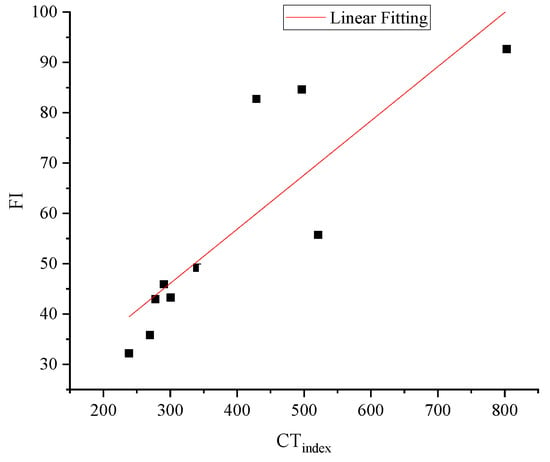
Figure 24.
Correlation analysis of CTindex and FI value.
4. Conclusions
This paper conducted experiments about the anti-cracking ability of several different kinds of asphalt mixtures with different characteristics using SCB and IDEAL-CT tests. The comprehensive evaluation about the effect of basalt fiber, gradation, nominal maximum aggregate size, and asphalt on the anti-cracking ability of asphalt mixtures were concluded. The normalization method was adopted to analyze the sensitivity of different test result indexes on the changing of test samples. The correlation about the CTindex and FI was also conducted. After conducting a series tests and analysis, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Basalt fiber can well enhance the initial cracking resistance and the crack propagation rate of different asphalt mixtures.
- The cracking resistance and crack propagation speed of SMA mixture is better than that of SUP mixture.
- Nominal maximum aggregate size is negatively correlated with the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures.
- SBS modified asphalt has better reinforcing effect on the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures and it can better slow down the crack propagation rate than pure asphalt.
- The FI value and the CTindex were more sensitive to the change of the test samples. There is a good correlation between CTindex of IDEAL test and FI value of SCB test.
This paper has certain impact on the guiding of design or construction of asphalt pavement having good anti-cracking ability. In the future studies, more characterization method, especially the advanced micro analysis method should be utilized to deeply analyze the spatio-temporal characteristics of crack generation and propagation of different types of asphalt mixture and better analyze the influence mechanism of different factors on the crack resistance performance of asphalt mixture.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.X.; methodology, K.L., X.W., and P.X.; software, K.L., X.W.; validation, P.X., A.K., and Z.W.; formal analysis, K.L., X.W., and Y.X.; investigation, K.L., X.W., and P.X.; data curation, Y.X., X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, X.W. and K.L.; writing—review and editing, K.L. and X.W.; visualization, K.L. and X.W.; supervision, P.X.; project administration, P.X. and A.K.; funding acquisition, P.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 51578480), Scientific Research and Innovation Plans for Postgraduate (Grant Number KYCX20_2809), Yangzhou University International Academic Exchange Fund (Grant Number 20190212) and Yangzhou University Scientific Research and Innovation Program (Grant Number YKYCX20_008).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the Yangzhou University Test Center for providing some of the test instruments, and also want to thank Applied Sciences Editorial Office for their patient editing and support during the writing of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nwakaire, C.M.; Yap, S.P.; Yuen, C.W.; Onn, C.C.; Koting, S.; Babalghaith, A.M. Laboratory study on recycled concrete ag-gregate based asphalt mixtures for sustainable flexible pavement surfacing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, D.; Oeser, M.; Leischner, S. Numerical Simulation of Crack Propagation in Flexible Asphalt Pavements Based on Cohesive Zone Model Developed from Asphalt Mixtures. Materials 2019, 12, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeli, S.; Solatiyan, E.; Carter, A.; Eng, P. Flexible Warm Mix Asphalt for Rural Roads in Canada—Laboratory Results and Case Studies; Canadian Technical Asphalt Association: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.-X. Crack and crack growth behavior analysis of asphalt mixtures based on the digital speckle correlation method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kringos, N.; Scarpas, A. Raveling of asphaltic mixes due to water damage: Computational identification of controlling parame-ters. Transp. Res. Rec. 2005, 1929, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Li, R.; Amirkhanian, S.; Yuan, J. Rutting-Resistance Investigation of Alternative Polymerized Asphalt Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akentuna, M.; Kim, S.S.; Nazzal, M.; Abbas, A.R.; Arefin, M.S. Study of the thermal stress development of asphalt mixtures using the Asphalt Con-crete Cracking Device (ACCD). Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, H.A.; Velasquez, R.; Bahia, H.U. Modeling thermal stress in asphalt mixtures undergoing glass transition and phys-ical hardening. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2296, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Peng, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of Fatigue Cracking in Asphalt Mixtures Based on Surface Energy. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 4015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Hu, L.; Xia, C.; Wang, X.; Cabrera, M.B.; Guo, S.; Chen, J. Development of fatigue damage model of asphalt mixtures based on small-scale accelerated pave-ment test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Pauli, T.; Sun, W. Investigation of the Asphalt Self-Healing Mechanism Using a Phase-Field Model. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Sun, W.; Das, P.; Song, X.; Wang, L.; Ge, Z.; Huang, Y. Coupled Navier–Stokes phase-field model to evaluate the microscopic phase separation in as-phalt binder under thermal loading. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Aliha, M.R.; Moniri, A.; Saghafi, Y. Crack resistance of hot mix asphalt containing different percentages of reclaimed as-phalt pavement and glass fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 117015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, D.; Shi, L.; Liang, X.; Tang, C. Use of digital images for fracture performance evaluation of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, E.; Le, J.-L.; Turos, M.; Marasteanu, M. Investigation of size effect in asphalt mixture fracture testing at low temperature. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2012, 13, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamegh, M.; Ameri, M.; Naeni, S.F.C. Performance evaluation of fatigue resistance of asphalt mixtures modified by SBR/PP polymer blends and SBS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskuła, P.; Stienss, M.; Szydłowski, C. Effect of Polymer Fibres Reinforcement on Selected Properties of Asphalt Mixtures. Procedia Eng. 2017, 172, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.; Zarei, M.; Janmohammadi, O. Evaluation of the Effect of Lignin and Glass Fiber on the Technical Properties of Asphalt Mixtures. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 4085–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, G.; Tan, G.; Sun, X.; Yang, S. Further Investigation on Damage Model of Eco-Friendly Basalt Fiber Modified Asphalt Mixture under Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Appl. Sci. 2018, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, C.; Wu, X.; Xiao, P.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Physical, Rheological, and Morphological Properties of Asphalt Reinforced by Basalt Fiber and Lignin Fiber. Materials 2020, 13, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Gu, X.; Zhou, G. Effect of basalt fiber on the bitumen binder and mastic at low temperature. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, A.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Wu, H. Effect of basalt fiber on the low-temperature performance of a bitumen mixture in a heavily frozen area. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guan, B.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, A. Investigation of the performance of basalt fibre reinforced bitumen mixture. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Bahia, H.U. Comparison between SCB-IFIT, un-notched SCB-IFIT and IDEAL-CT for measuring cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ni, F.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, J. Heterogeneous fracture simulation of asphalt mixture under SCB test with cohesive crack model. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Im, S.; Sun, L.; Scullion, T. Development of an IDEAL cracking test for asphalt mix design and QC/QA. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, L.N.; Kim, M.; Elseifi, M. Characterization of asphalt mixture’s fracture resistance using the semi-circular bending (SCB) test. In Proceedings of the 7th RILEM International Conference on Cracking in Pavements, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 20–22 June 2012; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Performance investigation and sustainability evaluation of multiple-polymer asphalt mixtures in airfield pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H. Moisture damage of asphalt mixture and its evaluation under the long-term soaked duration. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, K.; Xiao, P.; Kang, A.; Wu, Z.; Lu, P. Suitability of Fiber Lengths for Hot Mix Asphalt with Different Nominal Maximum Aggregate Size: A Pilot Experimental Investigation. Materials 2020, 13, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Occupation Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Specification for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavement; JTG F40; Occupation Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangsu Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Standard Specification for Superpave Construction; DS32/T 2798; Jiangsu Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision: Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Wang, D.; Xiao, X.; Qin, X. Meso-structural characteristics of asphalt mixture main skeleton based on meso-scale analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation and design of fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Qian, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Y. Microstructural characteristics of asphalt concrete with different gradations by X-ray CT. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2017, 32, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Chopra, T.; Jain, S.; Kaur, A.; Kamotra, S. Effect of aggregate type and polymer modification on the performance of bituminous concrete mixes. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).