Conversion of Glucose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, Levulinic Acid, and Formic Acid in 1,3-Dibutyl-2-(2-butoxyphenyl)-4,5-diphenylimidazolium Iodide-Based Ionic Liquid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Glucose Conversion
2.3. Analytical Methods
- CLA = real concentration of LA produced (mole);
- CHMF = real concentration of HMF produced (mole);
- CFA = real concentration of FA produced (mole);
- Wsample = weight of sample (gram).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
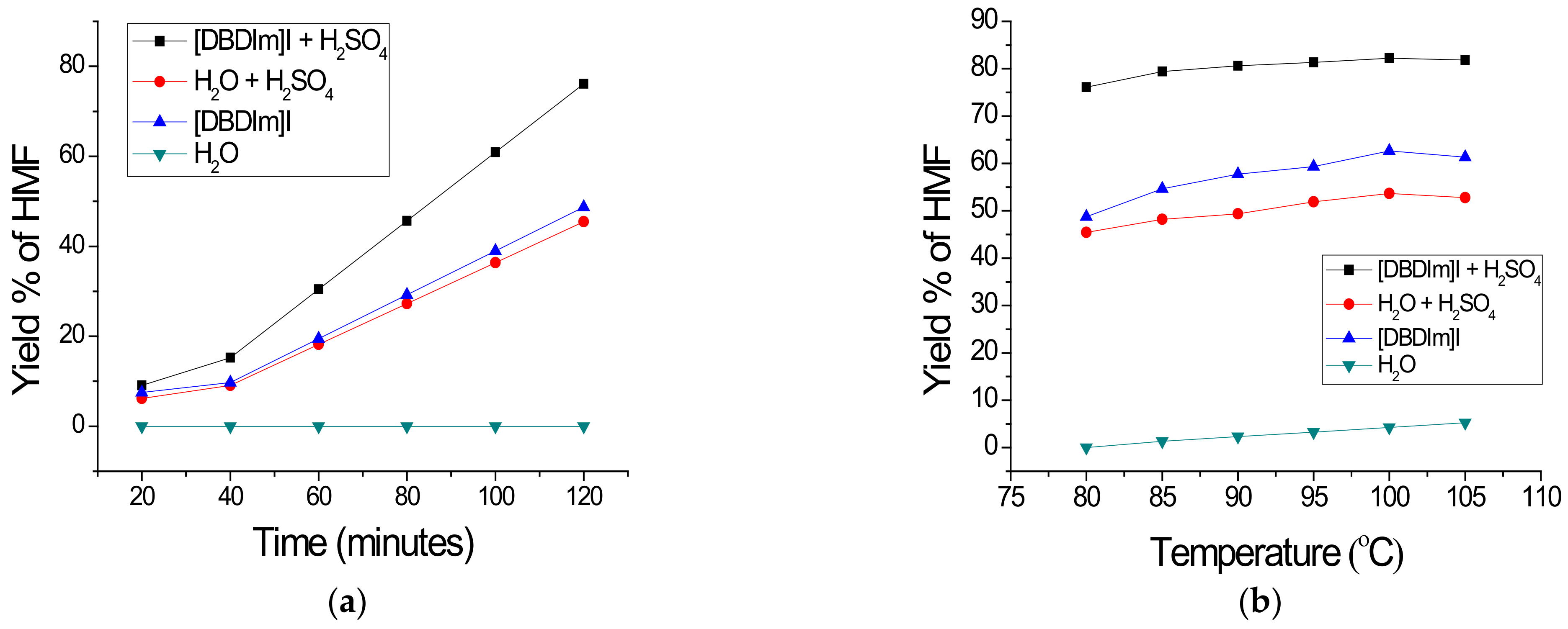
3.1. Determination of Optimum Conditions for Glucose Conversion
3.2. Performance of [DBDIm]I as a Solvent for Glucose Conversion
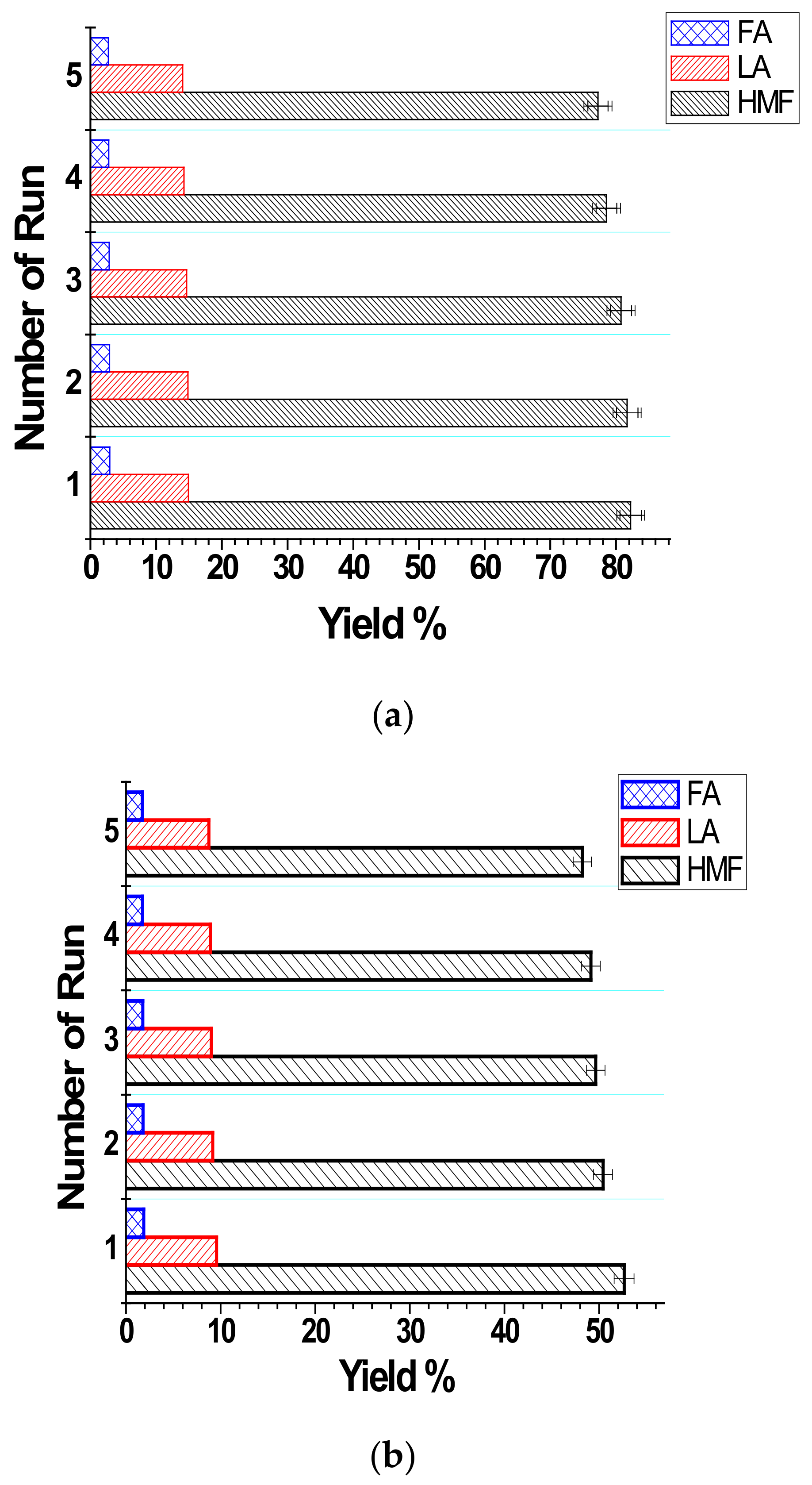
3.3. Recovery and Reusability of [DBDIm]I in Glucose Conversion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Biomass into chemicals: Conversion of sugars to furan derivatives by catalytic processes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 385, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y. Production of Levulinic Acid via Cellulose Conversion Over Metal Oxide-Loaded MOF Catalysts in Aqueous Medium. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, U.; Anand, N.; Kumar, D. Synergistic effect of modified activated carbon and ionic liquid in the conversion of microcrystalline cellulose to 5-Hydroxymethyl Furfural. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisen, A.; Christensen, T.; Fu, W.; Gorbanev, Y. Process integration for the conversion of glucose to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozell, J.J.; Petersen, G.R. Technology development for the production of biobased products from biorefinery carbohydrates—the US Department of Energy’s “Top 10” revisited. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegazzo, F.; Ghedini, E.; Signoretto, M. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) production from real biomasses. Molecules 2018, 23, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska, M.E.; Bogel-Łukasik, E.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Ionic liquid-mediated formation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural—A promising biomass-derived building block. Chem. Rev. 2010, 111, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, B. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). A review focussing on its manufacture. Starch Stärke 1990, 42, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosatella, A.A.; Simeonov, S.P.; Frade, R.F.; Afonso, C.A. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) as a building block platform: Biological properties, synthesis and synthetic applications. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 754–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhao, G.; Hao, W.; Tang, X. Catalytic conversion of biomass-derived carbohydrates into fuels and chemicals via furanic aldehydes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 11184–11206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chheda, J.N.; Román-Leshkov, Y.; Dumesic, J.A. Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural by dehydration of biomass-derived mono-and poly-saccharides. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Mittal, A.; Robichaud, D.J.; Pilath, H.M. Prediction of Hydroxymethylfurfural Yield in Glucose Conversion through Investigation of Lewis Acid and Organic Solvent Effects. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 14707–14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, P.M.; Bergs, C.; Domínguez de María, P. Chemo-Enzymatic Conversion of Glucose into 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Seawater. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, E.; Mao, M.; Peng, Y.; Li, X. The Direct Conversion of Cellulose into 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural with CrCl3 Composite Catalyst in Ionic Liquid under Mild Conditions. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Gan, M.; Ou, H. Acid–chromic chloride functionalized natural clay-particles for enhanced conversion of one-pot cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 11664–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Holladay, J.E.; Brown, H.; Zhang, Z.C. Metal chlorides in ionic liquid solvents convert sugars to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Science 2007, 316, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Watanabe, M.; Aida, T.M.; Smith, R.L. Synergistic conversion of glucose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquid–water mixtures. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 109, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.B.; Raines, R.T. Simple chemical transformation of lignocellulosic biomass into furans for fuels and chemicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, H. Effect of organic solvent and Brønsted acid on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural preparation from glucose over CrCl3. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27805–27813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Brown, H.M.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.-d. Single-step conversion of cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), a versatile platform chemical. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 361, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y. Production of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural from cellulose in CrCl2/Zeolite/BMIMCl system. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despax, S.; Estrine, B.; Hoffmann, N.; Le Bras, J. Isomerization of d-glucose into d-fructose with a heterogeneous catalyst in organic solvents. Catal. Commun. 2013, 39, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaye, S.; Pant, K.K.; Jain, S. Synergistic effect of ionic liquid and dilute sulphuric acid in the hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 148, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Z. Efficient conversion of cellulose into biofuel precursor 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in dimethyl sulfoxide-ionic liquid mixtures. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunita, M.; Wahyuningrum, D.; Bundjali, B.; Wenten, I.G.; Boopathy, R. The Performance of 1, 3-Dipropyl-2-(2-propoxyphenyl)-4, 5-diphenylimidazolium Iodide based Ionic Liquid for Biomass Conversion into Levulinic Acid and Formic Acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makertihartha, I.; Zunita, M.; Rizki, Z.; Dharmawijaya, P. Solvent extraction of gold using ionic liquid based process. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1805, 030008. [Google Scholar]
- Makertihartha, I.; Zunita, M.; Dharmawijaya, P.; Wenten, I. Supported ionic liquid membrane in membrane reactor. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1788, 040003. [Google Scholar]
- Makertihartha, I.; Rizki, Z.; Zunita, M.; Dharmawijaya, P. Dyes removal from textile wastewater using graphene based nanofiltration. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1840, 110006. [Google Scholar]
- Chiappe, C.; Rodriguez Douton, M.J.; Mezzetta, A.; Pomelli, C.S. Recycle and extraction: Cornerstones for an efficient conversion of cellulose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5529–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunita, M.; Wahyuningrum, D.; Bundjali, B.; Wenten, I.G.; Boopathy, R. Corrosion Inhibition Performances of Imidazole Derivatives-Based New Ionic Liquids on Carbon Steel in Brackish Water. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamavaram, V.; Reddy, R.G. Thermal stabilities of di-alkylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2008, 47, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Willauer, H.D.; Swatloski, R.P.; Visser, A.E. Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for ‘clean’liquid–liquid extraction. Chem. Commun. 1998, 1765–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhai, M.; Peng, J.; Xu, L. Synthesis of room temperature ionic liquids from carboxymethylated chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhen, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Tin phosphate as a heterogeneous catalyst for efficient dehydration of glucose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquid. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.K. Microwave-assisted conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into furans in ionic liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Peng, W.-H.; Wu, K.C.-W. Cellulosic conversion in ionic liquids: Effects of H2O/cellulose molar ratios, temperatures, times, and different ILs on the production of monosaccharides and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Catal. Today 2011, 174, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids. Green solvents for the future. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhlberg, T.; Sørensen, M.G.; Riisager, A. Direct conversion of glucose to 5-(hydroxymethyl) furfural in ionic liquids with lanthanide catalysts. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiong, Y.W.; Yap, C.L.; Gan, S.; Yap, W.S.P. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of oil palm mesocarp fiber cellulose conversion to levulinic acid and upgrading to ethyl levulinate via indium trichloride-ionic liquids. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Leshkov, Y.; Dumesic, J.A. Solvent effects on fructose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in biphasic systems saturated with inorganic salts. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Pei, Z.; Wang, D. Organic solvent pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and biochemicals: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicker, M.; Hirth, J.; Vogel, H. Dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in sub-and supercritical acetone. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappe, C.; Pieraccini, D. Ionic liquids: Solvent properties and organic reactivity. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2005, 18, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Y. Combination of Brønsted and Lewis Polymeric Catalysts for Efficient Conversion of Cellulose into 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) in Ionic Liquids. Energy Technol. 2016, 4, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X. Catalytic conversion of cellulose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over chromium trichloride in ionic liquid. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, H.; Zhan, S.; Wang, S. Catalytic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4179–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makertihartha, I.; Dharmawijaya, P.; Zunita, M.; Wenten, I. Post combustion CO2 capture using zeolite membrane. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1818, 020074. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.A.; Lee, J.W.; Yi, Y.B.; Hong, S.S. Direct conversion of starch to hydroxymethylfurfural in the presence of an ionic liquid with metal chloride. Starch Stärke 2010, 62, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowski, J. Synthesis, chemistry and applications of 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural and its derivatives. Arkivoc 2001, 1, 17–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunita, M.; Wahyuningrum, D.; Buchari, B.B. Investigation of corrosion inhibition activity of 3-butyl-2,4,5-triphenylimidazole and 3-butyl-2-(2-butoxyphenyl)-4, 5-diphenylimidazole toward carbon steel in 1% NaCl solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 3274–3288. [Google Scholar]
- Handy, S.T.; Okello, M. The 2-position of imidazolium ionic liquids: Substitution and exchange. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. The physical properties of aqueous solution of room-temperature ionic liquids based on imidazolium: Database and evaluation. J. Mol. Liq. 2008, 140, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
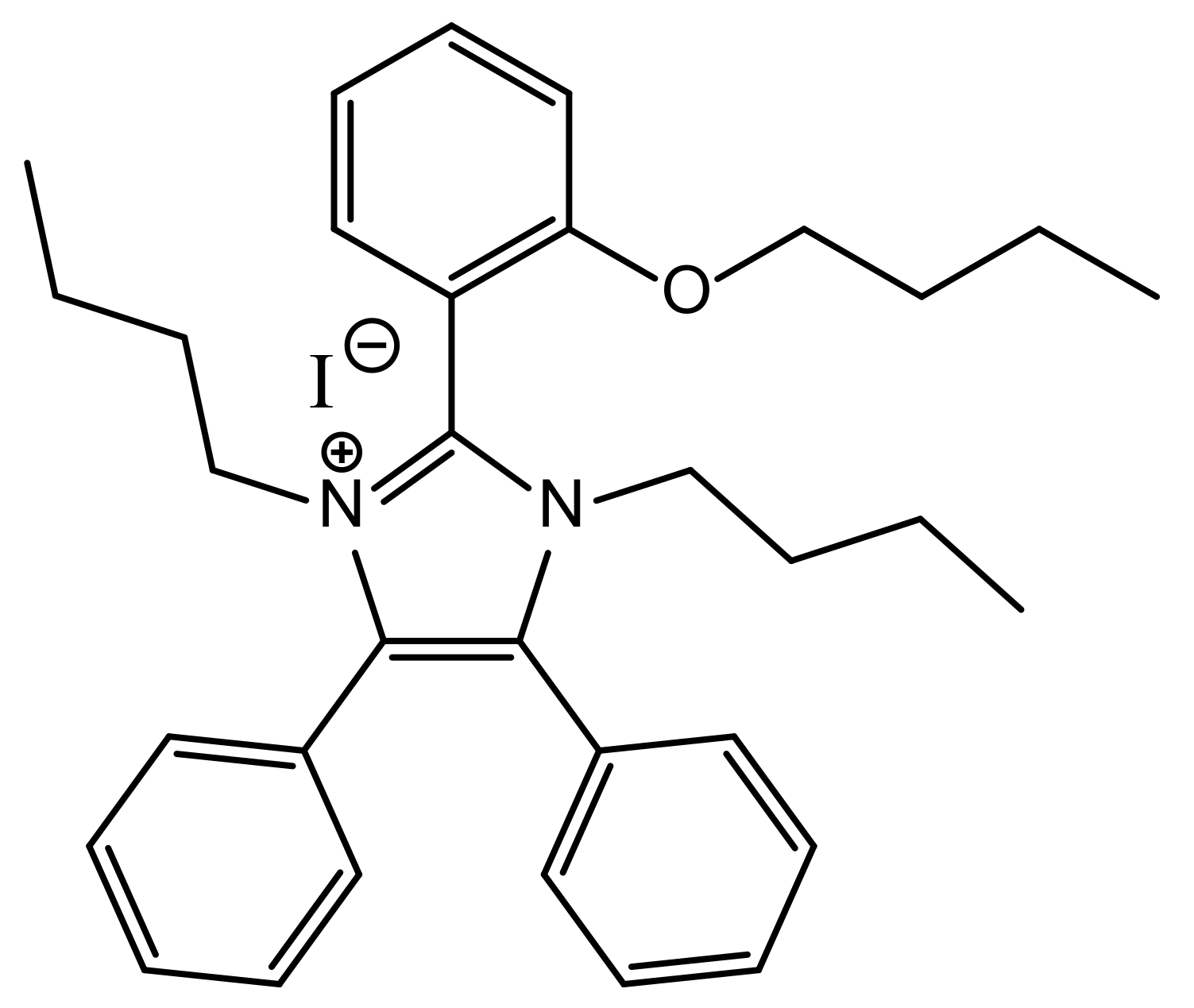


| Solvent | Catalyst | %Mole Yield of Product | Remark | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMF | Levulinic Acid | Formic Acid | |||
| [DBDIm]I | Non Catalyst | 52.1 ± 1.0 | 9.6 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | [DBDIm]I gives better performance as a solvent |
| H2O | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| [DBDIm]I | H2SO4 | 82.2 ± 2.1 | 14.9 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | [DBDIm]I performance as a solvent increased with the addition of H2SO4 |
| H2O | 49.1 ± 1.4 | 8.9 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zunita, M.; Wahyuningrum, D.; Buchari; Bundjali, B.; Wenten, I.G.; Boopathy, R. Conversion of Glucose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, Levulinic Acid, and Formic Acid in 1,3-Dibutyl-2-(2-butoxyphenyl)-4,5-diphenylimidazolium Iodide-Based Ionic Liquid. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11030989
Zunita M, Wahyuningrum D, Buchari, Bundjali B, Wenten IG, Boopathy R. Conversion of Glucose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, Levulinic Acid, and Formic Acid in 1,3-Dibutyl-2-(2-butoxyphenyl)-4,5-diphenylimidazolium Iodide-Based Ionic Liquid. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(3):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11030989
Chicago/Turabian StyleZunita, Megawati, Deana Wahyuningrum, Buchari, Bunbun Bundjali, I Gede Wenten, and Ramaraj Boopathy. 2021. "Conversion of Glucose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, Levulinic Acid, and Formic Acid in 1,3-Dibutyl-2-(2-butoxyphenyl)-4,5-diphenylimidazolium Iodide-Based Ionic Liquid" Applied Sciences 11, no. 3: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11030989
APA StyleZunita, M., Wahyuningrum, D., Buchari, Bundjali, B., Wenten, I. G., & Boopathy, R. (2021). Conversion of Glucose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, Levulinic Acid, and Formic Acid in 1,3-Dibutyl-2-(2-butoxyphenyl)-4,5-diphenylimidazolium Iodide-Based Ionic Liquid. Applied Sciences, 11(3), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11030989








