Abstract
Bionic reasoning is a significant process in product biologically inspired design (BID), in which designers search for creatures and products that are matched for design. Several studies have tried to assist designers in bionic reasoning, but there are still limits. Designers’ bionic reasoning thinking in product BID is vague, and there is a lack of fuzzy semantic search methods at the sentence level. This study tries to assist designers’ bionic semantic reasoning in product BID. First, experiments were conducted to determine the designer’s bionic reasoning thinking in top-down and bottom-up processes. Bionic mapping relationships, including affective perception, form, function, material, and environment, were obtained. Second, the bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) pretraining model was used to calculate the semantic similarity of product description sentences and biological sentences so that designers could choose the high-ranked results to finish bionic reasoning. Finally, we used a product BID example to show the bionic semantic reasoning process and verify the feasibility of the method.
1. Introduction
1.1. Product Biologically Inspired Design
People get inspiration from one domain and apply it to another domain, which is called analogy [1]. Biologically inspired design (BID) takes biology as the source domain, and engineering, architecture, and industrial products can be target domains [2,3]. Product BID is a biologically inspired design in which the target domain is the product appearance.
The BID strategy can be divided into a top-down approach and a bottom-up approach. In the top-down approach [4], there is always a well-defined problem, and designers search for analogous solutions in nature to solve it. In the bottom-up approach, designers start from biology to find suitable design objects.
There are two significant processes in product BID: bionic reasoning and bionic expression (Figure 1). In bionic reasoning, designers search for creatures and products that are matched according to the design goal [5,6]. In bionic expressions, designers use the creature and product obtained by reasoning to draw detailed sketches and build 3D models accomplishing the product BID [7].
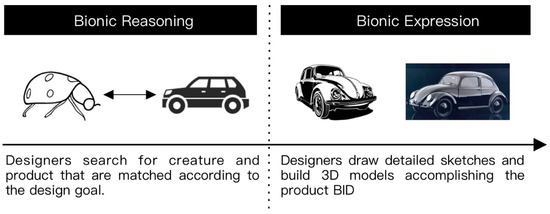
Figure 1.
Product design process.
1.2. Bionic Reasoning
Bionic reasoning is important for product BID. Choosing related creatures and products can make designers’ thinking and sketching in the subsequent bionic expression stage smoother, and the bionic product can convey harmonious imagery and aesthetics for users. This stage requires comprehensive knowledge of products, creatures and product design, which is difficult for designers, especially novices.
Several studies have attempted to assist designers in bionic reasoning accurately and efficiently through scientific methods, including (1) templates, (2) keyword-based search, (3) perceptual matching and (4) morphological matching.
(1) Templates are used to guide analogy thinking by asking designers to write down the corresponding information of the source domain and target domain and are proven to improve the accuracy of bionic reasoning [8,9].
(2) Biology and engineering databases are established to accomplish bionic reasoning by keyword-based search, which is a precise search, and the results are limited [10]. To improve keyword-based search, a ‘bridging’ method is introduced to identify nonobvious but highly relevant keywords, including nouns and verbs [11,12,13]. Biological or engineering keywords are expanded by adding their troponym or hypernym from the online lexical WordNet.
(3) The perceptual matching method is another semantic approach for bionic reasoning. By scoring the affective perception of creatures and products with the same index, researchers obtain creatures and products that have similar affective perceptions for subjects. Luo et al. [14] and Yuan et al. [15] used perceptual evaluation to predict users’ preference for creatures in BID.
(4) For morphological reasoning, Luo et al. [16] introduced a shape context algorithm to find a biological contour that is most similar to the given product contour. Zhu [17] used topological similarity to perform bionic morphological reasoning by analyzing the topological relation of organisms and products.
However, there are also limits in the above bionic reasoning methods. First, there is a lack of in-depth research on designers’ ideation in bionic reasoning. In addition, ‘bridging’ expanded the search result, but it is still a precise search and can only search for words, not sentences. There is a lack of fuzzy semantic search methods at the sentence level. Finally, perception matching requires a large number of users to score, which is inconvenient and inefficient.
1.3. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) Pretraining Model
BERT is a pretraining language model proposed by Google that has a deep understanding of natural language. There are two unsupervised pretraining tasks of BERT: the masking language model (MLM) and next sentence prediction (NSP) [18]. Learning on large-scale unlabeled training data through two pretraining tasks made BERT have great performance on various downstream nature language processing (NLP) tasks, such as machine translation, knowledge extraction, text classification and question answering systems [19,20,21,22].
Since there are few studies on designers’ real reasoning thinking and sentence-level fuzzy semantic rezoning in product BID, this study conducts two experiments to determine designers’ bionic reasoning thinking mode first, and then uses the natural language processing model BERT to realize bionic semantic reasoning.
2. Experiment
2.1. Study 1: Bionic Reasoning Experiment from Product to Biology
The purpose of this experiment is to explore designers’ bionic reasoning modes and their frequency in bottom-up product bionic design.
2.1.1. Subjects
A total of 12 industrial design graduate students (7 male and 6 female, aged from 22 to 29), all of whom had more than four years of product design experience, were chosen as subjects to perform the bionic reasoning task.
2.1.2. Stimuli
Three experts discussed bionic products with the goal of covering as many product categories and product use environments as possible. Eight common products are selected: airplane, desk lamp, humidifier, motorcycle helmet, sofa, automobile, water cup, and speedboat, which cover complex products and simple products.
2.1.3. Procedure
Participants are invited to come up with as many organisms as possible according to each product provided in Section 2.1.2, assuming they are working on a product BID. After their reasoning, participants are asked to write down in brief sentences the reason for each product-to-biology combination.
The specific product appearance is not displayed to avoid interfering with the subjects’ ideation. Meanwhile, subjects are given the authority to search for information from the internet.
2.1.4. Results
Statistics of the reasoning showed that on average, each subject inferred 3.09 corresponding organisms for each product. The common product-to-creature reasoning modes can be classified as ‘affective perception of product- affective perception of creature reasoning’, ‘product form- creature form reasoning’, ‘product function- creature function reasoning’, ‘product using environment- creature habitat reasoning’ and ‘product material- creature material reasoning’. When one reasoning mode refers to more than one creature, it is considered that the reasoning mode is used only once. Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5 show the main five reasoning modes, their frequency and examples. In addition, few subjects also used cultural association reasoning (four times), such as thinking of airplanes from tigers because of flying tigers.

Table 1.
Affective perception of product-affective perception of creature reasoning (72 times).

Table 2.
Product form- creature form reasoning (49 times).

Table 3.
Product function- creature function reasoning (34 times).

Table 4.
Product using environment- creature habitat reasoning (20 times).

Table 5.
Product material- creature material reasoning (19 times).
The reasoning from a creature to a product can contain more than one reasoning mode. For example, an eagle is chosen as a creature with an aircraft as a target product, and the reason is “The movement method of eagle and aircraft both is flying and the shape of eagle wings is similar to wings of aircraft.” It contains two reasoning modes: ‘product function- biological function reasoning’ and ‘product form- biological form reasoning’.
2.2. Study 2: Bionic Reasoning Experiment from Biology to Product
2.2.1. Subjects
A total of 12 industrial design graduate students, as in Section 2.1.1, were chosen as subjects to perform the bionic reasoning task.
2.2.2. Stimuli
Three experts discussed organisms to infer from trying to cover different types of creatures. Eight types of creatures were chosen: bald eagles, cheetahs, polar bears, jellyfish, beetles, cacti, elephants, and bees.
According to the research of Luo and Dong [23], providing subjects with textual descriptions of cultural relics can obtain more innovative solutions than pictures. To avoid fixation in bionic reasoning, only the names of creatures are provided, and subjects are allowed to surf the internet.
2.2.3. Procedure
Based on eight biological samples, the participants were invited to deduce the related products of each creature as many times as possible through bionic reasoning and to describe the reason for each biology-to-product reasoning in short sentences.
2.2.4. Results
Statistics of the reasoning showed that, on average, each subject inferred 2.66 corresponding products for each creature. The creature-to-product reasoning modes can be classified as ‘creature form- product form reasoning’, ‘affective perception of creature—affective perception of product reasoning’, ‘creature function- product function reasoning’, ‘creature material- product material reasoning’, ‘creature culture- product culture reasoning’ and ‘creature habitat reasoning- product using environment’. Table 6, Table 7, Table 8 and Table 9 show the main reasoning modes, their frequencies and examples. In addition, culture associations (five times) and environmental connections (three times) also occurred in biology-to-product reasoning.

Table 6.
Creature form- product form reasoning (60 times).

Table 7.
Affective perception of creature—affective perception of product reasoning (58 times).

Table 8.
Creature function- product function reasoning (27 times).

Table 9.
Creature material- product material reasoning (26 times).
2.3. Discussion
As shown in Table 10, on average, each subject could infer 3.09 matching organisms for each product. Each subject could infer 2.66 products for each organism with an average level. When inferring from the target domain product to the source domain organism, the subjects’ thinking is more open. This phenomenon could be explained by early-stage uncertainties in factors such as the product’s form, material, affective perception, and so on, causing the learner to pick less-educated guesses than it does under the normal circumstance. In a real design situation, the reasoning space may become smaller as more target users and functions of products are determined. In reverse inference from the source domain organism to the target domain product, participants’ ideas are relatively limited. After the experiment, some subjects mentioned that it was more difficult to think from creatures than products. This may be explained by the fact that products are familiar to subjects, but creatures are far from participants’ daily lives, which contributes to different knowledge backgrounds.

Table 10.
Comparison of biology-to-product and product-to-biology reasoning models.
The bionic mapping relationship between creatures and products is shown in Figure 2.
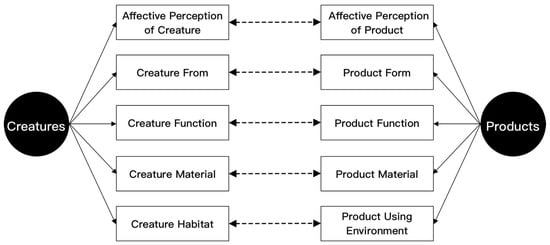
Figure 2.
Bionic mapping relationship between creatures and products.
3. Methodology
Affective perception, function, material and habitat of creatures, as well as affective perception, function, material and using environment of products, can all be described in natural language. Meanwhile, biological form and product form can be better expressed through pictures.
This study introduces the bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) pretraining model to accomplish semantic reasoning of product BID.
3.1. Product and Biology Semantic Database
A biological description dataset and product description dataset are established by describing the affective perception, function, environment, and material of common creatures and products. Some of the data are shown in Table 11 and Table 12.

Table 11.
Biological description dataset (display part of data).

Table 12.
Product description dataset (display part of data).
3.2. Product-Organism Semantic Similarity Calculation
The process of calculating the semantic similarity of sentences based on BERT is shown in Figure 3.
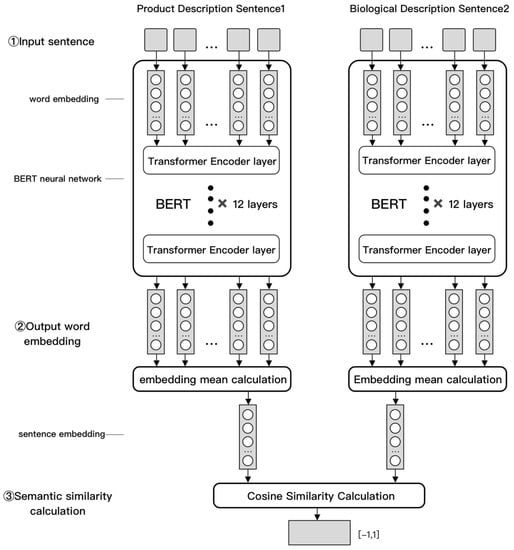
Figure 3.
Product-organism semantic similarity calculation process based on the BERT pretraining model.
(1) Input Sentence
Input a product description sentence and a biological description sentence.
(2) Word Embedding
The BERT model converts natural language into mathematical representation through word embedding. Each word in the input sentence is expressed as a word embedding with a fixed length of , which is convenient for subsequent processing and calculation.
(3) BERT Operation
After operation of the 12-layer transformer layer in the BERT model, the corresponding word embedding of the original sentence outputs. Suppose a sentence contains Chinese words; then, the word vector output of the sentence is denoted as ,….
(4) Sentence embedding calculation
Obtain the sentence embedding by calculating the mean value of the output word embedding. The sentence embedding is calculated as follows.
(5) Cosine similarity calculation
Cosine similarity is used to calculate the similarity between two sentences. If the feature vector of sentence 1 is , the feature vector of sentence 2 is , the dimension of sentence embedding is , and and are the components of and , then the cosine similarity between the two sentences is calculated as follows.
The value range of similarity is [−1,1]. −1 means the two vectors are opposite, and 1 means the two vectors are the same. The greater the cosine similarity value, the higher the semantic similarity of the two sentences.
3.3. Semantic Reasoning of Product BID Based on BERT
When inferring creatures through products, first input the description sentences of the product, and the semantic similarities between the product and every creature in the dataset of each reasoning mode are calculated using the algorithm in Section 3.2. Finally, the creatures inferred from each category are sorted according to the similarity from high to low (Figure 4). Designers can choose creatures with high similarity as the source to start bionic expressions. It is similar to infer from creature to product.
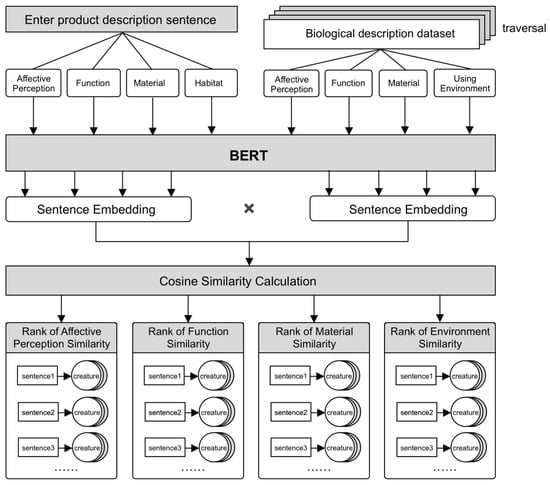
Figure 4.
Semantic reasoning process from product to biology.
3.4. Example
A bionic semantic reasoning system is developed on RoBERTa-wwm-ext, a derived Chinese model of BERT-base, which adapts whole word masking in the masked language model (MLM) pretraining task [24,25]. RoBERTa has been applied to text classification in many fields [26,27,28,29].
When using night light as the target product to search for suitable creatures for product BID, the designer first inputs descriptions of the night light, as shown in Table 13. The semantic reasoning results are shown in Figure 5 and Table 14, Table 15, Table 16 and Table 17.

Table 13.
Description of night light.
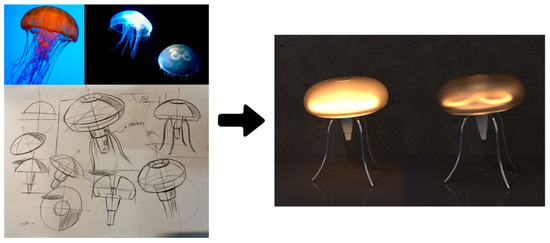
Figure 5.
Bionic night light design reference, concept sketch and rendering effect.

Table 14.
Semantic reasoning result of affective perception.

Table 15.
Semantic reasoning result of function.

Table 16.
Semantic reasoning result of material.

Table 17.
Semantic reasoning result of using environment.
According to the inference result, jellyfish ranked first in function reasoning, and the function description “illuminate” of night light corresponds to “glow” of jellyfish’s function. At the same time, jellyfish also ranked in the top five in environmental reasoning and affective perception reasoning. Therefore, jellyfish was chosen as the source domain creature of the night light.
The designer searched for more jellyfish pictures for reference, drew the conceptual sketches, performed modeling and rendering in the 3D modeling software Rhinoceros, and finally completed the product shape bionic design of the jellyfish night light (Figure 5).
4. Discussion and Conclusions
This study first conducted two experiments to determine designers’ bionic reasoning thinking in top-down and bottom-up processes and obtained bionic mapping relationships, including affective perception, form, function, material and environment. Based on the reasoning modes, the NLP pretraining model BERT was used to assist the bionic semantic reasoning. Sentence-level fuzzy semantic reasoning of product-to-creature and creature-to-product can both be realized.
The advantages of this method are listed as follows.
(1) Through experimental research, designers’ bionic reasoning thinking modes such as affective perception, form, function, material, and environment are obtained. Comparing with the previous bionic reasoning, which lacks research on real reasoning thinking, the applied methodology simulates designers’ real ideation in product BID, which makes bionic semantic reasoning more comprehensive and scientific.
(2) Unlike the keyword-based precise reasoning in the past, the usage of BERT in bionic reasoning helps achieve sentence-level fuzzy search in BID for the first time. Moreover, comparing with perception matching, the applied methodology does not require much labor on manual scoring, which improves the search range and efficiency of bionic reasoning.
(3) During the study, the researchers have built two scalable datasets, including a biological description dataset and a product description dataset, and both can serve as a foundation to broaden designers’ bionic reasoning thinking and knowledge, which will be helpful for product BID education and industry.
Future works of this article are listed as follows.
(1) First, work is the improvement of the datasets. Data in the biological dataset and product dataset are limited; therefore, the final reasoning similarity is not extremely high. Meanwhile, this study uses manual methods to get data instead of crawling because the data required are relatively special. In the future, we will expand the dataset and look for ways to automate the sourcing process.
(2) At present, the reasoning results under each reasoning mode are displayed independent of one another. One creature can be recommended by two different modes at the same time. Thus, a comprehensive recommendation system based on weights assigned to different modes is a potential future project to develop. At the same time, morphological reasoning and topological reasoning mentioned in Section 1.2 can also be included.
(3) At last, this semantic reasoning method can be applied in other analogy design fields, such as cultural product design, which takes cultural artefact as the source domain and product as the target domain.
Author Contributions
Z.B. designed and performed the experiments, analyzed the experimental data, and wrote the manuscript. S.L. designed the experiments and gave advice on experiment design and manuscript writing. F.Z. programed and realized bionic semantic reasoning function by BERT. L.W. and P.S. provided the datasets and drew the figures. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52075478), the key project of National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 21AZD056), the major art project of National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 20ZD09-5), and the major project of Zhejiang Social Science Foundation (No. 21XXJC01ZD).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alipour, L.; Faizi, M.; Moradi, A.M.; Gholamreza, A. The impact of designers’ goals on design-by-analogy. Des. Stud. 2017, 51, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigall, W.; Wisser, A. Building and climatization. In Bionics by Examples, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, M.S. Biomimicry as an approach for bio-inspired structure with the aid of computation. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neurohr, R.; Dragomirescu, C. Bionics in engineering-defining new goals in engineering education at “politehnica” university of bucharest. Conf. Eng. Educ. 2007, 1, 3–6. Available online: http://icee2007.dei.uc.pt/proceedings/papers/571.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Helms, M.; Vattam, S.S.; Goel, A.K. Biologically inspired design: Process and products. Des. Stud. 2009, 30, 606–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Cen, F.; Ruan, W.; Yang, C.; Li, H. Behavioral analysis of analogical reasoning in design: Differences among designers with different expertise levels. Des. Stud. 2015, 36, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Bian, Z.; Hu, Y. How can biological shapes inspire design activity in closed domains? Int. J. Technol. Des. Educ. 2020, 1–27. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10798-020-09593-y (accessed on 13 December 2021). [CrossRef]
- Cheong, H.; Shu, L.H. Using templates and mapping strategies to support analogical transfer in biomimetic design. Des. Stud. 2013, 34, 706–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.W.; Shu, L.H. Using descriptions of biological phenomena for idea generation. Res. Eng. Des. 2008, 19, 21–28. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00163-007-0041-y (accessed on 13 December 2021). [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.H.; Cheong, H. A Natural Language Approach to Biomimetic Design. In Biologically Inspired Design, 1st ed.; Goel, A.K., McAdams, D.A., Stone, R.B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 29–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, I.; Shu, L.H. Bridging cross-domain terminology for biomimetic design. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 24–28 September 2005; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 4742, pp. 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, I.; Shu, L.H. Biomimetic design through natural language analysis to facilitate cross-domain information retrieval. AI EDAM 2007, 21, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, H.; Shu, L.H.; Stone, R.B.; McAdams, D.A. Translating terms of the functional basis into biologically meaningful keywords. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, New York, NY, USA, 3–6 August 2008; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 43284, pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.H. A User Biology Preference Prediction Model Based on the Perceptual Evaluations of Designers for Biologically Inspired Design. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Q.; Chen, D.K.; Ynag, Y.P.; Qi, B. Bionic imagery associated with product form design. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2014, 50, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.J.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, Y.F.; Lu, J.W.; Lu, S.Z. A study on product bionic fusion design based on shape matching. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 26, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Cognitive Coupling Based Product Image Morphology Bionic Evolutionary Design Method. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL HLT, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1, pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, S.; Jiang, D.W.; Chen, G. BERT-JAM: Maximizing the utilization of BERT for neural machine translation. Neurocomputing 2021, 460, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnoune, A.; Rhanoui, M.; Mikram, M.; Yosifi, S.; Elkaimbillah, Z.; Asri, B.E. BERT Based Clinical Knowledge Extraction for Biomedical Knowledge Graph Construction and Analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. Update 2021, 1, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.A.; Taju, S.W.; Ho, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.T.D.; Qu, Y.Y. GT-Finder: Classify the family of glucose transporters with pre-trained BERT language models. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 131, 104259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, J. Exploration of text matching methods in Chinese disease Q&A systems: A method using ensemble based on BERT and boosted tree models. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 115, 103683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.J.; Dong, Y.N. Role of cultural inspiration with different types in cultural product design activities. Int. J. Technol. Des. Educ. 2017, 27, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Che, W.; Liu, T.; Qin, B.; Yang, Z. Pre-training with whole word masking for Chinese BERT. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, Maynooth, Ireland, 28 July–1 August 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/ymcui/Chinese-BERT-wwm (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wong, L.P.; Lee, L.K.; Zhang, H.; Hao, T. A Hybrid Neural Network RBERT-C Based on Pre-trained RoBERTa and CNN for User Intent Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Computing for Advanced Applications, Shenzhen, China, 27–30 August 2020; Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Wu, Z., Hao, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zeng, B.; Yin, X.; Wei, P. An improved aspect-category sentiment analysis model for text sentiment analysis based on RoBERTa. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 3522–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Sifuentes, C.E.; Angel, J.; Sidorov, G.; Kolesnikova, O.; Gelbukh, A. Virality Prediction for News Tweets Using RoBERTa. In Proceedings of the Advances in Soft Computing, MICAI, Mexico City, Mexico, 25–30 October 2021; Batyrshin, I., Gelbukh, A., Sidorov, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Iwaihara, M. Integrating RoBERTa Fine-Tuning and User Writing Styles for Authorship Attribution of Short Texts. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Web (APWeb) and Web-Age Information Management (WAIM) Joint International Conference on Web and Big Data, Guangzhou, China, 23–25 August 2021; U, L.H., Spaniol, M., Sakurai, Y., Chen, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).