Featured Application
The application of the work described herein is twofold: the possibility of routinely irradiating biological samples with high accuracy in energy and dose at a low-energy particle accelerator to gain insights into fundamental mechanisms of the biological action of charged particles; in a broader scenario, the possibility to potentiate the therapeutic capabilities of protontherapy through a method based on a nuclear physics reaction.
Abstract
Protontherapy (PT) is a fast-growing cancer therapy modality thanks to much-improved normal tissue sparing granted by the charged particles’ inverted dose-depth profile. Protons, however, exhibit a low biological effectiveness at clinically relevant energies. To enhance PT efficacy and counteract cancer radioresistance, Proton–Boron Capture Therapy (PBCT) was recently proposed. PBCT exploits the highly DNA-damaging α-particles generated by the p + 11B→3α (pB) nuclear reaction, whose cross-section peaks for proton energies of 675 keV. Although a significant enhancement of proton biological effectiveness by PBCT has been demonstrated for high-energy proton beams, validation of the PBCT rationale using monochromatic proton beams having energy close to the reaction cross-section maximum is still lacking. To this end, we implemented a novel setup for radiobiology experiments at a 3-MV tandem accelerator; using a scattering chamber equipped with an Au foil scatterer for beam diffusion on the biological sample, uniformity in energy and fluence with uncertainties of 2% and 5%, respectively, was achieved. Human cancer cells were irradiated at this beamline for the first time with 685-keV protons. The measured enhancement in cancer cell killing due to the 11B carrier BSH was the highest among those thus far observed, thereby corroborating the mechanistic bases of PBCT.
1. Introduction
The charged particle inverted dose-depth profile represents the physical pillar of protontherapy (PT), an advanced and rapidly spreading form of cancer radiotherapy (CRT) that makes use of high-energy (typically up to 230 MeV) accelerated proton beams to treat deep-seated tumours with elevated precision in dose deposition to the target volume [1,2]. The major benefit of PT resides in its greater sparing of normal tissue and/or organs at risk, compared to conventional CRT performed with photons/electrons. This in turn leads to a lower risk of adverse effects, most notably late-occurring radiation-induced secondary cancers [3]. Thus, PT is particularly attractive for pediatric cancers [4]. On the other hand, the low Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) exhibited by protons at the therapeutically useful energies [5] hinders, in principle, the treatment of radioresistant cancers by PT. In fact, tumour intrinsic or acquired radioresistance continues to represent a cause for failure in local tumour control, leading to recurrence, metastases and an overall poor prognostic outlook [6]. While unravelling existing uncertainties on proton radiobiology may lead to a re-assessment of both the clinical RBE used in PT, as well as of the cancer types eligible for PT [7,8], strategies aimed at potentiating proton biological efficacy are actively being sought [9,10]. In this context, Yoon et al. [11] proposed a novel binary approach termed Proton–Boron Capture Therapy (PBCT), based on the p + 11B→3α (pB) nuclear reaction, which presents a maximum of the cross-section for proton energy of 675 keV and can generate short-range α-particles that are densely ionizing, i.e., having a high Linear Energy Transfer (LET) [12]. This is poised to cause mainly unrepairable and highly localized DNA damage due to elevated lesion clustering along the alpha-particle tracks [13].
Using clonogenic cell death and FISH-labelled chromosome aberrations as radiobiological endpoints [14,15], experimental evidence supporting the feasibility of PBCT has been recently proven for the first time as the presence of the 11B carrier BSH exacerbated the cytogenetic damage induced by therapeutic proton beams, which was attributed to the occurrence of the pB reaction triggered by low-energy protons across the Spread-Out Bragg Peak (SOBP) [16,17]. In fact, chromosome aberrations, a widely used indicator of the detrimental action at the DNA level by a variety of genotoxic insults [18], well reflect the energy deposition pattern at the nanometer scale and so-called complex-type rearrangements are peculiar to exposure to high-LET particles [19]. Thus, the fact that the frequency of this type of aberrations was maximum in the presence of BSH at the distal position of the SOBP [17] where protons’ energy is the lowest across the SOBP, strongly argues for the high-LET α-particles from the pB reaction as the effectors of PBCT. However, theoretical studies have predicted a much lower yield of such particles than that deemed sufficient to cause the reported radiobiological effects, questioning the actual role of the pB reaction [20,21]. We therefore performed for the first time cellular irradiations in the presence of 11B with monochromatic proton beams having energy close to the reaction maximum cross-section to demonstrate the mechanistic rationale on which PBCT relies: If the pB reaction is indeed responsible for the radiobiological proton enhancement thus far reported, one may expect the greatest magnitude for such effects under these experimental conditions.
The paucity of dedicated facilities where radiobiological experiments with low-energy protons can be carried out [22], made necessary to design and implement a novel cellular sample irradiation setup at an existing accelerator, the 3-MV Tandem Pelletron accelerator of the Center for Isotopic Research on the Cultural and Environmental Heritage (CIRCE) laboratory, Dept. of Mathematics and Physics, Università della Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” (Caserta, Italy). The irradiation system mainly consists of a scattering chamber with a specially designed target-holder at its centre, provided with beam collimators and a beam scatterer Au foil; proton irradiation occurs through Rutherford scattering. Beam dosimetry is performed measuring proton fluence by Silicon Surface Barrier Detectors (SSBDs) placed at different angles [23], while beam uniformity is monitored by means of CR-39 Solid-State Nuclear Track Detectors (SSTDs). The tests of the facility performance are here presented and discussed here. Proton count rates corresponding to possible dose rates selectable in a range from 0.5–2 Gy/min were consistently obtained. Uniformity in energy and fluence was achieved with uncertainties of 2 and 5%, respectively. This allowed us to expose for the first time two cancer cell lines, DU-145 human prostate and PANC-1 pancreatic cells, to graded doses of monoenergetic proton beams with incident energy of ~685 keV in the presence or absence of the 11B carrier BSH. Occurrence of 11B-triggered pB reaction and resulting effects on cellular radioresponse were evaluated by clonogenic cell survival. The measured amplification of proton biological effectiveness at cancer cell killing was the highest among those observed thus far for such cell lines in radiobiological studies on PBCT along the clinical SOBPs of low- and high-energy proton beams [16,17]. This provides evidence in support of the biophysical rationale for PBCT-assisted enhancement of PT effectiveness.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Radiation Biophysics Beamline Setup and Experimental Procedures
The proton beam produced by the 3-MV Tandem Pelletron accelerator reaches the newly designed radiation biophysics experimental setup via the existing beam transport system for which details can be found in Gialanella et al. [24]. The novel setup is here described in its main components.
2.1.1. Scattering Chamber
The apparatus (Figure 1) mainly consists of:
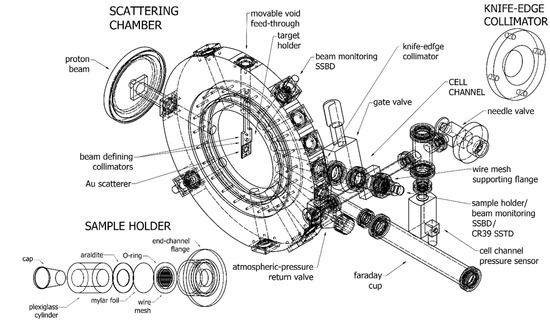
Figure 1.
Scheme of the: radiation biophysics beamline scattering chamber; the cell sample holder assembly; and the knife-edge collimator.
- A disk-shaped scattering chamber, in whose centre it is possible to mount a specially designed aluminium target-holder, provided with two beam collimators (3 and 5 mm diameter) and a frame-holder on which there is a beam scattering Au foil (10 mm diameter, 1 μm thickness, Goodfellow Cambridge Ltd., London, UK). The target holder can be moved in the vertical direction to remove it from the beam path. From the centre of the chamber depart several radial channels, by 15° steps in the forward direction, and some backwards channels.
- An SSBD (Si BU-011-05-300, useful area 0.50 cm2, 300 μm of minimum depletion depth, Ametek Ortec, Oak Ridge, TN, USA) for the beam monitoring, placed at the end of the forward channel at 60°.
- A channel, placed at the end of the forward channel at 15°, equipped with a gate valve and ending with a window (13 mm diameter); next to the window, it is possible to mount, alternatively, a second SSBD, identical to the one described above, or a CR39 SSTD (13 mm diameter and 0.5 mm thickness, Mi.AM Srl, Piacenza, Italy) for beam monitoring and flux calibration, respectively. During the irradiation of the biological samples, the detectors were replaced by the sample holder assembly (see Section 2.1.2); hence, in what follows, we shall refer to this channel as cell channel. A knife-edge collimator (Figure 1) is mounted on the outlet of the scattering chamber, (8 mm internal diameter, 12 mm external diameter) to collimate the scattered beam on the solid angle intercepted by the cell sample or by the detectors placed at the bottom of the channel.
- A Faraday Cup (FC), placed at the end of the 0° forward channel, which allows to measure the current intensity of the beam.
The irradiation of the cell sample was achieved by inserting the Au foil at the centre of the chamber, thus diverting the particles through Rutherford scattering. The presence of a silicon detector placed at a different angle with respect to the cells, allows to carry out live-time dosimetry (see Section 2.2), thanks to the known angular dependence of the Rutherford scattering. Such an experimental procedure was chosen to de-focus the primary beam using a very short distance between the target and the biological samples (less than 40 cm). This, in turn, allows to use higher currents, which guarantees more stable operating conditions and radiobiologically meaningful dose rates (i.e., in the order of Gy/min).
2.1.2. Sample Holder Assembly
The sample-holder was designed to fit the end-channel flange and the beam geometry. It consists of a cave plexiglass cylinder (Figure 1). Each of the two bases has an opening window (13 mm in diameter); one of them provides the entrance for the beam towards the cells to be irradiated, passing through a mylar foil that acts both as a vacuum-holding window and, on the cylinder internal side, as the substrate on which the cells are attached. The mylar foil (6 μm thickness, Goodfellow Cambridge Ltd., London, UK) adheres to the cylinder by gluing it to the dish base by epoxy adhesive (Araldite, Huntsman Corp., The Woodlands, TX, USA), which permits the isolation of the internal volume from the outside; the other base is closed by a removable plastic cap designed to permit the handling of the sample and preserving cell culture sterility.
Finally, a Tungsten–Rhenium alloy wire mesh (20 μm wire thickness, spacing = 0.5 mm, 4% opacity, Figure 1) is glued by araldite epoxy adhesive to a brass ring and used to support the mylar foil and guarantee the tightness of the vacuum chamber.
2.2. Irradiation System and Dosimetry
The proton beam is produced by sputtering graphite cathodes; the extracted 12CH molecules are dissociated in passing through a gas stripper (Ar) and subsequently the hydrogen ions are selected using the appropriate values for the analysis magnets [25]. Before dosimetry and irradiation, the beam passes through a 3-mm-diameter collimator mounted on the target-holder present at the scattering chamber centre. The FC, placed at the end of the 0° forward channel, is connected to a current digitizer for beam focusing and control; the overall beam alignment is obtained by using both a telescopic alignment system and the proton beam current, with an external micrometric device additionally used for refining the collimator alignment. All current intensities were obtained as an average of at least ten samples. A couple of SSBDs and several SSTDs were used for dosimetry. The FAst Intercrate Readout (FAIR) data acquisition system was used to collect data from the silicon detectors as described in [26].
The different detectors can be mounted on all outputs of the scattering chamber or on the output of the cell channel. In particular, beam dosimetry is performed measuring the proton energy and fluence with the two SSBDs, one placed on the channel at 60° (SSBD60°) and the other at 15° (SSBD15°) and in the same position of the sample to be irradiated. They are encapsulated within an insulating support or connected to the cell channel body using an insulating O-ring, respectively (Figure 2a). The relationship between the counts provided by the two SSBDs is as follows:
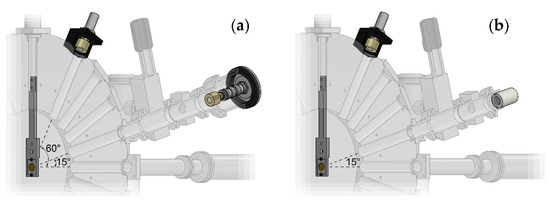
Figure 2.
Positioning of the different type of detectors used during the dosimetry measurements: (a) Positioning of the two SSBDs; (b) Positioning of the CR-39 SSTD.
This is determined before each experimental run. During irradiation of the samples, proton fluence and energy are measured by the SSDB60°.
Particle fluence and beam spatial uniformity, before and after irradiation, can be also measured and monitored by means of the CR-39 detectors placed at the same position of the sample-holder (SSTD15°) using a special centering tool (Figure 2b).
After exposure to protons, SSTDs are scored by manually counting the number of tracks, made visible through an etching process [27,28] of 90 min in NaOH 6N solution at 80°C, on at least 20 random fields observed by a light microscope using a 32X objective, corresponding to a field area of 1.25 10−4 cm2. Using the obtained value of the and the count values of the spectrum at 60°, the expected dose on the SSBD15° or the SSTD15°, and therefore the expected nominal dose given to the cells, can be calculated using the formulas:
where the fluence values are obtained normalizing the number of counts to the areas of the irradiated detector and the LET values are derived from the SRIM library [29]; the numerical factor in Formula (3) include the appropriate conversions between the units of measurement chosen [23,30]. Fast shutters on each FC allow the irradiation of the samples to be stopped when the desired number of counts is reached on the monitoring SSBD.
2.3. Biological Sample Preparation
2.3.1. Cell Culture
Primary prostate adenocarcinoma DU145 cells (kindly gifted by Dr. P. Chaudhary, CCRCB, Queens University, Belfast, UK) were cultured as previously described [16] in RPMI medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), complemented with 10% foetal bovine serum, 1% of penicillin/streptomycin and 1% of L-glutamine. Human pancreatic epithelioid carcinoma PANC-1 cells (courtesy of Dr. A. Facoetti, CNAO, Pavia, Italy) were cultured in high-glucose (4.5 g/L) DMEM medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), supplemented as mentioned above. Both cell lines are also commercially available (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA). Cells, routinely grown in standard culture tissue flasks incubated at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere, were seeded one day before exposure in ad hoc ethanol-sterilized plexiglass sample holders, adhering to a 6 μm mylar surface base (see also Section 2.1.2), at a concentration of ~1.5·105 cells/cylinder. Cylinders were then filled with 3 mL of cell growth medium and incubated until the moment of pre-irradiation boron treatment.
2.3.2. Boron Carrier
Sodium mercaptododecaborate (BSH) Na2B12H12S (Katchem Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic), with naturally occurring boron isotopic abundance (80% 11B and 20% 10B), was used as boron carrier in accordance with previous studies on PBCT [16,17]. Prior to irradiation, BSH was weighted and dissolved in the appropriate volume of cell growth culture medium as to yield a working concentration of 80 ppm of 11B by weight, which corresponds to approximately 0.17 mg/mL of BSH [16]. To ensure sterility, BSH-containing medium was syringe-filtered (0.22 μm pores) before being added to cell cultures. About 6–8 h before irradiation, boron treatment started by replacing cell culture growth medium with the BSH-enriched one. Cylinders were then transferred to the accelerator, leaving about 1 mL per cylinder, to avoid possible medium leaking from the ending cap of the cylinders due to the oblique position the samples during irradiation at CIRCE and, at the same time, to guarantee that the cell monolayer was fully covered by the medium during transportation and irradiation. Thus, stress to cells was minimized and, more importantly, BSH-treated cells were irradiated in the presence of 11B. The same procedure was followed for control flasks filled up with BSH-free medium.
2.4. Measurement of pB-Mediated Enhancement of Proton Biological Effectiveness
Following exposure to the low-energy proton beam made available by the novel radiobiological setup, PBCT was tested by measuring cell death in prostate cancer DU-145 and pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells using the well-established clonogenic assay, hence by quantifying the dose-dependent loss of colony-forming ability [31]. Three replicates were used for each dose point and treatment condition, i.e., irradiation in the presence or the absence of BSH, for both cell lines. After irradiation, cells were detached by trypsinization from the cylinders and an appropriate number of cells was inoculated in 60 mm Petri dishes incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere to allow for colony formation. Specifically, between 250 and 2500 cells were seeded according to the delivered radiation doses (0–4 Gy). Post-irradiation incubation times were 12 and 14 days for DU145 and PANC-1 cells, respectively. At these times, cells were rinsed with PBS and fixed in methanol for at least 15 min at room temperature (RT); staining of macroscopically visible colonies by 0.5% crystal violet dye for 30–45 min at RT followed. Manually counted colonies with more than 50 cells were considered as survivors [31]. As described elsewhere [32], Surviving Fractions (SF) are obtained by dividing the number of colonies by the number of cells seeded at a given dose D, normalized by the cloning ability of unirradiated control samples, the plating efficiency (PE). Possible BSH-induced cytotoxicity was assessed by measuring the PE from unirradiated controls that had been pre-treated with the 11B carrier. Dose-response curves were thus constructed fitting the SF values to the linear–quadratic equation:
by least square minimization according to the modified Marquardt–Levenberg Algorithm for weighted nonlinear regressions (SigmaPlot, v. 14.0, Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). The fitting procedure was repeated setting as the only free parameter if was found consistent with zero [17].
3. Results
3.1. Test of the Facility Performance
During the design phase of the experimental setup, various simulations were conducted to evaluate the energy loss of the protons after the scattering on the Au target and the passage in the mylar window as well as the final spatial and energy distribution of the protons incident on the cellular samples and/or detectors used.
In Figure 3, the comparison between the counts obtained on the SSBD detector positioned on the cell channel (15°) in the presence and in the absence of the mylar window (6 μm thickness) is reported. SimNRA software (Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Garching, Germany, [33]), was used to simulate the incident proton beam (beam diameter Ø = 3 mm, 1 nA I for 60 s, 1050 keV proton energy), the layers’ thickness and the detector geometry.
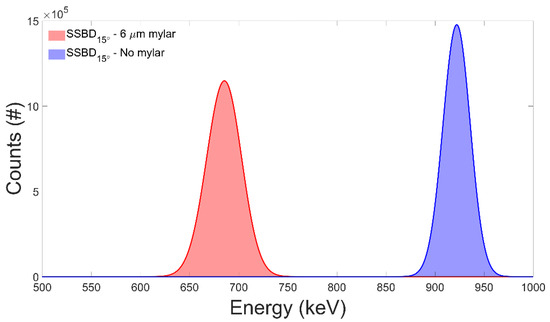
Figure 3.
Simulated spectra obtained for the SSBD15° using a proton beam of energy = 1050 keV, in the presence (red) or absence (blue) of a mylar foil (6 μm thickness).
As clearly shown, a 1050 keV monoenergetic proton beam is expected to yield on the detectors, and therefore on the cell sample, a spectrum centred at ≈685 keV, close to that corresponding to the maximum of the cross-section for the pB reaction (Emax = 675 keV).
Based on these results, a series of spectra for protons of E = 1050 keV obtained with the two SSBDs placed at 15° and 60° (Figure 2a) were acquired and a value of the between the counts of the two detectors was obtained; in Figure 4, an example is reported. Using the obtained value of the ratio and the count values of the spectrum at 60°, the number of counts on the SSBD15° or SSTD15° CR-39, and therefore the dose to be used for the cell irradiation experiments, can be calculated, using Formulas (2) and (3).
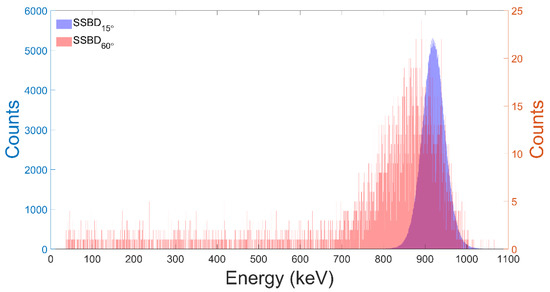
Figure 4.
Spectra obtained for the SSBD15° (blue line and axis) and SSBD60° (red line and axis) using a proton beam of energy = 1050 keV, acquisition time = 600 s, dead time = 8%, R60°/15° = (8.10 ± 0.11)·10−3.
For a current on the FC of 52.5 pA, a theoretical dose rate equal to or min is obtained; dose rate values of this order are those commonly used in radiobiological experiments.
Using this setup, two CR-39 SSTDs, positioned in place of the SSBD15° (Figure 2b), were irradiated for two different exposure times; during the irradiation, the spectrum of the SSBD60° was also acquired. Using the formulas reported in Formulas (2) and (3), the number of expected counts, hence the fluence/dose values, was estimated. The irradiated CR39 were then developed and scored; it was possible to observe the presence of a single family of tracks, homogeneous in diameter, which can therefore be associated with a single energy value (and LET). Moreover, the tracks appeared to be evenly distributed, for both detectors over the entire surface. A detailed count was performed by moving along the two main diagonals of the detectors. In Figure 5, the number of counts along the two diagonals for two SSTDs detectors together with the mean values are reported, while in Table 1 the obtained data are reported.
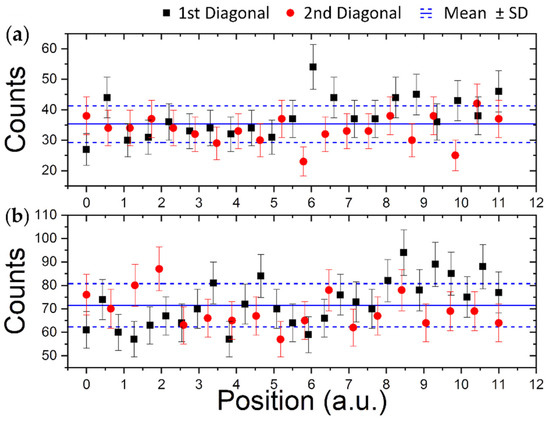
Figure 5.
Counts obtained for two SSTDs CR39 (a) #1 and (b) #2 moving along the two main diagonals; the mean value with standard deviation is reported as solid and dashed blue line.

Table 1.
Values of measured and expected counts, fluence and doses for the irradiated SSTDs CR-39; all values are reported as MEAN ± SEM.
The counts along the diagonals are distributed within 1 σ from the mean value, indicating that the chosen setup ensures a satisfactory beam homogeneity.
The entire test experiment was repeated three times in three successive shifts obtaining comparable values for both proton energies on SSBDs and uniformity of track density distribution on SSTDs CR-39, with uncertainties lower than 2% and 5%, respectively.
3.2. Increase in Cancer Cell Death Following Proton Irradiation in the Presence of BSH
Exposure of the two cancer cell lines DU145 and PANC-1 at the newly designed beamline with 685-keV monoenergetic protons (calculated incident LET ≈ 30 keV/μm) in the presence of the 11B carrier BSH resulted in a significant reduction in clonogenic survival compared to cultures irradiated in the absence of BSH. Survival dose-response curves for the two cell lines are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7; fitting parameters and values for Dose-Modifying Factor at 10% survival level (DMF10) are reported in Table 2 and Table 3.
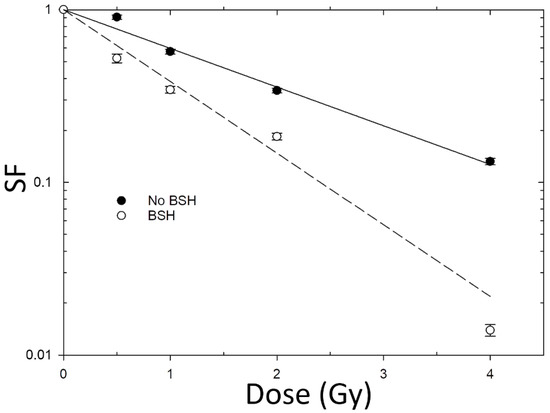
Figure 6.
Clonogenic cell death induced in DU145 prostate cancer cells by the monoenergetic proton beam at the newly implemented beamline: Dose-responses obtained after irradiation in the presence (black circles) or the absence (white circles) of the 11B carrier BSH are shown. Data are averaged from three separate experiments. Error bars represent the SEM.
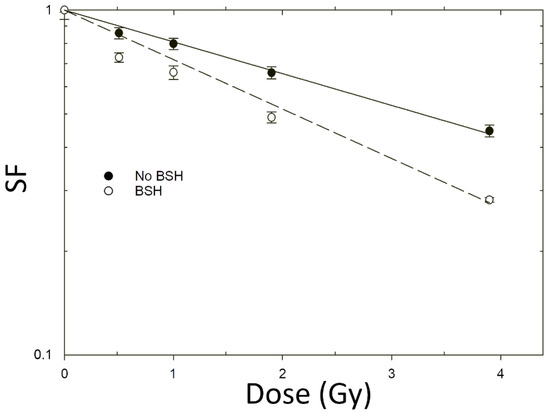
Figure 7.
Clonogenic cell death induced in PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cells by the monoenergetic proton beam at the newly implemented beamline: Dose-responses obtained for irradiation in the presence (black circles) or the absence (white circles) of the 11B carrier BSH are shown. Data represent the averaged mean from two independent experiments. Error bars represent the SEM.

Table 2.
Linear–quadratic fitting parameters for DU145 dose-response clonogenic curves and the corresponding Dose-Modifying Factor at 10% survival level (DMF10) due to the action of the pB reaction.

Table 3.
Linear–quadratic fitting parameters for PANC-1 dose-response clonogenic curves and the corresponding Dose-Modifying Factor at 10% survival level (DMF10) due to the action of the pB reaction.
In line with previously obtained results at other facilities [16,17], in our hands BSH did not exert any cytotoxic effect per se: the measured PE, which expresses the proliferative ability of unirradiated cells, was the same for samples treated or untreated with BSH, yielding values of around 0.64 and 0.46 for PANC-1 and DU145 cell lines, respectively.
All dose-response curves obtained from proton-irradiated cell cultures exhibit loss of cancer cell proliferative competence that is linearly dependent on the dose, as shown by the absence of a significant β value (Table 2 and Table 3) when experimental SFs data were fitted to the linear–quadratic Equation (4). For non-BSH treated cells, lack of a shouldered dose response, and hence of an appreciable portion of radiation-induced sublethal damage at low dose, reflects the relatively high LET of the incident proton beam. The presence of the BSH, on the other hand, results in a significant increase in the ability of proton irradiation to cause cancer cell death as clearly shown by even steeper clonogenic dose-response curves obtained for the two examined cell lines compared to those for cells exposed to protons in the absence of BSH (Figure 6 and Figure 7). Specifically, the DMF10, which quantifies BSH-associated exacerbation of proton-induced cell death, was found to be about 1.85 for the DU145 cell line and 1.56 for PANC-1 cells (Table 2 and Table 3), indicating that the pB reaction leads to an enhancement of proton biological effectiveness by over 80% and 50%, respectively. These are the largest values thus far measured for DU145 cells in previous studies on PBCT: the dose-modifying effect attributable to the pB reaction ranged between 1.46 and 1.29 when examined at mid-SOBP for clinical low-energy [16] and high-energy [17] proton beams, respectively. As for PANC-1, this is the first time that similar data are reported: the relatively smaller, yet significant, increase in pB-dependent effectiveness of proton irradiation at cell killing is in keeping with the known greater radioresistance associated with pancreatic cancer [34,35]. This is confirmed when comparing the non-BSH dose-response curve data obtained for DU145 (Figure 6 and Table 2) with those for PANC-1 cells (Figure 7 and Table 3). These results, taken together, confirm that the main biophysical rationale for the ability of PBCT to radiosensitize cancer cell lines hinges on the reaction between low-energy protons and 11B. Irradiating boron-treated cells with a monoenergetic proton beam with incident energy close to the predicted maximum cross section for the pB reaction has allowed to record the maximum effectiveness ever measured by the PBCT approach until now.
4. Discussion
Low-energy particle accelerators are useful for a variety of applications in physics and industry. One such a facility is the 3-MV Tandem Pelletron accelerator at the CIRCE laboratory [24,25]. However, there exists a paucity of such facilities equipped for radiobiological studies [22], which have stringent requirements in terms of dosimetry and beam parameter control. We therefore designed and implemented a radiobiology-dedicated beamline at the −40° beamline of the CIRCE accelerator. This allowed us to investigate in vitro the mechanistic basis of Proton–Boron Capture Therapy (PBCT) using low-energy monoenergetic proton beams. PBCT is an approach that had been hypothesized a few years ago to potentiate the limited usefulness of protontherapy (PT) towards radioresistant cancers based on the nuclear fusion reaction p + 11B→3α (pB) [11]. The working hypothesis is that the high-LET α-particles emitted by the pB reaction would cause more unrepairable damage than the low-LET clinical proton beam, and that such an increase in effectiveness would not spoil the favourable sparing of normal tissue granted by the inverse dose-depth profile of the proton Bragg curve, since the reaction is triggered by protons of around 675 keV; such low-energy protons in a clinical scenario can only be found in the tumour volume as they slow down across the tumour-confined SOBP. Although recent experimental radiobiological studies performed on PBCT have indeed shown an increase in the effectiveness by clinically used proton beams at cancer cell killing in the presence of 11B [16,17], the only circumstantial evidence supporting the role of the pB reaction in such an effect, hence of the high-LET particles generated by it as the main effectors of PBCT, has thus far relied on chromosomal aberration data [17]. Thus, it was important to corroborate the physical rationale of PBCT. This was done by investigating whether, under the same 11B treatment experimental conditions previously used, cellular irradiation with monoenergetic proton beams of energy as close as possible to the maximum for the pB reaction cross section would lead to an even greater biological effect, such as the induction of clonogenic cell death. Thus, not only has the novel setup here described allowed us to achieve a more than satisfactory reproducibility and uniformity in terms of dosimetry and beam parameters (e.g., energy monochromaticity, beam stability, irradiation field homogeneity) but, more importantly, it has enabled us to provide, for the first time, the radiobiological and pre-clinical evidence in support of the mechanistic bases on which the PBCT approach relies to improve the ability of PT to overcome tumour radioresistance.
The reliability of the new beamline for performing radiobiological experiments has been demonstrated by the results obtained for proton-induced cancer cell death when irradiation was performed in the absence of the 11B. Clinically used proton beams do exhibit a low LET, which is the very reason of the poor biological effectiveness of PT, yielding usually shouldered survival curves in the low-dose region; however, it is known that close to the distal portion of the SOBP, where the LET increases, the RBE also increases [36] and the clonogenic survival curves tend to become steeper and with a predominance of the α parameter: the dose-response curves obtained here for non-BSH irradiated cancer cells are in line with this observation and in fact appear as a purely decreasing exponential functions of the dose, as the incident LET is actually higher than that for typical high-energy PT facilities. More significantly, the clonogenic dose-response curves obtained at the newly developed proton beamline in the presence of BSH are also described by a pure exponential function of the dose and present a much steeper slope, typical of high-LET radiation, strongly supporting a role for the high-LET α-particles from the pB reaction. Moreover, they clearly show that the enhancement due to the pB reaction is the greatest thus far reported and as evaluated by the Dose-Modifying Factor at 10% cell survival level or DMF10. This was 1.85 for DU145 cells and around 1.56 for the more radioresistant PANC-1 cells: the former is actually higher than the maximum value reported for the DU145 in the first experimental study on PBCT at a relatively low-energy clinical proton beamline (INFN-LNS, Catania, Italy), which was of around 1.7 but just on the distal portion of the proton SOBP [16]. The significant pB-mediated radiosensitization observed for PANC-1 cells is novel and particularly relevant in view of making PT amenable for RT resilient cancer given the inherent radioresistance of the tumour histological type from which these cells originate.
In conclusion, the availability of the newly developed beamline at the CIRCE tandem accelerator will provide the opportunity to perform a wide range of radiobiology experiments and, in the context of PBCT, to further corroborate the mechanistic basis for this potentially clinically relevant strategy which, together with other physics-based approaches such as those envisaging the use of nanoparticles [10], as well as FLASH [37] or ultra-high dose rate irradiation regimes [38,39], may render PT even more readily available, safe and effective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.R. and L.M.; methodology, V.R., L.G. and L.M.; design of the irradiation setup: V.R., R.B. and G.P.; software, V.R. and K.M.; formal analysis, V.R., L.M. and P.B.; investigation, V.R., G.P. and G.C. (Giuseppina Crescente), R.B. and L.M.; resources, S.P. and L.M.; data curation, V.R. and L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, V.R. and L.M.; writing—review and editing, V.R. and L.M.; funding acquisition, G.C. (Giacomo Cuttone), L.G., L.M. and S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by INFN grant NEPTUNE (Nuclear process-driven Enhancement of Proton Therapy UNravEled) and MIUR PRIN Proton-Boron Capture Therapy 2017XKWWK9.
Data Availability Statement
Data are not publicly available but can be made available on request by the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Antonio Palmieri and Lorenzo Panico from the technical staff of the Università della Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” and INFN mechanical workshops for their support in the design and original mechanical components’ production phase.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Newhauser, W.D.; Zhang, R. The physics of proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, R155–R209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particle Therapy Co-Operative Group (PTCOG). Available online: https://www.ptcog.ch/index.php/facilities-in-operation (accessed on 19 September 2021).
- Eaton, B.R.; MacDonald, S.M.; Yock, T.I.; Tarbell, N.J. Secondary Malignancy Risk Following Proton Radiation Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, M.; Murayama, S.; Akimoto, T.; Demizu, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Ishida, Y.; Oshiro, Y.; Numajiri, H.; Fuji, H.; Okumura, T.; et al. Long-term follow-up after proton beam therapy for pediatric tumors: A Japanese national survey. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H.; Niemierko, A.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Gerweck, L.E.; Goitein, M.; Loeffler, J.S.; Suit, H.D. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values for proton beam therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, S.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Hammond, E.M. Cyclic Hypoxia: An Update on Its Characteristics, Methods to Measure It and Biological Implications in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petringa, G.; Romano, F.; Manti, L.; Pandola, L.; Attili, A.; Cammarata, F.; Cuttone, G.; Forte, G.; Manganaro, L.; Pipek, J.; et al. Radiobiological quantities in proton-therapy: Estimation and validation using Geant4-based Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Med. 2019, 58, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwaeren, L.; Dok, R.; Verstrepen, K.; Nuyts, S. Clinical Progress in Proton Radiotherapy: Biological Unknowns. Cancers 2021, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjolet, C.; Nicol, A.; Limagne, E.; Mura, C.; Richard, C.; Morgand, V.; Rousseau, M.; Boidot, R.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Noel, G.; et al. Impact of proton therapy on antitumor immune response. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.; de Kock, M.; Engelbrecht, M.; Miles, X.; Slabbert, J.; Vandevoorde, C. Radiosensitization Effect of Gold Nanoparticles in Proton Therapy. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 699822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.-K.; Jung, J.-Y.; Suh, T.S. Application of proton boron fusion reaction to radiation therapy: A Monte Carlo simulation study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 223507/1–223507/4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.W.; Rolfs, C.; Trautvetter, H.P. Low-energy cross sections for 11B(p,3alpha). Z. Phys. At. Nucl. 1987, 327, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkins, P.S.; O’Neil, P.; Stevens, D.; Fairman, M.P. The severity of alpha-particle-induced DNA damage is revealed by exposure to cell-free extracts. Radiat. Res. 1996, 146, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasai, K.; Evans, J.W.; Kovacs, M.S.; Brown, J.M. Prediction of human cell radiosensitivity: Comparison of clonogenic assay with chromosome aberrations scored using premature chromosome condensation with fluorescence in situ hybridization. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 30, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, L.; Durante, M.; Grossi, G.; Lattuada, M.; Pugliese, M.; Sabini, M.G.; Scampoli, P.; Valastro, L.; Gialanella, G. Modelled microgravity does not modify the yield of chromosome aberrations induced by high-energy protons in human lymphocytes. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2005, 81, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirrone, G.A.P.; Manti, L.; Margarone, D.; Petringa, G.; Giuffrida, L.; Minopoli, A.; Picciotto, A.; Russo, G.; Cammarata, F.; Pisciotta, P.; et al. First experimental proof of Proton Boron Capture Therapy (PBCT) to enhance protontherapy effectiveness. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bláha, P.; Feoli, C.; Agosteo, S.; Calvaruso, M.; Cammarata, F.P.; Catalano, R.; Ciocca, M.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Conte, V.; Cuttone, G.; et al. The Proton-Boron Reaction Increases the Radiobiological Effectiveness of Clinical Low-and High-Energy Proton Beams: Novel Experimental Evidence and Perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 682647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manti, L.; Braselmann, H.; Calabrese, M.L.; Massa, R..; Pugliese, M.; Scampoli, P.; Sicignano, G.; Grossi, G. Effects of modulated microwave radiation at cellular–telephone frequency (1.95 GHz) on X ray-induced chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes in vitro. Radiat. Res. 2008, 169, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignalosa, D.; Bertucci, A.; Gialanella, G.; Grossi, G.; Manti, L.; Pugliese, M.; Scampoli, P.; Durante, M. Chromosome inter- and intrachanges detected by arm-specific DNA probes in the progeny of human lymphocytes exposed to energetic heavy ions. Radiat. Res. 2008, 170, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaledi, N.; Wang, X.; Hosseinabadi, R.; Samiei, F. Is the proton–boron fusion therapy effective? J. Radiother. Pract. 2021, 20, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucconi, D.; Bortot, D.; Pola, A.; Fazzi, A.; Cazzola, L.; Conte, V.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Petringa, G.; Cuttone, G.; Manti, L.; et al. Experimental investigation at CATANA facility of n-10B and p-11B reactions for the enhancement of proton therapy. Phys. Med. 2021, 89, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IonBeamCenters.eu. Available online: https://www.ionbeamcenters.eu/ion-beam-facilities (accessed on 19 September 2021).
- Belli, M.; Cherubini, R.; Galeazzi, G.; Mazzucato, S.; Moschini, G.; Sapora, O.; Simone, G.; Tabocchini, M.A. Proton irradiation facility for radiobiological studies at a 7 MV Van de Graaff accelerator. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 1987, 256, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialanella, L.; Di Leva, A.; Terrasi, F. Nuclear Astrophysics at CIRCE. Nucl. Phys News 2018, 28, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrasi, F.; Rogalla, D.; De Cesare, N.; D’Onofrio, A.; Lubritto, C.; Marzaioli, F.; Passariello, I.; Rubino, M.; Sabbarese, C.; Casa, G.; et al. A new AMS facility in Caserta/Italy. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 2007, 259, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAIR-INFN Sezione di Napoli. Available online: http://www.esalerno.com/gerardogiordano/products/fair/index_lllita.html (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Durante, M.; Grossi, G.; Pugliese, M.; Manti, L.; Nappo, M.; Gialanella, G. Single-charged particle damage to living cells: A new method to detect traversals based on track-etch detectors. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 1994, 94, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, F.; Durante, M.; Gialanella, G.; Grossi, G.; Manti, L.; Pugliese, M.; Scampoli, P. Development of an automated scanning system for the analysis of heavy ions’ fragmentation reactions by nuclear track detectors. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ziegler, J.F.; Ziegler, M.D.; Biersack, J.P. SRIM—The stopping and range of ions in matter. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 2010, 268, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, L.; Jamali, M.; Prise, K.M.; Michael, B.D.; Trott, K.R. Genomic instability in Chinese hamster cells after exposure to X-rays, neutrons or alpha-particles of different LET. Radiat. Res. 1997, 147, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puck, T.T.; Marcus, P.I. Action of X-rays on mammalian cells. J. Exp. Med. 1956, 103, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manti, L.; Davies, H.E.; Venables, S.; Bowen, I.D.; Court, J.B. Correlation between the clonogenic initial slope and the response of polykaryon-forming units: The behavior of strains defective in XRCC5 and ATM and the heritability of small variations in radioresponse. Radiat. Res. 2000, 154, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M. SIMNRA, a simulation program for the analysis of NRA, RBS and ERDA. AIP Conf. Proc. 1999, 475, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanuma, K.; Moriai, R.; Yajima, T.; Yagihashi, A.; Yamada, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Watanabe, N. Survivin as a radioresistance factor in pancreatic cancer. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2000, 91, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordes, N.; Frick, S.; Brunner, T.; Pilarsky, C.; Grützmann, R.; Sipos, B.; Klöppel, G.; McKenna, W.G.; Bernhard, E.J. Human pancreatic tumor cells are sensitized to ionizing radiation by knockdown of caveolin-1. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6851–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Marshall, T.I.; Perozziello, F.M.; Manti, L.; Currell, F.J.; Hanton, F.; McMahon, S.J.; Kavanagh, J.N.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Romano, F.; et al. Relative biological effectiveness variation along monoenergetic and modulated Bragg peaks of a 62-MeV therapeutic proton beam: A preclinical assessment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, S.; Owen, H.; Schippers, M.; Welsch, C. Technical challenges for FLASH proton therapy. Phys. Med. 2020, 78, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, F.; Anzalone, A.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Carpinelli, M.; Cuttone, G.; Cutroneo, M.; De Martinis, C.; Giove, D.; Korn, G.; Maggiore, M.; et al. ELIMED, MEDical and multidisciplinary applications at ELI-Beamlines. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 508, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, L.; Perozziello, F.M.; Borghesi, M.; Candiano, G.; Chaudhary, P.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Doria, D.; Gwynne, D.; Leanza, R.; Prise, K.M.; et al. The radiobiology of laser-driven particle beams: Focus on sub-lethal responses of normal human cells. J. Instr. 2017, 12, C03084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).