Abstract
Hexavalent chromium contamination in groundwater has become a very serious and challenging problem. Identification of the groundwater chemical characteristics of the sites and their control mechanisms for remediation of pollutants is a significant challenge. In this study, a contaminated site in Xinxiang City, Henan Province, was investigated and 92 groundwater samples were collected from the site. Furthermore, the hydrogeochemical characteristics and the distribution patterns of components in the groundwater were analyzed by a combination of multivariate statistical analysis, Piper diagram, Gibbs diagram, ions ratio and hydrogeochemical simulation. The results showed that the HCO3-Cl-Mg-Ca type, SO4-HCO3-Na type, and HCO3-Mg-Ca-Na type characterize the hydrogeochemical composition of shallow groundwater and HCO3-Cl-Mg-Ca type, HCO3-Na-Mg type, and HCO3-SO4-Mg-Na-Ca type characterize the hydrogeochemical composition of deep groundwater. Ion ratios and saturation index indicated that the groundwater hydrogeochemical characteristics of the study area are mainly controlled by water–rock action and evaporative crystallization. The dissolution of halite, gypsum and anhydrite, the precipitation of aragonite, calcite and dolomite, and the precipitation of trivalent chromium minerals other than CrCl3 and the dissolution of hexavalent chromium minerals occurred in groundwater at the site. The minimum value of pH in groundwater at the site is 7.55 and the maximum value is 9.26. The influence of pH on the fugacity state of minerals was further investigated. It was concluded that the saturation index of dolomite, calcite, aragonite and MgCr2O4 increases with the increase of pH, indicating that these minerals are more prone to precipitation, and the saturation index of Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and CrCl3 decreases with the increase of pH, implying that Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and CrCl3 are more prone to dissolution. The saturation index of the remaining minerals is less affected by pH changes. The study can provide a scientific basis for groundwater remediation.
1. Introduction
In many parts of the world, water scarcity has posed a great threat to socio-economic development and the ecological environment [,]. Due to the limited surface water resources and precipitation, groundwater resources have become indispensable freshwater resources for domestic drinking, irrigation water and industrial activities [,,,]. With large-scale industrial activities, groundwater pollution has become a serious problem affecting human health and life in many countries and regions, and as of 2018, the number of declared contaminated sites in 31 provincial capitals in China reached 174. In the process of industrial development, chromium has been used in a growing number of industries, and chromium salt production has subsequently developed to a certain extent [,,,,]. At the same time, a large amount of chromium slag was produced, and after its long-term open piling, Cr(VI) will seep into the soil and groundwater with surface runoff, thus causing pollution to the surrounding soil and groundwater, and since Cr(VI) is a highly migratory and toxic pollutant, chromium pollution in groundwater has therefore become a serious worldwide problem [,,,]. Cr(VI) has been identified as highly toxic and one of the carcinogens, posing a threat to human health when chromium exceeds drinking water standards.
Groundwater contamination investigation and remediation is urgent, and the analysis of hydrogeochemical parameters are important to grasp the groundwater quality status [,,,,,]. The study of hydrogeochemical composition and its origins is the basis of groundwater protection and restoration. There are many methods, with the most common ones being multivariate statistical analysis [,], the isotope labeling method and the hydrogeochemical simulation method [,,]. Xiao Yong et al. studied the characteristics and controlling factors of groundwater chemistry in the long-term use area of reclaimed water in Beijing by Piper’s trilinear diagram, ionic proportional relationship and saturation index method, and concluded that the changes in the types of groundwater chemistry and water–rock action during the rainy and dry season, and believed that the hydrogeological conditions of the area should be fully considered when reclaimed water was used for agricultural irrigation and ecological landscape []. Zhang Jingtao et al. explored the hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Dachaidan area from the pre-mountain alluvial fan to the salt lake by ion ratio analysis, Gibbs plot and hydrogeochemical simulation, and concluded that the water–rock interaction was dominated by the dissolution of halite and gypsum and positive cation exchange []. Ashwani used a multivariate statistical and hydrogeochemical approach to analyze Cr(VI) concentration levels, pollutant sources and groundwater geochemistry in an industrial town in Italy to provide an effective aid for water resource management in the region []. By testing chemical parameters related to fluoride in groundwater during the periods of abundance, flatness and depletion, D. Laxmankumar concluded that weathering, ion exchange and anthropogenic activities played an important role on the chemical composition of groundwater using Gibbs plot and principal component analysis [].
Chromium exists in groundwater mainly as trivalent chromium and hexavalent chromium []. The migration and transformation of chromium in groundwater is influenced by the redox potential, acidity and concentration [,]. Under acidic conditions with low redox potential, chromium mainly exists as Cr(III). As pH increases, the solubility of Cr(III) decreases and Cr(OH)3 precipitation is formed. Under alkaline conditions with high redox potential, chromium is mainly present as Cr(VI) [,]. Most of the research focused on the chromium migration and transformation by performing batch and column experiments indoors. The chromium presence pattern was analyzed by varying different pH and concentration values by the controlled variable method. Column experiments usually take a lot of time to complete. In this study, the presence pattern of Cr in representative samples was characterized by numerical simulation using saturation index.
Xinxiang City is a significant industrial base in the North China Plain. To date, there are many left industrial contaminated sites. Thus, it is necessary to get insight into the influence of contaminants on groundwater. Although it has been determined that the groundwater quality at the contaminated site exceeds the Class III water standard, the groundwater hydrogeochemical characteristics and their governing mechanisms are still poorly known. The purpose of this work was to investigate the level of contamination in groundwater, hydrogeochemical characteristics and their origins at a contaminated site in Xinxiang by using mathematical statistics, correlation analysis, ion ratio analysis and saturation index, and to study the hydrogeochemical processes controlling the evolution of groundwater chemistry and the influencing factors of chromium-containing mineral by means of hydrogeochemical simulation. This study will provide effective assistance for groundwater remediation in the region.
2. Description of the Study Area
The study area is located in the northwestern part of Xinxiang City, Henan Province (Figure 1), with a temperate continental monsoon climate and a multi-year average temperature of 14 °C. The multi-year average precipitation is 586.32 mm, with more than 70% occurring in the rainy season spanning June to September. The multi-year average evaporation is 1772.62 mm, which is three to four times the precipitation with the strongest evaporation in June.
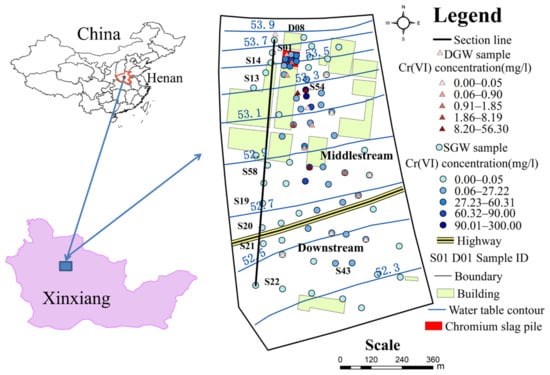
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and the sampling sites. DGW represents deep groundwater. SGW represents shallow groundwater. Dots represent shallow sampling points. Triangles represent deep sampling points. The boundary represents the boundary of the numerical model. Henan is located in the central part of China. Xinxiang City is located in the north of Henan Province.
Xinxiang City is located at the southeastern foot of Taihang Mountains and the northern edge of the alluvial plain in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. The terrain generally inclines from northwest to southeast. The regional landform types are divided into three types of landforms: alluvial valley, alluvial sloping plains and alluvial plains. The geomorphological type of the study area is alluvial sloping plain. The surface of the study area reveals the Quaternary river-phase sedimentary layer with a thickness of 50–60 m, and the lithology is mainly clay and sand. The groundwater type is pore water of loose rock of the Quaternary, and the media of the aquifer are mainly medium sand and fine sand, with coarse sand locally. According to the profile, it can be seen that the lithology from 56 m to 49 m is silty clay and silt. The lithology from 59 m to 49 m is silty clay and silt. This is followed by a shallow aquifer with a thickness of 3 m. However, the aquifer thickness increased significantly at borehole S22. The lithology from 46 m to 36 m is mainly silty clay. The bottom lithology is mainly fine sand. The aquifer is mainly recharged by atmospheric precipitation, lateral runoff and irrigation recharge, and groundwater discharge is mainly exploitation, evaporation and lateral runoff.
Chromium salt chemical plants existed in the study area during the historical period, and chromium slag from the production process brought serious contamination to the site soil and groundwater (Figure 2). Test results showed that the average concentration of total chromium in the soil was 12,100 mg/kg, and work has been carried out to remediate the soil and groundwater.
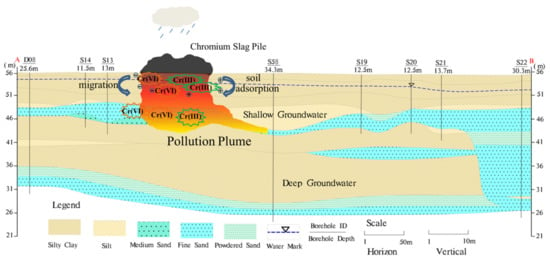
Figure 2.
The hydrogeological cross section along the A–B and pollution conceptual model. In the pollution plume, the red color represents the high concentration value. Yellow color represents low concentration value.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
In groundwater contamination investigation sampling, determining the location of sampling sites was a key factor. This sampling was mainly based on the following principles. Firstly, samples should uniformly along the groundwater flow direction. Secondly, the sampling points are encrypted in the seriously polluted areas. Thirdly, the general shape of the contamination plume can be determined according to the sampling points.
In December 2020, field investigations and sampling were conducted in the study area, and 92 groundwater samples were collected, including 73 shallow groundwater (SGW) samples and 19 deep groundwater (DGW) samples, with the locations of the sampling sites as shown in Figure 1. The total dissolved solids (TDS) and pH were measured in the field using a multiparameter tester. Other chemical indicators (Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Cr(VI), HCO3−, SO42−, Cl−, NO3−) were measured in the laboratory of Henan Province Rock and Mineral Testing Center. The charge balance errors of all samples were within 5%, and the accuracy of each indicator met the quality requirements.
3.2. Multivariate Statistical Analyses
Statistical methods are an effective tool in groundwater quality assessment. Groundwater contamination can be determined by graphical and multivariate statistical methods, such as, Piper diagram, Gibbs diagram and Ion ratio. Multivariate statistical methods play an important role in the identification of pollution sources, such as correlation analysis. It can determine the degree of correlation between different parameters. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to analyze the degree of dependency of one parameter to the other [,].
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemistry
The analysis of groundwater chemistry data can help to determine the geochemical parameters of groundwater and the distribution characteristics of contaminants. The statistics and analysis of the test results of groundwater samples were shown below.
The minimum value of pH of shallow groundwater in the study area was 7.55 and the maximum value was 9.26, which was alkaline overall and favorable to the precipitation and oxidation of trivalent chromium. The average distribution of the main cation concentrations: Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Cr > K+ > Fe > Mn > NH4+ > As > Pb, and the average distribution of the main anion concentrations: HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− > CO32− > NO2−. The order of triple nitrogen content in groundwater in the study area was NO3− > NO2− > NH4+, which mainly polluted groundwater in the form of nitrate nitrogen [].
Among the ionic components of shallow groundwater, the coefficients of variation of SO42−, Cl−, NO3−, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3− and Fe were relatively small, and the contents of these ions in shallow groundwater were relatively stable. In contrast, the coefficients of variation (C.V.) of NO2−, Mn, NH4+, As, Pb, Cr(VI), CO32− and K+ all exceeded 100%, which belonged to a strong degree of variation, indicating that the contents of these ions in shallow groundwater were highly variable, and at the same time these ions were sensitive factors that vary with environmental and anthropogenic factors.
The pH of deep groundwater in the study area was 7.8 at minimum and 8.34 at maximum, which was alkaline overall. The distribution of the main cation concentration: Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Cr(VI) > K+ > Fe > Mn > NH4+, the distribution of the main anion concentration: HCO3−> SO42− > Cl− > NO3− > NO2−, and As, Pb, CO32− were not detected in the deep aquifer. The distribution of the remaining ions was similar to that of the shallow layer.
As can be seen from Table 1, the coefficients of variation of SO42−, Cl−, NO3−, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, Fe and K+ in the deep groundwater were relatively small, and the contents of these ions in deep groundwater were relatively stable. The coefficients of variation of NO2−, Mn, NH4+, Cr(VI) and CO32− all exceeded 100%, which belonged to strong degree of variation.

Table 1.
Statistical descriptions of chemical parameters.
4.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Groundwater Chemistry
4.2.1. Hydrogeochemical Facies
A Piper diagram can help to evaluate the geochemical relationships between different dissolved ions and dominant types of water chemistry in groundwater []. The TDS of shallow groundwater was 738.4–2532.6 mg/L []. The shallow groundwater was highly variable with HCO3−, SO42−, Cl−, NO3− as the main anions and Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+ as the main cations. The NO3− concentration in the water samples was high and exceeded the quality standard for domestic drinking water, probably due to the inappropriate use of fertilizers making NO3− enter the groundwater with rainfall and irrigation []. The HCO3-Cl-Mg-Ca type, SO4-HCO3-Na type and HCO3-Mg-Ca-Na type characterized the hydrogeochemical composition of shallow groundwater (Figure 3). The groundwater below the chromium slag pile (CSP) was SO4-HCO3-Na type. The reason was related to the production process of chromium salt, and the specific chemical reaction was 2Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 = Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O, so SO42− and Na+ will enter the groundwater under the leaching effect of chromium slag. The downstream was basically uncontaminated, and the groundwater was HCO3-Mg-Ca-Na type. The groundwater of middle reaches and east of the chromium slag piles was HCO3-Cl-Mg-Ca type.
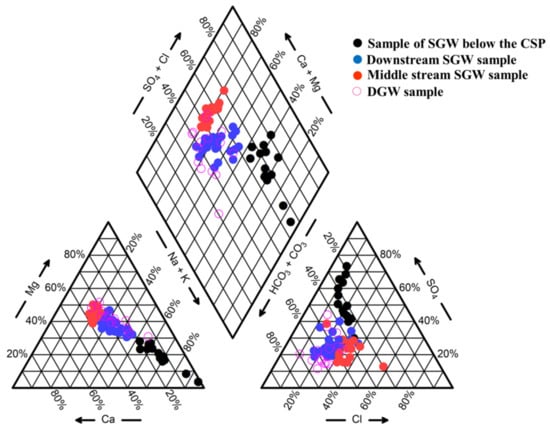
Figure 3.
Piper diagram for shallow and deep groundwater. CSP represents chromium slag pile.
The TDS of deep groundwater in the site was 504–1198.26 mg/L. The anions were mainly HCO3−, SO42−, Cl−, NO3−, and the cations were mainly Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+. The NO3− concentration in the deep groundwater was lower than that in the shallow groundwater, but still exceeded the quality standard of domestic drinking water. It may be that the shallow groundwater overflowed into the deep groundwater, resulting in abnormal NO3− concentration in the deep groundwater. The deep hydrogeochemical composition was simpler than the shallow ones, and the groundwater was mainly HCO3-Cl-Mg-Ca type, HCO3-Na-Mg type and HCO3-SO4-Mg-Na-Ca type.
4.2.2. Spatial Distribution Pattern of Ions
Spatial Distribution Pattern of Ions in Shallow Groundwater
Based on the analytical results of shallow groundwater samples, the spatial distribution pattern of ions was analyzed to study the spatial contamination characteristics of each ion component in groundwater (Figure 4a). The pollutant correlation coefficient matrix was plotted using R (Figure 4b). The Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to characterize the correlation between different pollutants.
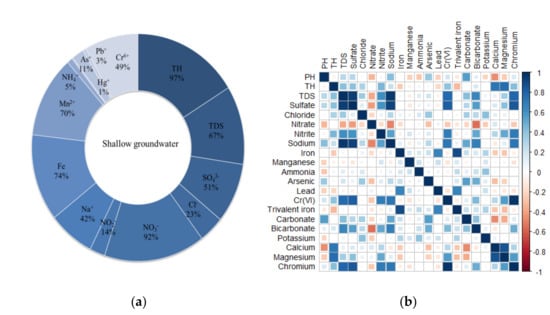
Figure 4.
(a) Exceedance rate of each component of groundwater, (b) pollutant correlation coefficient matrix.
The TDS of 67% of the shallow groundwater samples exceeded three types of groundwater standards, especially the TDS concentration below the chromium slag pile and near the slag pile was the highest, and the water quality was poor, which was seriously affected by the chromium slag pile. Among the tested samples, the total hardness of 97% of the groundwater samples exceeded three types of groundwater standards, and the distribution of total hardness was similar to that of Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentration distribution, and the correlation coefficient reached 75%, indicating that the total hardness was mainly affected by the Ca2+ and Mg2+. The SO42− concentration of 51% of the groundwater samples exceeded three types of groundwater standards, and the distribution of sulfate concentration was extremely similar to that of TDS, and the correlation coefficient reached 95%. Generally, SO42− ions came from the dissolution of gypsum or sulfate sedimentary rocks. However, it can be seen that a large amount of sulfuric acid was used in the production of chromium salt, so it can be concluded that the SO42− exceeded the standard in groundwater and was closely related to the production of chromium salt, and the correlation coefficient with Cr(VI) reached 83%. The NO3− concentration of 92% of the groundwater samples exceeded three types of groundwater standard. Na+ concentration distribution was similar to that of TDS and SO42− with a correlation coefficient of 96%, and the correlation coefficient between Na+ and Cr(VI) was 0.72, mainly due to the fact that a large amount of sodium chromate and sodium sulfate will be produced in the chromium salt production process, resulting in the exceedance of Na+ concentration in groundwater. The exceedance of Fe and Mn reached 74% and 70%, respectively. The exceedance of Cr(VI) was 49%, which had a certain contribution rate to TDS, and the correlation coefficient reached 78%. Pb and Hg concentrations in groundwater samples had low exceedance rates, which may be related to human activities.
Spatial Distribution Pattern of Ions in Deep Groundwater
According to the analysis results of deep groundwater samples, it can be concluded that the total hardness of 68% of the tested samples exceeded the three groundwater standards, and the distribution of total hardness was similar to the distribution of Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations, with a correlation coefficient of 75% (Figure 5). The over-standard rate of TDS was 16%. For cations, Mg2+ had the highest correlation coefficient with TDS, reaching 0.81, followed by Cr(VI), reaching 0.79, indicating that Mg2+ contributed the most to the increase of TDS, and for anions, SO42− had the highest correlation coefficient with TDS, reaching 0.89, indicating that SO42− contributed the most to the increase of TDS. Na+ exceeded the standard by 5%, and the correlation coefficient reached 79% with hexavalent chromium. The over-standard rate of NO3− was 79%. The over-standard rates of Fe and Mn reached 68% and 74%, respectively, which were comparable to those of Fe and Mn in shallow groundwater. The 58% of Cr(VI) concentration exceeded the standard in deep groundwater, and the highest correlation coefficient between Cr(VI) and SO42− reached 0.92. Deep groundwater was less polluted than shallow groundwater, and the ion concentration was less than that of shallow groundwater, and the overall exceedance rate of each component was lower than that of shallow groundwater. The reason for exceeding the standard was mainly due to the shallow groundwater overflowing into deep groundwater.
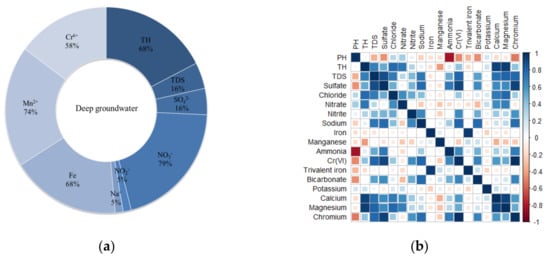
Figure 5.
(a) Exceedance rate of each component of groundwater, (b) pollutant correlation coefficient matrix.
4.3. Analysis of the Causes of Groundwater Chemistry Types
4.3.1. Groundwater Chemistry Control Mechanisms
A Gibbs plot can be used to illustrate the causal mechanism of water chemical composition []. In the Gibbs plot, if the TDS value is high and the Na+/(Na++Ca2+) or Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−) ratio is close to 1, the ion control mechanism is evaporative crystallization. If the TDS value is medium and the Na+/(Na++Ca2+) or Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−) ratio is less than 0.5, the ion control mechanism is water rock effect. If TDS value is low and the Na+/(Na++Ca2+) or Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−) ratio is close to 1, the water chemistry component control mechanism is the rainfall effect [,]. From the Figure 6, it can be seen that the chemical composition of groundwater in the study area is mainly dominated by water–rock action.
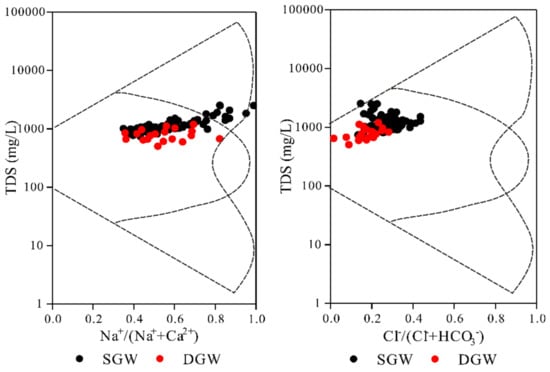
Figure 6.
Gibbs diagrams showing the groundwater chemistry controlling mechanisms.
4.3.2. Major Ion Ratio Relationship
In order to further explore the process of site water chemistry, the interrelationship between each major ion was analyzed []. As can be seen from Figure 7a, most of the shallow groundwater samples were distributed along the Na/Cl ratio 1:1 line (halite dissolution line), and the Na/Cl ratio of a few samples was greater than 1, indicating that there were other sources of Na+ in the groundwater in addition to halite dissolution filtration, mainly related to the production process of sodium dichromate, which led to the increase of Na+ concentration in the groundwater around the chromium slag dumps. Most of the deep groundwater samples were distributed along the Na/Cl ratio 1:1 line, and the Na/Cl ratio values of a few samples were greater than 1, mainly because the shallow contaminated groundwater entered the deep aquifer, leading to the Na+ concentration to increase.
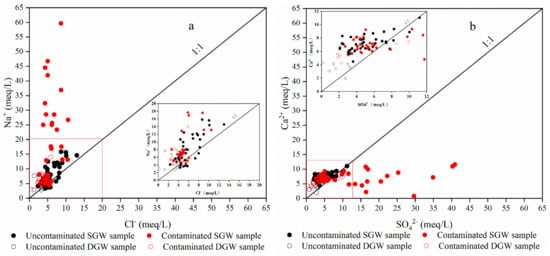
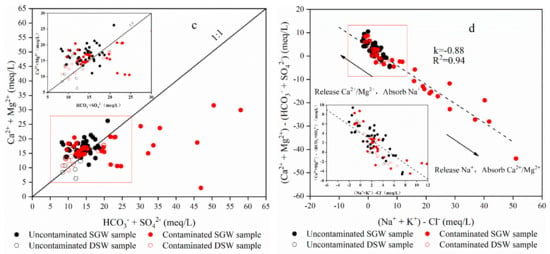
Figure 7.
Groundwater main ion relationship diagram. (a) represents the ratio of Na+ and Cl−, which generally indicates the dissolution of halite. (b) rep-resents the ratios of Ca2+ and SO42−, which generally indicates the dissolution of gypsum and an-hydrite. (c) indicates the dissolution of calcite and dolomite. (d) can indicate the presence or ab-sence of ion exchange interaction.
The sources of Ca2+ and SO42− are commonly the dissolution of gypsum and anhydrite. As can be seen from Figure 7b, most of the shallow groundwater samples were distributed along the Ca/SO4 ratio 1:1 line (gypsum and anhydrite dissolution line), and a few samples had Ca/SO4 ratio less than 1, mainly because the plant will use a large amount of sulfuric acid in the production process leading to the increase of SO42− concentration in groundwater around the chromium slag pile, while the groundwater sample points near the Ca/SO4 ratio 1:1 line showed most samples with Ca/SO4 ratios greater than 1, and it may be alternate cation adsorption with constant Ca2+ release. The deep groundwater samples were all distributed along the Ca/SO4 ratio 1:1 line, but most of the samples presented Ca/SO4 ratios greater than 1, indicating that the dissolution of aragonite, calcite and dolomite was a potential source of Ca2+ in the site groundwater.
From the relationship pattern of (Ca2++Mg2+)/(SO42−+HCO3−) [], it was clear that the majority of water samples were distributed along the 1:1 line, except for groundwater samples with heavily contaminated samples, further indicating that calcite, dolomite, gypsum and anhydrite dissolution were potential sources of major ions in the groundwater mineralization process (Figure 7c).
In addition, the relationship between (Ca2++Mg2+)-(SO42−+HCO3−) and (Na++K+)-Cl− can usually be used to determine whether there is an ion alternate adsorption reaction in the aquifer. If the two are linear and the slope is close to –1, it indicates the existence of ion exchange, where the sample points distributed along the fitted line on the right side of the origin are the cation alternate. The sample points distributed along the fitted line to the left of the origin were the reverse reaction of alternate cation adsorption, and R2 = 0.94 as shown in Figure 7d. This indicated that ion exchange existed in the groundwater of the site, which further illustrated that the part of groundwater sample points continuously released Ca2+ under the reverse reaction of alternate cation adsorption. It verified the result that the Ca/SO4 ratio was greater than 1.
4.4. Hydrogeochemical Simulation and Analysis
The potential hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater were investigated through ion ratio relationships. In this section, the minerals saturation index (SI) was calculated by Phreeqc 2.8 [] to further determine the forms of the various minerals present and the geochemical interactions.
4.4.1. Mineral Saturation Index Analysis
The saturation index of minerals can visualize the dissolved equilibrium state of components in groundwater. Three representative water samples were selected for this study: the severely contaminated water sample S54 with hexavalent chromium concentration of 257 mg/L, the moderately contaminated water sample S01 with hexavalent chromium concentration of 60.3 mg/L, and the lightly contaminated water sample S43 with hexavalent chromium concentration of 0.729 mg/L. For the water sample S54, the saturation index of hexavalent chromium minerals was CaCrO4 > Na2CrO4 > MgCrO4 > K2CrO4 > Na2Cr2O7 > K2Cr2O7 > CrO3, and the saturation index was less than 0, which indicated that hexavalent chromium minerals were easily dissolved in the groundwater, and the proportion of chromium oxide was the largest among chromium minerals. The saturation index of trivalent chromium minerals was ordered as Cr2O3 > MgCr2O4 > Cr(OH)3 > CrCl3, and the saturation index of Cr2O3, MgCr2O4 and Cr(OH)3 were greater than 0, while the saturation indices of CrCl3 were less than 0. It can be concluded from the saturation index of trivalent chromium minerals that most of the trivalent chromium minerals were insoluble in groundwater, and CrCl3 made the greatest contribution to the concentration of trivalent chromium ions. For groundwater sample S01, the saturation index of hexavalent chromium minerals and trivalent chromium minerals showed the same variation pattern with S54. For groundwater sample S43, the saturation index of hexavalent chromium minerals was ranked as CaCrO4 > Na2CrO4 > MgCrO4 > K2CrO4 > CrO3 > K2Cr2O7 > Na2Cr2O7, and the saturation index of hexavalent chromium minerals was less than 0, indicating that hexavalent chromium minerals were easy to dissolve into groundwater, but the order of mineral saturation index had changed, and the Na2Cr2O7 component had the largest proportion in chromium-containing minerals. The saturation index of trivalent chromium minerals showed the same change pattern as S54 and S01(Figure 8a).
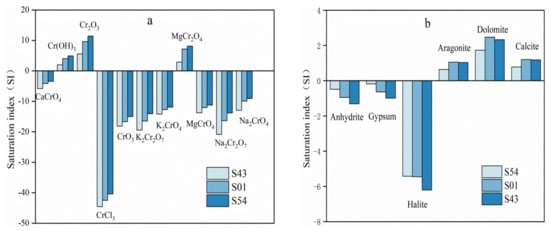
Figure 8.
Comparison of saturation index (SI) at three points, (a) refers to chromium-containing minerals, including trivalent chromium and hexavalent chromium. (b) contains anhydrite, gypsum, halite, aragonite, dolomite and calcite.
By comparing the saturation index of chromium-containing minerals at S54, S01 and S43, and it can be concluded that the higher the chromium ion concentration in the aquifer, the greater the saturation index of chromium-containing minerals, the smaller the tendency for hexavalent chromium minerals to dissolve and the greater the tendency for trivalent chromium minerals to precipitate.
Figure 8b showed the simulation results of the saturation index of the main minerals. The results showed that anhydrite, gypsum and halite were under unsaturated state in groundwater, and halite was the most prone to dissolution, and calcite, aragonite and dolomite were under saturated state, and dolomite was the most prone to precipitation.
4.4.2. Analysis of the Effect of pH on Minerals
After statistical analysis, the pH variation range of the site groundwater was 7.55–9.26, so the trend of minerals in the aquifer was further determined by analyzing the effect of pH variation on the saturation index of minerals. Taking S01 as an example, the pH was taken as 7.55, 8, 8.26, 9 and 9.26, respectively, which can truly reflect the trend of dissolution and precipitation of minerals in the aquifer.
As can be seen from Figure 9, the saturation index of dolomite, calcite, aragonite and MgCr2O4 is increasing with the increase of pH, indicating that MgCr2O4 was more prone to precipitation in the alkaline environment, mainly because the ionic activity product increases with the increase of pH under the condition of constant temperature, which led to the easy precipitation. With the increase of pH, the saturation index of Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and CrCl3 were decreasing, indicating that the dissolution of Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and CrCl3 was more likely to occur in the alkaline environment, mainly because the ionic activity product decreased with the increase of pH under the condition of constant temperature, which led to the dissolution to occur easily, and the saturation index of the remaining minerals was less affected by the change of pH.
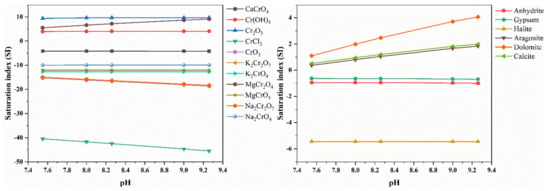
Figure 9.
The influence of pH on the SI of minerals.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the distribution pattern of hydrogeochemical characteristics at a contaminated site in Xinxiang was analyzed by combination of multivariate statistical analysis and hydrochemistry, and the following conclusions were drawn.
- 1.
- The hydrochemical type of groundwater in the study area have obvious differences in the horizontal and the vertical directions, reflecting the influence of the chromium slag pile on groundwater. In the shallow groundwater, the groundwater below the chromium slag heap is the SO4-HCO3-Na type, the hydrogeochemical composition east of the chromium slag heap and in the midstream is the HCO3-Cl-Mg-Ca type, and the downstream is basically uncontaminated with the HCO3-Mg-Ca-Na type. The deep groundwater shows the HCO3 type.
- 2.
- Gibbs plots, ion ratios and saturation index indicated that the hydrogeochemical characteristics of the study area are mainly controlled by water-rock action and evaporative crystallization, with dissolution of halite, gypsum and anhydrite, precipitation of aragonite, calcite and dolomite, and precipitation of trivalent chromium minerals other than CrCl3 and dissolution of hexavalent chromium minerals occurring in the groundwater of the site.
- 3.
- The groundwater in the study area is generally alkaline with a minimum pH of 7.55, which is conducive to the precipitation of trivalent chromium and the dissolution of hexavalent chromium. With the increase of pH, the saturation index of dolomite, calcite, aragonite and MgCr2O4 keeps increasing, and these minerals are more likely to precipitate. The saturation index of Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and CrCl3 is decreasing, and the more easily Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and CrCl3 dissolve, and the saturation index of the remaining minerals is less affected by the change of pH.
- 4.
- Currently, the groundwater at the site is heavily contaminated and the groundwater chemistry type is altered. First, we should analyze the effects of other contaminants on chromium remediation in conjunction with indoor experiments. Second, we should maintain the concept of joint management of soil and groundwater. Third, the site groundwater runoff conditions are relatively poor and can be remediated by permeable reactive barriers technology and in situ injection of pharmaceuticals.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, Y.C. and Q.Z.; investigation, Y.Z., Y.S., W.S. and Z.L.; writing-original draft preparation, W.C.; writing-review and editing, W.C. and Y.Z. (Co-first authors); supervision, Y.C. and Q.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Provincial Department of Natural Resources (Yu Natural Resources Letter [2019] No. 373-8); National Key R&DProgram of China (No. 2019YFC1804801).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the reviewers for useful comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
References
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Shao, J.; Pan, X.; Niu, Y.; Huang, J. Groundwater level response to hydrogeological factors in a semi-arid basin of Beijing, China. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2017, 66, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgallal, M.; Fletcher, L.; Evans, B. Assessment of potential risks associated with chemicals in wastewater used for irrigation in arid and semiarid zones: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili-Vardanjani, M.; Rasa, I.; Amiri, V.; Yazdi, M.; Pazand, K. Evaluation of groundwater quality and assessment of scaling potential and corrosiveness of water samples in Kadkan aquifer, Khorasan-e-Razavi Province, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Gu, X.; Yin, S.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, Y. Geostatistical interpolation model selection based on ArcGIS and spatio-temporal variability analysis of groundwater level in piedmont plains, northwest China. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liang, P. Influence of drip irrigation by reclaimed water on the dynamic change of the nitrogen element in soil and tomato yield and quality. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Jiang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Wu, H. The transport of silica powders and lead ions under unsteady flow and variable injection concentrations. Powder Technol. 2021, 387, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megharaj, M.; Avudainayagam, S.; Naidu, R. Toxicity of hexavalent chromium and its reduction by bacteria isolated from soil contaminated with tannery waste. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xia, J. Chromium Contamination Accident in China: Viewing Environment Policy of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8605–8606. [Google Scholar]
- Priti, S.; Vipin, B.; Agarwal, S.K.; Vipin, V.; Kesavachandran, C.N.; Pangtey, B.S.; Neeraj, M.; Pal, S.K.; Mithlesh, S.; Goel, S.K. Groundwater Contaminated with Hexavalent Chromium [Cr (VI)]: A Health Survey and Clinical Examination of Community Inhabitants (Kanpur, India). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47877. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, M.; Shozugawa, K.; Matsuo, M. Hexavalent chromium pollution caused by dumped chromium slag at the urban park in Tokyo. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwary, R.K.; Srivastava, K.K. Physico-Chemical Analysis and Correlation Study of Water Resources of the Sukinda Chromite Mining Area, Odisha, India. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, W. Cotransport of heavy metals and SiO2 particles at different temperatures by seepage. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 125771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, H.; Yan, S.; Xiu, W.; Coyte, R.M.; Vengosh, A. High Hexavalent Chromium Concentration in Groundwater from a Deep Aquifer in the Baiyangdian Basin of the North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10068–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Rao, D.; Chang, T.; Guo, Z. A nonlinear attachment-detachment model with adsorption hysteresis for suspension-colloidal transport in porous media. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Long, F.; Rao, D.; Xu, T. The effect of temperature on the seepage transport of suspended particles in a porous medium. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, K.M.; King, A.M.; Harter, T. Identifying sources of groundwater nitrate contamination in a large alluvial groundwater basin with highly diversified intensive agricultural production. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 151, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F. Evaluation of hydrogeochemical parameters of groundwater for suitability of domestic and irrigational purposes: A case study from central Ganga Plain, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 4121–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Graf, T.; Ptak, T. Impact of climate change on freshwater resources in a heterogeneous coastal aquifer of Bremerhaven, Germany: A three-dimensional modeling study. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 177–178, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H. Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: A case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, M.J.; Ebrahimi, P.; Razmara, M.; Ghasemi, A. Hydrogeochemical investigations and groundwater quality assessment of Torbat-Zaveh plain, Khorasan Razavi, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Pisciotta, A.; Maio, M.D. Evaluation of groundwater salinization and pollution level on Favignana Island, Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Hayati, M.; Jabbari, N.; Barzegar, R. Risk assessment and ranking of heavy metals concentration in Iran’s Rayen groundwater basin using linear assignment method. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 1317–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Jabbari, N. Evaluation of groundwater quality and assessment of pollution indices for heavy metals in North of Isfahan Province, Iran. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H. Hydrogeochemistry study and groundwater quality assessment in the north of Isfahan, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 583–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Hassani, S.; Jabbari, N.; Fard Mousavi, S.B.; Rezaei, S. Evaluation of groundwater quality and heavy metal pollution indices in Bazman basin, southeastern Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Tziritis, E.; Fard Mousavi, S.B.; Jabbari, N. Hydrochemical characterization and evaluation of groundwater quality in Dalgan basin, SE Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Gu, X.; Yin, S.; Pan, X.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y. Investigation of Geochemical Characteristics and Controlling Processes of Groundwater in a Typical Long-Term Reclaimed Water Use Area. Water 2017, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, Z.; Wang, G. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolutionary laws of groundwater in Dachaidan area, Qaidam Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2020, 28, 194. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Orioli, S.; De Maio, M. Assessment of groundwater geochemistry and diffusion of hexavalent chromium contamination in an industrial town of Italy. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 225, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmankumar, D.; Satyanarayana, E.; Dhakate, R.; Saxena, P.R. Hydrogeochemical characteristics with respect to fluoride contamination in groundwater of Maheshwarm mandal, RR district, Telangana state, India–ScienceDirect. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, W. Remediation of hexavalent chromium in column by green synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron/nickel: Factors, migration model and numerical simulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausladen, D.M.; Fendorf, S. Hexavalent Chromium Generation within Naturally Structured Soils and Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z. Efficient removal of hexavalent chromium from water and soil using magnetic ceramsite coated by functionalized nano carbon spheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Yan, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y. Processes of chromium (VI) migration and transformation in chromate production site: A case study from the middle of China. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausladen, D.M.; Alexander-Ozinskas, A.; Mcclain, C.; Fendorf, S. Hexavalent Chromium Sources and Distribution in California Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Mousavi, S.B.F.; Jabbari, N. Evaluation Of Heavy Metals Concentration In Jajarm Bauxite Deposit In Northeast Of Iran Using Environmental Pollution Indices. Malays. J. Geosci. 2019, 3, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B. Nitrate contamination in irrigation groundwater, Isfahan, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Xu, T.; Nie, Q.; Li, P. Temperature-driven migration of heavy metal Pb2+ along with moisture movement in unsaturated soils. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 153, 119573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagh, V.M.; Panaskar, D.B.; Varade, A.M.; Mukate, S.V.; Gaikwad, S.K.; Pawar, R.S.; Muley, A.; Aamalawar, M.L. Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of the groundwater resources of Nanded tehsil, a part of southeast Deccan Volcanic Province, Maharashtra, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagüzel, R.; Irlayici, A. Groundwater pollution in the Isparta Plain, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 1998, 34, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, G.; Elango, L. Hydrogeochemical processes and impact of tanning industries on groundwater quality in Ambur, Vellore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 24364–24383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q. Groundwater circulation and hydrogeochemical evolution in Nomhon of Qaidam Basin, northwest China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Song, F.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J. Distinct groundwater recharge sources and geochemical evolution of two adjacent sub-basins in the lower Shule River Basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 1967–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wu, X.; Ge, J.; Liu, F.; Wu, C. Influence of mining activities on groundwater hydrochemistry and heavy metal migration using a self-organizing map (SOM). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).