Integrative Assessment of Sediments Affected by CO2 Enrichment: A Case Study in the Bay of Santos—SP, Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Stations
2.2. CO2 Injection System
2.3. Toxicity Tests
2.3.1. Acute Test
2.3.2. Chronic Test
2.4. Macro-Benthic Community
2.5. Chemical Analyses
2.6. WoE Approach
3. Results
3.1. Tabular Matrix
3.2. Pie Charts
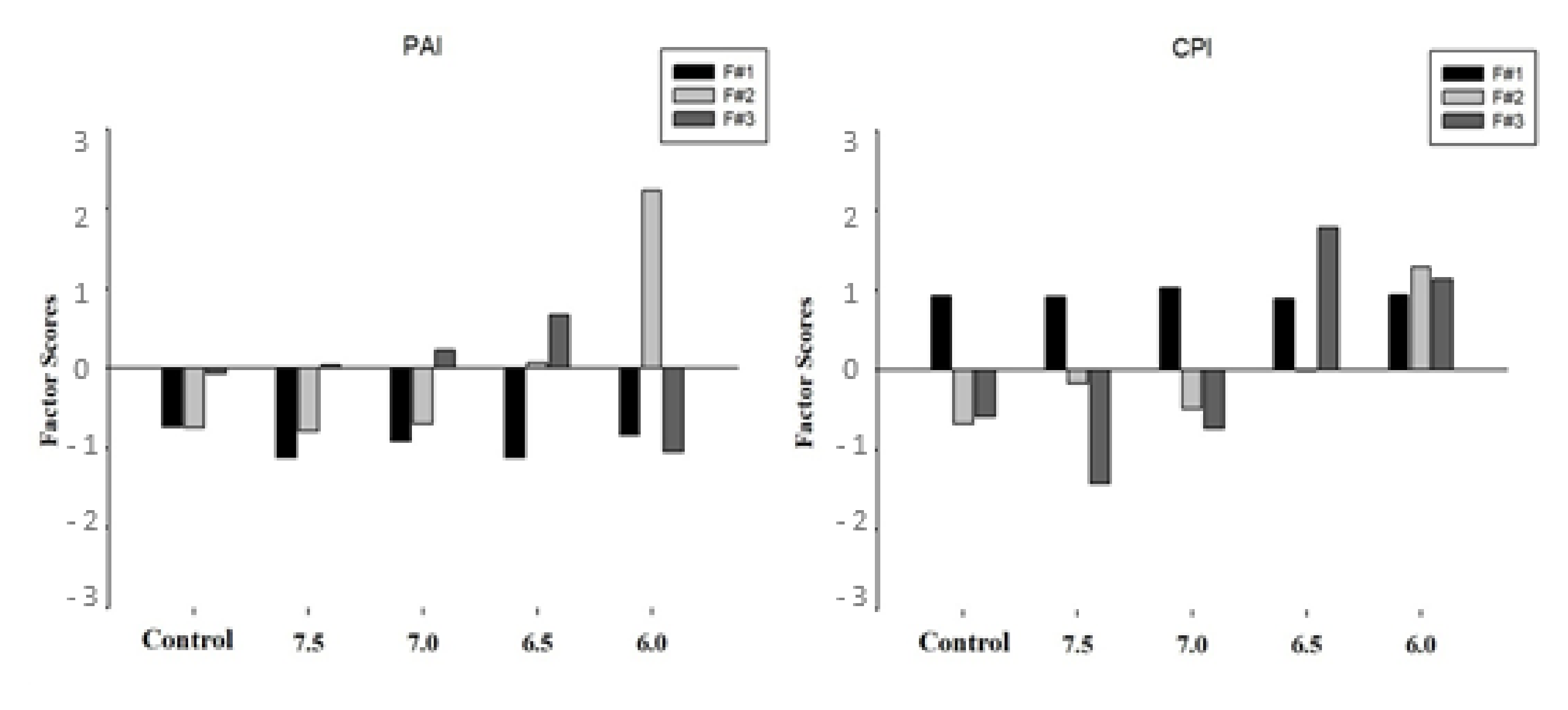
3.3. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edenhofer, O.; Pichs-Madruga, R.; Sokona, Y.; Minx, J.C.; Farahani, E. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Global Monitoring Laboratory. In Earth System Research Laboratories. Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide; 2021. Available online: https://gml.noaa.gov/ccgg/trends/weekly.html (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Adoptions of the Paris Agreement. 2015. Available online: http://unfccc.int/files/essential_background/convention/application/pdf/english_paris_agreemen.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Energy Technology Perspectives 2010: Scenarios & Strategies to 2050, Strategies; IEA: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Blackford, J.; Bull, J.M.; Cevatoglu, M.; Connelly, D.; Hauton, C.; James, R.H.; Lichtschlag, A.; Stahl, H.; Widdicombe, S.; Wright, I.C. Marine baseline and monitoring strategies for carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS). Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 38, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DelValls, T.Á.; Forja, J.M.; Gómez-Parra, A. Integrative assessment of sediment quality in two littoral ecosystems from the Gulf of Cadiz, Spain. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Romero, A.; Jiménez-Tenorio, N.; Basallote, M.D.; Orte, M.R.D.; Blasco, J.; Riba, I. Predicting the impacts of CO2 leakage from sub-seabed storage: Effects of metal accumulation and toxicity on the model benthic organism Ruditapes philippinarum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12292–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Romero, A.; Jiménez-Tenorio, N.; Riba, I.; Blasco, J. Laboratory simulation system, using Carcinus maenas as the model organism, for assessing the impact of CO2 leakage from sub-seabed injection and storage. Environ. Res. 2016, 144, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szalaj, D.; De Orte, M.R.; Goulding, T.A.; Medeiros, I.D.; DelValls, T.A.; Cesar, A. The effects of ocean acidification and a carbon dioxide capture and storage leak on the early life stages of the marine mussel Perna perna (Linneaus, 1758) and metal bioavailability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2017, 24, 765–781. [Google Scholar]
- Goulding, T.; De Orte, M.R.; Szalaj, D.; Basallote, M.D.; DelValls, T.A.; Cesar, A. Assessment of the environmental impacts of ocean acidification (OA) and Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) leaks using the amphipod Hayle youngi. Ecotoxicology 2017, 6, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Orte, M.R.; Bonnail, E.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Bautista-Chamizo, E.; Basallote, M.D.; Riba, I. Metal fractionation in marine sediments acidified by enrichment of CO2: A risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, L.S.; Bonnail, E.; Maranho, L.; Pusceddu, F.H.; Cortez, F.S.; Cesar, A.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Riba, I.; de Souza Abessa, D.M.; DelValls, Á.; et al. Sub-lethal combined effects of illicit drug and decreased pH on marine mussels: A short-time exposure to crack cocaine in CO2 enrichment scenarios. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelValls, T.Á. Diseño y Aplicación de Modelos Integrados de Evaluación de la Contaminación y Sus Efectos Sobre los Sistemas Marinos y Litorales y la Salud Humana; Cent. para la Prevención y Lucha contra la Contam. Maritíma y Litoral; Serie Investigación Madrid; Ministerio de la Presidencia: Madrid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cesar, A.; Choueri, R.B.; Riba, I.; Moralles-Caselles, C.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Santos, A.R.; Abessa, D.M.S.; DelValls, T.A. Comparative sediment quality assessment in different littoral ecosystems from Spain (Gulf of Cadiz) and Brazil (Santos and São Vicente estuarine system). Environ. Intern. 2007, 33, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueri, R.B.; Cesar, D.M.S.; Torres, R.J.; Morais, R.D.; Riba, I.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Nascimento, M.R.L.; Mozeto, A.A.; DelValls, T.A. Development of site-specific sediment quality guidelines for North and South Atlantic littoral zones: Comparison against national and international sediment quality benchmarks. J. Hazard. Mat. 2009, 170, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.J.; Cesar, A.; Pastor, V.A.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Choueri, R.B.; Cortez, F.S.; Morais, R.D.; Abessa, D.M.S.; Nascimento, M.R.L.; Morais, C.R.; et al. A Critical Comparison of Different Approaches to Sediment- Quality Assessments in the Santos Estuarine System in Brazil. Arch. Environ. Cont. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riba, I.; Casado-Martínez, C.; Forja, J.M.; DelValls, T.Á. Sediment quality in littoral regions of the Gulf of Cádiz: A triad approach to address the influence of mining activities. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riba, I.; Kalman, J.; Vale, C.; Blasco, J. Influence of sediment acidification on the bioaccumulation of metals in Ruditapes philippinarum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2010, 17, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Basallote, M.D.; DelValls, T.Á.; Riba, I. Studying the effect of CO2-Induced acidification on sediment toxicity using acute amphipod toxicity test. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8864–8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basallote, M.; Rodríguez-Romero, A.; De Orte, M.R.; DelValls, A.; Riba, I. Evaluation of the threat of marine CO2 leakage-associated acidification on the toxicity of sediment metals to juvenile bivalves. Aq. Toxicol. 2015, 166, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarelli, M.C.; Riba, I.; Cesar, A.; Serrano-Bernando, F.; DelValls, T.A. Assessing the influence of ocean acidification to marine amphipods: A comparative study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarelli, M.C.; Cesar, A.; Riba, I.; DelValls, T.A. Comparative evaluation of sea-urchin larval stage sensitivity to ocean acidification. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar, A.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Santos, A.R.; Abessa, D.M.S.; Fernández, N.; Choueri, R.B.; DelValls, T.A. Ecotoxicological assessment of sediments from the Santos and São Vicente estuarine system- Brazil. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2006, 56, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelValls, T.A.; Souza, L.D.S.; De Seabra, A.A.; Bonnail, E.; Riba, I. Integrative assessment of sediment quality in acidification scenarios associated with carbón capture and storage operations. Environ. Rev. 2019, 27, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abessa, D.M.S.; Carr, R.S.; Sousa, E.C.P.M.; Rachid, B.R.; Zaroni, L.P.; Pinto, Y.A.; Gasparro, M.R.; Bícego, M.C.; Hortellani, M.A.; Sarkis, J.E.S.; et al. Integrative Ecotoxicological Assessment of a Complex Tropical Estuarine System. Hoffer, T.N., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 125–159. [Google Scholar]
- Cesar, A.; Lia, L.R.B.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Santos, A.R.; Cortez, F.S.; Choueri, R.B.; De Orte, M.R.; Rachid, B.R.F. Environmental assessment of dredged sediment in the major Latin American seaport (Santos, São Paulo—Brazil): An integrated approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.D.S.; Martin-Díaz, M.L.; Zanette, J.; Cesar, A.; Choueri, R.B.; Abessa, D.M.S.; Catharino, M.G.M.; Vasconcelos, M.B.A.; Bayne, A.C.D.; Sousa, E.C.P.M.; et al. Integrated biomarker responses as environmental status descriptors of coastal zone (São Paulo, Brazil). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2011, 74, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecotoxicologia Aquática—Toxicidade Crônica de Curta Duração—Método de Ensaio Com Ouriço-do-Mar (Echinodermata: Echinoidea); Norma Brasileira; ABNT NBR 15350 de 08/2020; 2020. Available online: https://www.abntcatalogo.com.br/norma.aspx?Q=M01JRFMraml6a0lnWlN2OElPRUVvRXUyL2J5d3kwajViSEdxU0h0TmFCQT0= (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Almagro-Pastor, V.; Conradi, M.; DelValls, T.A.; Riba, I. Alterations in the macrobenthic fauna from Guadarranque River (Southern Spain) associated with sediment–seawater acidification deriving from CO2 leakage. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.M.; Wang, F.; Janssen, C.R.; Goulet, R.R.; Kamunde, C.N. Conducting ecological risk assessments of inorganic metals and metalloids: Current status. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 641–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.G. No exit: Thinking about leakage from geologic carbon storage sites. Energy 2004, 29, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCCS Scottish Carbon Capture & Storage. 2017. Available online: http://www.sccs.org.uk/expertise/map.html (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Cetesb. Qualidade das Águas Costeiras do Estado de São Paulo. Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo. 2017. Available online: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-costeiras/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2018/06/Relat%C3%B3rio-de-Qualidade-das-%C3%81guas-Costeiras-do-Estado-de-S%C3%A3o-Paulo-2017.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Abessa, D.M.; Carr, R.S.; Rachid, B.R.; Sousa, E.C.; Hortelani, M.A.; Sarkis, J.E. Influence of a Brazilian sewage outfall on the toxicity and contamination of adjacent sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buruaem, L.M.; Castro, I.B.; Hortellani, M.A.; Taniguchi, S.; Fillman, G.; Sasaki, S.T.; Petti, M.A.V.; Sarkis, J.E.S.; Bicego, M.C.; Maranho, L.A.; et al. Integrated quality assessment of sediments from harbor areas in Santos-São Vicente Estuarine System. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAMA 454. Estabelece as Diretrizes Gerais e os Procedimentos Referenciais para o Gerenciamento do Material a ser Dragado em Águas sob Jurisdição Nacional; Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente (CONAMA): Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, W.J.; Kimerle, R.A.; Mosher, R.G. Aquatic safety assessment of chemicals sorbed to sediments. In Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Assessment: 7th Symposium; Cardwell, R.D., Purdy, R., Bahner, R.C., Eds.; STP 854; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1985; pp. 429–453. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Technical Basis for the Derivation of Equilibrium Partitioning Sediment Guidelines (ESG) for the Protection of Benthic Organisms: Nonionic Organics; EPA-822-R-00-001; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Methods for Collection, Storage and Manipulation of Sediments for Chemical and Toxicological Analyses: Technical Manual; EPA 823-B-01-002; Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Millero, F.J.; Woosley, R.; Ditrolio, B.; Waters, J. Effect of ocean acidification on the speciation of metals in seawater. Oceanography 2009, 22, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Organisms | pH Range | T (°C) | DO (%) | Duration | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. youngi | 8.0–6.0 | 25 ± 1 | >80 | 10 days | Mortality |
| L. variegatus | 8.0–6.0 | 25 ± 1 | >80 | 24 h | Pluteus stage |
| Macrobenthos | 8.0–6.0 | 25 ± 1 | >80 | 21 days | Biological indexes |
| pH Values | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAI | CPI | |||||||||
| 8.0 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 6.0 | |
| Contamination | ||||||||||
| Cu elu | 3.0 | 2.8 | 4.8 | 3.0 | 5.7 | 2.5 | 5 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 2.5 |
| Cu sw | 6.7 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 5 | 6.86 | 6.84 | 7 |
| Cu sed | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 7.3 | 11 | 11.1 | 10.8 | 10.9 | 11 |
| Cr elu | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 3.12 | 2.81 | - | 1.66 | 1.47 | 2.5 | 1.53 |
| Cr sw | 1.85 | 4.3 | 6.92 | 5.88 | 2.3 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 2.23 | 2.6 | 2.28 |
| Cr sed | 27.6 | 27.4 | 27.7 | 27.9 | 27.4 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 31.1 | 30.8 | 30.9 |
| Zn elu | - | - | 34 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 91 | 54 | 60.4 | 38.8 |
| Zn sw | 24 | 23 | 26 | 40 | 35 | 39 | 26 | 48 | 54 | 96 |
| Zn sed | 123 | 122 | 126 | 127 | 125 | 133 | 134 | 133 | 137 | 138 |
| Ni elu | - | - | 1.12 | - | 0.16 | 1.22 | 1.18 | 1.23 | 1.12 | 1.14 |
| Ni sw | - | - | 1.8 | 2.12 | 4.9 | 1.7 | 1.82 | 2.13 | 3.75 | 6.2 |
| Ni sed | 13.7 | 13.7 | 13.6 | 13.7 | 13.8 | 5.92 | 5.96 | 5.96 | 5.94 | 5.95 |
| As elu | 40 | 75 | 45 | 100 | 142 | 65 | 65 | 60 | 60 | 95 |
| As sw | 57 | - | - | - | 150 | 58 | 48 | 59 | 64 | 130 |
| As sed | 3.16 | 3.14 | 3.15 | 3.17 | 3.16 | 2.83 | 2.83 | 2.85 | 2.89 | 2.85 |
| Toxicity | ||||||||||
| Mort_A (%) | 18 | 27 | 24 | 38 | 100 | 20 | 26 | 22 | 47 | 100 |
| Inh_SU (%) | 17.25 | 16 | 70 | 72 | 100 | 6 | 10 | 17 | 100 | 100 |
| Macrobenthic | ||||||||||
| Diversity | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 0.22 | 0.31 |
| T. abundance | 54 | 57 | 65.5 | 54 | 21 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 20 |
| Richness | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 1.01 | 1.07 | 0.27 | 0.51 |
| Site, pH Treatment | Metals | Toxicity | Benthic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | Mobility | Acute | Chronic | ||
| PAI, pH 8.0 | − | − | − | − | − |
| PAI, pH 7.5 | − | − | − | − | − |
| PAI, pH 7.0 | − | ± | − | + | − |
| PAI, pH 6.5 | − | + | − | + | − |
| PAI, pH 6.0 | − | + | + | + | − |
| CPI, pH 8.0 | − | − | − | − | + |
| CPI, pH 7.5 | − | ± | − | − | + |
| CPI, pH 7.0 | − | ± | − | − | + |
| CPI, pH 6.5 | − | + | + | + | + |
| CPI, pH 6.0 | − | + | + | + | + |
| Variables | Components | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | #2 | #3 | |
| Variance | 43.38 | 28.56 | 10.80 |
| Mobility of metals | |||
| As sw | 0.82 | ||
| Cr sw | −0.65 | ||
| Cu sw | 0.76 | ||
| Ni sw | 0.85 | ||
| Zn sw | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.54 |
| As elu | 0.88 | ||
| Cr elu | 0.62 | ||
| Cu elu | −0.45 | 0.37 | −0.57 |
| Ni elu | 0.84 | ||
| Zn elu | 0.74 | ||
| Sediment metal concentration | |||
| As sed | −0.99 | ||
| Cr sed | 0.99 | ||
| Cu sed | 0.99 | ||
| Ni sed | −0.99 | ||
| Zn sed | 0.92 | ||
| Toxicity | |||
| Larval Inhibition | 0.72 | 0.60 | |
| Amphipod Mortality | 0.96 | ||
| Acidification (H+) | 0.96 | ||
| Ecological Integrity | |||
| Diversity | −0.84 | ||
| T. Abundance | −0.88 | ||
| Richness | −0.87 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Passarelli, M.C.; Bonnail, E.; Cesar, A.; DelValls, T.Á.; Riba, I. Integrative Assessment of Sediments Affected by CO2 Enrichment: A Case Study in the Bay of Santos—SP, Brazil. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11603. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411603
Passarelli MC, Bonnail E, Cesar A, DelValls TÁ, Riba I. Integrative Assessment of Sediments Affected by CO2 Enrichment: A Case Study in the Bay of Santos—SP, Brazil. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(24):11603. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411603
Chicago/Turabian StylePassarelli, Marina Cunha, Estefanía Bonnail, Augusto Cesar, T. Ángel DelValls, and Inmaculada Riba. 2021. "Integrative Assessment of Sediments Affected by CO2 Enrichment: A Case Study in the Bay of Santos—SP, Brazil" Applied Sciences 11, no. 24: 11603. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411603
APA StylePassarelli, M. C., Bonnail, E., Cesar, A., DelValls, T. Á., & Riba, I. (2021). Integrative Assessment of Sediments Affected by CO2 Enrichment: A Case Study in the Bay of Santos—SP, Brazil. Applied Sciences, 11(24), 11603. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411603






