Prevention Effect of TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitor in Esophageal Stricture Formation after Corrosive Burn
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antifibrotic Drug
2.2. Animals
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.4. Fluoroscopic Esophagogram
2.5. Esophageal Histopathology
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Drug on Esophageal Stenosis
3.2. Effect of the Drug on Fibrosis
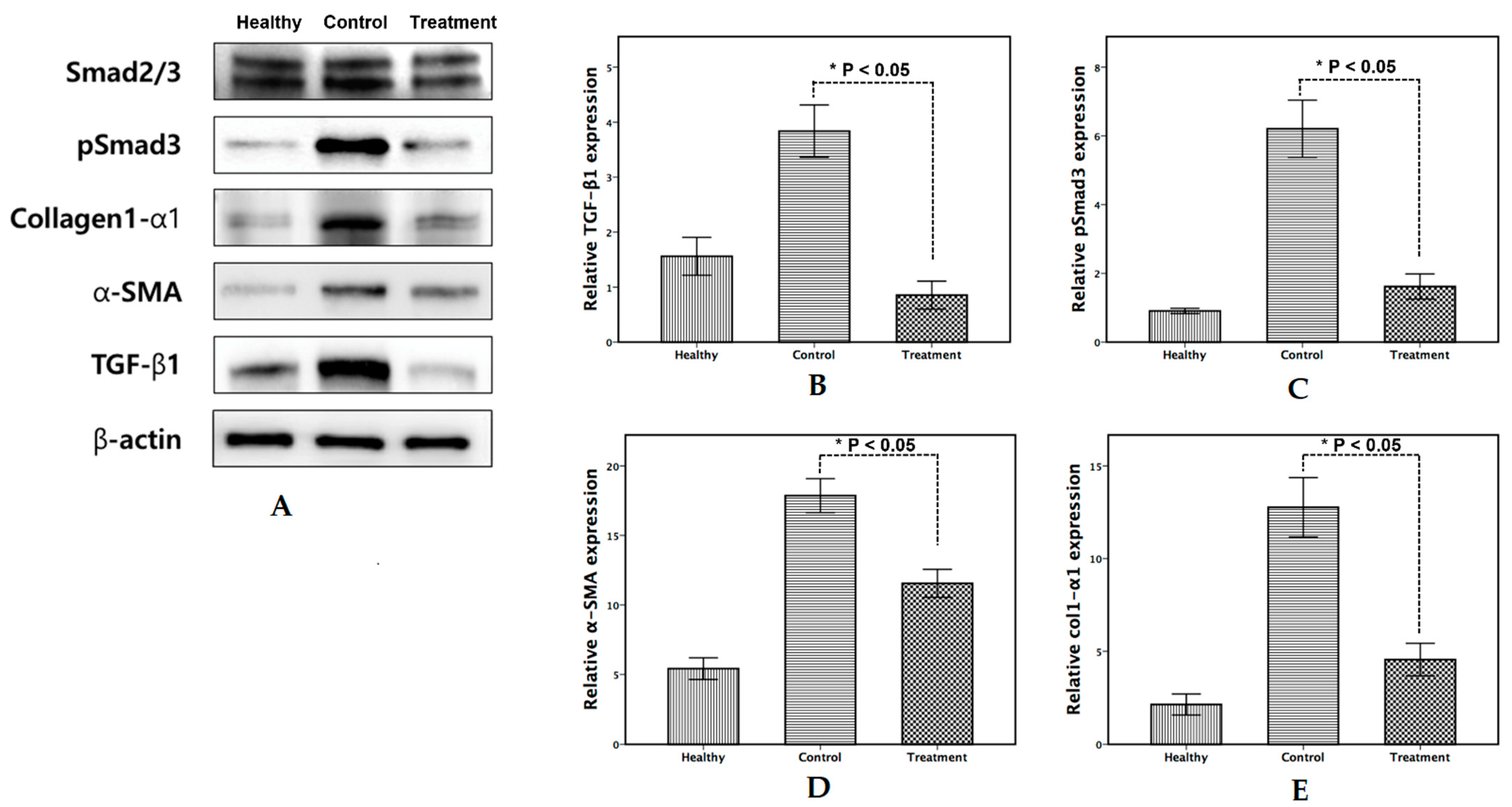
3.3. Effect of the Drug on Protein Expression
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.H.; Song, H.-Y.; Kim, H.-C.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, K.R.; Park, S.W.; Jung, H.-Y.; Lee, G.H.; Park, S.-I. Corrosive esophageal strictures: Long-term effectiveness of balloon dilation in 117 patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. JVIR 2008, 19, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.Y.; Han, Y.M.; Kim, H.N.; Kim, C.S.; Choi, K.C. Corrosive esophageal stricture: Safety and effectiveness of balloon dilation. Radiology 1992, 184, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbell, D.; Udassin, R.; Koplewitz, B.Z.; Ohana, M.; Genina, O.; Pines, M.; Nagler, A. Prevention of esophageal strictures in a caustic burn model using halofuginone, an inhibitor of collagen type I synthesis. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1632–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkyılmaz, Z.; Sönmez, K.; Demirtola, A.; Karabulut, R.; Poyraz, A.; Gülen, Ş.; Dinçer, S.; Başaklar, A.C.; Kale, N. Mitomycin C prevents strictures in caustic esophageal burns in rats. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 123, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukselen, V.; Vardar, E.; Yukselen, O.; Karaoglu, A.O.; Yenisey, C.; Ozutemiz, O. Colchicine in experimental alkaline burns of the rat esophagus: An old drug, a new indication? Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2006, 22, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makay, O.; Yukselen, V.; Vardar, E.; Yenisey, C.; Bicakci, T.; Ersin, S.; Ozutemiz, O. Role of allopurinol on oxidative stress in caustic burn: Cure for stricture? Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2007, 23, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larios-Arceo, F.; Ortiz, G.G.; Huerta, M.; Leal-Cortés, C.; Saldana, J.A.; Bitzer-Quintero, O.K.; Rodriguez-Reynoso, S. Protective effects of melatonin against caustic esophageal burn injury in rats. J. Pineal. Res. 2008, 45, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herek, O.; Karabul, M.; Yenisey, C.; Erkus, M. Protective effects of ibuprofen against caustic esophageal burn injury in rats. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2010, 26, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Perez, J.; Aguirre-Jauregui, O.; Salazar-Montes, A.; Navarro, A.A.S.; Lucano-Landeros, M.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J. Pirfenidone prevents rat esophageal stricture formation. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 194, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygielko, E.T.; Martin, W.M.; Tweed, C.; Thornton, P.; Harling, J.; Brooks, D.P.; Laping, N.J. Inhibition of gene markers of fibrosis with a novel inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase in puromycin-induced nephritis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonniaud, P.; Margetts, P.J.; Kolb, M.; Schroeder, J.A.; Kapoun, A.M.; Damm, D.; Murphy, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Dugar, S.; Higgins, L.; et al. Progressive transforming growth factor beta1-induced lung fibrosis is blocked by an orally active ALK5 kinase inhibitor. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gouville, A.-C.; Boullay, V.; Krysa, G.; Pilot, J.; Brusq, J.-M.; Loriolle, F.; Gauthier, J.-M.; Papworth, S.A.; Laroze, A.; Gellibert, F.; et al. Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling by an ALK5 inhibitor protects rats from dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 145, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, J.-A.; Kim, H.-T.; Cho, I.-S.; Sheen, Y.; Kim, D.-K. IN-1130, a novel transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase (ALK5) inhibitor, suppresses renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Song, H.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Yoon, H.-J.; Park, H.G.; Kim, D.-K. IN-1233, an ALK-5 inhibitor: Prevention of granulation tissue formation after bare metallic stent placement in a rat urethral model. Radiology 2010, 255, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.H.; Krishnaiah, M.; Sreenu, D.; Subrahmanyam, V.B.; Rao, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.-J.; Park, H.-J.; Lee, K.; Sheen, Y.Y.; et al. Discovery of N-((4-([1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-6-yl)-5-(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-2 -yl)methyl)-2-fluoroaniline (EW-7197): A highly potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of TGF-beta type I receptor kinase as cancer immunotherapeutic/antifibrotic agent. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4213–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaiah, M.; Jin, C.H.; Sheen, Y.Y.; Kim, D.-K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 5-(fluoro-substituted-6-methylpyridin-2-yl)-4-([1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-6-yl )imidazoles as inhibitors of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5228–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.-A.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.-K.; Nam, J.-S.; Sheen, Y.Y. EW-7197, a novel ALK-5 kinase inhibitor, potently inhibits breast to lung metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.-A.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, S.-J.; Woo, H.A.; Kim, D.-K.; Nam, J.-S.; Sheen, Y.Y. EW-7197 inhibits hepatic, renal, and pulmonary fibrosis by blocking TGF-beta/Smad and ROS signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2023–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, E.J.; Park, J.-H.; Tsauo, J.; Yang, S.-G.; Kim, D.-K.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, M.T.; Yoon, S.-H.; Lim, Y.J.; Song, H.-Y. EW-7197, an activin-like kinase 5 inhibitor, suppresses granulation tissue after stent placement in rat esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijburg, F.A.; Beukers, M.M.; Heymans, H.S.; Bartelsman, J.F.; Jager, F.C.D.H. Nasogastric intubation as sole treatment of caustic esophageal lesions. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1985, 94 Pt 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-H.; Jiang, Y.-G.; Wang, R.-W.; Lin, Y.-D.; Gong, T.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Ma, Z.; Tan, Q.-Y. Management of corrosive esophageal burns in 149 cases. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 130, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gumaste, V.V.; Dave, P.B. Ingestion of corrosive substances by adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1992, 87, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, Y.-C.; Han, D.-K.; Kim, M.T. Therapeutic effect of local photothermal heating of gold nanoparticle-coated self-expandable metallic stents for suppressing granulation tissue formation in the mouse colon. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Border, W.A.; Okuda, S.; Languino, L.; Sporn, M.B.; Ruoslahti, E. Suppression of experimental glomerulonephritis by antiserum against transforming growth factor beta 1. Nature 1990, 346, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeming, W.; Somme, S.; Chenren, S.; Huiming, J.; Ming, Z.; Liu, D.C. Balloon catheter dilatation in children with congenital and acquired esophageal anomalies. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2002, 37, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehanno, P.; Guedon, C. Inhibition of experimental esophageal lye strictures by penicillamine. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1981, 107, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-T.; Kim, K.-Y. Prevention Effect of TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitor in Esophageal Stricture Formation after Corrosive Burn. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11536. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311536
Kim M-T, Kim K-Y. Prevention Effect of TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitor in Esophageal Stricture Formation after Corrosive Burn. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(23):11536. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311536
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Tae, and Kun-Yung Kim. 2021. "Prevention Effect of TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitor in Esophageal Stricture Formation after Corrosive Burn" Applied Sciences 11, no. 23: 11536. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311536
APA StyleKim, M.-T., & Kim, K.-Y. (2021). Prevention Effect of TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitor in Esophageal Stricture Formation after Corrosive Burn. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11536. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311536





