Tri-Partition Alphabet-Based State Prediction for Multivariate Time-Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Tri-state. It provides three kinds of symbols for each variable simultaneously. The proposed deviation degree-based alphabet tri-partition strategy makes the outliers more noticeable for experts. Moreover, the IFS and RFS are designed to obtain a completed tri-state.
- Along–across similarity model. The similarities between time stamps and variables are considered simultaneously. This model provides a framework for the integration of the popular similarity or distance metrics.
- Combination of the popular numerical or symbolic metrics. The PAA- and SAX-MTSs are simultaneously used in the above similarity model. The PAA-MTS is available for the numerical metrics, while the SAX-MTS fits the symbolic ones.
2. Time-Series Prediction
3. Models and Problem Statement
3.1. Data Model
3.2. State
3.3. Tri-State
- ; and
- .
- ;
- ; and .
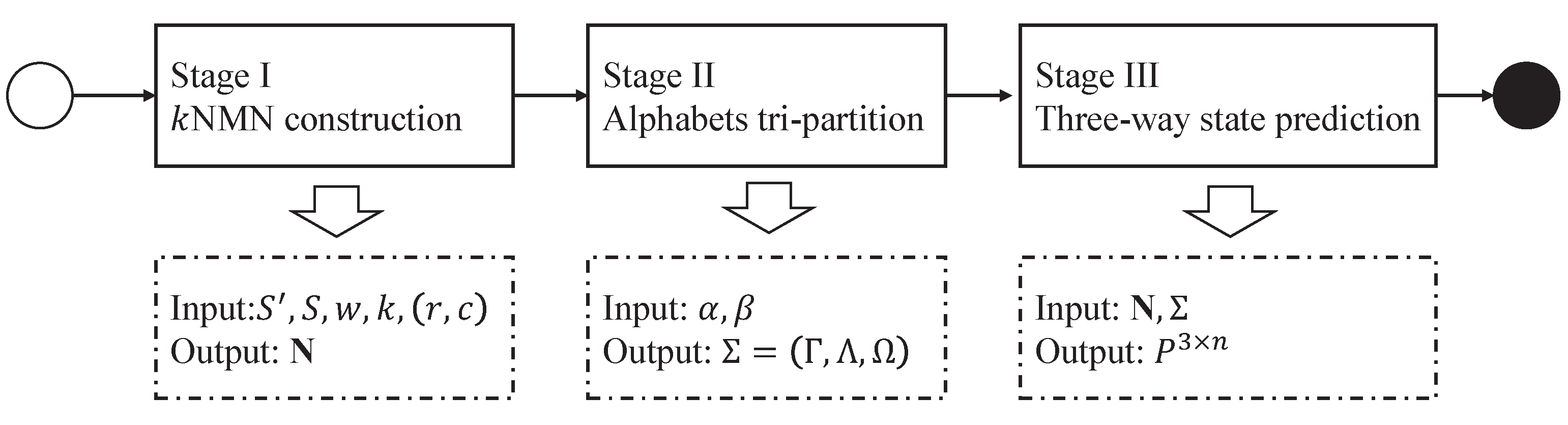
4. Algorithms
4.1. Stage I
| Algorithm 1kNMN construction. |
| Input: , , w, k and ; |
| Output: ; |
| Method: Construction. |
|
| Algorithm 2 Similarity computation. |
| Input: , and ; |
| Output: ; |
| Method: Similarity. |
|
4.2. Stage II
| Algorithm 3 Alphabet tri-partition. |
| Input: , , and ; |
| Output: ; |
| Method: Tri-partition. |
|
4.3. Stage III
| Algorithm 4 Three-way state prediction. |
| Input: , , N and ; |
| Output: ; |
| Method: Prediction. |
|
5. Experiments
- The prediction performance of our along–across similarity model;
- The stability of the similarity metrics combination.
5.1. Dataset and Experiment Settings
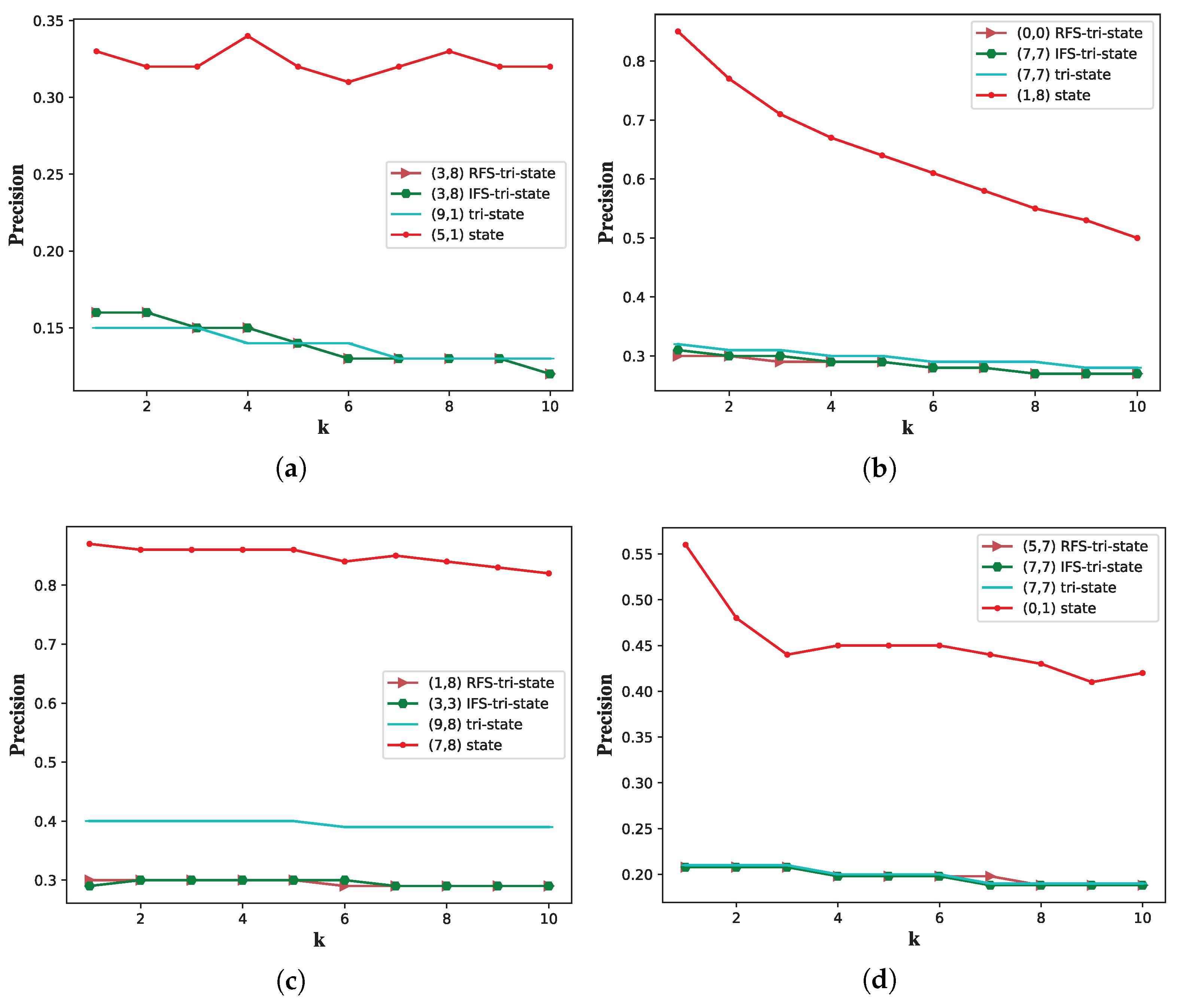
5.2. Prediction Performance
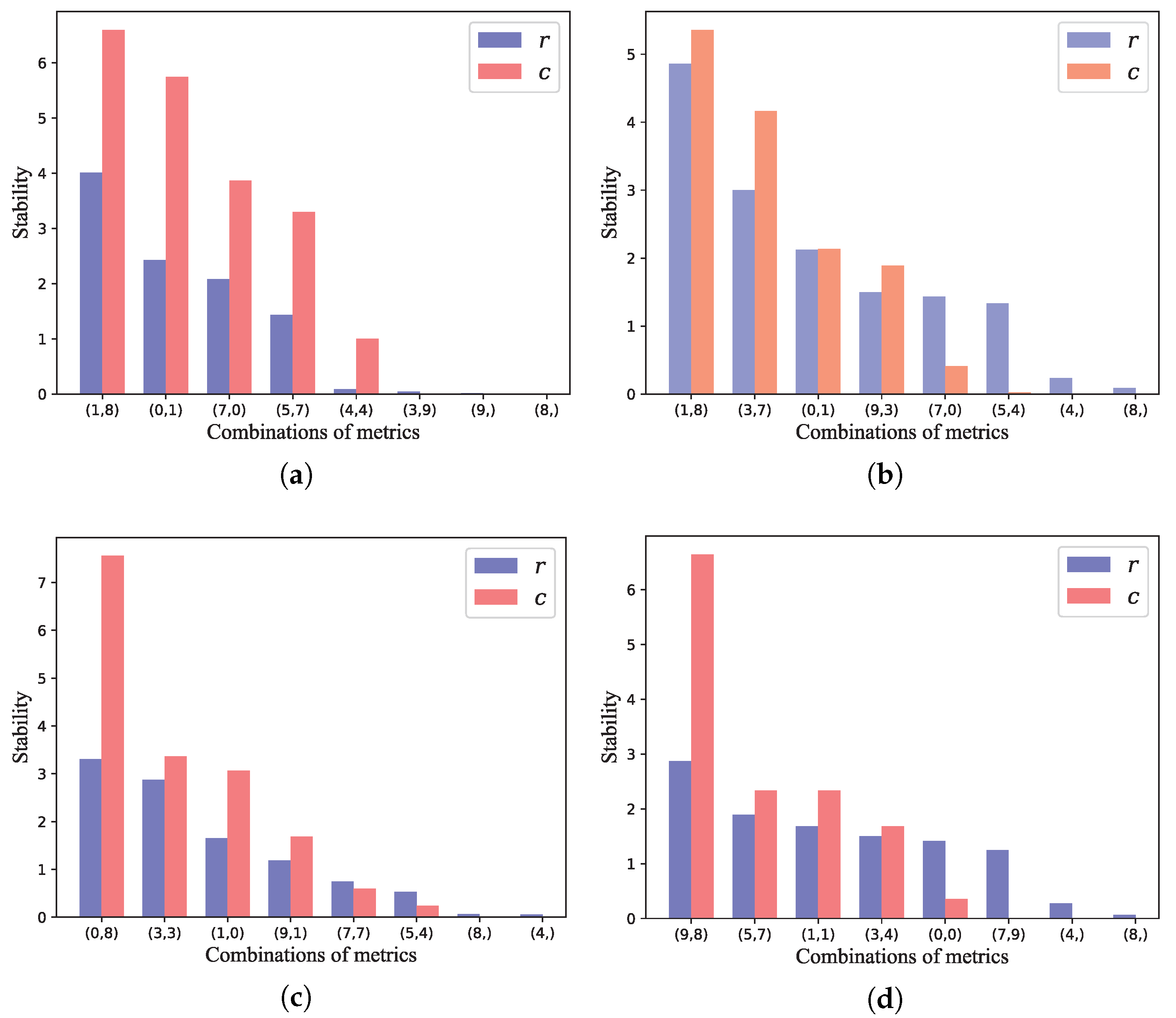
5.3. Stability
6. Conclusions
- More alphabet tri-partition strategies;
- More tri-state completion strategies;
- Adaptive learning of the parameters by cost-sensitive learning; and
- More intelligent metrics combination strategies, e.g., integrated learning.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, W.W.S. Multivariate Time Series Analysis and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Jung, J.Y. SAX-ARM: Deviant event pattern discovery from multivariate time series using symbolic aggregate approximation and association rule mining. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, L.; Zeng, C.; Li, T. Pattern discovery via constraint programming. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 94, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Min, F. Frequent state transition patterns of multivariate time series. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 142934–142946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Min, F.; Chen, G.S.; Shen, S.P.; Wen, Z.C.; Zhou, X.B. Tri-Partition state alphabet-based sequential pattern for multivariate time series. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Hu, H.; Tan, X.; Bai, Y. Initialization by a novel clustering for wavelet neural network as time series predictor. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.L. Multivariate time series clustering based on common principal component analysis. Neurocomputing 2019, 349, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Liu, Z.C. Multivariate time series clustering based on complex network. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 115, 107919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldán, F.J.; Benítez, J.M. Multivariate times series classification through an interpretable representation. Inf. Sci. 2021, 569, 596–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydogan, M.G.; Runger, G. Learning a symbolic representation for multivariate time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2015, 29, 400–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.D.A. A class of hybrid morphological perceptrons with application in time series forecasting. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2011, 24, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, G.; May, R.; Ye, H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Deyle, E.; Fogarty, M.; Munch, S. Detecting Causality in Complex Ecosystems. Science 2012, 338, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.R.; Liu, M.M.; Li, Z.W.; Pedrycz, W. A piecewise aggregate pattern representation approach for anomaly detection in time series. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017, 135, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Sun, G.Y.; Chen, Q.H.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, H.X.; Rehman, M.U. A model combining convolutional neural network and LightGBM algorithm for ultra-short-term wind power forecasting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 28309–28318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lin, A.; Shang, P. Multidimensional k-nearest neighbor model based on EEMD for financial time series forecasting. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 477, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Liu, J.; Wu, K. Multivariate Time Series Forecasting based on Elastic Net and High-Order Fuzzy Cognitive Maps: A Case Study on Human Action Prediction through EEG Signals. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 2336–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.W.; Wang, Y.D.; Peng, P.; Shen, B.L.; Deng, Z.; Guo, H.F. Real-time road traffic state prediction based on kernel-kNN. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2020, 16, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Shang, P.J. Forecasting traffic time series with multivariate predicting method. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 291, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, J.C.; Lin, C.Q.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, J.C. Improving air quality prediction accuracy at larger temporal resolutions using deep learning and transfer learning techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.H.; Liu, J.; Wu, K. CNN-FCM: System modeling promotes stability of deep learning in time series prediction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 203, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Frías, M.P.; Pérez, M.D.; Rivera, A.J. A methodology for applying k-nearest neighbor to time series forecasting. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weytjens, H.; Lohmann, E.; Kleinsteuber, M. Cash flow prediction: MLP and LSTM compared to ARIMA and Prophet. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 21, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheung, Y.M. Bayesian low-tubal-rank robust tensor factorization with multi-rank determination. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, H.; Cheung, Y.M. Probabilistic rank-one tensor analysis with concurrent regularizations. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 3496–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Lee, S.J. A weighted LS-SVM based learning system for time series forecasting. Inf. Sci. 2015, 299, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, F.; Palma, J.; Sanchez, G.; Marin, D.; Palacios, M.F.; López, M.L. Feature selection based multivariate time series forecasting: An application to antibiotic resistance outbreaks prediction. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 104, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Suganthan, P.N.; Amaratunga, G.A.J. Oblique random forest ensemble via least square estimation for time series forecasting. Inf. Sci. 2017, 420, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Y. The geometry of three-way decision. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 6298–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Y. Set-theoretic models of three-way decision. Granul. Comput. 2021, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Y. Tri-level thinking: Models of three-way decision. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, B.B.; Guo, Y.T.; Shi, D.R.; Xu, W.H. Decision-theoretic rough set model of multi-source decision systems. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2018, 9, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Huang, C.C.; Qi, J.J.; Qian, Y.H.; Liu, W.Q. Three-way cognitive concept learning via multi-granularity. Inf. Sci. 2017, 378, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Y. Three-way decisions and cognitive computing. Cogn. Comput. 2016, 8, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.F.; Yao, Y.Y. Decision-theoretic three-way approximations of fuzzy sets. Inf. Sci. 2014, 279, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.Q. Three-way decisions space and three-way decisions. Inf. Sci. 2014, 281, 21–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Liu, C.H.; Miao, D.Q.; Yue, X.D. Sequential three-way decisions via multi-granularity. Inf. Sci. 2020, 507, 606–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Yi, H.J.; She, Y.H.; Sun, B.Z. Generalized three-way decision models based on subset evaluation. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2017, 83, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liang, D.C.; Wang, C.C. A novel three-way decision model based on incomplete information system. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 91, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Li, M.M.; Wang, X.Z. Information Fusion Based on Information Entropy in Fuzzy Multi-source Incomplete Information System. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 19, 1200–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Min, F.; Shi, B. Regression-based three-way recommendation. Inf. Sci. 2017, 378, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Min, F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wu, Y.X. Active learning through density clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 85, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, G.Y.; Zeng, X.H. An active three-way clustering method via low-rank matrices for multi-view data. Inf. Sci. 2020, 507, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.D.; Chen, Y.F.; Miao, D.Q.; Qian, J. Tri-partition neighborhood covering reduction for robust classification. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2016, 83, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yao, Y.Y.; Luo, J.G. Cost-sensitive three-way email spam filtering. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2014, 42, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Zhang, L.B.; Huang, B.; Zhou, X.Z. Sequential three-way decision and granulation for cost-sensitive face recognition. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 91, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhai, W.J.; Shen, R.P. Frequent pattern discovery with tri-partition alphabets. Inf. Sci. 2020, 507, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Keogh, E.; Wei, L.; Lonardi, S. Experiencing SAX: A novel symbolic representation of time series. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2007, 15, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.Q.; Yin, J.M.; Cai, J.J.; Cichocki, A.; Yokota, T.; Chen, L.; Yuan, M.X.; Zeng, J. Block Hankel tensor ARIMA for multiple short time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volumr 34, pp. 5758–5766. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, Z.C.; Chen, G.; Xiao, Z.L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.T. Large-scale user visits understanding and forecasting with deep spatial-temporal tensor factorization framework. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2403–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.Y.; Sun, L.J. Low-rank autoregressive tensor completion for multivariate time series forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10436. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.K.; Zhuang, D.Y.; Labbe, A.; Sun, L.J. Inductive graph neural networks for spatiotemporal kriging. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.07527. [Google Scholar]
- Lonardi, S.; Lin, J.; Keogh, E.; Chiu, B.Y.C. Efficient discovery of unusual patterns in time series. New Gener. Comput. 2006, 25, 61–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Charalampopoulos, P.; Pissis, S.P.; Radoszewski, J. Dynamic and internal longest common substring. Algorithmica 2020, 82, 3707–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behara, K.N.; Bhaskar, A.; Chung, E. A novel approach for the structural comparison of origin-destination matrices: Levenshtein distance. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 111, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, N.C.; Miasojedow, B.; Startek, M.; Gambin, A. Jaccard/Tanimoto similarity test and estimation methods for biological presence-absence data. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Dong, X.L.; Zhang, H.R.; Li, T.J.; Zhang, L.; Min, F. Integrating triangle and jaccard similarities for recommendation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
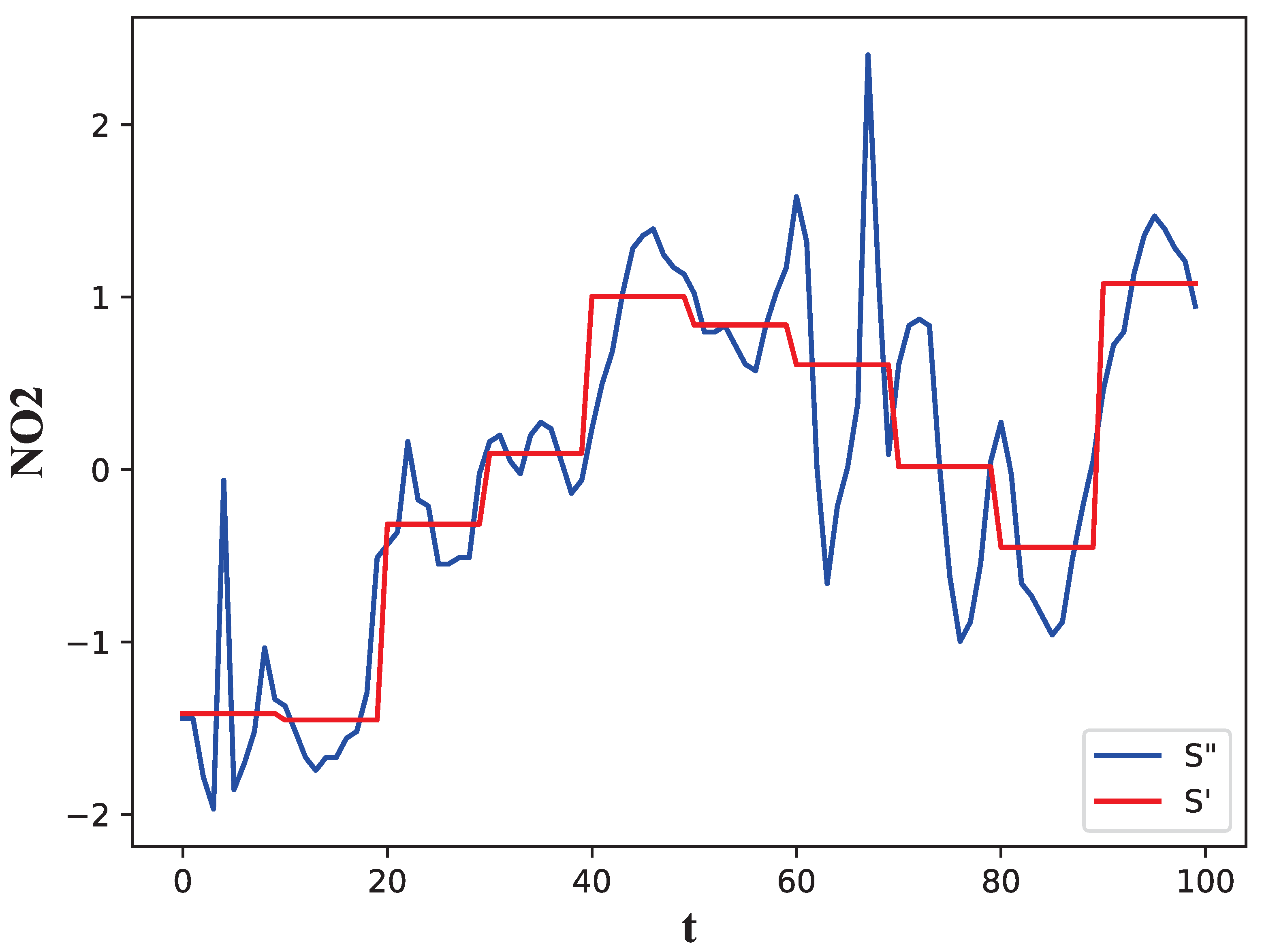
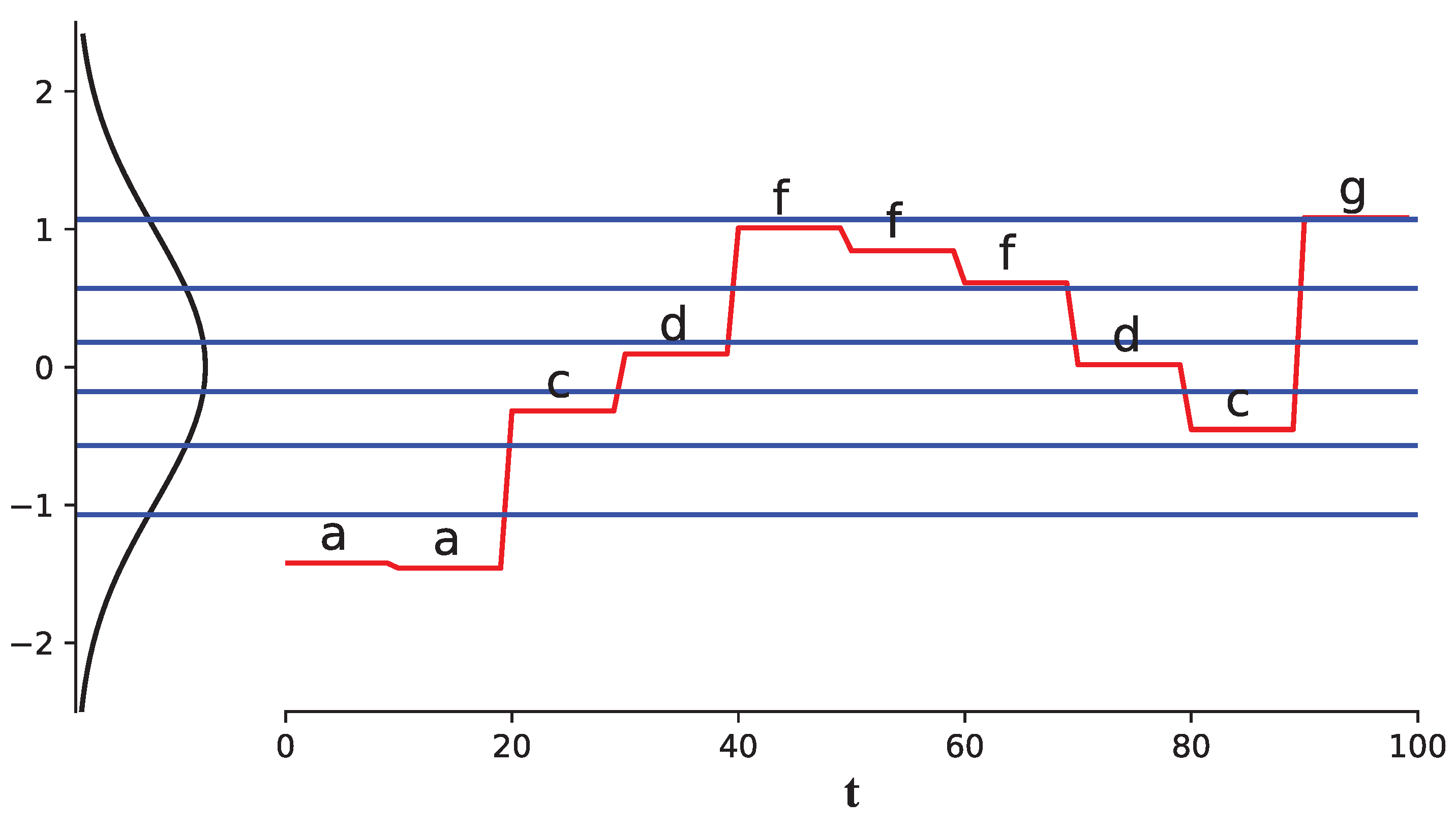


| Notations | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| The original numerical MTS. | |
| The PAA version of numerical . | |
| The SAX version of numerical . | |
| m | The number of all time stamps, . |
| n | The number of all variables, . |
| g | The number of partitions; , . |
| D | The set of breakpoints for S, . |
| . | |
| The strong region. | |
| The medium region. | |
| The weak region. | |
| Tri-partition alphabet. | |
| The threshold for the weak region. | |
| The threshold for the strong region. | |
| A symbolic state occurring at time . | |
| A numerical state occurring at time . | |
| A prediction of state occurring at time . | |
| w | The length of sliding window. |
| O | A matrix instance; . |
| The similarity of two matrix instances. | |
| k | The number of nearest matrix neighbors. |
| The set of k-nearest matrix neighbors. | |
| The form of the tri-state with area . |
| D | g | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| −0.43 | −0.67 | −0.84 | −0.97 | −1.07 | −1.15 | −1.22 | −1.28 | |
| 0.43 | 0 | −0.25 | −0.43 | −0.57 | −0.67 | −0.76 | −0.84 | |
| 0.67 | 0.25 | 0 | −0.18 | −0.32 | −0.43 | −0.52 | ||
| 0.84 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 0 | −0.14 | −0.25 | |||
| 0.97 | 0.57 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 0 | ||||
| 1.07 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.25 | |||||
| 1.15 | 0.76 | 0.52 | ||||||
| 1.22 | 0.84 | |||||||
| 1.28 | ||||||||
| T | A | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SO | NO | PM2.5 | |
| b (−0.989) | a (−1.422) | b (−0.857) | |
| b (−0.966) | a (−1.460) | b (−0.770) | |
| b (−0.615) | c (−0.318) | b (−0.752) | |
| d (−0.106) | d (0.095) | b (−0.681) | |
| g (1.173) | f (1.007) | f (0.922) | |
| g (1.496) | f (0.842) | g (1.490) | |
| e (0.272) | f (0.609) | f (0.959) | |
| c (−0.203) | d (0.016) | c (−0.465) | |
| c (−0.508) | c (−0.453) | b (−0.691) | |
| e (0.447) | g (1.083) | f (0.846) | |
| IDs | Name | Type | Availability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAA | SAX | |||
| 0 | Euclidean | distance | True | False |
| 1 | Manhattan | distance | True | False |
| 2 | LCSubstring [53] | distance | False | True |
| 3 | Levenshtein [54] | distance | False | True |
| 4 | Cosine | similarity | True | False |
| 5 | Pearson | similarity | True | False |
| 6 | Tanimoto [55] | similarity | True | False |
| 7 | Triangle [56] | similarity | True | False |
| 8 | Jaccard | similarity | False | True |
| 9 | Jaro | similarity | False | True |
| 0.051 | 0.059 | 0.243 | 0.334 | 0.105 | 0.109 | 0 | 0.063 |
| Dataset | Name | Fields | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | WanLiu | 35,064 | 12 | Environment |
| II | Stocks | 4300 | 12 | Finance |
| III | IPES | 33,001 | 11 | Healthy |
| IV | CACS | 88,840 | 37 | Industry |
| Dataset | Type of State | Metric Combinations () |
|---|---|---|
| I | State | (5, 1), (7, 1), (4, 1), (7, 8), (3, 7), (9, 1), (1, 8), (5, 8), (1, 7), (0, 8) |
| Tri-state | (9, 1), (9, 8), (3, 8), (5, 1), (7, 8), (3, 0), (7, 1), (4, 1), (4, 7), (3, 1) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (3, 8), (9, 1), (9, 8), (5, 1), (3, 0), (7, 8), (8, 8), (7, 1), (4, 1), (4, 7) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (3, 8), (9, 1), (9, 8), (5, 1), (3, 0), (7, 8), (8, 8), (7, 1), (4, 1), (4, 7) | |
| II | State | (1, 8), (1, 7), (5, 0), (0, 7), (0, 4), (0, 0), (7, 7), (0, 9), (1, 4), (1, 0) |
| Tri-state | (7, 7), (9, 0), (8, 8), (1, 7), (8, 1), (1, 1), (1, 3), (1, 9), (1, 8), (9, 8) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (7, 7), (3, 0), (3, 1), (3, 7), (1, 4), (1, 0), (1, 8), (1, 9), (1, 3), (1, 1) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (0, 0), (3, 1), (0, 7), (5, 0), (4, 1), (5, 7), (1, 0), (1, 7), (9, 1), (1, 3) | |
| III | State | (7, 8), (0, 8), (7, 4), (1, 4), (1, 8), (4, 8), (7, 7), (1, 7), (7, 9), (8, 8) |
| Tri-state | (9, 8), (3, 3), (1, 7), (8, 8), (1, 4), (7, 8), (0, 4), (0, 8), (4, 8), (8, 0) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (3, 3), (7, 8), (4, 8), (9, 8), (1, 8), (0, 8), (8, 8), (9, 7), (1, 4), (0, 4) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (1, 8), (9, 8), (8, 1), (0, 7), (0, 1), (1, 4), (0, 8), (1, 0), (0, 4), (1, 1) | |
| IV | State | (0, 1), (0, 7), (0, 0), (1, 0), (5, 7), (3, 7), (5, 0), (1, 1), (7, 1), (7, 0) |
| Tri-state | (7, 7), (5, 7), (4, 0), (5, 0), (0, 0), (5, 1), (0, 7), (4, 7), (4, 1), (7, 0) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (7, 7), (5, 7), (4, 0), (5, 0), (0, 0), (5, 1), (0, 7), (4, 7), (4, 1), (7, 0) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (5, 7), (4, 4), (0, 7), (7, 1), (7, 8), (7, 0), (5, 1), (5, 0), (5, 4), (4, 0) |
| Dataset | Type of State | Metric Combinations () |
|---|---|---|
| I | State | (5, 1), (7, 1), (4, 1), (7, 8), (3, 7), (9, 1), (1, 8), (5, 8), (1, 7), (0, 8) |
| Tri-state | (3, 8), (9, 8), (8, 8), (4, 8), (5, 1), (5, 8), (9, 1), (3, 7), (3, 0), (5, 7) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (3, 8), (9, 8), (8, 8), (9, 1), (5, 1), (0, 8), (5, 8), (4, 8), (3, 7), (3, 0) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (3, 8), (9, 8), (8, 8), (9, 1), (5, 8), (4, 8), (0, 8), (5, 1), (3, 7), (5, 7) | |
| II | State | (1, 8), (1, 7), (5, 0), (0, 7), (0, 4), (0, 0), (7, 7), (0, 9), (1, 4), (1, 0) |
| Tri-state | (7, 7), (0, 1), (3, 1), (3, 7), (1, 4), (1, 0), (1, 8), (1, 3), (1, 1), (1, 7) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (0, 0), (3, 1), (0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 8), (4, 0), (7, 0), (5, 0), (0, 8), (7, 7) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (9, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (5, 1), (9, 7), (0, 8), (0, 9), (7, 7), (1, 7), (1, 0) | |
| III | State | (7, 8), (0, 8), (7, 4), (1, 4), (1, 8), (4, 8), (7, 7), (1, 7), (7, 9), (8, 8) |
| Tri-state | (9, 8), (3, 3), (1, 8), (0, 8), (4, 3), (8, 8), (7, 3), (0, 3), (1, 4), (1, 3) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (3, 3), (9, 8), (0, 8), (1, 4), (1, 8), (1, 3), (8, 8), (0, 4), (4, 3), (7, 3) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (9, 8), (1, 8), (0, 8), (1, 4), (0, 7), (1, 7), (8, 8), (0, 4), (4, 1), (1, 1) | |
| IV | State | (0, 1), (0, 7), (0, 0), (1, 0), (5, 7), (3, 7), (5, 0), (1, 1), (7, 1), (7, 0) |
| Tri-state | (7, 7), (4, 7), (0, 0), (0, 7), (7, 1), (7, 0), (0, 4), (5, 0), (5, 7), (5, 1) | |
| IFS-tri-state | (7, 7), (4, 7), (0, 0), (0, 7), (7, 1), (7, 0), (0, 4), (5, 0), (5, 7), (5, 1) | |
| RFS-tri-state | (5, 4), (7, 7), (4, 7), (0, 0), (5, 0), (0, 7), (7, 1), (7, 0), (4, 1), (7, 4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Z.-C.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhou, X.-B.; Gu, J.-G.; Shen, S.-P.; Chen, G.-S.; Deng, W. Tri-Partition Alphabet-Based State Prediction for Multivariate Time-Series. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311294
Wen Z-C, Zhang Z-H, Zhou X-B, Gu J-G, Shen S-P, Chen G-S, Deng W. Tri-Partition Alphabet-Based State Prediction for Multivariate Time-Series. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(23):11294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311294
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Zuo-Cheng, Zhi-Heng Zhang, Xiang-Bing Zhou, Jian-Gang Gu, Shao-Peng Shen, Gong-Suo Chen, and Wu Deng. 2021. "Tri-Partition Alphabet-Based State Prediction for Multivariate Time-Series" Applied Sciences 11, no. 23: 11294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311294
APA StyleWen, Z.-C., Zhang, Z.-H., Zhou, X.-B., Gu, J.-G., Shen, S.-P., Chen, G.-S., & Deng, W. (2021). Tri-Partition Alphabet-Based State Prediction for Multivariate Time-Series. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311294







