Assessment of Respiratory System Resistance during High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation Based on In Vitro Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
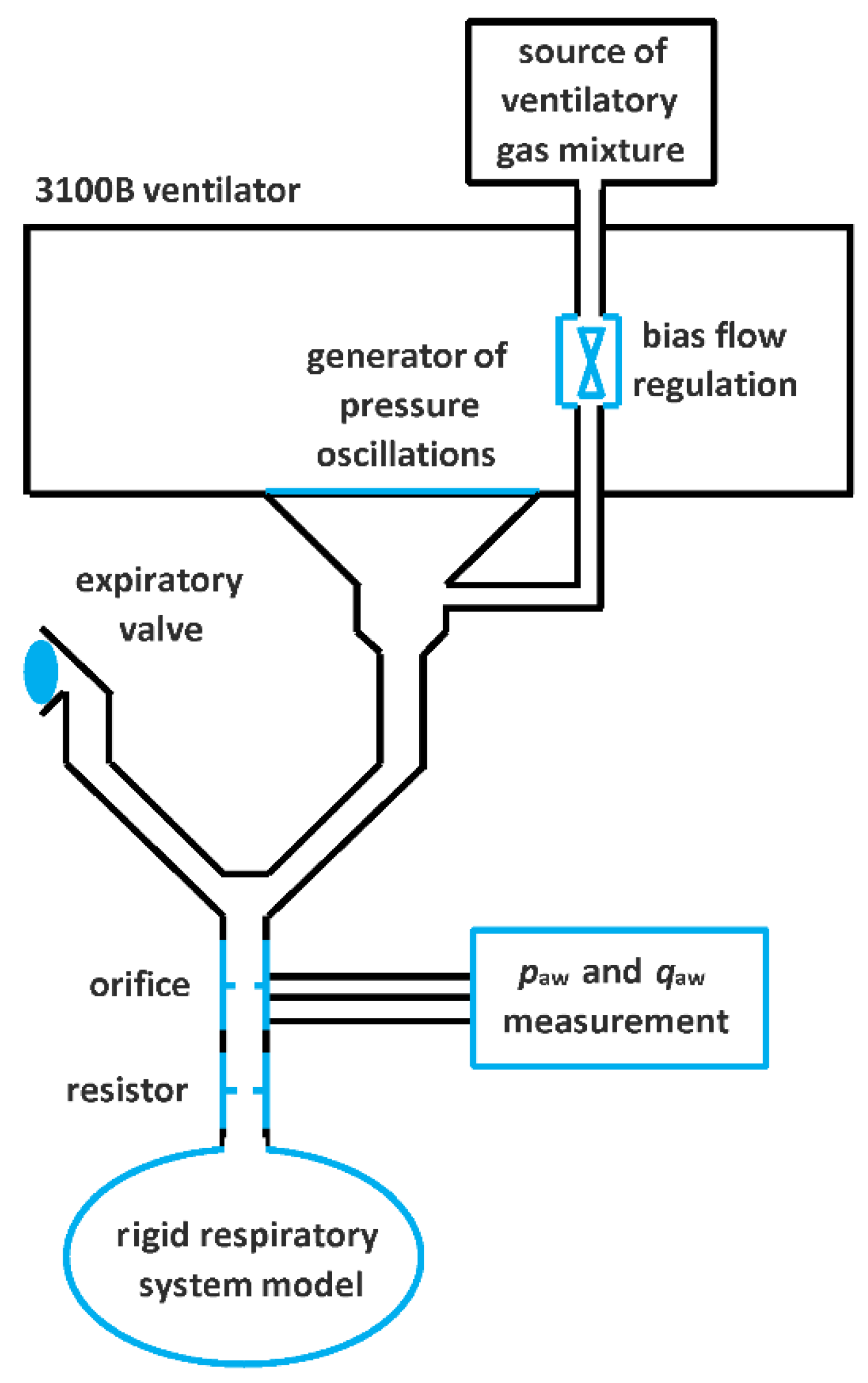
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meade, M.O.; Young, D.; Hanna, S.; Zhou, Q.; Bachman, T.E.; Bollen, C.; Slutsky, A.S.; Lamb, S.E.; Adhikari, N.K.; Mentzelopoulos, S.D.; et al. Severity of Hypoxemia and Effect of High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genderingen, H.R.; van Vught, A.J.; Duval, E.L.; Markhorst, D.G.; Jansen, J.R. Attenuation of pressure swings along the endotracheal tube is indicative of optimal distending pressure during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in a model of acute lung injury. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2002, 33, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sud, S.; Sud, M.; Friedrich, J.O.; Meade, M.O.; Ferguson, N.D.; Wunsch, H.; Adhikari, N.K. High frequency oscillation in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010, 340, c2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meduri, G.U.; Annane, D.; Confalonieri, M.; Chrousos, G.P.; Rochwerg, B.; Busby, A.; Ruaro, B.; Meibohm, B. Pharmacological principles guiding prolonged glucocorticoid treatment in ARDS. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.W.; Berg, N.K.; Reskallah, A.; Yuan, X.; Eltzschig, H.K. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklar, M.C.; Fan, E.; Goligher, E.C. High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation in Adults with ARDS: Past, Present, and Future. Chest 2017, 152, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, P.; Kamp, T.; Dijkstra, S.K.; Burgerhof, J.G.; Markhorst, D.G.; Curley, M.A.; Cheifetz, I.M.; Kneyber, M.C. Feasibility of an alternative, physiologic, individualized open-lung approach to high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in children. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, P.; Burgerhof, J.G.; Koopman, A.A.; Markhorst, D.G.; Kneyber, M.C. Physiologic responses to a staircase lung volume optimization maneuver in pediatric high-frequency oscillatory ventilation. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Tan, L.; Wang, L.; Möller, K.; Frerichs, I.; Yu, T.; Huang, Y.; Pan, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Optimal mean airway pressure during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in an experimental model of acute respiratory distress syndrome: EIT-based method. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lista, G.; Bresesti, I.; Cavigioli, F.; Castoldi, F.; Lupo, E.; LoMauro, A.; Aliverti, A. Efficacy of lung volume optimization maneuver monitored by optoelectronic pletismography in the management of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 22, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannin, E.; Dellaca, R.L.; Dognini, G.; Marconi, L.; Perego, M.; Pillow, J.J.; Tagliabue, P.E.; Ventura, M.L. Effect of frequency on pressure cost of ventilation and gas exchange in newborns receiving high-frequency oscillatory ventilation. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneyber, M.C.; Markhorst, D.G. Do We Really Know How to Use High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation in Critically Ill Children? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 1067–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneyber, M.C.; Markhorst, D.G. Any trial can (almost) kill a good technique. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1092–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, M.; Rodrigues, N.; Ari, A. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation: A narrative review. Can. J. Respir. Ther. 2019, 55, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macklem, P.T.; Mead, J. Resistance of central and peripheral airways measured by a retrograde catheter. J. Appl. Physiol. 1967, 22, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briscoe, W.A.; Dubois, A.B. The relationship between airway resistance, airway conductance and lung volume in subjects of different age and body size. J. Clin. Investig. 1958, 37, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedema, M.; de Jongh, F.H.; Frerichs, I.; van Veenendaal, M.B.; van Kaam, A.H. The effect of airway pressure and oscillation amplitude on ventilation in preterm infants. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, P.; Myers, S.; Chia, C.; Weber, H.C.; Young, S.; Williams, A.D.; Sohal, S.S. Clinical Application of Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT) in Early Detection of Airway Changes in Smokers. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashier, B.; Salvi, S. Measuring lung function using sound waves: Role of the forced oscillation technique and impulse oscillometry system. Breathe 2015, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellacà, R.L.; Zannin, E.; Ventura, M.L.; Sancini, G.; Pedotti, A.; Tagliabue, P.; Miserocchi, G. Assessment of dynamic mechanical properties of the respiratory system during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannin, E.; Ventura, M.L.; Dellacà, R.L.; Natile, M.; Tagliabue, P.; Perkins, E.J.; Sourial, M.; Bhatia, R.; Dargaville, P.A.; Tin-gay, D.G. Optimal mean airway pressure during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation determined by measurement of respiratory system reactance. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 75, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lavizzari, A.; Veneroni, C.; Ottaviani, V.; Francesco, B.; Fumagalli, C.; Colnaghi, M.; Mosca, F.; Dellacà, R.L. Respiratory reactance (Xrs) by Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT) during the first 24h of life in non-intubated preterm infants. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, PA1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannin, E.; Dellacà, R.L.; Neumann, R.; Schulzke, S. Assessment of lung mechanics for the prediction and evaluation of pulmonary outcome in preterm infants. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, OA306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejka, J.; Rozanek, M.; Rafl, J.; Kudrna, P.; Roubik, K. In Vitro Estimation of Relative Compliance during High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, H.E.; Derdak, S.; Ferguson, N.D.; Hager, D.N.; Kacmarek, R.M.; Thompson, B.T.; Brower, R.G. A protocol for high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in adults: Results from a roundtable discussion. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubik, K. Measuring and evaluating system designed for high-frequency oscillatory ventilation monitoring. Biomed. Tech. 2014, 59, S979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, T.; Obase, Y.; Nagasaka, Y.; Kishikawa, R.; Mukae, H.; Iwanaga, T. Peripheral bronchial obstruction evaluation in patients with asthma by lung sound analysis and impulse oscillometry. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronsson, D.; Hesselstrand, R.; Bozovic, G.; Wuttge, D.M.; Tufvesson, E. Airway resistance and reactance are affected in systemic sclerosis. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2015, 2, 28667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellacà, R.L.; Zannin, E.; Kostic, P.; Olerud, M.A.; Pompilio, P.P.; Hedenstierna, G.; Pedotti, A.; Frykholm, P. Optimisation of positive end-expiratory pressure by forced oscillation technique in a lavage model of acute lung injury. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannin, E.; Dellacà, R.L.; Kostic, P.; Pompilio, P.P.; Larsson, A.; Pedotti, A.; Hedenstierna, G.; Frykholm, P. Optimizing positive end-expiratory pressure by oscillatory mechanics minimizes tidal recruitment and distension: An experimental study in a lavage model of lung injury. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
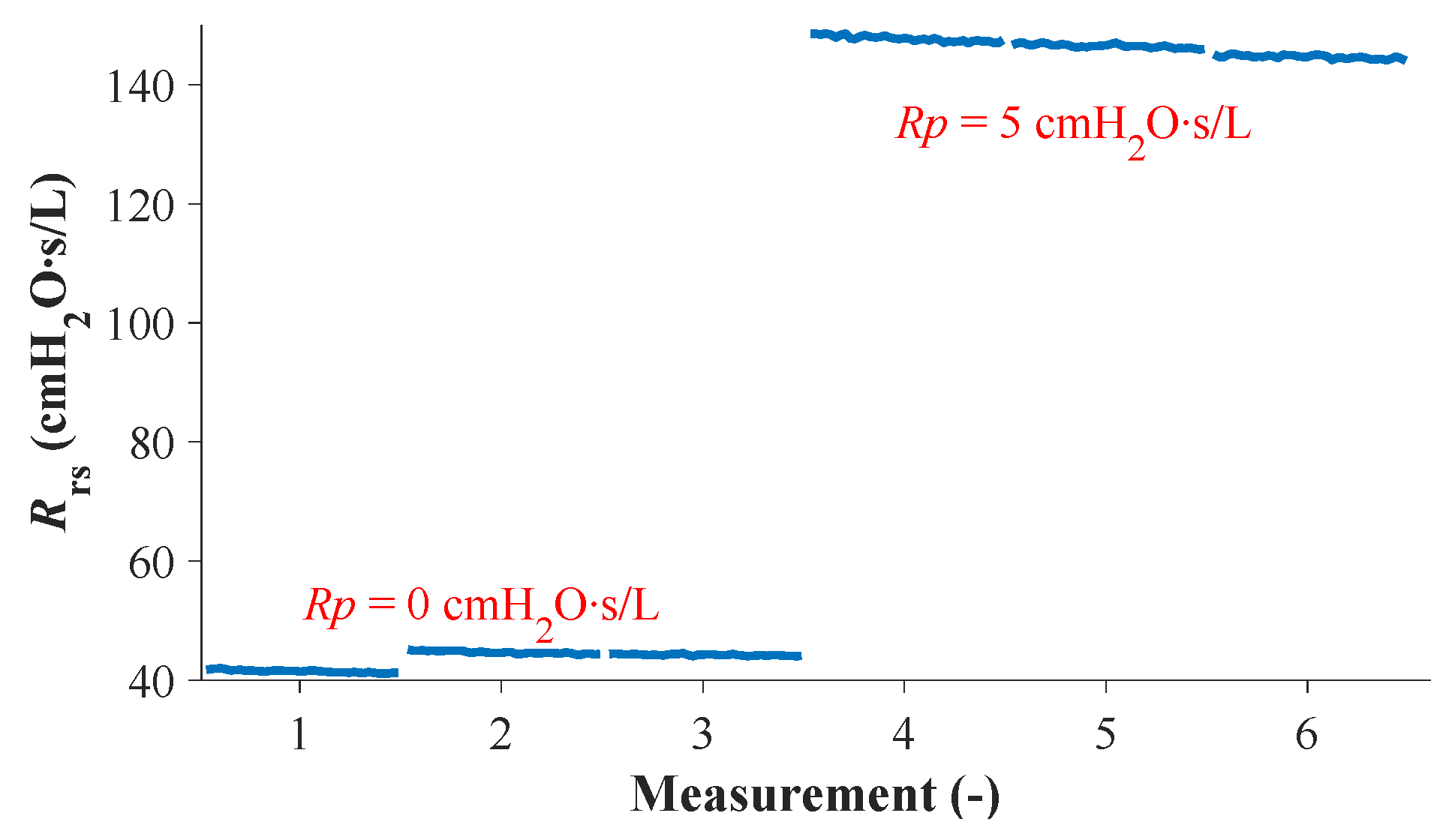


| C | Rrs with No Resistor | Rrs with Resistor Rp5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mL/cmH2O) | Mean | SD 1 | Mean | SD 1 |
| 37 | 41.5 | 0.2 | 147.8 | 0.5 |
| 24 | 44.7 | 0.2 | 146.6 | 0.3 |
| 17 | 44.3 | 0.1 | 144.7 | 0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matejka, J.; Rozanek, M.; Rafl, J. Assessment of Respiratory System Resistance during High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation Based on In Vitro Experiment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311279
Matejka J, Rozanek M, Rafl J. Assessment of Respiratory System Resistance during High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation Based on In Vitro Experiment. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(23):11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311279
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatejka, Jan, Martin Rozanek, and Jakub Rafl. 2021. "Assessment of Respiratory System Resistance during High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation Based on In Vitro Experiment" Applied Sciences 11, no. 23: 11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311279
APA StyleMatejka, J., Rozanek, M., & Rafl, J. (2021). Assessment of Respiratory System Resistance during High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation Based on In Vitro Experiment. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311279






