Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Detection of Chromium (VI) by Maleic Acid-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation and Functionalization of Au NPs
2.3. Detection of Aqueous Cr(VI) by MA-Capped Au NPs
2.4. Characterization
3. Results
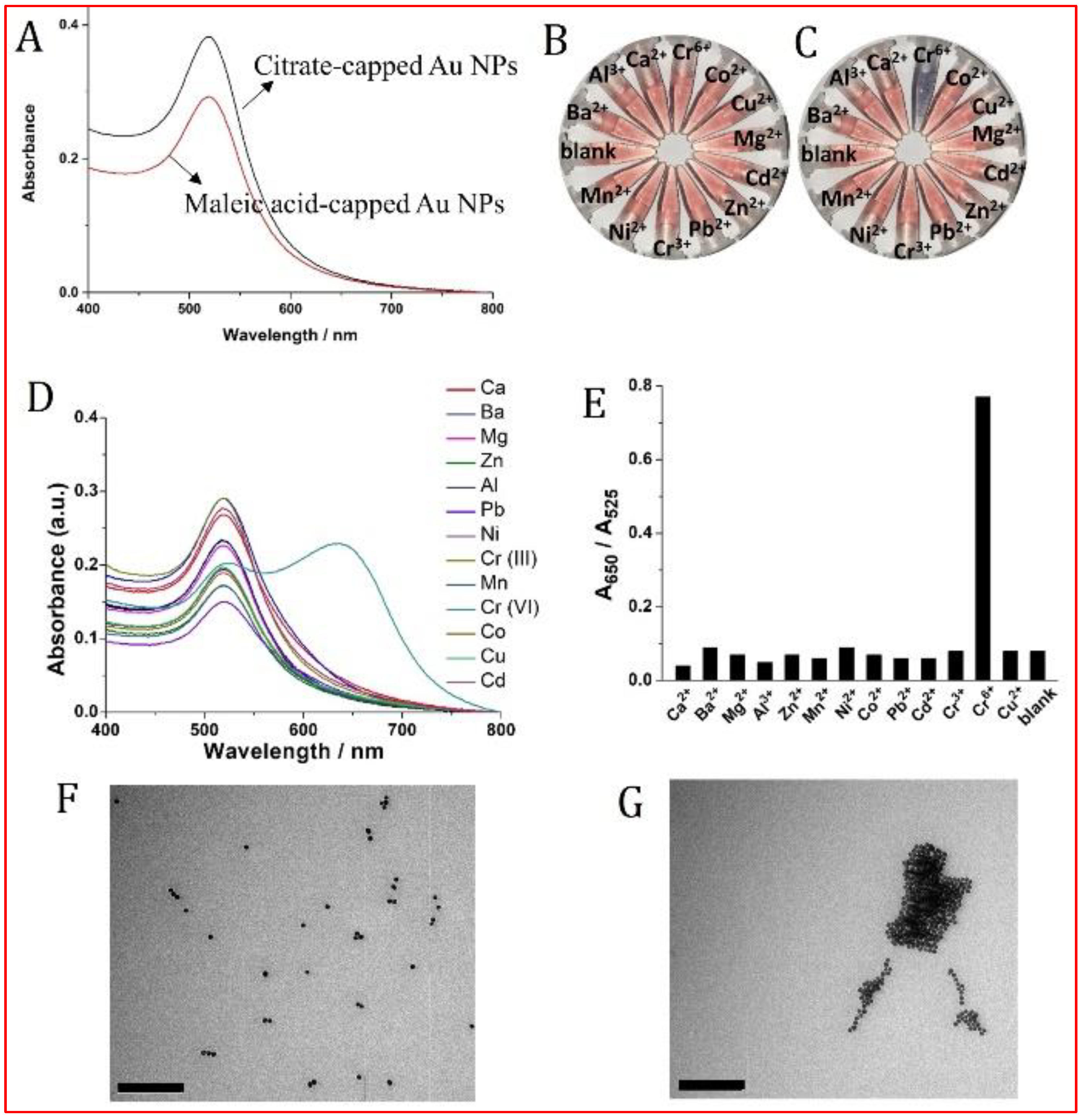
3.1. Selectivity and Sensitivity Investigation of MA-Capped Au NPs to Aqueous Cr(VI)
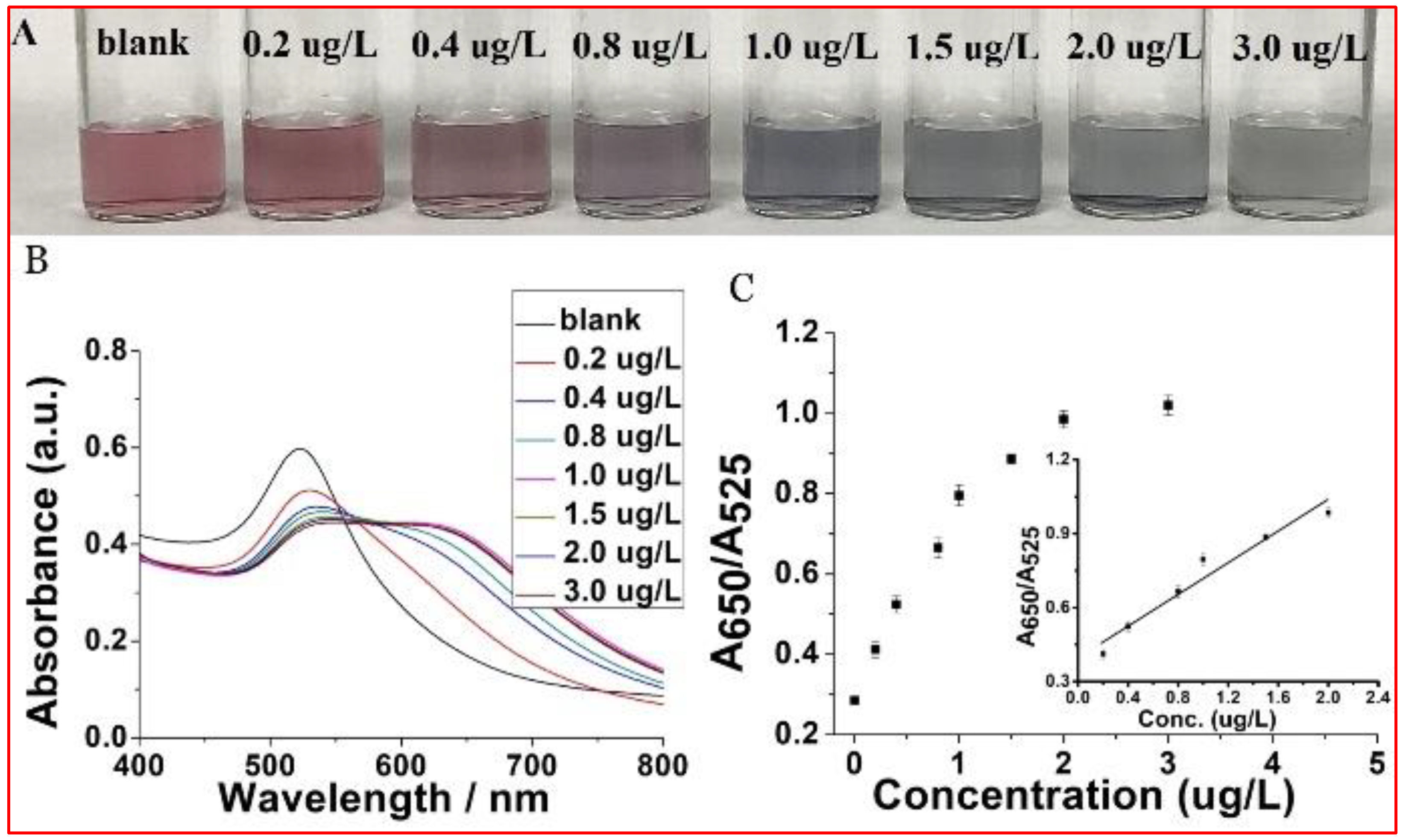
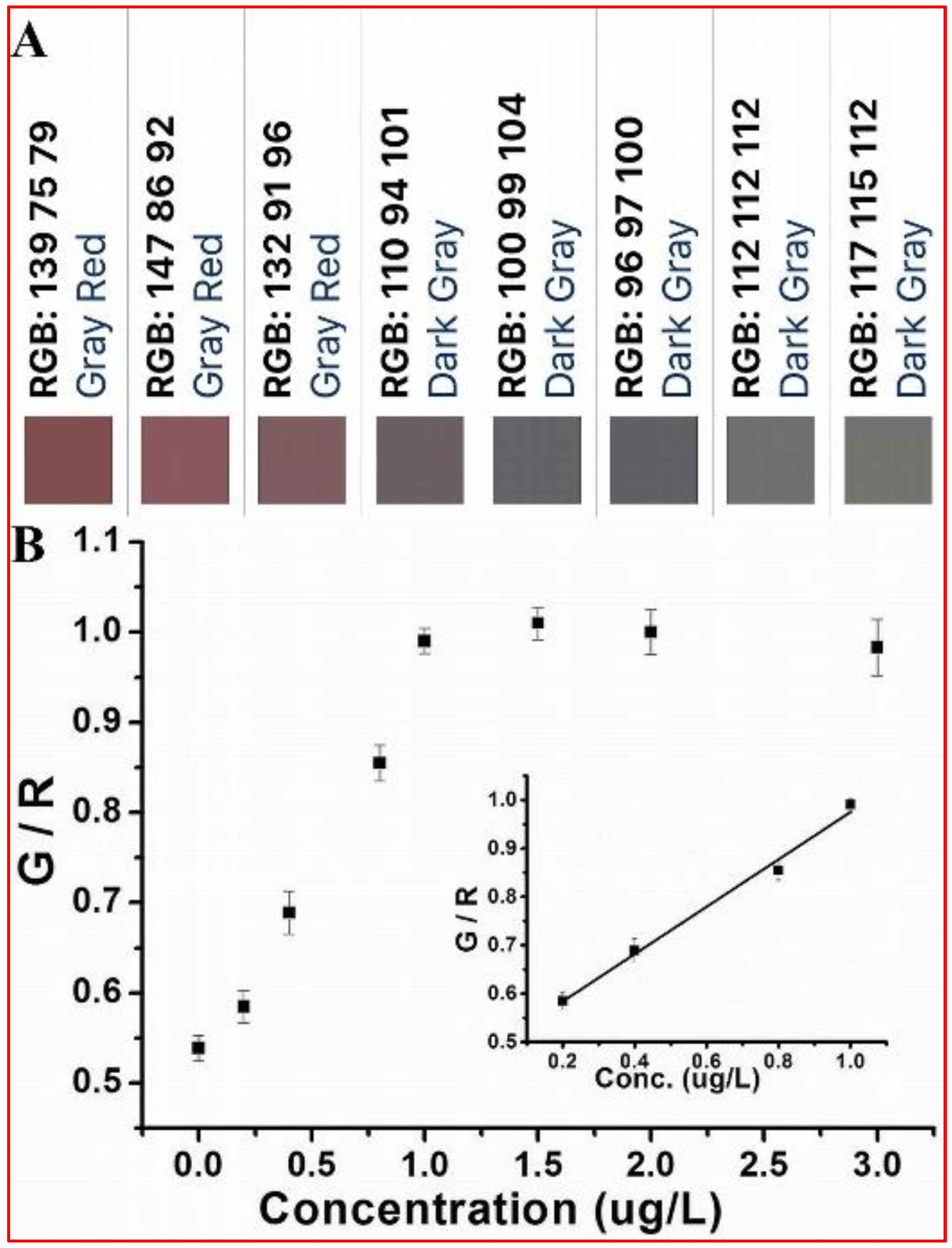
3.2. Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Assay
3.3. Real Sample Detection Based on Smartphone Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barceloux, D.G. Chromium. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ma, C.; Kang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, D. Field analysis of Cr(vi) in water samples by using a smartphone-based ultralong absorption path reflection colorimetric device. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Madhwal, D.; Jain, V.K.; Suman, A. POC device for on-the-spot detection of hexavalent chromium in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alula, M.T.; Madingwane, M.L. Colorimetric quantification of chromium(VI) ions based on oxidoreductase-like activity of Fe3O4. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 324, 128726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.M.; Zhou, T.; Fang, F.; Wu, Z.Y. Colorimetric speciation of Cr on paper-based analytical devices based on field amplified stacking. Talanta 2020, 210, 120635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, P.; Peng, H.; Niu, X. Polyethylenimine-stabilized silver nanoclusters act as an oxidoreductase mimic for colorimetric determination of chromium(VI). Mikrochim. Acta 2020, 187, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Choi, E.; Lee, C.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H.; Yu, T.; Piao, Y. Highly sensitive and selective visual detection of Cr(VI) ions based on etching of silver-coated gold nanorods. Nano Converg. 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nghia, N.N.; Huy, B.T.; Lee, Y.I. Colorimetric detection of chromium(VI) using graphene oxide nanoparticles acting as a peroxidase mimetic catalyst and 8-hydroxyquinoline as an inhibitor. Mikrochim. Acta 2018, 186, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayyem, S.; Swaidan, A.; Barras, A.; Dolci, M.; Faridbod, F.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Colorimetric detection of chromium(VI) ion using poly(N-phenylglycine) nanoparticles acting as a peroxidase mimetic catalyst. Talanta 2021, 226, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Gao, S.; Yao, L.; Wang, L.; Qu, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L. Single-atom nanozyme enabled fast and highly sensitive colorimetric detection of Cr(VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamane, S.D.; Bhojwani, V.; Balkunde, P.L.; Bhattacharya, M.; Gupta, I.; Mohapatra, A.K.; Shekhar, A.; Singh, A. Smartphone-enabled field monitoring tool for rapid hexavalent chromium detection in water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 3455–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagchi, D.; Stohs, J.S.; Downs, B.W.; Bagchi, M.; Preuss, H.G. Cytotoxicity and oxidative mechanisms of different forms of chromium. Toxicology 2002, 180, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhitkovich, A. Importance of Chromium-DNA Adducts in Mutagenicity and Toxicity of Chromium(VI). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, A.L.; Wise, S.S.; Wise, J.R. Carcinogenicity of hexavalent chromium. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Klein, C.B. Toxicity and Carcinogenicity of Chromium Compounds in Humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 36, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, A.K.; Barnes, C.; Yedjou, C.; Velma, V.R.; Tchounwou, P.B. Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and antioxidant enzyme activity induced by hexavalent chromium in Sprague-Dawley rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 24, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiran, K.; Kumar, K.S.; Prasad, B.; Suvardhan, K.; Lekkala, R.B.; Janardhanam, K. Speciation determination of chromium(III) and (VI) using preconcentration cloud point extraction with flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). J. Hazard Mater. 2008, 150, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hansen, E.H. Coupling on-line preconcentration by ion-exchange with ETAAS A novel flow injection approach based on the use of a renewable microcolumn as demonstrated for the determination of nickel in environmental and biological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 424, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, M.T.S.; Alonso, E.I.V.; de Torres, A.G.; Pavón, J.M.C. Development of a new system for the speciation of chromium in natural waters and human urine samples by combining ion exchange and ETA-AAS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2004, 19, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejeta, S.Y.; Imae, T. Selective colorimetric and electrochemical detections of Cr(III) pollutant in water on 3-mercaptopropionic acid-functionalized gold plasmon nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1152, 338272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Shan, X.Q.; Lian, J. Separation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in river and reservoir water with 8-hydroxyquinoline immobilized polyacrylonitrile fiber for determination by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 2002, 56, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegário, A.A.; Smichowski, P.; Polla, G. On-line preconcentration and speciation analysis of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) using baker′s yeast cells immobilised on controlled pore glass. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 546, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoori, J.L.; Shemirani, F. Determination of chromium(vi) and total chromium by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry after preconcentration using solvent extraction and back-extraction. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1995, 10, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, N.L.; Mirkin, C.A. Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Han, M.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Colorimetric detection of mercuric ion (Hg2+) in aqueous media using DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2007, 46, 4093–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, N.; Ma, Y.; Mao, L. Colorimetric detection of glucose in rat brain using gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 4800–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, M.S.; Mirkin, C.A. A gold-nanoparticle-based real-time colorimetric screening method for endonuclease activity and inhibition. Angew. Chem. 2007, 46, 3468–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ouyang, W.; Xie, P.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G.; Guo, L. Highly uniform gold nanobipyramids for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of influenza virus. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.Y.; Hai, X.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, J.H. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane polymer-caged silver nanoparticle as a smart colorimetric probe for the detection of hydrogen sulfide. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Su, X.; Yang, K.; Pan, L.; Liu, Q.; Gong, L.; Wang, P.; Yang, J.; He, Y. Antibody-Free Colorimetric Detection of Total Aflatoxins in Rice Based on a Simple Two-Step Chromogenic Reaction. Anal. Chem 2016, 88, 3775–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, S.; Liu, H.; Ren, N.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Paper-based device for colorimetric and photoelectrochemical quantification of the flux of H2O2 releasing from MCF-7 cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5369–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiu, F.R.; Gao, X. Determination of Cr(VI) based on the peroxidase mimetic catalytic activity of citrate-capped gold nanoparticles. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, X.S.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wu, D.Y.; et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelon, G.; Montes-Garcia, V.; Lopez-Puente, V.; Hill, E.H.; Hamon, C.; Sanz-Ortiz, M.N.; Rodal-Cedeira, S.; Costas, C.; Celiksoy, S.; Perez-Juste, I.; et al. Detection and imaging of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm communities by surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, K.M.; Hafner, J.H. Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3828–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Xu, F.; Wang, S.; Xu, K.; Hou, X.; Wu, P. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for selenium detection via hydride generation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4695–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, G.G.; Ye, H.; Rauschendorfer, R.; Tang, D.; Xia, X. Facile colorimetric detection of silver ions with picomolar sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3622–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Gao, P.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Glutathione modified gold nanoparticles for sensitive colorimetric detection of pb(2+) ions in rainwater polluted by leaking perovskite solar cells. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12316–12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Su, Z. Colorimetric detection of Pb2+ using glutathione functionalized gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgadas, C.V.; Lakshmi, V.N.; Sharma, C.P.; Sreenivasan, K. Sensing of lead ions using glutathione mediated end to end assembled gold nanorod chains. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Yun, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. Facile preparation of glutathione-stabilized gold nanoclusters for selective determination of chromium (III) and chromium(VI) in environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 770, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.K.; Oh, S.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, Y. Colorimetric detection of Co2+ ion using silver nanoparticles with spherical, plate, and rod shapes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8978–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chang, T.W.; Lin, G.; Gartia, M.R.; Liu, G.L. Self-referenced smartphone-based nanoplasmonic imaging platform for colorimetric biochemical sensing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Sun, R.; Vasile, T.; Chang, Y.C.; Li, L. high-throughput optical sensing immunoassays on smartphone. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8302–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico-Yuste, A.; Gonzalez-Vallejo, V.; Benito-Pena, E.; de Las Casas Engel, T.; Orellana, G.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Furfural determination with disposable polymer films and smartphone-based colorimetry for beer freshness assessment. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3959–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gu, Z. Smartphone-based point-of-care testing of salivary alpha-amylase for personal psychological measurement. Analyst 2015, 140, 7399–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, H.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Nie, Z.; Yao, S. A colorimetric and smartphone readable method for uracil-DNA glycosylase detection based on the target-triggered formation of G-quadruplex. Analyst 2015, 140, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Hasan, B.; Sasan, A.; Nasim, F.; Abbas, A. New portable smartphone-based PDMS microfluidic kit for the simultaneous colorimetric detection of arsenic and mercury. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 27091–27100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, G.; Tao, L.; Qiongwen, H.; Longjie, Z.; Xinyi, W.; Hao, W.; Ping, W. In-situ detection of cadmium with aptamer functionalized gold nanoparticles based on smartphone-based colorimetric system. Talanta 2020, 208, 120231. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd, F.S.; Soocheol, K.; Hyoil, J.; Taeho, K.; Chulmin, J.; Seungkyung, P. Miniaturized Sample Preparation and Rapid Detection of Arsenite in Contaminated Soil Using a Smartphone. Sensors 2018, 18, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supattra, M.; Siriwan, T. On-site detection of heavy metals in wastewater using a single paper strip integrated with a smartphone. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Yuanyuan, C.; Yingnan, L.; Fan, L.; Shuwen, G.; Yuhang, S.; Hanyue, X.; Li, W. Portable colorimetric detection of copper ion in drinking water via red beet pigment and smartphone. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104176. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd, F.S.; Zeeshan, A.K.; Hyoil, J.; Seungkyung, P. SPE based soil processing and aptasensor integrated detection system for rapid on site screening of arsenic contamination in soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110559. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Cao, F.; Zheng, W.; Tian, Y.; Xianyu, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Deng, K.; Jiang, X. Detection of the nanomolar level of total Cr[(iii) and (vi)] by functionalized gold nanoparticles and a smartphone with the assistance of theoretical calculation models. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2042–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.Q.; Li, H.W.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Wu, Y. Selective detection of trace Cr3+ in aqueous solution by using 5,5’-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid)-modified gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Liu, X.; Quan, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, H. Selective detection of nanomolar Cr(vi) in aqueous solution based on 1,4-dithiothreitol functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.J.; Tseng, W.L. Role of 5-thio-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)-capped gold nanoparticles in the sensing of chromium(vi): Remover and sensor. Analyst 2011, 136, 2712–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample b | The Concentration of Cr(VI) (µg L−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AAS Method | UV-Vis Method/CV | Smartphone/CV | |
| South lake | 1.01 ± 0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.06/12.43% | 1.08 ± 0.04/14.48% |
| Yezhi lake | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 0.96 ± 0.02/13.67% | 1.06 ± 0.03/14.52% |
| Tangxun lake | 1.04 ± 0.04 | 1.00 ± 0.03/12.28% | 0.88 ± 0.02/13.88% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, A.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Yuan, C.; Barakat, H. Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Detection of Chromium (VI) by Maleic Acid-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210894
Mohamed A, Li X, Li C, Li X, Yuan C, Barakat H. Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Detection of Chromium (VI) by Maleic Acid-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210894
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Ahmed, Xuemeng Li, Chengfei Li, Xuegang Li, Chao Yuan, and Hassan Barakat. 2021. "Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Detection of Chromium (VI) by Maleic Acid-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210894
APA StyleMohamed, A., Li, X., Li, C., Li, X., Yuan, C., & Barakat, H. (2021). Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Detection of Chromium (VI) by Maleic Acid-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210894







