Postmortem Documentation of SARS-CoV-2 in Utero and Postpartum Transmission, through Amniotic Fluid, Placental, and Pulmonary Tissue RT-PCR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Maternal death due to severe COVID-19 and in utero fetal demise (27 weeks).
- In utero fetal demise (29 weeks) with living confirmed COVID-19 mother.
- 2-month-old infant death with confirmed COVID-19 caregivers.
2.1. Manual Pre-Processing
2.2. Automated RNA Extraction
2.3. Amplification of the Products
3. Results
3.1. Case One: Maternal Death due to Severe COVID-19 and In Utero Fetal Demise
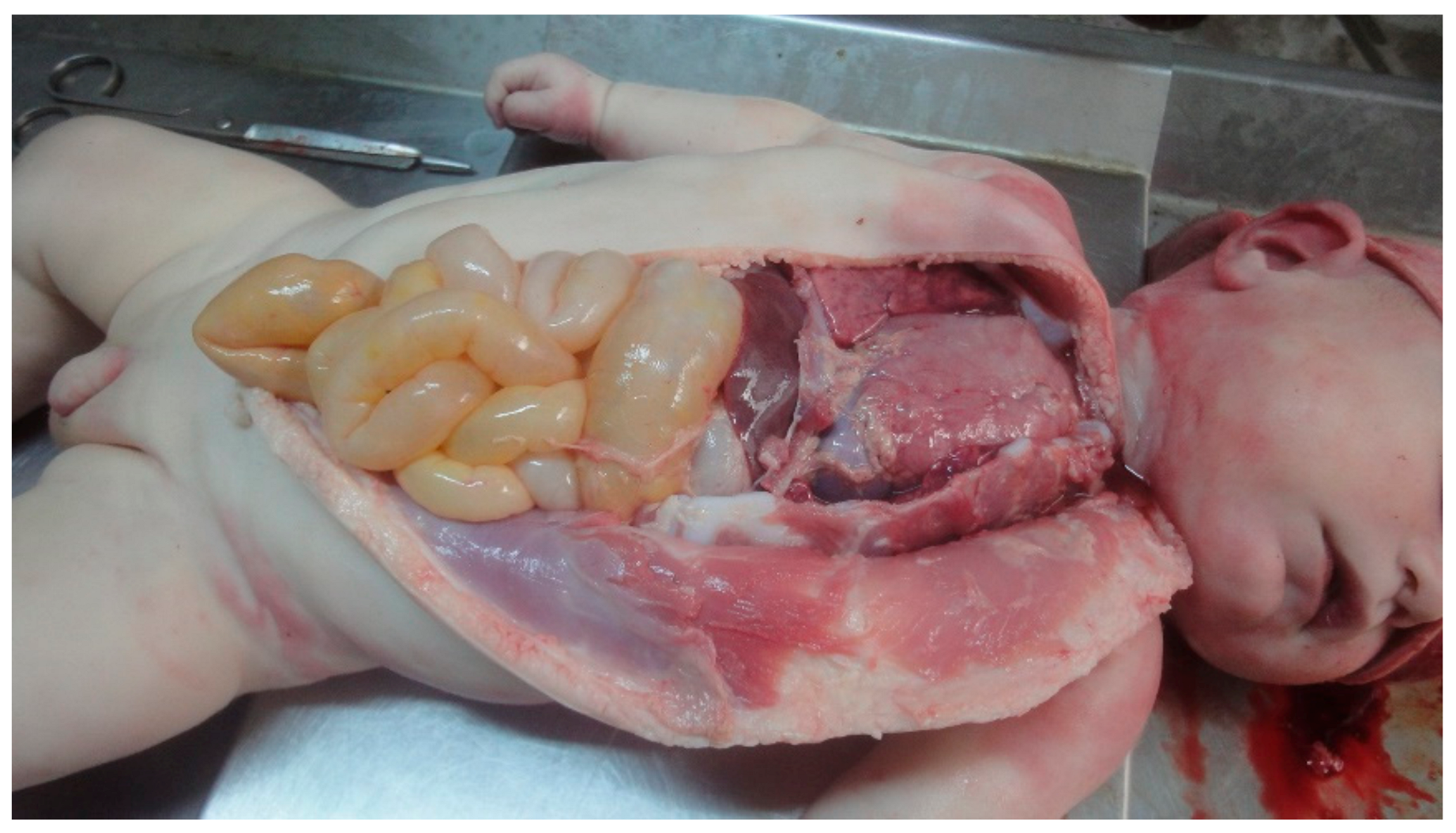
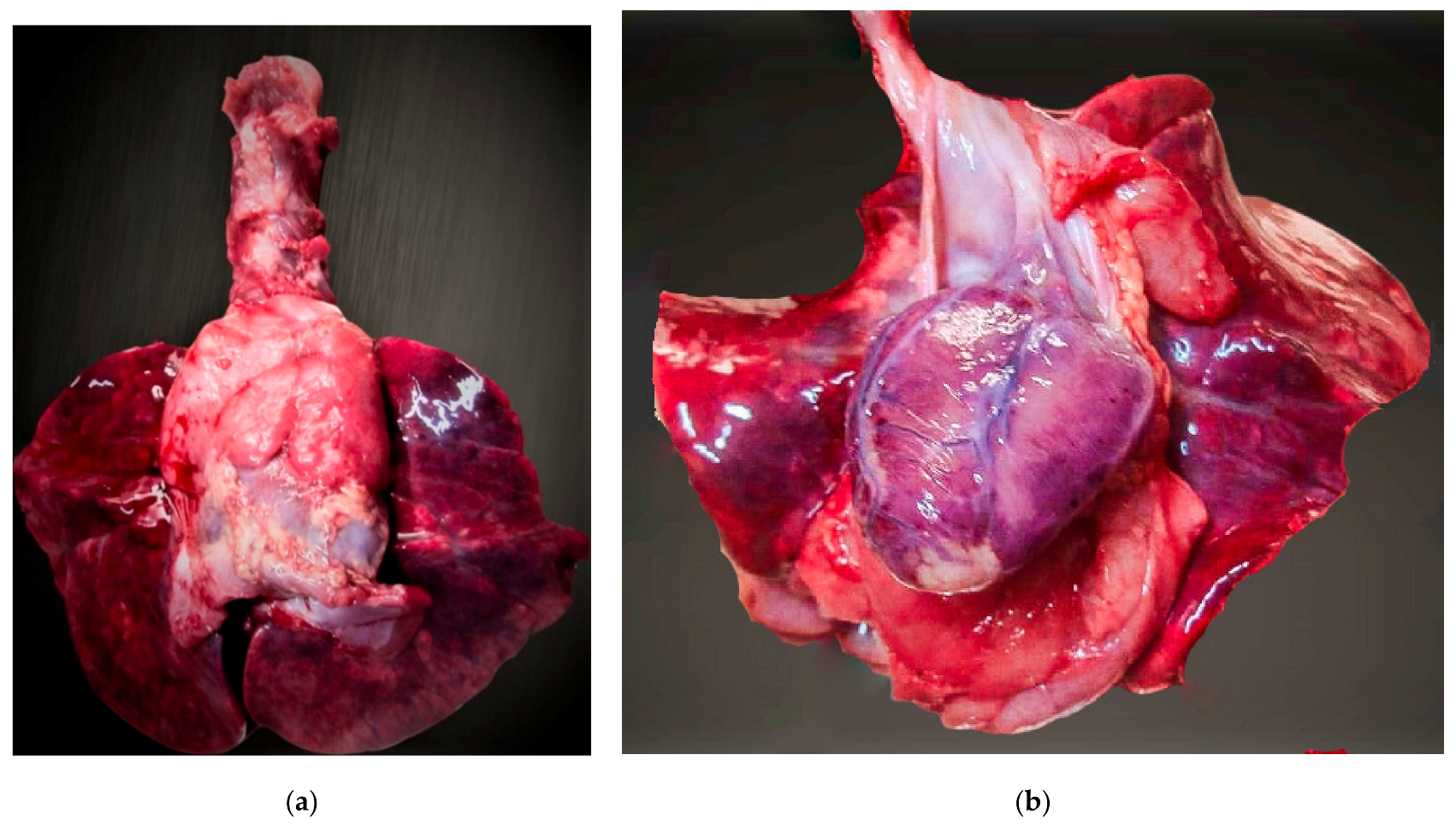
3.1.1. Relevant Autopsy Findings
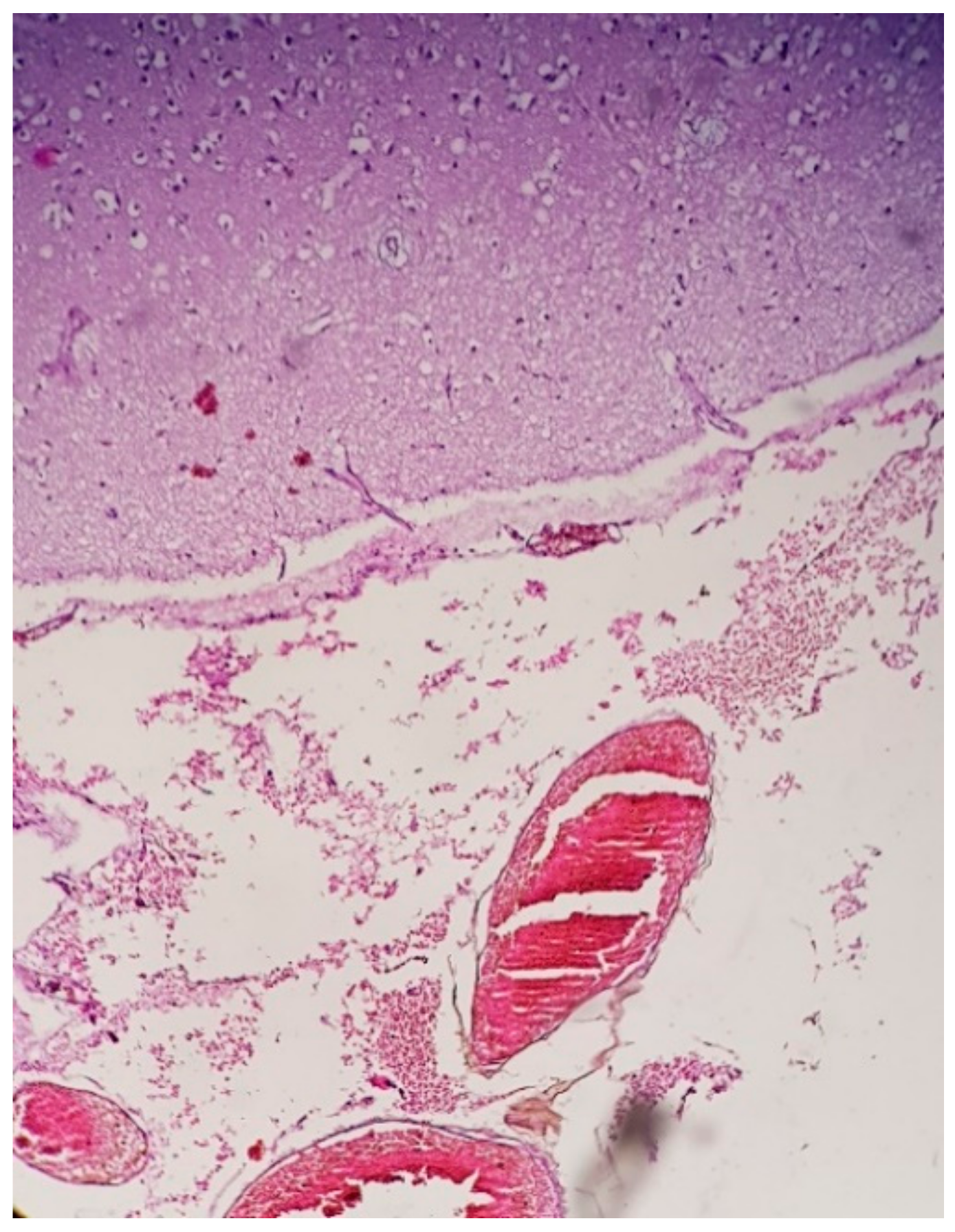
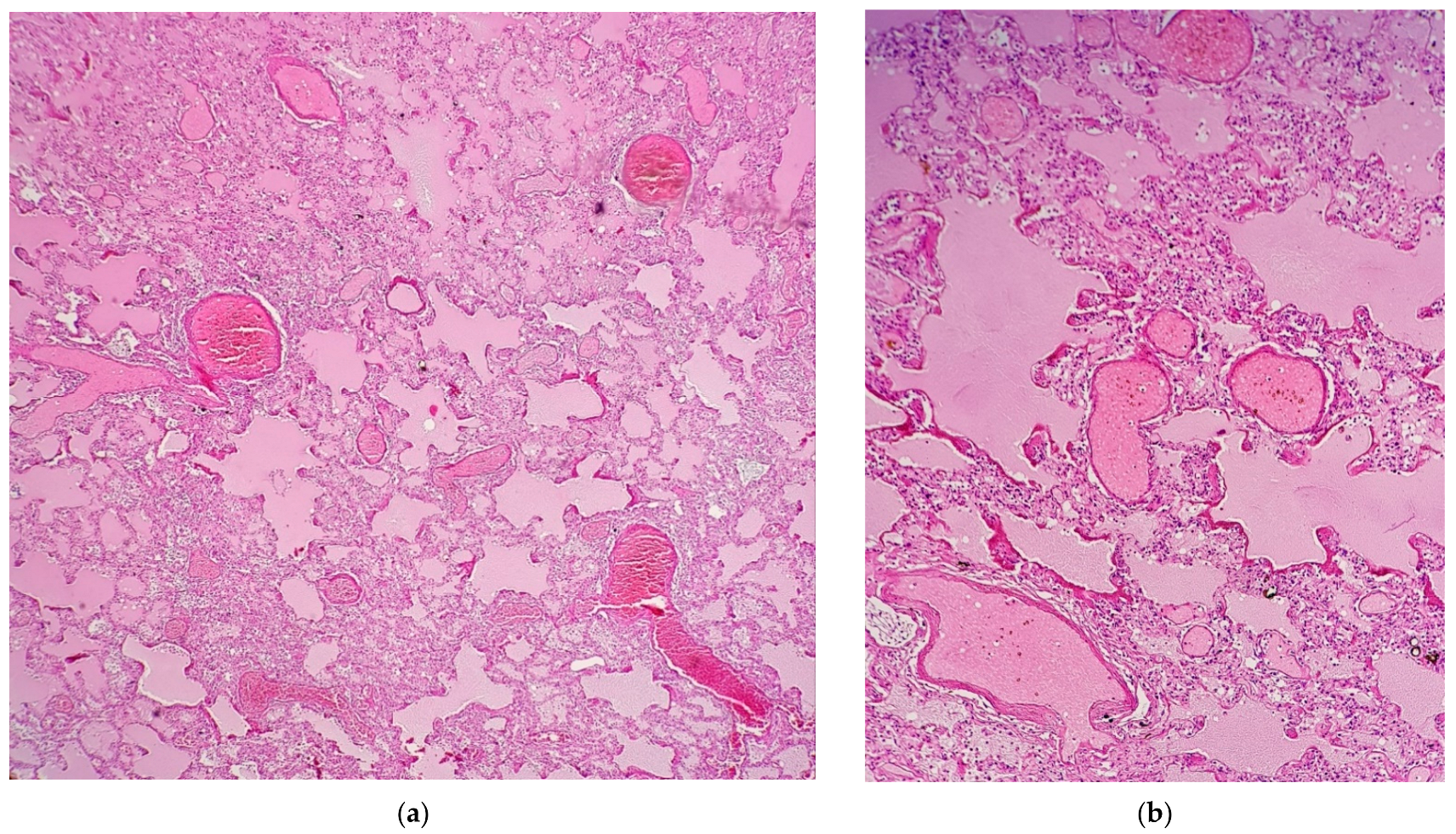
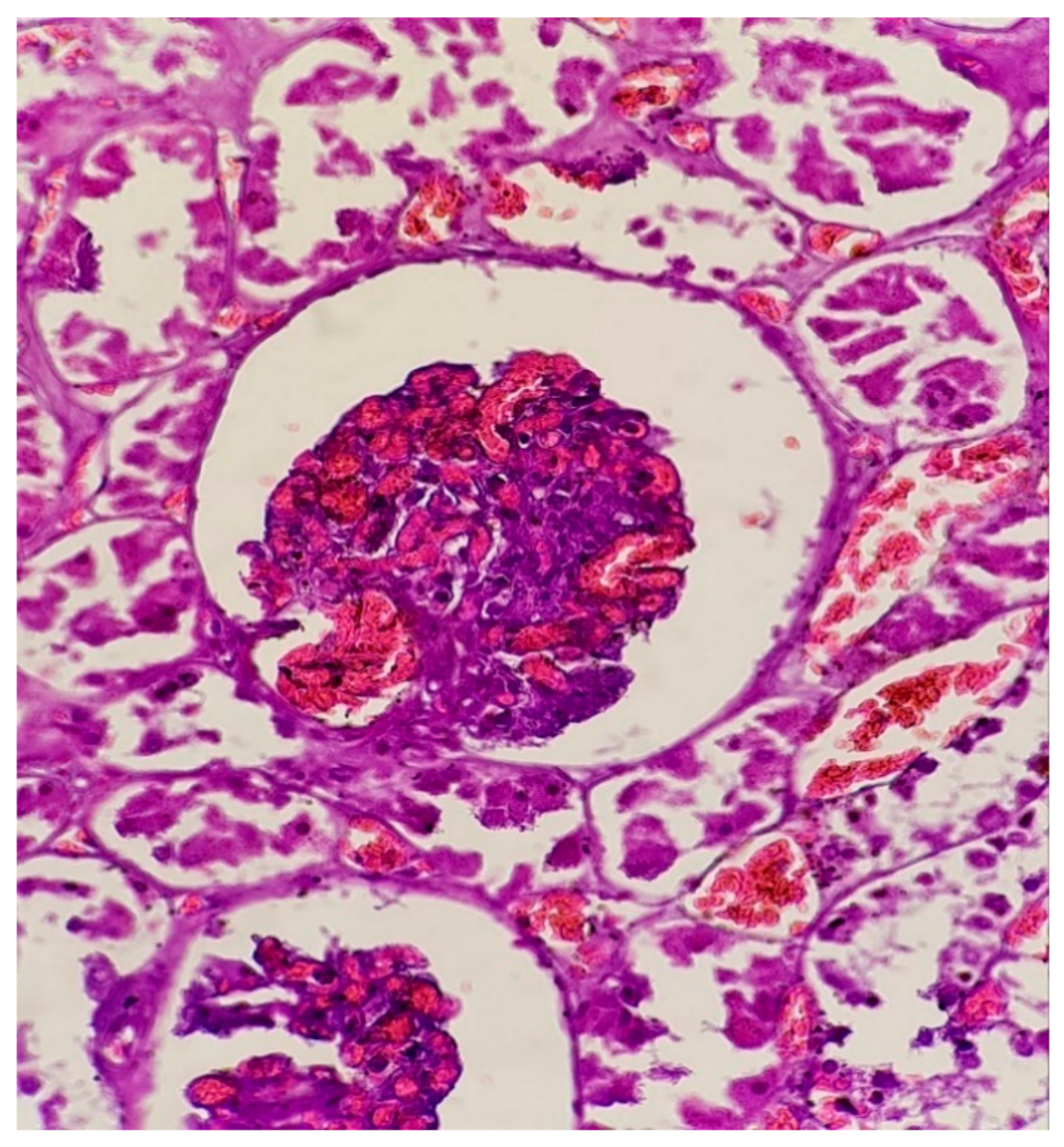
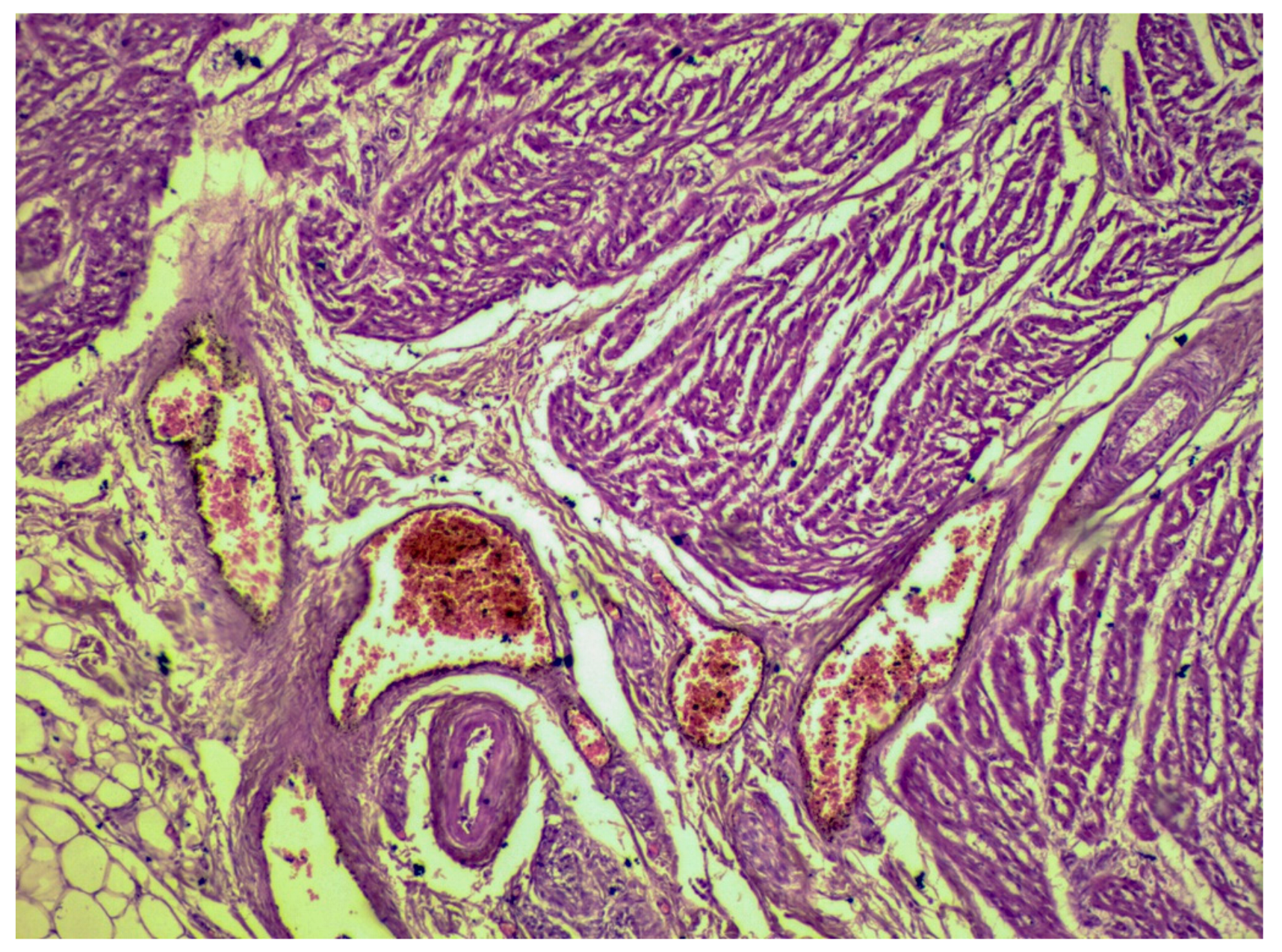
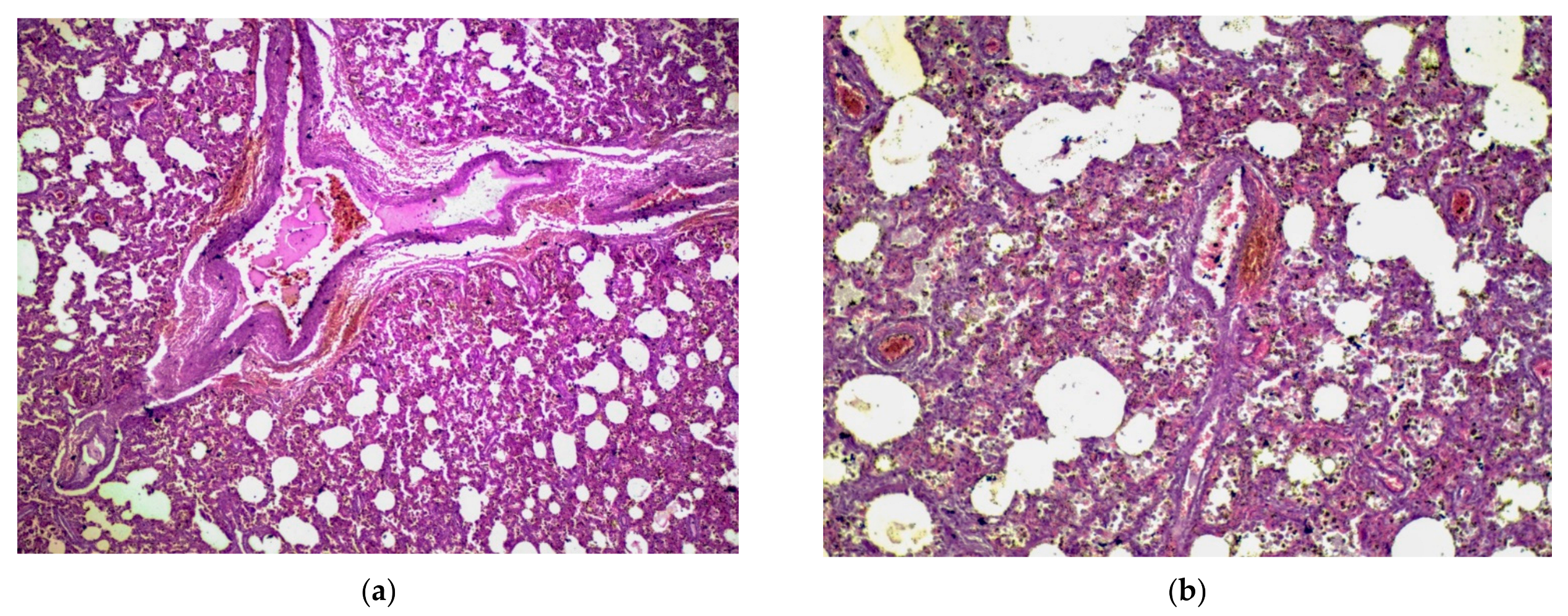
3.1.2. Microscopic Findings
3.1.3. Viral RNA SARS-CoV-2 Detection
3.2. Case Two: In Utero Fetal Demise with Living Confirmed COVID-19 Mother
3.2.1. Relevant Autopsy Findings
3.2.2. Microscopic Findings
3.2.3. Viral RNA SARS-CoV-2 Detection
3.3. Case Three: 2-Month-Old Infant Death with Confirmed COVID-19 Caregivers
3.3.1. Relevant Autopsy Findings
3.3.2. Microscopic Findings
3.3.3. Viral RNA SARS-CoV-2 Detection
4. Discussion
- Identification of the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome in the placenta or amniotic fluid, prior to the onset of labor;
- Identification of the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome in umbilical cord blood or neonatal blood/respiratory samples/bodily fluids;
- −
- Inflammation (34.7% of cases)—in order of frequency: chorioamnionitis/subchorionitis, intervillositis, fetal vasculitis/choriovasculitis, vilitis, and deciduitis;
- −
- Maternal vascular malperfusion (37.8% of cases)—in order of frequency: increased fibrin deposition, infarction, decidual vasculopathy, intervillous/subchorionic thrombosis, accelerated villous maturation, distal villous hypoplasia, and retroplacental hemorrhage;
- −
- Fetal vascular malperfusion (9.2% of cases)—in order of frequency: villous stromal-vascular karyorrhexis, chorangiosis, delayed villous maturation, avascular villi, and thrombi in fetal circulation;
- −
- Others (16.3% of cases)—in order of frequency: presence of meconium, villous edema, extravillous trophoblasts, subchorionic laminar necrosis, placental accrete, and Hofbauer cell hyperplasia [79].
- −
- Heart (endarteritis in small arteries, with CD68+ interstitial inflammatory infiltrate, edema between cardiomyocytes, and ischemic changes, while the pulmonary artery and aorta showed no alterations);
- −
- Lungs (in the pseudoglandular stage of development, with reactive bronchial epithelium and hypercellularity composed of CD68+ inflammatory macrophages—also seen in interstitium and pleura);
- −
- Skeletal muscle (myositis was observed as a mononuclear inflammation between the fascicles of striated muscle cells of the neck, extremities, and diaphragm, causing severe damage in fibers, with apoptotic cells, atrophy, and intercellular edema);
- −
- Kidneys (scattered cellular detritus and mild interstitial inflammation, with enhanced infiltration of CD68+ cells) [77].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roser, M.; Ritchie, H.; Ortiz-Ospina, E.; Hasell, J. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). Our World in Data 2020. Available online: https://www.ourworldindata.org/covid-cases (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The Species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, A.G.; Lin, T.; Wang, P. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 1100–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Xu, Y.; Bao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, P.; Qu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, W.; Han, Y.; Qin, C. From SARS to MERS, Thrusting Coronaviruses into the Spotlight. Viruses 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Guo, J.; Fan, C.; Juan, J.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Feng, L.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnant women: A report based on 116 cases. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 111.e1–111.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A. An Analysis of 38 Pregnant Women with COVID-19, Their Newborn Infants, and Maternal-Fetal Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Maternal Coronavirus Infections and Pregnancy Outcomes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamieson, D.; Honein, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Williams, J.L.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Biggerstaff, M.; Lindstrom, S.; Louie, J.K.; Christ, C.M.; Bohm, S.R.; et al. H1N1 2009 influenza virus infection during pregnancy in the USA. Lancet 2009, 374, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A. Maternal and Infant Death and the rVSV-ZEBOV Vaccine Through Three Recent Ebola Virus Epidemics-West Africa, DRC Équateur and DRC Kivu: 4 Years of Excluding Pregnant and Lactating Women and Their Infants from Immunization. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2019, 6, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, D.A. Maternal Filovirus Infection and Death from Marburg and Ravn Viruses: Highly Lethal to Pregnant Women and Their Fetuses Similar to Ebola Virus. IntechOpen 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Anoko, J.N.; Abramowitz, S.A. Pregnant in the Time of Ebola: Women and Their Children in the 2013–2015 West African Epidemic Global Maternal and Child Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado, M.G.; Schwartz, D.A. Zika Virus Infection in Pregnancy, Microcephaly, and Maternal and Fetal Health: What We Think, What We Know, and What We Think We Know. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 141, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wastnedge, E.A.N.; Reynolds, R.M.; Van Boeckel, S.R.; Stock, S.J.; Denison, F.C.; Maybin, J.A.; Critchley, H.O.D. Pregnancy and COVID-19. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, G.C.; Giardina, I. Coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: Consider thromboembolic disorders and thromboprophylaxis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhao, S.-J.; Kwak-Kim, J.; Mor, G.; Liao, A.-H. Why are pregnant women susceptible to COVID-19? An immunological viewpoint. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2020, 139, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Yang, W.; Wei, X.; Wu, K.; Huang, D. The Unique Microbiome and Innate Immunity during Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, A.J.M.; Fernandes, A.C.L.; Guzen, F.P.; Pinheiro, F.I.; de Azevedo, E.P.; Cobucci, R.N. Susceptibility to COVID-19 in Pregnancy, Labor, and Postpartum Period: Immune System, Vertical Transmission, and Breastfeeding. Front. Glob. Women’s Health 2021, 2, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savasi, V.M.; Parisi, F.; Patanè, L.; Ferrazzi, E.; Frigerio, L.; Pellegrino, A.; Spinillo, A.; Tateo, S.; Ottoboni, M.; Veronese, P.; et al. Clinical Findings and Disease Severity in Hospitalized Pregnant Women with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 136, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, R.; Alrahmani, L.; Monzer, N.; Debiane, L.G.; Berbari, E.; Fares, J.; Fitzpatrick, F.; Murad, M.H. Clinical Presentation and Outcomes of Pregnant Women with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allotey, J.; Stallings, E.; Bonet, M.; Yap, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Kew, T.; Debenham, L.; Llavall, A.C.; Dixit, A.; Zhou, D.; et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: Living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, m3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, M.; Neovius, M.; Saltvedt, S.; Söderling, J.; Pettersson, K.; Brandkvist, C.; Stephansson, O. Association of SARS-CoV-2 Test Status and Pregnancy Outcomes. JAMA 2020, 324, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.Q.; Bilodeau-Bertrand, M.; Liu, S.; Auger, N. The impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2021, 193, E540–E548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: Update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laza, R.; Musta, V.F.; Nicolescu, N.D.; Marinescu, A.R.; Mocanu, A.; Vilceanu, L.; Paczeyka, R.; Cut, T.G.; Lazureanu, V.E. Cutaneous Manifestations in SARS-CoV-2 Infection—A Series of Cases from the Largest Infectious Diseases Hospital in Western Romania. Healthcare 2021, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.P.; Look, D.C.; Shi, L.; Hickey, M.; Pewe, L.; Netland, J.; Farzan, M.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Perlman, S.; McCray, P.B. ACE2 Receptor Expression and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection Depend on Differentiation of Human Airway Epithelia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14614–14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.; Lely, A.; Navis, G.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus–induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, C.G.; Allon, S.J.; Nyquist, S.K.; Mbano, I.M.; Miao, V.N.; Tzouanas, C.N.; Cao, Y.; Yousif, A.; Bals, J.; Hauser, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues. Cell 2020, 181, 1016–1035.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Gu, L.; Ma, L.; Duan, Y. Atlas of ACE2 Gene Expression in Mammals Reveals Novel Insights in Transmisson of SARS-Cov-2. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shulla, A.; Heald-Sargent, T.; Subramanya, G.; Zhao, J.; Perlman, S.; Gallagher, T. A Transmembrane Serine Protease Is Linked to the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Receptor and Activates Virus Entry. J. Virol. 2010, 85, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zuo, W. Single-Cell RNA Expression Profiling of ACE2, the Receptor of SARS-CoV-2. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.C.; Sausville, E.L.; Girish, V.; Yuan, M.L.; Vasudevan, A.; John, K.M.; Sheltzer, J.M. Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Inflammatory Signaling Increase the Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 in the Respiratory Tract. Dev. Cell 2020, 53, 514–529.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnihan, K.; Neves, L.; Anton, L.; Joyner, J.; Valdes, G.; Merrill, D. Enhanced expression of Ang-(1-7) during pregnancy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narang, K.; Enninga, E.A.L.; Gunaratne, M.D.; Ibirogba, E.R.; Trad, A.T.A.; Elrefaei, A.; Theiler, R.N.; Ruano, R.; Szymanski, L.M.; Chakraborty, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 During Pregnancy: A Multidisciplinary Review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 1750–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, C.; Li, X. The SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 expression of maternal-fetal interface and fetal organs by single-cell transcriptome study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardon, V.F.; Isnard, P.; Roux, N.; Leruez-Ville, M.; Molina, T.; Bessieres, B.; Ville, Y. Protein expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, a SARS-CoV -2-specific receptor, in fetal and placental tissues throughout gestation: New insight for perinatal counseling. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 57, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.; Yagil, Y.; Bursztyn, M.; Barkalifa, R.; Scharf, S.; Yagil, C. ACE2 expression and activity are enhanced during pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1953–R1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gengler, C.; Dubruc, E.; Favre, G.; Greub, G.; de Leval, L.; Baud, D. SARS-CoV-2 ACE-receptor detection in the placenta throughout pregnancy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 489–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pique-Regi, R.; Romero, R.; Tarca, A.L.; Luca, F.; Xu, Y.; Alazizi, A.; Leng, Y.; Hsu, C.-D.; Gomez-Lopez, N. Does the human placenta express the canonical cell entry mediators for SARS-CoV-2? eLife 2020, 9, e58716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, G.; Neves, L.; Anton, L.; Corthorn, J.; Chacón, C.; Germain, A.; Merrill, D.; Ferrario, C.; Sarao, R.; Penninger, J.; et al. Distribution of Angiotensin-(1-7) and ACE2 in Human Placentas of Normal and Pathological Pregnancies. Placenta 2006, 27, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyar, A.M.; Grechukhina, O.; Chen, A.; Popkhadze, S.; Grimshaw, A.; Tal, O.; Taylor, H.S.; Tal, R. Vertical transmission of coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 224, 35–53.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlow, A.G.; Li, J.Z.; Collier, A.Y.; Atyeo, C.; James, K.E.; Boatin, A.A.; Gray, K.J.; Bordt, E.A.; Shook, L.L.; Yonker, L.M.; et al. Assessment of Maternal and Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load, Transplacental Antibody Transfer, and Placental Pathology in Pregnancies During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3, e2030455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Run-Qian, L.; Hao-Ran, W.; Hao-Ran, C.; Ya-Bin, L.; Yang, G.; Fei, C. Potential influence of COVID-19/ACE2 on the female reproductive system. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 26, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.I.; Arancibia-Carcamo, C.V.; Auckland, K.; Baillie, J.K.; Barnes, E.; Beneke, T.; Bibi, S.; Brooks, T.; Carroll, M.; Crook, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RNA detected in blood products from patients with COVID-19 is not associated with infectious virus. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Definition and Categorization of the Timing of Mother-to-Child Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/WHO-2019-nCoV-mother-to-child-transmission-2021.1 (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Sharps, M.C.; Hayes, D.J.; Lee, S.; Zou, Z.; Brady, C.A.; Almoghrabi, Y.; Kerby, A.; Tamber, K.K.; Jones, C.J.; Waldorf, K.M.A.; et al. A structured review of placental morphology and histopathological lesions associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Placenta 2020, 101, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baergen, R.N.; Heller, D.S. Placental Pathology in Covid-19 Positive Mothers: Preliminary Findings. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2020, 23, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanes, E.D.; Mithal, L.B.; Otero, S.; Azad, H.; Miller, E.S.; Goldstein, J. Placental Pathology in COVID-19. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, M.; Debenham, L.; Kew, T.; Chatterjee, S.R.; Allotey, J.; Stallings, E.; Coomar, D.; Lee, S.I.; Qiu, X.; Yuan, M.; et al. Clinical manifestations, prevalence, risk factors, outcomes, transmission, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19 in pregnancy and postpartum: A living systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e041868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenizia, C.; Biasin, M.; Cetin, I.; Vergani, P.; Mileto, D.; Spinillo, A.; Gismondo, M.R.; Perotti, F.; Callegari, C.; Mancon, A.; et al. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 vertical transmission during pregnancy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorn, A.S.; Meijer, B.; Frampton, C.M.A.; Barclay, M.L.; De Boer, N.K.H. Systematic review with meta-analysis: SARS-CoV-2 stool testing and the potential for faecal-oral transmission. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carosso, A.; Cosma, S.; Borella, F.; Marozio, L.; Coscia, A.; Ghisetti, V.; Di Perri, G.; Benedetto, C. Pre-labor anorectal swab for SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 pregnant patients: Is it time to think about it? Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 249, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermesch, A.C.; Horve, P.; Edelman, A.; Dietz, L.; Constant, D.; Fretz, M.; Messer, W.B.; Martindale, R.; Wymelenberg, K.V.D. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Environmental Contamination and Childbirth. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 136, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschetti, R.; Vivanti, A.J.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Loi, B.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D. Synthesis and systematic review of reported neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, L.C.; Yang, H.; Dumont, S.; Lee, J.C.S.; Copel, J.A.; Danneels, L.; Wright, A.; Costa, F.D.S.; Leung, T.Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. ISUOG Interim Guidance on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during pregnancy and puerperium: Information for healthcare professionals—An update. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 55, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and Breastfeeding. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/maternal-or-infant-illnesses/covid-19-and-breastfeeding.html (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Centeno-Tablante, E.; Medina-Rivera, M.; Finkelstein, J.L.; Rayco-Solon, P.; Garcia-Casal, M.N.; Rogers, L.; Ghezzi-Kopel, K.; Ridwan, P.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Mehta, S. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 through breast milk and breastfeeding: A living systematic review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1484, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Breastfeeding and COVID-19: Scientific Brief, 23 June 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Demers-Mathieu, V.; Do, D.M.; Mathijssen, G.B.; Sela, D.A.; Seppo, A.; Järvinen, K.M.; Medo, E. Difference in levels of SARS-CoV-2 S1 and S2 subunits- and nucleocapsid protein-reactive SIgM/IgM, IgG and SIgA/IgA antibodies in human milk. J. Perinatol. 2020, 41, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legislative Portal. Available online: http://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocument/223812?fbclid=IwAR03roBO_iSyatI4H_FrBj_l6_4TChh_9-asAulZ8Z1tIXtwlMtFR5iDMSA (accessed on 6 July 2021).
- Chen, Y.; Peng, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y. Infants Born to Mothers with a New Coronavirus (COVID-19). Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, C.; Peng, S.; Zhang, L.; Chang, G.; Xia, S.; Zhou, W. Clinical analysis of 10 neonates born to mothers with 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, F.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, D.; Xu, D.; Gong, Q.; et al. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: A retrospective review of medical records. Lancet 2020, 395, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, C.; Fan, J.; Tang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Long, X. Antibodies in Infants Born to Mothers With COVID-19 Pneumonia. JAMA 2020, 323, 1848–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Tian, J.; He, S.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, J. Possible Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 From an Infected Mother to Her Newborn. JAMA 2020, 323, 1846–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamaniyan, M.; Ebadi, A.; Aghajanpoor, S.; Rahmani, Z.; Haghshenas, M.; Azizi, S. Preterm delivery, maternal death, and vertical transmission in a pregnant woman with COVID-19 infection. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 1759–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzamora, M.C.; Paredes, T.; Caceres, D.; Webb, C.; Valdez, L.M.; La Rosa, M. Severe COVID-19 during Pregnancy and Possible Vertical Transmission. Am. J. Perinatol. 2020, 37, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Gao, J.; Luo, X.; Feng, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D.; Chen, L. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Vertical Transmission in Neonates Born to Mothers with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 136, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanti, A.J.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Prevot, S.; Zupan, V.; Suffee, C.; Cao, J.D.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D. Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, C.M.; Fascina, L.P.; Annicchino, G.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Yoshida, R.D.A.M.; Zacharias, R.S.B. Vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant mother to the neonate detected by cord blood real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Pediatr. Res. 2020, 89, 1592–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchetti, F.; Bugatti, M.; Drera, E.; Tripodo, C.; Sartori, E.; Cancila, V.; Papaccio, M.; Castellani, R.; Casola, S.; Boniotti, M.B.; et al. SARS-CoV2 vertical transmission with adverse effects on the newborn revealed through integrated immunohistochemical, electron microscopy and molecular analyses of Placenta. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Gasparinho, G.; Sepúlveda, F.; Matos, T. Signs suggestive of congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection with intrauterine fetal death: A case report. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 256, 508–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdespino-Vázquez, M.Y.; Helguera-Repetto, C.A.; León-Juárez, M.; Villavicencio-Carrisoza, O.; Flores-Pliego, A.; Moreno-Verduzco, E.R.; Díaz-Pérez, D.L.; Villegas-Mota, I.; Carrasco-Ramírez, E.; López-Martínez, I.E.; et al. Fetal and placental infection with SARS-CoV-2 in early pregnancy. J. Med Virol. 2021, 93, 4480–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, D.A.; Underwood, M.A.; Hedriana, H.; Lakshminrusimha, S. Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: What is the Optimal Definition? Am. J. Perinatol. 2020, 37, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.P.; Khong, T.Y.; Tan, G.C. The Effects of COVID-19 on Placenta and Pregnancy: What Do We Know So Far? Diagnostics 2021, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.S.; Diambomba, Y.; Acharya, G.; Morris, S.K.; Bitnun, A. Classification system and case definition for SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnant women, fetuses, and neonates. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuzaki, H.; Miura, K.; Miura, S.; Yoshiura, K.-I.; Mapendano, C.K.; Nakayama, D.; Yoshimura, S.; Niikawa, N.; Ishimaru, T. Labor Increases Maternal DNA Contamination in Cord Blood. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1709–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Mohagheghi, P.; Beigi, B.; Zafaranloo, N.; Moshfegh, F.; Yazdani, A. Spectrum of neonatal COVID-19 in Iran: 19 infants with SARS-CoV-2 perinatal infections with varying test results, clinical findings and outcomes. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, C.A.; Brubaker, S.G.; Limaye, M.A.; Lighter, J.; Ratner, A.J.; Thomas, K.M.; Meyer, J.A.; Roman, A. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in placental and fetal membrane samples. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Greub, G.; Favre, G.; Gengler, C.; Jaton, K.; Dubruc, E.; Pomar, L. Second-Trimester Miscarriage in a Pregnant Woman With SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA 2020, 323, 2198–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, C.; James-Todd, T.; Stichling, S. SARS-CoV-2 in diabetic pregnancies: A systematic scoping review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Morris, E.; Goyder, C.; Kinton, J.; Perring, J.; Nunan, D.; Mahtani, K.; Buse, J.B.; Del Prato, S.; Ji, L.; et al. Diabetes and COVID-19: Risks, Management, and Learnings from Other National Disasters. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbillon, L.; Fermaut, M.; Benbara, A.; Boujenah, J. COVID-19, Virchow’s triad and thromboembolic risk in obese pregnant women. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 593–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, G.; Bassareo, P.P.; Mehta, J.L. Letter in response to “ COVID -19, Virchow’s triad and thromboembolic risk in obese pregnant women”. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.-C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.; Garcia-Ruiz, I.; Maiz, N.; Rodo, C.; Garcia-Manau, P.; Serrano, B.; Lopez-Martinez, R.M.; Balcells, J.; Fernandez-Hidalgo, N.; Carreras, E.; et al. Pre-eclampsia-like syndrome induced by severe COVID-19: A prospective observational study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 127, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado-Arroyo, J.C.; Concepción-Zavaleta, M.J.; Zavaleta-Gutiérrez, F.E.; Concepción-Urteaga, L.A. Is COVID-19 a risk factor for severe preeclampsia? Hospital experience in a developing country. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 256, 502–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todros, T.; Masturzo, B.; De Francia, S. COVID-19 infection: ACE2, pregnancy and preeclampsia. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 253, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patberg, E.T.; Adams, T.; Rekawek, P.; Vahanian, S.A.; Akerman, M.; Hernandez, A.; Rapkiewicz, A.V.; Ragolia, L.; Sicuranza, G.; Chavez, M.R.; et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 infection and placental histopathology in women delivering at term. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 224, 382.e1–382.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Cardenas, I. The Immune System in Pregnancy: A Unique Complexity. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ander, S.E.; Diamond, M.S.; Coyne, C.B. Immune responses at the maternal-fetal interface. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaat6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, H.; Liu, C.; Qu, F.; Feng, X. Analysis of the susceptibility to COVID-19 in pregnancy and recommendations on potential drug screening. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Zarchi, M.; Neamatzadeh, H.; Dastgheib, S.A.; Abbasi, H.; Mirjalili, S.R.; Behforouz, A.; Ferdosian, F.; Bahrami, R. Vertical Transmission of Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) from Infected Pregnant Mothers to Neonates: A Review. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2020, 39, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Racicot, K.; Kwon, J.-Y.; Aldo, P.; Silasi, M.; Mor, G. Understanding the Complexity of the Immune System during Pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014, 72, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; Macary, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.-C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.-R.; Cao, Q.-D.; Hong, Z.-S.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-D.; Jin, H.-J.; Tan, K.-S.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yan, Y. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak—An update on the status. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, Y. Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Tools. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, K.; Shang, K.; Wang, W.; et al. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients with Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, B.; Zheng, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z.; Xu, X.; Wei, H. Pathogenic T-cells and inflammatory monocytes incite inflammatory storms in severe COVID-19 patients. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Tanaka, T.; Inoue, H.; Ono, C.; Hashimoto, S.; Kioi, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Matsuura, H.; Matsubara, T.; Shimizu, K.; et al. IL-6 trans-signaling induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from vascular endothelial cells in cytokine release syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22351–22356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood 2020, 135, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappanavar, R.; Perlman, S. Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: Causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuwen, L.-A.; Geldhof, V.; Pasut, A.; Carmeliet, P. COVID-19: The vasculature unleashed. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, X.; Carmeliet, P. Hallmarks of Endothelial Cell Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudoran, C.; Tudoran, M.; Lazureanu, V.; Marinescu, A.; Pop, G.; Pescariu, A.; Enache, A.; Cut, T. Evidence of Pulmonary Hypertension after SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Subjects without Previous Significant Cardiovascular Pathology. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumache, R.; Daescu, E.; Ciocan, V.; Mureşan, C.; Talida, C.; Gavrilita, D.; Enache, A. Molecular Testing of SARS-CoV-2 Infection from Blood Samples in Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) and Elevated D-Dimer Levels. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudoran, M.; Tudoran, C.; Lazureanu, V.; Marinescu, A.; Pop, G.; Pescariu, A.; Enache, A.; Cut, T. Alterations of Left Ventricular Function Persisting during Post-Acute COVID-19 in Subjects without Previously Diagnosed Cardiovascular Pathology. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudoran, M.; Tudoran, C.; Vlad, M.; Balas, M.; Abu Awwad, A.; Pop, G.N. Impact of Therapy with L-Thyroxine on the Evolution of Arterial and Aortic Stiffness in Female Patients with Overt and Subclinical Hypothyroidism. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.X.; Hsieh, B.; Xiong, Z.; Halsey, K.; Choi, J.W.; Tran, T.M.L.; Pan, I.; Shi, L.-B.; Wang, D.-C.; Mei, J.; et al. Performance of Radiologists in Differentiating COVID-19 from Non-COVID-19 Viral Pneumonia at Chest CT. Radiology 2020, 296, E46–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harcourt, J.; Tamin, A.; Lu, X.; Kamili, S.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Murray, J.; Queen, K.; Tao, Y.; Paden, C.R.; Zhang, J.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 from Patient with Coronavirus Disease, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Wei, Y.; Yue, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhang, S.; Cao, T.; Yang, C.; Li, M.; et al. Histopathologic Changes and SARS-CoV-2 Immunostaining in the Lung of a Patient With COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, D.; Guo, M.; Jiang, A.; Guo, D.; Hu, W.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; et al. Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falasca, L.; Nardacci, R.; Colombo, D.; Lalle, E.; Di Caro, A.; Nicastri, E.; Antinori, A.; Petrosillo, N.; Marchioni, L.; Biava, G.; et al. Postmortem Findings in Italian Patients With COVID-19: A Descriptive Full Autopsy Study of Cases with and Without Comorbidities. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Human kidney is a target for novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney impairment is associated with in-hospital death of COVID-19 patients. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, G.; Zheng, K.; Yan, Q.-Q.; Rios, R.S.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Van Poucke, S.; Liu, W.-Y.; Zheng, M.-H. COVID-19 and Liver Dysfunction: Current Insights and Emergent Therapeutic Strategies. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ernst, L.M. Maternal vascular malperfusion of the placental bed. APMIS 2018, 126, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stonoga, E.T.S.; Lanzoni, L.D.A.; Rebutini, P.Z.; de Oliveira, A.L.P.; Chiste, J.A.; Fugaça, C.A.; Prá, D.M.M.; Percicote, A.P.; Rossoni, A.; Nogueira, M.B.; et al. Intrauterine Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, P.S.; da Cunha, A.J.L.A.; Chimelli, L.; Avvad-Portari, E.; Andreiuolo, F.D.M.; de Oliveira-Szejnfeld, P.S.; Mendes, M.A.; Gomes, I.C.; Souza, L.R.Q.; Guimarães, M.Z.; et al. Case Report: SARS-CoV-2 Mother-to-Child Transmission and Fetal Death Associated with Severe Placental Thromboembolism. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, E.K.; Zambrano, L.D.; Anderson, K.N.; Marder, E.P.; Raz, K.M.; Felix, S.E.B.; Tie, Y.; Fullerton, K.E. Coronavirus Disease 2019 Case Surveillance—United States, January 22–May 30, 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götzinger, F.; Santiago-García, B.; Noguera-Julián, A.; Lanaspa, M.; Lancella, L.; Carducci, F.I.C.; Gabrovska, N.; Velizarova, S.; Prunk, P.; Osterman, V.; et al. COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: A multinational, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixler, D.; Miller, A.D.; Mattison, C.P.; Taylor, B.; Komatsu, K.; Pompa, X.P.; Moon, S.; Karmarkar, E.; Liu, C.Y.; Openshaw, J.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2–Associated Deaths Among Persons Aged <21 Years—United States, February 12–July 31, 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguoro, I.; Pilotto, C.; Bonanni, M.; Ferrari, M.E.; Pusiol, A.; Nocerino, A.; Vidal, E.; Cogo, P. SARS-COV-2 infection in children and newborns: A systematic review. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 179, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, P.; Johnson, C.L.; Halabi, K.C.; Ahn, D.; Sen, A.I.; Fischer, A.; Banker, S.L.; Giordano, M.; Manice, C.S.; Diamond, R.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Disease Severity in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Children’s Hospital in New York City, New York. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e202430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAN Archive–00432|Health Alert Network (HAN). Available online: https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2020/han00432.asp (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Adolescents with COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-and-adolescents-with-covid-19 (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Levin, M. Childhood Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome—A New Challenge in the Pandemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Caldini, E.G.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Kanamura, C.T.; Monteiro, R.A.D.A.; Ferranti, J.F.; Ventura, A.M.C.; Regalio, F.A.; Fiorenzano, D.M.; Gibelli, M.A.B.C.; et al. An autopsy study of the spectrum of severe COVID-19 in children: From SARS to different phenotypes of MIS-C. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 35, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolhnikoff, M.; Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Monteiro, R.; Da Silva, L.F.F.; De Oliveira, E.P.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Mauad, T.; Negri, E.M. Pathological evidence of pulmonary thrombotic phenomena in severe COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goshua, G.; Pine, A.B.; Meizlish, M.; Chang, C.-H.; Zhang, H.; Bahel, P.; Baluha, A.; Bar, N.; Bona, R.D.; Burns, A.J.; et al. Endotheliopathy in COVID-19-associated coagulopathy: Evidence from a single-centre, cross-sectional study. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e575–e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mannan, O.; Eyre, M.; Löbel, U.; Bamford, A.; Eltze, C.; Hameed, B.; Hemingway, C.; Hacohen, Y. Neurologic and Radiographic Findings Associated With COVID-19 Infection in Children. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolhnikoff, M.; Ferranti, J.F.; Monteiro, R.; Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Degaspare, N.V.; Delgado, A.F.; Fiorita, C.M.; Leal, G.N.; Rodrigues, R.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 in cardiac tissue of a child with COVID-19-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonzogni, A.; Previtali, G.; Seghezzi, M.; Alessio, M.G.; Gianatti, A.; Licini, L.; Morotti, D.; Zerbi, P.; Carsana, L.; Rossi, R.; et al. Liver histopathology in severe COVID 19 respiratory failure is suggestive of vascular alterations. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, M.; Wan, C.; Yi, L.-X.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.-C.; Fogo, A.B.; Nie, X.; et al. Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Steps | Time | Temperature | Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Reverse transcription | 10 min | 55 °C | 1 |
| 2. Denaturation (Taq activation) | 2 min | 95 °C | 1 |
| 3. Denaturation | 10 s | 95 °C | 45 |
| 4. Annealing and extension | 60 s | 60 °C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enache, A.; Ciocan, V.; Muresan, C.O.; Cut, T.G.; Novacescu, D.; Paul, C.; Andreescu, N.; Mihailescu, A.; Raica, M.; Dumache, R. Postmortem Documentation of SARS-CoV-2 in Utero and Postpartum Transmission, through Amniotic Fluid, Placental, and Pulmonary Tissue RT-PCR. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209505
Enache A, Ciocan V, Muresan CO, Cut TG, Novacescu D, Paul C, Andreescu N, Mihailescu A, Raica M, Dumache R. Postmortem Documentation of SARS-CoV-2 in Utero and Postpartum Transmission, through Amniotic Fluid, Placental, and Pulmonary Tissue RT-PCR. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(20):9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209505
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnache, Alexandra, Veronica Ciocan, Camelia Oana Muresan, Talida Georgiana Cut, Dorin Novacescu, Corina Paul, Nicoleta Andreescu, Alexandra Mihailescu, Marius Raica, and Raluca Dumache. 2021. "Postmortem Documentation of SARS-CoV-2 in Utero and Postpartum Transmission, through Amniotic Fluid, Placental, and Pulmonary Tissue RT-PCR" Applied Sciences 11, no. 20: 9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209505
APA StyleEnache, A., Ciocan, V., Muresan, C. O., Cut, T. G., Novacescu, D., Paul, C., Andreescu, N., Mihailescu, A., Raica, M., & Dumache, R. (2021). Postmortem Documentation of SARS-CoV-2 in Utero and Postpartum Transmission, through Amniotic Fluid, Placental, and Pulmonary Tissue RT-PCR. Applied Sciences, 11(20), 9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209505









