Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Calculations of Complex DNA Damage for Incidents of Environmental Ionizing Radiation Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monte Carlo (MC) Codes: MCNP and MCDS
2.2. MCNP Setting for the Simulations of Our Study
2.3. MCDS-Based Estimates of DNA Damage
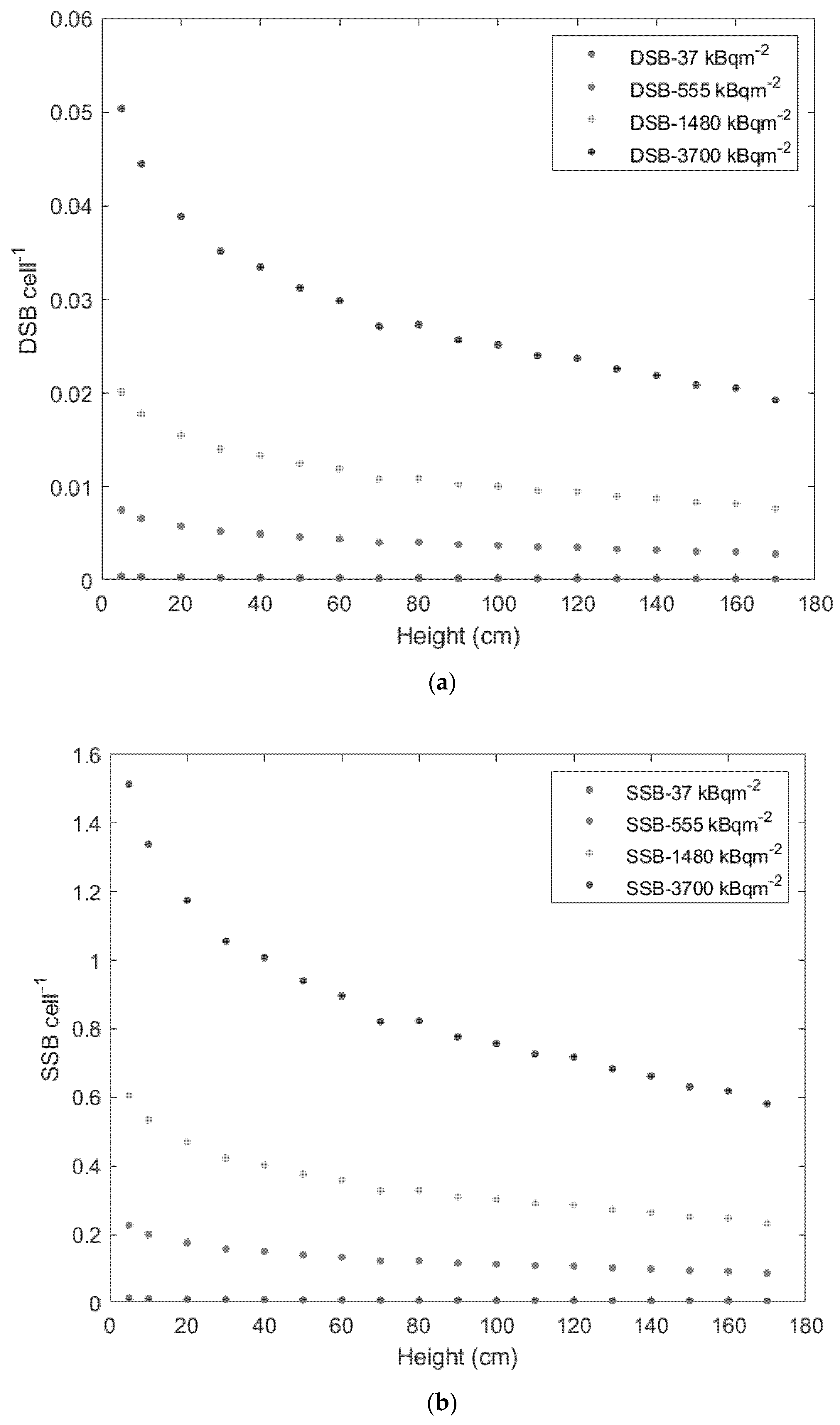
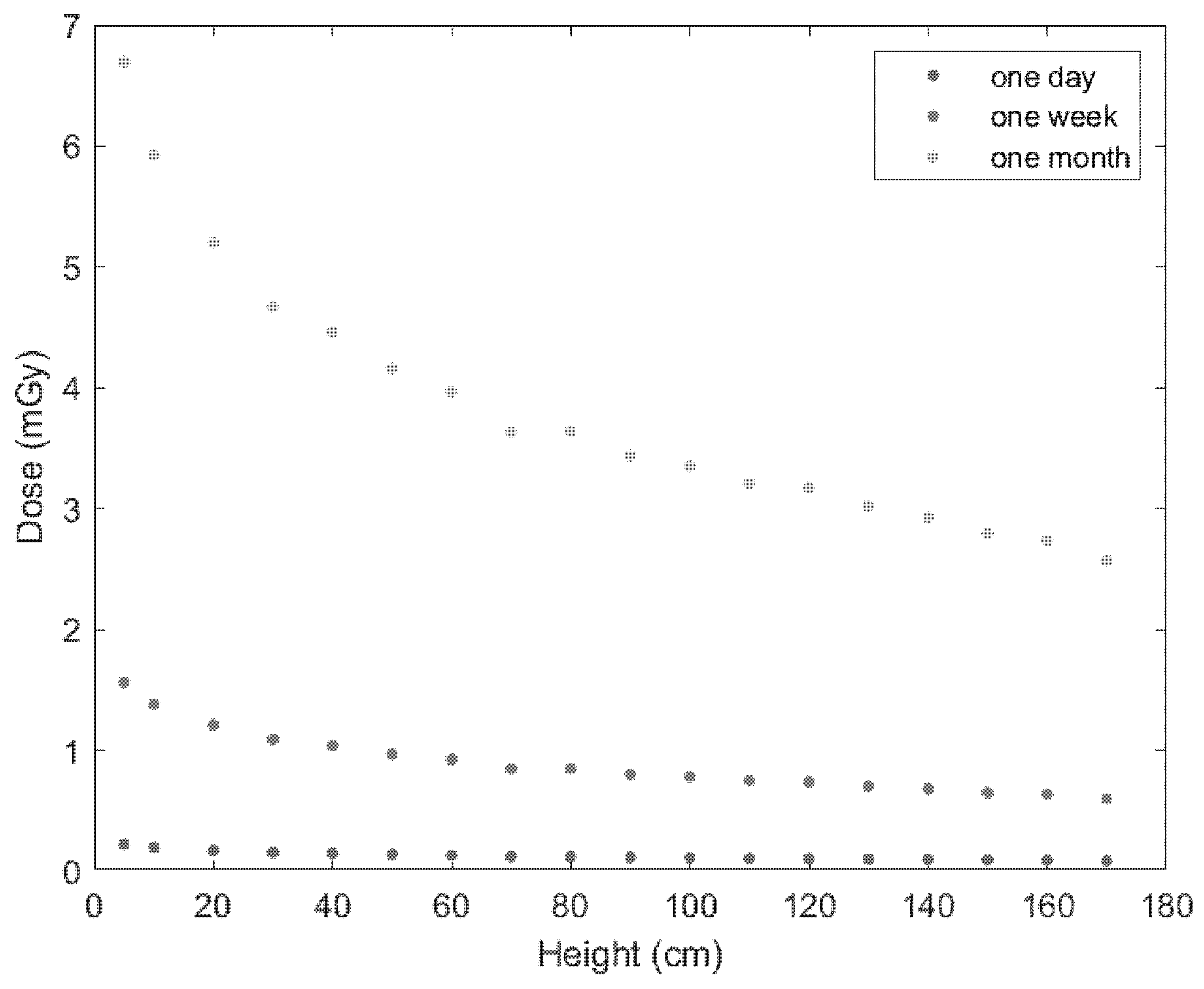
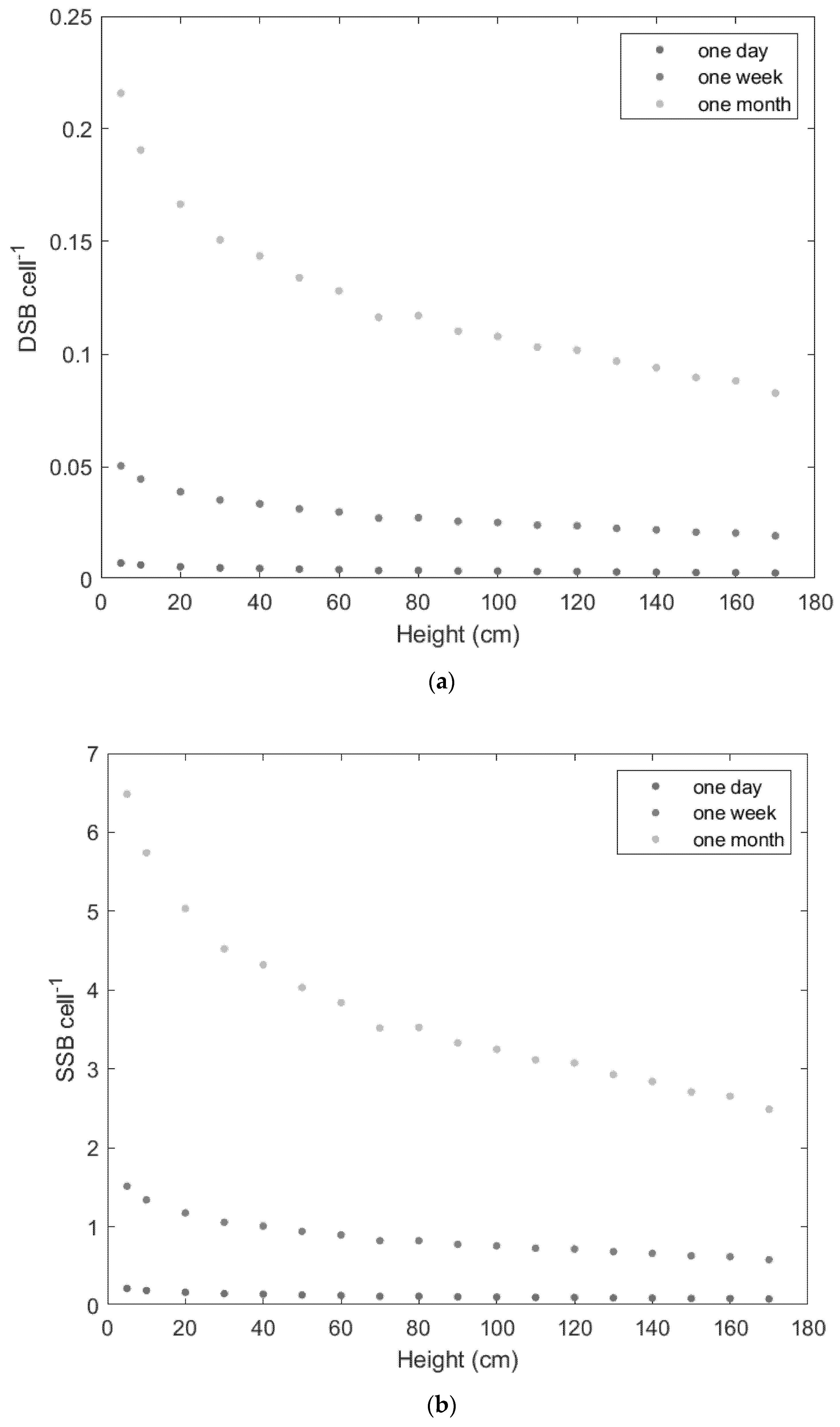
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balonov, M. The Chernobyl accident as a source of new radiological knowledge: Implications for Fukushima rehabilitation and research programmes. J. Radiol. Prot. 2013, 33, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, G.; Brandl, A.; Johnson, T.E. Comparison of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear accidents: A review of the environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) 2008 Report; United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume II. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.S.; Evangeliou, N.; Mousseau, T.A.; Wu, J.; Ramli, A.T. An overview of current knowledge concerning the health and environmental consequences of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladygienė, R.; Orentienė, A.; Žukauskienė, L. Investigation into 137Cs found in the soil profile within Vilnius region and estimation of inhabitants exposed to 137Cs transfered through the food chain. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2012, 20, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salbu, B.; Lind, O.C.; Skipperud, L. Radionuclide speciation and its relevance in environmental impact assessments. J. Environ. Radioact. 2004, 74, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, P.A. Radiological Terrorism. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2005, 11, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.G.; Roed, J.; Fogh, C.L. Weathering of radiocaesium contamination on urban streets, walls and roofs. J. Environ. Radioact. 2002, 62, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodouleas, J.P.; Forrest, R.D.; Ainsley, C.G.; Tochner, Z.; Hahn, S.M.; Glatstein, E. Short-term and long-term health risks of nuclear-power-plant accidents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. INES: The International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale User’s Manual; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kashparov, V.A.; Lundin, S.M.; Zvarych, S.I.; Yoshchenko, V.I.; Levchuk, S.E.; Khomutinin, Y.V.; Maloshtan, I.M.; Protsak, V.P. Territory contamination with the radionuclides representing the fuel component of Chernobyl fallout. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 317, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publications Office of the EU. Atlas of Caesium Deposition on Europe after the Chernobyl Accident. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/el/publication-detail/-/publication/110b15f7-4df8-49a0-856f-be8f681ae9fd (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- Balonov, M.I. On protecting the inexperienced reader from Chernobyl myths. J. Radiol. Prot. 2012, 32, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, L.A.; Balonov, M.I.; Buldakov, L.A. Radiocontamination patterns and possible health consequences of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power station. J. Radiol. Prot. 1990, 10, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarkrog, A. Past and recent trends in radioecology. Environ. Int. 1994, 20, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroumova, E.; Rozhko, A.; Hatch, M.; Furukawa, K.; Polyanskaya, O.; McConnell, R.J.; Nadyrov, E.; Petrenko, S.; Romanov, G.; Yauseyenka, V.; et al. Measures of thyroid function among Belarusian children and adolescents exposed to iodine-131 from the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Il’in, L.A. The Chernobyl Experience in the Context of Contemporary Radiation Protection Problems; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 1988; pp. 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Braverman, E.R.; Blum, K.; Loeffke, B.; Baker, R.; Kreuk, F.; Yang, S.P.; Hurley, J.R. Managing terrorism or accidental nuclear errors, preparing for iodine-131 emergencies: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4158–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Kavasi, N.; Sorimachi, A.; Arae, H.; Tokonami, S.; Mietelski, J.W.; Łokas, E.; Yoshida, S. Strontium-90 activity concentration in soil samples from the exclusion zone of the Fukushima daiichi nuclear power plant. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Atomic Energy Agency, V. Chernobyl’s Legacy: Health, Environmental and Socio-Economic Impacts and Recommendations to the Governments of Belarus, the Russian Federation and Ukraine The Chernobyl Forum; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2005; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Chiaravalle, A.E.; Mangiacotti, M.; Marchesani, G.; Bortone, N.; Tomaiuolo, M.; Trotta, G. A ten-year survey of radiocontamination of edible Balkan mushrooms: Cs-137 activity levels and assessed dose to the population. Food Control 2018, 94, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Pugliese, M.; Quarto, M.; Adamo, P.; Loffredo, F.; De Cicco, F.; Roca, V. Thirty years after Chernobyl: Long-term determination of (137)Cs effective half-life in the lichen Stereocaulon vesuvianum. J. Environ. Radioact 2017, 172, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNSCEAR. Levels and Effects of Radiation Exposure Due to the Nuclear Accident after the 2011 Great East-Japan Earthquake and Tsunami; United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Taira, Y.; Hayashida, N.; Yamashita, S.; Kudo, T.; Matsuda, N.; Takahashi, J.; Gutevitc, A.; Kazlovsky, A.; Takamura, N. Environmental contamination and external radiation dose rates from radionuclides released from the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2012, 151, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarkov, M.D.; Zheltonozhsky, V.A.; Zheltonozhskaya, M.V.; Kulich, N.V.; Maksimenko, A.M.; Farfan, E.B.; Jannik, G.T.; Marra, J.C. Vertical migration of radionuclides in the vicinity of the chernobyl confinement shelter. Health Phys. 2011, 101, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. The Fukushima Daiichi Accident; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dohi, T.; Ohmura, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Sasaki, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Kanaizuka, S.; Nakama, S.; Iijima, K. Radiocaesium accumulation capacity of epiphytic lichens and adjacent barks collected at the perimeter boundary site of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Environmental Consequences of the Chernobyl Accident and their Remediation: Twenty Years of Experience; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- UNSCEAR. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation; United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Santivasi, W.L.; Xia, F. Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavragani, I.V.; Nikitaki, Z.; Kalospyros, S.A.; Georgakilas, A.G. Ionizing Radiation and Complex DNA Damage: From Prediction to Detection Challenges and Biological Significance. Cancers 2019, 11, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y. Monte Carlo simulation of ionizing radiation induced DNA strand breaks utilizing coarse grained high-order chromatin structures. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, L.J.; O’Neill, P.; Lomax, M.E. Delayed repair of radiation induced clustered DNA damage: Friend or foe? Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenenko, V.A.; Stewart, R.D. A fast Monte Carlo algorithm to simulate the spectrum of DNA damages formed by ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2004, 161, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzipapas, K.P.; Papadimitroulas, P.; Emfietzoglou, D.; Kalospyros, S.A.; Hada, M.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Kagadis, G.C. Ionizing Radiation and Complex DNA Damage: Quantifying the Radiobiological Damage Using Monte Carlo Simulations. Cancers 2020, 12, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikjoo, H.; Emfietzoglou, D.; Liamsuwan, T.; Taleei, R.; Liljequist, D.; Uehara, S. Radiation track, DNA damage and response—A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 116601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikjoo, H.; Uehara, S.; Emfietzoglou, D.; Cucinotta, F.A. Track-structure codes in radiation research. Radiat. Meas. 2006, 41, 1052–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, J.S.; Adam, K.J.; Booth, T.E.; Briesmeister, J.F.; Carter, L.L.; Cox, L.J.; Favorite, J.A.; Forster, R.A.; McKinney, G.W.; Prael, R.E. Present and future capabilities of MCNP. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2000, 53, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goorley, J.T. Initial MCNP6 Release Overview—MCNP6 Version 1.0; Los Alamos National Lab.(LANL): Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2013.
- Hsiao, Y.; Stewart, R.D. Monte Carlo simulation of DNA damage induction by X-rays and selected radioisotopes. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikjoo, H.; O’Neill, P.; Terrissol, M.; Goodhead, D.T. Modelling of radiation-induced DNA damage: The early physical and chemical event. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1994, 66, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikjoo, H.; O’Neill, P.; Goodhead, D.T.; Terrissol, M. Computational modelling of low-energy electron-induced DNA damage by early physical and chemical events. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1997, 71, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikjoo, H.; O’Neill, P.; Wilson, W.E.; Goodhead, D.T. Computational approach for determining the spectrum of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2001, 156, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikjoo, H.; Bolton, C.E.; Watanabe, R.; Terrissol, M.; O’Neill, P.; Goodhead, D.T. Modelling of DNA damage induced by energetic electrons (100 eV to 100 keV). Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2002, 99, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, W.; Jacob, P.; Bernhardt, P.; Paretzke, H.G.; Dingfelder, M. Simulation of DNA damage after proton irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2003, 159, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, W.; Dingfelder, M.; Jacob, P.; Paretzke, H.G. Calculated DNA double-strand break and fragmentation yields after irradiation with He ions. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (1993) 2005, 72, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenenko, V.A.; Stewart, R.D. Fast Monte Carlo simulation of DNA damage formed by electrons and light ions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkus, D.; Konstantinova, M. Modelling vertical migration of 137Cs in Lithuanian soils. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2008, 16, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vukašinović, I.; Todorović, D.; Životić, L.; Kaluđerović, L.; Đorđević, A. An analysis of naturally occurring radionuclides and 137Cs in the soils of urban areas using gamma-ray spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Saggar, S.; Gong, D.; Zhang, Q. Distribution of 137Cs and 60Co in plough layer of farmland: Evidenced from a lysimeter experiment using undisturbed soil columns. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabovskyy, V.; Dzendzelyuk, O.; Katerynchuk, I.; Furgala, Y. Monitoring of radionuclides contamination of soils in Shatsk National Natural Park (Volyn region, Ukraine) during 1994–2001. J. Environ. Radioact 2004, 72, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, D.-K.; Kim, B.-H.; Lim, K.-M.; Choi, Y.-H. Radiation exposure to Marine biota around the Fukushima Daiichi NPP. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2949–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, E.; Volford, P. Depth and Areal Distribution of Cs-137 in the Soil of a Small Water Catchment in the Sopron Mountains. Acta Silv. Lignaria Hung. 2014, 9, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Evangeliou, N.; Hamburger, T.; Talerko, N.; Zibtsev, S.; Bondar, Y.; Stohl, A.; Balkanski, Y.; Mousseau, T.A.; Møller, A.P. Reconstructing the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (CNPP) accident 30 years after. A unique database of air concentration and deposition measurements over Europe. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IAEA. Present and Future Environmental Impact of the Chernobyl Accident; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Zhang, J.; Na, Y.H.; Caracappa, P.F.; Xu, X.G. Modelling and Monte Carlo organ dose calculations for workers walking on ground contaminated with Cs-137 and Co-60 gamma sources. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2010, 141, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunzl, K.; Schimmack, W.; Zelles, L.; Albers, B.P. Spatial variability of the vertical migration of fallout 137Cs in the soil of a pasture, and consequences for long-term predictions. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2000, 39, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNSCEAR. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation; United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimova, N.V.; Marchenko, T.A.; Shoigu, S.K. Twenty Years of the Chernobyl Accident: Results and Problems in Eliminating Its Consequences in Russia 1986–2006 Russian National Report; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2006; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, I.; Grady, H. Quick-Start Guide to Low-Energy Photon/Electron Transport in MCNP6; Los Alamos National Lab.(LANL): Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2013.
- Delacroix, D.; Guerre, J.P.; Leblanc, P.; Hickman, C. Radionuclide and radiation protection data handbook 2nd edition (2002). Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2002, 98, 9–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlizov, A. MCNP-CP: A correlated particle radiation source extension of a general purpose monte carlo N-particle transport code. ACS Symp. Ser. 2006, 945, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, R.D.; Streitmatter, S.W.; Argento, D.C.; Kirkby, C.; Goorley, J.T.; Moffitt, G.; Jevremovic, T.; Sandison, G.A. Rapid MCNP simulation of DNA double strand break (DSB) relative biological effectiveness (RBE) for photons, neutrons, and light ions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 8249–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.D.; Yu, V.K.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Koumenis, C.; Park, J.H.; Carlson, D.J. Effects of radiation quality and oxygen on clustered DNA lesions and cell death. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Fujii, K.; Kajimoto, T.; Tanaka, K.; Stepanenko, V.; Kolyzhenkov, T.; Petukhov, A.; Akhmedova, U.; Bogacheva, V. Comparison of calculated beta- and gamma-ray doses after the Fukushima accident with data from single-grain luminescence retrospective dosimetry of quartz inclusions in a brick sample. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.F. DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: Identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1988, 35, 95–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, S.E.; Jackson, S.P. Dynamics of DNA damage response proteins at DNA breaks: A focus on protein modifications. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breckow, J. Linear-no-threshold is a radiation-protection standard rather than a mechanistic effect model. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2006, 44, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbrich, M.; Rief, N.; Kühne, M.; Heckmann, M.; Fleckenstein, J.; Rübe, C.; Uder, M. In vivo formation and repair of DNA double-strand breaks after computed tomography examinations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8984–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Doll, R.; Goodhead, D.T.; Hall, E.J.; Land, C.E.; Little, J.B.; Lubin, J.H.; Preston, D.L.; Preston, R.J.; Puskin, J.S.; et al. Cancer risks attributable to low doses of ionizing radiation: Assessing what we really know. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13761–13766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averbeck, D. Does scientific evidence support a change from the LNT model for low-dose radiation risk extrapolation? Health Phys. 2009, 97, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbeck, D. Non-targeted effects as a paradigm breaking evidence. Mutat. Res. 2010, 687, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A. Influence of Dose and Its Distribution in Time on Dose-Response Relationships for Low-LET Radiations; National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1981; Volume 39, p. 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, D.M.; Hanlon, A.L.; Hanks, G.E. Diabetes mellitus: A predictor for late radiation morbidity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 43, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauchinger, M. Quantification of low-level radiation exposure by conventional chromosome aberration analysis. Mutat. Res. 1995, 339, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.A. Biomarkers for human radiation exposure. J. Biomed. Sci. 2008, 15, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Lee, A.; Nussenzweig, M.; Nussenzweig, A. H2AX: The histone guardian of the genome. DNA Repair 2004, 3, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedelnikova, O.A.; Rogakou, E.P.; Panyutin, I.G.; Bonner, W.M. Quantitative detection of (125)IdU-induced DNA double-strand breaks with gamma-H2AX antibody. Radiat. Res. 2002, 158, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.; Salomaa, S.; Wright, E.; Hildebrandt, G.; Belyakov, O.V.; Prise, K.M.; Little, M.P. Non-targeted effects of ionising radiation--implications for low dose risk. Mutat. Res. 2013, 752, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothkamm, K.; Löbrich, M. Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low X-ray doses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipov, A.N.; Pustovalova, M.; Grekhova, A.; Eremin, P.; Vorobyova, N.; Pulin, A.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Roumiantsev, S.; Klokov, D.Y.; Eremin, I. Low doses of X-rays induce prolonged and ATM-independent persistence of γH2AX foci in human gingival mesenchymal stem cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27275–27287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Natarajan, A.T.; Obe, G.; van Zeeland, A.A.; Palitti, F.; Meijers, M.; Verdegaal-Immerzeel, E.A. Molecular mechanisms involved in the production of chromosomal aberrations. II. Utilization of Neurospora endonuclease for the study of aberration production by X-rays in G1 and G2 stages of the cell cycle. Mutat. Res. 1980, 69, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, Y.E.; Rowland, J.M.; Bove, K.E.; Monforte-Munoz, H.; Fagin, J.A. Distinct pattern of ret oncogene rearrangements in morphological variants of radiation-induced and sporadic thyroid papillary carcinomas in children. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 1690–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, N.; Lamartine, J.; Frouin, V.; Le Minter, P.; Petat, C.; Leplat, J.-J.; Libert, F.; Gidrol, X.; Martin, M.T. Low-Dose Exposure to γ Rays Induces Specific Gene Regulations in Normal Human Keratinocytes. Radiat. Res. 2005, 163, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Folkard, M.; Held, K.D.; Prise, K.M. Estrogen enhanced cell-cell signalling in breast cancer cells exposed to targeted irradiation. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, J.; Viaene, T.; Blondeel, P.; Roche, N.; Van den Broecke, R.; Thierens, H.; Vral, A. DNA double strand breaks induced by low dose mammography X-rays in breast tissue: A pilot study. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3394–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, J.; Baert, A.; Vandersickel, V.; Thierens, H.; Vral, A. Relative biological effectiveness of mammography X-rays at the level of DNA and chromosomes in lymphocytes. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2013, 89, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beels, L.; Bacher, K.; De Wolf, D.; Werbrouck, J.; Thierens, H. gamma-H2AX foci as a biomarker for patient X-ray exposure in pediatric cardiac catheterization: Are we underestimating radiation risks? Circulation 2009, 120, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beels, L.; Werbrouck, J.; Thierens, H. Dose response and repair kinetics of gamma-H2AX foci induced by in vitro irradiation of whole blood and T-lymphocytes with X- and gamma-radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groesser, T.; Cooper, B.; Rydberg, B. Lack of bystander effects from high-LET radiation for early cytogenetic end points. Radiat. Res. 2008, 170, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Prise, K.M.; Folkard, M.; Michael, B.D. A review of the bystander effect and its implications for low-dose exposure. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2003, 104, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, T.K.; Zhou, H.; Chai, Y.; Ponnaiya, B.; Ivanov, V.N. Radiation induced non-targeted response: Mechanism and potential clinical implications. Curr. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 4, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, N.; Kojima, S.J.D.-R. The Lowest Radiation Dose Having Molecular Changes in the Living Body. Dose Response 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halm, B.M.; Franke, A.A.; Lai, J.F.; Turner, H.C.; Brenner, D.J.; Zohrabian, V.M.; DiMauro, R. γ-H2AX foci are increased in lymphocytes in vivo in young children 1 h after very low-dose X-irradiation: A pilot study. Pediatr. Radiol. 2014, 44, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevoorde, C.; Franck, C.; Bacher, K.; Breysem, L.; Smet, M.H.; Ernst, C.; De Backer, A.; Van De Moortele, K.; Smeets, P.; Thierens, H. γ-H2AX foci as in vivo effect biomarker in children emphasize the importance to minimize X-ray doses in paediatric CT imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, S.C.; Olsen, J.H.; Doll, R.; Thakrar, B.; Brown, P.D.; Storm, H.H.; Barlow, L.; Langmark, F.; Teppo, L.; Tulinius, H. Trends in childhood leukaemia in the Nordic countries in relation to fallout from atmospheric nuclear weapons testing. BMJ 1992, 304, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhtarev, I.A.; Sobolev, B.G.; Kairo, I.A.; Tronko, N.D.; Bogdanova, T.I.; Oleinic, V.A.; Epshtein, E.V.; Beral, V. Thyroid cancer in the Ukraine. Nature 1995, 375, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, O.; Mitchell, G.C.; Limesand, K.H. Sensitivity of salivary glands to radiation: From animal models to therapies. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; World Health Organization. Evaluation of certain food contaminants: Sixty-fourth report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series 930; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 930, pp. 1–99. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. A Protocol for the Derivation of Environmental and Human Health Soil Quality Guidelines; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2006.
- Ministry for the Environment. Toxicological Intake Values for Priority Contaminants in Soil; Ministry for the Environment: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011.
- Noshchenko, A.G.; Bondar, O.Y.; Drozdova, V.D. Radiation-induced leukemia among children aged 0–5 years at the time of the Chernobyl accident. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridou, E.; Trichopoulos, D.; Dessypris, N.; Flytzani, V.; Haidas, S.; Kalmanti, M.; Koliouskas, D.; Kosmidis, H.; Piperopoulou, F.; Tzortzatou, F. Infant leukaemia after in utero exposure to radiation from Chernobyl. Nature 1996, 382, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, J.; Kaletsch, U.; Burkart, W.; Grosche, B. Infant leukaemia after the Chernobyl accident. Nature 1997, 387, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, E.P.; Tolochko, G.V.; Shuvaeva, L.P.; Ivanov, V.E.; Iaroshevich, R.F.; Becker, S.; Nekolla, E.; Kellerer, A.M. Infant leukemia in Belarus after the Chernobyl accident. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 1998, 37, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumniczky, K.; Impens, N.; Armengol, G.; Candéias, S.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Hornhardt, S.; Martin, O.A.; Rödel, F.; Schaue, D. Low dose ionizing radiation effects on the immune system. Environ. Int. 2021, 149, 106212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.H. Origin, Recognition, Signaling and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Mammalian Cells; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation: BEIR VII, Phase I; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [CrossRef]
- Asaithamby, A.; Chen, D.J. Cellular responses to DNA double-strand breaks after low-dose gamma-irradiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3912–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löbrich, M.; Rydberg, B.; Cooper, P.K. Repair of X-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in specific Not I restriction fragments in human fibroblasts: Joining of correct and incorrect ends. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 12050–12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, H.; Sugimachi, K. Carcinogenic Risk Factors. J. Jpn. Med. Assoc. 2001, 125, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkevich, A.N.; Martin, O.A.; Smith, A.J.; Redon, C.E.; Bonner, W.M.; Martin, R.F.; Lobachevsky, P.N. γH2AX foci as a measure of DNA damage: A computational approach to automatic analysis. Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.M.; Redon, C.E.; Dickey, J.S.; Nakamura, A.J.; Sedelnikova, O.A.; Solier, S.; Pommier, Y. GammaH2AX and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sex | BirthYear | Exp. Year | Organ | S. Activ. (kBq/m2) | Tot. Exp. Time (Days) | Exp. Rate | Dose (mGy) | Elcr | Risk Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 1970 | 1986 | Prostate | 3700 | 30 | chronic | 3.44 | 3.91 × 10−5 | H |
| F | 1926 | 1986 | Breast | 3700 | 30 | chronic | 3.02 | 2.15 × 10−5 | H |
| F | 1970 | 1986 | Breast | 3700 | 1 | acute | 0.1 | 0.58 × 10−5 | M |
| F | 1970 | 1986 | all organs | 3700 | 1 | acute | 0.1 | 2.4 × 10−5 | H |
| F | 1970 | 1986 | leukemia | 3700 | 1 | acute | 0.1 | 0.08 × 10−5 | L |
| M | 1936 | 1986 | pancreas | 3700 | 30 | chronic | 3.20 | 0.66 × 10−5 | M |
| F | 1970 | 1986 | ovaries | 37 | 7 | acute | 0.008 | 0.005 × 10−5 | L |
| F | 1956 | 1986 | brain | 555 | 7 | acute | 0.068 | 0.004 × 10−5 | L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalospyros, S.A.; Gika, V.; Nikitaki, Z.; Kalamara, A.; Kyriakou, I.; Emfietzoglou, D.; Kokkoris, M.; Georgakilas, A.G. Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Calculations of Complex DNA Damage for Incidents of Environmental Ionizing Radiation Exposure. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198985
Kalospyros SA, Gika V, Nikitaki Z, Kalamara A, Kyriakou I, Emfietzoglou D, Kokkoris M, Georgakilas AG. Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Calculations of Complex DNA Damage for Incidents of Environmental Ionizing Radiation Exposure. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(19):8985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198985
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalospyros, Spyridon A., Violeta Gika, Zacharenia Nikitaki, Antigoni Kalamara, Ioanna Kyriakou, Dimitris Emfietzoglou, Michael Kokkoris, and Alexandros G. Georgakilas. 2021. "Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Calculations of Complex DNA Damage for Incidents of Environmental Ionizing Radiation Exposure" Applied Sciences 11, no. 19: 8985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198985
APA StyleKalospyros, S. A., Gika, V., Nikitaki, Z., Kalamara, A., Kyriakou, I., Emfietzoglou, D., Kokkoris, M., & Georgakilas, A. G. (2021). Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Calculations of Complex DNA Damage for Incidents of Environmental Ionizing Radiation Exposure. Applied Sciences, 11(19), 8985. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198985