Synthesis and Application of the Magnetic Nanocomposite GO-Chm for the Extraction of Benzodiazepines from Surface Water Samples Prior to HPLC-PDA Analysis
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentaion and Chromatographic Conditions
2.3. Preparation of the Adsorbents
2.3.1. Synthesis of Magnetic Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Their Comparison as Adsorbents in the Extraction of the Two Benzodiazepines
2.3.2. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide-Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposite (GO-Chm)
2.3.3. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide-Magnetic Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Beads (GO-Chm@SA)
2.4. Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.5. Optimization of the Stir Bar Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Procedure
2.6. Validation of the Analytical Method
2.7. Application to Real Samples
3. Results
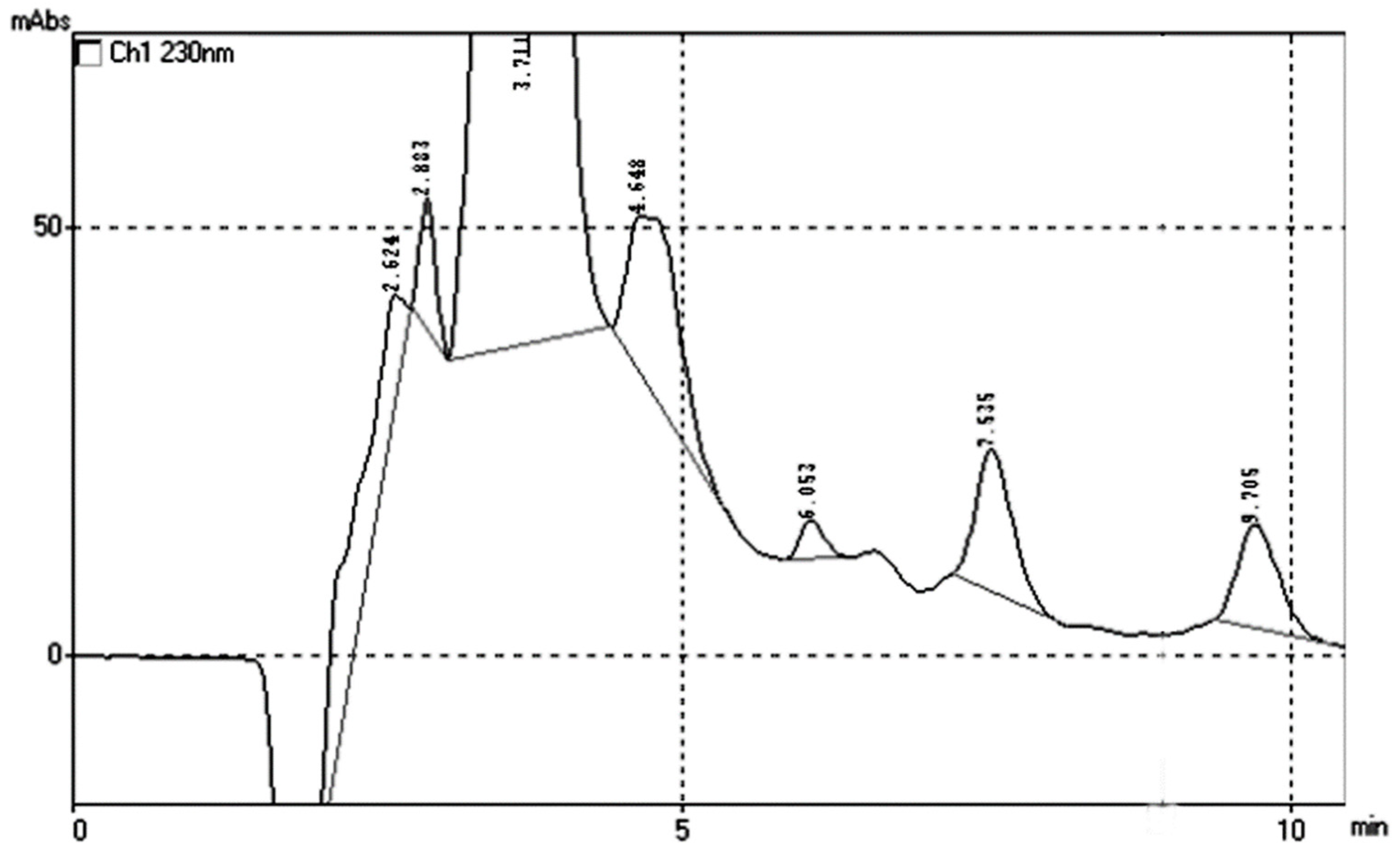
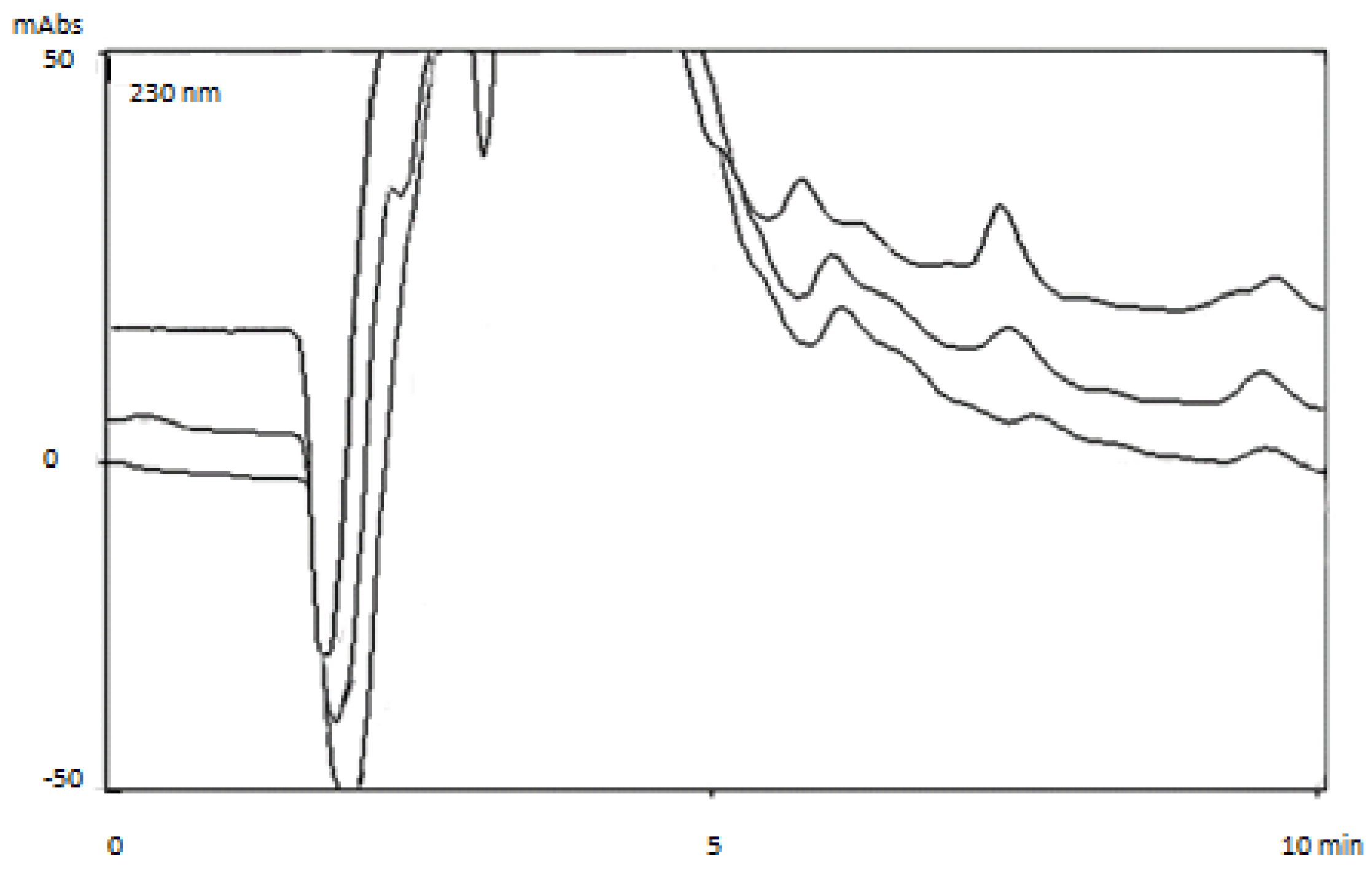
3.1. Chromatographic Separation
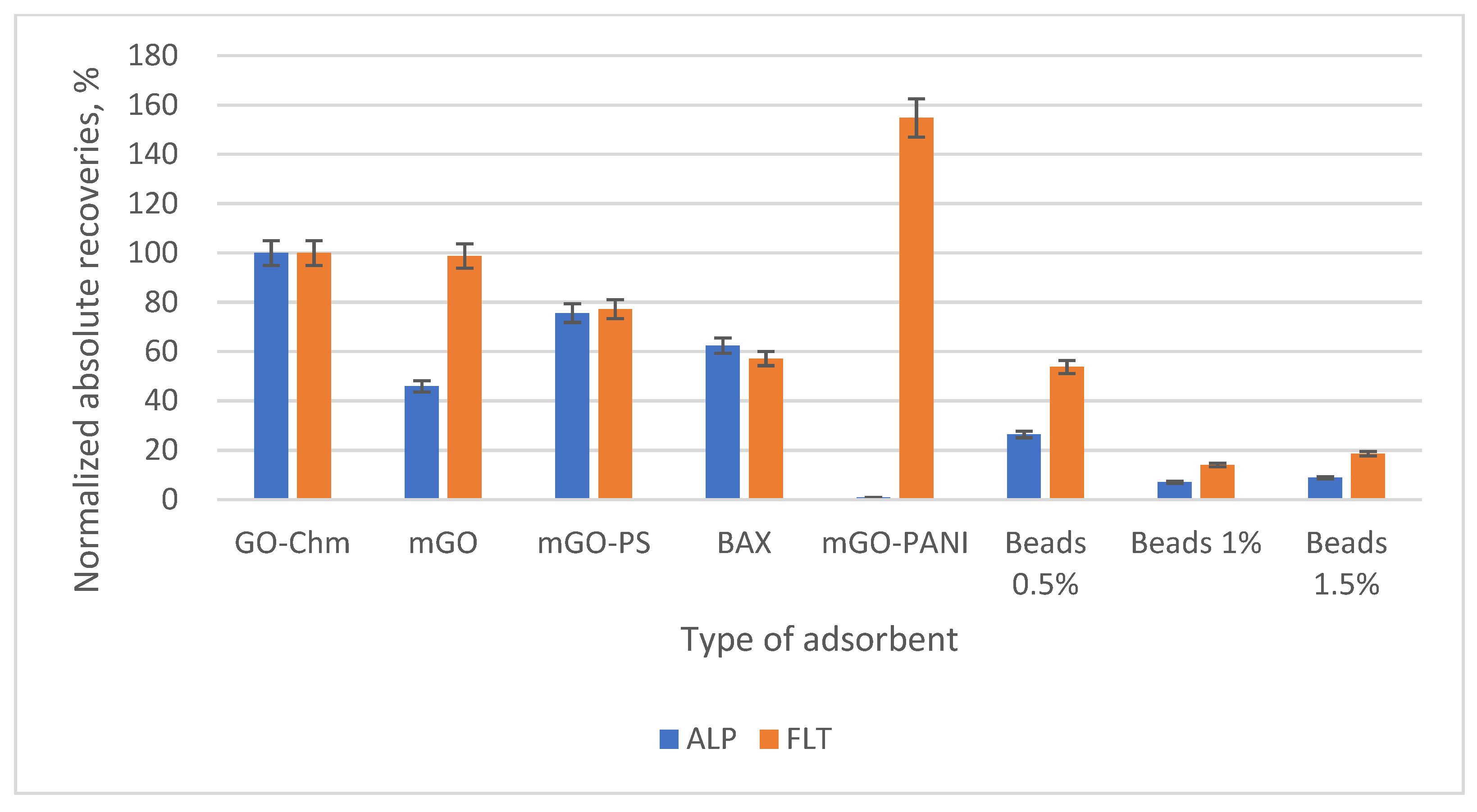
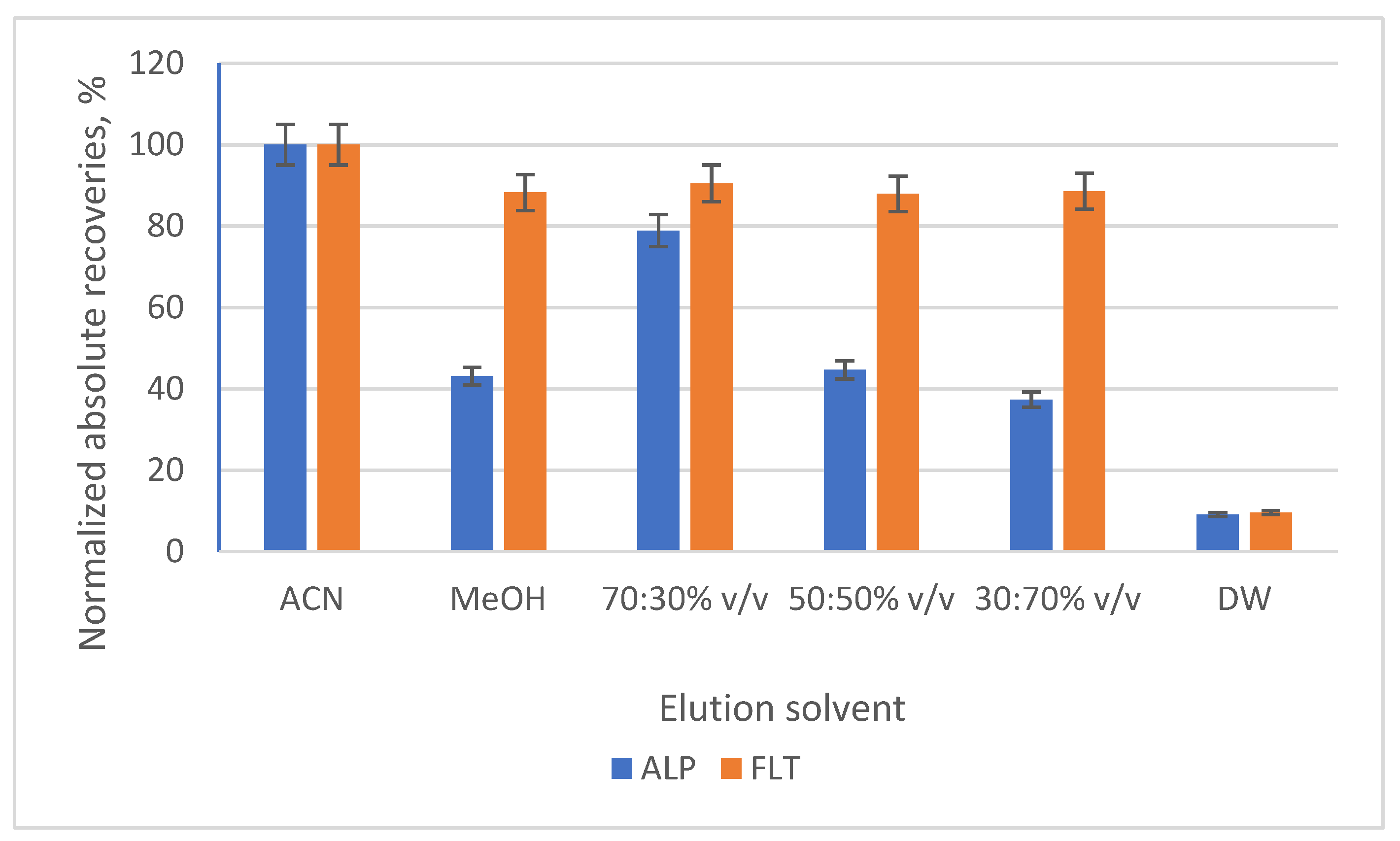
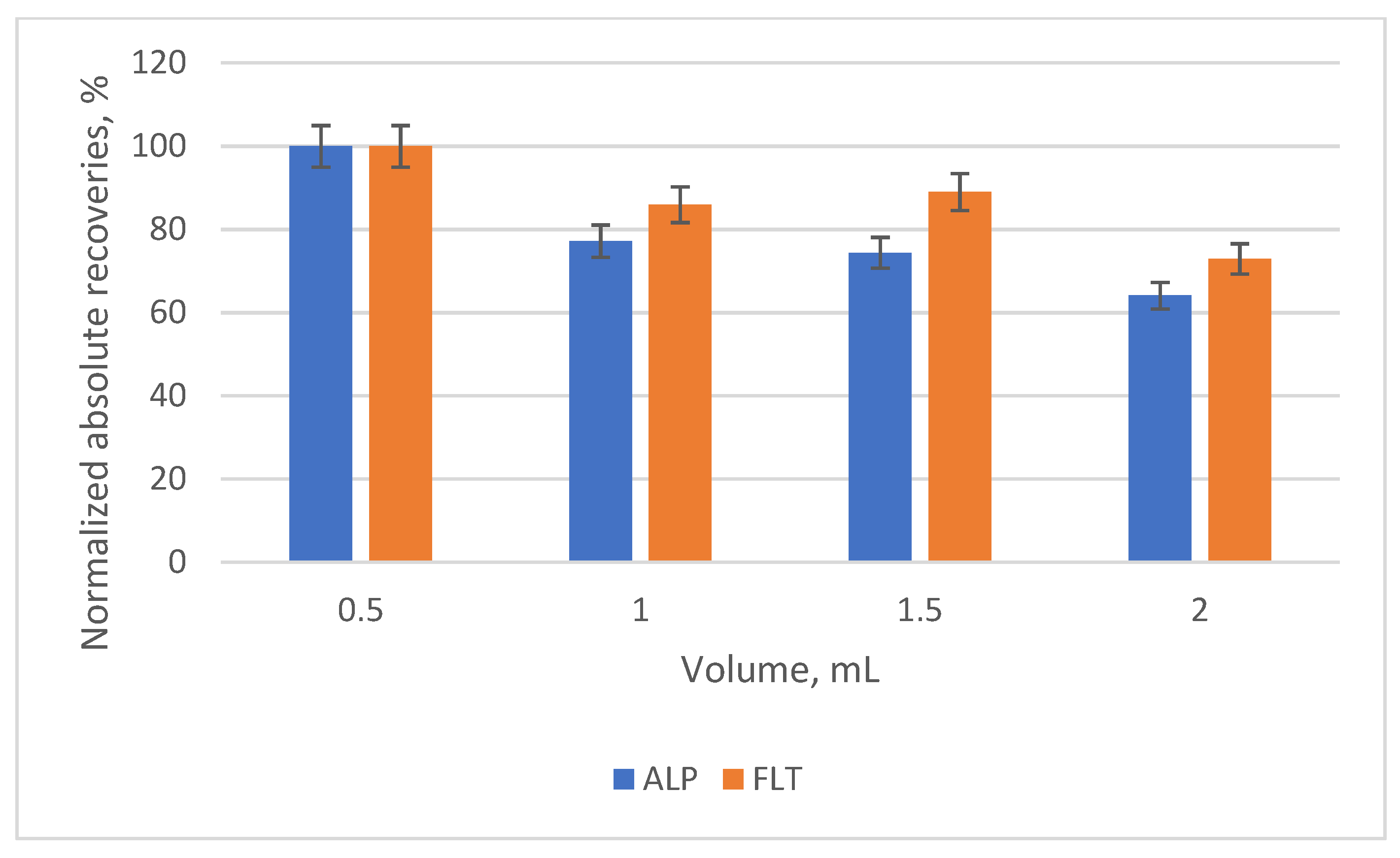
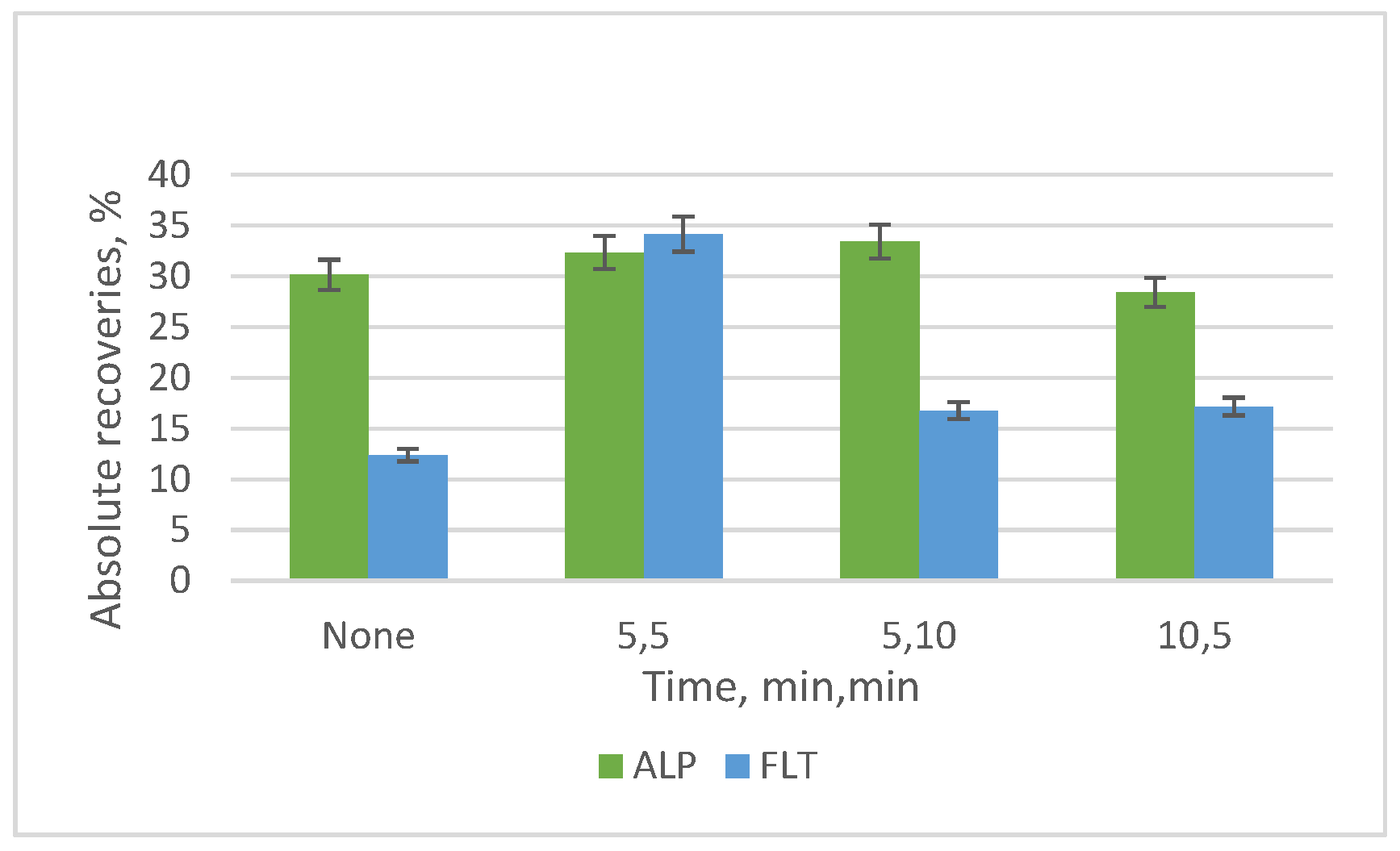
3.2. Optimization of the SB-MSPE Procedure
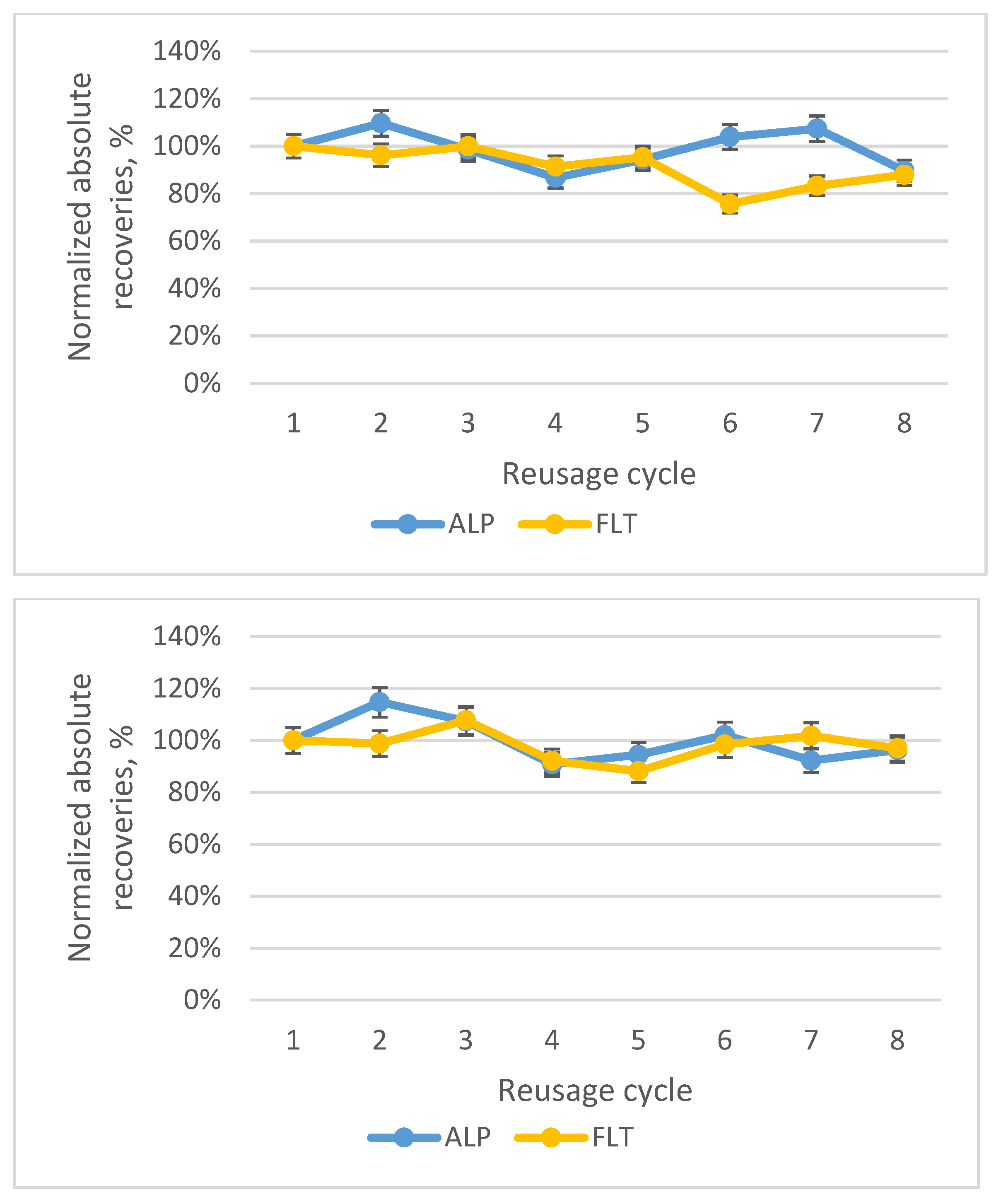
3.3. Optimal SB-MSPE Protocl
3.4. Validation of the Method
3.5. Application to Real Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sherma, J.; Zweig, G. History and introduction. Pap. Chromatogr. 1971, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluck, M. Medicolegal considerations. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1989, 141, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gláz, E.; Vecsei, P. Biological activity. Aldosterone 1971, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, T.; Maurer, H. Chapter 6 Sedatives and Hypnotics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 6, pp. 243–286. [Google Scholar]
- Drillia, P.; Stamatelatou, K.; Lyberatos, G. Fate and mobility of pharmaceuticals in solid matrices. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogiouri, N.P.; Tsalbouris, A.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Samanidou, V.F. Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted polymers using sol–gel matrix imprinting technology for the efficient solid-phase extraction of BPA from water. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Fontela, M.; Galceran, M.T.; Ventura, F. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and hormones through drinking water treatment. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, N.; Deliyanni, E.; Rosenberg, E.; Zachariadis, G. Ultrasound-assisted magnetic solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples with a magnetic polyaniline modified graphene oxide nanocomposite. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1645, 462104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosjek, T.; Perko, S.; Zupanc, M.; Hren, M.Z.; Dragičević, T.L.; Žigon, D.; Kompare, B.; Heath, E. Environmental occurrence, fate and transformation of benzodiazepines in water treatment. Water Res. 2012, 46, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastiras, O.-E.; Andreasidou, E.; Samanidou, V. Microextraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. Molecules 2020, 25, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alampanos, V.; Samanidou, V. Current trends in green sample preparation before liquid chromatographic bioanalysis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 31, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, N.; Plastiras, O.-E.; Deliyanni, E.; Zachariadis, G. Green bioanalytical applications of graphene oxide for the extraction of small organic molecules. Molecules 2021, 26, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastiras, O.-E.; Deliyanni, E.; Samanidou, V. Applications of graphene-based nanomaterials in environmental analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vállez-Gomis, V.; Grau, J.; Benedé, J.L.; Giokas, D.L.; Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A. Fundamentals and applications of stir bar sorptive dispersive microextraction: A tutorial review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1153, 338271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeeb, M.; Farahani, H. Graphene oxide/Fe3O4@polythionine nanocomposite as an efficient sorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of duloxetine in human plasma. Chem. Pap. 2017, 72, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Deliyanni, E.A. Functionalization of graphite oxide with magnetic chitosan for the preparation of a nanocomposite dye adsorbent. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Travlou, N.A.; Kalogirou, O.; Deliyanni, E.A. Magnetic graphene oxide: Effect of preparation route on reactive black 5 adsorption. Materials 2013, 6, 1360–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rekos, K.; Kampouraki, Z.-C.; Sarafidis, C.; Samanidou, V.; Deliyanni, E. Graphene oxide based magnetic nanocomposites with polymers as effective bisphenol–A nanoadsorbents. Materials 2019, 12, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippou, O.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Samanidou, V.F. Fabrication and evaluation of magnetic activated carbon as adsorbent for ultrasonic assisted magnetic solid phase dispersive extraction of bisphenol A from milk prior to high performance liquid chromatographic analysis with ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1479, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelgund, G.M.; Bliznyuk, V.N.; Oki, A. Photocatalytic activity and NIR laser response of polyaniline conjugated graphene nanocomposite prepared by a novel acid-less method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 187, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazaridis, N.; Charalambous, C. Sorptive removal of trivalent and hexavalent chromium from binary aqueous solutions by composite alginate–goethite beads. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4385–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.N.; Sultana, N.; Arayne, M.S.; Qayoom, A. Liquid chromatographic determination of alprazolam with ace inhibitors in bulk, respective pharmaceutical products and human serum. Sci. Int. (Lahore) 2016, 28, 3815. [Google Scholar]
- Pongampai, S.; Amornpitoksuk, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Rujiralai, T.; Suwanboon, S.; Leesakul, N. Detection of flunitrazepam through photocatalytic reaction of ZnO particles in coloured spirits by UV-Vis spectrophotometer. Sci. Asia 2011, 37, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.J.; Sánchez, M.I.; Muñoz, B.E.; Pardo, R. Persistence of alprazolam in river water according to forced and non-forced degradation assays: Adsorption to sediment and long-term degradation products. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racamonde, I.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodil, R.; Cela, R. Application of polypropylene tubes as single-use and low-cost sorptive extraction materials for the determination of benzodiazepines and zolpidem in water samples. Microchem. J. 2015, 119, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, R.; Ghetia, M.; White, J.M.; Gerber, C. Determination of prescribed and designer benzodiazepines and metabolites in influent wastewater. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 3637–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, C.N.; Pauluk, L.E.; Dos Anjos, V.E.; Lopes, M.C.; Quináia, S.P. New approach to the determination of contaminants of emerging concern in natural water: Study of alprazolam employing adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6171–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, E.; Mastroianni, N.; Postigo, C.; Barceló, D.; de Alda, M.L. A fully automated approach for the analysis of 37 psychoactive substances in raw wastewater based on on-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1576, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariño, I.; Castro, V.; Montes, R.; Rodil, R.; Lores, A.; Cela, R.; Quintana, J.B. Multi-residue determination of psychoactive pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs and related metabolites in wastewater by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1569, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




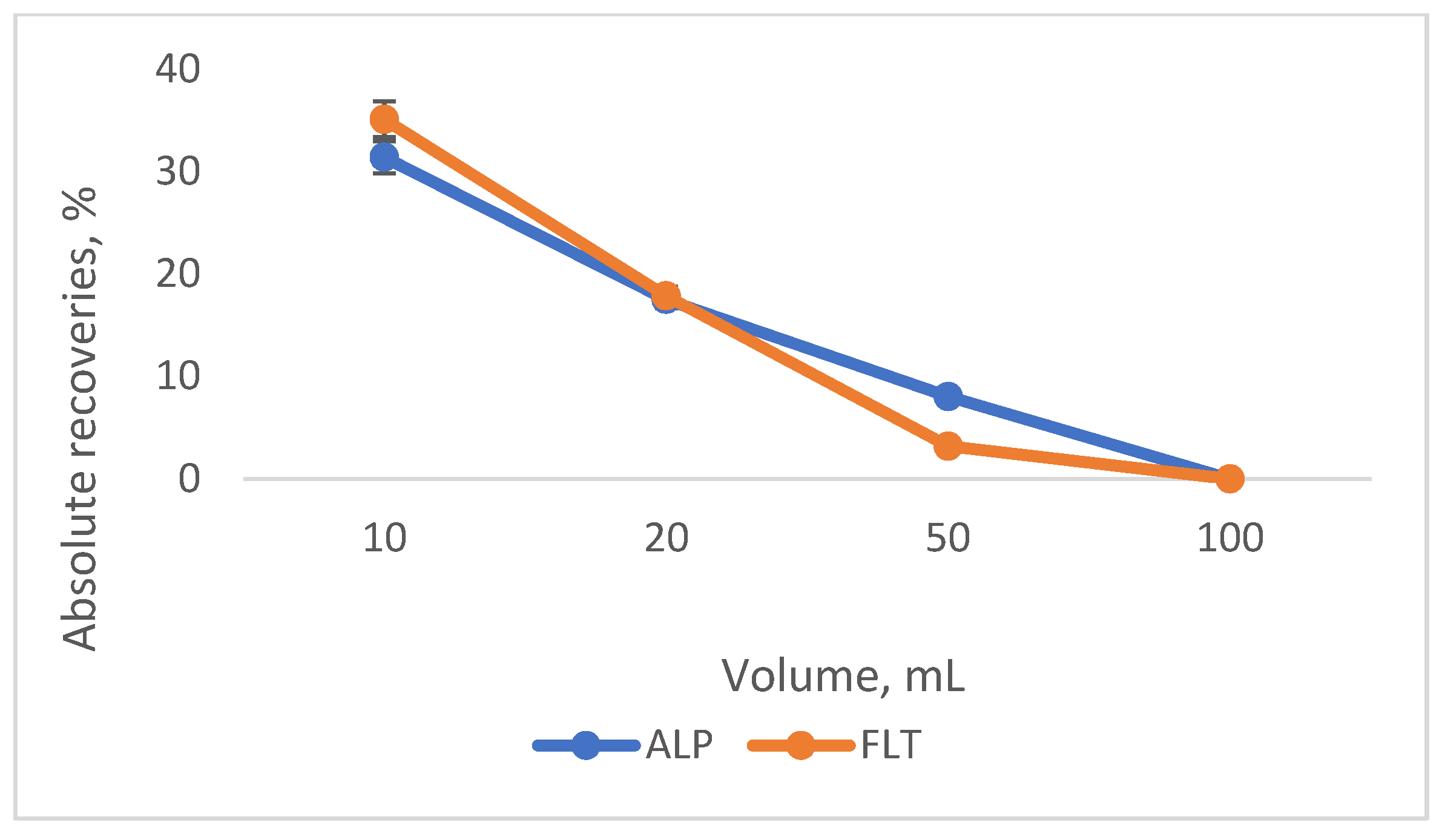
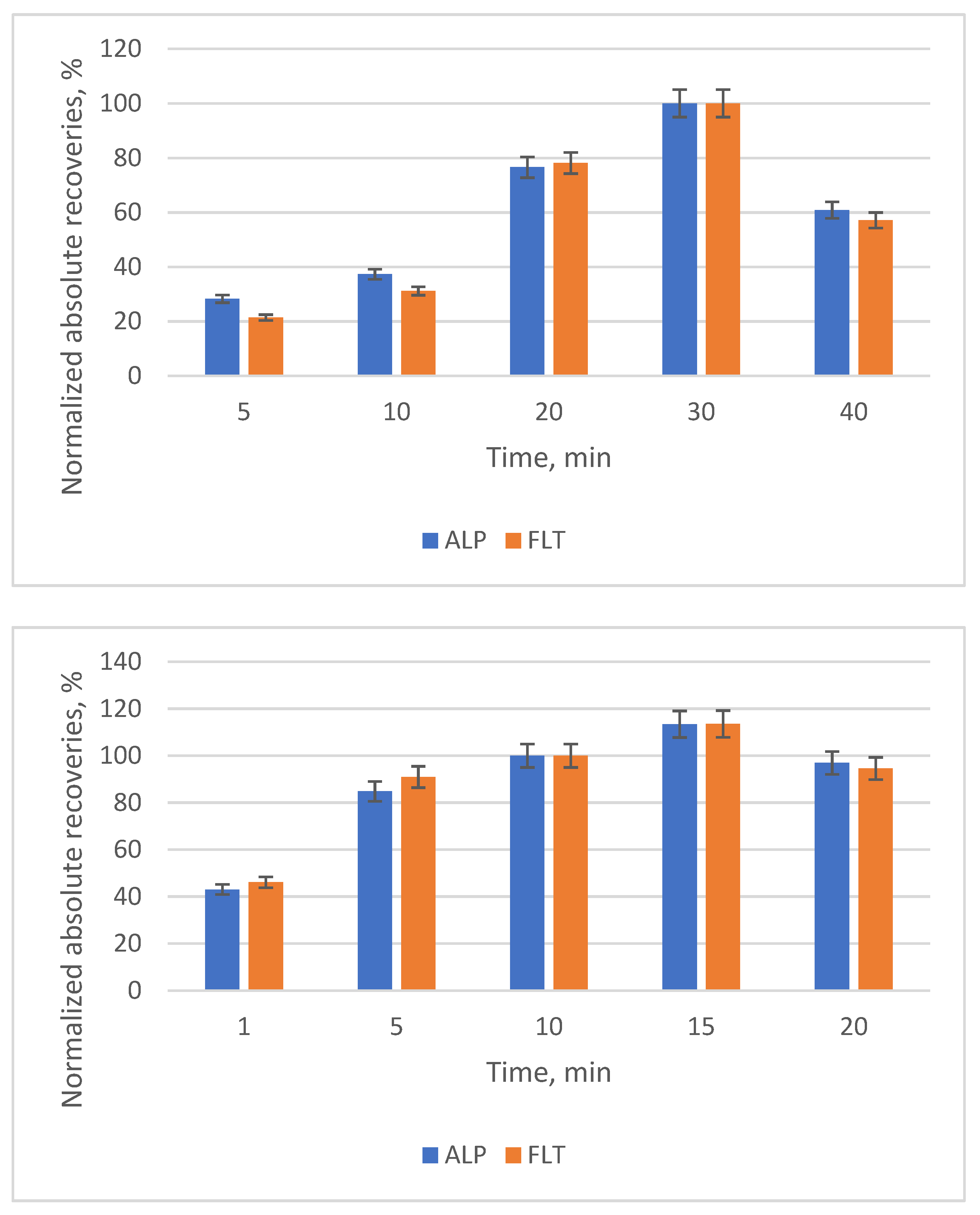

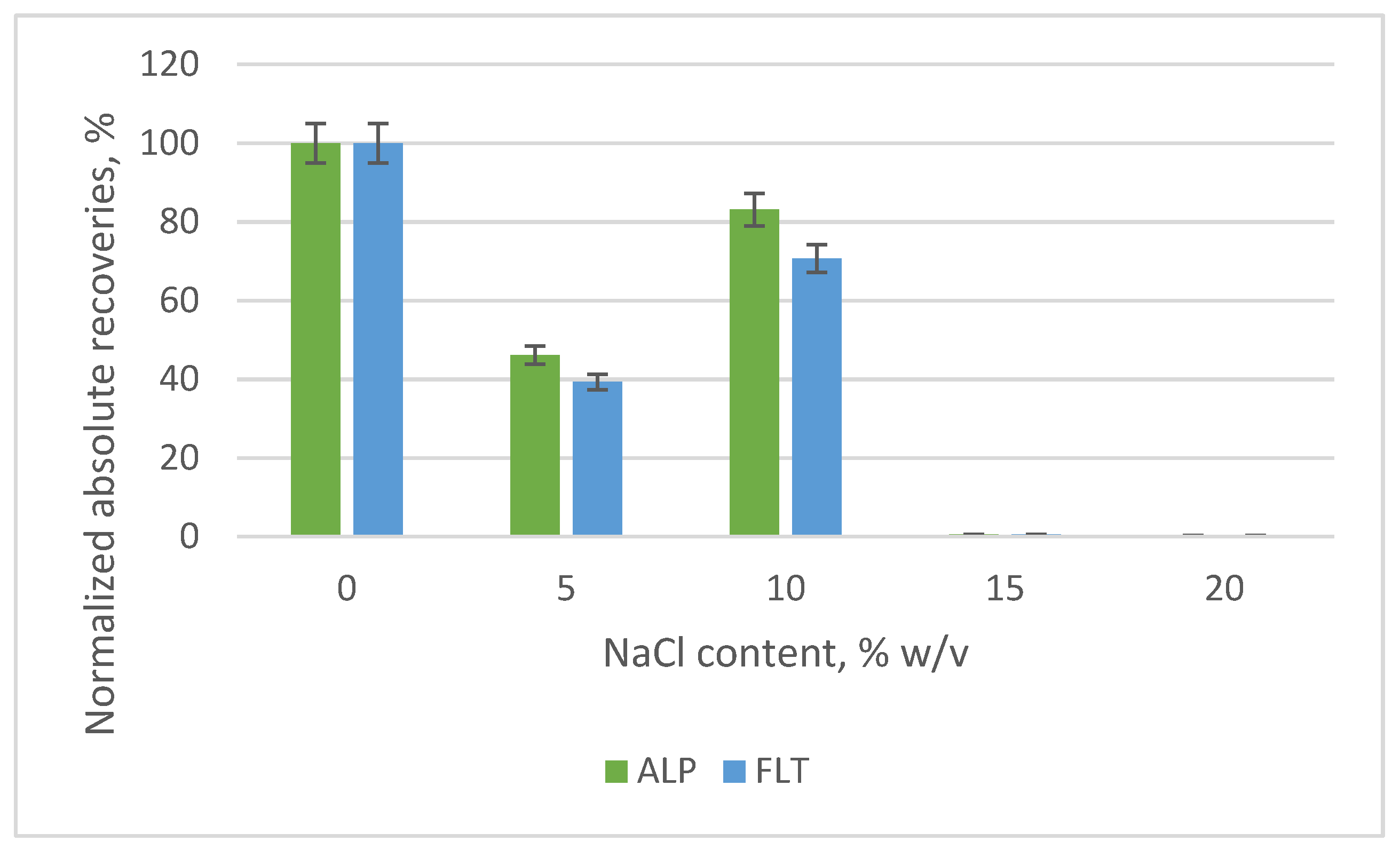
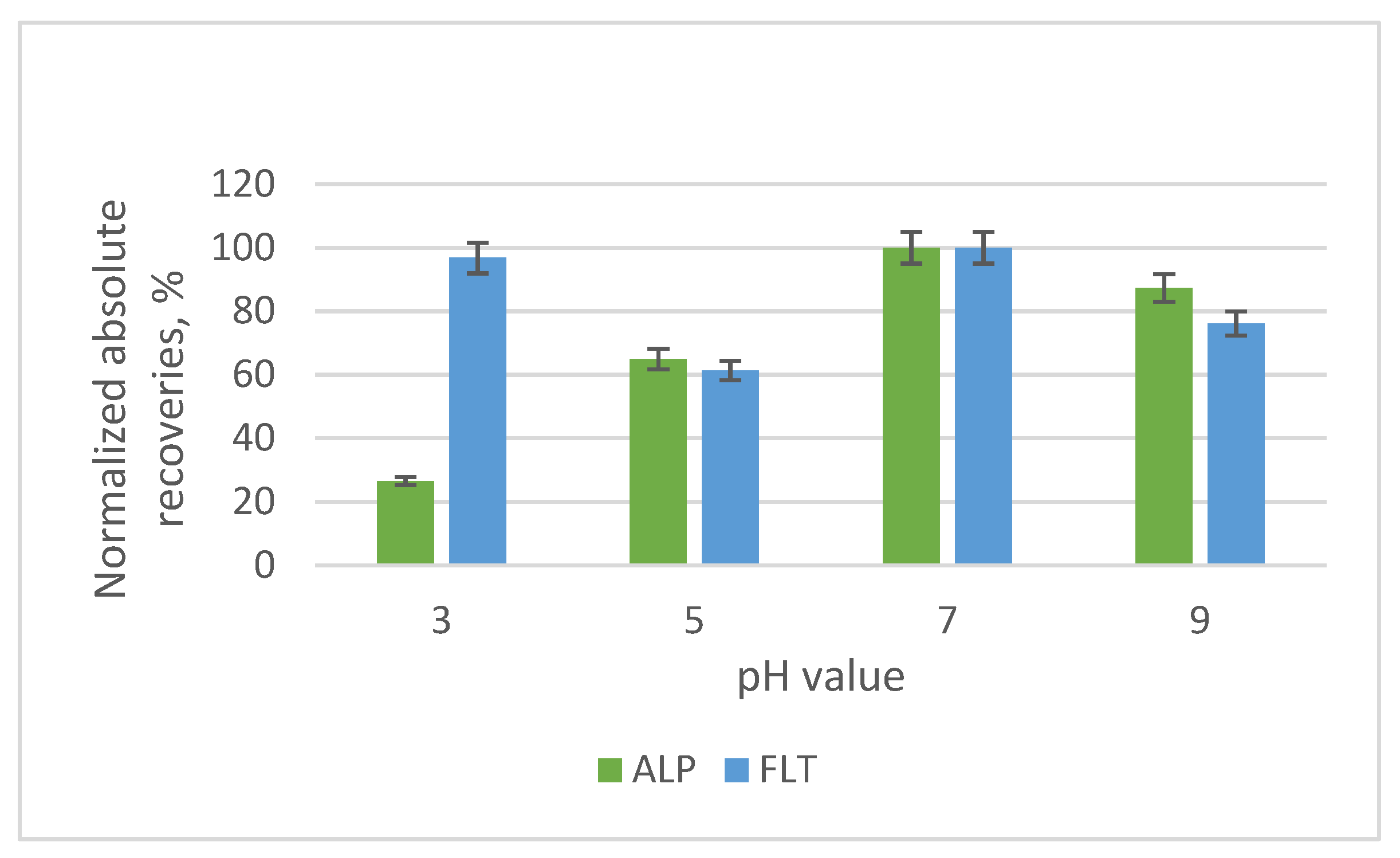
| Examined Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Elution Solvent | CH3CN (ACN) |
| Adsorbent Mass | 40 mg |
| Volume of Elution Solvent | 0.5 mL |
| Volume of Sample | 10 mL |
| Stirring Speed | 750 rpm |
| Addition of Salt | 0% w/v |
| pH | 7 |
| Activation Time with MeOH | 5 min |
| Activation Time with DW 1 | 5 min |
| Duration of Extraction | 30 min |
| Duration of Elution | 10 min |
| Total Duration | 50 min |
| Benzodiazepine | Regression Equation 1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Alprazolam (ALP) | Y = 3826.3 X + 5528 | 0.992 |
| Flunitrazepam (FLT) | Y = 3043.6 X + 4838.2 | 0.9999 |
| Precision and Accuracy | Spiked ng/mL | RSD% (ALP, FLT) | Rrel% (ALP, FLT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-day (n = 3) repeatability | 25 | 2.2, 2.2 | 102.1, 103.9 |
| 50 | 1.7, 3.9 | 103.8, 100.2 | |
| 100 | 5.9, 9.1 | 103.0, 102.0 | |
| Inter-day (n = 2 × 4) precision | 25 | 7.3, 11.9 | 98.0, 104.1 |
| 50 | 7.7, 10.3 | 103.7, 103.5 | |
| 100 | 9.4, 9.6 | 100.7, 100.8 |
| Spiked ng/mL | Sample | Found ALP, FLT | RSD% (ALP, FLT) | Rrel% (ALP, FLT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xaverage ± s | ||||
| 0 | RW 1 | N/D 1, N/D | - | - |
| RW 2 | N/D, N/D | - | - | |
| SW 1 | N/D, N/D | - | - | |
| SW 2 | N/D, N/D | - | - | |
| SW 3 | N/D, N/D | - | - | |
| 25 | RW 1 | 24.0 ± 1.4, 25.3 ± 1.4 | 5.8, 5.4 | 96.1, 101.0 |
| RW 2 | 24.7 ± 1.2, 26.0 ± 0.8 | 4.8, 2.9 | 98.9, 104.1 | |
| SW 1 | 24.2 ± 1.9, 26.0 ± 0.8 | 7.8, 6.2 | 96.6, 95.9 | |
| SW 2 | 25.8 ± 1.7, 26.9 ± 1.4 | 6.6, 5.4 | 103.1, 107.5 | |
| SW 3 | 23.4 ± 0.9, 28.2 ± 2.7 | 3.8, 9.5 | 93.6, 112.9 | |
| 50 | RW 1 | 47.2 ± 2.0, 48.5 ± 0.8 | 4.2, 1.6 | 94.3, 97.0 |
| RW 2 | 50.9 ± 2.0, 49.5 ± 2.4 | 4.0, 4.9 | 101.8, 98.9 | |
| SW 1 | 48.8 ± 2.7, 48.1 ± 2.0 | 5.6, 4.1 | 97.6, 96.3 | |
| SW 2 | 48.8 ± 3.4, 45.8 ± 0.5 | 7.0, 1.1 | 97.6, 91.7 | |
| SW 3 | 48.5 ± 1.5, 48.2 ±3.7 | 3.0, 7.7 | 97.0, 96.3 |
| Compounds | Sample Pretreatment Technique | Determination Technique | Time of Sample Pretreatment | Time of Determination | LOD (ng/L) | LOQ (ng/L) | Rrel% | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP | SPE | UPLC-MS/MS | ~40 min | 6.5 min | 20 | 50 | 97 | [24] |
| 17 BZs (ALP + FLT) | Single use PP Tubes | LC-MS/MS | ~14 h | 29 min | 1, 3 | 3, 10 | 87–117 | [25] |
| 22 BZs (ALP + FLT) | SPE | UPLC-MS/MS | N/R 1 | 20 min | 0.25, 2 | 1, 4 | 80–120 | [26] |
| ALP | N/R | PD-AdsCSV 2 | N/R | 120 s | 100 | 400 | 93–120 | [27] |
| 9 BZs (ALP) | On-line SPE | LC-MS/MS | Some minutes | 47 min | 0.6 | 1.9 | 80–120 | [28] |
| 8 BZs (ALP) | SPE | UHPLC-MS/MS | ~40 min | 6.5 min | N/R | 0.9 | 65–134 | [29] |
| ALP + FLT | SB-MSPE | HPLC-PDA | 50 min | 10 min | 3000 | 10,000 | 93.6–112.9 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plastiras, O.-E.; Deliyanni, E.; Samanidou, V. Synthesis and Application of the Magnetic Nanocomposite GO-Chm for the Extraction of Benzodiazepines from Surface Water Samples Prior to HPLC-PDA Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177828
Plastiras O-E, Deliyanni E, Samanidou V. Synthesis and Application of the Magnetic Nanocomposite GO-Chm for the Extraction of Benzodiazepines from Surface Water Samples Prior to HPLC-PDA Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(17):7828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177828
Chicago/Turabian StylePlastiras, Orfeas-Evangelos, Eleni Deliyanni, and Victoria Samanidou. 2021. "Synthesis and Application of the Magnetic Nanocomposite GO-Chm for the Extraction of Benzodiazepines from Surface Water Samples Prior to HPLC-PDA Analysis" Applied Sciences 11, no. 17: 7828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177828
APA StylePlastiras, O.-E., Deliyanni, E., & Samanidou, V. (2021). Synthesis and Application of the Magnetic Nanocomposite GO-Chm for the Extraction of Benzodiazepines from Surface Water Samples Prior to HPLC-PDA Analysis. Applied Sciences, 11(17), 7828. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177828








