Indoor Positioning Systems Can Revolutionise Digital Lean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
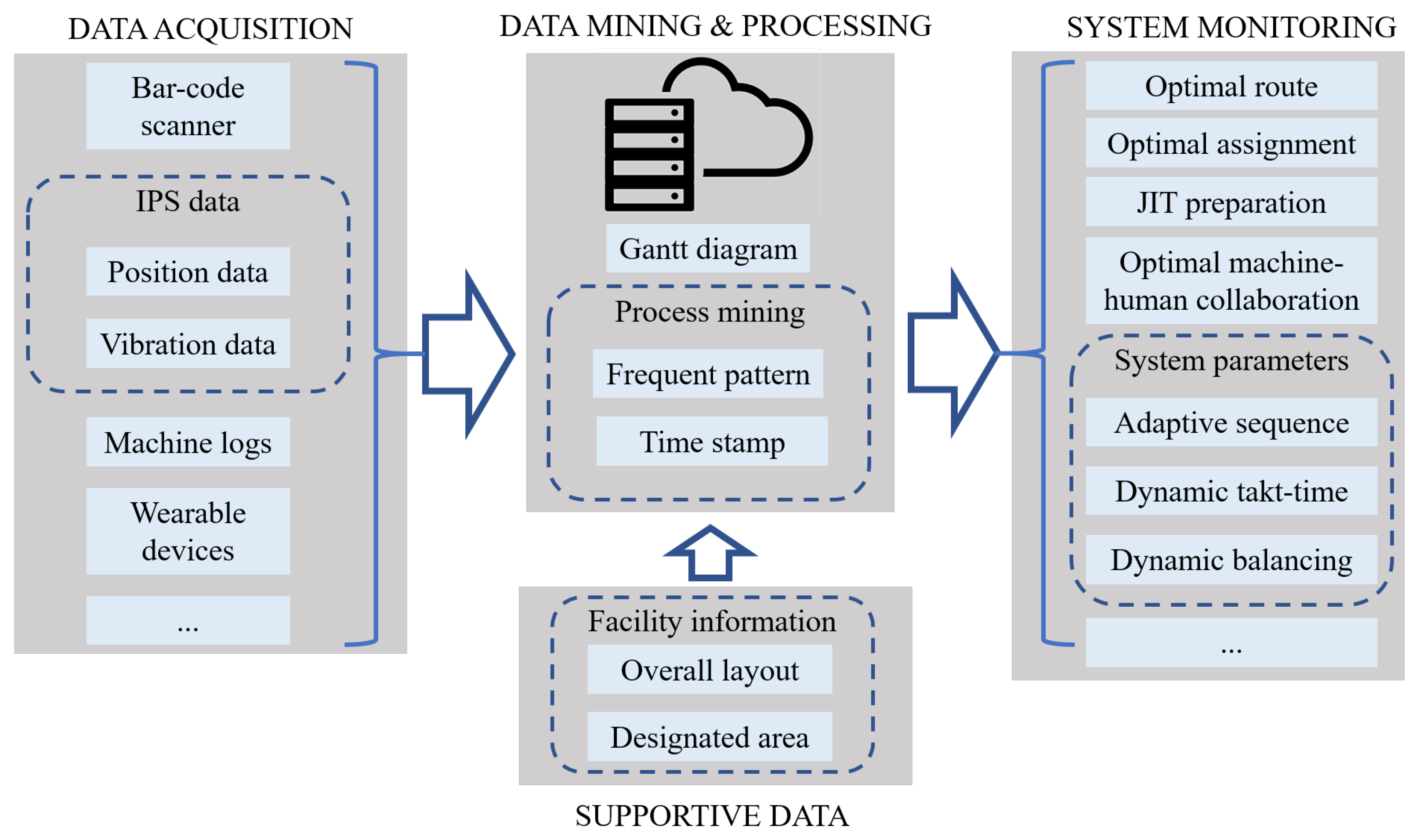
- We explored and categorized the possible situations in which the IPS can be applied in LM in Section 2. The novelty of this section is that it defines how positional data can be transformed into actionable information for LM.
- We developed a data-based framework to integrate and analyze positional and manufacturing data. As Section 3 presents, the novelty of the methodology lies in the process-mining-based identification of VSMs.
- We provided a detailed industrial case study with several KPIs to demonstrate the applicability of the proposed framework in Section 4. Our case study is based on a real manufacturing problem where the IPS monitors the day by day production, so the applicability of the developed framework is demonstrated.
2. Utilisation of Location-Information in Lean 4.0
3. IPS-Driven Development Framework for Lean 4.0
4. Application to the Monitoring of a Flexible Manufacturing Process
4.1. Purpose of the Project
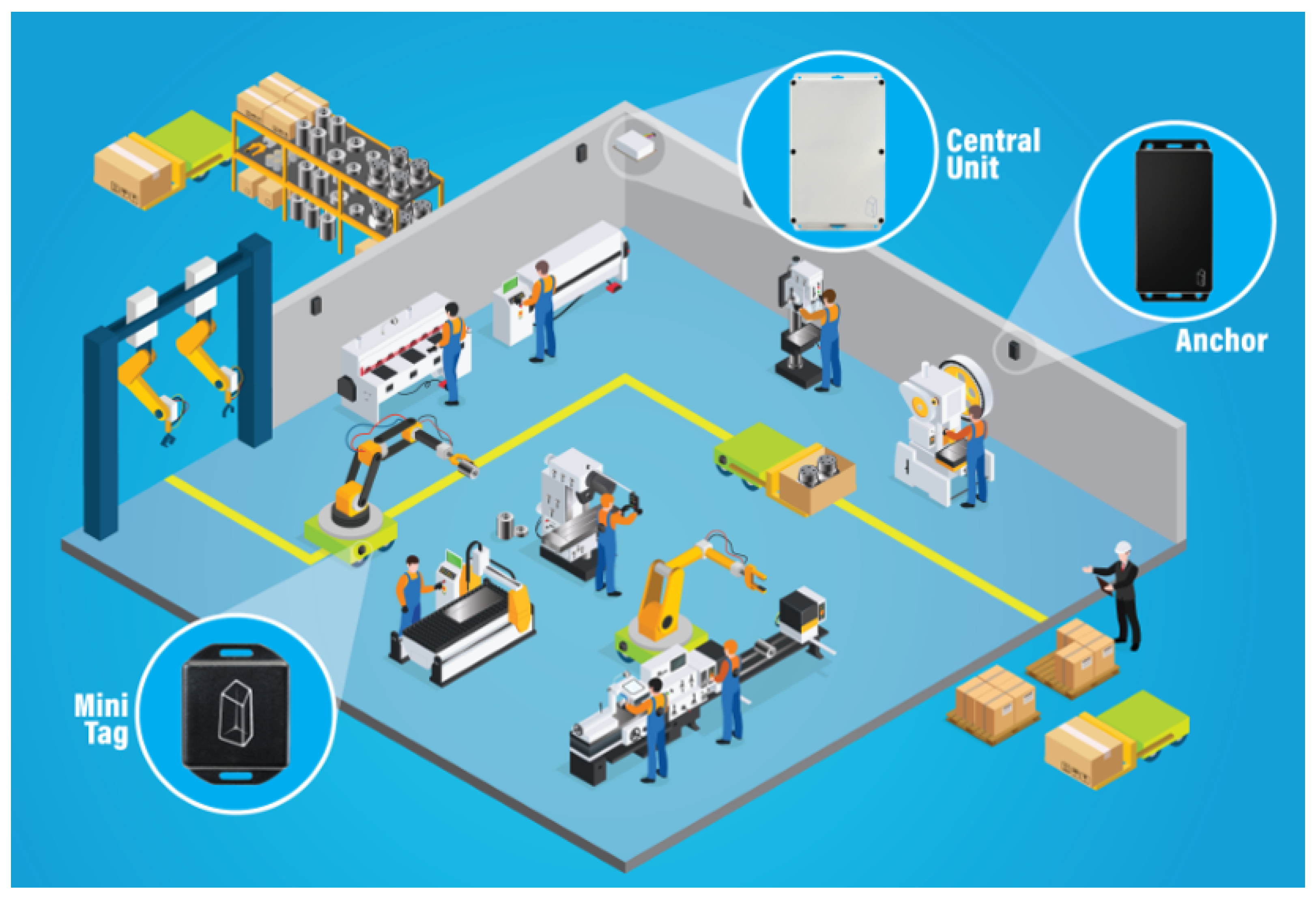
4.2. Description of the Applied IPS
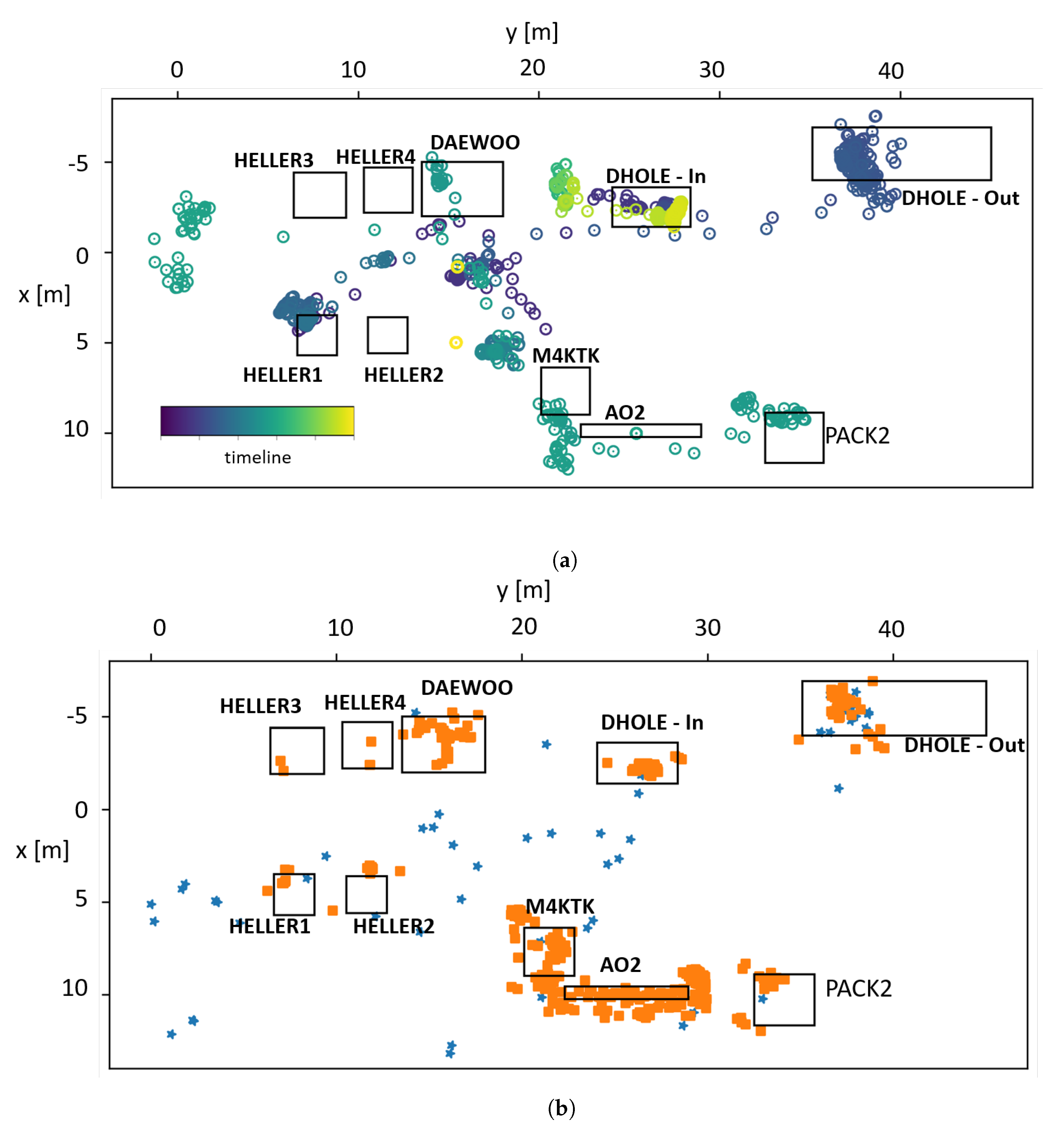
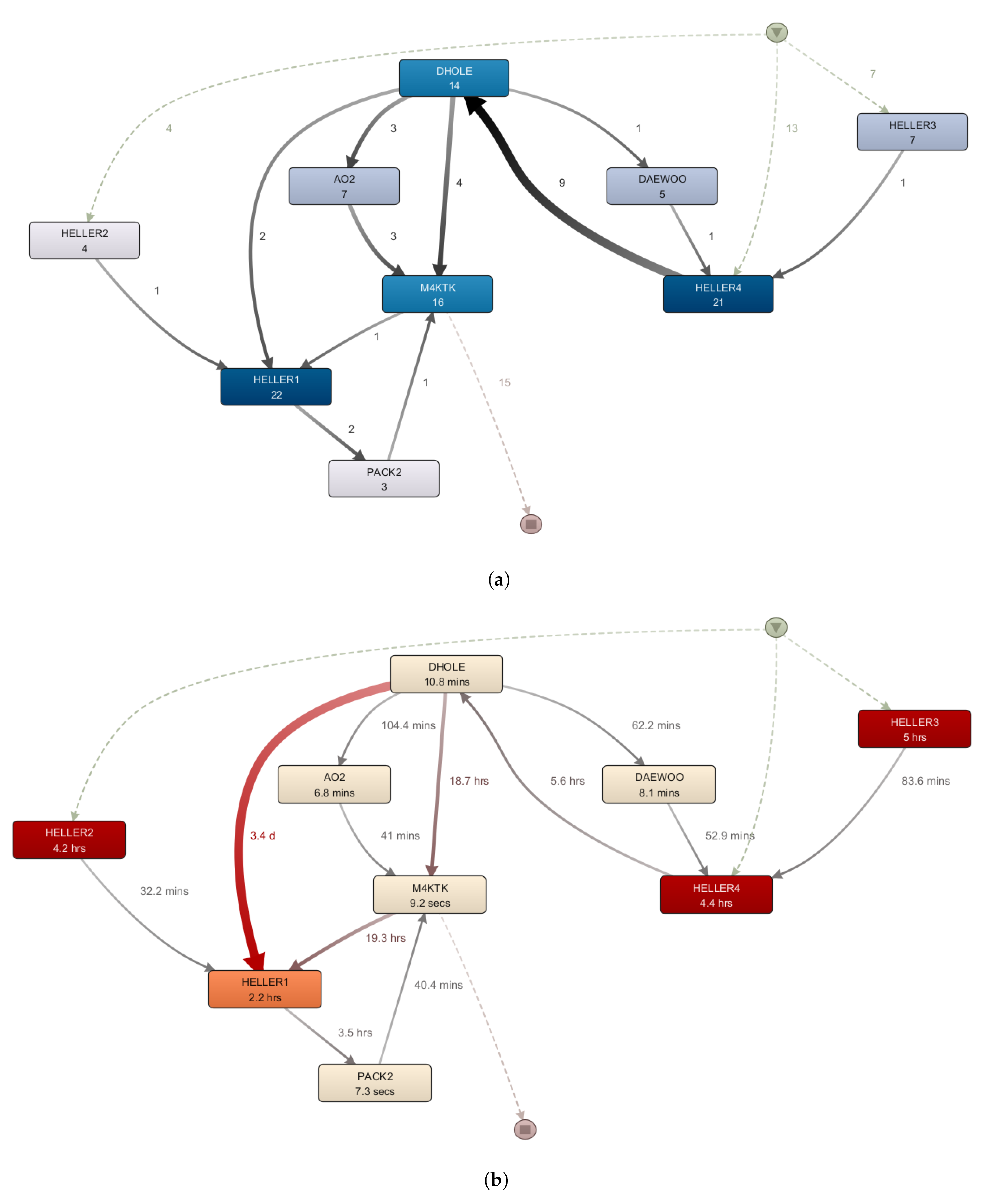
4.3. Calculation of the IPS-Based Indicators
4.4. Discussion, Utilisation of the Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rácz-Szabó, A.; Ruppert, T.; Bántay, L.; Löcklin, A.; Jakab, L.; Abonyi, J. Real-Time Locating System in Production Management. Sensors 2020, 20, 6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liker, J.K. The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles from the World’s Greatest Manufacturer, 1st ed.; Mc Graw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Womack, J.P.; Jones, D.T.; Roos, D. The Machine that Changed the World; 2007. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Machine_That_Changed_the_World_(book) (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Holweg, M. The genealogy of lean production. J. Oper. Manag. 2007, 25, 420–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, H. Legend and Future Horizon of Lean Concept and Technology. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, A.G.; Ng, A.H.; Moris, M.U. Supporting the lean journey with simulation and optimization in the context of Industry 4.0. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 25, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beregi, R.; Szaller, Á.; Kádár, B. Synergy of multi-modelling for process control. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, A.C.; Sato, D.M.V.; Scalabrin, E.E.; Santos, E.A.P. An extended model for remaining time prediction in manufacturing systems using process mining. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 56, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.F.; Zambrano-Rey, G.; Aguirre, S.; Trentesaux, D. Using process-mining for understating the emergence of self-organizing manufacturing systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 1618–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, B.; Huh, M.; Cho, S.; Park, S.; Lee, D. Mining transportation logs for understanding the after-assembly block manufacturing process in the shipbuilding industry. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.S.; Kim, K.J. A data mining approach considering missing values for the optimization of semiconductor-manufacturing processes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 2590–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, N.; Xu, Z.Y.; Wu, K. The internet of things-based decision support system for information processing in intelligent manufacturing using data mining technology. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 142, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazan, P.; Janikova, D.; Tanuska, P.; Kebisek, M.; Cervenanska, Z. Using data mining methods for manufacturing process control. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 6178–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charaniya, S.; Le, H.; Rangwala, H.; Mills, K.; Johnson, K.; Karypis, G.; Hu, W.S. Mining manufacturing data for discovery of high productivity process characteristics. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 147, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buer, S.V.; Fragapane, G.I.; Strandhagen, J.O. The Data-Driven Process Improvement Cycle: Using Digitalization for Continuous Improvement. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buer, S.V.; Strandhagen, J.O.; Chan, F.T.S. The link between Industry 4.0 and lean manufacturing: Mapping current research and establishing a research agenda. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 2924–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dombrowski, U.; Richter, T.; Krenkel, P. Interdependencies of Industrie 4.0 & Lean Production Systems: A Use Cases Analysis. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, A.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, S.; Lv, J.; Peng, T.; Waqar, S.; Yin, E. A big data-driven framework for sustainable and smart additive manufacturing. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 67, 102026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, E.; Fumagalli, L.; Macchi, M. A Review of the Roles of Digital Twin in CPS-based Production Systems. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Starly, B.; Cohen, P.; Lee, Y.S. Sensor Data and Information Fusion to Construct Digital-twins Virtual Machine Tools for Cyber-physical Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 10, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlemann, T.H.; Lehmann, C.; Steinhilper, R. The Digital Twin: Realizing the Cyber-Physical Production System for Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP 2017, 61, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Kevin, I.; Wang, K.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. Digital Twin-driven smart manufacturing: Connotation, reference model, applications and research issues. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.D.; Teng, S.Y.; How, B.S.; Ngan, S.L.; Rahman, A.A.; Tan, C.P.; Ponnambalam, S.G.; Lam, H.L. Enhancing the adaptability: Lean and green strategy towards the Industry Revolution 4.0. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyulai, D.; Pfeiffer, A.; Nick, G.; Gallina, V.; Sihn, W.; Monostori, L. Lead time prediction in a flow-shop environment with analytical and machine learning approaches. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, O.; Iztok, P.; Borut, B. Real-Time manufacturing optimization with a simulation model and virtual reality. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 38, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, C.; Staehr, T.; Cohen, S.; Stricker, N.; Haefner, B.; Lanza, G. Augmented Go & See: An approach for improved bottleneck identification in production lines. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 31, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Blaga, A.; Militaru, C.; Mezei, A.D.; Tamas, L. Augmented reality integration into MES for connected workers. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 68, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, T.; Egger, J. Augmented reality in support of Industry 4.0—Implementation challenges and success factors. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 58, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeen Gavin Lai, N.; Hoong Wong, K.; Halim, D.; Lu, J.; Siang Kang, H. Industry 4.0 Enhanced Lean Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Industrial Technology and Management (ICITM), Cambridge, UK, 2–4 March 2019; pp. 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Kolberg, D.; Zühlke, D. Lean Automation enabled by Industry 4.0 Technologies. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 1870–1875, In Proceedings of the 15th IFAC Symposium onInformation Control Problems in Manufacturing, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1–13 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Jannat, N.E.; Schmidt, D.; Kim, K.Y. Data-driven cyber-physical system framework for connected resistance spot welding weldability certification. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 67, 102036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, M. Industry 4.0 and lean management: A proposed integration model and research propositions. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2018, 6, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayr, A.; Weigelt, M.; Kühl, A.; Grimm, S.; Erll, A.; Potzel, M.; Franke, J. Lean 4.0—A conceptual conjunction of lean management and Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP 2018, 72, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont, K.; Gladysz, B.; Corti, D.; Castaño, F.; Mohammed, W.M.; Martinez Lastra, J.L. Towards ’Lean Industry 4.0’-Current trends and future perspectives. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2020, 7, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, K.; Furey, E.; Lunney, T.; Santos, J.; Woods, D.; McCaughey, A. An evaluation of indoor location determination technologies. J. Locat. Based Serv. 2011, 5, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliffe, J. Hofmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H. & Collins, J. 1994. Global Positioning System. Theory and Practice, xxiii+ 355 pp. Wien, New York: Springer-Verlag. Price DM 79.00, Ös 550.00 (soft covers). ISBN 3 211 82591 6. Geol. Mag. 1998, 135, 143–158. [Google Scholar]
- Miclo, R.; Fontanili, F.; Marquès, G.; Bomert, P.; Lauras, M. RTLS-based Process Mining: Towards an automatic process diagnosis in healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), IEEE, Gothenburg, Sweden, 24–28 August 2015; pp. 1397–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, W.C.; Machado, G.S.; Sales, A.; de Lucena, M.M.; Jazdi, N.; de Lucena, V.F. A Review of Technologies and Techniques for Indoor Navigation Systems for the Visually Impaired. Sensors 2020, 20, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.A.; Vieira, M.; Louro, P.; Mateus, L.; Vieira, P. Indoor positioning system using a WDM device based on a-SiC:H technology. J. Lumin. 2017, 191, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhou, W.; Tang, W.; Zheng, X.; Peng, A.; Zheng, H. A 3D indoor positioning system based on low-cost MEMS sensors. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2016, 65, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, S.S.; Nakad, Z.S. A Standalone RFID Indoor Positioning System Using Passive Tags. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, T.; Abonyi, J. Industrial internet of things based cycle time control of assembly lines. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Future IoT Technologies (Future IoT), Eger, Hungary, 18–19 January 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert, T.; Abonyi, J. Software sensor for activity-time monitoring and fault detection in production lines. Sensors 2018, 18, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zang, Y.; Wu, L. Application of RFID and RTLS Technology in Supply Chain Enterprise. In Proceedings of the 2010 6th International Conference on Wireless Communications Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM), Chengdu, China, 23–25 September 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirch, M.; Poenicke, O.; Richter, K. RFID in Logistics and Production –Applications, Research and Visions for Smart Logistics Zones. Procedia Eng. 2017, 178, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Lee, H.S.; Park, M.S.; Kim, H.; Baek, Y.J. RFID-Based Real-Time Locating System for Construction Safety Management. Korean J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awolusi, A.; Akinyokun, O.; Iwasokun, G. RFID and RTLS-Based Human Resource Monitoring System. Br. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2016, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.; McDermott, O.; Noonan, J. Applying Lean Six Sigma Methodology to a Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Facility: A Case Study. Processes 2021, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalgund, A.B.; Kulkarni, S. Implementation of Six Sigma Principles to Improve Supply Chain and Assembly Process. Management 2020, 2, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Knoll, D.; Reinhart, G.; Prüglmeier, M. Enabling value stream mapping for internal logistics using multidimensional process mining. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 124, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graafmans, T.; Turetken, O.; Poppelaars, H.; Fahland, D. Process Mining for Six Sigma. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, J.P.; Jones, D.T. Lean thinking-banish waste and create wealth in your corporation. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1997, 48, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmalek, F.A.; Rajgopal, J. Analyzing the benefits of lean manufacturing and value stream mapping via simulation: A process sector case study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2007, 107, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, F.; Villalobos, J.R.; Roderick, L. Evaluation of Just-In-Time alternatives in the electric wire-harness industry. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1997, 35, 1993–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.L.N.; Do, N.H.; Nam, K.C. Modeling and simulation of a Lean system. Case study of a paint line in a furniture company. Manag. Res. Pract. 2010, 2, 284–298. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, H.; Roy, P.K.; Karim, R.; Biswas, P.K. Effective Way To Estimate the Standard Minute Value ( Smv ) of a T-Shirt By Work Study. Eur. Sci. J. 2014, 10, 196–203. [Google Scholar]
- Rahani, A.R.; Al-Ashraf, M. Production flow analysis through Value Stream Mapping: A lean manufacturing process case study. Procedia Eng. 2012, 41, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen Thi, L.; Le Minh, T.; Vu Thi Thanh, T.; Do, N.H. Lean Line Balancing for an Electronics Assembly Line. Procedia CIRP 2016, 40, 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, D.; Rich, N. Lean TPM: A Blueprint for Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Baluch, N.; Abdullah, C.S.; Mohtar, S. TPM and Lean Maintenance—A Critical Review. Interdiscip. J. Contemp. Res. Bus. 2012, 4, 850–857. [Google Scholar]
- Zelbst, P.; Green, J.; Sower, V.; Abshire, R. Impact of RFID and information sharing on JIT, TQM and operational performance. Manag. Res. Rev. 2014, 37, 970–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydos, T.F.; Ferreira, J.C. RFID-based system for Lean Manufacturing in the context of Internet of Things. IEEE Int. Conf. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Chongwatpol, J.; Sharda, R. Achieving Lean Objectives through RFID: A Simulation-Based Assessment*. Decis. Sci. 2013, 44, 239–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teizer, J.; Neve, H.; Li, H.; Wandahl, S.; König, J.; Ochner, B.; König, M.; Lerche, J. Construction resource efficiency improvement by Long Range Wide Area Network tracking and monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2020, 116, 103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinbold, A.; Seppänen, O.; Peltokorpi, A.; Singh, V.; Dror, E. Integrating indoor positioning systems and BIM to improve situational awareness. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference of the International Group for Lean Construction, IGLC 2019, Dublin, Ireland, 1–7 July 2019; pp. 1141–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Brintrup, A.; Ranasinghe, D.; Mcfarlane, D. RFID Opportunity Analysis for Leaner Manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2010, 48, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Qu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. RFID-enabled real-time manufacturing for automotive part and accessory suppliers. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Computers & Indutrial Engineering, Awaji City, Japan, 25–28 July 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, T.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Dai, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, G.; Luo, H. RFID-enabled smart assembly workshop management system. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th Ieee International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Paris-Evry, France, 10–12 April 2013; pp. 895–900. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, K.M. Application of ORFPM system for lean implementation: An industrial case study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.M.; Chen, J.; Cox, R. Real time facility performance monitoring system using RFID technology. Assem. Autom. 2012, 32, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotarski, P.; Paslawski, J.; Skrzypczak, M.; Krygier, R. RTLS Systems as a Lean Management Tool for Productivity Improvement. ISARC. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Taipei, Taiwan, 28 June–1 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gladysz, B.; Santarek, K.; Lysiak, C. Dynamic Spaghetti Diagrams. A Case Study of Pilot RTLS Implementation. In Intelligent Systems in Production Engineering and Maintenance—ISPEM 2017; Burduk, A., Mazurkiewicz, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizerland, 2018; pp. 238–248. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, H.; Brandl, F.; Lock, C.; Reinhart, G. Integration of Industrie 4.0 in Lean Manufacturing Learning Factories. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 23, 147–152, Advanced Engineering Education & Training for Manufacturing Innovation. In Proceedings of the 8th CIRP Sponsored Conference on Learning Factories (CLF 2018), Patras, Greece, 12–13 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, P.H.A.; Saraiva, J. Time and motion study applied to a production line of organic lenses in Manaus Industrial Hub. Gestão Produção 2018, 25, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astromskis, S.; Janes, A.; Sillitti, A.; Succi, G. Implementing organization-wide gemba using noninvasive process mining. Cutter IT J. 2013, 26, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli, D.; Bruno, G. Application of Process Mining and Semantic Structuring Towards a Lean Healthcare Network. In Proceedings of the Working Conference on Virtual Enterprises, Albi, France, 23–25 September 2015; pp. 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Macoir, N.; Bauwens, J.; Jooris, B.; Van Herbruggen, B.; Rossey, J.; Hoebeke, J.; De Poorter, E. Uwb localization with battery-powered wireless backbone for drone-based inventory management. Sensors 2019, 19, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Liu, T. The application of Wi-Fi RTLS in automatic warehouse management system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International conference on automation and logistics (ICAL), Chongqing, China, 15–16 August 2011; pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, S.K.; Jayakumar, V.; Kumar, S.S. Defect analysis and lean six sigma implementation experience in an automotive assembly line. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; You, D.; Gao, X.; Zhang, N.; Gao, P.P. Welding defects detection based on deep learning with multiple optical sensors during disk laser welding of thick plates. J. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 51, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Tian, G.Y.; Zhang, J. IQ signal based RFID sensors for defect detection and characterisation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 269, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.A.; Khadem, M.M.; Sarder, M. Application of RFID in Supply Chain System. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 9–10 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert, T.; Jaskó, S.; Holczinger, T.; Abonyi, J. Enabling technologies for operator 4.0: A survey. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karam, A.A.; Liviu, M.; Cristina, V.; Radu, H. The contribution of lean manufacturing tools to changeover time decrease in the pharmaceutical industry. A SMED project. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 22, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferradás, P.G.; Salonitis, K. Improving Changeover Time: A Tailored SMED Approach for Welding Cells. Procedia CIRP 2013, 7, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruppert, T.; Csalodi, R.; Abonyi, J. Estimation of machine setup and changeover times by survival analysis. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 153, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

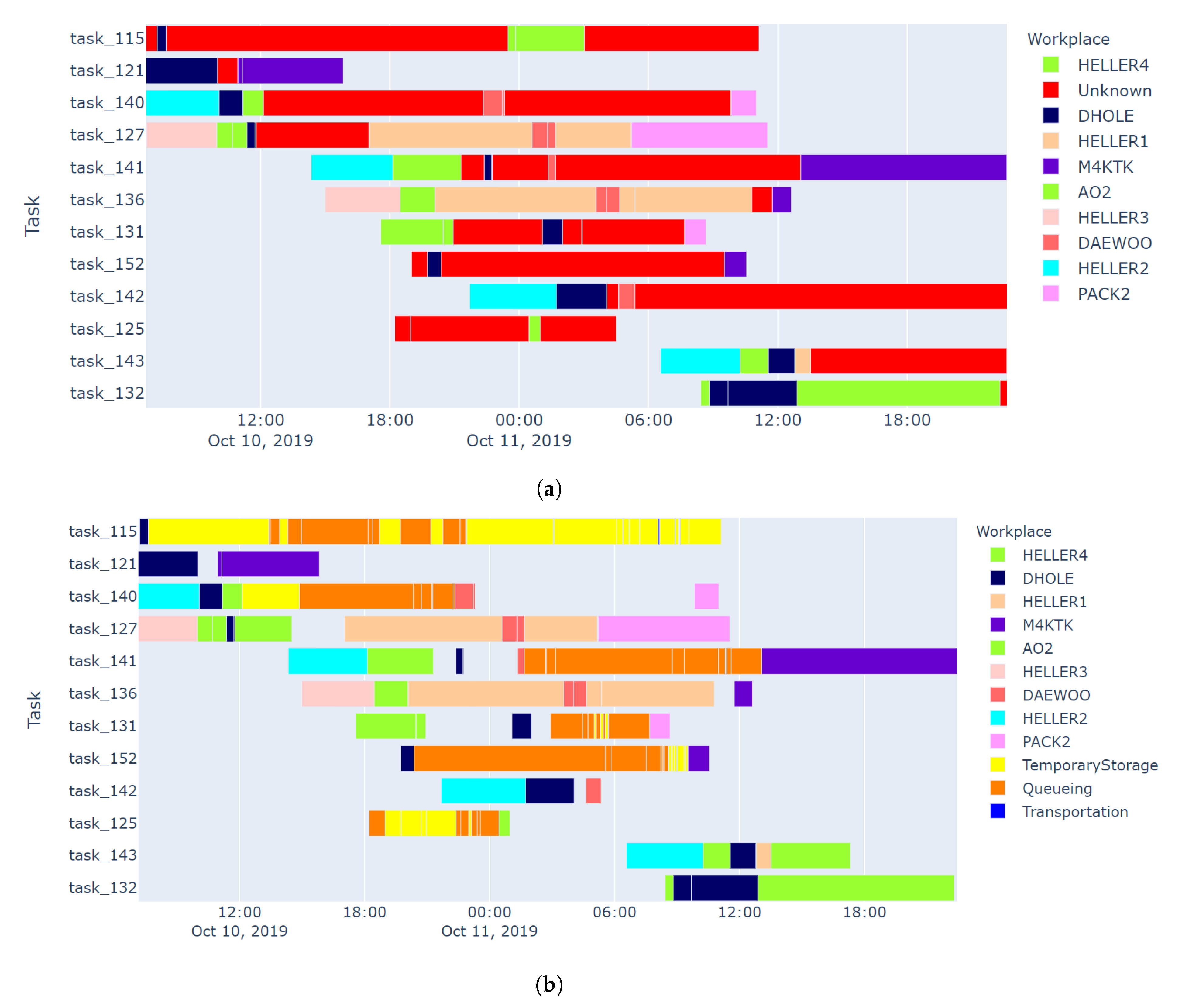
| Lean Concept | KPIs | Measurement Tools | Potential of IPS | Relevant Application of IPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shortest lead time | Average lead and cycle time | Camera [73,74]; Bar-code scanner [73]; RFID [62,75]; Machine/Event logs [76]; IPS [37] | high | Real-time monitoring of the position of semi-finished products and resources, calculation of the lead and cycle times [42,43]. |
| 7 wastes elimination | Waste of Transportation | RFID [66]; Machine/Event logs [76]; IPS [72] | high | Real-time spaghetti diagram [72]. |
| Waste of Inventory | Camera [30]; RFID [62,66]; IPS [72] | high | Tracked items in inventory areas [77,78]. | |
| Waste of Motion | Camera [74] | low | - | |
| Waste of Waiting | Camera [73,74]; Bar-code scanner [73]; RFID [62,75]; Machine logs [76]; IPS [37] | high | Tracked semi-finished products, waiting times, internal stock levels [71]. | |
| Waste of Over-processing | Manual audit [79] | low | - | |
| Waste of Over-production | RFID [66]; IPS [37,72] | high | Discovered overproduction based on the tracked semi-finished products [71]. | |
| Waste of Defect | Optical sensors [80]; RFID [81]; [72] | medium | Reduced defect based on IPS-based poke-yoke solutions and better monitored rework flows. | |
| Less inventory | inventory value | RFID [66]; IPS [72] | high | Improved control of the inventory level [78] and e-kanban solutions reduce internal inventories [82]. |
| Standardized work | Deviation from standardized work | Camera [74]; RFID [62]; IPS [37] | high | IPS based dynamic work instructions improve operator work (Smart operator) [83] |
| Continuous flow | Queueing time | RFID [62]; IPS [37,72] | high | Discovered queueing areas near the workstations [1]. |
| Line balancing | Line balance factor | Camera [74]; RFID [62]; IPS [37] | high | Improved activity time analyses thanks to sensor fusion [43]. |
| Quick changeover | Set-up and changeover time | Machine logs [84]; Manual audit [85] | high | Supported SMED projects [86] |
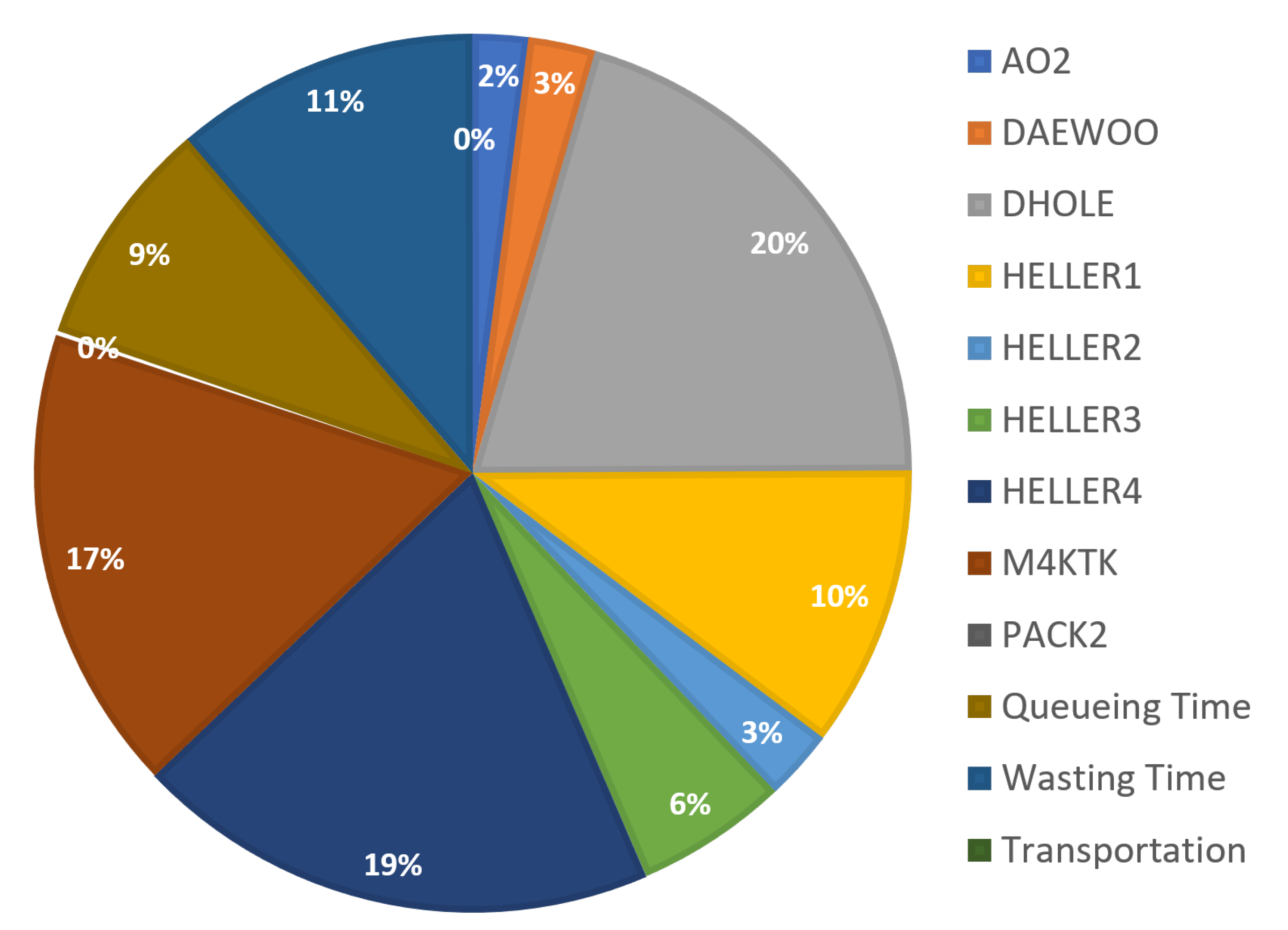
| Workplace | Average Cycle Time [min] | Queueing Time [min] | Produced Tasks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waiting time | 119.47 | - | 54 |
| Waste of transportation | 2.73 | - | 27 |
| AO2 | 77.73 | 102.86 | 56 |
| DAEWOO | 84.71 | 84.05 | 49 |
| DHOLE | 88.69 | 5.09 | 163 |
| HELLER1 | 99.36 | 91.80 | 72 |
| HELLER2 | 228.53 | 46.74 | 34 |
| HELLER3 | 197.16 | 59.56 | 32 |
| HELLER4 | 124.82 | 42.18 | 146 |
| M4KTK | 61.91 | 84.61 | 145 |
| PACK2 | 30.30 | 47.72 | 31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, T.-A.; Ruppert, T.; Abonyi, J. Indoor Positioning Systems Can Revolutionise Digital Lean. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5291. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115291
Tran T-A, Ruppert T, Abonyi J. Indoor Positioning Systems Can Revolutionise Digital Lean. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(11):5291. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115291
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Tuan-Anh, Tamás Ruppert, and János Abonyi. 2021. "Indoor Positioning Systems Can Revolutionise Digital Lean" Applied Sciences 11, no. 11: 5291. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115291
APA StyleTran, T.-A., Ruppert, T., & Abonyi, J. (2021). Indoor Positioning Systems Can Revolutionise Digital Lean. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 5291. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11115291








