Path Planning for Localization of Radiation Sources Based on Principal Component Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
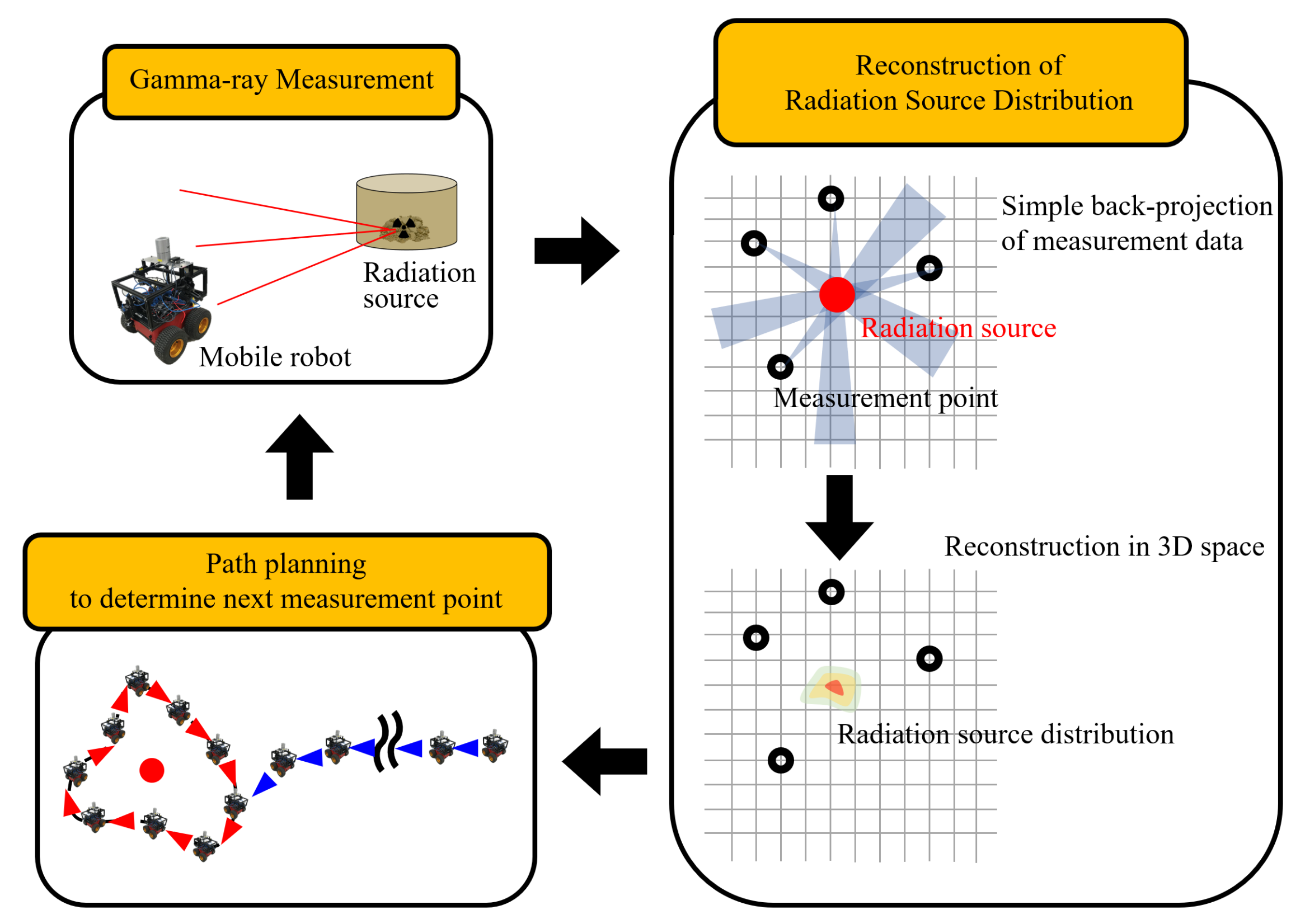
2.1. Overview
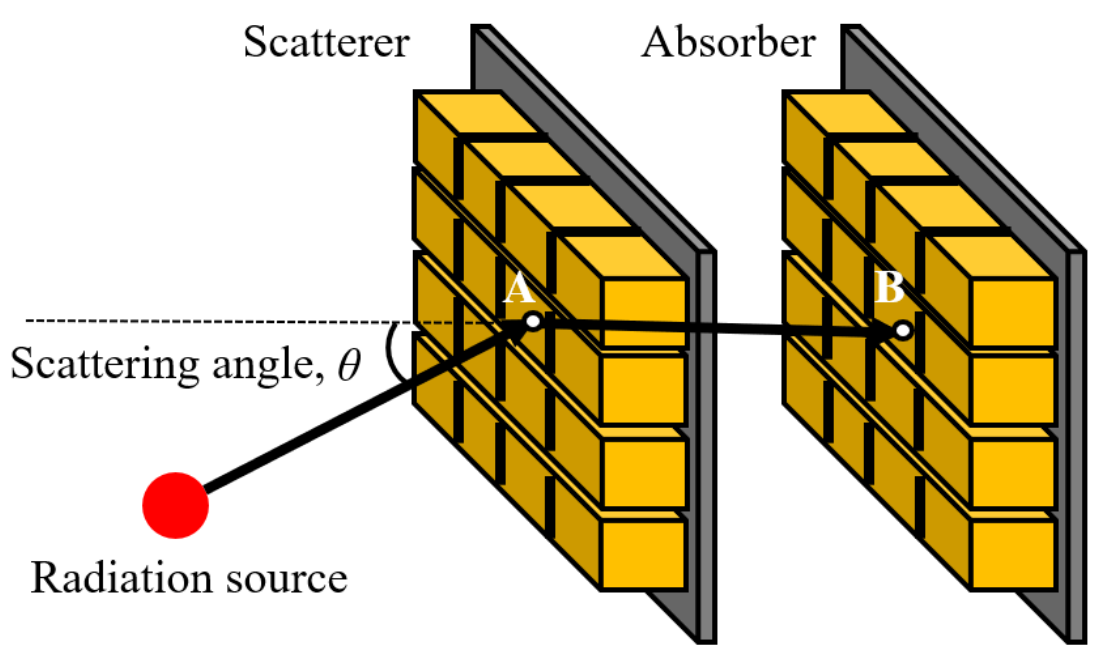
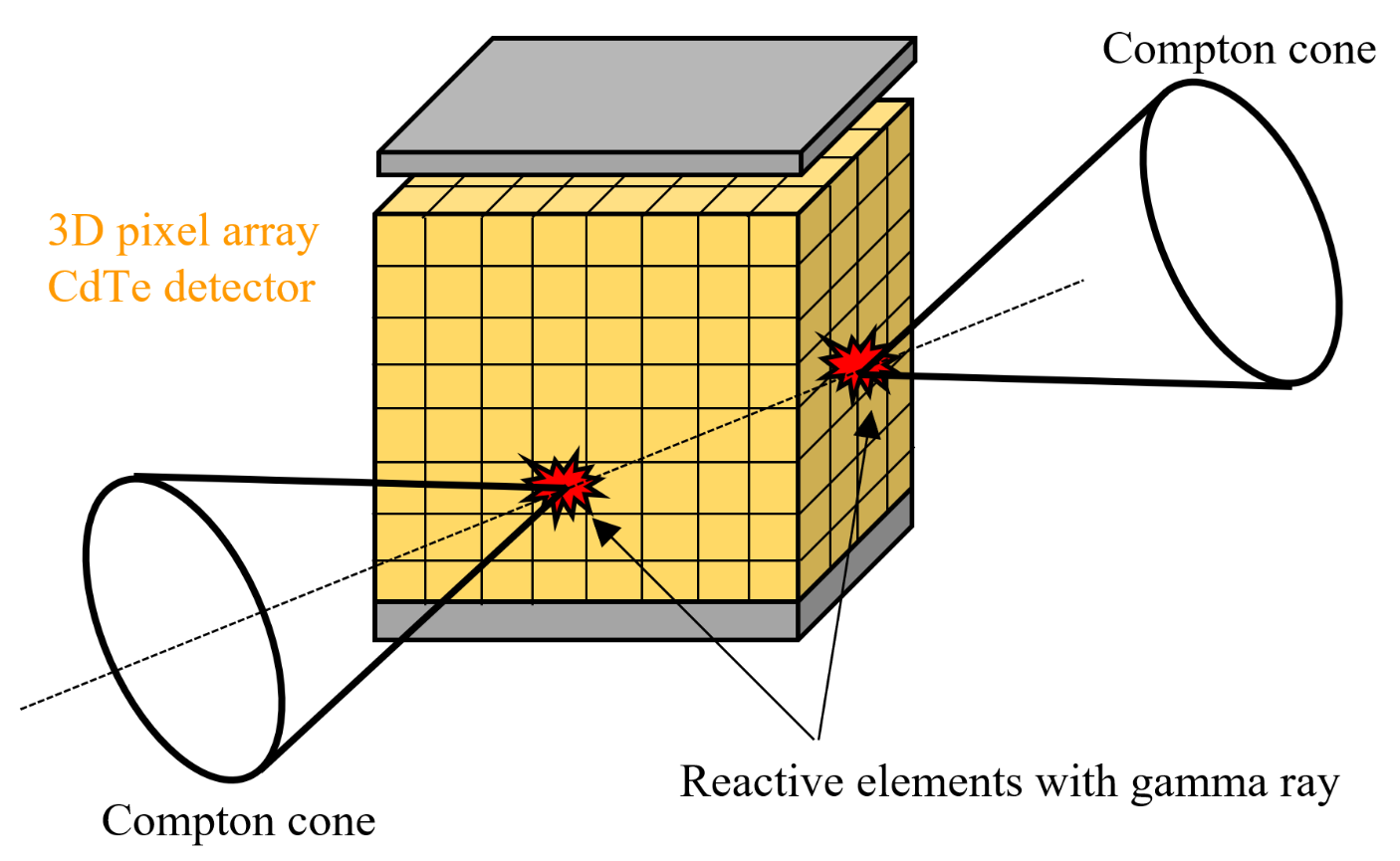
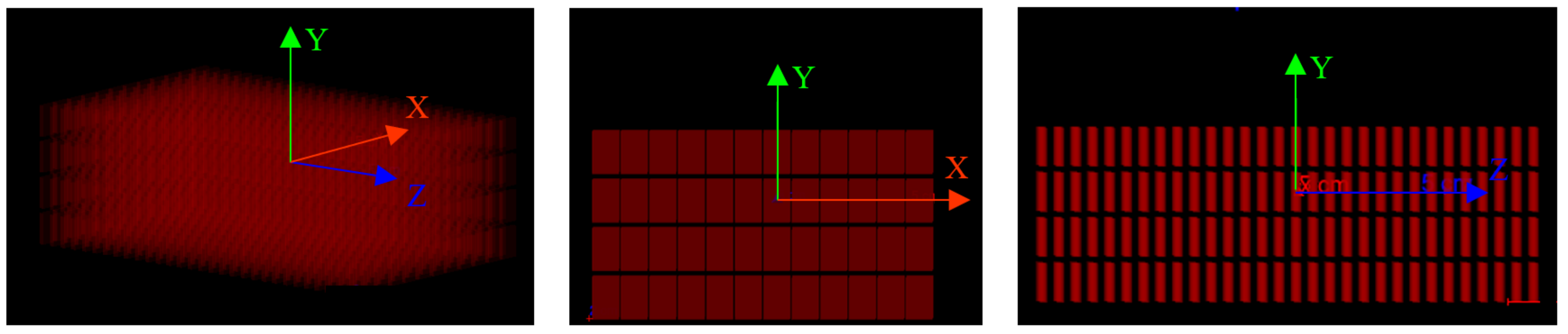
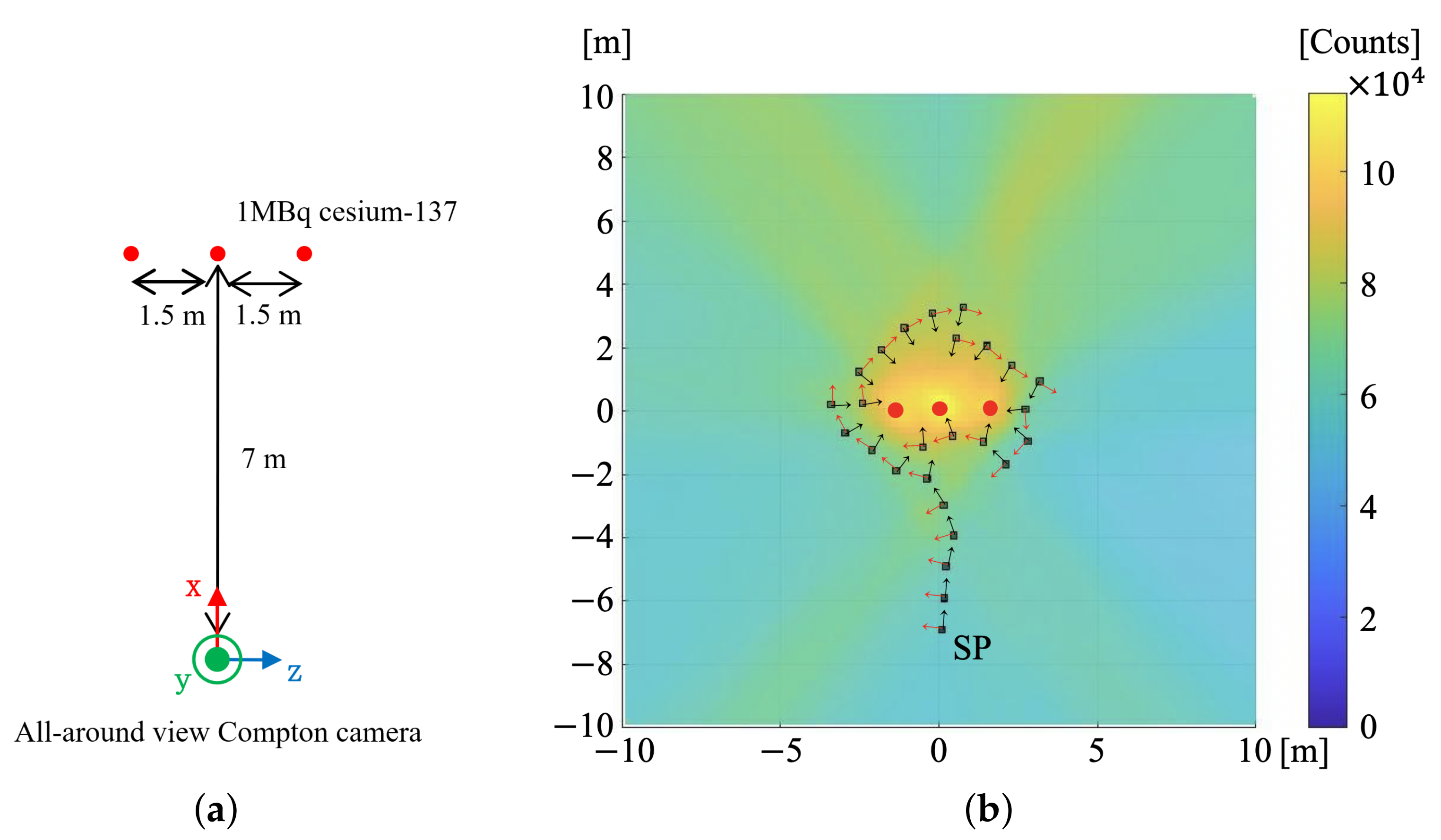
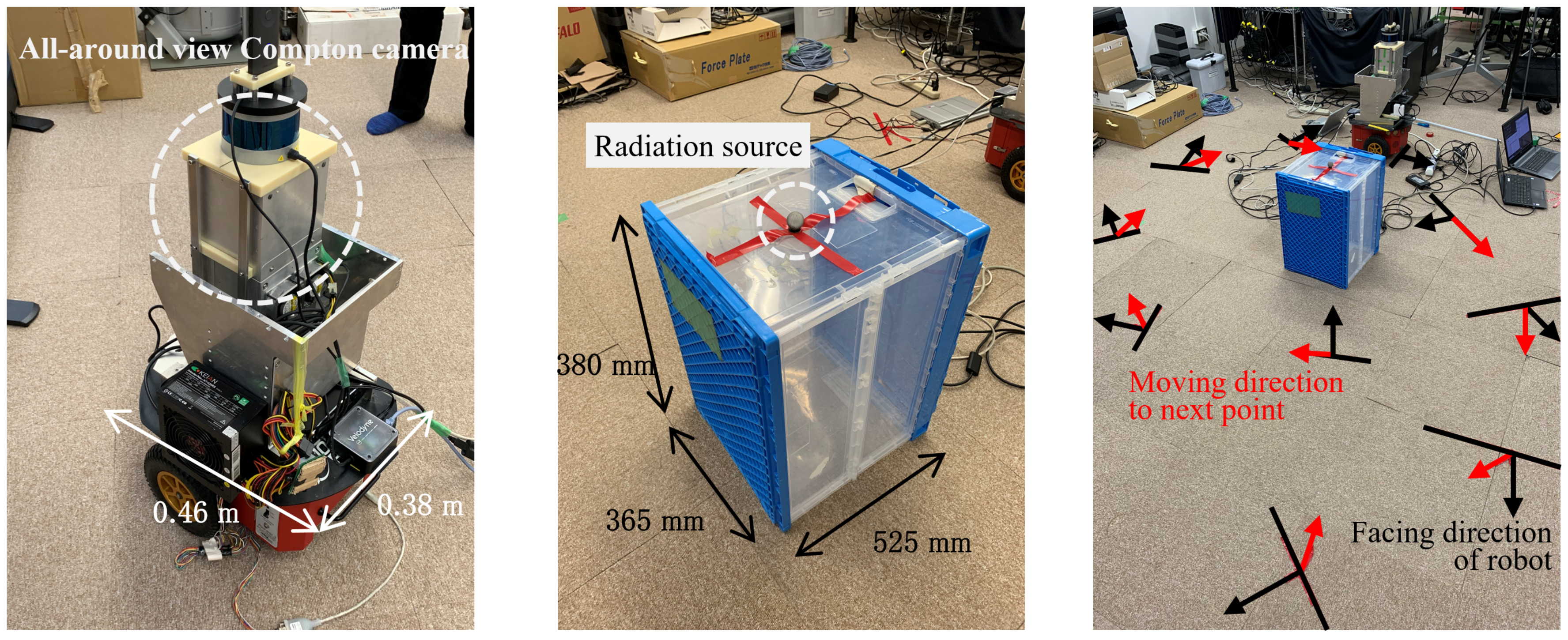
2.2. Gamma-Ray Measurement Using All-Around View Compton Camera
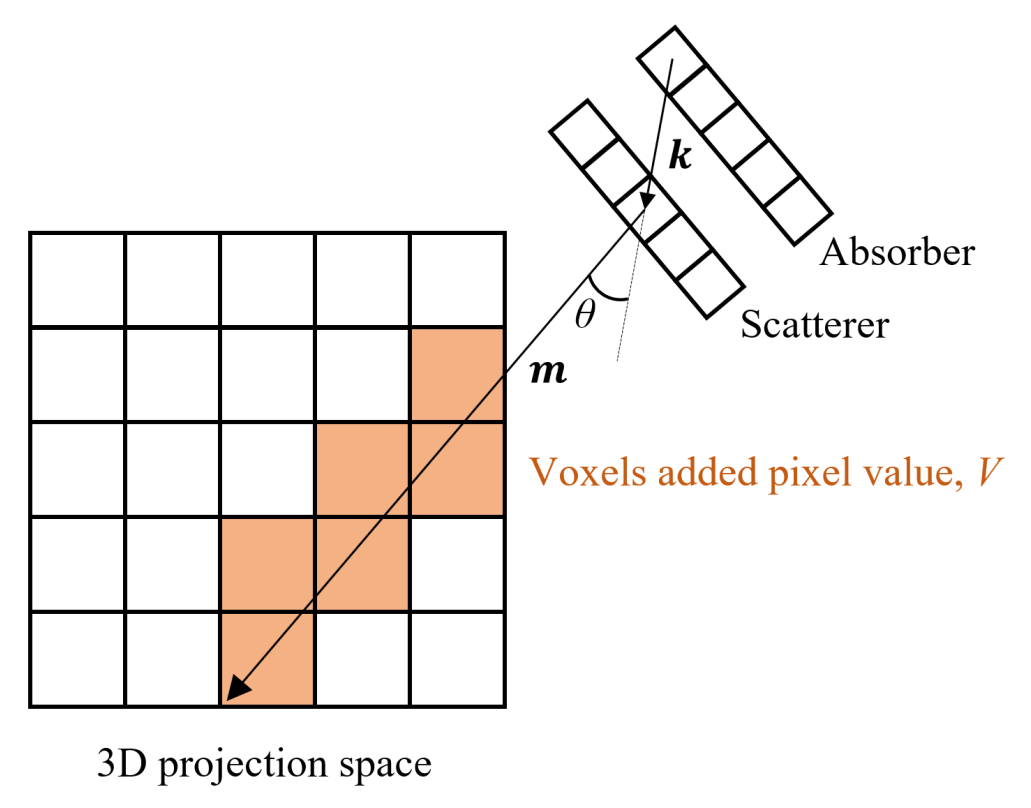
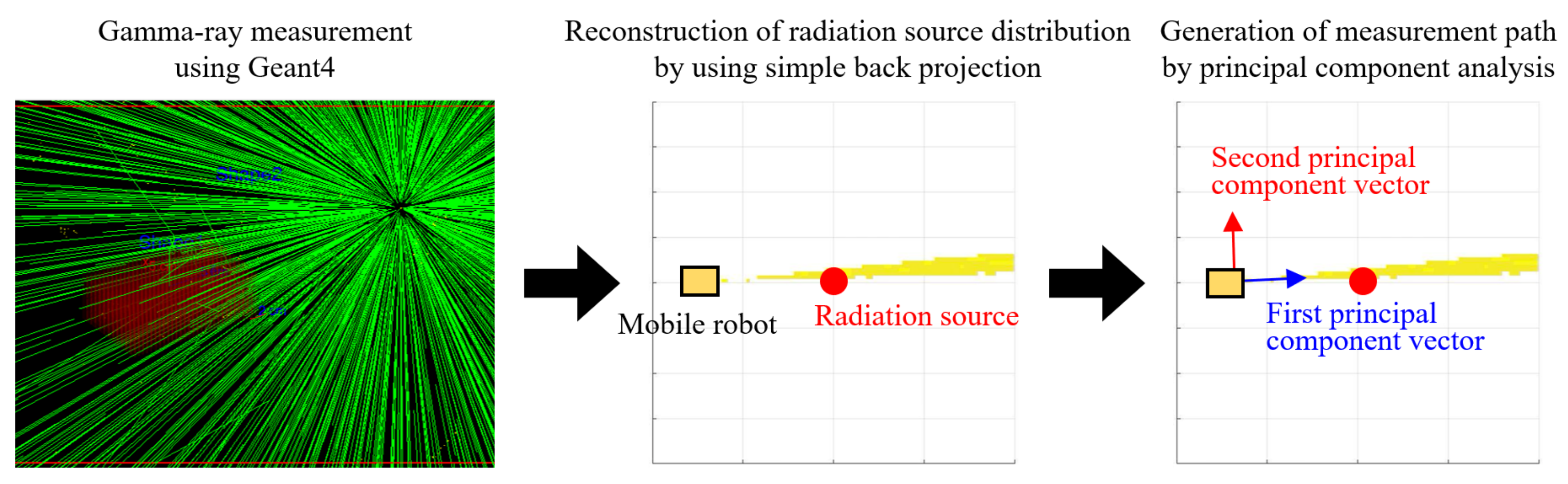
2.3. Reconstruction of Radiation Source Distribution via Simple Back-Projection
| Algorithm 1: Simple Back Projection |
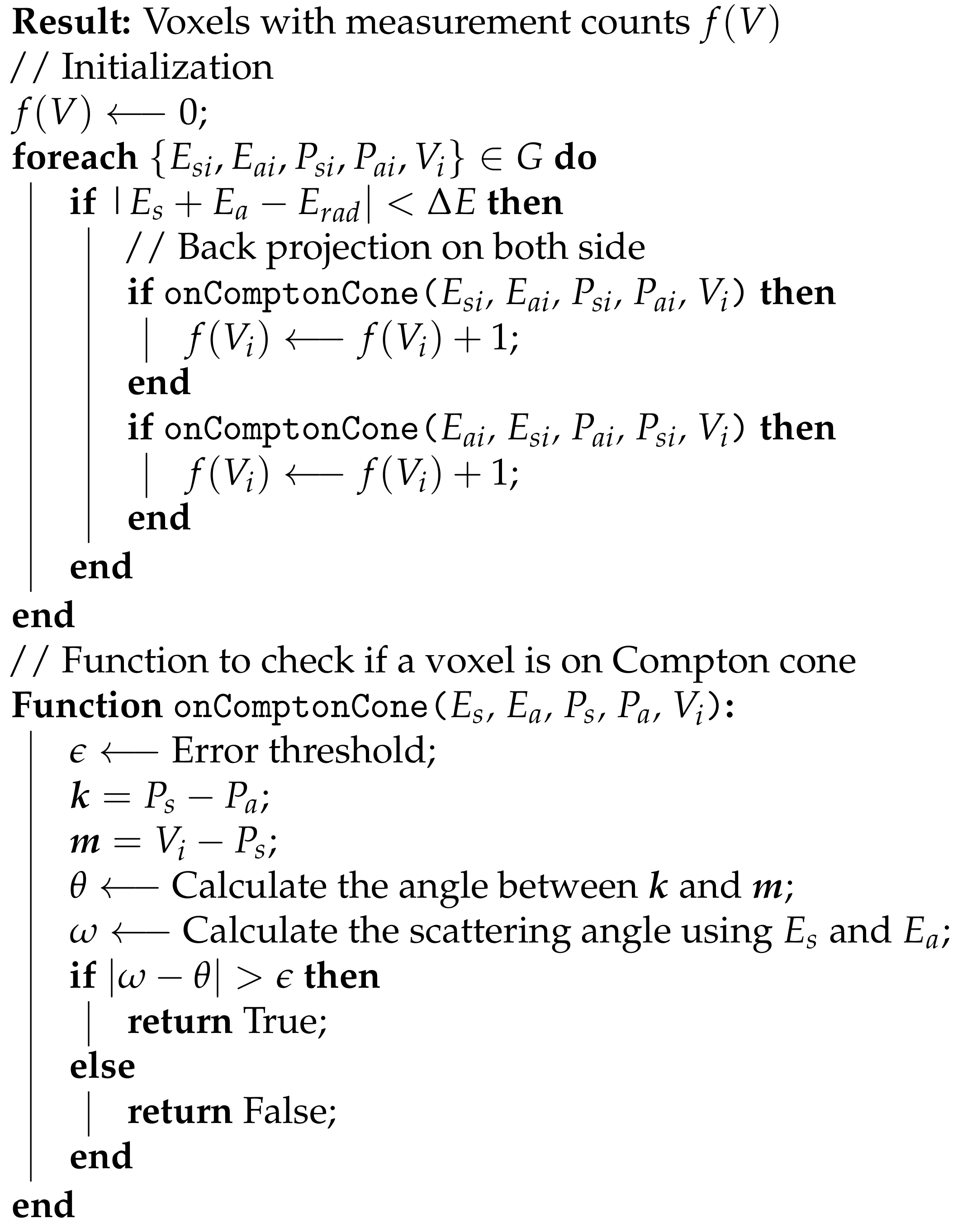 |
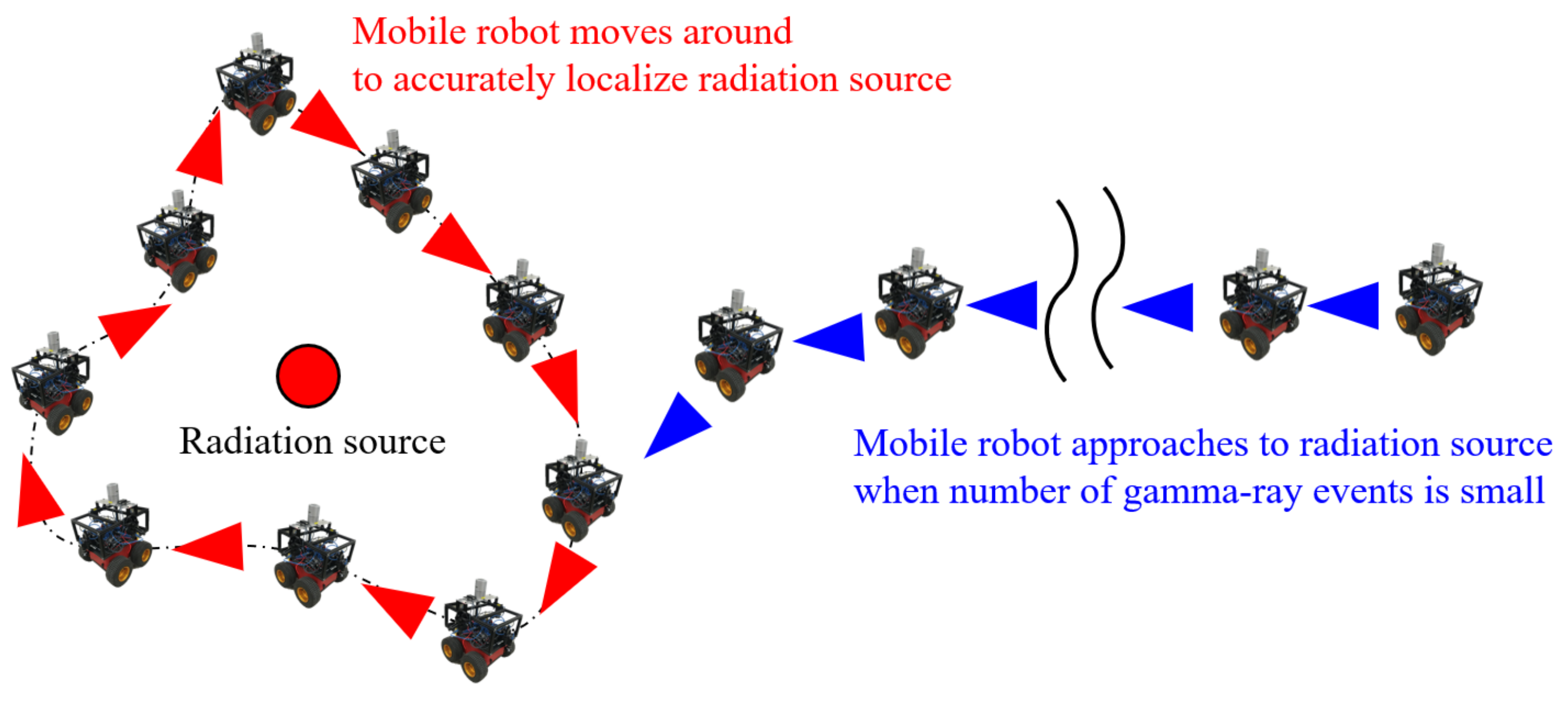
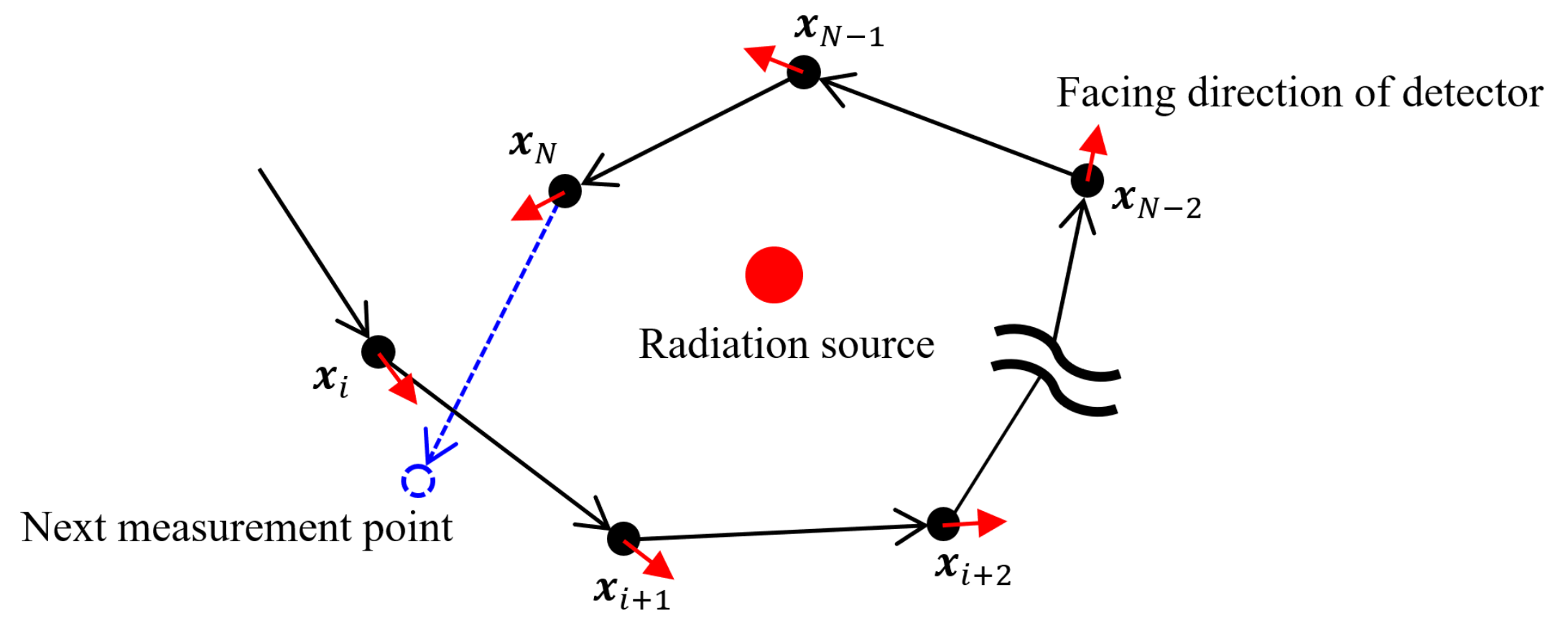
2.4. Path Planning via PCA
| Algorithm 2: Order of measuring |
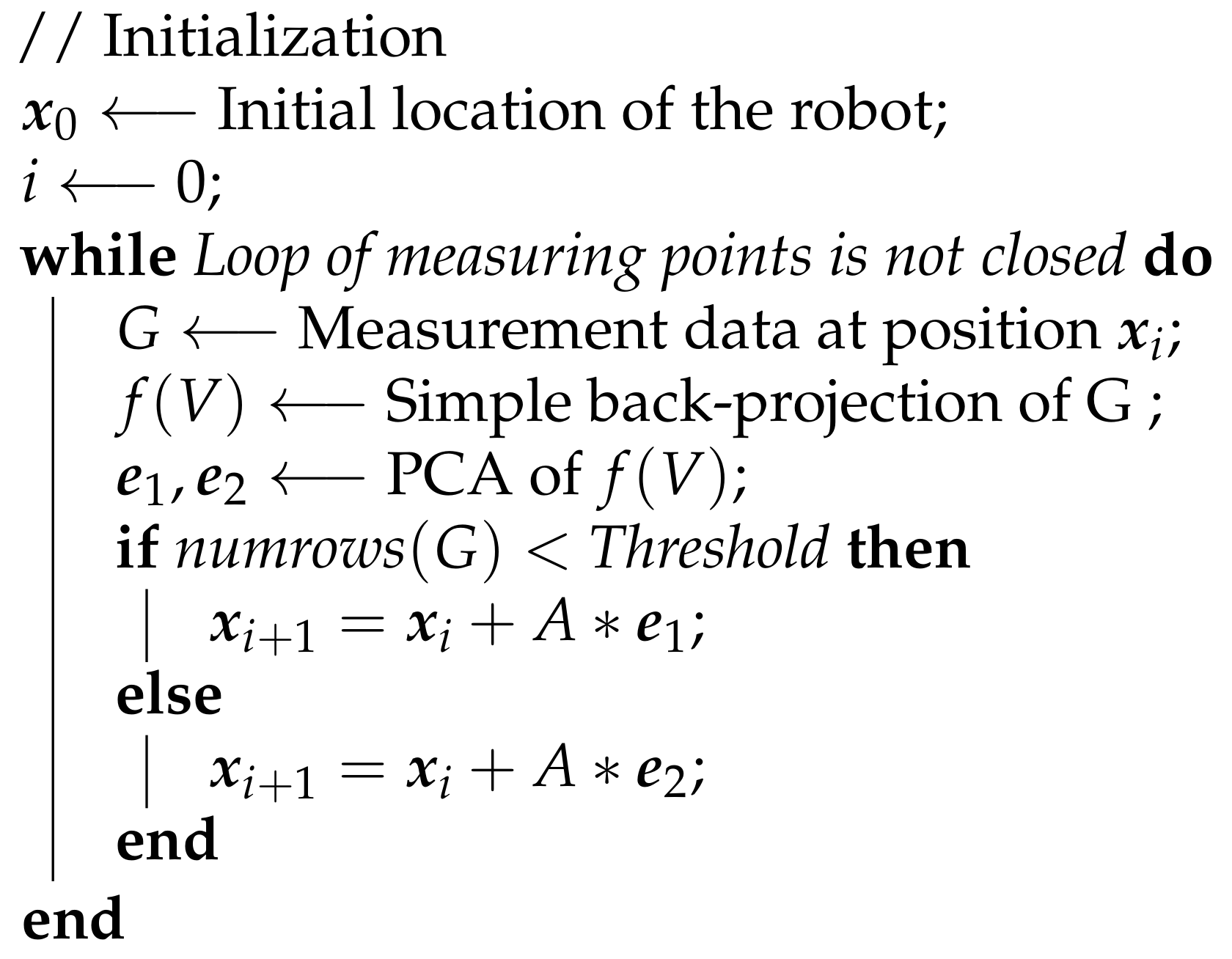 |
2.5. Localization of Multiple Radiation Sources
3. Experiments
3.1. Simulations
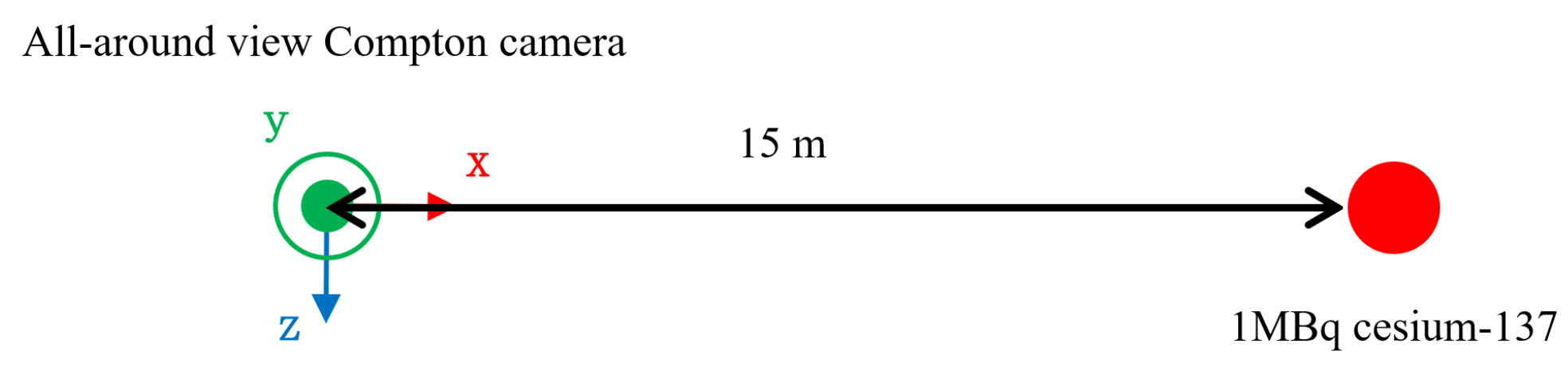
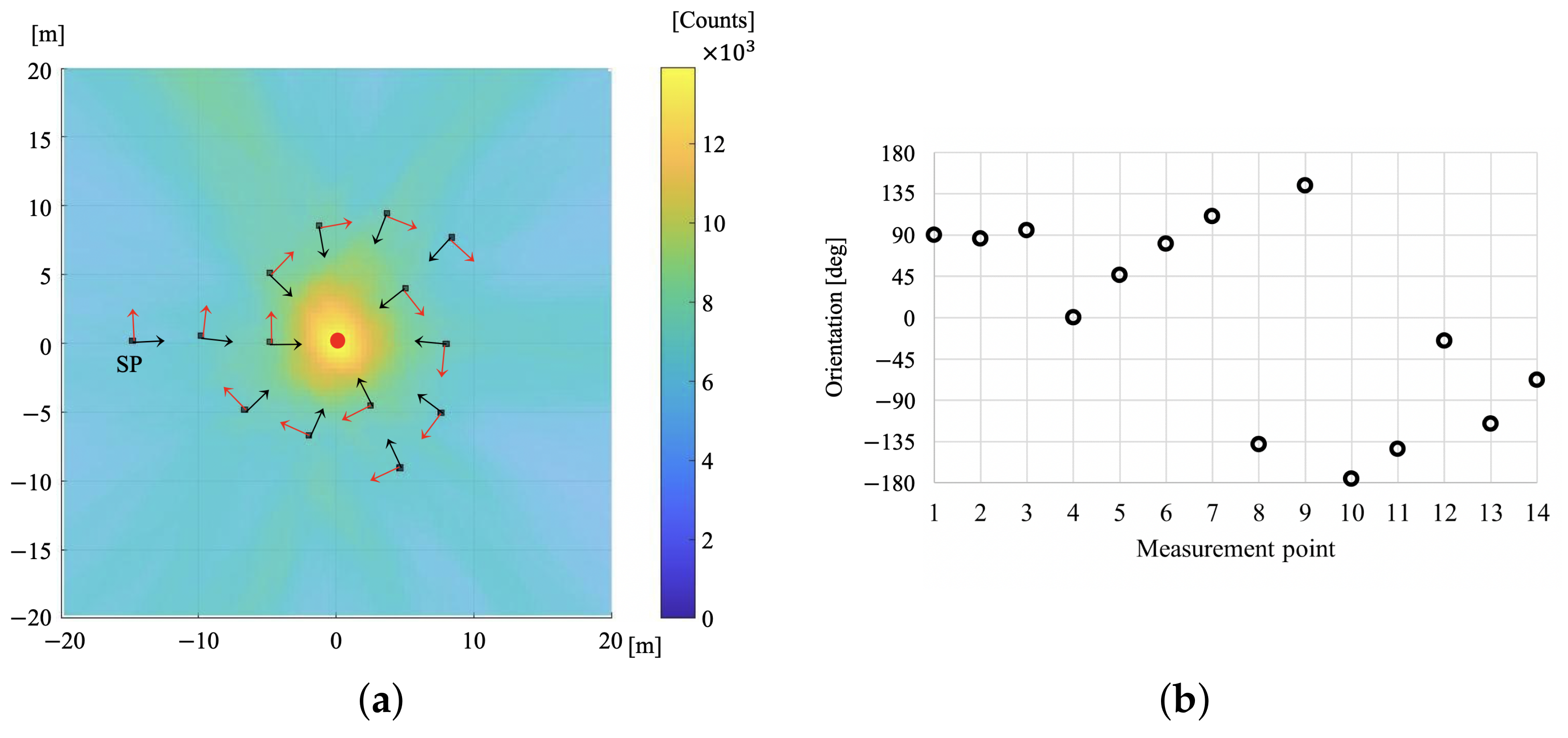
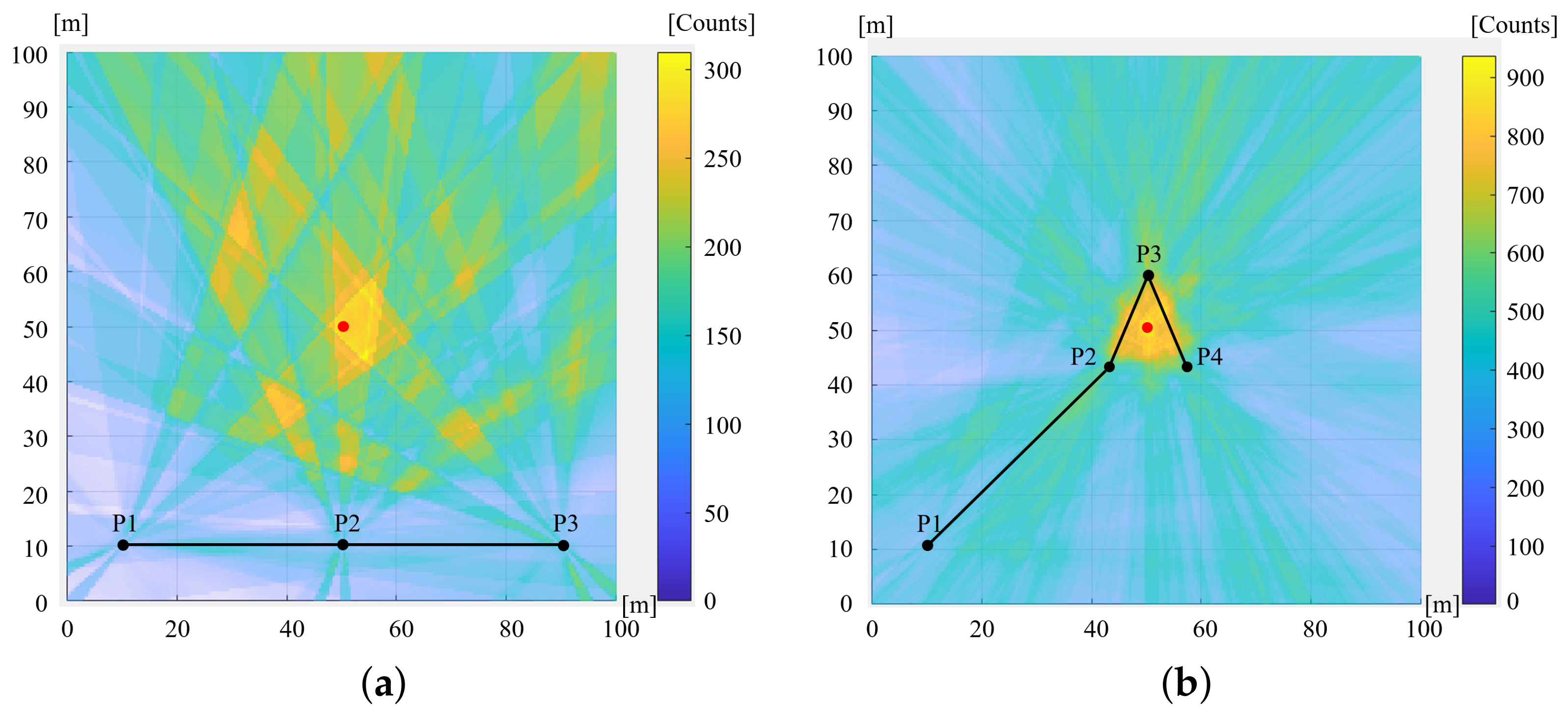
3.1.1. Condition (a) Single Radiation Source
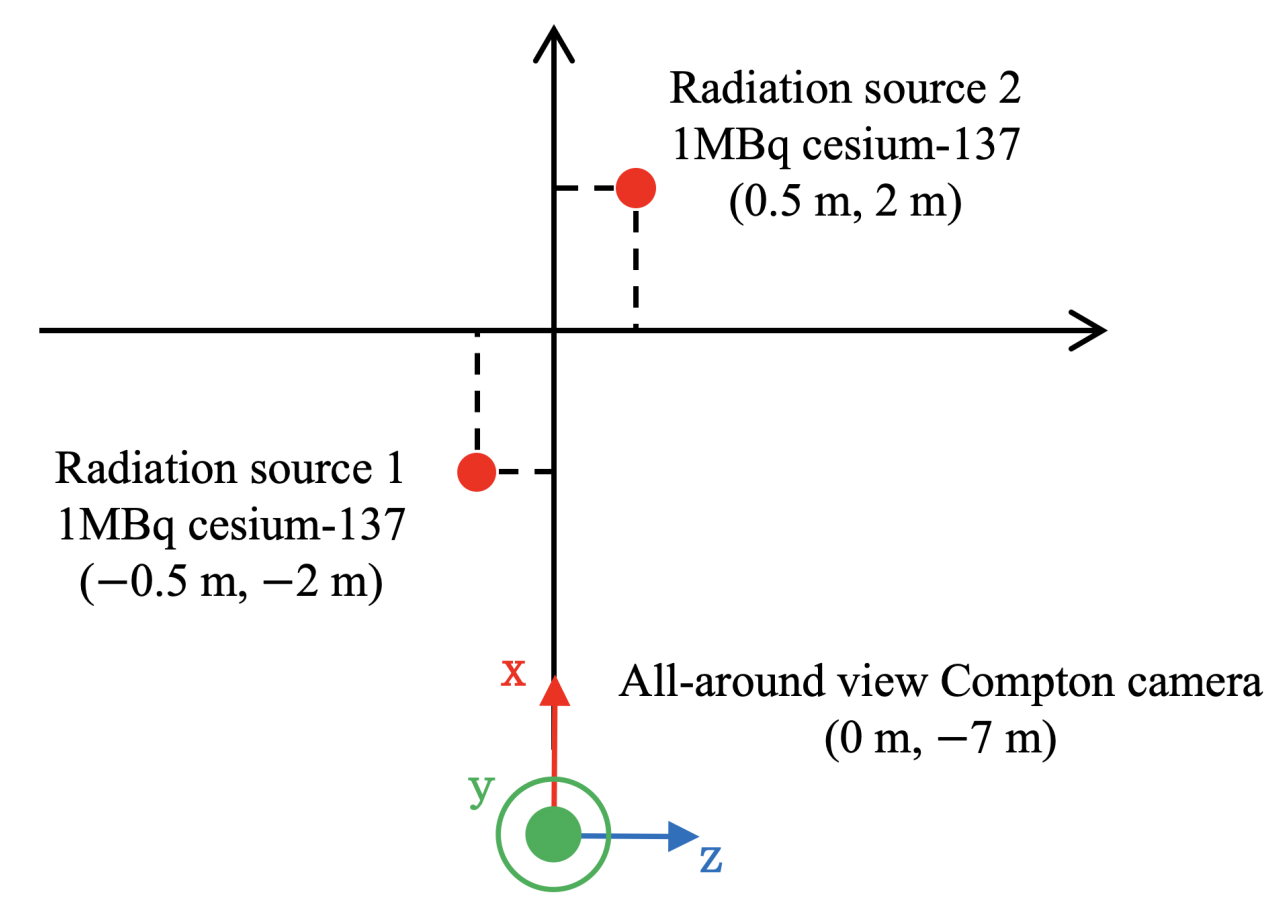
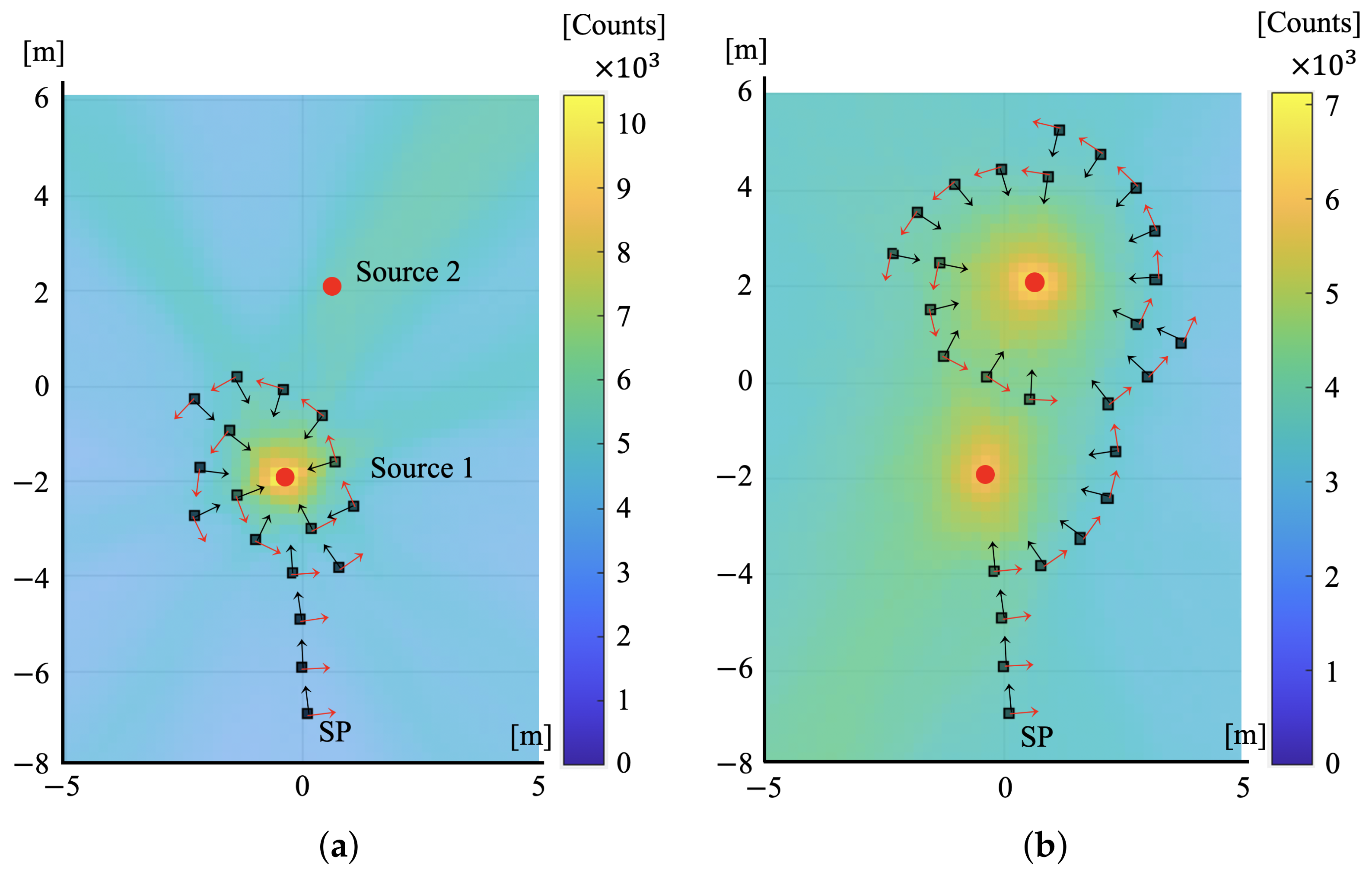
3.1.2. Condition (b) Multiple Radiation Sources Concentrated in a Specific Area
3.1.3. Condition (c) Multiple Radiation Sources Dispersed
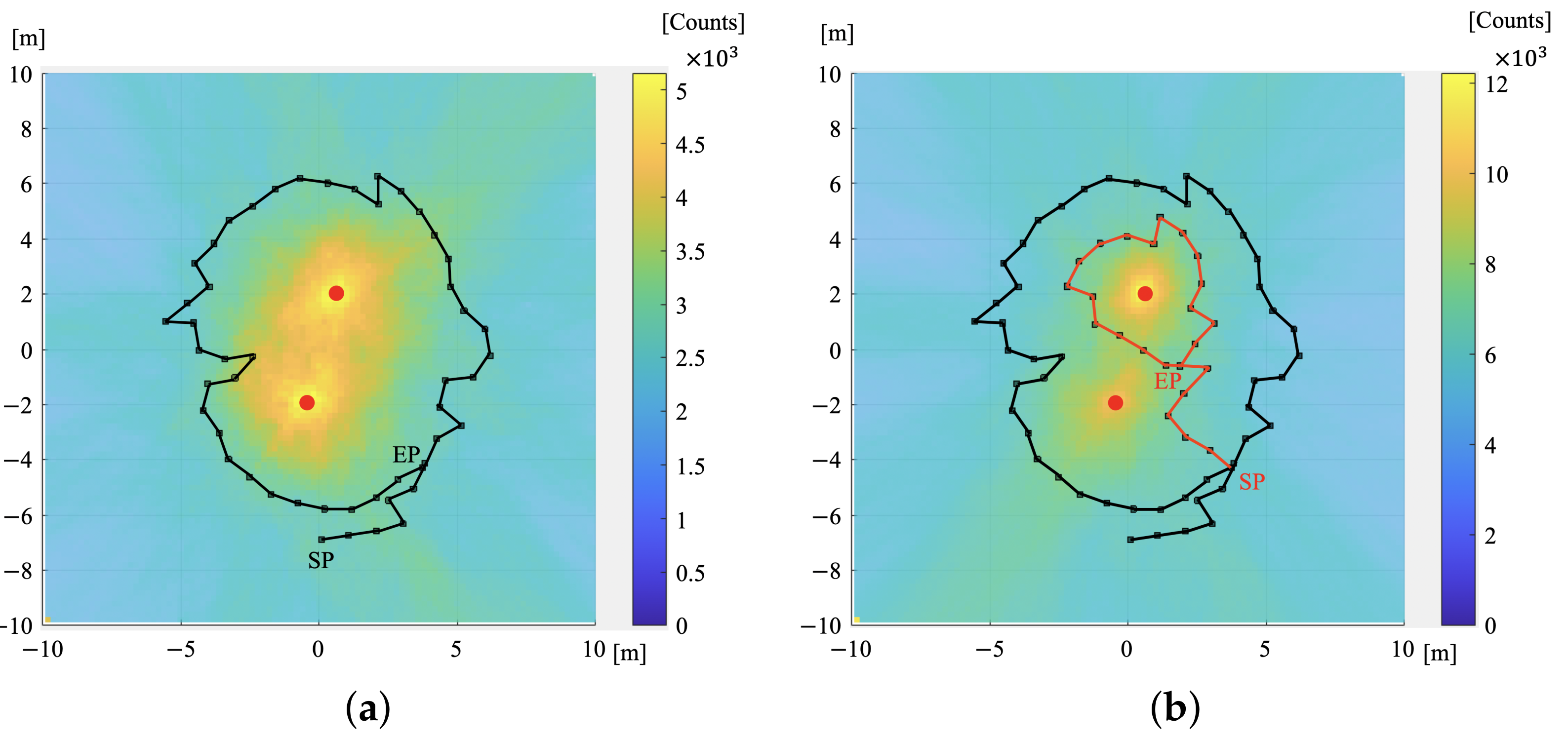
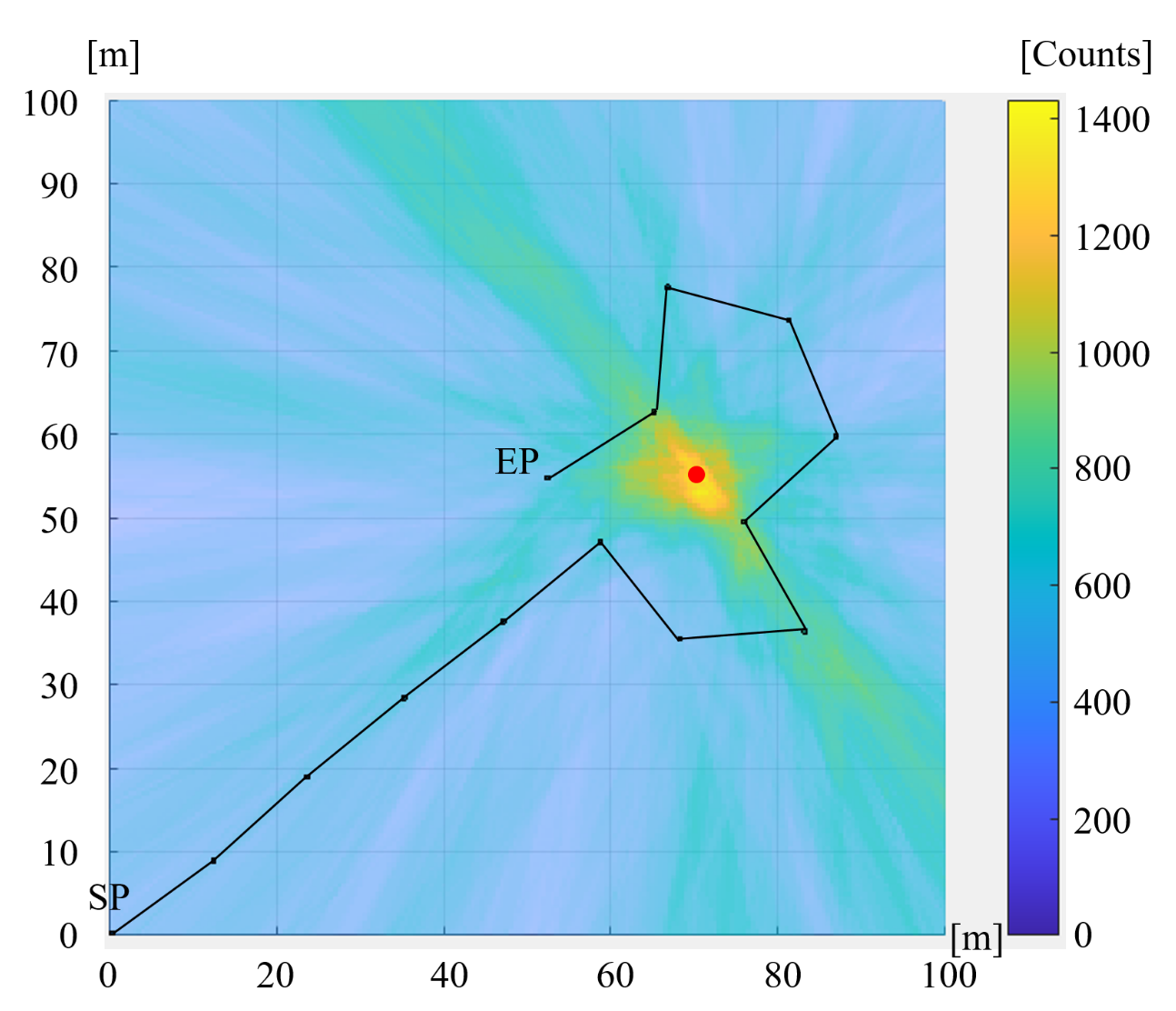
3.1.4. Performance Comparison
3.1.5. Discussion
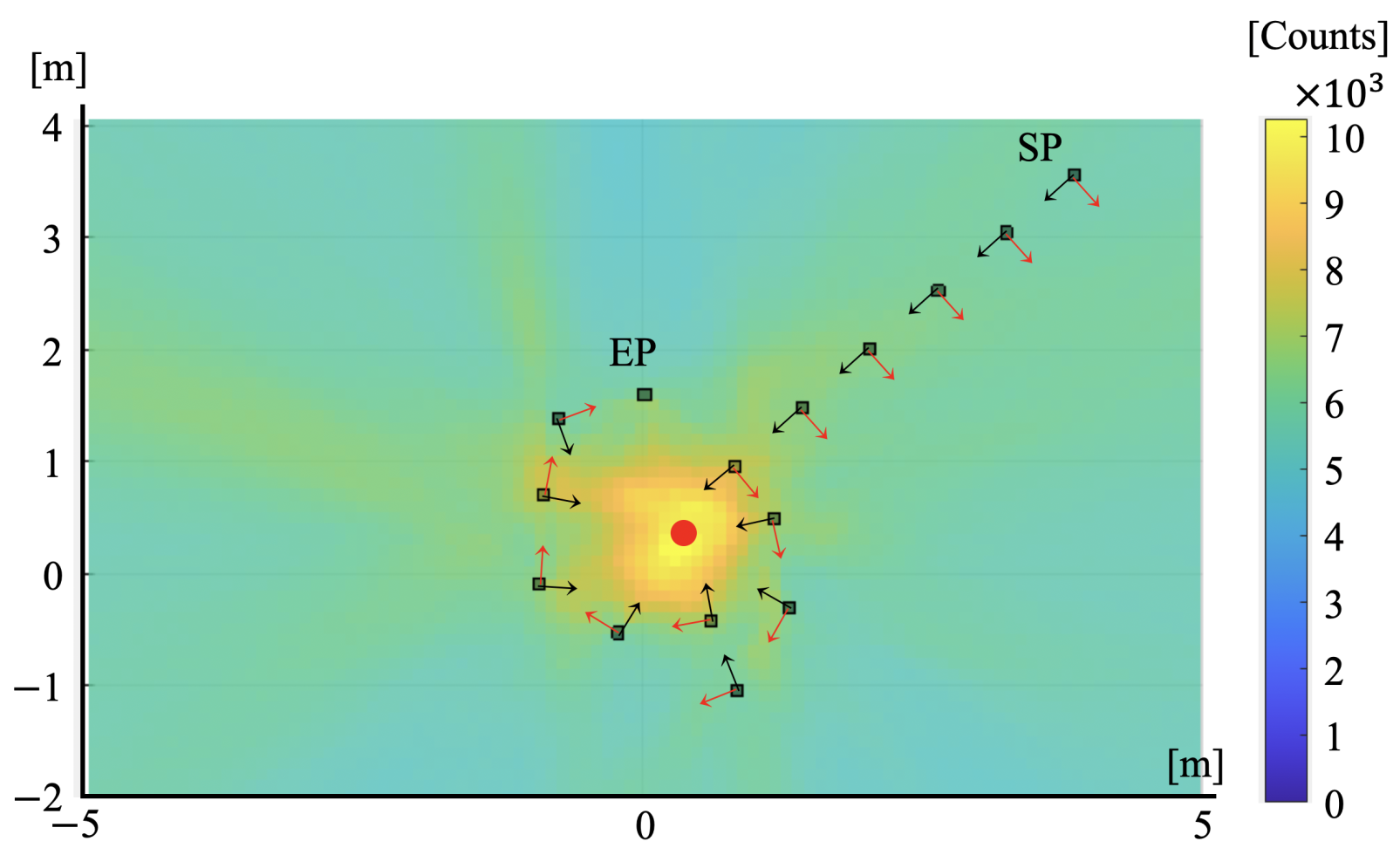
3.2. Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IAEA. Combating Illicit Trafficking in Nuclear and Other Radioactive Material. 2008. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/publications/7806/combating-illicit-trafficking-in-nuclear-and-other-radioactive-material (accessed on 11 March 2021).
- Haefner, A.; Barnowski, R.; Luke, P.; Amman, M.; Vetter, K. Handheld real-time volumetric 3-D gamma-ray imaging. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2017, 857, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatani, K.; Kiribayashi, S.; Okada, Y.; Otake, K.; Yoshida, K.; Tadokoro, S.; Nishimura, T.; Yoshida, T.; Koyanagi, E.; Fukushima, M.; et al. Emergency response to the nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants using mobile rescue robots. J. Field Robot. 2013, 30, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Nagatani, K.; Tadokoro, S.; Nishimura, T.; Koyanagi, E. Improvements to the rescue robot quince toward future indoor surveillance missions in the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Field and Service Robotics, Matsushima, Miyagi, Japan, 16–19 July 2014; pp. 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ziock, K.P.; Goldstein, W.H. The lost source, varying backgrounds and why bigger may not be better. Proc. AIP Conf. 2002, 632, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Klimenko, A.V.; Priedhorsky, W.C.; Hengartner, N.W.; Borozdin, K.N. Efficient strategies for low-statistics nuclear searches. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2006, 53, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.; Oh, H.; Chen, W. Adaptive Bayesian sensor motion planning for hazardous source term reconstruction. IFAC Pap. Online 2017, 50, 2812–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.; Morelande, M.; Gunatilaka, A. Information driven search for point sources of gamma radiation. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 1225–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Abbaszadeh, S. Double Q-learning for radiation source detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Woo, H.; Ji, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Asama, H. 3D radiation imaging using mobile robot equipped with radiation detector. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Taipei, Taiwan, 11–14 December 2017; pp. 444–449. [Google Scholar]
- Shikaze, Y.; Nishizawa, Y.; Sanada, Y.; Torii, T.; Jiang, J.; Shimazoe, K.; Takahashi, H.; Yoshino, M.; Ito, S.; Endo, T.; et al. Field test around Fukishima Daiichi nuclear power plant site using improved Ce:Gd3(Al,Ga)5O12 scintillator Compton camera mounted on an unmanned helicopter. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.; Vale, A.; Vaz, P. State-of-the-Art Mobile Radiation Detection Systems for Different Scenarios. Sensors 2021, 21, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, J.; Kishimoto, A.; Nishiyama, T.; Fujita, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Kato, T.; Nakamori, T.; Ohsuka, S.; Nakamura, S.; Hirayanagi, M.; et al. Handy Compton camera using 3D position-sensitive scintillators coupled with large-area monolithic MPPC arrays. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2013, 732, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Mukai, A.; Kanamori, K.; Shimazoe, K.; Woo, H.; Tamura, Y.; Hara, S.; Terabayashi, R.; Uenomachi, M.; Nurrachman, A.; et al. Gamma-ray source identification by a vehicle-mounted 4π Compton imager. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 January 2020; pp. 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ardiny, H.; Witwicki, S.; Mondada, F. Autonomous Exploration for Radioactive Hotspots Localization Taking Account of Sensor Limitations. Sensors 2019, 19, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, G.F. Radiation Detection Measurement; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarich, F.; Wilson, T.; Papachristos, C.; Alexis, K. Radiation source localization in GPS-denied environments using aerial robots. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 6537–6544. [Google Scholar]
- Hellfeld, D.; Barton, P.; Gunter, D.; Mihailescu, L.; Vetter, K. A spherical active coded aperture for 4π gamma-ray imaging. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017, 64, 2837–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellfeld, D.; Barton, P.; Gunter, D.; Haefner, A.; Mihailescu, L.; Vetter, K. Real-time free-moving active coded mask 3D gamma-ray imaging. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2019, 66, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shimazoe, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Shikaze, Y.; Nishizawa, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Sanada, Y.; Torii, T.; Yoshino, M.; et al. A prototype of aerial radiation monitoring system using an unmanned helicopter mounting a GAGG scintillator Compton camera. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilderman, S.J.; Fessler, J.A.; Clinthorne, N.H.; Rogers, W.L. Improved modeling of system response in list mode EM reconstruction of Compton scatter camera images. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2001, 48, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.; McCormick, N.J. Identification of low-level point radiation sources using a sensor network. Transp. Theory Stat. Phys. 2008, 37, 236–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hite, J.M.; Mattingly, J.K.; Schmidt, K.L.; Stefanescu, R.; Smith, R. Bayesian metropolis methods applied to sensor networks for radiation source localization. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, Baden-Baden, Germany, 19–21 September 2016; pp. 389–393. [Google Scholar]
- Jarman, K.D.; Miller, E.A.; Wittman, R.S.; Gesh, C.J. Bayesian radiation source Localization. Nucl. Technol. 2011, 175, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, H.H.; White, T.; Parra, L.C. List-mode likelihood. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1997, 14, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, L.; Barrett, H.H. List-mode likelihood: EM algorithm and image quality estimation demonstrated On 2-D PET. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, S.; Allison, J.; Amak, K.; Apostolakis, J.; Araujo, H.; Arcel, P.; Asai, M.; Axen, D.; Banerjee, S.; Barrand, G.; et al. Geant4-a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2003, 506, 250–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.; Amako, K.; Apostolakis, J.; Araujo, H.; Dubois, P.A.; Asai, M.; Barrand, G.; Capra, R.; Chauvie, S.; Chytracek, R.; et al. Geant4 developments and applications. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2006, 53, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amako, K.; Guatelli, S.; Ivanchencko, V.; Maire, M.; Mascialino, B.; Murakami, K.; Pandola, L.; Parlati, S.; Pia, M.; Piergentili, M.; et al. Validation of Geant4 electromagnetic physics versus protocol data. Proc. IEEE Symp. Conf. Rec. Nucl. Sci. 2004, 4, 2115–2119. [Google Scholar]
- Adept MobileRobots, Pioneer-3DX. Available online: https://www.generationrobots.com/media/Pioneer3DX-P3DX-RevA.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2021).


| Information-Driven [8] | Uniform Deterministic [8] | Proposed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of measurement points | 24 | 20 | 14 |
| Localization error in X [m] | 0.75 | 3.55 | 0.10 |
| Localization error in Y [m] | 0.72 | 2.18 | 0.69 |
| Total measurement time [s] | 89.9 | 90.1 | 242 |
| Path (a) | Path (b) | |
|---|---|---|
| Localization error in X [m] | 3.10 | 0.33 |
| Localization error in Y [m] | 0.27 | 0.09 |
| Total measurement time [s] | 80 | 35 |
| Total moving distance [m] | 80 | 83.4 |
| Total search time [s] | 160 | 118.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kishimoto, T.; Woo, H.; Komatsu, R.; Tamura, Y.; Tomita, H.; Shimazoe, K.; Yamashita, A.; Asama, H. Path Planning for Localization of Radiation Sources Based on Principal Component Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104707
Kishimoto T, Woo H, Komatsu R, Tamura Y, Tomita H, Shimazoe K, Yamashita A, Asama H. Path Planning for Localization of Radiation Sources Based on Principal Component Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104707
Chicago/Turabian StyleKishimoto, Takuya, Hanwool Woo, Ren Komatsu, Yusuke Tamura, Hideki Tomita, Kenji Shimazoe, Atsushi Yamashita, and Hajime Asama. 2021. "Path Planning for Localization of Radiation Sources Based on Principal Component Analysis" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104707
APA StyleKishimoto, T., Woo, H., Komatsu, R., Tamura, Y., Tomita, H., Shimazoe, K., Yamashita, A., & Asama, H. (2021). Path Planning for Localization of Radiation Sources Based on Principal Component Analysis. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104707








