Magnetic Resonance-Electrical Properties Tomography by Directly Solving Maxwell’s Curl Equations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Method
2.1. GPU-Accelerated FDTD Solver
2.2. Optimization
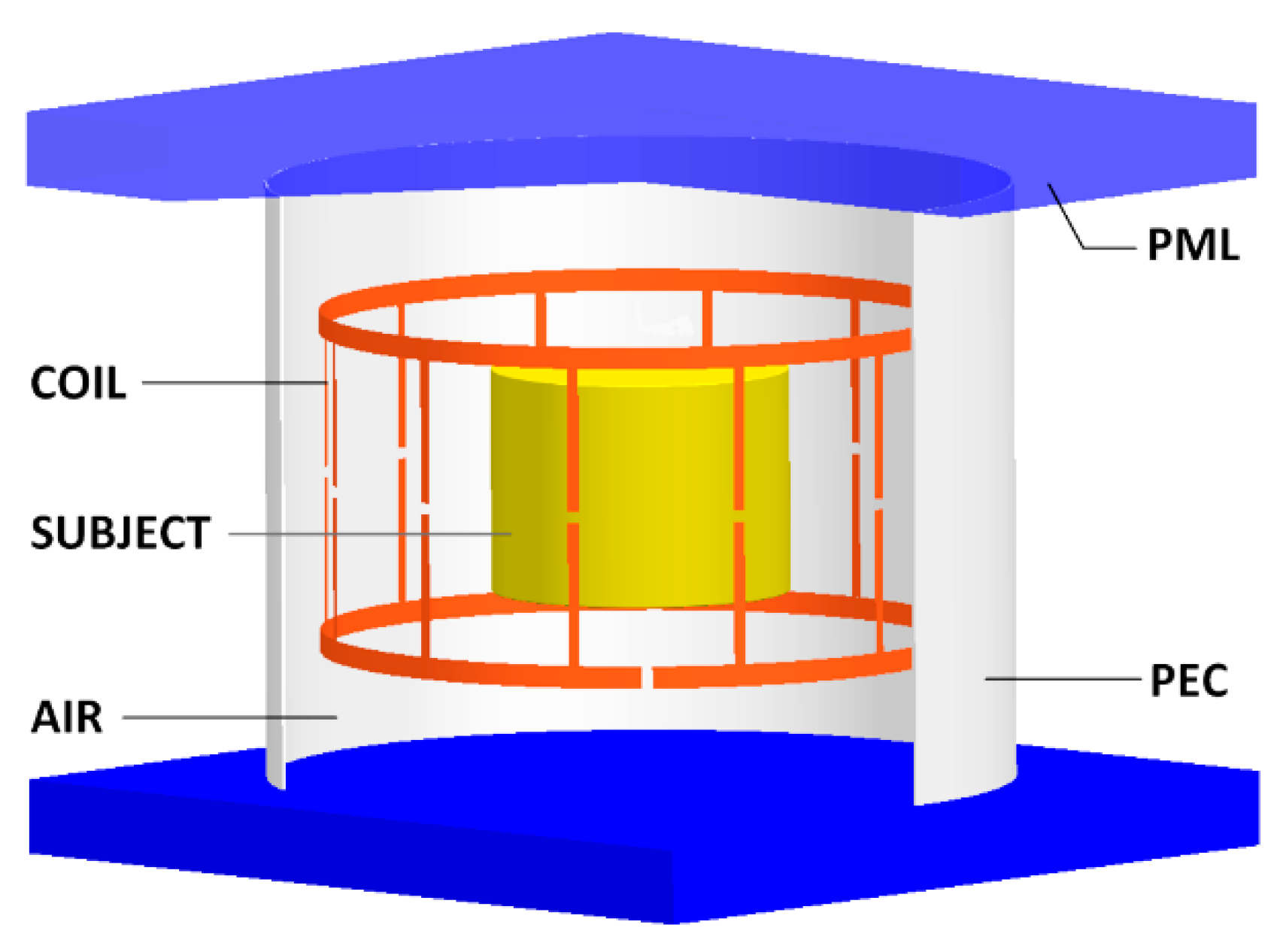
2.3. Simulation Study
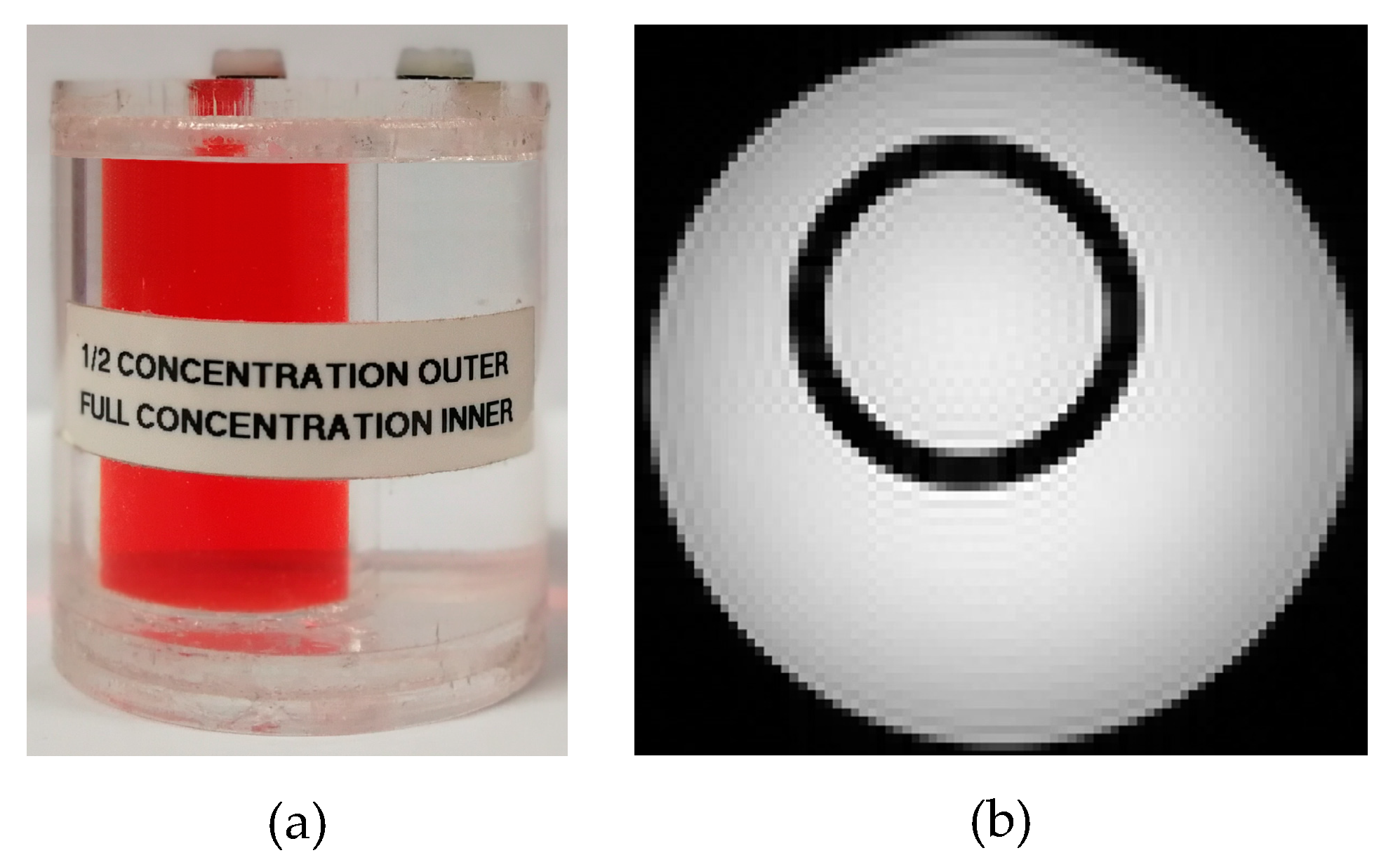
2.4. Experimental Setup
3. Results
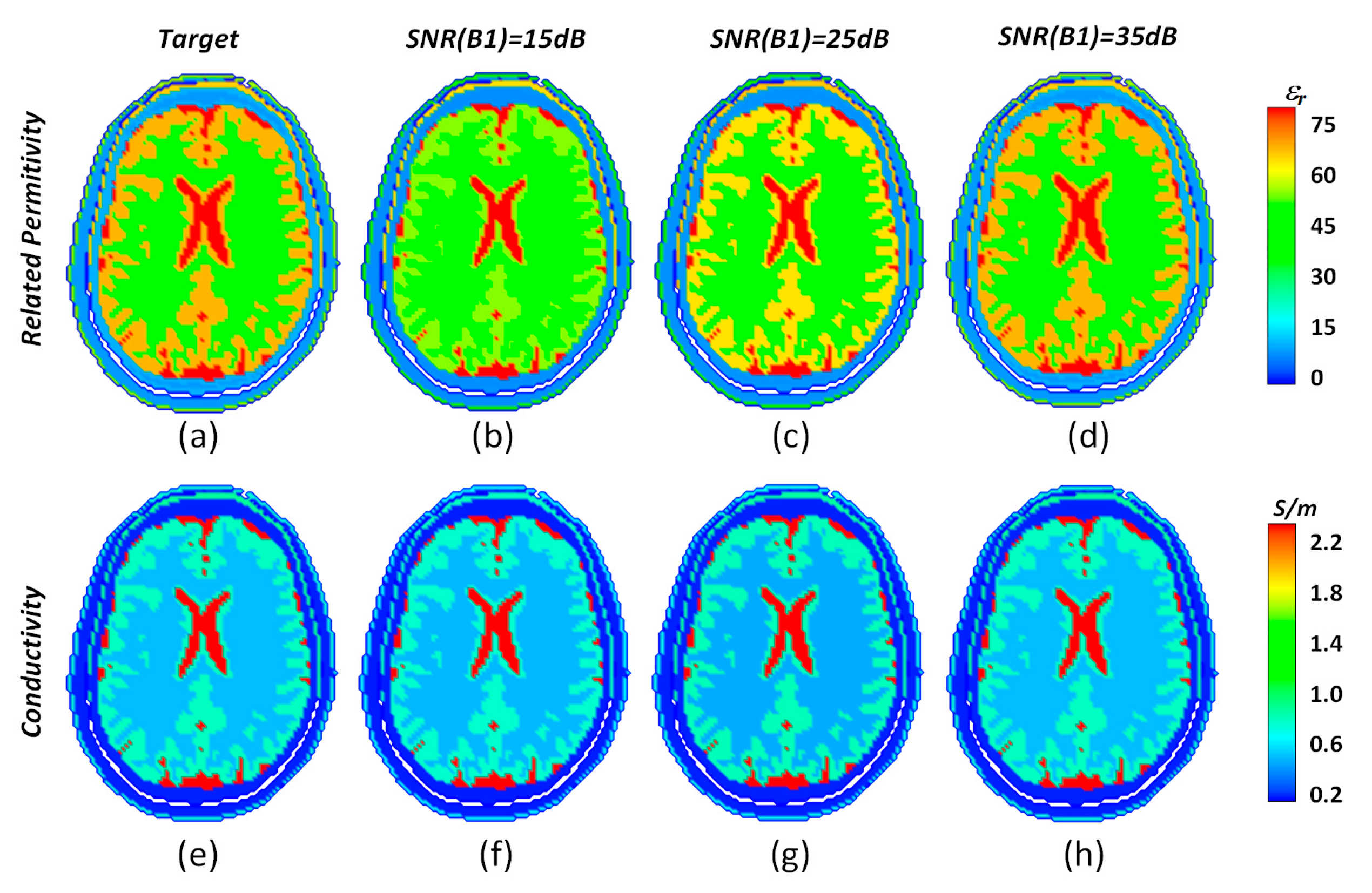
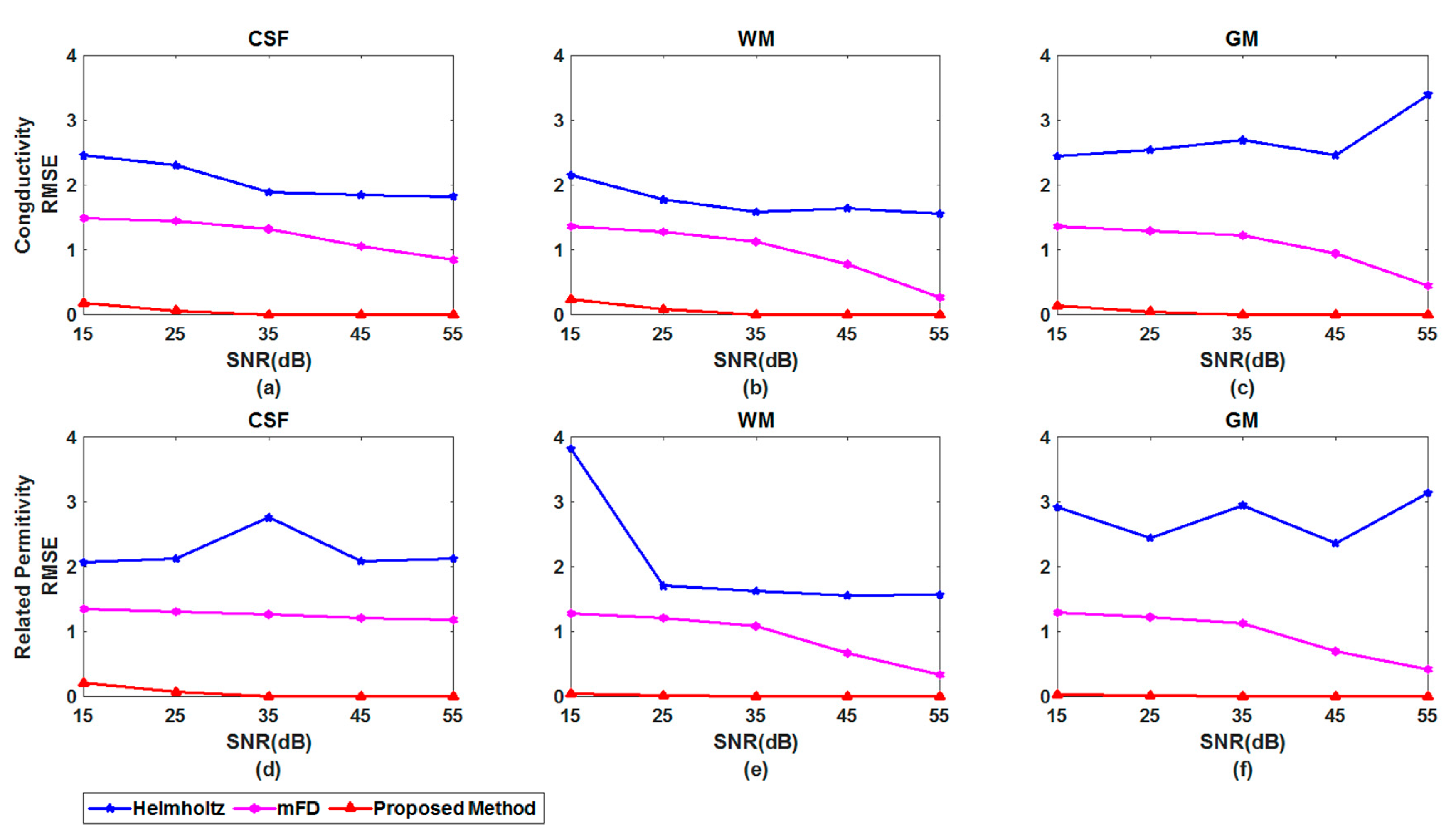
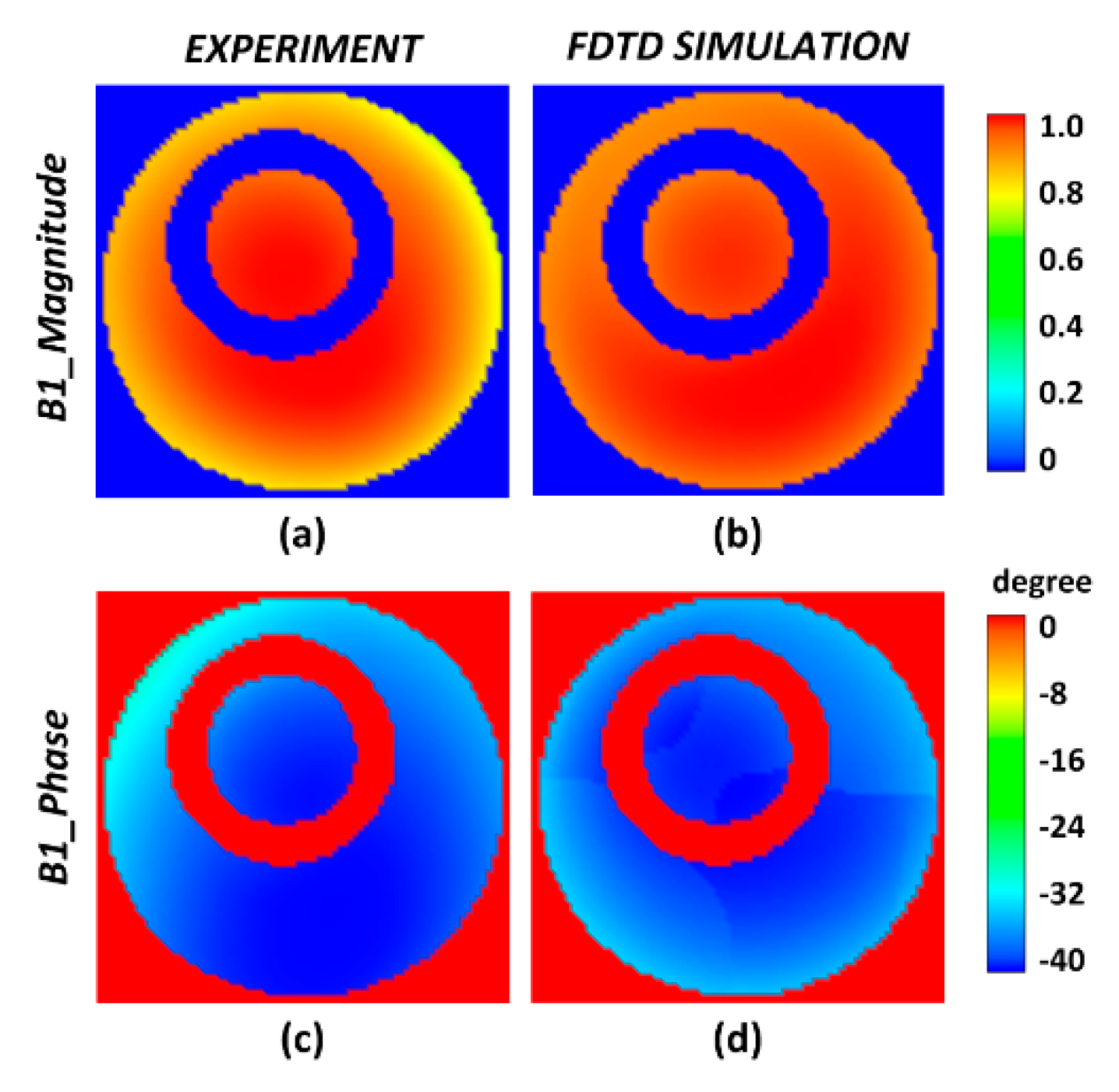
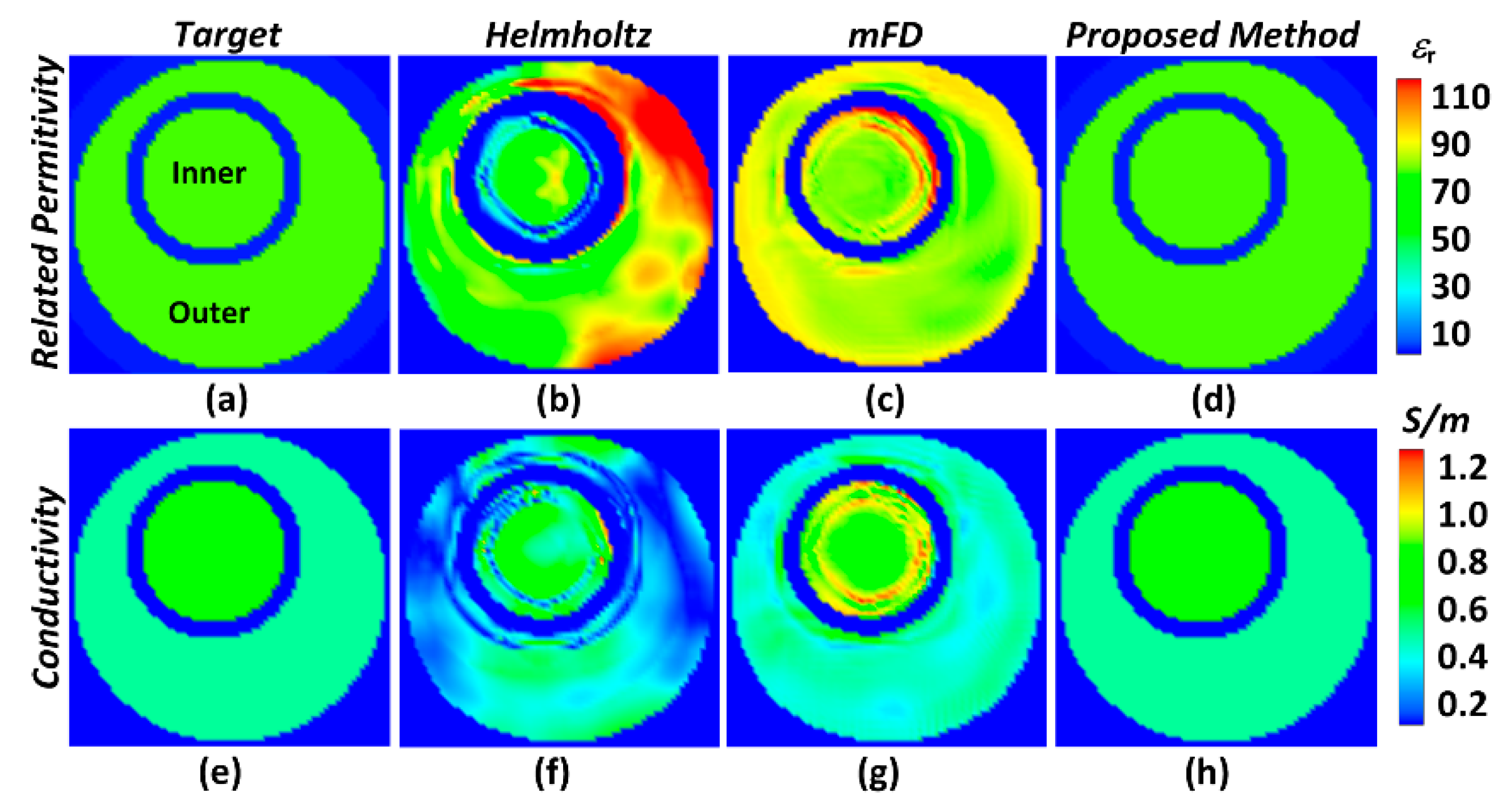
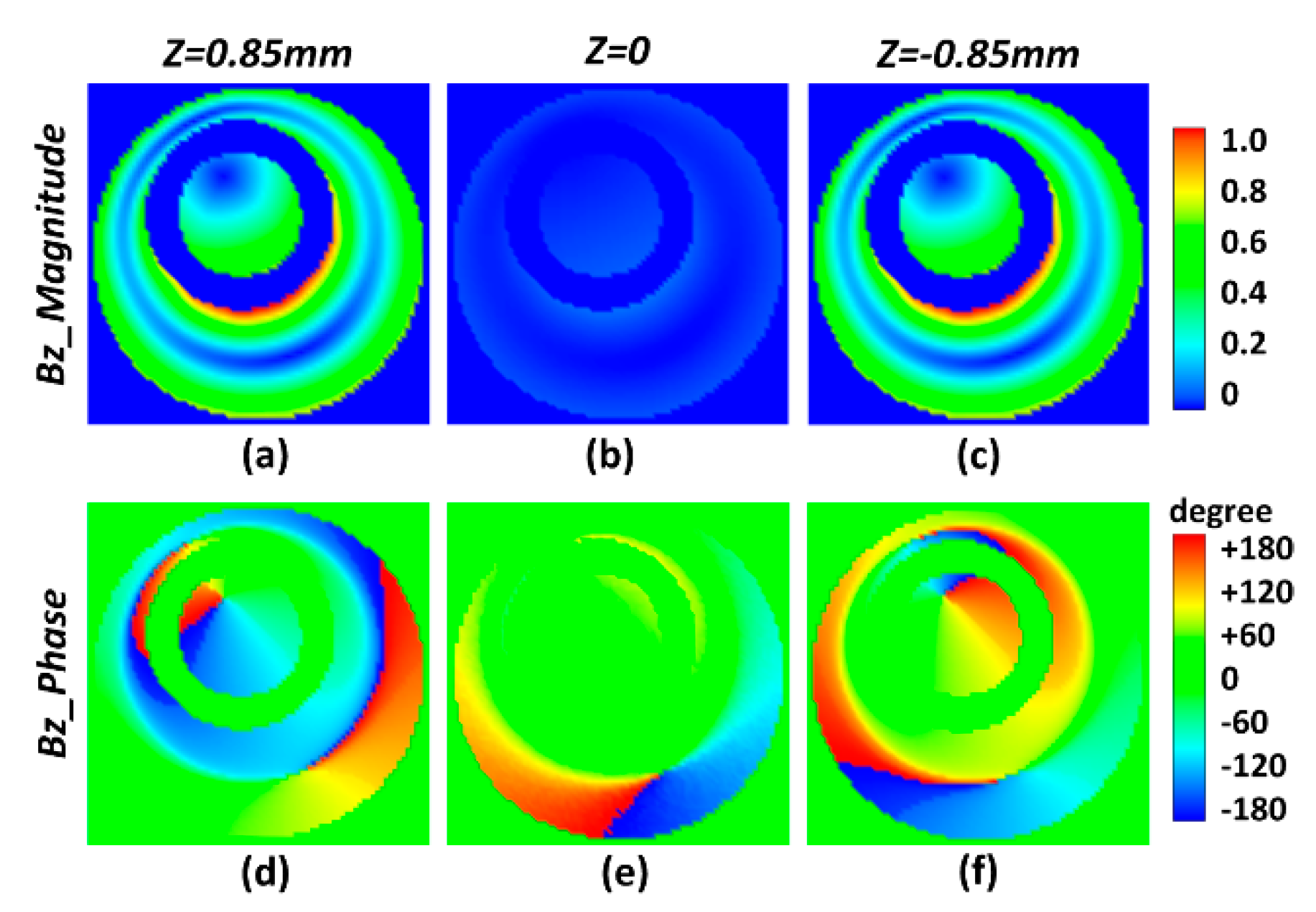
3.1. Simulation Results
3.2. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages of the Proposed Method
4.2. Limitations of the Proposed Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, C.M.; Liu, W.Z.; Wang, J.H.; Gruetter, R.; Vaughan, J.T.; Ugurbil, K.; Smith, M.B. Temperature and SAR calculations for a human head within volume and surface coils at 64 and 300 MHz. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 19, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberg, P.; Nicander, I.; Hansson, J.; Geladi, P.; Holmgren, U.; Ollmar, S. Skin cancer identification using multifrequency electrical impedance-a potential screening tool. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halter, R.; Schned, A.; Heaney, J.; Hartov, A.; Schutz, S. and Paulsen, K. Electrical impedance spectroscopy of benign and malignant prostatic tissues. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balidemaj, E.; Kok, H.; Schooneveldt, G.; Van Lier, A.; Remis, R.; Stalpers, L.; Westerveld, H.; Nederveen, A.; van den Berg, C.; Crezee, J. Hyperthermia treatment planning for cervical cancer patients based on electrical conductivity tissue properties acquired in vivo with EPT at 3T MRI. Int. J. Hyperther. 2016, 32, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haacke, E.; Petropoulos, L.; Nilges, E.; Wu, D. Extraction of conductivity and permittivity using magnetic resonance imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 1991, 36, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H. Noninvasive quantitative mapping of conductivity and dielectric distributions using RF wave propagation effects in high-field MRI. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2003 Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–20 February 2003; pp. 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Katscher, U.; Voigt, T.; Findeklee, C.; Vernickel, P.; Nehrke, K.; Dossel, O. Determination of electric conductivity and local SAR via B1 mapping. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 28, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, T.; Katscher, U.; Doessel, O. Quantitative conductivity and permittivity imaging of the human brain using electric properties tomography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Choi, N.; Woo, E.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.; Kim, D. Error analysis of nonconstant admittivity for MR-based electric property imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katscher, U.; Kim, D.; Seo, J. Recent progress and future challenges in MR electric properties tomography. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsic, A.; Perreard, I.; Mahara, A.; Halter, R. An inverse problems approach to MR-EPT image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropella, K.; Noll, D. A regularized, model-based approach to phase-based conductivity mapping using MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 78, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Van de Moortele, P.; Schmitter, S.; He, B. Complex B1 mapping and electrical properties imaging of the human brain using a 16-channel transceiver coil at 7T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Kim, M.; Cho, S.; Kim, D. Fast spin echo imaging based electric property tomography with k-space weighting via T2 relaxation (rEPT). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Bulumulla, S.; Hancu, I. Theoretical investigation of random noise-limited signal-to-noise ratio in MR-based electrical properties tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Adriany, G.; Bischof, J.; Van de Moortele, P.; He, B. In vivo imaging of electrical properties of an animal tumor model with an 8-channel transceiver array at 7T using electrical properties tomography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Schmitter, S.; Moortele, P.; He, B. Gradient-based electrical properties tomography (gEPT): A robust method for mapping electrical properties of biological tissues in vivo using magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jin, J.; Guo, L.; Li, M.; Tesiram, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, F.; Xin, X.; Crozier, S. MR-based electrical property tomography using a modified finite difference scheme. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurler, N.; Ider, Y. Gradient-based electrical conductivity imaging using MR phase. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 77, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafalir, F.; Oran, O.; Gurler, N.; Ider, Y. Convection-reaction equation based magnetic resonance electrical properties tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Van de Moorele, P.; He, B. Contrast conformed electrical properties tomography (CONCEPT) based on multi-channel transmission and alternating direction method of multipliers. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 99, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Webb, A. A new approach for electrical properties estimation using a global integral equation and improvements using high permittivity materials. J. Magn. Reson. 2016, 262, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leijsen, R.; Brink, W.; van den Berg, C.; Webb, A.; Remis, R. 3-D contrast source inversion-electrical properties tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Jin, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Crozier, S. An efficient integral-based method for three-dimensional MR-EPT and the calculation of the RF-coil induced Bz field. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Jin, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Crozier, S. Reference-based integral MR-EPT: Simulation and experiment studies on the 9.4T MRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q. 3-D MRI-Based Electrical Properties Tomography Using the Volume Integral Equation Method. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 4802–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenius, E.; Strand, B. Solving inverse electromagnetic problems using FDTD and gradient-based minimization. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 2006, 68, 650–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, T.; Tanaka, T.; Harada, H.; He, S. FDTD approach to time-domain inverse scattering problem for stratified lossy media. Microw. Opt. Techn. Let. 1997, 16, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Liu, F.; Weber, E.; Li, Y.; Crozier, S. GPU-accelerated FDTD modeling of radio-frequency field-tissue interactions in high-field MRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Taflove, A.; Hagness, S. Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method, 3rd ed.; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hoult, D. The principle of reciprocity in signal strength calculations—A mathematical guide. Concepts Magn. Reson. 2000, 12, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, C.; Wolfgang, K.; Eckhart, G.; Katharina, H.; Marcel, Z.; Esra, N.; Rascher, W.; Janka, R.; Bautz, W.; Chen, J. The virtual family-development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys. Med. Biology. 2010, 55, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Joines, W.; Dhenxing, Y.; Jirtle, R. The measured electrical properties of normal and malignant human tissues from 50 to 900 MHz. Med. Phys. 1994, 21, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, O.; Raya, J.G.; Reeder, S.B.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: Influence of multi-channel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2007, 26, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoka, S.; Franconi, F.; Seguin, F.; Pape, A. Radiofrequency map of an NMR coil by imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1993, 11, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.; Pauly, J.; Nayak, K. Saturated double-angle method for rapid mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 55, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lier, A.; Brunner, D.; Pruessmann, K.; Klomp, D.; Luijten, P.; Lagendijk, J.; van den Berg, C. B1+ phase mapping at 7T and its application for in vivo electrical conductivity mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ider, Y.; Boga, C. Inverse problem approach to cr-MREPT. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 27th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–16 May 2019. abstract number 5052. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimov1, A.; Litman, A.; Ferrand, G. MRI-based electric properties tomography with a quasi-Newton approach. Inv. Prob. 2017, 33, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, C.; Chandrasekharan, A.; Sundararaman, V.; Alex, Z. Neonatal brain MRI segmentation: A review. Comput. Biol. Medicine. 2015, 64, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despotovic, I.; Goossens, B.; Philips, W. MRI segmentation of the human brain: Challenges, methods, and applications. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Beck, B.; Xu, B.; Fitzsimmons, J.; Blackband, S.; Crozier, S. Numerical modelling of 11.1 T MRI of a human head using a MoM/FDTD method. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2005, 24, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Liu, F.; Weber, E.; Crozier, S. Improving SAR estimations in MRI using subject-specific models. Phys. Biol. Med. 2012, 57, 8153–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SNR | Inner | Outer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| εr | σ(S/m) | εr | σ | |
| Target | 78.5 | 0.43 | 78.5 | 0.78 |
| Noise-free | 78 | 0.4309 | 78 | 0.7784 |
| SNR = 15 | 77 | 0.4428 | 79 | 0.7644 |
| SNR = 25 | 77 | 0.4212 | 78 | 0.7918 |
| SNR = 35 | 78 | 0.4278 | 78 | 0.7843 |
| SNR = 45 | 78 | 0.4326 | 78 | 0.7762 |
| SNR = 55 | 78 | 0.4322 | 78 | 0.7824 |
| Compartment | Probe Measurement | Reconstructed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inner | εr | 78.5 | 78 |
| σ | 0.78 | 0.7768 | |
| Outer | εr | 78.5 | 78 |
| σ | 0.43 | 0.4324 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, J.; Guo, L.; Destruel, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Weber, E.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Xin, X.; et al. Magnetic Resonance-Electrical Properties Tomography by Directly Solving Maxwell’s Curl Equations. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093318
Chi J, Guo L, Destruel A, Wang Y, Liu C, Li M, Weber E, Liu Q, Yang J, Xin X, et al. Magnetic Resonance-Electrical Properties Tomography by Directly Solving Maxwell’s Curl Equations. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(9):3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093318
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Jieru, Lei Guo, Aurelien Destruel, Yaohui Wang, Chunyi Liu, Mingyan Li, Ewald Weber, Qinghuo Liu, Jie Yang, Xuegang Xin, and et al. 2020. "Magnetic Resonance-Electrical Properties Tomography by Directly Solving Maxwell’s Curl Equations" Applied Sciences 10, no. 9: 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093318
APA StyleChi, J., Guo, L., Destruel, A., Wang, Y., Liu, C., Li, M., Weber, E., Liu, Q., Yang, J., Xin, X., & Liu, F. (2020). Magnetic Resonance-Electrical Properties Tomography by Directly Solving Maxwell’s Curl Equations. Applied Sciences, 10(9), 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093318






