Sparse Low-Rank Based Signal Analysis Method for Bearing Fault Feature Extraction
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- A fault information-based sparse low-rank algorithm (FISLRA) is proposed and applied for fault feature extraction of rolling bearing.
- 2.
- A correlated kurtosis-based thresholding (CKT) scheme is proposed and it is incorporated to solve the proposed low-rank spare model.
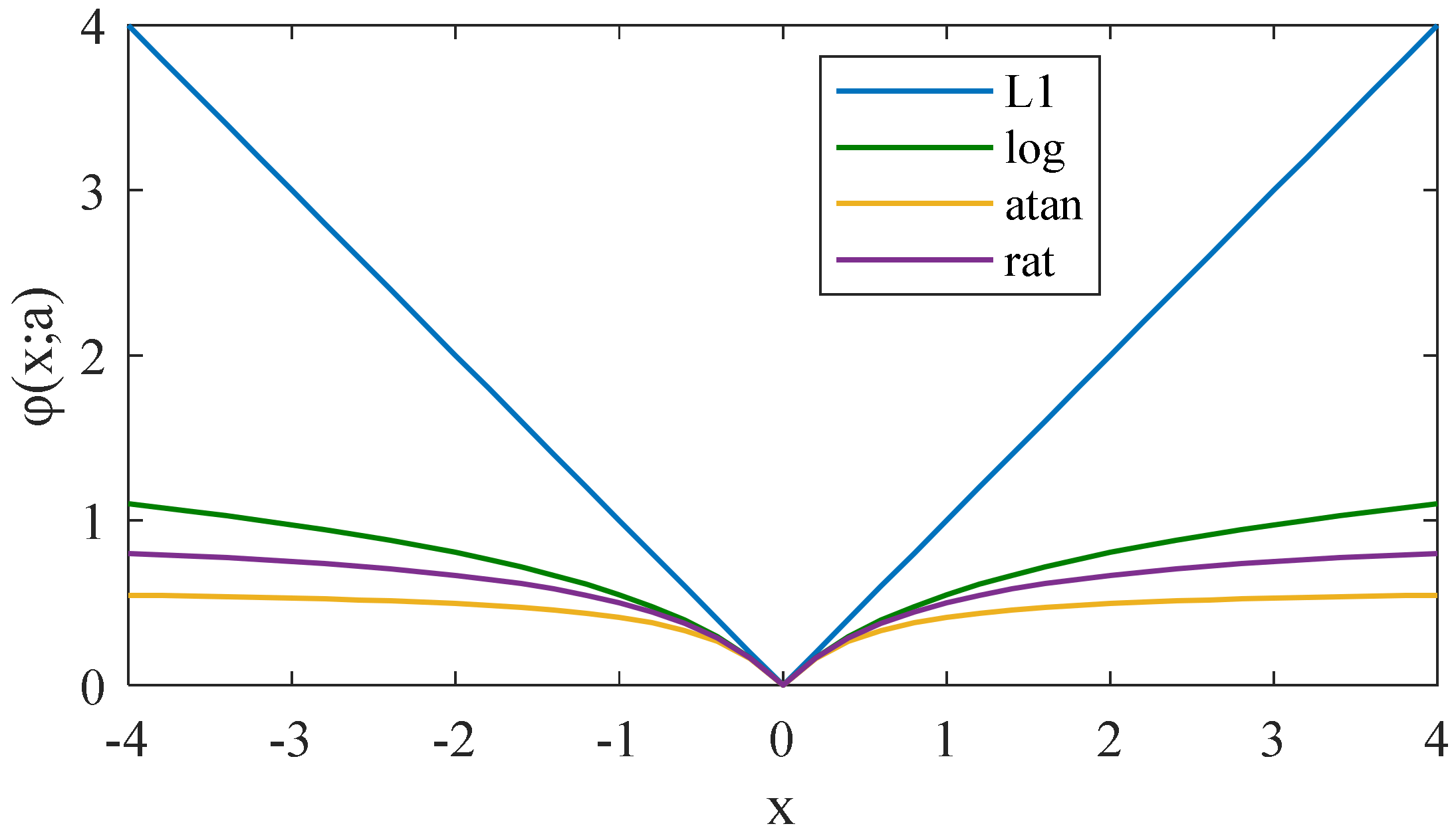
2. Prior Knowledge of Sparsity and Low-Rank Characteristic
3. The Proposed Fault Information-Based Sparse Low-Rank Algorithm
3.1. Convexity Condition
3.2. Algorithm Derivation
3.3. Correlated Kurtosis-Based Thresholding (CKT) Scheme Proposed in This Paper
| Algorithm 1. Algorithm of fault information-based sparse low-rank algorithm (FISLRA) for bearing fault feature extraction |
| Require: Raw signal y needs to be converted into a matrix Y through the STFT operator AT and maximum iteration number I is set. |
| 1. Input: Y, λ1, μ, a, k |
| 2. Initialization: X, Z, D |
| 3. for i ≤ I do |
| 4. |
| 5. |
| 6. Calculate CK value of each component of X |
| 7. |
| 8. |
| 9. End |
| 10. Output: X |
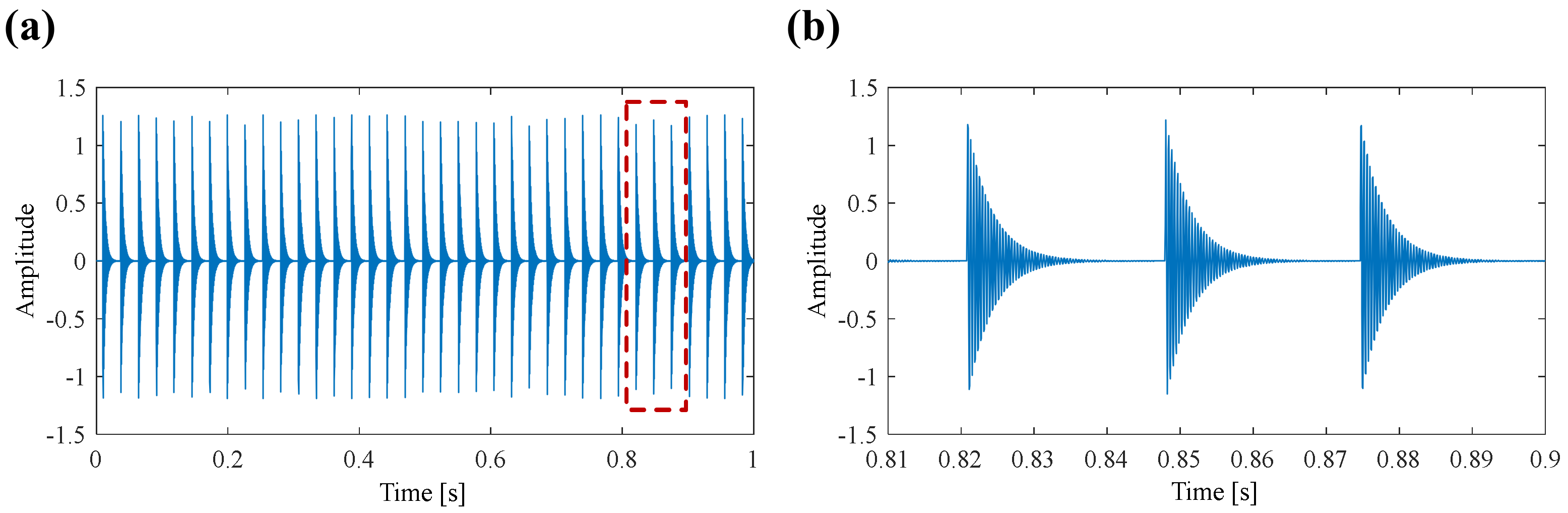
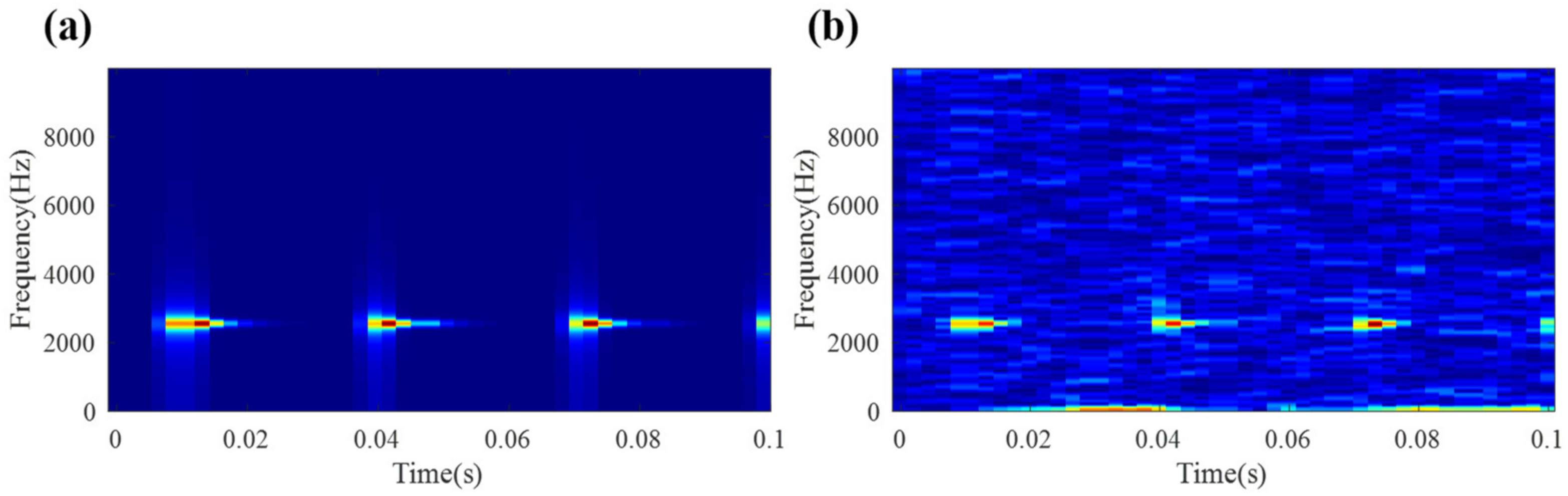
4. Simulation Analysis
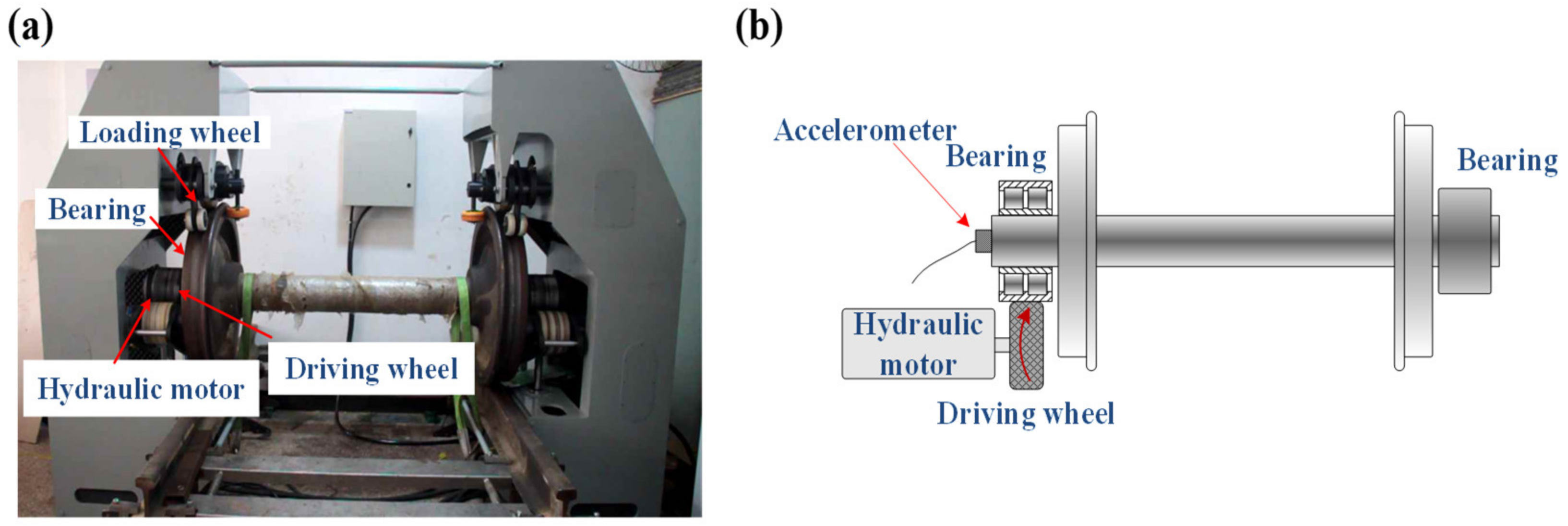
5. Experimental Verification
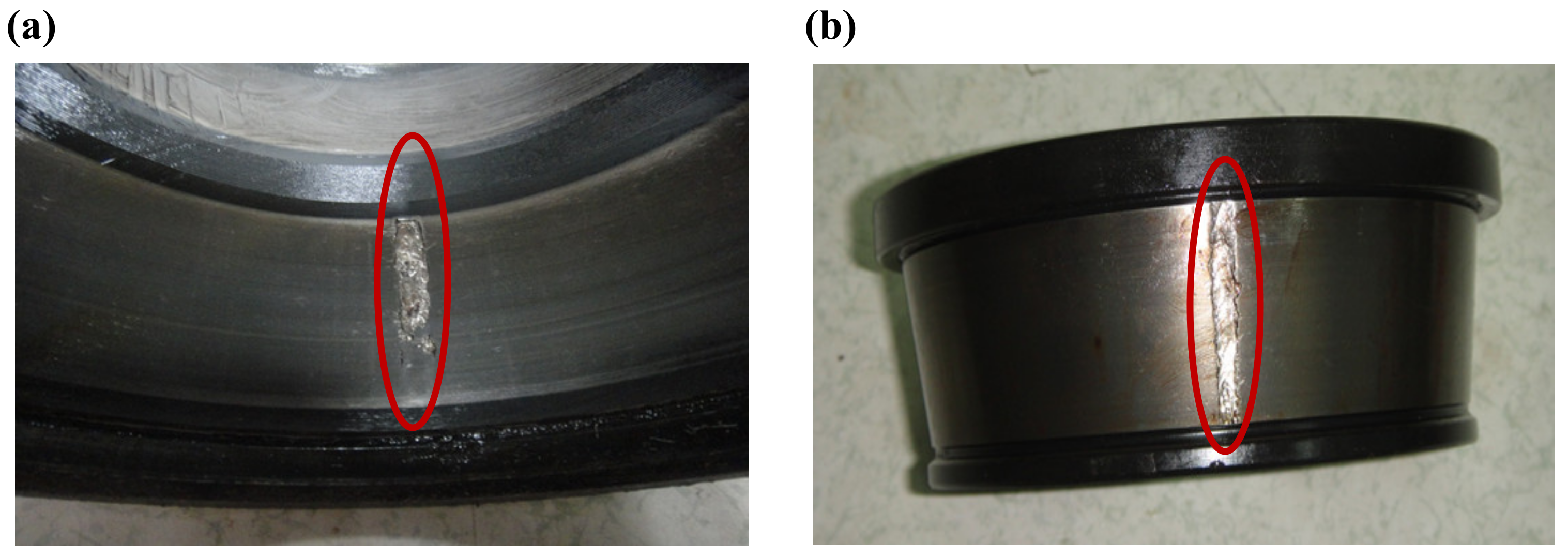
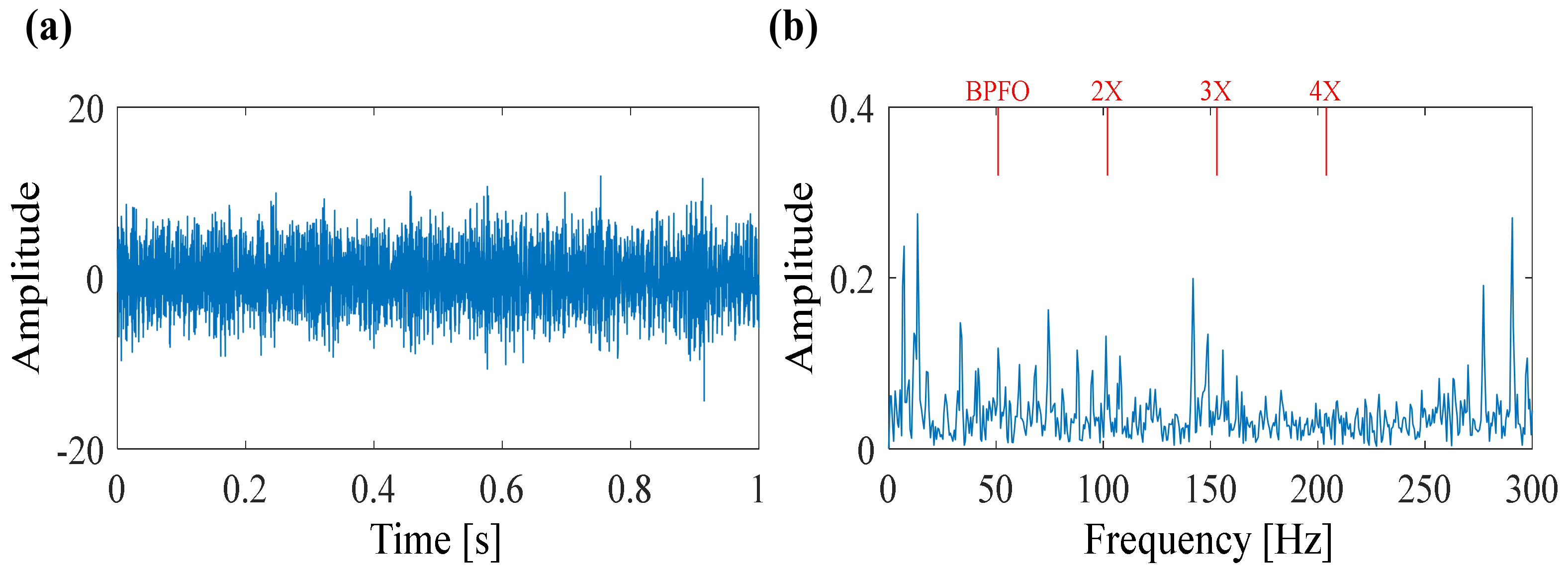
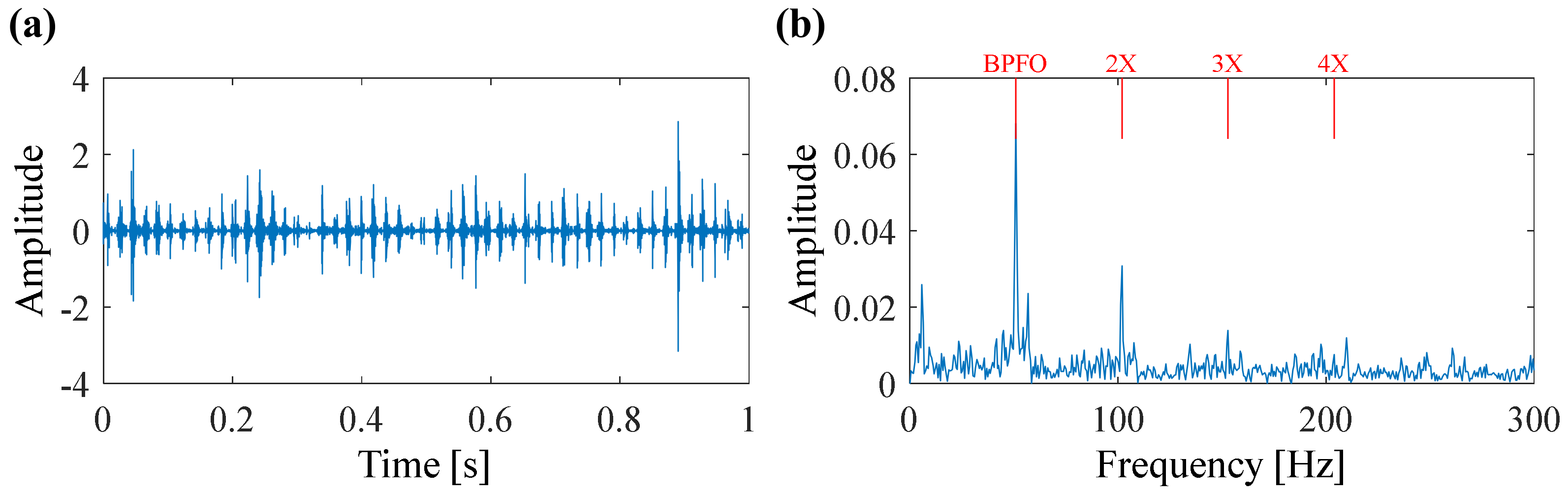
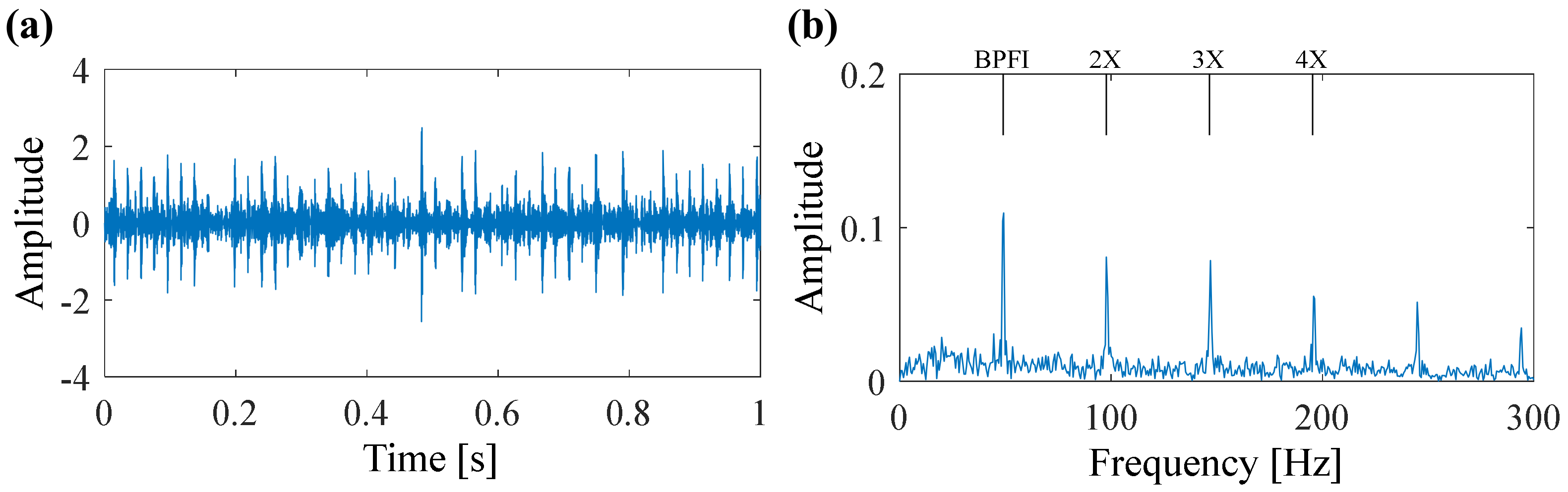
5.1. Case 1: Bearing Outer Race Fault Detection
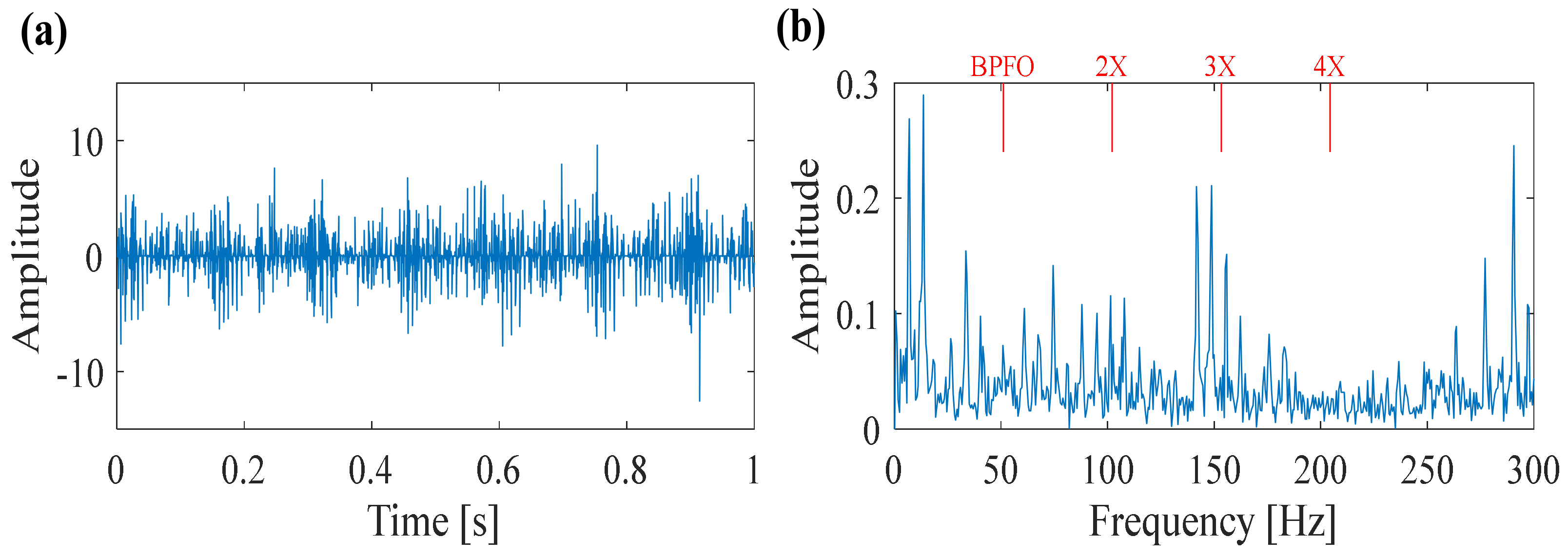
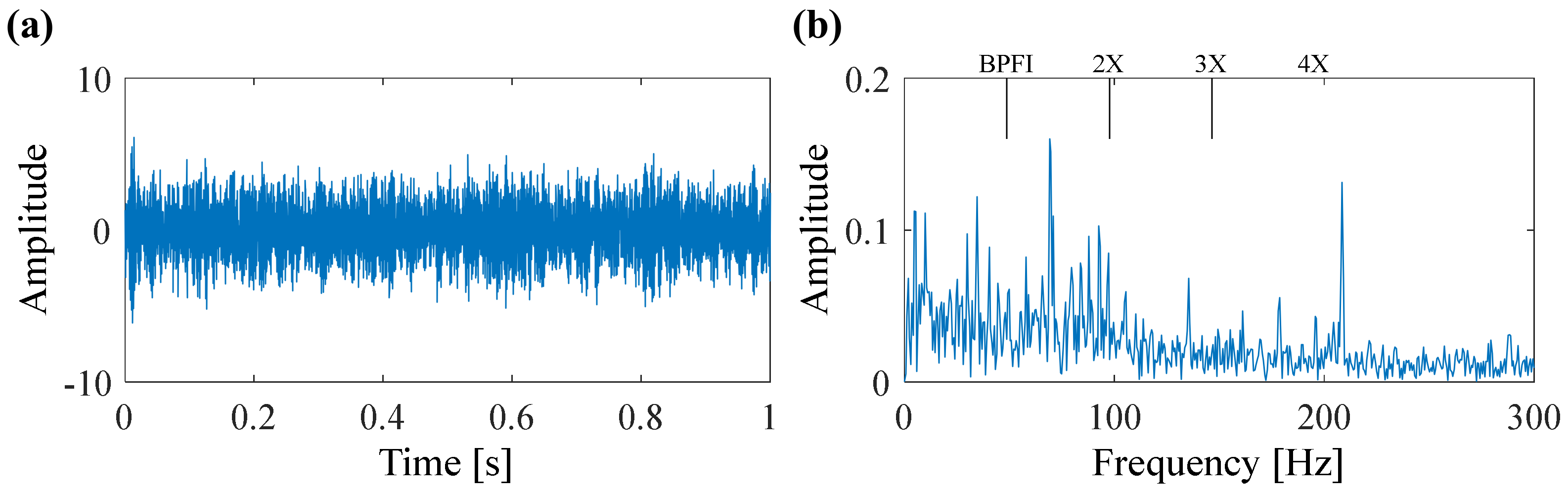
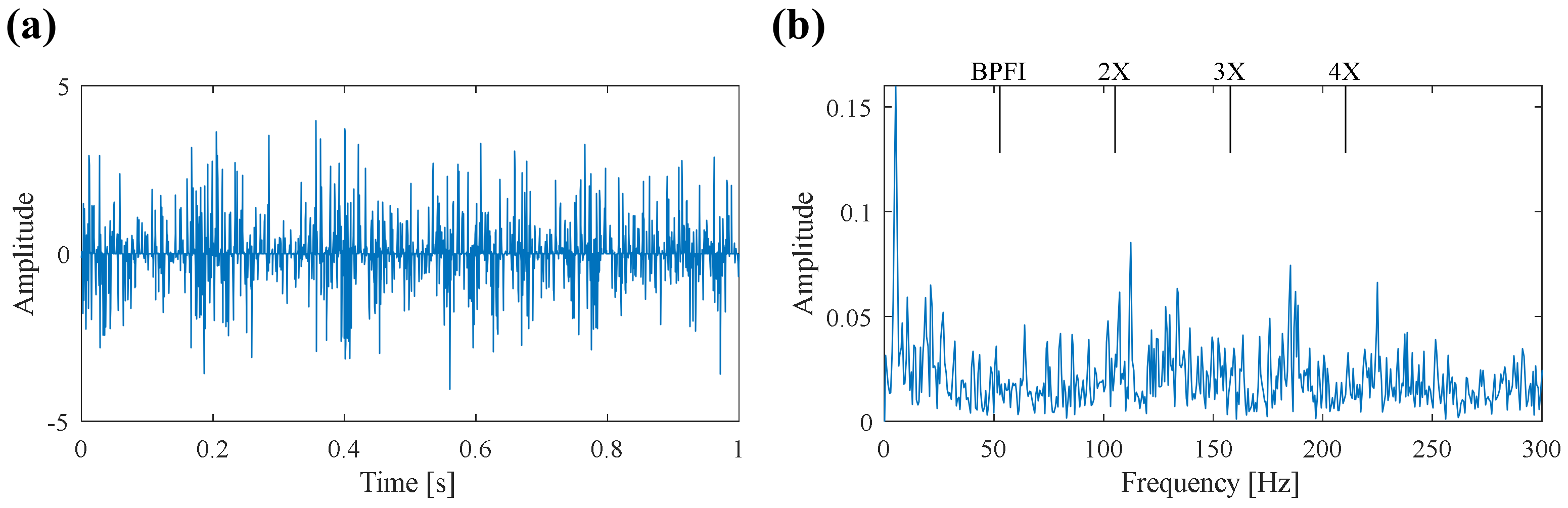
5.2. Case 2: Bearing Inner Race Fault Detection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guzmán-Rabasa, J.A.; López-Estrada, F.-R.; González-Contreras, B.M.; Valencia-Palomo, G.; Chadli, M.; Pérez-Patricio, M. Actuator fault detection and isolation on a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle modeled as a linear parameter-varying system. Meas. Control 2019, 52, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, P.; Cesaro, U.; Chadli, M.; Coppier, H.; De Vito, L.; Esposito, A.; Gargiulo, F.; Pezzetti, M. Fault detection on fluid machinery using Hidden Markov Models. Measurement 2020, 151, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhenak, A.; Chadli, M.; Maquin, D.; Ragot, J. Sliding mode multiple observer for fault detection and isolation. In Proceedings of the 42nd IEEE International Conference on Decision and Control (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37475), Maui, HI, USA, 9–12 December 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Akhenak, A.; Chadli, M.; Maquin, D.; Ragot, J. State estimation via multiple observer with unknown inputs: Application to the three tank system. In Proceedings of the 5th IFAC Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety for Technical Processes, Safeprocess 2003, Washington, DC, USA, 9–11 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- El Hajjaji, A.; Chadli, M.; Oudghiri, M.; Pages, O. Observer-based robust fuzzy control for vehicle lateral dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2006 American Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 14–16 June 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, W.; Lu, D. A Survey on Wind Turbine Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis—Part II: Signals and Signal Processing Methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6546–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Selesnick, I.W.; Wang, S.; Dai, W.; Zhu, Z. Sparsity-enhanced signal decomposition via generalized minimax-concave penalty for gearbox fault diagnosis. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 432, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, M. A Data-Driven Fault Diagnosis Methodology in Three-Phase Inverters for PMSM Drive Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5590–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Duan, W.; Liang, T.; Wu, S. Rolling bearing fault feature learning using improved convolutional deep belief network with compressed sensing. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 100, 743–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.B.; Antoni, J. Rolling element bearing diagnostics—A tutorial. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 485–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.B. Vibration-Based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Antoni, J. The infogram: Entropic evidence of the signature of repetitive transients. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 74, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhao, M.; Lin, J.; Jiao, J. Multi-objective iterative optimization algorithm based optimal wavelet filter selection for multi-fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings. ISA Trans. 2019, 88, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, F.; Orfali, W.; Gadala, M.S. Roller bearing acoustic signature extraction by wavelet packet transform, applications in fault detection and size estimation. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 104, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, J. The spectral kurtosis: A useful tool for characterising non-stationary signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2006, 20, 282–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, J. Fast computation of the kurtogram for the detection of transient faults. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; He, Z.; Zuo, M.J.; Zuo, M.J. A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liang, M.; Chu, F. Recent advances in time–frequency analysis methods for machinery fault diagnosis: A review with application examples. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 38, 165–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shuming, W.; Qiao, B.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhibin, Z. Enhanced Sparse Period-Group Lasso for Bearing Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ding, Y.; Zi, Y.; Selesnick, I.W. Sparsity-based algorithm for detecting faults in rotating machines. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 72, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, B.; Zeng, N.; Zi, Y. Sparsity-based signal extraction using dual Q-factors for gearbox fault detection. ISA Trans. 2018, 79, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selesnick, I.; Farshchian, M. Sparse Signal Approximation via Nonseparable Regularization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 2561–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckstein, A.M.; Donoho, D.L.; Elad, M. From Sparse Solutions of Systems of Equations to Sparse Modeling of Signals and Images. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 34–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Selesnick, I. Translation-invariant shrinkage/thresholding of group sparse signals. Signal Process. 2014, 94, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Selesnick, I. Group-Sparse Signal Denoising: Non-Convex Regularization, Convex Optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 3464–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; He, W.; Chen, B.; Zi, Y.; Selesnick, I. Detection of faults in rotating machinery using periodic time-frequency sparsity. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 382, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Chen, X.; He, Z. Sparsity-enabled signal decomposition using tunable Q-factor wavelet transform for fault feature extraction of gearbox. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 41, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. Feature extraction of rolling bearing’s early weak fault based on EEMD and tunable Q-factor wavelet transform. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2014, 48, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selesnick, I.W.; Parekh, A.; Bayram, I. Convex 1-D Total Variation Denoising with Non-convex Regularization. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 22, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, A.; Selesnick, I.W. Convex Denoising using Non-Convex Tight Frame Regularization. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.; Savalle, P.-A.; Vayatis, N. Estimation of simultaneously sparse and low rank matrices. arXiv, 2012; arXiv:1206.6474. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Liu, X.-L. Convex Relaxation Algorithm for a Structured Simultaneous Low-Rank and Sparse Recovery Problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China 2015, 3, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ghanem, B.; Liu, S.; Xu, C.; Ahuja, N. Low-Rank Sparse Coding for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, G.; Qin, Y.; Jia, L.-M.; Zhang, S.-J.; Antoni, J. Low-rank and sparse model: A new perspective for rolling element bearing diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Rail Transportation (ICIRT), Singapore, 12–14 December 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Parekh, A.; Selesnick, I.W. Enhanced Low-Rank Matrix Approximation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, A.; Selesnick, I.W. Improved sparse low-rank matrix estimation. Signal Process. 2017, 139, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D. De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1995, 41, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, G.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, M.J. Maximum correlated Kurtosis deconvolution and application on gear tooth chip fault detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 33, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
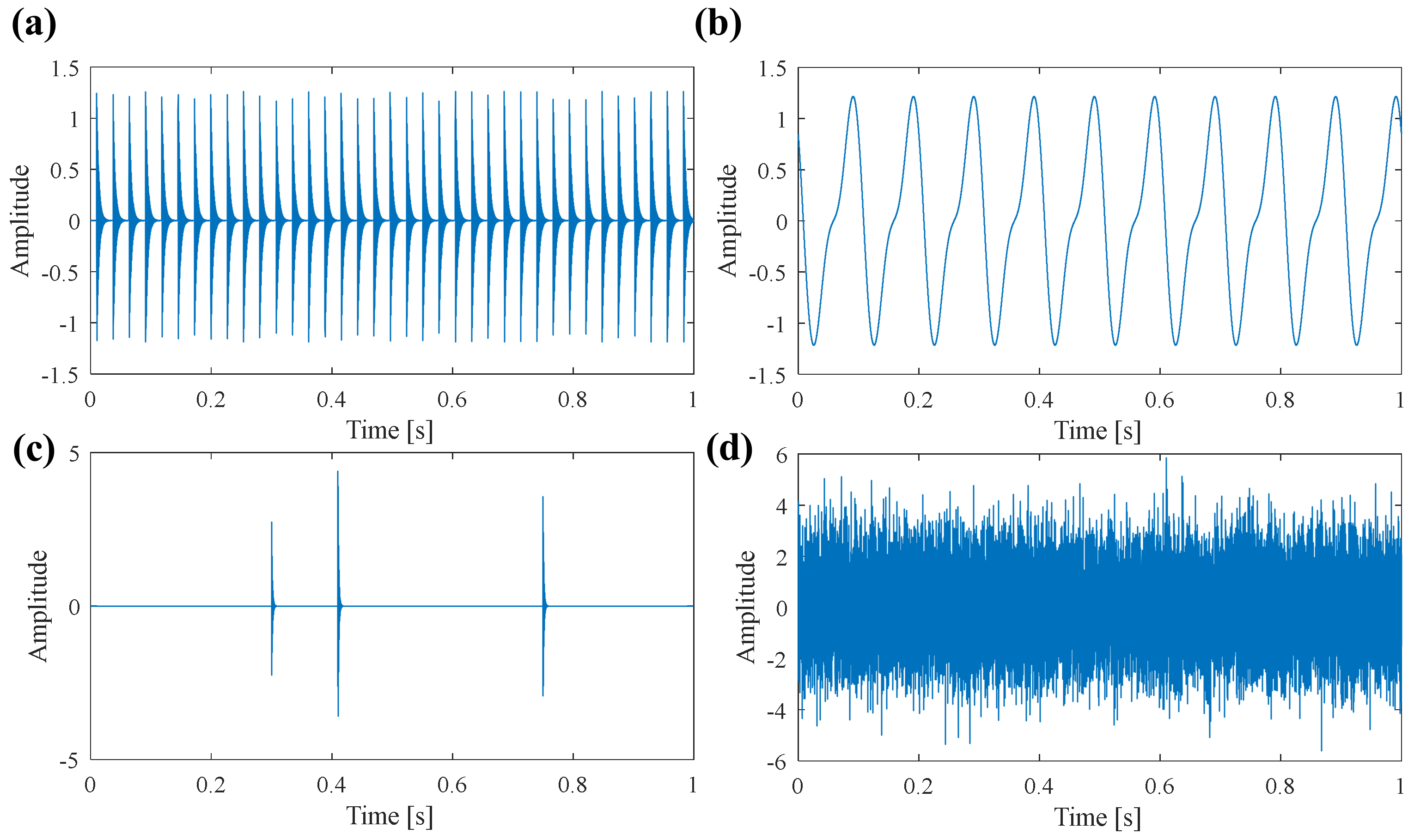

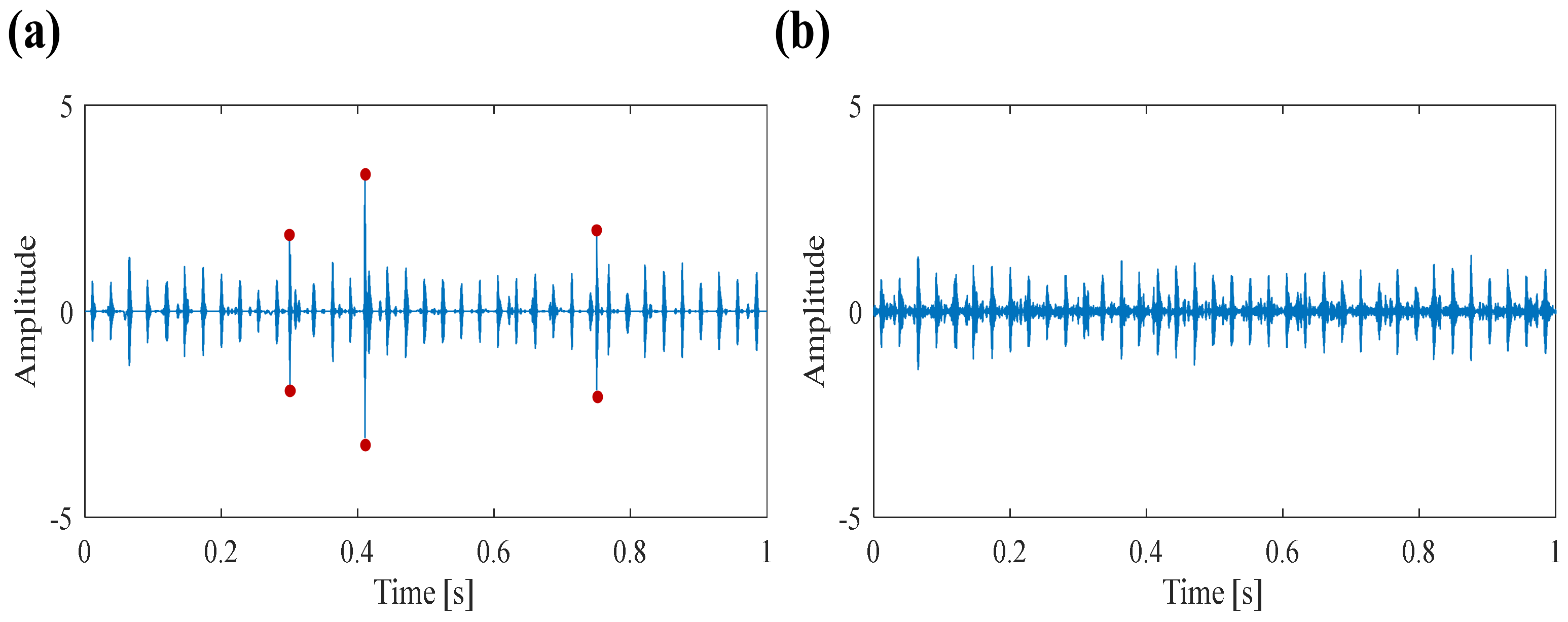
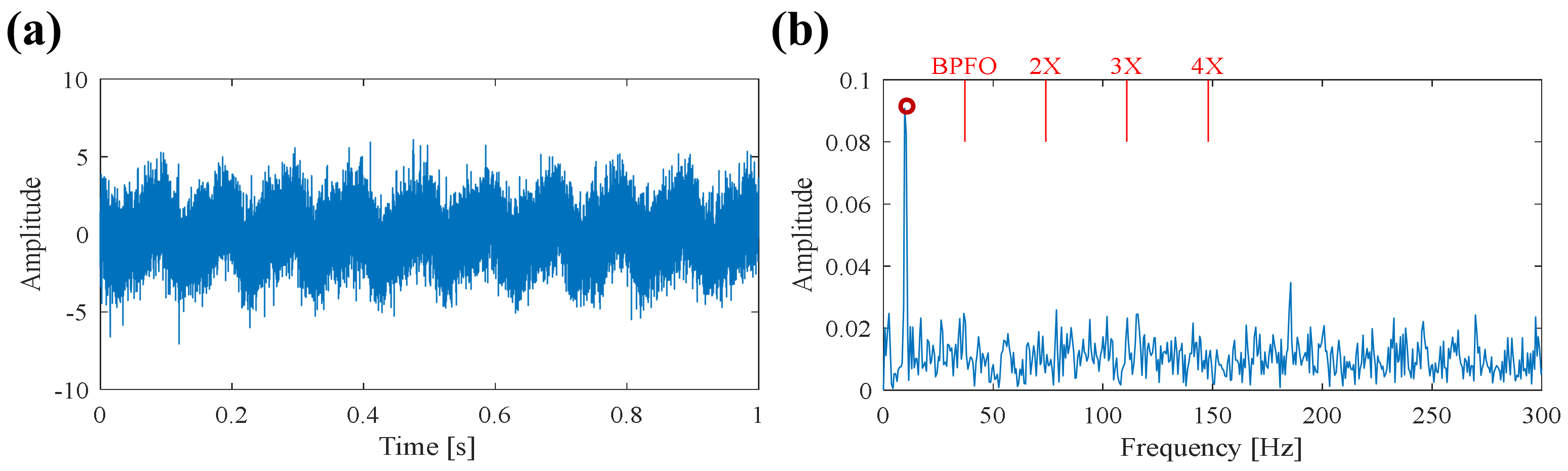
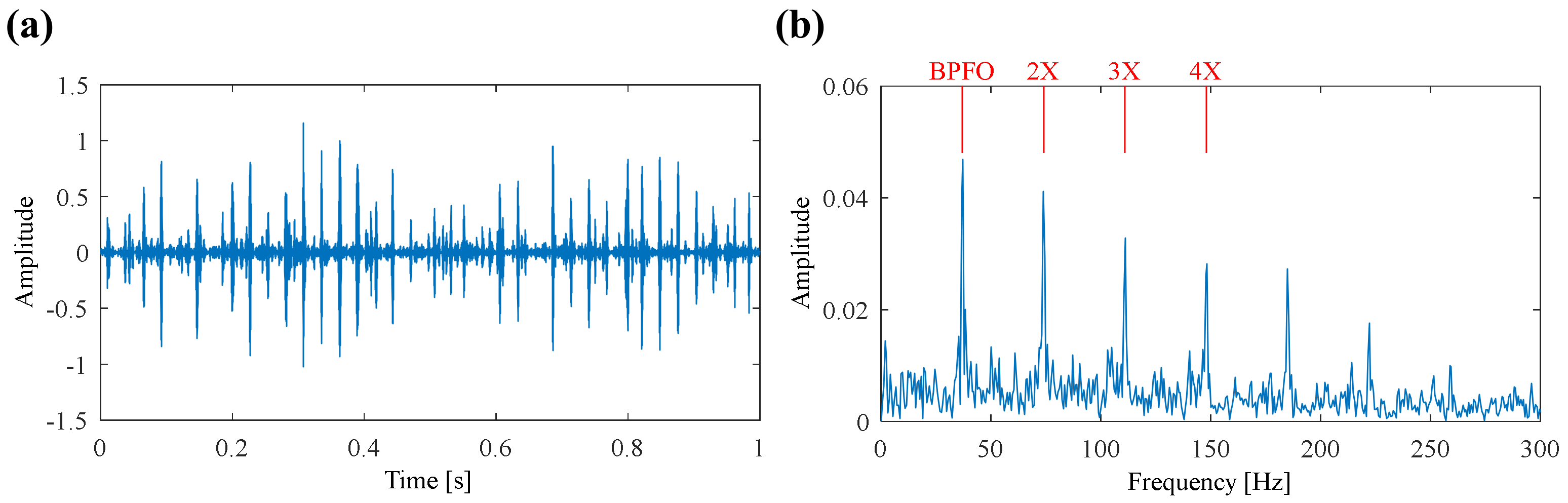
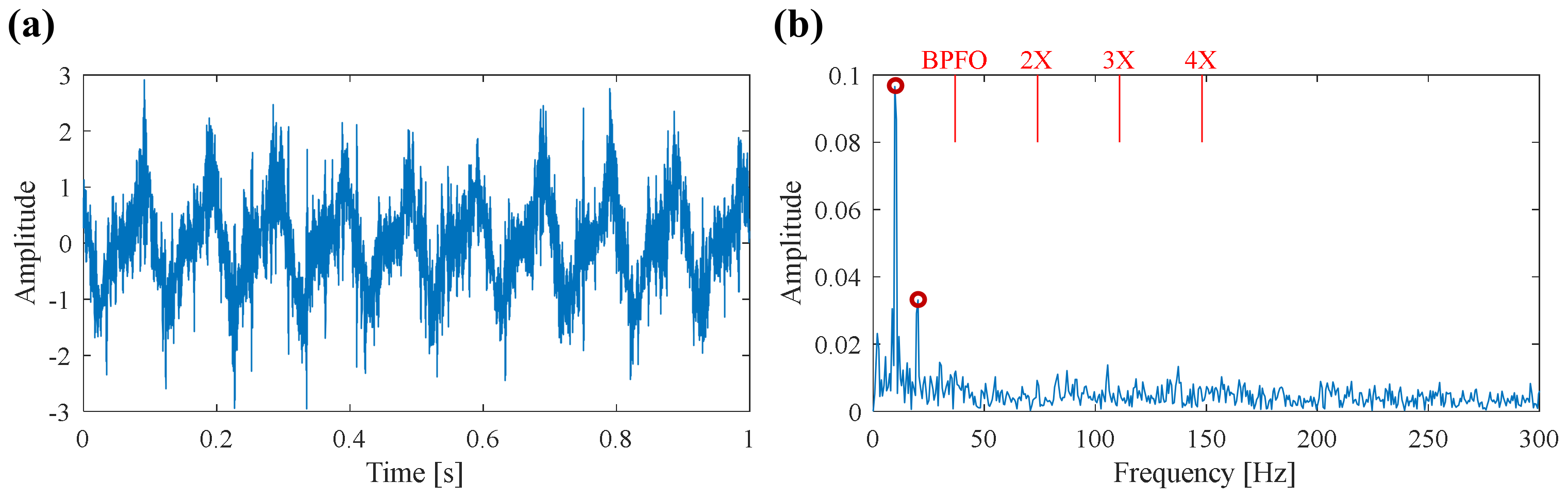

| Repetitive Transients | Harmonic Components | Random Shocks | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Td | fr | αr | f1 | f2 | A1 | A2 | α1 | α2 | fr | αr |
| 1.3 | 1/37 | 2500 | 300 | 10 | 20 | 1 | 0.4 | π/3 | π/6 | 6000 | 800 |
| Number of Rollers | Pitch Diameter (mm) | Roller Diameter (mm) | Contact Angle (Degree) |
| 20 | 180 | 23.775 | 9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Liao, Y.; Duan, R.; Zhang, X. Sparse Low-Rank Based Signal Analysis Method for Bearing Fault Feature Extraction. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072358
Wang B, Liao Y, Duan R, Zhang X. Sparse Low-Rank Based Signal Analysis Method for Bearing Fault Feature Extraction. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072358
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Baoxiang, Yuhe Liao, Rongkai Duan, and Xining Zhang. 2020. "Sparse Low-Rank Based Signal Analysis Method for Bearing Fault Feature Extraction" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072358
APA StyleWang, B., Liao, Y., Duan, R., & Zhang, X. (2020). Sparse Low-Rank Based Signal Analysis Method for Bearing Fault Feature Extraction. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072358





