Magnetic and Hydrophobic Composite Polyurethane Sponge for Oil–Water Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
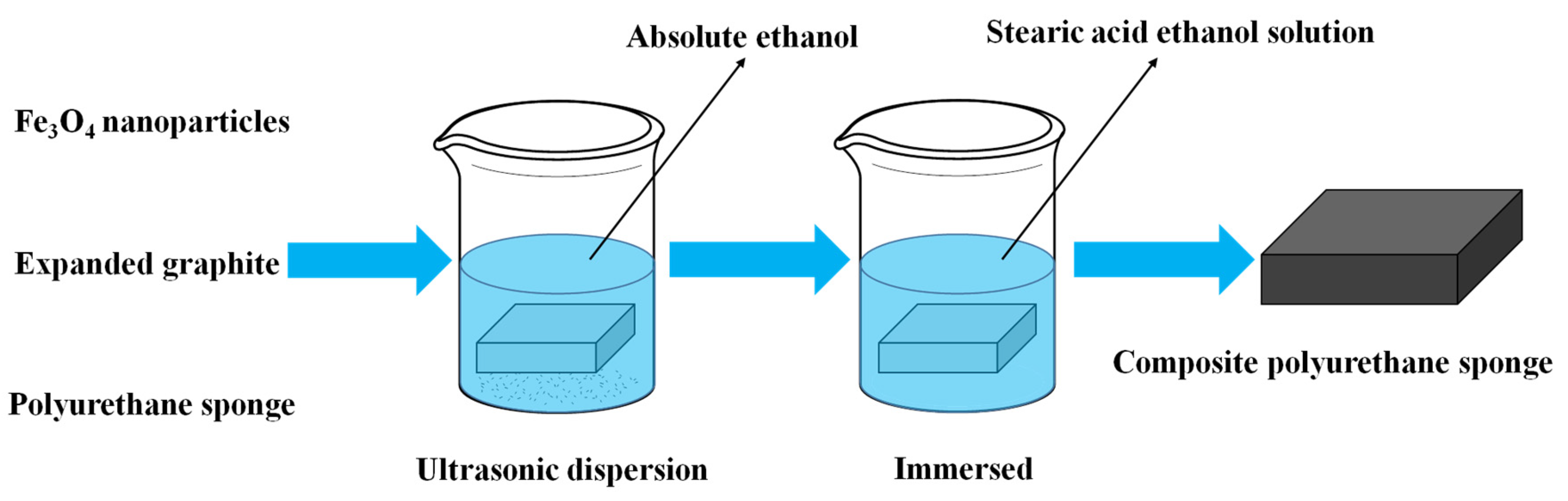
2.3. Preparation of Composite Sponge Samples
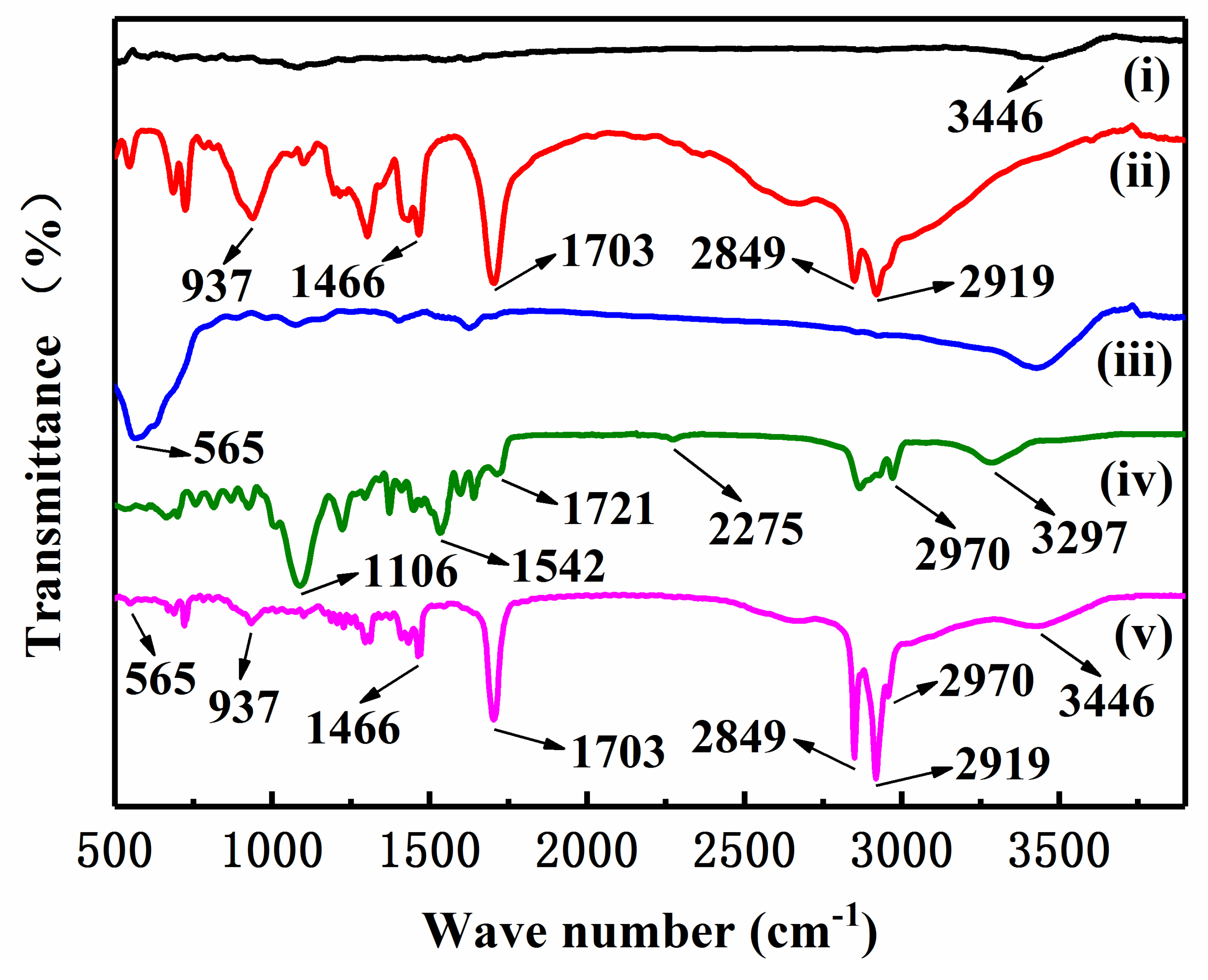
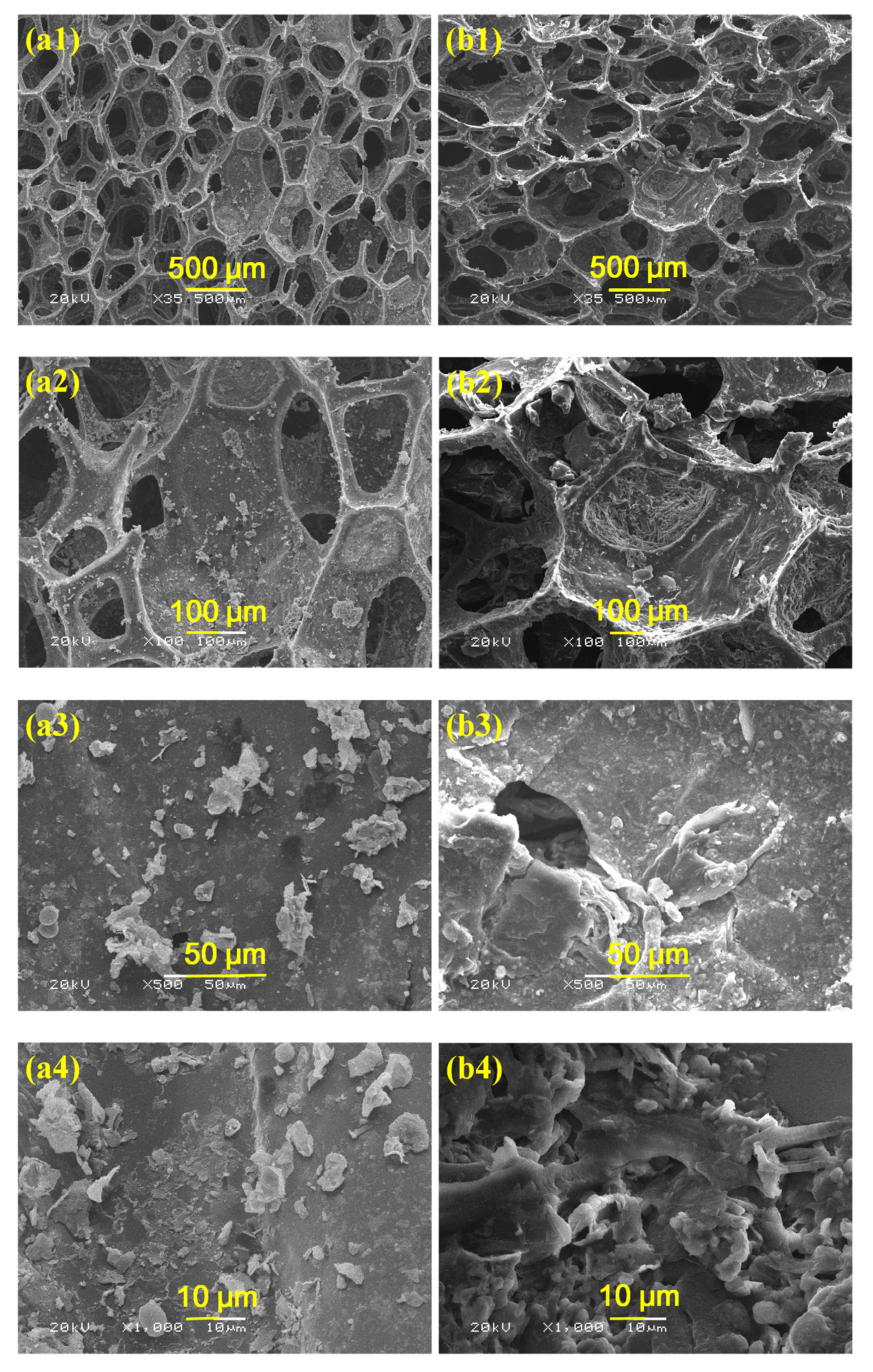
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Method for the Oil Adsorption Tests
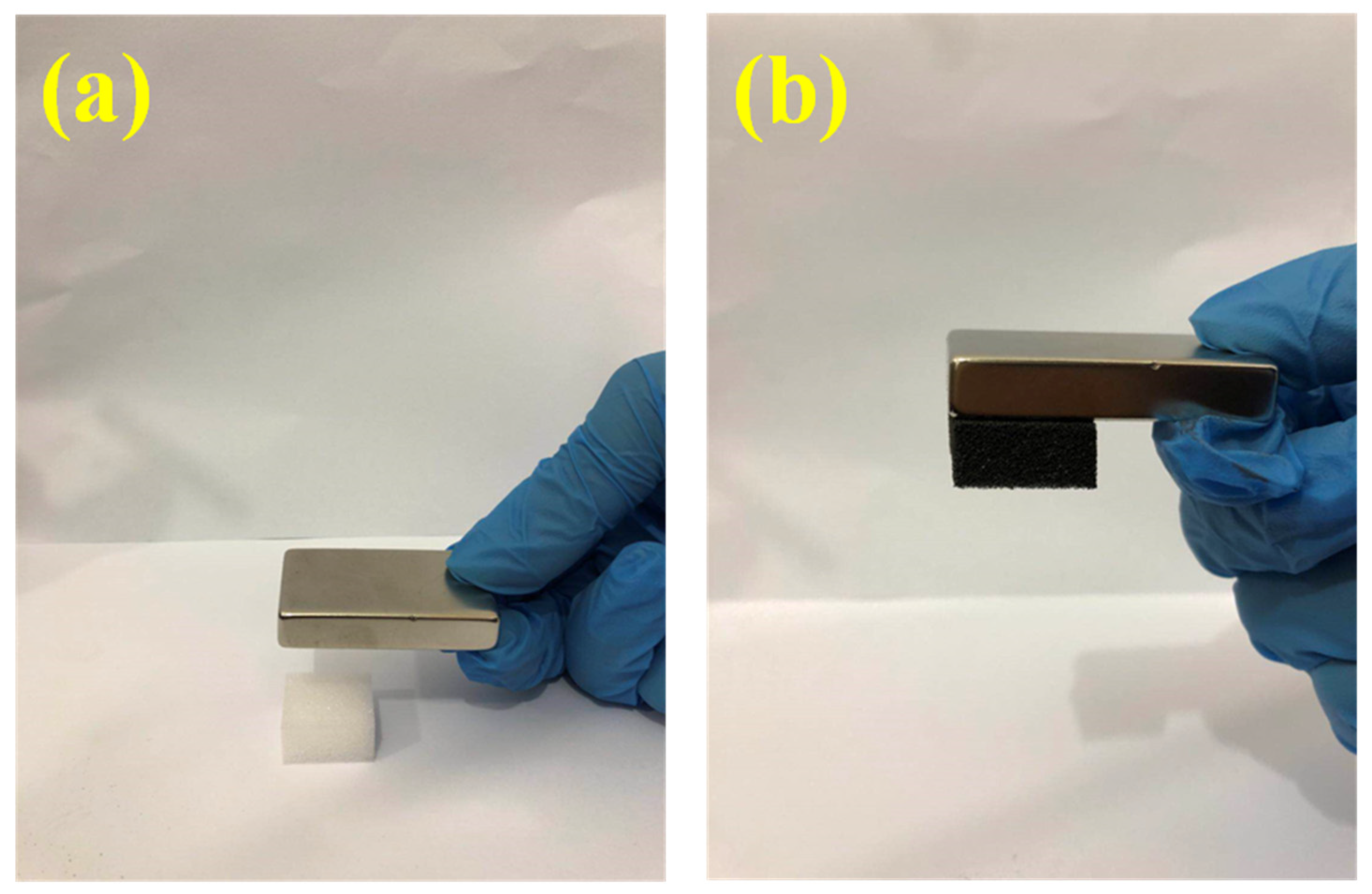
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Majed, A.A.; Adebayo, A.R.; Hossain, M.E. A sustainable approach to controlling oil spills. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, J.A.; Crist, T.O.; Day, R.H.; Murphy, S.M.; Hayward, G.D. A canonical correspondence analysis of the effects of the Exxon Valdez oil spill on marine birds. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, T.; Jin, D. Extent and frequency of vessel oil spills in US marine protected areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radetic, M.M.; Jocic, D.M.; Jovancic, P.M.; Petrovic, Z.L.; Thomas, H.F. Recycled wool-based nonwoven material as an oil sorbent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, N.A.; Shukry, N.; El-Kalyoubi, S.F. Preparation and characterization of polymer coated partially esterified sugarcane bagasse for separation of oil from seawater. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, D.S.; Debs, K.B.; Lemos, S.G.; Vitale, G.; Nassar, N.N.; Carrilho, E.N.V.M.; Semensatto, D.; Labuto, G. A comparison study of cleanup techniques for oil spill treatment using magnetic nanomaterials. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceylan, D.; Dogu, S.; Karacik, B.; Yakan, S.D.; Okay, O.S.; Okay, O. Evaluation of Butyl Rubber as Sorbent Material for the Removal of Oil and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Macoveanu, M.; Cretescu, I. Peat-based sorbents for the removal of oil spills from water surface: Application of artificial neural network modeling. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 384, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Ngai, T.; Wang, C. Nitrogen-Rich and Fire-Resistant Carbon Aerogels for the Removal of Oil Contaminants from Water. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6351–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, J. A two-step hydrophobic fabrication of melamine sponge for oil absorption and oil/water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 339, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Qiu, F. Recent progress and future prospects of oil-absorbing materials. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, B.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, G.; Guan, X. Simple and Green Fabrication of a Superhydrophobic Surface by One-Step Immersion for Continuous Oil/Water Separation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 5617–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Chen, K.; Du, R.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Ruemmeli, M.H.; Xie, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Scalable Seashell-Based Chemical Vapor Deposition Growth of Three-Dimensional Graphene Foams for Oil-Water Separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6360–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Guo, Z. Stable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic soft porous materials for oil/water separation. Rsc Adv. 2013, 3, 16469–16474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halake, K.; Bae, S.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.; Jo, H.; Heo, J.; Park, K.; Kim, H.; Ju, H.; Kim, Y.; et al. Strategies for Fabrication of Hydrophobic Porous Materials Based on Polydimethylsiloxane for Oil-Water Separation. Macromol. Res. 2019, 27, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, K.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Dai, Z. A three-dimensional porous metal foam with selective-wettability for oil-water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5371–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L. Superwetting Porous Materials for Wastewater Treatment: From Immiscible Oil/Water Mixture to Emulsion Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Ren, R.; Han, L.; Bi, F.; Zhang, Z.; Han, K.; Gu, W. Facile fabrication of asphaltene-derived graphene-polyurethane sponges for efficient and selective oil-water separation. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Zhang, B.; Xie, L.; Wang, F. MWCNTs polyurethane sponges with enhanced super-hydrophobicity for selective oil-water separation. Surf. Eng. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, N. Robust and Durable Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Sponge for Oil/Water Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11260–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Guo, J.; Boukherroub, R.; Shao, Q.; Zang, X.; Li, J.; Lin, X.; Ju, H.; Liu, E.; Zhou, C.; et al. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge functionalized with perfluorinated graphene oxide for efficient immiscible oil/water mixture, stable emulsion separation and crude oil dehydration. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yin, X.; Li, J. Robust superhydrophobic/superoleophilic sponge for efficient removal of oils from corrosive aqueous solutions. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 1426–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fang, Y.; Miao, X.; Pei, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wu, L. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge towards oil water separation with exceptional flame-retardant performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Halouane, F.; Mathias, D.; Barras, A.; Wang, Z.; Lv, A.; Lu, S.; Xu, W.; Meziane, D.; Tiercelin, N.; et al. Preparation of magnetic, superhydrophobic/superoleophilic polyurethane sponge: Separation of oil/water mixture and demulsification. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guan, N. An environmentally friendly and cost-effective method to fabricate superhydrophobic PU sponge for oil/water separation. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjandra, R.; Lui, G.; Veilleux, A.; Broughton, J.; Chiu, G.; Yu, A. Introduction of an Enhanced Binding of Reduced Graphene Oxide to Polyurethane Sponge for Oil Absorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3657–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, B.; Luo, H.; Zhi, L. Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto Secondary Expanded Graphite. Adv. Build. Mater. 2011, 168, 2571–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Shi, P.-H.; Su, R.-J.; Zhu, M.-C. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by powdered expanded graphite: Adsorption isotherms and thermodynamics. Adv. Res. Eng. Mater. Energy Manag. Control 2012, 424, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, P. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by modified expanded graphite powder. Desalination 2009, 249, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedenyapina, M.D.; Borisova, D.A.; Simakova, A.P.; Proshina, L.P.; Vedenyapin, A.A. Adsorption of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solutions on expanded graphite. Solid Fuel Chem. 2013, 47, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedenyapina, M.D.; Vedenyapin, A.A. Dynamic adsorption of drug preparations from aqueous solutions on thermally expanded graphite. Solid Fuel Chem. 2015, 49, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emken, E.A. Metabolism of dietary stearic acid relative to other fatty acids in human subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 1023S–1028S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M. Influence of stearic acid on cholesterol metabolism relative to other long-chain fatty acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 986S–990S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livesey, G. The absorption of stearic acid from triacylglycerols: An inquiry and analysis. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2000, 13, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Premphet, K.; Horanont, P. Influence of stearic acid treatment of filler particles on the structure and properties of ternary-phase polypropylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.I.; Shim, J.; Li, T.; Lee, J.; Park, H.G. Fabrication of Nanoporous Nanocomposites Entrapping Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles and Oxidases for Colorimetric Biosensing. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 10700–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics and their applications in H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2250–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Salazar, P.; Villalonga, R.; Campuzano, S.; Manuel Pingarron, J.; Luis Gonzalez-Mora, J. Preparation of core-shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for biosensor construction. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Lin, Z.; Tang, H. Sono-assisted preparation of highly-efficient peroxidase-like Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for catalytic removal of organic pollutants with H2O2. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Sun, A.; Zhai, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Volinsky, A.A. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1882–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Kamyar, S.; Mansor, A.; Khalantari, K.; Khandanlou, R. Synthesis of talc/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites using chemical co-precipitation method. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1817. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L. In situ reduced graphene oxide-based polyurethane sponge hollow tube for continuous oil removal from water surface. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4837–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Tian, M.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Liang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Stearic acid surface modifying Mg(OH)2: Mechanism and its effect on properties of ethylene vinyl acetate/Mg(OH)2 composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 3325–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, S.; Hou, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, M. Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 80, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Ma, L.; Lin, A. Expanded Graphite Modified by CTAB-KBr/H3PO4 for Highly Efficient Adsorption of Dyes. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, D.X. Preparation of Modified Expanded Graphite by KOH. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 347, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshkar, F.; Khojasteh, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Recyclable magnetic superhydrophobic straw soot sponge for highly efficient oil/water separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 497, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hao, G.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Yu, L. One-pot Synthesis of Robust Superhydrophobic, Functionalized Graphene/Polyurethane Sponge for Effective Continuous Oil-water Separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.-T.; He, F.-A.; Li, D.-H. Superhydrophobic modification of polyurethane sponge for the oil-water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 359, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Liu, Z.; Gao, D.; Yuan, R.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y. A novel carbon nanotubes reinforced superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polyurethane sponge for selective oil-water separation through a chemical fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


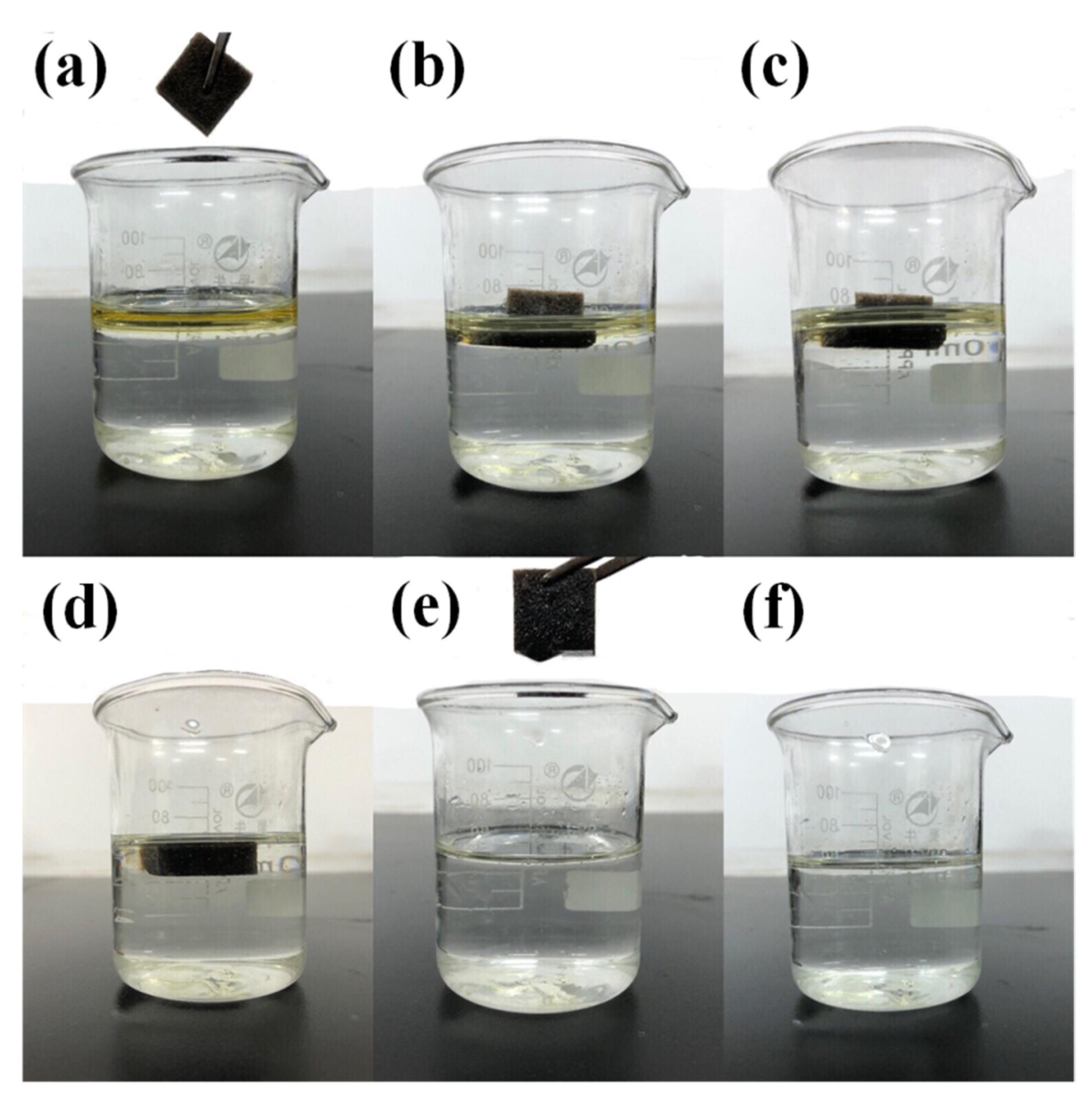
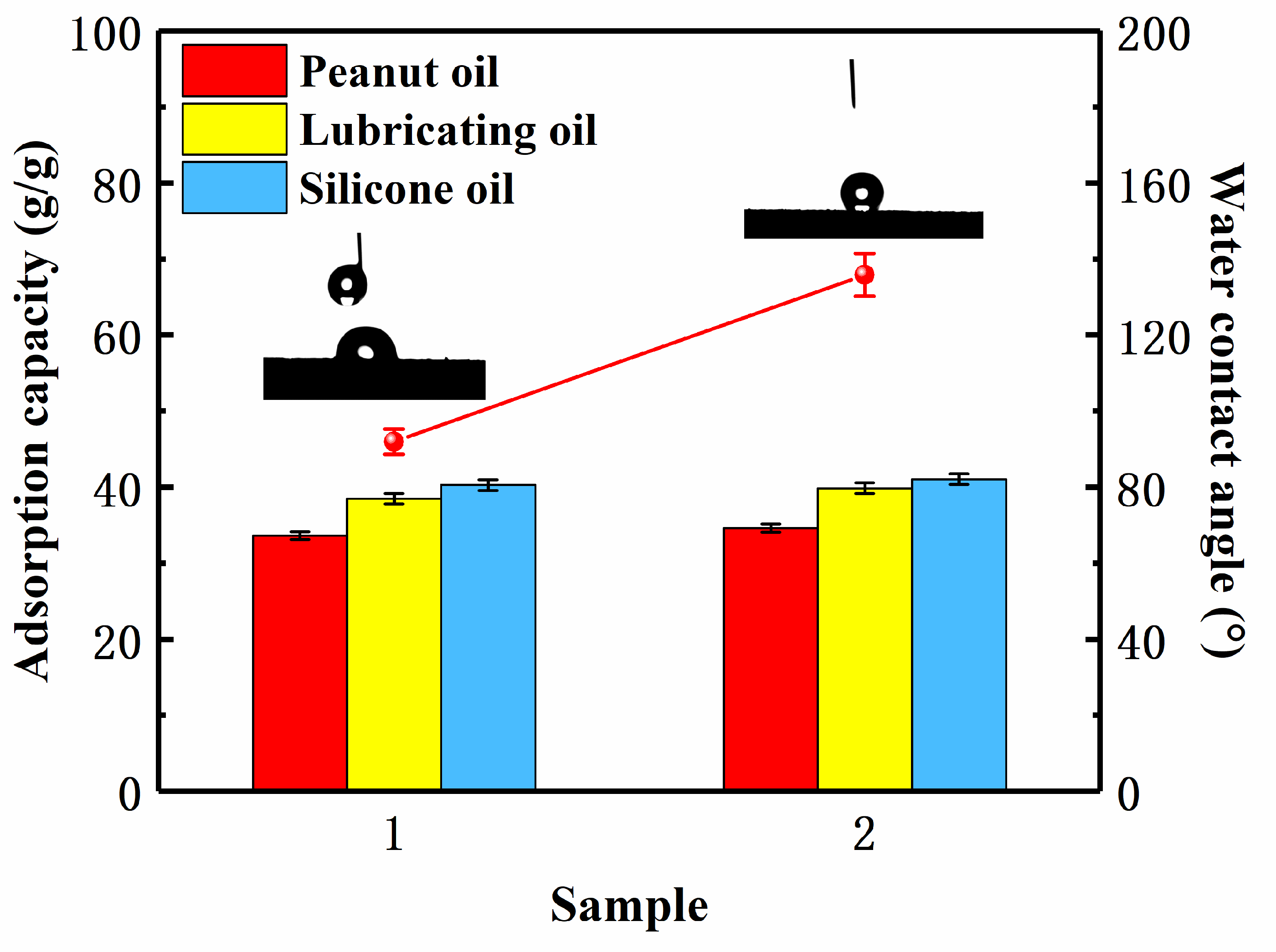
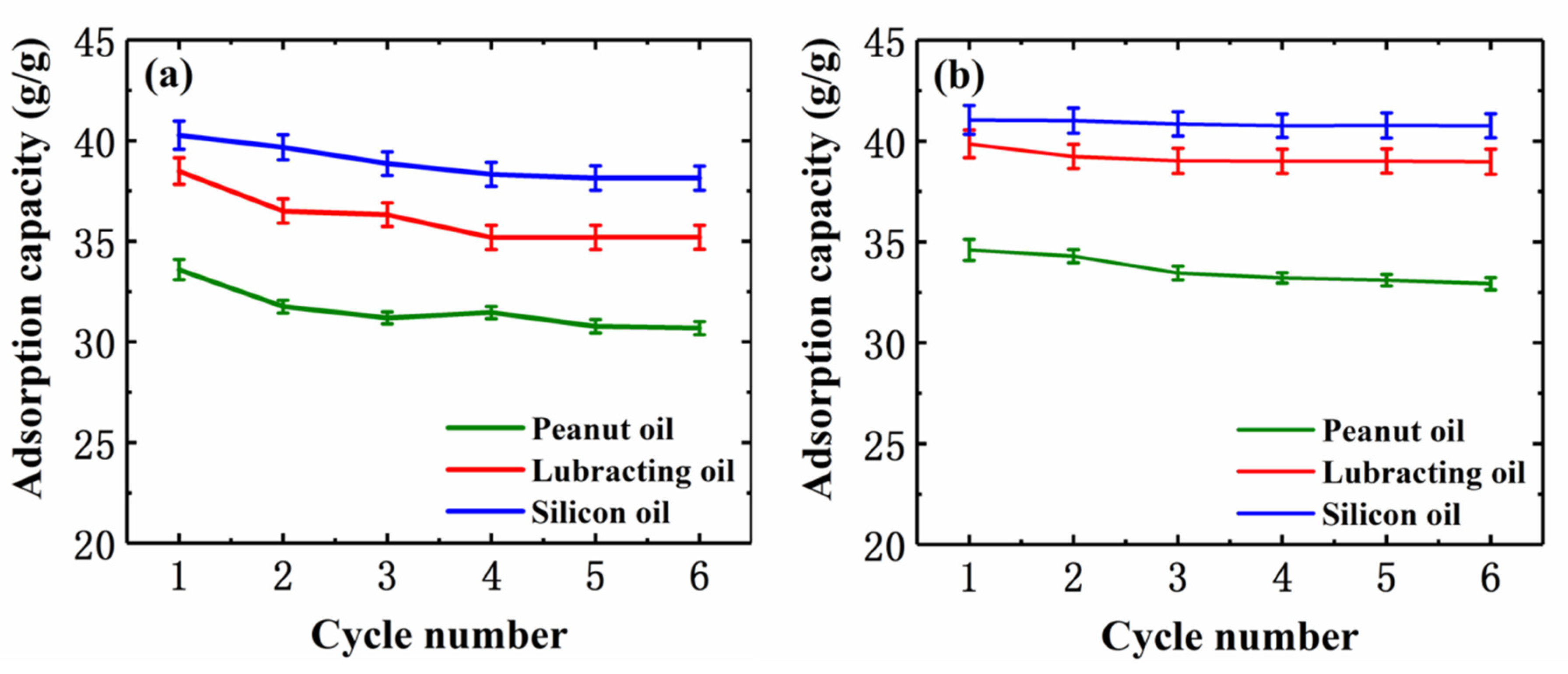
| Sample | Fe3O4 Nanoparticles (g) | Expanded Graphite (g) | Stearic Acid (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 1 |
| Adsorbent Materials | Types of Oil | Oil Adsorption Capacity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane sponge | Lubricating oil | 28.5 g/g | [49] |
| FGN/polyurethane sponge | Lubricating oil | 34.2 g/g | [49] |
| Superhydrophobic sponge | Lubricating oil | 24 g/g | [27] |
| F-SiO2/polyurethane sponge | Peanut oil | 15 g/g | [50] |
| U-SiO2/polyurethane sponge | Peanut oil | 28 g/g | [50] |
| PU–CNT–PDA–ODA sponge | Lubricating oil | 26g/g | [51] |
| PU–CNT–PDA–ODA sponge | Silicone oil | 29 g/g | [51] |
| IRGO/polyurethane sponge | Pump oil | 26.5 g/g | [43] |
| IRGO/polyurethane sponge | Soybean oil | 31.2 g/g | [43] |
| IRGO/polyurethane sponge | Olive oil | 36.1 g/g | [43] |
| Sample | Types of Oil | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Peanut oil | 20.56 ± 0.26 |
| Lubricating oil | 21.31 ± 0.75 | |
| Silicon oil | 21.76 ± 0.58 | |
| 2 | Peanut oil | 19.91 ± 0.72 |
| Lubricating oil | 20.96 ± 0.57 | |
| Silicon oil | 21.38 ± 0.63 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, P.; Li, K.; Chen, X.; Dan, R.; Yu, Y. Magnetic and Hydrophobic Composite Polyurethane Sponge for Oil–Water Separation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041453
Jiang P, Li K, Chen X, Dan R, Yu Y. Magnetic and Hydrophobic Composite Polyurethane Sponge for Oil–Water Separation. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(4):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041453
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Peng, Kun Li, Xiquan Chen, Ruiqi Dan, and Yang Yu. 2020. "Magnetic and Hydrophobic Composite Polyurethane Sponge for Oil–Water Separation" Applied Sciences 10, no. 4: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041453
APA StyleJiang, P., Li, K., Chen, X., Dan, R., & Yu, Y. (2020). Magnetic and Hydrophobic Composite Polyurethane Sponge for Oil–Water Separation. Applied Sciences, 10(4), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041453






