Structural Properties of the Fluid Mixture Confined by a Semipermeable Membrane: A Density Functional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Model
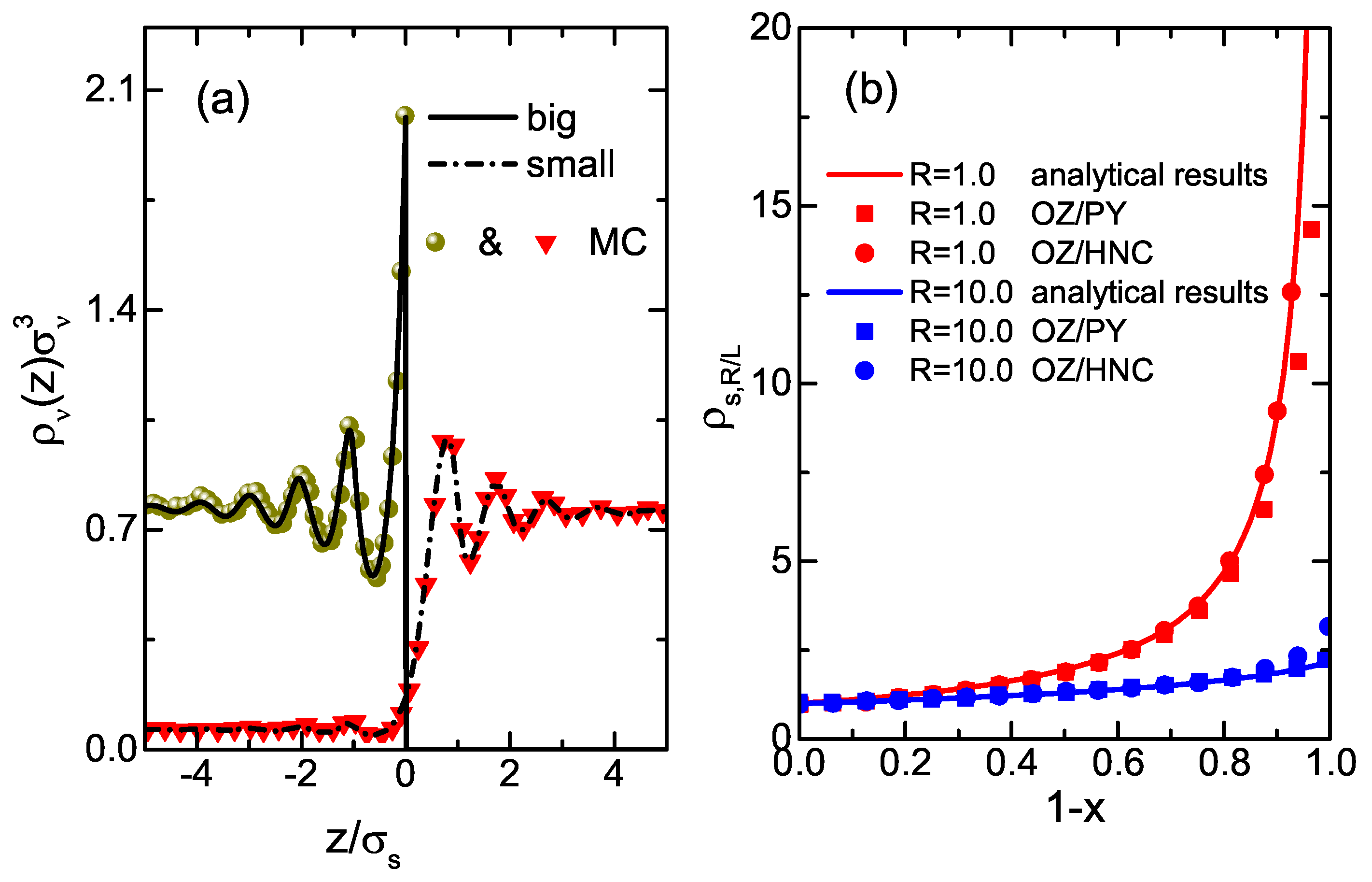
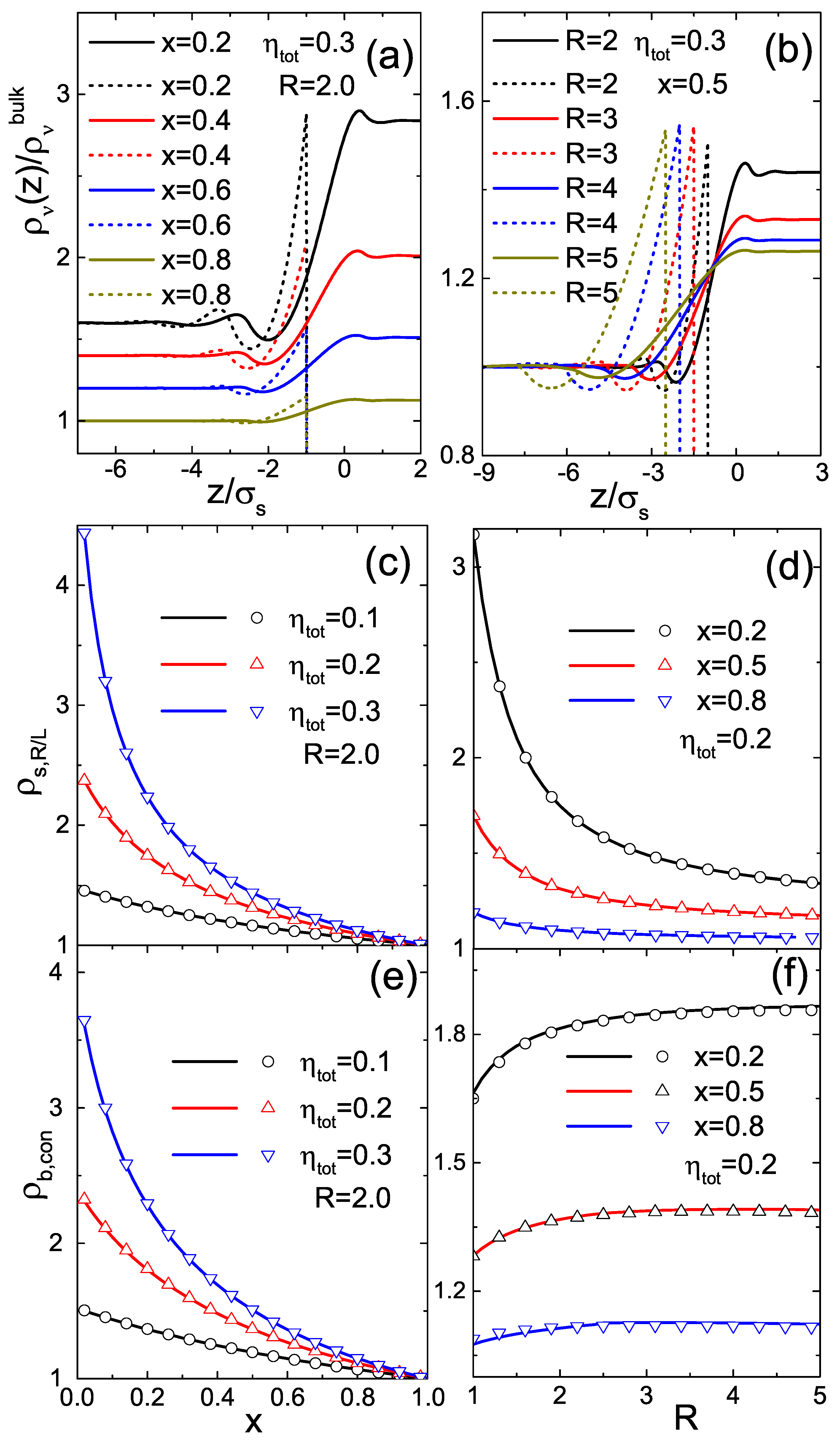
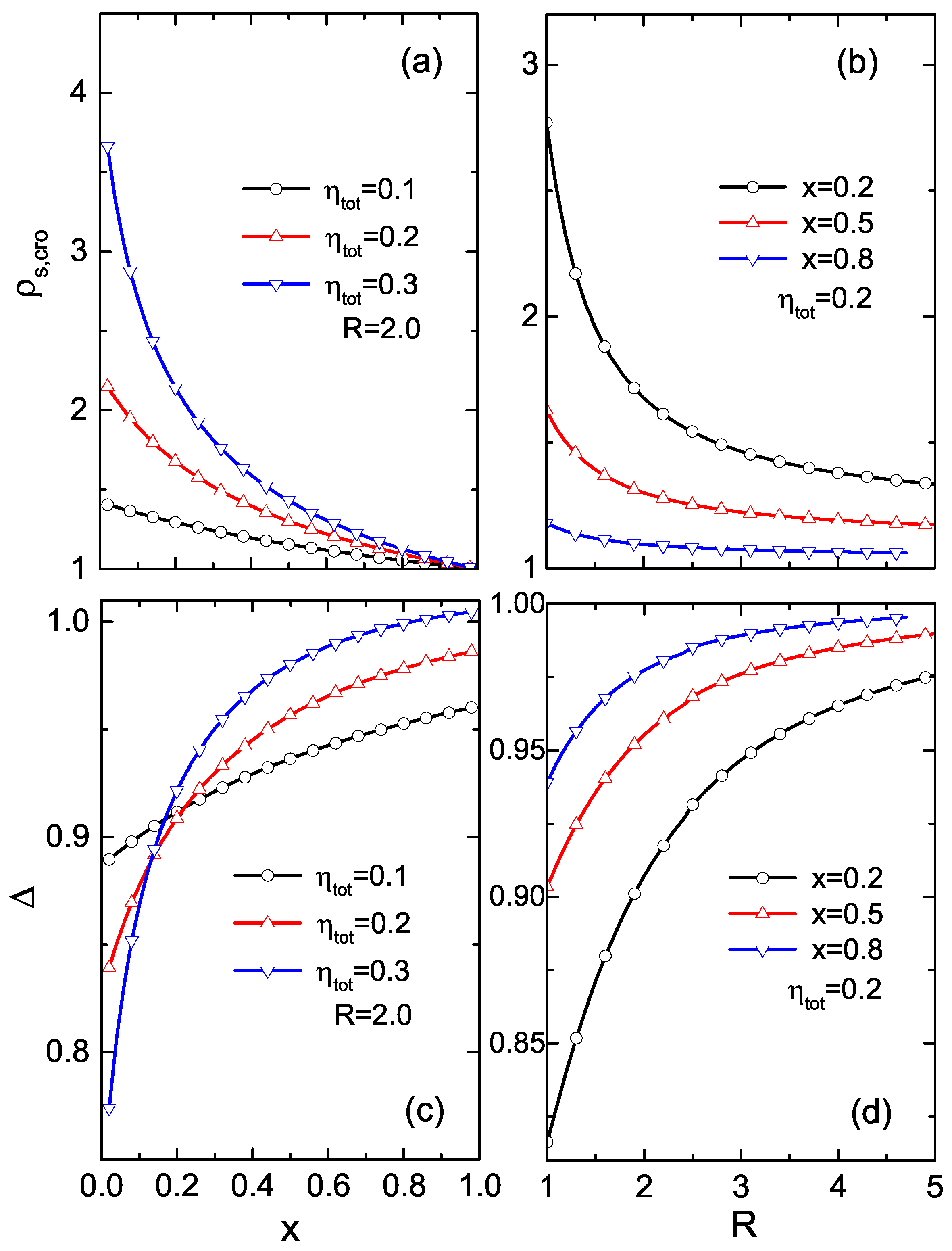
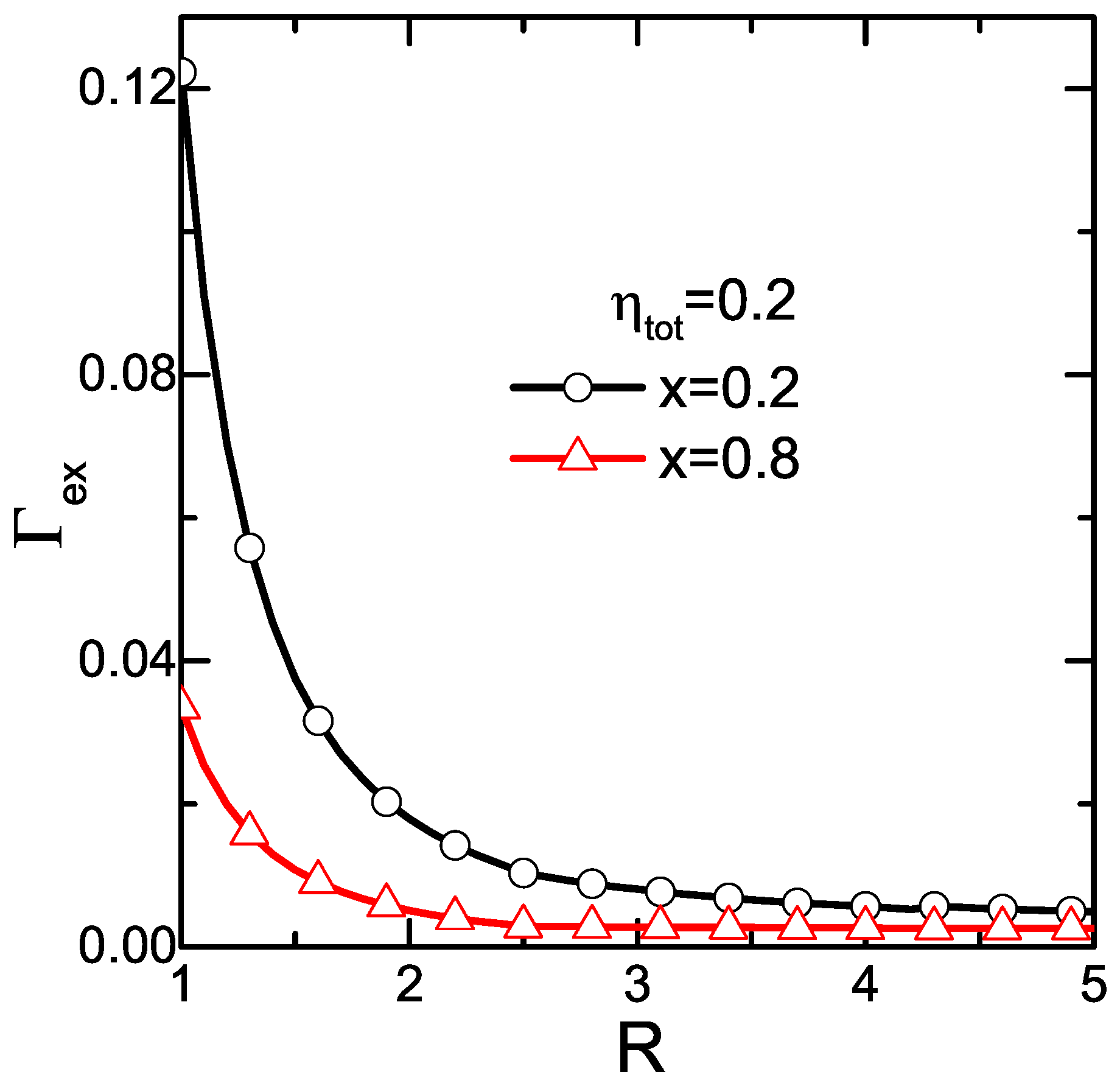
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henderson, D. Fundamentals of Inhomogeneous Fluids; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 85–175. [Google Scholar]
- Russo1, A.; Durán-Olivencia, M.A.; Kalliadasis, S.; Hartkamp, R. Macroscopic relations for microscopic properties at the interface between solid substrates and dense fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 214705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, A.; Wu, P.; Wasan, D. Structure and stability of nanofluid films wetting solids: An overview. Adv. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2019, 264, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, B.; Snoeijer, J.H. Statics and dynamics of soft wetting. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2020, 52, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, E.; Tan, S.P.; Piri, M.; Chen, J.H. Capillary-condensation hysteresis in naturally-occurring nanoporous media. Fuel 2020, 263, 116441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Benson, J.D.; Kearsley, A.J. Numerical solution of inward solidifcation of a dilute ternary solution towards a semi-permeable spherical cell. Math. Biosci. 2019, 316, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, J.; Imbrogno, J.; Kilduff, J.; Belfort, G. New class of synthetic membranes: Organophilic pervaporation brushes for organics recovery. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4142–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, A.; Cseri, L.; Hajaj, A.A.; Szekely, G.; Budd, P.; Zou, L. Electrostatically-coupled graphene oxide nanocomposite cation exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Stell, G. The theory of semipermeable vesicles and membranes: An integral-equation approach. I. General formalism and application to a hard mixture. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 89, 7010–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Stell, G. The theory of semipermeable vesicles and membranes: An integral-equation approach. II. Donnan equilibrium. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 89, 7020–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R. The nature of the liquid-vapour interface and other topics in the statistical mechanics of non-uniform, classical fluids. Adv. Phys. 1979, 28, 143–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.P.; McDonald, I.R. Theory of Simple Liquids, 4th ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 61–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bryk, P.; Cyrankiewicz, W.; Borowko, M.; Sokolowski, S. A fluid in contact with a semipermeable membrane: Density functional approach. Mol. Phys. 1998, 93, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, P.; Sokolowski, S.; Pizio, O. Lennard-Jones fluid mixtures in contact with semipermeable membranes. A density functional approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 3366–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, P.; Patrykiejew, A.; Reszko-Zygmunt, J.; Sokolowski, S. Phase behaviour of a Lennard-Jones fluid in a pore with permeable walls of a finite thickness: A density functional approach. Mol. Phys. 1999, 96, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryk, P. Effective interactions in colloid-semipermeable membrane systems. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, X.N.; Xu, Z.J. Structure of hard-core Yukawa fluid mixtures near a semi-permeable membrane: A density functional study. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G.; Wang, R.; Hu, M.X. Synthetic membranes for water purification: Status and future. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3368–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienken, J.; Diamantoglou, M.; Henne, W.; Nederlof, B. Artificial dialysis membranes: From concept to large scale production. Am. J. Nephrol. 1999, 19, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Lin, X.; Si, T.; He, Q. Gold nanoshell-functionalized polymer nanoswimmer for photomechanical poration of single cell membrane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6601–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Sheppard, D.N.; Smith, B.D. Development of synthetic membrane transporters for anions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, I.K.; Hess, H. A biomimetic, self-pumping membrane. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4823–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xu, L.; Tian, F.; Su, Q.; Zheng, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Zhu, C.; Guo, S.; et al. Rapid transport of deformation-tuned nanoparticles across biological hydrogels and cellular barriers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathijssen, A.J.T.M.; Jeanneret, R.; Polin, M. Universal entrainment mechanism controls contact times with motile cells. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2018, 3, 033103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, C.; Slabu, I.; Wiekhorst, F.; Bergemann, C.; von Eggeling, F.; Hochhaus, A.; Trahms, L.; Clement, J. Magnetic particle spectroscopy allows precise quantification of nanoparticles after passage through human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 3986–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenk, F.; Werner, S.; Rabel, M.; Jacobs, F.; Bergemann, C.; Clement, J.H.; Fischer, D. Comprehensive analysis of the in vitro and ex ovo hemocompatibility of surface engineered iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3271–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, E.K.; Gräfe, C.; Wiekhorst, F.; Bergemann, C.; Weidner, A.; Dutz, S.; Clement, J.H. Magnetic nanoparticles interact and pass an in vitro co-culture blood-placenta barrier model. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y. Penetration of lipid membranes by gold nanoparticles: Insights into cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, and their relationship. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5421–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Auth, T.; Gompper, G. Nano- and microparticles at fluid and biological interfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 373003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Wu, J.Z. Structures of hard-sphere fluids from a modified fundamental-measure theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 10156–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Wu, J.Z. Density functional theory for inhomogeneous mixtures of polymeric fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.; Evans, R.; Lang, A.; Kahl, G. Fundamental measure theory for hard-sphere mixtures revisited: The White Bear version. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 12063–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, G.A.; Carnahan, N.F.; Starling, K.E.; Leland, T.W., Jr. Equilibrium thermodynamic properties of the mixture of hard spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 54, 1523–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Kang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Kang, Y. Structural Properties of the Fluid Mixture Confined by a Semipermeable Membrane: A Density Functional Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041407
Zhang L, Kang Y, Sun Z, Kang Y. Structural Properties of the Fluid Mixture Confined by a Semipermeable Membrane: A Density Functional Study. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(4):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041407
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lihong, Yanshuang Kang, Zongli Sun, and Yanmei Kang. 2020. "Structural Properties of the Fluid Mixture Confined by a Semipermeable Membrane: A Density Functional Study" Applied Sciences 10, no. 4: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041407
APA StyleZhang, L., Kang, Y., Sun, Z., & Kang, Y. (2020). Structural Properties of the Fluid Mixture Confined by a Semipermeable Membrane: A Density Functional Study. Applied Sciences, 10(4), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041407




