Indian Gooseberry and Barley Sprout Mixture Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis Activity in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. Water Soluble Tetrazolium Salt (WST) Assay
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Oil Red O Staining
2.7. Glycerol Release Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
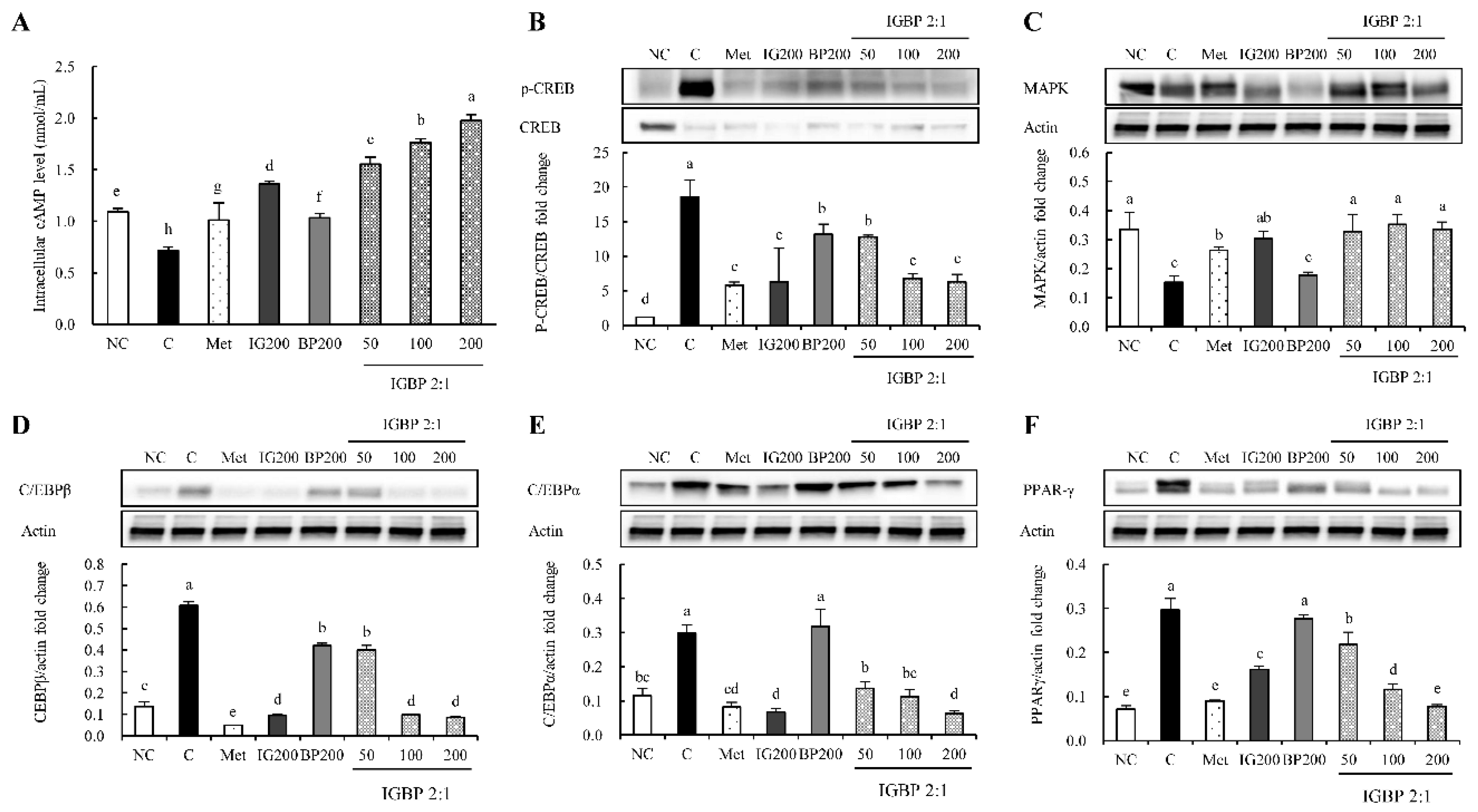
3.1. The IGBP Mixture Activated the cAMP Level Related to the Adipogenesis Mechanism in Adipocytes
3.2. The IGBP Mixture Regulated the Protein Expression Levels Related to the Adipogenesis Mechanism in Adipocytes
3.3. The IGBP Mixture Regulated the Protein Expression Levels Related to the Adipogenic Gene in Adipocytes
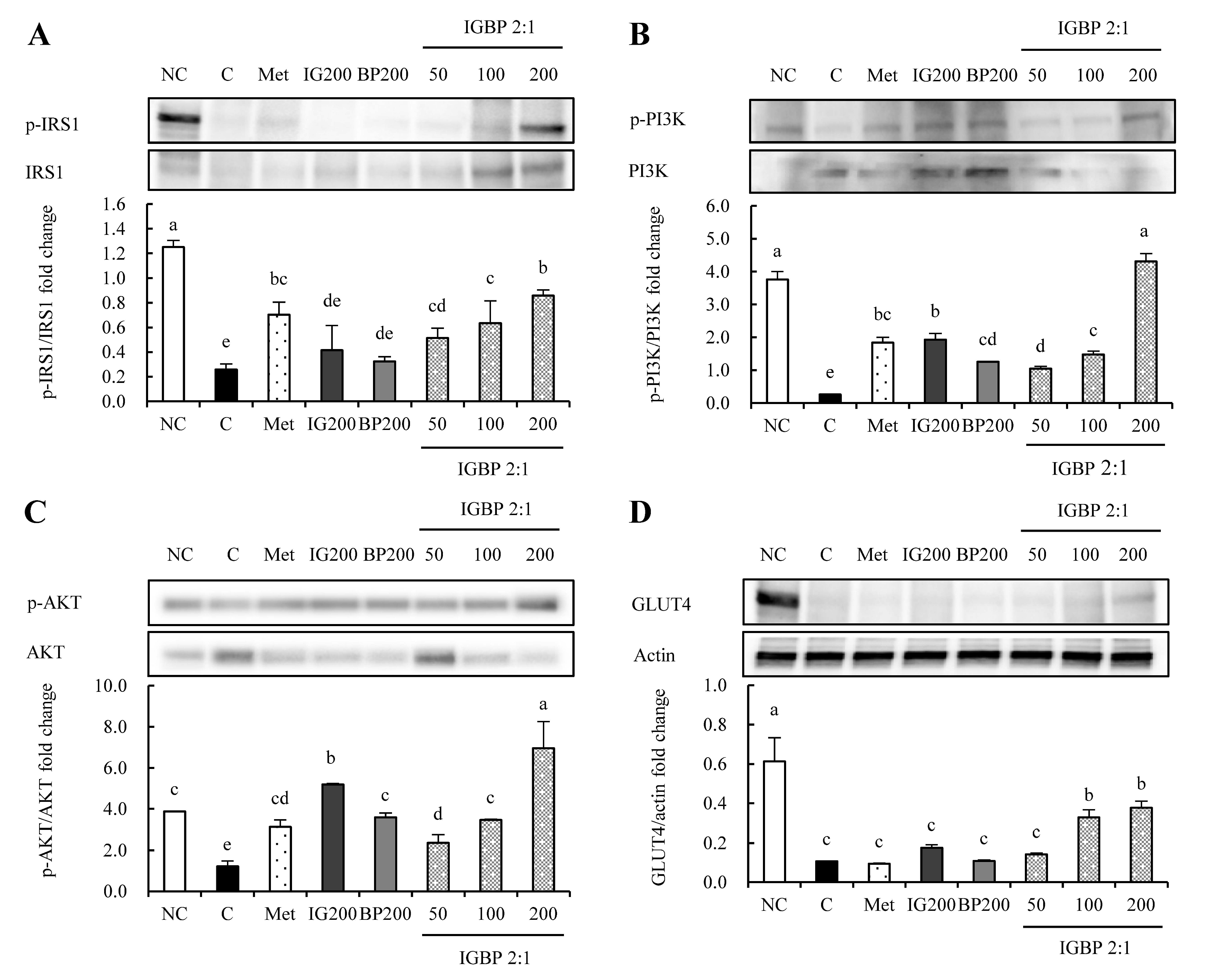
3.4. The IGBP Mixture Regulated the Protein Expression Levels Related to GLUT4 Signaling in Adipocytes
3.5. The IGBP Mixture Regulated the Protein Expression Levels Related to Lipogenesis Mechanism in Adipocytes
3.6. The IGBP Mixture Inhibited the FA Levels in Adipocytes
3.7. The IGBP Mixture Inhibited the Lipid Accumulation in Adipocytes
3.8. The IGBP Mixture Increased the Glycerol Release in Adipocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mark, D.H. Deaths attributable to obesity. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005, 293, 1918–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, B.; Rippmann, J.F.; Tadayyon, M.; Hamilton, B.S. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase prevents preadipocyte differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephered, P.R.; Gnudi, L.; Tozzo, E.; Yang, H.; Leach, F.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose cell hyperplasia and enhanced glucose disposal in transgenic mice overexpressing GLUT4 selectively in adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 22243–22246. [Google Scholar]
- Gnudi, L.; Shepherd, P.R.; Kahn, B.B. Overexpression of GLUT4 selectively in adipose tissue in transgenic mice. Implications for nutrient partitioning. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1996, 55, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolins, N.E.; Quaynor, B.K.; Skinner, J.R.; Tzekov, A.; Park, C.; Choi, K.; Bickel, P.E. OP9 mouse stromal cells rapidly differentiate into adipocytes. Characterization of a useful new model of adipogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.S.; Chung, C.S.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, T.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, C.S. Inhibitory effect of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on lipid accumulation of 3T3-L1 cells. Obestiy 2007, 15, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; Lane, M.D. Sequential gene promoter interactions of C/EBPβ, C/EBPα, and PPARγ during adipogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 319, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, U.A.; Stephens, J.M. Transcriptional factors that promote formation of white adipose tissue. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 318, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Wu, P.; Liu, J.; Gong, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, W. Identification of the potential key genes for adipogenesis from human mesenchymal stem cells by RNA-Seq. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 20217–20227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Rong, Y.; Bao, L.; Nie, B.; Ren, G.; Zheng, C.; Amin, R.; Arnold, R.D.; Jeganathan, R.B.; Huggins, K.W. Suppression of adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation by stearidonic acid (SDA) in 3T3-L1 cells. Lipid Health Dis. 2017, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Garcia, Z.; Oliveira, M.C.; Lima, R.L.; Soriani, F.M.; Cisalpino, D.; Botion, L.M.; Teixeira, M.M.; Souza, D.; Ferreira, A.V.M. Lack of platelet-activating factor receptor protects mice against diet-induced adipose inflammation and insulin-resistance despite fat pad expansion. Obesity 2014, 22, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, J.F. Fruits of Warm Climates; Florida Flair Books: Miami, FL, USA, 1987; pp. 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaveni, M.; Mirunalini, S. Therapeutic potential of Phyllanthus emblica (amla): The ayurvedic wonder. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 21, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, S.; Aggarwal, A. Indigenous drugs insichemic heart disease in patients with diabetes. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2009, 15, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, K. Plant foods in the management of diabetes mellitus: Spices as beneficial antidiabetic food adjuncts. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltanov, E.A.; Shikov, A.N.; Dorman, H.J.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Makarov, V.G.; Tikhonov, V.P.; Hiltunen, R. Chemical and antioxidant evaluation of Indian gooseberry (Emblica officinalis Gaertn., syn. Phyllanthus emblica L.) supplements. Phytother Res. 2009, 23, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensi, M.; Ortega, A.; Mena, S.; Feddi, F.; Estrela, J.M. Natural polyphenols in cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011, 48, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Park, D.-H.; Lee, W.-Y. Optimization of microwave assisted extraction process of Hordeum vulgare L. by response surface methodology. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2017, 24, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paulíčková, I.; Ehrenbergerová, J.; Fiedlerová, V.; Gabrovsá, D.; Havlová, M.; Kopáček, J.; Ouhrabková, J.; Pinkrová, J.; Rysová, J.; Vaculová, K.; et al. Evaluation of barley grass as a potential source of some nutritional substances. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2008, 25, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, M.; Shibamoto, T. Flavonoids with potent antioxidant activity found in young green barley leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6260–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M. Quality characteristics of cookies added with barley sprout powder. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2015, 28, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, A.R.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, H.S.; Shim, K.W. Effects of a dietary supplement with barley sprout extract on blood cholesterol metabolism. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.-K.; Lee, Y.-M.; Park, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-J. Effect of young barley leaf powder on glucose control in the diabetic rats. Korean J. Community Living Sci. 2016, 27, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Lee, M.; Yun, J.-M.; Kim, D.; Lim, H. Anti-obesity effects of combined extracts of Terminalia chebula and Phyllanthus emblica (FBF-TC) in matured 3T3-L1 adipocytes and high fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 48, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.; Lee, M.; In, G.; Han, S.-T.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, O.-K.; Lee, J. The non-saponin fraction of Korean Red Ginseng (KGC05P0) decreases glucose uptake and transport in vitro and modulates glucose production via down-regulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in vivo. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.-T.; Nguyet, N.T.M.; Dinh, T.C.; Lien, N.V.T.; Nguyen, K.-H.; Ngoc, V.T.N.; Tao, Y.; Son, L.H.; Le, D.-H.; Nga, V.B.; et al. An update on physical health and economic consequences of overweight and obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Willer, C.J.; Berndt, S.I. Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J. Who cares for nutrition information at a restaurant? Foo-related lifestyles and their association to nutrition information conscious behaviors. Brit. Food J. 2016, 118, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Kim, C.-T.; Kim, I.-H.; Kim, Y. Inhibitory effects of green tea catechin on the lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesanya, O.A.; Senuga, T.O.; Oyenike, M.A.; Adam, M.A.; Adeoye, A.O.; Shittu, L.A.J. Effects of ethanolic extract of Irvingia gabonensis on the liver of progesterone induced obesity in female Swiss mice. Res. J. Health Sci. 2019, 7, 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-R.; Lee, Y.-S.; Choi, B.-K.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.-B.; Kim, T.-M.; Oh, H.J.; Yang, S.H.; Suh, J.-W. Root extracts of adenophora triphylla var. japonica improve obesity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K.E.; Colton, L.A.; Erickson, P.F.; Friedman, J.E.; Cha, H.C.; Keller, P.; MacDougald, O.A.; Klemm, D.J. Regulation of cyclin D1 and wnt10b gene expression by cAMP-responsive element-binding protein during early adipogenesis involves differential promotor methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35096–35105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Puig, A.; Jimenez-Liñan, M.; Lowell, B.B.; Hamann, A.; Hu, E.; Spiegelman, B.; Flier, J.S.; Moller, D.E. Regulation of PPAR gamma gene expression by nutrition and obesity in rodents. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzo, E.; Shepherd, P.R.; Gnudi, L.; Kahn, B.B. Transgenic GLUT-4 overexpression in fat enhances glucose metabolism: Preferential effect on fatty acid synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, E956–E964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; DeFronzo, R.A. Pathogenesis of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. J. Biomed. Biotechonol. 2010, 2010, 476279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.C.; Pessin, J.E. Ins (endocytosis) and outs (exocytosis) of GLUT4 trafficking. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Cha, B.-Y.; Choi, S.-S.; Choi, B.-K.; Yonezawa, T.; Teruya, T.; Nagai, K.; Woo, J.-T. Nobiletin improves obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 24, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenear, A.; Mao, J.; Oden, K.; Seyfert, H.M. All three promoters of the acetyl-coenzyme A-carboxylase ALPA-encoding gene are expressed in mammary epithelial cells of ruminants. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. The animal fatty acid synthase: One gen, one polypeptide, seven enzymes. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, J.D.; Horton, J.D. Molecular mediators of hepatic steatosis and liver injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Pacot, C.; Dugail, I.; Lemarchand, P.; Guichard, C.; Lièpvre, X.I.; Berthelier-Lubrana, C.; Spiegelman, B.; Kim, J.B.; Ferré, P.; et al. ADD1/SREBP-1c is required in the activation of hepatic lipogenic geneexpression by glucose. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 3760–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-K.; Park, S.-B.; Lee, D.-R.; Lee, H.J.; Jin, Y.-Y.; Yang, S.H.; Suh, J.-W. Green coffee bean extract improves obesity by decreasing body fat in high-fat diet induced obese mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Jung, Y.; Seo, S.J.; Kim, S.-M.; Shim, Y.J.; Cho, S.H.; Chung, S.-I.; Yoon, Y. Berberine activates AMPK to suppress proteolytic processing, nuclear translocation and target DNA binding of SREBP-1c in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4139–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hietanen, E.; Greenwood, M.R. A comparison of lipoprotein lipase activity and adipocyte differentiation in growing male rats. J. Lipid Res. 1977, 18, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-J.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.-L.; Park, M.-R.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, O.-K.; Nam, D.-E. Indian Gooseberry and Barley Sprout Mixture Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis Activity in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249078
Park S-J, Kim D, Kim J-L, Park M-R, Kim TG, Kim O-K, Nam D-E. Indian Gooseberry and Barley Sprout Mixture Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis Activity in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(24):9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249078
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Soo-Jeung, Dakyung Kim, Jong-Lae Kim, Mi-Ryeong Park, Tae Gi Kim, Ok-Kyung Kim, and Da-Eun Nam. 2020. "Indian Gooseberry and Barley Sprout Mixture Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis Activity in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes" Applied Sciences 10, no. 24: 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249078
APA StylePark, S.-J., Kim, D., Kim, J.-L., Park, M.-R., Kim, T. G., Kim, O.-K., & Nam, D.-E. (2020). Indian Gooseberry and Barley Sprout Mixture Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis Activity in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Applied Sciences, 10(24), 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10249078




