Abstract
In this paper, the anisotropic mechanical properties of rolled AZ31 magnesium alloys are investigated using nanoindentation tests at room temperature. Nanoindentation was carried out at four angles, including the rolling direction (0°), diagonal direction (45°), transverse direction (90°), and vertical direction (ND). Experimental results show that hardness increases as the rolling angle increases from 0° to 90° and is lowest in the ND direction. The hardness independent of the effect of indentation depth is obtained by analyzing the indentation size effect and then converting hardness values into yield strengths. A new criterion is proposed on the basis of the Hill48 yield criterion. The data obtained through the above experiments are used to determine the parameters in the new criterion. Finally, a solution to the challenge of modeling a function that accurately describes the anisotropic yielding behavior of AZ31 magnesium alloys is proposed using the nanoindentation technique to solve the requirements of specimen size and experimental methods of the macro test.
1. Introduction
Magnesium alloys have aroused great research interest and are used in many applications on account of their excellent properties, which include high strength and good wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. However, although magnesium alloys present many advantages over other alloys, they are not perfect metals, because of their poor formability and corrosion resistance at ambient temperature. Magnesium alloys have a hexagonal closed-packed crystal structure with a limited number of available slip systems (basal {0001}, prismatic {1010}, and pyramidal {1011}), which leads to their poor formability during cold working [1]. While cast magnesium alloys are used more extensively than deformed magnesium alloys, the strength, ductility, and mechanical properties of the former are poorer than those of the latter. AZ31 is one of the most widely used alloys currently available. Rolling is an important means to improve the properties of this type of alloy. Under annealing and mechanical twinning, magnesium can show anisotropy at room temperature; thus, the nature of the plastic deformation of magnesium is quite complex [2]. Studies on the deformation and damage behavior of magnesium indicate that anisotropy clearly occurs during magnesium alloy deformation. Initial textures can impact the shape and stress–strain behavior of the samples [1]. The anisotropic mechanical characteristics of AZ31 magnesium alloys have a significant influence on their plastic deformation. Therefore, obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the anisotropic mechanical behavior of magnesium alloys is important.
An accurate description of the magnesium alloy yielding behavior is essential to predict its forming processes. Industrial applications require an overall understanding of the mechanical properties of rolled AZ31 alloys. An accurate mathematical description is significant for predicting material deformation and yielding behaviors; thus, researchers have exerted considerable efforts over the last several decades to establish a solid foundation through which the magnesium yielding and deformation behaviors may be described. In 1864, Tresca established a phenomenological model to describe the yield of materials using the concept of maximum shear stress. Hu proposed an anisotropic yield criterion that satisfies the anisotropic presentation under uniaxial and equibiaxial tension [3]. Masse et al. [4] concluded that taking plastic anisotropy into account obviously improves the estimation of the final width. Many reports on the measurement of mechanical properties at the macro scale have been published. However, the in situ acquisition of the micro-scale mechanical properties of AZ31 alloys has yet to be conducted. Basu et al. [5] investigated size-dependent plastic responses by nanomechanical testing, high-resolution microscopy, and phase analysis and showed that the local microstructure has an obvious influence on small-scale plastic responses. Knowledge of the micro-scale mechanical properties of AZ31 alloys could provide a fundamental basis for its applications.
Most traditional experimental approaches, such as compression, tension, and torsion, are based on conventional bulk-scale testing, are destructive, and require a large number and volume of materials. The nanoindentation testing technique, a non- or semi-destructive approach, is considered a reliable, convenient, and robust approach with which to study the mechanical properties of materials at the nano- and micro-scales. Many scholars have proposed a series of simple mechanical properties for AZ31 alloys determined from indentation tests. However, in-depth studies of the mechanical properties of AZ31 alloys obtained via nanoindentation must be carried out, which can solve the impact due to the local deformation of the indentation test and complex operating conditions. In this study, nanoindentation tests were conducted using the continuous stiffness measurement technique (CSM), and the hardness of AZ31 alloys independent of size effects is obtained from the Nix model. The hardness values obtained are converted into strength values by using Tabor’s factor, and the material parameters in the criteria were calculated to establish the anisotropic yield criterion of AZ31 alloys.
2. Materials and Experimental Procedure
The chemical composition of the material was Mg-90 wt.% Al-0.3 wt.% Zn-0.1 wt.%. The magnesium sheet was produced by the traditional rolling method. As shown in Figure 1, the specimens were machined into dimensions of 5 mm × 5 mm × 5 mm in the rolling direction (0°), diagonal direction (45°), transverse direction (90°), and vertical direction (ND). The nanoindentation tests were performed using a Nanoindenter G200 test system produced by Agilent Technologies with a triangular pyramid Berkovich diamond indenter. The optical microscopic images were performed using the GX53 Metallographic Microscope produced by OLYMPUS. Prior to indentation testing, the test surface was ground using a series of SiC sand papers with gradually finer grains and polished to a scratch-free mirror-like finish. In this study, the maximum indentation depth was set to 2000 nm and the indentation strain rate was 0.001. Each test was performed at room temperature and repeated thrice. The mean hardness was used for the following discussion. The maximum indentation depth and Poisson’s ratio of the AZ31 alloys were set to 2000 nm and 0.28, respectively. A constant indentation strain rate was implemented by maintaining a constant loading rate () during the test. The hardness values were obtained during loading in CSM mode [6,7], and the dwell time at a constant load of 45 mN was set to 100 s.
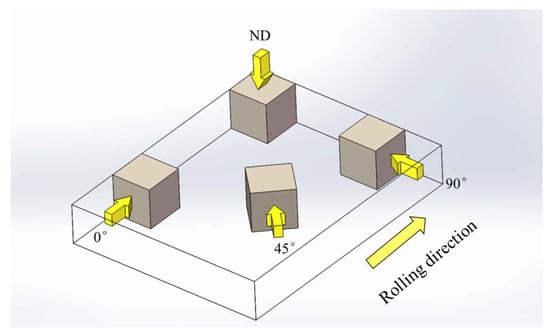
Figure 1.
Schematic of the loading of rolled AZ31 alloys in four directions.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows the optical microscopic images of the rolled AZ31 samples in the 0°, 45°, 90°, and ND directions (these directions are marked by the arrows in Figure 1); coarse grains of 5–20 µm could be observed in the samples. Barnett et al. found that grain size affects the mechanical responses of wrought magnesium [8]. The grain sizes of the rolled samples in the four directions were significantly different, which could explain the observed differences in their strength. The nanoindentation experiments were carried out in four directions, as shown in Figure 1.
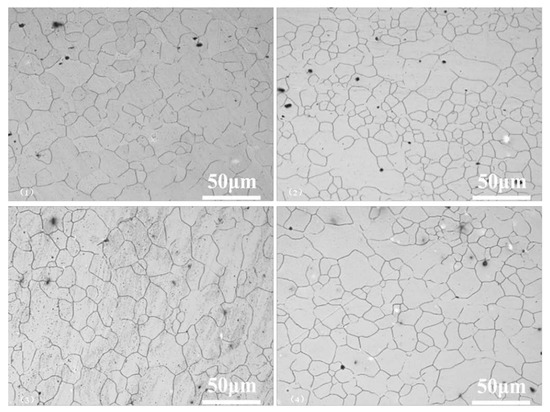
Figure 2.
Optical microscopic images of the rolled AZ31 samples in the 0°, 45°, 90°, and vertical (ND) directions.
In CSM mode, the function of contact stiffness can be expressed as follows [6]:
where , , and are the contact stiffness, amplitude of the harmonic excitation force, and response displacement amplitude, respectively. In addition, is the phase shift, is the angular frequency (), and , and m are the spring constant in the vertical direction, frame stiffness, and mass of the indenter, respectively. The contact stiffness increases nearly linearly with indentation depth in the three directions, as shown in Figure 3.
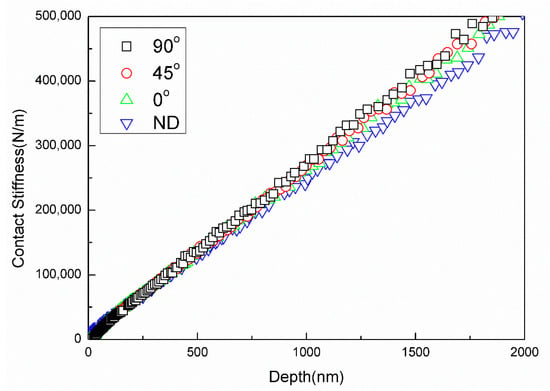
Figure 3.
Nanoindentation contact stiffness-depth curves obtained during the loading of rolled AZ31 alloys in four directions.
The projected contact area of a perfect Berkovich diamond indenter can be calculated as follows [9,10]:
where is the contact depth and calculated by the equation:
where and are the contact load and a contact for the Berkovich indenter, respectively. Hardness () is defined by the follow equation:
where is the contact load. The hardness–depth curves of the samples in four directions can then be obtained. As shown in Figure 4, the experimental data of 45° have better repetition.
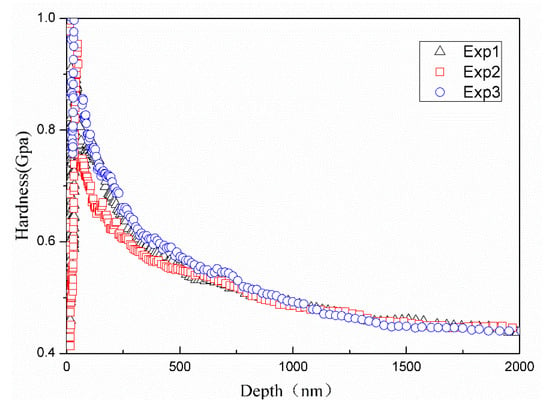
Figure 4.
Nanoindentation hardness-depth curves of 45° from three repeated experiments.
The hardness values of rolled AZ31 alloys during loading in the 0°, 45°, 90°, and ND directions clearly differ, as shown in Figure 5. As the indentation depth increases, the hardness values decrease. The hardness increases as the angle increases from 0° to 90° and is smallest in the ND direction. Hardness is affected by the plate texture during rolling and shows significant anisotropy. Some factors of uncertainty and error in nanoindentation tests include surface roughness and surface texture, among others. In this study, the maximum penetration depth of the sample was approximately 2000 nm; such a depth is sufficiently large to assume that the contribution of surface inconsistencies is negligible. The hardness values observed in the 0°, 45°, 90°, and ND directions are listed in Table 1.
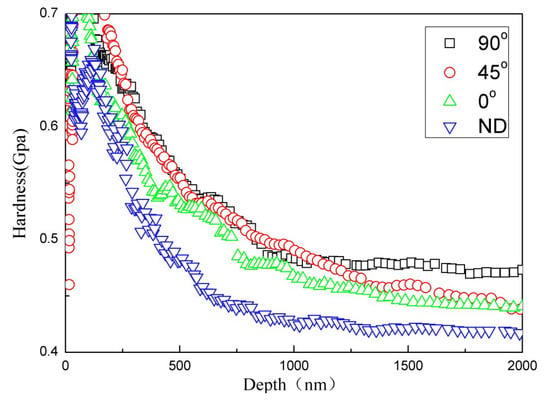
Figure 5.
Nanoindentation hardness-depth curves obtained during the loading of rolled AZ31 alloys in four directions.

Table 1.
Fitting values of hardness under different angles.
The indentation size effect refers to the variation in the indentation hardness (or indentation stress) as a function of indentation depth [11]. The effects of indentation depth on the mechanical properties of metals must be considered. Under the limit of infinite depth, Nix et al. [12,13] proposed a hardness model to investigate the indentation size effect of metal hardness as follows:
where is the hardness in the limit of infinite depth and is the characteristic length. The relationship between the square of hardness () and the reciprocal of indentation depth () should be linear, as shown in Equation (6). We performed the linear fitting of vs. . Based on the indentation data collected between 500 and 1500 nm, the slope and intercept of the fitted straight line are and , respectively. Thus, independent of the indentation size effect can be obtained (Figure 6).
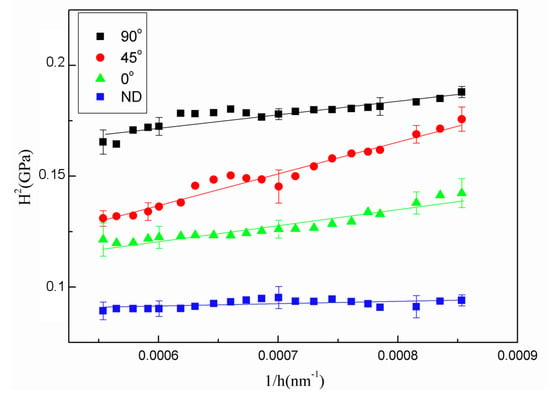
Figure 6.
H2 versus curves of the rolled AZ31 alloys in four angles.
may be determined from the results of linear fitting, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Fitting values of under different angles.
A Tabor’s factor of 3 can be used to convert the hardness values into yield stress values [14]:
The strength of magnesium alloys can be obtained using Equation (7). The yield stresses in different directions are presented in Table 3

Table 3.
Strength of the magnesium AZ31 alloys.
The anisotropy yield criterion of rolled AZ31 magnesium alloys is established according to the Hill 1948 yield function. The three-dimensional yield function proposed by Hill [15] is defined as follows:
where are used to describe direction-dependent yield stresses.
These coefficients can be obtained by considering the uniaxial compression at some angle relative to the rolling direction and denoting the uniaxial compressive yield stress . The stress components in the Cartesian axis system are:
Substituting (9) for in Equation (8) yields:
Based on the primitive function, the uniaxial compressive yield stresses for the rolling direction (0°), diagonal direction (45°), and transverse direction (90°) are formulated as follows:
The yield stress in the rolled-plane direction, which is denoted , can be concisely expressed as follows (12):
The following expression can be acquired by finding the primitive function, and four anisotropic parameters are formulated by solving Equations (11) and (12) as follows:
Through-thickness anisotropic parameters related to shear and are assumed to be identical to the anisotropic parameters of and calculated as follows [16]:
The yield stress clearly increases as the angle along the rolling direction increases. This result is consistent with the results of macroscopic compression yield strength. The anisotropic parameters in the yield function can be calibrated using the data in Table 2. The yield stress in the vertical direction is used to represent the effective yield stress . The calibrated anisotropic parameters are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Anisotropic parameters in the Hill yield function for rolled AZ31 alloys.
The anisotropic yield function determined via the nanoindentation test is utilized to describe the yield behavior of rolled AZ31 magnesium alloys. The following expression can be acquired by obtaining the primitive function:
4. Conclusions
The Hill48 yield function is calibrated using data obtained from nanoindentation tests because the proposed plasticity model is applied to the rolling process, during which materials mainly experience compression. The mechanical behavior of the AZ31 alloys is investigated via nanoindentation tests with the CSM technique. The indentation hardness exhibits anisotropic behavior and is relatively large under high angles along the rolling direction, that is, the hardness values increase as the angle increases from 0° to 90°. The hardness in the ND direction is smallest among the values obtained. The anisotropic mechanical behavior of the alloys is analyzed, and the hardness independent of the effect of indentation depth is calculated. Tabor’s factor can be used to convert hardness values into yield stress values. The Hill48 yield function of rolled AZ31 magnesium alloys is calibrated using the experimental results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W. and T.J.; methodology, T.J.; software, X.H.; validation, J.Q., X.L. and T.J.; formal analysis, X.S.; investigation, Z.W.; resources, Z.W. and T.J.; data curation, J.Q.; writing—originaldraft preparation, X.S.; writing—review and editing, T.J., Z.W. and X.H.; supervision, X.S.; project administration, X.L. and X.H.; funding acquisition, T.J. and X.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China [11772215, 11772217, and 11802199]. Tao Jin is grateful to the Open Fund of the State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical Structures, Xi’An Jiaotong University [SV2019-KF-15] for its support. All financial contributions are gratefully acknowledged. And The APC was funded by [11772215].
Conflicts of Interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Del Valle, J.; Pérez-Prado, M.; Ruano, O. Texture evolution during large-strain hot rolling of the Mg AZ61 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 355, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, M.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Gupta, M. Indentation-based rate-dependent plastic deformation of polycrystalline pure magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 716, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W. Characterized behaviors and corresponding yield criterion of anisotropic sheet metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 345, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, T.; Chastel, Y.; Montmitonnet, P.; Bobadilla, C.; Persem, N.; Foissey, S. Impact of mechanical anisotropy on the geometry of flat-rolled fully pearlitic steel wires. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, I.; Ocelík, V.; De Hosson, J.T.M. Size dependent plasticity and damage response in multiphase body centered cubic high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 150, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Cripps, A.; Johnsonm, K. Introduction to Contact Mechanics. Mechanical Engineering Series. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2002, 55, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Liu, E.; Jin, T.; Shu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, G.; Yang, X. Mechanical properties of cured isotropic conductive adhesive (ICA) under hygrothermal aging investigated by micro-indentation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2017, 122, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.R.; Keshavarz, Z.; Beer, A.G. Influence of grain size on the compressive deformation of wrought Mg–3Al–1Zn. Acta Materialia 2004, 52, 5093–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.S.; Yuan, G.Z.; Jia, C.N.; Yang, X.X.; Li, Z.G.; Shu, F.X. Strain rate sensitivity of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cusolder investigated by nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 613, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Xiao, G.; Jin, T.; Su, B.; Shu, X.; Ma, S. Indentation Strain Rate Sensitivity of CoCrFeNiAl0.3 High-Entropy Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri V, K. Springer Science+Business Media. J. Inf. Technol. Cases Appl. 2019, 21, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Nix, W.D.; Gao, H. Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: A law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Yang, X.; Qiu, J.; Chang, C.; Liu, E.; Duan, Q.; Shu, X.; Wang, Z.-H. Determination of power hardening elastoplastic constitutive relation of metals through indentation tests with plural indenters. Mech. Mater. 2019, 138, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, D. A simple theory of static and dynamic hardness. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London; Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character; The Royal Society: London, UK, 1948; Volume 192, pp. 247–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, R. A theory of the yielding and plastic flow of anisotropic metals. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London; Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character; The Royal Society: London, UK, 1948; Volume 193, pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Hou, H.; Liu, Y.; Lou, Y. A Study on Compressive Anisotropy and Nonassociated Flow Plasticity of the AZ31 Magnesium Alloy in Hot Rolling. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).