Abstract
As the existence of non-zero reflection coefficients in the real component of continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CV-QKD) systems, Eve can probe the system by sending the bright light pulses into Alice’s set-up. With the analysis of back-reflections, Eve only takes a few back-reflected photons to intercept information and obtain the raw key bit. In this paper, the attack problems are converted into the information leakage problems. First, we analyzed the Trojan horse attacks with different wavelengths and confirmed its side effects, such as crosstalk and anti-Stokes Raman scattering, by a numerical simulation. Then, based on the wavelength-dependent property of beam splitter, we presented a practical way to estimate the deviation of shot noise and therefore correct the excess noise by inserting different wavelength pulses under joint attacks. Finally, we specified the security bounds of the system through quantifying the excess noise bounds caused by the Trojan horse attacks and provided a theoretical reference for the secret key transmission of system. As a consequence, the transmission errors within the security bounds can be negligible and the legitimate users will not perceive the presence of Eve.
1. Introduction
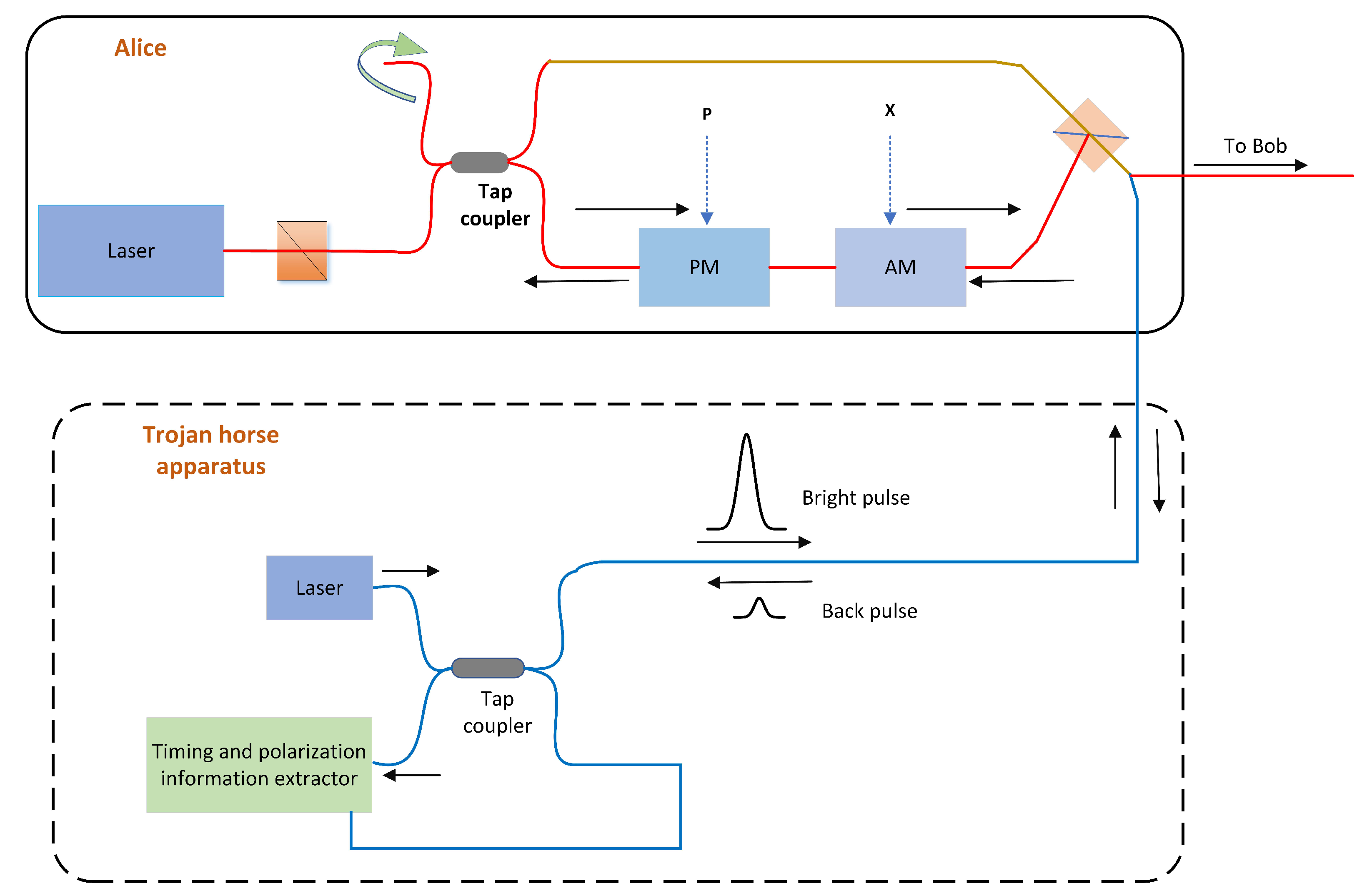
Quantum key distribution (QKD) refers to a method in which the two parties of communication share the key by transmitting the information on the quantum channel with the quantum state as the information carrier [1,2,3]. Its security is guaranteed by a quantum physical mechanism [1,4,5]. The theoretical and actual security analysis for continuous-variable (CV)-QKD has also been continuously developed in recent years [6]. Some researchers proved the security of CV-QKD based on the transmission of squeezed quantum states from the aspect of error correction code [7,8]. Subsequently, some researchers conducted general research on coherent attacks of arbitrary finite size against the system. They mainly analyzed the security of the coherent state protocol under the individual attack [9]. A Gaussian collective attack, as the optimal attack, was also confirmed in the subsequent research works [10,11,12,13,14,15]. The practical security analysis of CV-QKD has also begun to gain attention in recent years. Intercept-resent attack [16,17], calibration attack [18,19], local oscillator intensity attack [20], saturation attack [21], and wavelength attack [22,23] are more attractive. The quantum channel is a portal that eavesdroppers can use (see in Figure 1). The multiphoton mode potentially allows an attacker to organize unauthorized access to the quantum channel. The purpose of unauthorized access can be not only to intercept and read information, but also to synchronize the device of the attacker with the aim of interfering with the operation of the CV-QKD system [24]. Eve can also be used with legitimate users Alice and Bob: bright pulses emitted by Eve from the quantum channel to a QKD subsystem, such as Alice, will encounter multiple reflections and scattering sites. Therefore, the reflected pulse stream can be expected to propagate from the Alice device on the quantum channel. If Alice is not careful enough, Eve could find out exactly which quantum state she prepared and thus access the entire key. In general, the goal of Eve is to get as much information as possible about Alice’s sending status [25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. By measuring characteristics of reflected photons, Eve could make some conclusions on modulator’s settings or transmitted bits, then at least know transmission or detection bases. In order to limit Trojan horse attacks, the design of the system should satisfy only light of appropriate wavelengths can enter the optical fiber; the encoding optical components are only active for a short time; the amount of reflected light that Eve can use is limited by the known boundary. However, even these measures cannot completely prevent Trojan horse attacks.
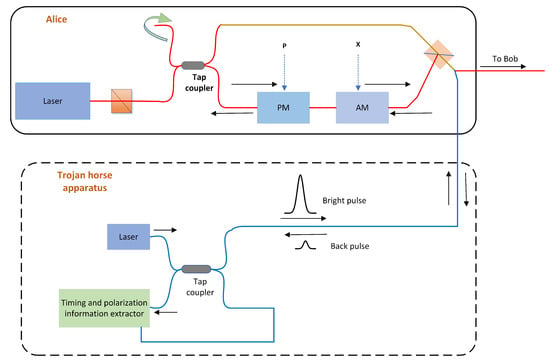
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of Trojan horse attacks. PM, phase modulation; AM, amplitude modulation; BS, beam splitter.
These attacks will inevitably increase the excess noise of the system, leading to system performance degradation, which will be discovered by users. In an actual CV-QKD system, Eve can first intercept the signals and the local oscillator (LO) sent by Alice, and then use the heterodyne detector to measure. Assume that Eve can control the beam splitter (BS) at Bob to have wavelength-independent characteristics. Eve uses the heterodyne detection protocol to attack the actual CV-QKD system by switching signals and different wavelengths LOs to estimate the deviation of shot noise and correct the excess noise [23,32,33,34]. Not only in this case, even if Bob monitors the total strength or LO strength, Eve can implement Trojan horse attacks without being discovered.
This article analyzed Trojan horse attacks on one-way CV-QKD systems. We deduced and calculated the numerical changes of excess noise under attacks with the same wavelength and different wavelength as the original pulse. Unfortunately, Eve’s bright pulse have a side effect, resulting in a large quantum bit error rate that effectively protects the system from our attacks. To eliminate this impact, we make use of the wavelength-dependent property of BS, making Eve can estimate the deviation of shot noise and then correct the excess noise by inserting different wavelengths pulses. As a consequence, the transmission errors within the security bounds can be negligible and the legitimate users will not perceive the presence of Eve. The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we turn attacks into an information leakage problem, and conducted a theoretical analysis of the security boundary of the system. In Section 3, we analyzed the Trojan horse attacks with the same wavelength and different wavelengths as the original pulse and confirm the impact of Trojan horse attacks on the excess noise in both cases. In Section 4, based on the imperfection that the BS has a wavelength-dependent property, we present a practical way for Eve to estimate the deviation of shot noise and therefore correct the excess noise by inserting different wavelength pulses under joint attacks. Then we quantified the excess noise bounds caused by the Trojan horse attacks to specify the security bounds of the system. We reached the conclusion in Section 5.
2. Theoratical Description
Eve’s action should be restricted to prevent Trojan horse attacks. She is physically limited by Raman scattering when retrieving quantum states. Obviously, the Trojan horse pulses will increase the excess noise, so the secret key rate will be reduced. The source of the increased excess noise is blind for legitimate parties. Therefore, when the excess noise increases, Alice and Bob do not know where the excess noise comes from. This may be caused by a defect in the device or a mutation in the communication environment. In this case, Trojan horse attacks will not be easily discovered. The only requirement to consider during Trojan horse attacks is the secret key rate should be positive. In the case of the collective attack, the reverse reconciliation CVQKD without the finite length effect, the key rate can be expressed as:
where represents the efficiency of information reconciliation, and represent the mutual information between Alice and Bob and the Holevo bound representing Eve’s possible information on Bob’s key. The upper bound on an eavesdropper’s information, the Holevo information , (assuming reverse reconciliation) reads:
where is the von Neumann entropy of the state accessible to Eve for collective measurement and is the von Neumann entropy of the same state after a projective (homodyne or heterodyne) measurement has been performed by Bob. Obviously, from the above analysis, we can see that in order to extract the key information, the secret key rate should be positive. Only in this case can the key sharing between Alice and Bob be successfully realized, and Eve can effectively obtain the key information by attacks. When the transmission distance of the system is constant, there is a maximum excess noise value satisfies this condition.
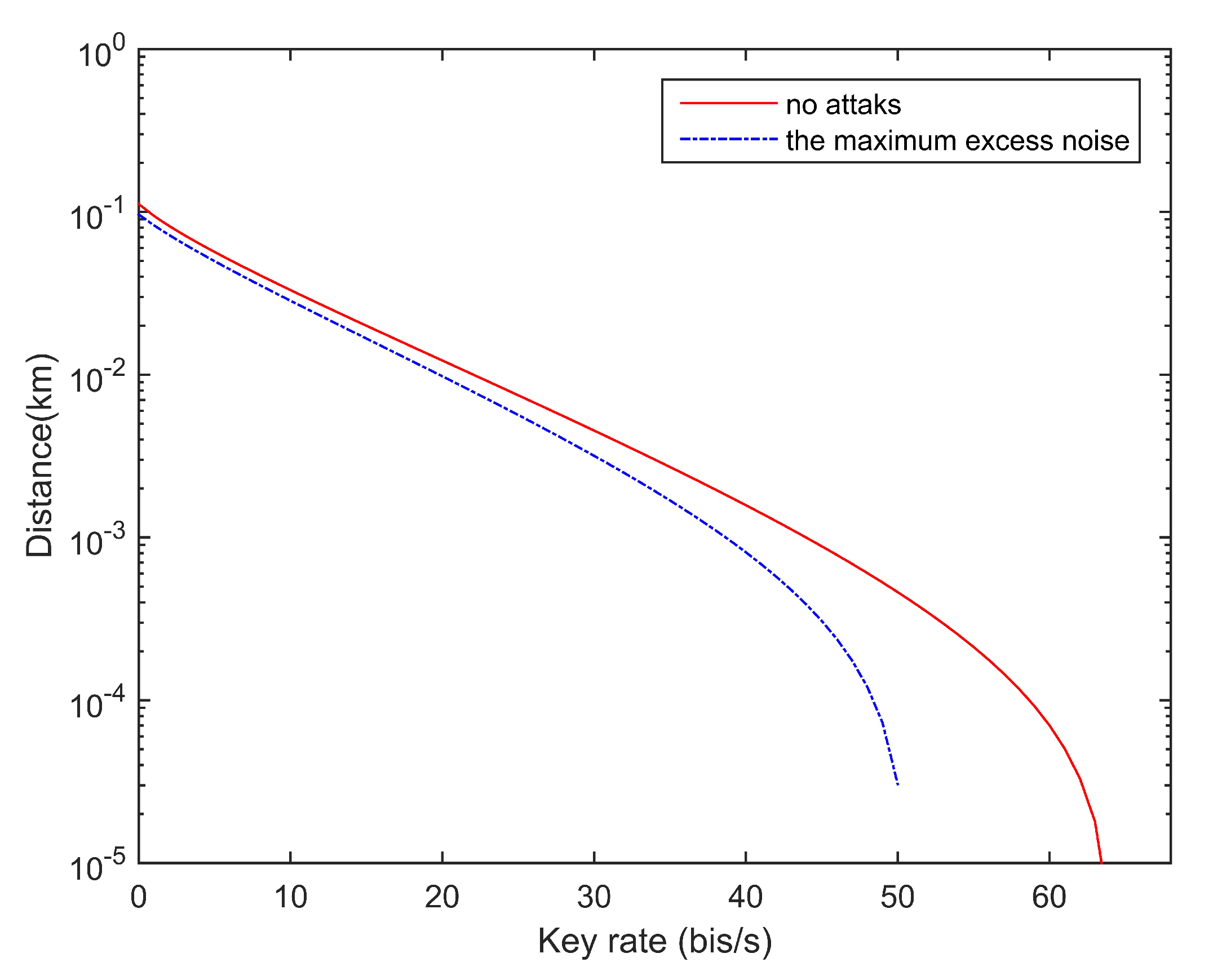
In Figure 2 above, we simulated the variation of the secret key rate with distance under different excess noises. The modulation variance is optimized, the quantum efficiency is 0.6, the electronic noise is 0.01 (in shot noise units), the practical reconciliation efficiency is . When the transmission distance is 50 km, as long as the excess noise satisfies , Alice and Bob can think that the key has been successfully transmitted.
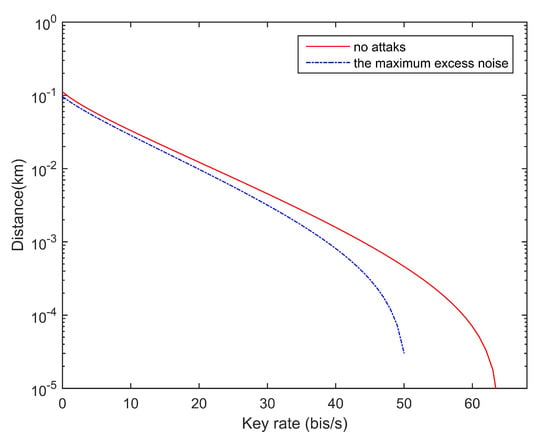
Figure 2.
Change of secret key rate with transmission distance under different excess noise levels. The excess noise without attacks is set to 0.01, the maximum excess noise when the transmission distance is 50 km is 0.0145.
3. Trojan Horsse Attacks
The characteristics of most optical components, such as the attenuation through the fiber or the reflectivity of the connector, vary with wavelength. Ideally, in order to describe the CV-QKD system, we analyzed Trojan horse attacks with different attack wavelengths.
3.1. Attacks at the Same Wavelength as the Original Pulses
The security certification of the CV-QKD protocol provides a verifiable mechanism for the safe operation of the system. However, practical CV-QKD implementations may deviate from these assumptions, leading to security loopholes [1,35,36,37]. Every optical element backscatters some amount of any incoming light. Consequently, every optical apparatus can be examined from the outside by shining into it a well-controlled light and analyzing the backscattered light. In a Trojan horse attack, an eavesdropper Eve may probe the CV-QKD system by injecting bright light pulses and analyzing the back reflections (Figure 1). These reverse reflections stem from a change inrefractive index, such as a connection between two optical components or a density fluctuations within the optical device. A back-reflected signal containing an imprint of the optical modulator used to encode the quantum states may allow the eavesdropper to extract parts of the raw key. Eve’s equipment is built around a standard optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR). Send in short optical pulses and analyze the backscattered light intensity is a function of time. From the known speed of light, the time can be translated into distances. Eve can indeed probe the setting of phase modulator by exploiting the change in birefringence in Titan-indiffus integrated waveguides.
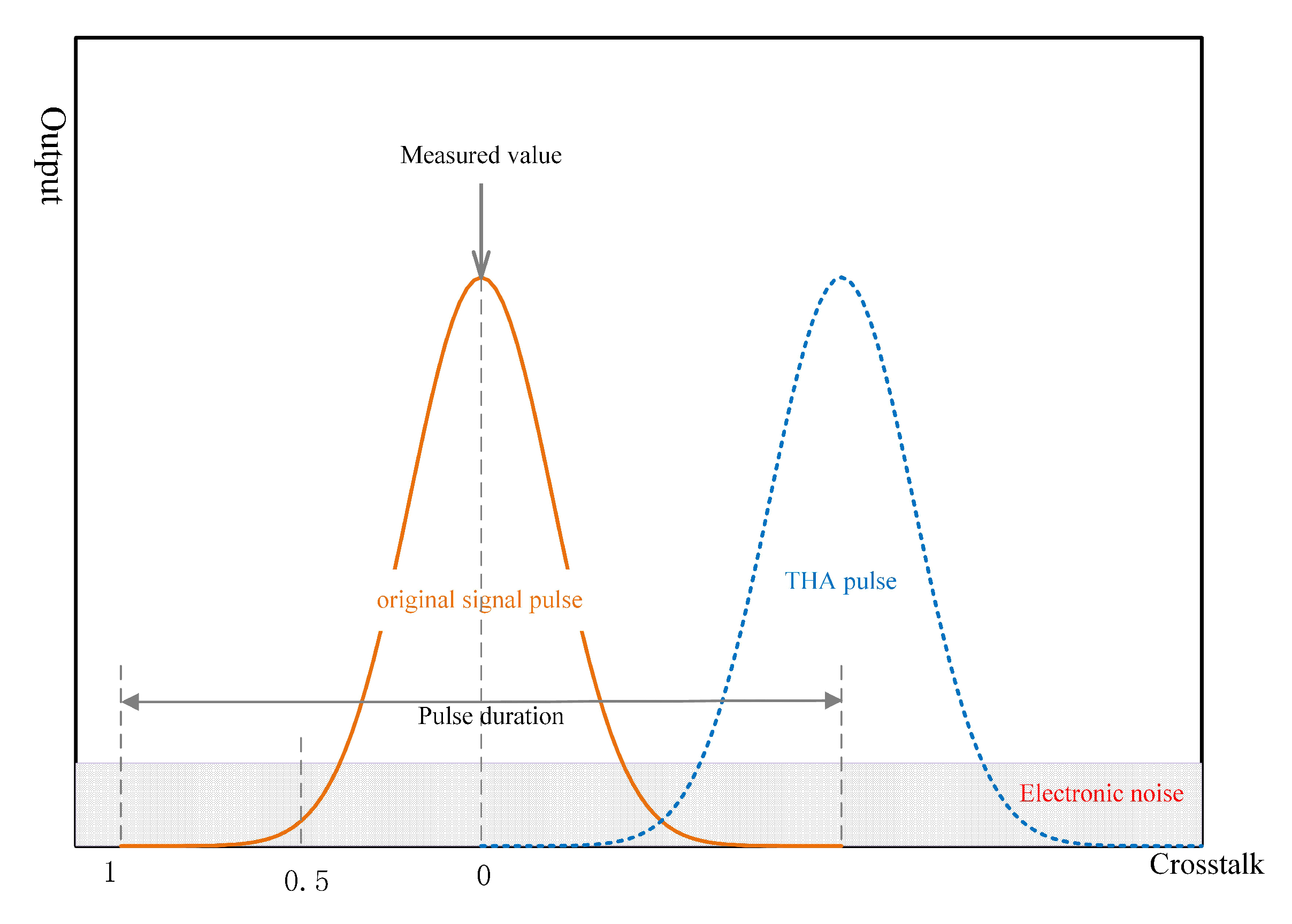
In practical operations, when the wavelength of the Trojan horse attack pulses are the same as the original pulse of the CV-QKD system which is 1550 nm in this article, crosstalk may occur between the pulses (see in Figure 3). In order to judge the impact of our Trojan horse attacks strategy, we need to quantitatively describe the effect of crosstalk between the Trojan horse pulses and original signal pulses.
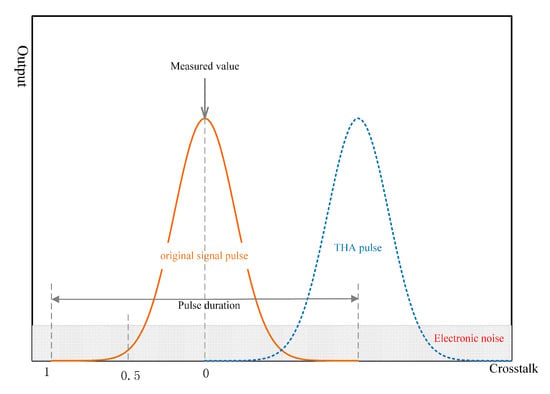
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of time-domain waveforms of Trojan horse pulse and original pulse. The solid red line represents the original pulse, and the dashed blue line represents the Trojan horse pulse. THA: Trojan horse attack.
In this paper, we define a parameter representing the degree of the crosstalk. The change of will affect the excess noise of the system, which will be analyzed in the following part.
The quantum channel involved in the CVQKD system is a normal linear model, and the relationship between Alice and Bob is as follows:
where , the parameter T is the transmission efficiency of the quantum channel and denotes the efficiency of homodyne detector. Vector , vector , N is the total number of pulses received. Vector z is the noise term following a central normal distribution with variance . is the shot noise variance. The electronic noise is not affected by the shift of pulses. The total channel-added noise expressed in shot noise units referred to the input is defined as:
where is the excess noise.
In order to perform parameter estimation, i.e., to estimate the parameter T and and then calculate the secret key rate, Alice and Bob reveal part of their data and use the following equation:
In the actual model, Eve has no access to the homodyne detector, so and would not be changed. For a chaotic source with an average noise photons number , the excess noise contributed in matched mode is given by:
where is the transmittance of the Bob’s system in the Gaussian modulation coherent state (GMCS). contributed from outside of Bob’s system can be expressed as:
where is the parameter contributed by the original CV-QKD system.
There is no crosstalk between Trojan horse signals and original signals when , which means the Trojan horse attacks operation will not increase the excess noise of the system. As the parameter increases, the excess noise of the system increases and the key rate decreases. Assuming that the measured value is equal to the peak value of the pulse, if the degree of crosstalk is too large and the added excess noise exceeds the tolerable range of the system, Trojan horse attacks will be easily discovered by Alice and Bob. Previous research results show that when the Trojan horse attacks pulses reach Alice’s side, the reflected pulse will return to Eve around 43 ns [28]. Eve emits bright pulses with an average photon number of about and will obtain a reflected average photon number of about Equation (4). Therefore the average number of photons leaked per nanosecond in Equation (6) can be calculated:
The transmittance of Bob’s system in the GMCS is set to 0.6. The excess noise of the original system is set to 0.01. When , the excess noise has nearly doubled, indicating that the crosstalk between pulses has a greater impact on the key rate and transmission distance at this time. From the calculation results show in Table 1, we can see that even if the crosstalk between the Trojan horse pulse and the original pulse is small, the effect of the total excess noise superimposed on the system is not negligible. In addition, as the degree of crosstalk increases, it will affect the transmission distance. Therefore, when performing Trojan horse attacks operations, in order to ensure that the attacks are not discovered by the legitimate parties of the communication, the crosstalk between the pulses should be controlled as small as possible.

Table 1.
The total excess noise of the system under different crosstalk levels .
3.2. Attacks with Different Wavelengths from the Original Pulses
The characteristics of most optical components, such as attenuation through an optical fiber or reflection from a connector, vary with wavelength. In order to characterize the CV-QKD system, we must perform OTDR measurements in a larger spectral range to prove that Trojan horse attacks are feasible [38,39].
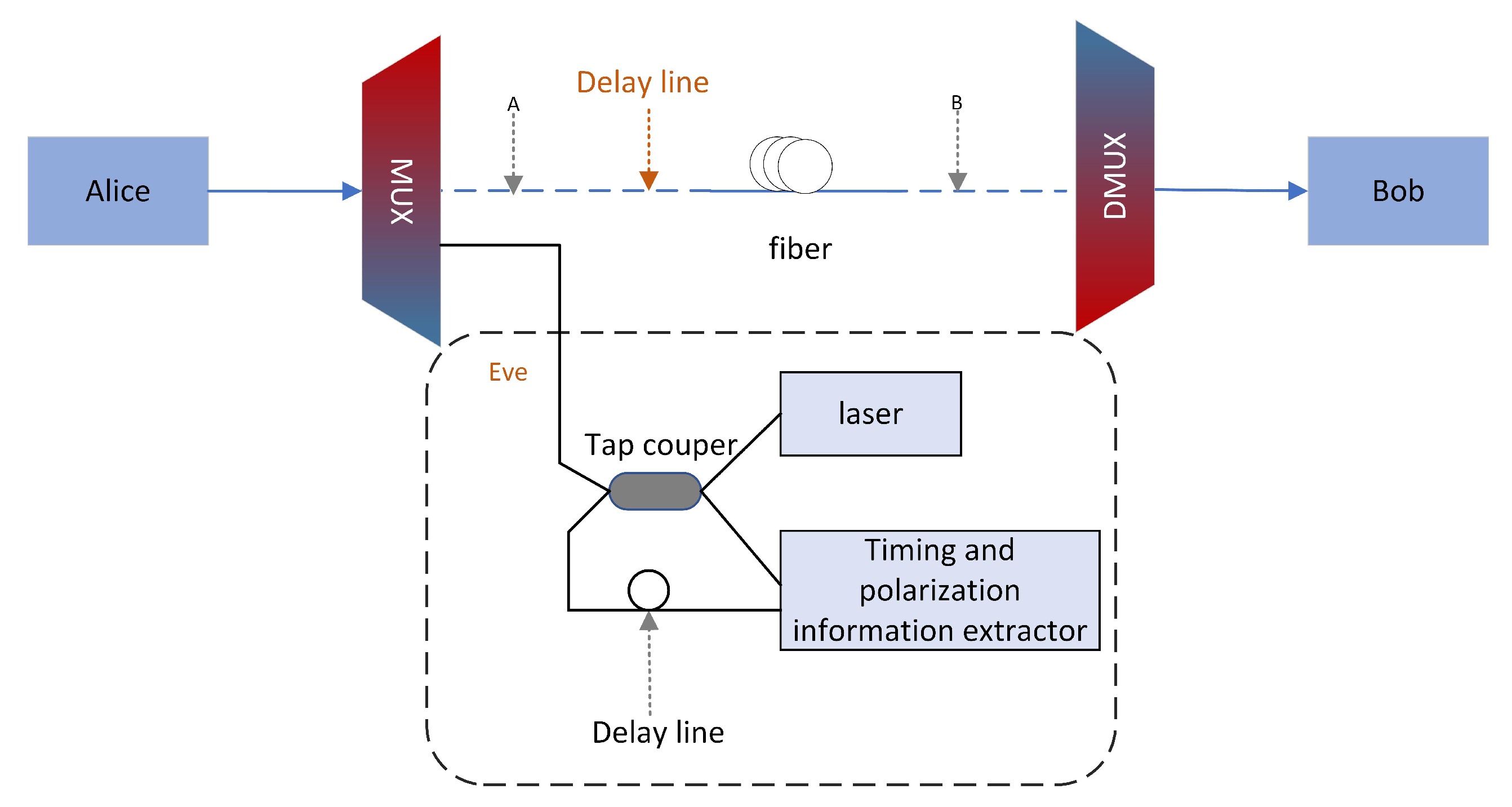
The optical pulse generated by Eve’s laser is divided into a reference pulse and an attack pulse on the coupler. The attack pulse is transmitted to Alice’s device through the multiplexer, then reflected back, and detected after passing through the original multiplexer and coupler. In this article, it is assumed that the detection scheme adopted is homodyne detection, so a reference pulse is needed. Assuming that the reference pulse is delayed in the transmission path, it can enter the homodyne detection together with the reflected pulse. In order to prevent Alice’s photons from being disturbed, a multiplexer must be used.
In this section, we use dense wavelength division multiplexing(DWDM) [40,41] technology to attack the system with Trojan horse pulses that are different from the original pulse wavelength (Figure 4). The pulses travel back and forth, Rayleigh backscattered light can considerably increase the noise. The actual transmission uses the concept of frames, a train of pulses that entirely fit in delay line in order to prevent errors that would otherwise result from Rayleigh backscattered. We will calculate and analyze the influence of WDM on excess noise and CV-QKD system performance. In fact, the number of noise photons generated by Trojan horse attacks when using DWDM technology will affect the assessment of shot noise.
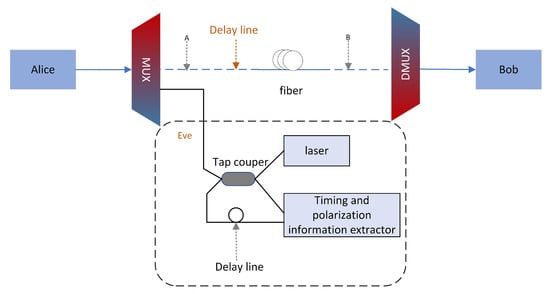
Figure 4.
Scheme of a Trojan horse attacks with different wavelengths from original pulse.
Due to the limited isolation of the demultiplexer (DEMUX), a small part of the Trojan horse attack signals will leak into the quantum channel. In order to analyze the noise, we made the following assumptions and restrictions on the existing system:
(a) Eve cannot modify the equipment in the Alice and Bob boxes, but can take advantage of the internal defects of both parties, such as the inherent laser phase noise on the Alice side, unbalanced homodyne detection or imperfect modulation.
(b) Since the positions of the reflective elements in Alice and Bob’s device are not controlled by Eve, she cannot always schedule her measurements in such a situation that the pulse can pass through the modulator during or when it is very close to the bit slot. In this case, the control voltage will cause a certain phase error, but this is acceptable to Eve, she does not need high precision to most of the bit information.
(c) The phase modulation efficiency of the Trojan horse pulses and the original pulses is the same.
(d) When Eve sends a bright pulse to Alice, the number of reflected photons is only a few, so the noise caused by the reflected photons passing through the DWDM device is ignored.
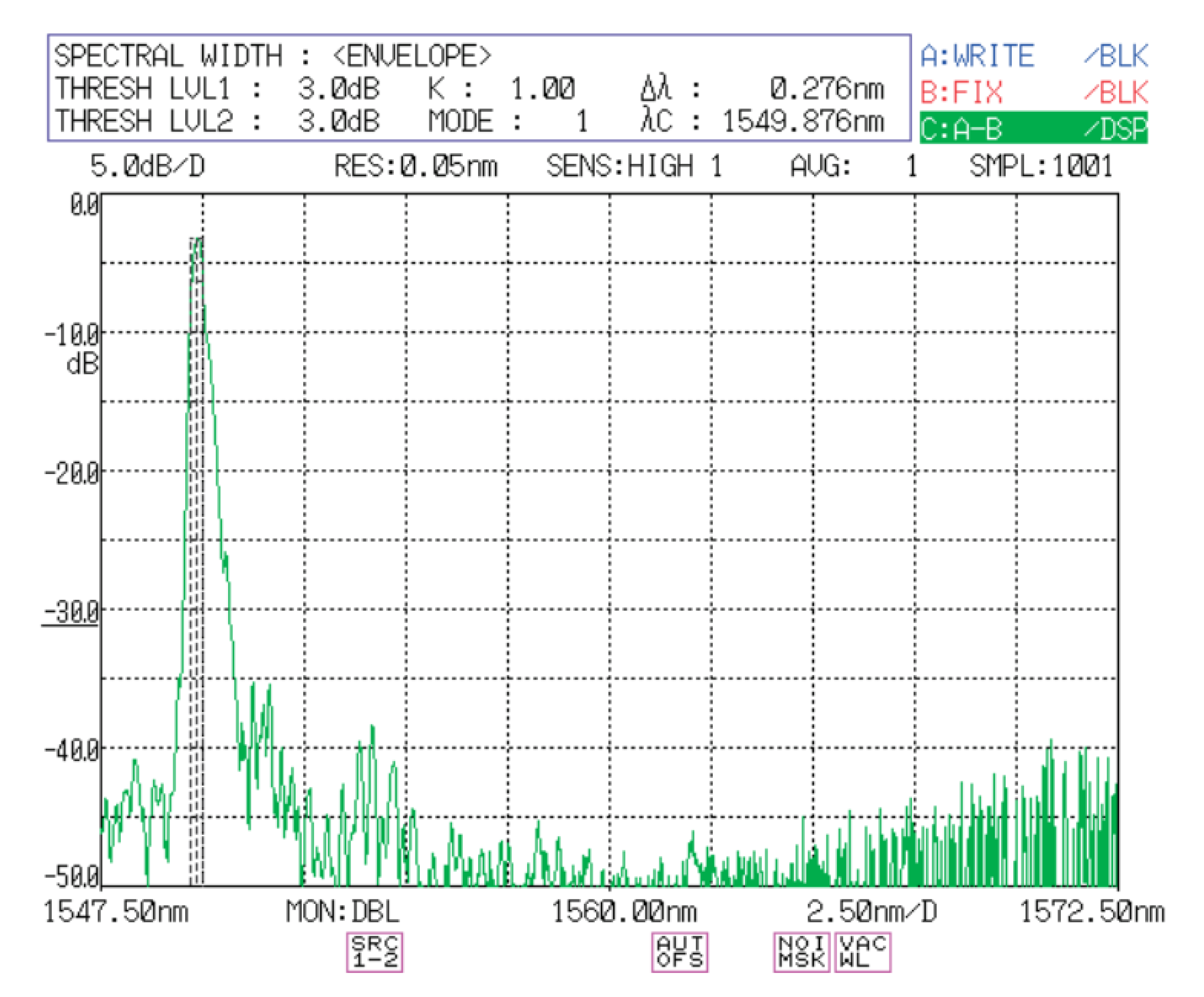
However, this defense measure still has certain loopholes: Take the wideband tunable filter WTF-200-T03 produced by Alnair Labs as an example, as shown in the Figure 5. The pulse can still be transmitted normally when the wavelength is within 1549.7–1550.3 nm. So when the original pulse is 1550 nm, our Trojan horse pulse adopts any wavelength of 1549.7–1550.3 nm to achieve the attack.
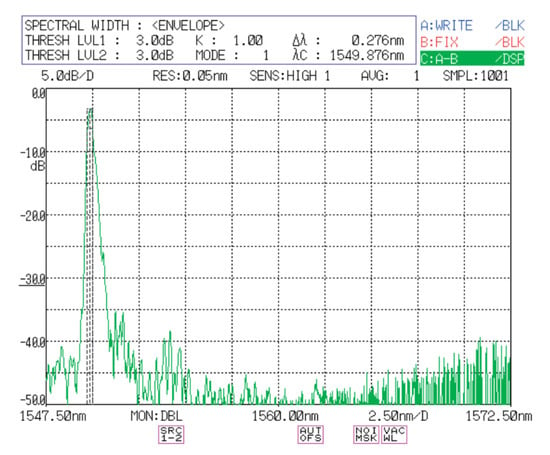
Figure 5.
Spectral responses of the band-pass output of WTF-T03-1550.
In the GMCS CV-QKD system, the signals leaked from the classical channel into the quantum channel will cause the noise photons to be in the “unmatched mode” of the LO. Assuming the output power of the Trojan horse signals from the fiber is (measured at point B in Figure 4), and the isolation of DMUX is defined as . The power of leakage photons received by Bob’side can be expressed as:
So the number of leaked noise photons is
where h is the Planck’s constant, f is the frequency of the Trojan horse attacks signals.
Raman scattering is caused by the inelastic interaction between the pump light and the optical photons in the fiber. When scattered photons are generated at frequencies above and below the pump light, corresponding to anti-Stokes scattering and Stokes scattering, respectively. As the Trojan horse signals propagate along the light in the channel, it can generate noise photons through different nonlinear processes. Existing research results indicate that when the wavelength of the quantum channel is shorter than the classical channel, anti-Stokes Raman scattering (SARS) is the most important linear process [42,43]. The corresponding noise photons are given by:
where is the Raman scattering coefficient, c is the speed of light, is the fiber attenuation coefficient, (measured at point A in Figure 4) is the input power of the Trojan horse attacks. L is the fiber length. Ref. [42] points out that we can get the following relationship between the input power Pin and output power Pout of the Trojan horse signal in the fiber:
So the Equation (10) can be rewritten as
the excess noise contribute of the matched mode impinging to Bob device is given by:
The total noise caused by the outside world to Bob’s side can be composed of the following two parts
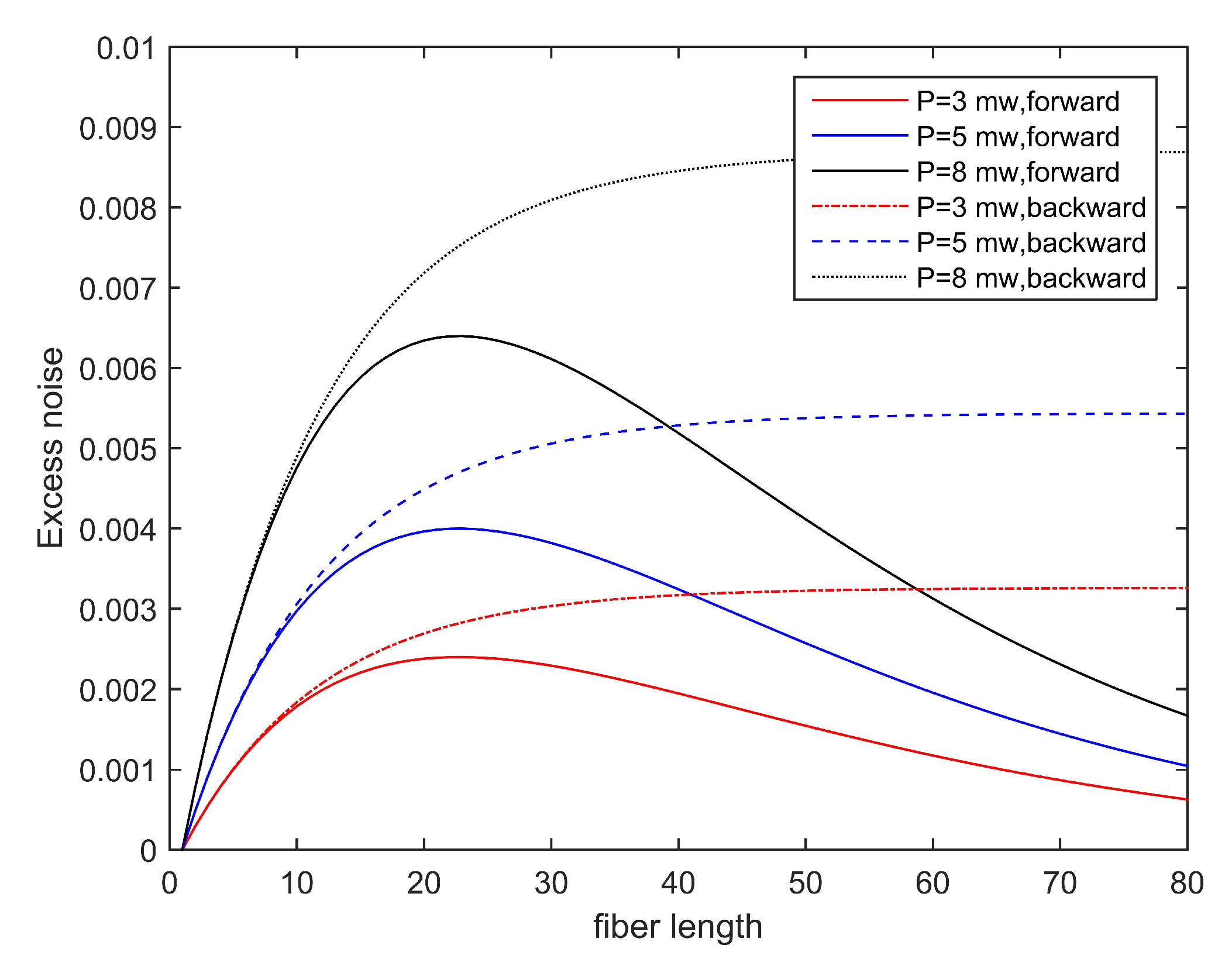
The two parts of Equation (11) respectively represent the number of Raman scattered noise photons in the forward and backward transmissions. We simulated the Raman noise of the forward and backward transmission channel and total excess noise when the input noise power is 1, 5, and 8 mw according to Equations (11) and (15). The fiber attenuation coefficient is set to be the fiber attenuation per km. is the transmittance of the channel. The transmittance of the multiplexer and demultiplexer are both set to 0.071. The transmittance of Bob’s system is set to 0.6. From the simulation results, it can be seen in the Figure 6 that when the transmission distance is equal to (i.e., 21 km), the forward Raman noise is the largest, and when the backward transmission, the Raman noise reaches a saturated state. Figure 7 shows the total excess noise of different input powers.
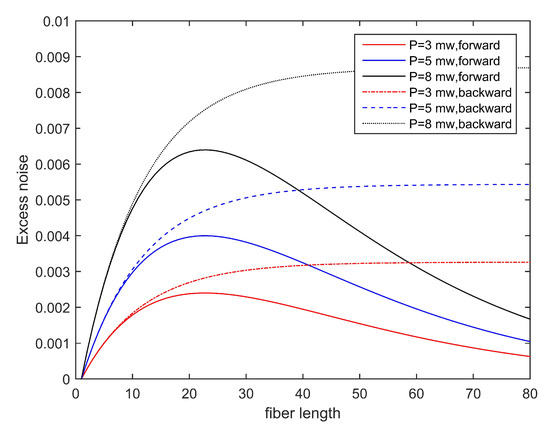
Figure 6.
Total excess noise induced by Trojan horse attacks with various input powers in homodyne detection.
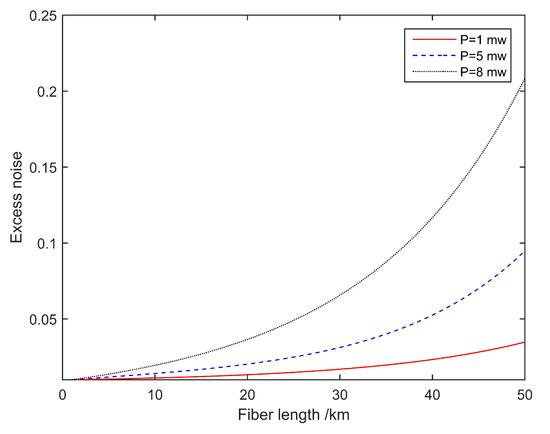
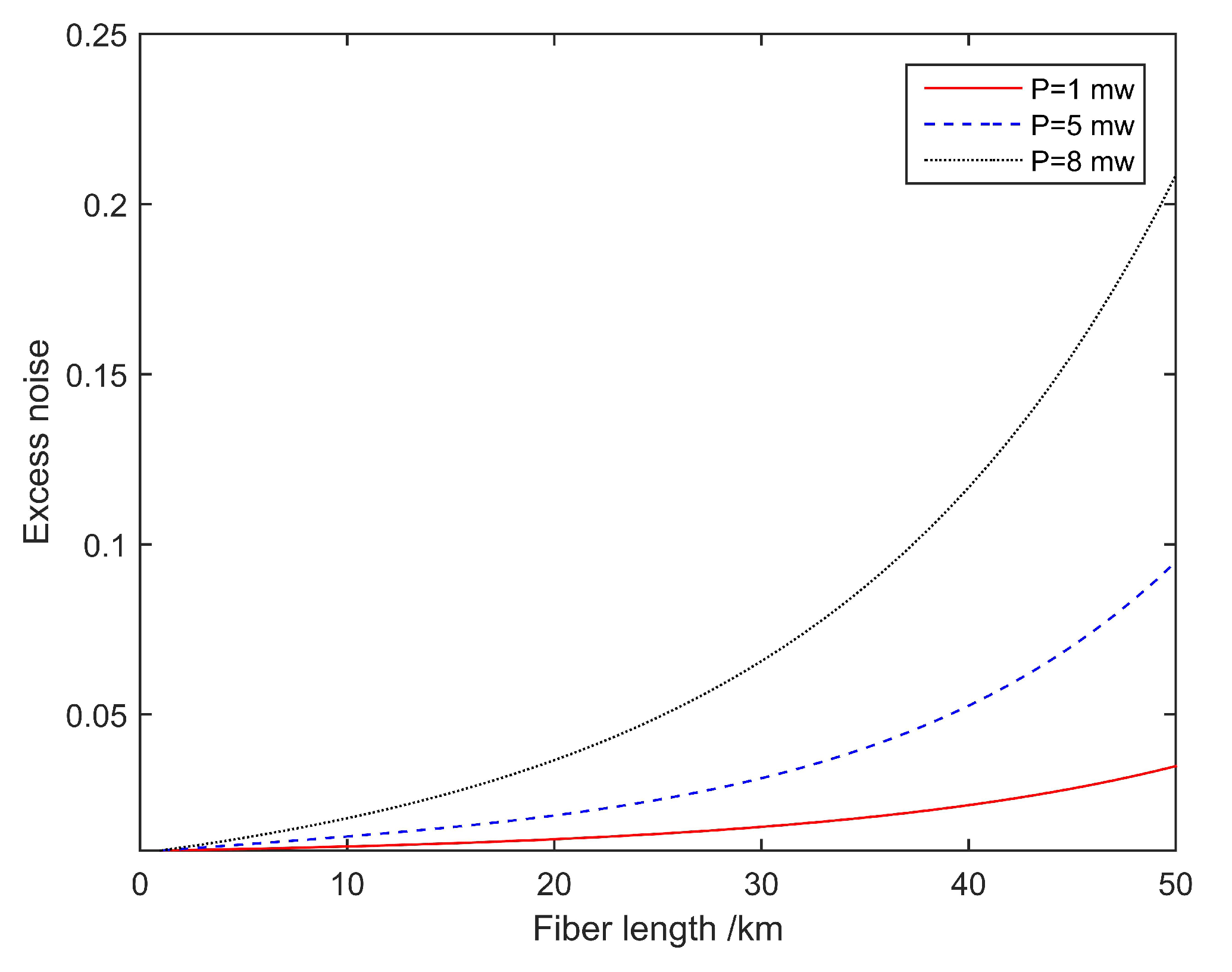
Figure 7.
Noise induced by Trojan horse attacks with various input powers in homodyne detection.
4. Bounds on Excess Noise
In our security analysis, the excess noise plays an important role. Here we provide more details about the threshold and describe a way to quantify it. Through the analysis in the previous two sections, we can conclude that when Eve uses Trojan horse attacks, there will always be a certain impact on the excess noise of the CV-QKD system. This kind of influence is easily noticed by Alice and Bob, leading to the failure of the attack. So how to steal information without being discovered will be a problem we have to consider.
4.1. Excess Noise Correction
Obviously, if we can offset the excess noise caused by Trojan horse attacks, then this will not be discovered by Alice and Bob. Previous studies have shown that Eve can estimate the deviation of emitted noise by inserting pulses of different wavelengths. The coupling ratio of fiber BS is closely related to the wavelength of input light: at the specified central wavelength, the fused biconical taper fiber BS has good working characteristics. However, if it deviates from the central wavelength, the BS ratio will periodically vary with the input wavelength. In the practical homodyne detection CV-QKD system, the transmittance of BS is controlled by preparing photons of different wavelengths. Then, by selecting the appropriate light intensity, the excessive noise added by the Trojan horse attack can be corrected.
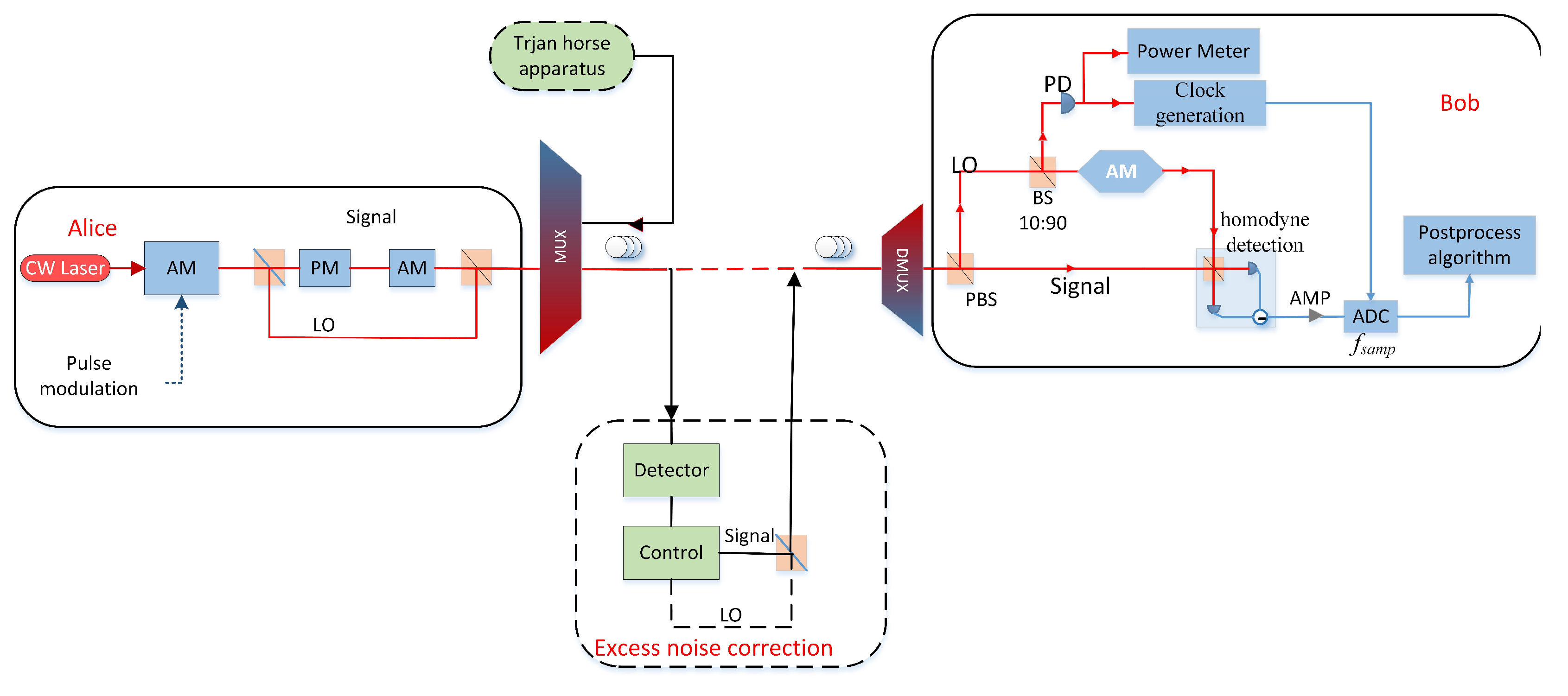
In our CV-QKD system, Alice’s laser source is divided into two coherent signal beams: a strongly attenuated quantum signal and a strong LO. The x and p quadratures of the coherent state are modulated according to the modulation variance by using a 5 GS/s digital-to-analog converter. The signal light and LO light are modulated in phase and amplitude, using time and polarization multiplexing, and then they are sent together into standard telecommunication fiber. Polarization multiplexing is achieved by using Faraday mirrors(FM) and polarizing beam splitters(PBS). On the receiving side, Bob randomly measures the x or p quadrature of these states by using the LO in the homodyne detector of the 1 GHz bandwidth shot-noise limit of the quantum signal pulse interference. The security of the system depends on the estimation of light transmittance and excess noise during the parameter estimation process. This CV-QKD system has certain loopholes: the proportional relationship between the shot noise measured by the detector and the light intensity of the LO is pre-determined by Bob. Using the relationship between the two, Bob can estimate the size of shot noise by detecting the light intensity of LOs, and take it as a unit to measure the excess noise (see in Figure 8).
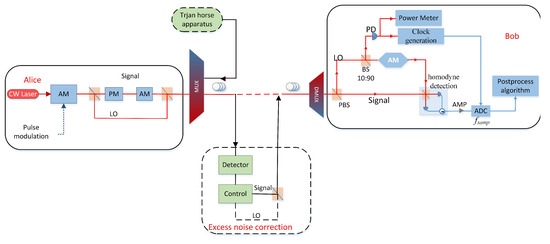
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of CV-QKD with excess noise correction. PM, phase modulation; AM, Amplitude modulation; PD, photodiode; PBS, polarization beam splitter; ADC, analog-to-digital; AMP, amplifier.
Eve intercepts the signal light and LO light sent by Alice, and uses heterodyne detection to simultaneously obtain the information of the X and P variables of the signal state, denoted as and . Applying the measurement results, Eve prepares the coherent state with the same polarization as the original signal state. Prepare the LO with amplitude , the polarization is the same as the original. Eve compresses and delays the width of the pulses to delay Bob’s measurement time, reducing the measurement result to times the peak value. Prepare two additional light pulses, denoted s and . Polarization of pulse s is the same as the original signal state, polarization of pulse is the same as the original LO. Finally, Eve places the prepared four pulses within the same original pulse width time, and sends them to Bob through the non-attenuation channel. In the latest CV-QKD system, an amplitude modulator (AM) is added to the signal path. Bob randomly applies an AM with attenuation ratios and to measure the real-time emission noise level. In this paper, we set and to 0.001 and 1, respectively.
The input light wavelength and transmittance of the fused biconical taper BS have the following relationship:
where C, denotes the coupling coefficient and the maximum coupling ratio, respectively. , . Take the fused biconical taper BS produced by Thorlabs (center wavelength is 1550 nm) as an example, when = 1550 nm, . The above formula can be rewritten as:
When center wavelength is 1310 nm, the relationship between transmittance and wavelength of the BS can be expressed as:
According to Equations (17) and (18), the relationship between their coupling ratios and wavelength with center wavelength of 1550 nm and 1310 nm are shown in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively. Only a set of false signal state and false LO cannot escape the real-time detection at Bob’s side. Another set of signal pulse and LO must be added to maintain the output of shot noise at a normal level. The two sets of wavelengths and their transmittance are expressed as: , , , , , , , . In order to make , , the wavelength and its corresponding transmittance are:

Table 2.
The transmittance T at different wavelengths of 50:50 BS with a center wavelength of 1550 nm.

Table 3.
The transmittance T at different wavelengths of 50:50 BS with a center wavelength of 1310 nm.
The corresponding differential currents are expressed as:
where denotes the differential currents of corresponding wavelength, is the detector efficiency of different wavelengths. In order to make the average value of equal to 0, the simplest method is to select the wavelength corresponding to the transmittance of . Then choose the right light intensity to make . In order to keep the variance of Bob’s measured grainy noise as , let . When Bob measures the signal state, it is assumed that the differential currents generated by and can cancel each other, i.e., Eve selects two wavelengths with the same probability and satisfies , .
Through comprehensive analysis, the following relationship can be obtained:
According to Equation (5), the excess noice can be estimated as
Suppose the real shot noise is . Therefore, the estimation of shot noise level and excessive noise can be expressed as (see Appendix A for more details):
To correct the noise caused by Trojan horse attacks and the impefection of BS at the same time, must satisfy:
By selecting the appropriate , and , the shot noise and excess noise under the joint attack can be corrected simultaneously, so that and is arbitrarily close to 0. Take = 0.032 (i.e., fiber length L = 50 km), as an example in this article. The original LO intensity, the original shot noise unit and the detector efficiency of different wavelength are set to , , . Calculated by the above formula, , . To make , according to Equation (24), we should choose .
4.2. Threshold of Excess Noise
In the previous section, we took advantage of the BS wavelength-dependent coupling ratio defect to correct the excess noise changes caused by Trojan horse attacks and the imperfection of BS. Assuming that the excess noise in the two methods are (in shot noise units) and respectively. It can be seen from Section 2 that the shared key between Alice and Bob must satisfy:
where
According to Equation (26), the excess noise caused by the imperfection of BS can be expressed as:
Bring specific values into the Equation (30), is arbitrarily close to 0. Therefore, the bounds on excess noise caused by Trojan horse attacks are as follows:
Combined with the analysis in Section 3, when the Trojan horse pulses wavelength are equal to the original, the total excess noise should satisfy:
According to Table 1, the crosstalk level is set to . When the Trojan horse pulses wavelengths are different from the original, the total excess noise should also satisfy Equation (32). Assuming fiber length L = 50 km, the bounds on input power of Trojan horse pulses are as follows:
We take this number as an example to quantify the boundary of excess noise caused by Eve’s Trojan horse attacks. However, we can adopt a more conservative threshold for to arrange different uses for applications that require stronger bound.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
This article analyzed one-way Trojan-horse attacks on CV-QKD systems. We derived and calculated the numerical changes of excess noise under attacks with the same and different wavelengths as the original pulse. We turned attacks into an information leakage problem and then quantified the excess noise bounds caused by the Trojan horse attacks to specify the security bounds of the system. From the simulation results, it can be seen that the Trojan password attacks in both cases will affect the excessive noise of the system. When the excess noise is too large, the existence of Eve will be discovered. In order to successfully implement the attack, we can achieve it in two ways: on the one hand, based on the imperfection that the beam splitter has a wavelength-dependent property, Eve can estimate the deviation of shot noise and then correct the excess noise by inserting different wavelength pulses. On the other hand, we can calculate the security bounds and then control the amount of crosstalk by controlling the time when the Trojan horse pulse enters the system, or the input power of the Trojan horse pulse to control the amount of excess noise. As a consequence, the transmission errors within the security bounds can be negligible and the legal users will not perceive the presence of Eve.
This article takes the transmission distance of 50 km as an example to quantify the threshold of excess noise. Through calculation and simulation results, it can be known that when Trojan horse attacks use the same wavelength as the original, the degree of crosstalk should be less than 0.3. When using Trojan horse attacks with a different wavelength from the original, the input power of the attack pulse should be less than 0.7 mW.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and formal analysis, L.Z.; methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, Y.P.; writing—review and editing and supervision, D.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11904410 and 61801522), and National Nature Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2019JJ40352).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CV-QKD | Continuous-variable quantum key distribution |
| QKD | Quantum key distribution |
| LO | Local oscillator |
| BS | Beam splitter |
| GMCS | Gaussian modulation coherent state |
| OTDR | Optical time-domain reflectometry |
| WDM | Wavelength division multiplexing |
| DEMUX | Demultiplxer |
| SARA | Spontaneous anti-Stokes Raman scattering |
| FM | Faraday mirrors |
| PBS | Polarizing beam splitter |
| AM | Amplitude modulation |
Appendix A
Usually, is used for shot noise estimation, is used for quadrature measurement. The variance of under the two attenuation rates can be expressed as:
The real-time measured shot noise variance value and the excess noise variance value using this value as a unit are estimated by the following:
The total variance is given by [23]:
where
References
- Scarani, V.; Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H.; Cerf, N.J.; Dušek, M.; Lütkenhaus, N.; Peev, M. The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 1301–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Qian, L.; Lo, H.K. A brief introduction of quantum cryptography for engineers. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1002.1237. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G. Quantum Private Communication, 1st ed.; Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 145–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, S.; Winter, A. Entropic uncertainty relations—A survey. New J. Phys 2010, 12, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleni, D.; Anthony, L. Distributing Secret Keys with Quantum Continuous Variables: Principle, Security and Implementations. Entropy 2015, 17, 6072–6092. [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman, D.; Preskill, J. Secure quantum key distribution using squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 63, 022309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladyslav, U.; Radim, F. Trusted Noise in Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution: A Threat and a Defense. Entropy 2016, 18, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Grosshans, F.; Cerf, N.J. Continuous-variable quantum cryptography is secure against non-gaussian attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 047905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, R.; Cirac, J.I. De Finetti Representation Theorem for Infinite-Dimensional Quantum Systems and Applications to Quantum Cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Patrón, R.; Cerf, N.J. Unconditional Optimality of Gaussian Attacks against Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 190503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navascués, M.; Grosshans, F.; Acín, A. Optimality of Gaussian Attacks in Continuous-Variable Quantum Cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 190502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossier, S.; Diamanti, E.; Debuisschert, T.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Grangier, P. Improvement of continuous-variable quantum key distribution systems by using optical preamplifiers. J. Phys. B-AT. Mol. Opt. 2009, 42, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverrier, A.; Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Finite-size analysis of a continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverrier, A. Composable security proof for continuous-variable quantum key distribution with coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, T.; Inoue, K. Intensity modulation and direct detection quantum key distribution based on quantum noise. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 013018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyck, J.; Debuisschert, T.; García-Patrón, R.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Grangier, P. Experimental Implementation of Non-Gaussian Attacks on a Continuous-Variable Quantum-Key-Distribution System. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 030503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G. Robust continuous-variable quantum key distribution against practical attacks. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 052302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Qin, H.; Huang, D.; Guo, Y. Hidden-Markov-model-based calibration-attack recognition for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 101, 062320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.C.; Sun, S.H.; Jiang, M.S.; Liang, L.M. Local oscillator fluctuation opens a loophole for Eve in practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 022339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Kumar, R.; Alléaume, R. Quantum hacking: Saturation attack on practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 012325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.C.; Sun, S.H.; Jiang, M.S.; Liang, L.M. Wavelength attack on practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system with a heterodyne protocol. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 052309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Weedbrook, C.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Li, H.W.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Quantum hacking of a continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system using a wavelength attack. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 062329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pljonkin, A.P. Vulnerability of the Synchronization Process in the Quantum Key Distribution System. Int. J. Cloud Appl. Comput. 2019, 9, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhitov, A.; Makarov, V.; Hjelme, D.R. Large pulse attack as a method of conventional optical eavesdropping in quantum cryptography. J. Mod. Opt. 2001, 48, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisin, N.; Fasel, S.; Kraus, B.; Zbinden, H.; Ribordy, G. Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73, 022320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucamarini, M.; Choi, I.; Ward, M.B.; Dynes, J.F.; Shields, A.J. Practical Security Bounds Against the Trojan-Horse Attack in Quantum Key Distribution. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 031030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Anisimova, E.; Khan, I.; Makarov, V.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. Trojan-horse attacks threaten the security of practical quantum cryptography. New J. Phys 2014, 16, 123030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Stiller, B.; Khan, I.; Makarov, V.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. Risk Analysis of Trojan-Horse Attacks on Practical Quantum Key Distribution Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 2015, 21, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeed, S.; Radchenko, I.; Kaiser, S.; Bourgoin, J.P.; Pappa, A.; Monat, L.; Legré, M.; Makarov, V. Attacks exploiting deviation of mean photon number in quantum key distribution and coin tossing. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 032326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Jain, N.; Stiller, B.; Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Diamanti, E.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. Trojan horse attacks on practical continuous-variables quantum key distribution systems. In Proceedings of the Conference on Quantum Cryptography (QCRYPT), Paris, France, 1–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.W.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.Z.; Chen, W.; Yin, Z.Q.; Li, F.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, G.C.; et al. Attacking a practical quantum-key-distribution system with wavelength-dependent beam-splitter and multiwavelength sources. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 062308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Jouguet, P.; Weedbrook, C.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Quantum hacking on quantum key distribution using homodyne detection. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 032304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz-Jacques, S.; Jouguet, P. Robust shot-noise measurement for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 022307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarani, V.; Kurtsiefer, C. The black paper of quantum cryptography: Real implementation problems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, P.; Huang, D.; Lin, D.; Zeng, G. Practical security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with finite sampling bandwidth effects. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 022315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, P.; Huang, D.; Wang, T.; Zeng, G. Practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution without finite sampling bandwidth effects. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 20481–20493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.G. Single-Mode Fibers: Springer Series in Optical Sciences; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wegmuller, M.; Scholder, F.; Gisin, N. Photon-Counting OTDR for Local Birefringence and Fault Analysis in the Metro Environment. J. Light. Technol. 2004, 22, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Zhu, W.; Qian, L.; Lo, H.K. Feasibility of quantum key distribution through a dense wavelength division multiplexing network. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 103042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Qin, H.; Alléaume, R. Coexistence of continuous variable QKD with intense DWDM classical channels. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 043027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuran, T.E.; Toliver, P.; Peters, N.A.; Jackel, J.; Goodman, M.S.; Runser, R.J.; McNown, S.R.; Dallmann, N.; Hughes, R.J.; McCabe, K.P.; et al. Optical networking for quantum key distribution and quantum communications. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraerds, P.; Walenta, N.; Legré, M.; Gisin, N.; Zbinden, H. Quantum key distribution and 1Gbps data encryption over a single fibre. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 063027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).