A Multi-Level Non-Uniform Spatial Sampling Method for Accuracy Assessment of Remote Sensing Image Classification Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
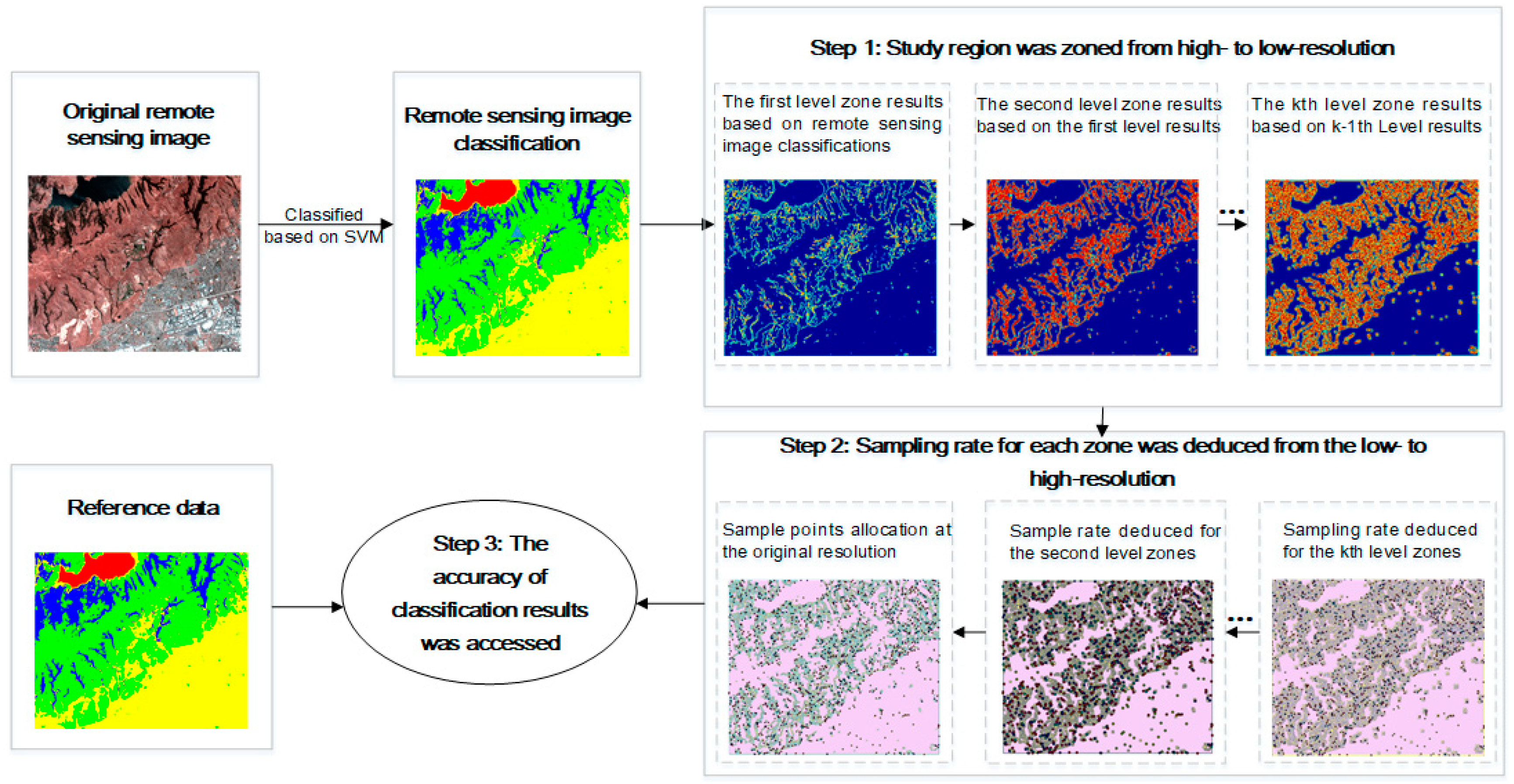
2. Methodology
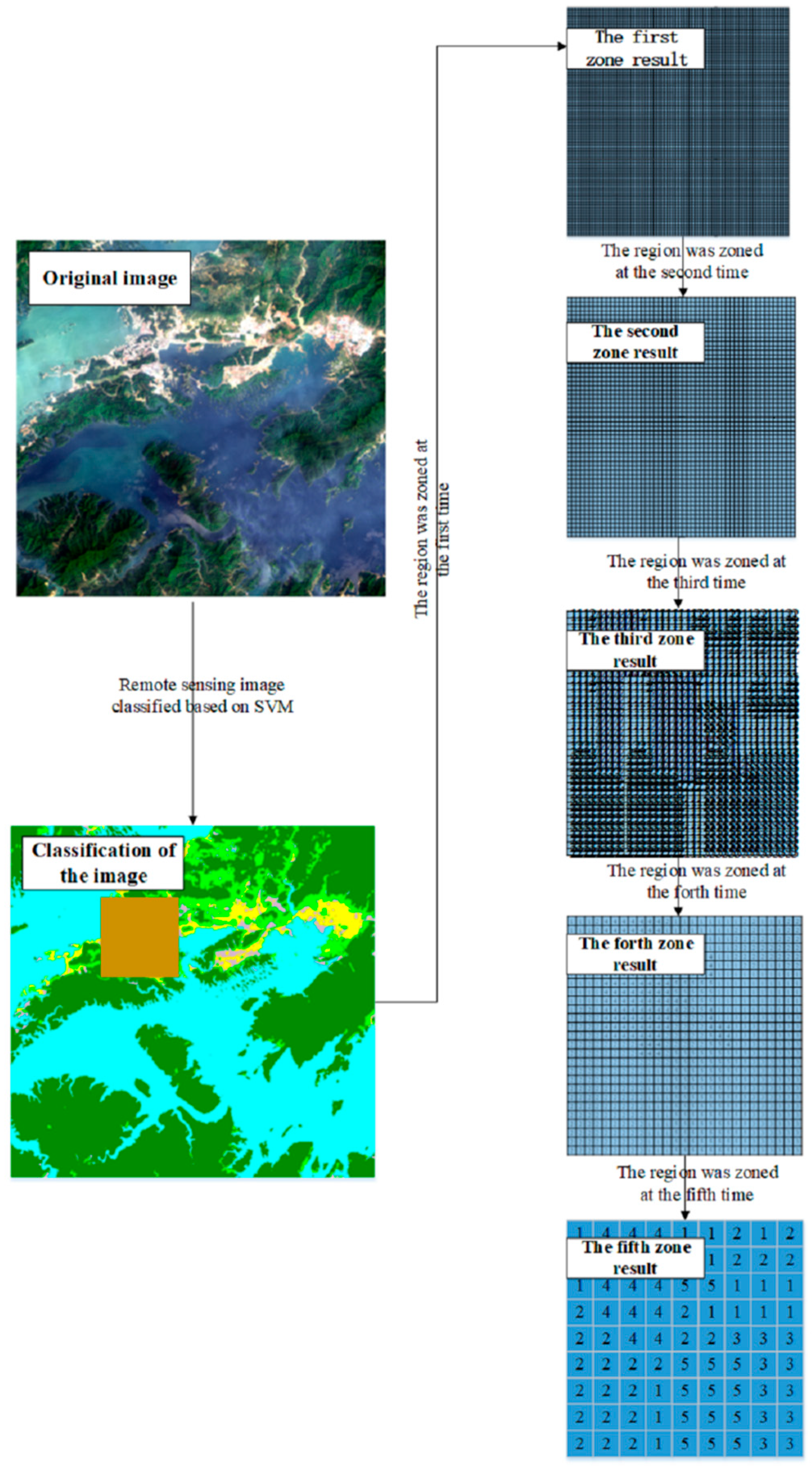
2.1. Step 1: The Studied Region was Zoned from High to Low Resolution
2.2. Step 2: The Sampling Rate was Deduced from Low to High Resolution
2.3. Step 3: Accuracy Assessment of the Classification Results
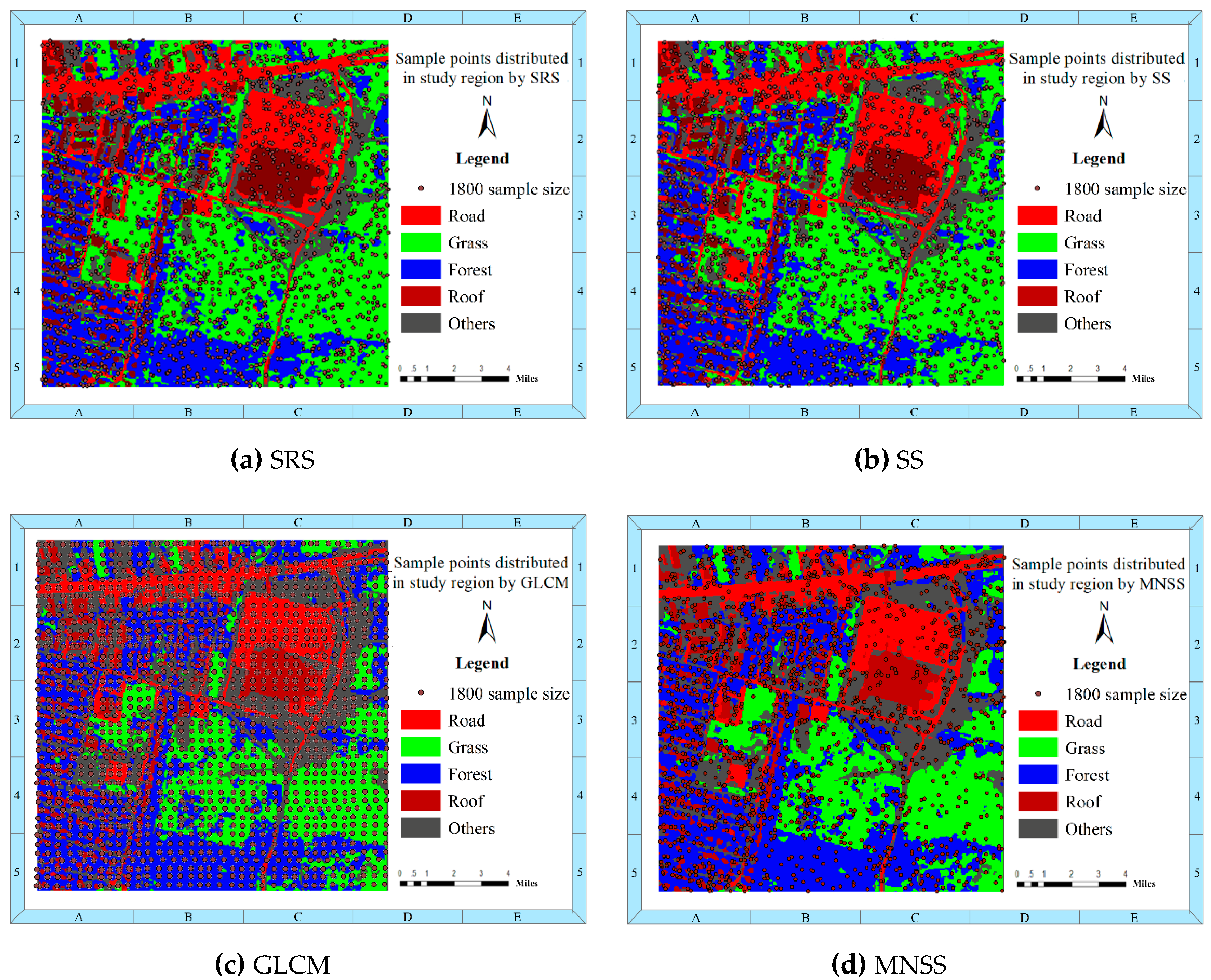
3. Experiment
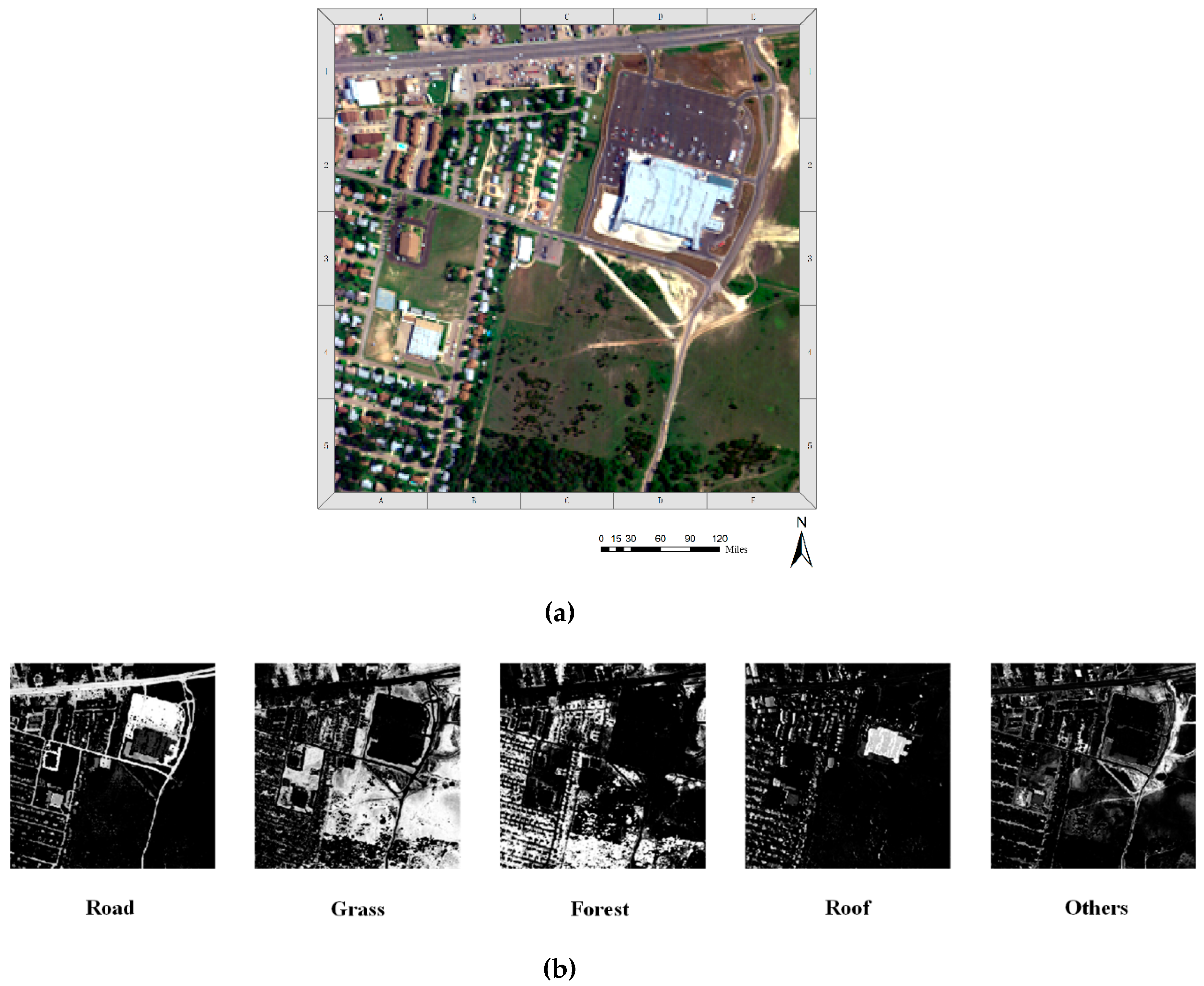
3.1. Experimental Data
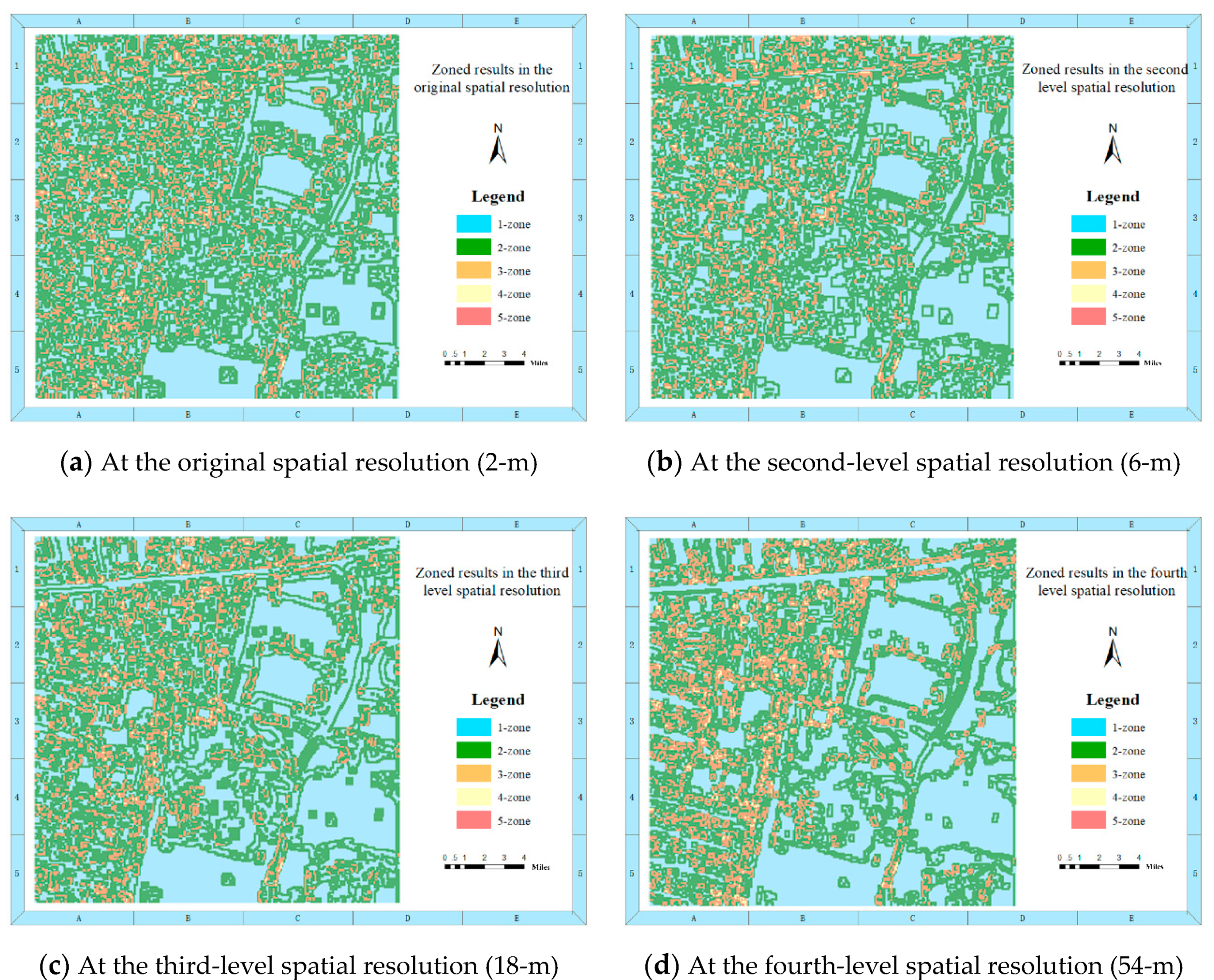
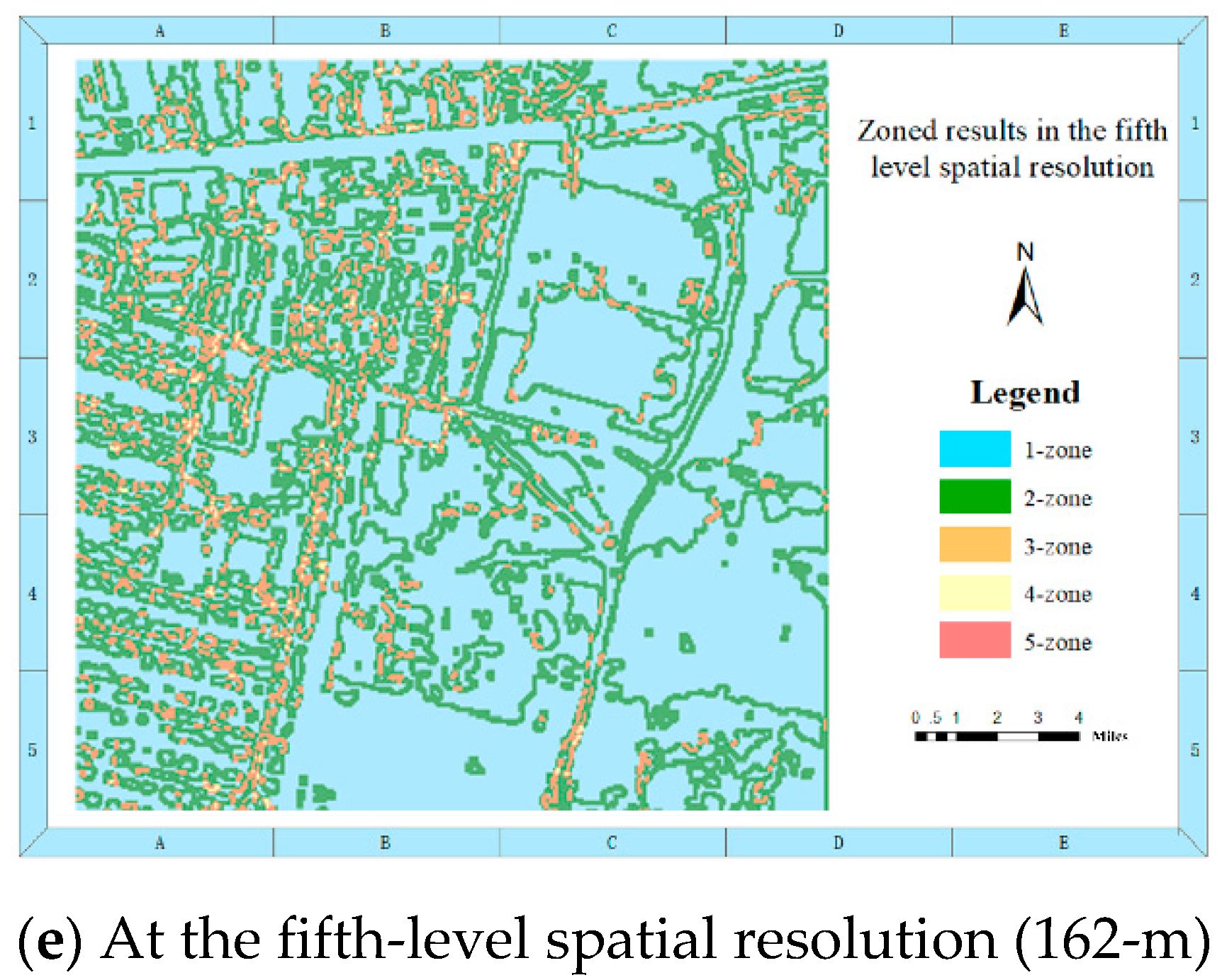
3.2. Performance of the Proposed MNSS
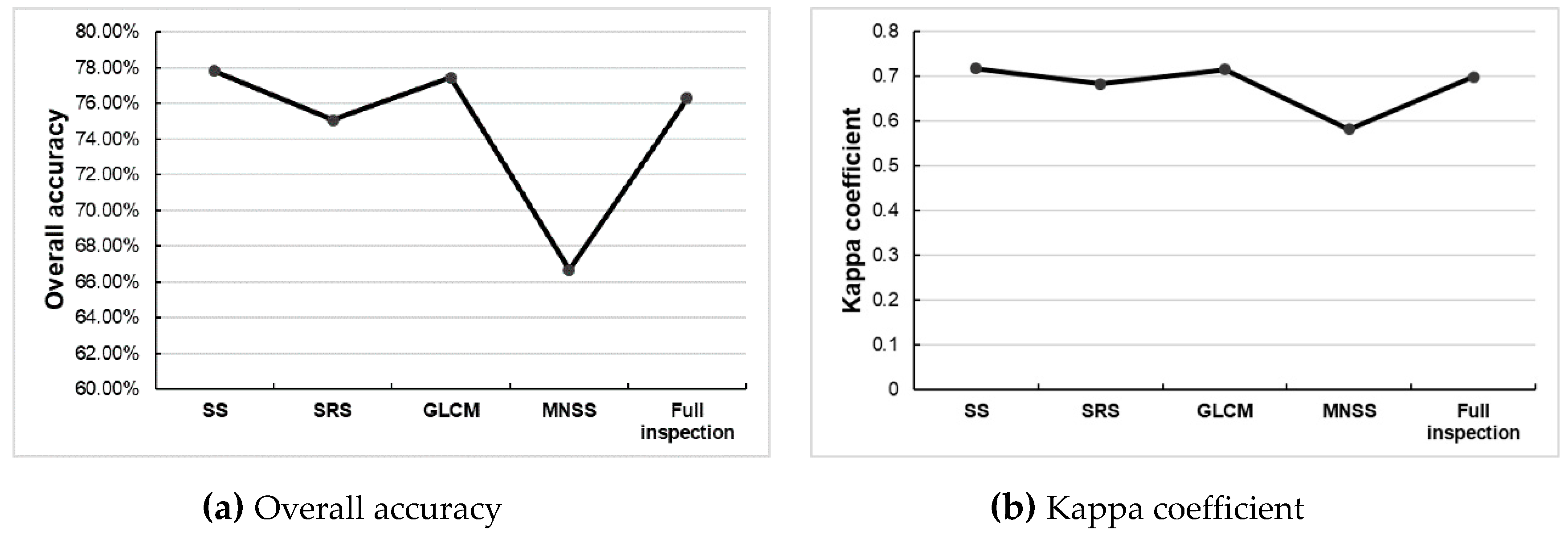
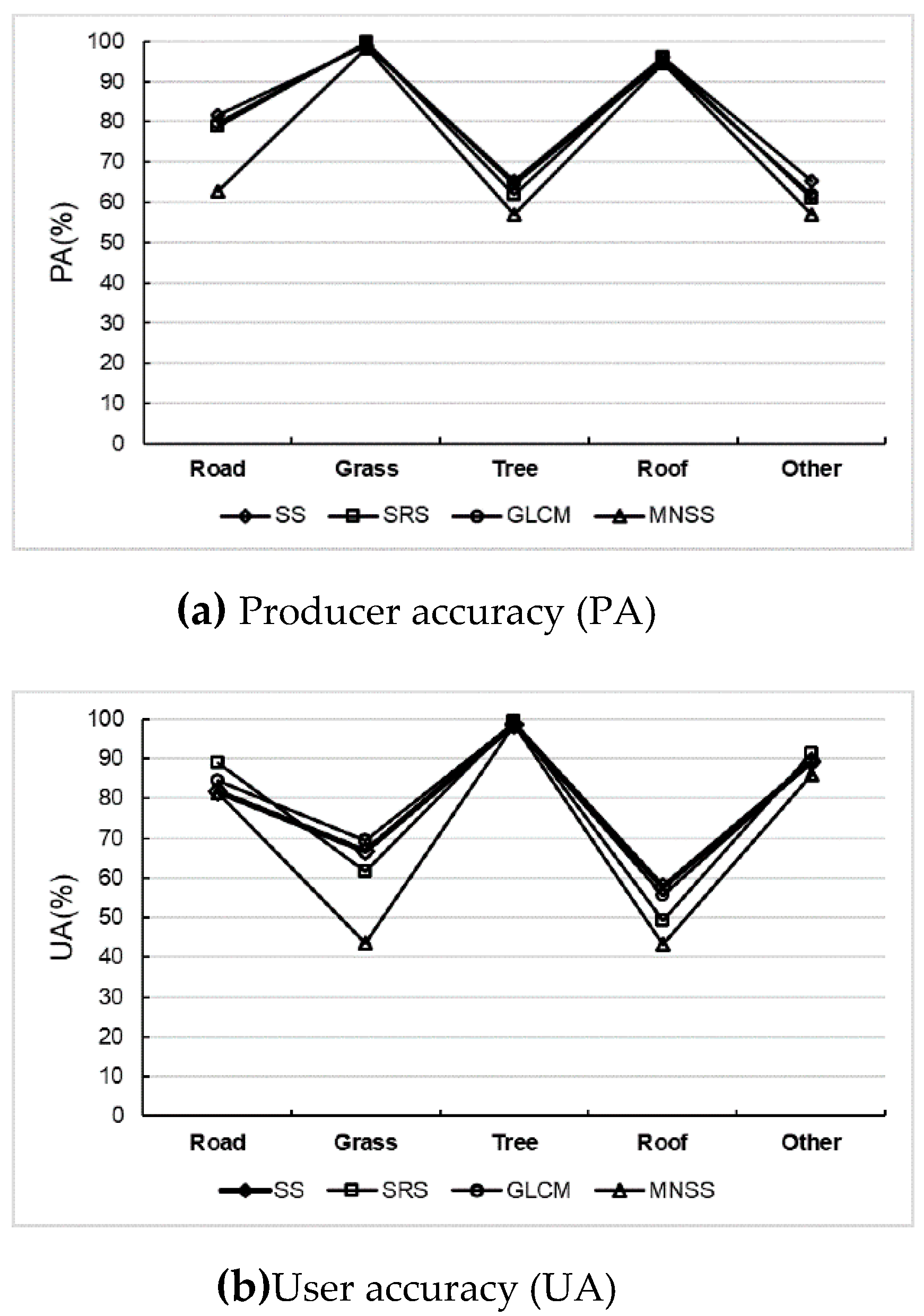
3.3. Comparison of Accuracy Assessment Efficiency between Different Sampling Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stehman, S.V.; Czaplewski, R.L. Design and analysis for thematic map accuracy assessment: Fundamental principles. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xu, S.; Sun, J.; Liang, S.; Song, W.; Wang, Z. Accuracy assessment model for classification result of remote sensing image based on spatial sampling. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 046023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Latent Class Modeling for Site- and Non-Site-Specific Classification Accuracy Assessment Without Ground Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2827–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.; Stehman, S.V.; Gass, L.; Dewitz, J.A.; Sorenson, D.G.; Granneman, B.J.; Baer, L.A. Thematic accuracy assessment of the 2011 national land cover database (NLCD). Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, L.; Yadav, K.; Congalton, R.G. Sampling Simulations for Assessing the Accuracy of US Agricultural Crop Mapping from Remotely Sensed Imagery. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017; Volume 19, p. 10981. [Google Scholar]
- Al Ghayab, H.R.; Li, Y.; Abdulla, S.; Diykh, M.; Wan, X. Classification of epileptic EEG signals based on simple random sampling and sequential feature selection. Brain Inform. 2016, 3, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, J.; Dang, C. A stratified sampling based clustering algorithm for large-scale data. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 163, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etikan, I.; Bala, K. Sampling and sampling methods. Biom. Biostat. Int. J. 2017, 5, 00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humm, J.M.; McCown, J.W.; Scheick, B.K.; Clark, J.D. Spatially explicit population estimates for black bears based on cluster sampling. J. Wildl. Manag. 2017, 81, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, N.; Kadilar, C. Calibration weighting in stratified random sampling. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2016, 45, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.B.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Z.X. Design of a spatial sampling scheme considering the spatial autocorrelation of crop acreage included in the sampling units. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Tong, X.H. Accuracy Assessmentfor Regional Land Cover Remote Sensing Mapping Product Based on Spatial Sampling: A Case Study of Shan xi Province. China 2015, 17, 742G749. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Haining, R.; Liu, T.J.; Li, L.F.; Jiang, C.S. Sandwich estimation for multi-unit reporting on a stratified heterogeneous surface. Environ. Plan. A 2013, 45, 2515–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V. Model-assisted estimation as a unifying framework for estimating the area of land cover and land-cover change from remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 113, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaux, P.; Eva, H.; Gallego, J.; Strahler, A.H.; Herold, M.; Agrawal, S.; Kopin, Y. Validation of the global land cover 2000 map. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, M.J.; Wu, S.; Lu, J.; Toh, H.L. Face recognition with radial basis function (RBF) neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, P.; Riitters, K.H.; Estreguil, C.; Kozak, J.; Wade, T.G.; Wickham, J.D. Mapping spatial patterns with morphological image processing. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tong, X.H.; Liang, D.; Xie, H. Sampling inspection schemes for continuous lot spatial data. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2010, 38, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Liang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J. Designing a two-rank acceptance sampling plan for quality inspection of geospatial data products. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Bansal, R.K.; Mittal, M.; Goyal, L.M.; Kaur, I.; Verma, A.; Hoang Son, L. Mixed pixel decomposition based on extended fuzzy clustering for single spectral value remote sensing images. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Fan, B.; Pan, C. Structured sparse method for hyperspectral unmixing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwanga, S.S.; Ndambuki, J.M. Accuracy assessment of land use/land cover classification using remote sensing and GIS. Int. J. Geosci. 2017, 8, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, J.E.; Hickey, A.; Staudenmayer, J.; John, D.; Kent, J.A.; Freedson, P.S. Performance of activity classification algorithms in free-living older adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pořízka, P.; Klus, J.; Hrdlička, A.; Vrábel, J.; Škarková, P.; Prochazka, D.; Kaiser, J. Impact of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy data normalization on multivariate classification accuracy. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Boryan, C.G. Impact of Non-Proportional Training Sampling of Imbalanced Classes on Land Cover Classification Accuracy with See5 Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 9466–9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, W.G., Jr.; Chhoker, A. Design of economically optimal acceptance sampling plans with inspection error. Comput. Oper. Res. 2002, 29, 1283–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 28590. Sampling Procedures for Inspection by Attributes—Part 0: Introduction to the ISO 2859 Attribute Sampling System; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- ISO-19113. Geographic Information-Quality Principles; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- ISO-19114. Geographic Information-Quality Evaluation Procedures; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; p. 36. [Google Scholar]


| 1-Zone at the Fifth Level | 2-Zone at the Fifth Level | 3-Zone at the Fifth Level | 4-Zone at the Fifth Level | 5-Zone at the Fifth Level | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling rate (%) | 0.0276 | 1.4717 | 20.9721 | 55.5315 | 21.9971 | 100.00 |
| Zones at the fourth-level spatial resolution | Sampling Rate (%) | 1-Zone at the Fourth Level | 2-Zone at the Fourth Level | 3-Zone at the Fourth Level | 4-Zone at the Fourth Level | 5-Zone at the Fourth Level |
| 1-zone at the fifth level | 0.0031 | 0.0034 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 2-zone at the fifth level | 0.0000 | 0.0021 | 0.0005 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 3-zone at the fifth level | 0.0037 | 0.0097 | 0.0039 | 0.0004 | 0.0000 | |
| 4-zone at the fifth level | 0.0560 | 0.2786 | 0.2881 | 0.0590 | 0.0024 | |
| 5-zone at the fifth level | 0.0000 | 49.6437 | 0.0000 | 49.6437 | 0.0000 |
| Zones at the third-level spatial resolution | Sampling Rate (%) | 1-Zone at the Third Level | 2-Zone at the Third Level | 3-Zone at the Third Level | 4-Zone at the Third Level | 5-Zone at the Third Level |
| 1-zone at the fourth level | 0.0354 | 0.0288 | 0.0005 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 2-zone at the fourth level | 14.1534 | 28.3277 | 7.4032 | 0.0530 | 0.0000 | |
| 3-zone at the fourth level | 0.0523 | 0.1596 | 0.0721 | 0.0085 | 0.0001 | |
| 4-zone at the fourth level | 4.0870 | 20.6986 | 19.2484 | 5.4054 | 0.2637 | |
| 5-zone at the fourth level | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0012 | 0.0012 | 0.0000 |
| Zones at the second-level spatial resolution | Sampling Rate (%) | 1-Zoneat the Second Level | 2-Zoneat the Second Level | 3-Zoneat the Second Level | 4-Zoneat the Second Level | 5-Zoneat the Second Level |
| 1-zone at the third level | 11.0840 | 6.3841 | 0.8449 | 0.0150 | 0.0000 | |
| 2-zone at the third level | 12.9716 | 29.8952 | 6.1544 | 0.1925 | 0.0011 | |
| 3-zone at the third level | 0.7111 | 19.7215 | 5.9626 | 0.3240 | 0.0061 | |
| 4-zone at the third level | 0.0000 | 1.5535 | 3.6684 | 0.2395 | 0.0068 | |
| 5-zone at the third level | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.2232 | 0.0406 | 0.0000 |
| Zones at the original spatial resolution | Sampling Rate (%) | 1-Zoneat the Original Level | 2-Zoneat the Original Level | 3-Zoneat the Original Level | 4-Zoneat the Original Level | 5-Zoneat the Original Level |
| 1-zone at the second level | 15.1425 | 8.2901 | 1.2994 | 0.0355 | 0.0000 | |
| 2-zone at the second level | 6.7153 | 38.5560 | 11.7212 | 0.5592 | 0.0017 | |
| 3-zone at the second level | 0.1393 | 8.6040 | 7.3503 | 0.7383 | 0.0209 | |
| 4-zone at the second level | 0.0000 | 0.0814 | 0.5928 | 0.1345 | 0.0035 | |
| 5-zone at the second level | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0084 | 0.0042 | 0.0014 |
| Classification | Reference Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road | Grass | Forest | Roof | Others | Total | ||
| Experimental data | Road | 9637 | 29 | 1 | 1372 | 900 | 11939 |
| Grass | 1 | 20282 | 56 | 7 | 110 | 20456 | |
| Forest | 13 | 8098 | 19442 | 2270 | 532 | 30355 | |
| Roof | 179 | 31 | 36 | 8805 | 161 | 9212 | |
| Others | 1260 | 2974 | 71 | 4269 | 13713 | 22287 | |
| Total | 11090 | 31414 | 19606 | 16723 | 15416 | 94249 | |
| Overall accuracy = 76.27%, Kappa = 0.6995 | |||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Ji, Q.; Song, W.; Wang, L. A Multi-Level Non-Uniform Spatial Sampling Method for Accuracy Assessment of Remote Sensing Image Classification Results. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5568. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165568
Wang Z, Xu L, Ji Q, Song W, Wang L. A Multi-Level Non-Uniform Spatial Sampling Method for Accuracy Assessment of Remote Sensing Image Classification Results. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(16):5568. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165568
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhenhua, Lizhi Xu, Qing Ji, Wei Song, and Lingqun Wang. 2020. "A Multi-Level Non-Uniform Spatial Sampling Method for Accuracy Assessment of Remote Sensing Image Classification Results" Applied Sciences 10, no. 16: 5568. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165568
APA StyleWang, Z., Xu, L., Ji, Q., Song, W., & Wang, L. (2020). A Multi-Level Non-Uniform Spatial Sampling Method for Accuracy Assessment of Remote Sensing Image Classification Results. Applied Sciences, 10(16), 5568. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165568





