Lateral Migration in a Wandering Reach of the Middle Yellow River in Response to Different Boundary Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
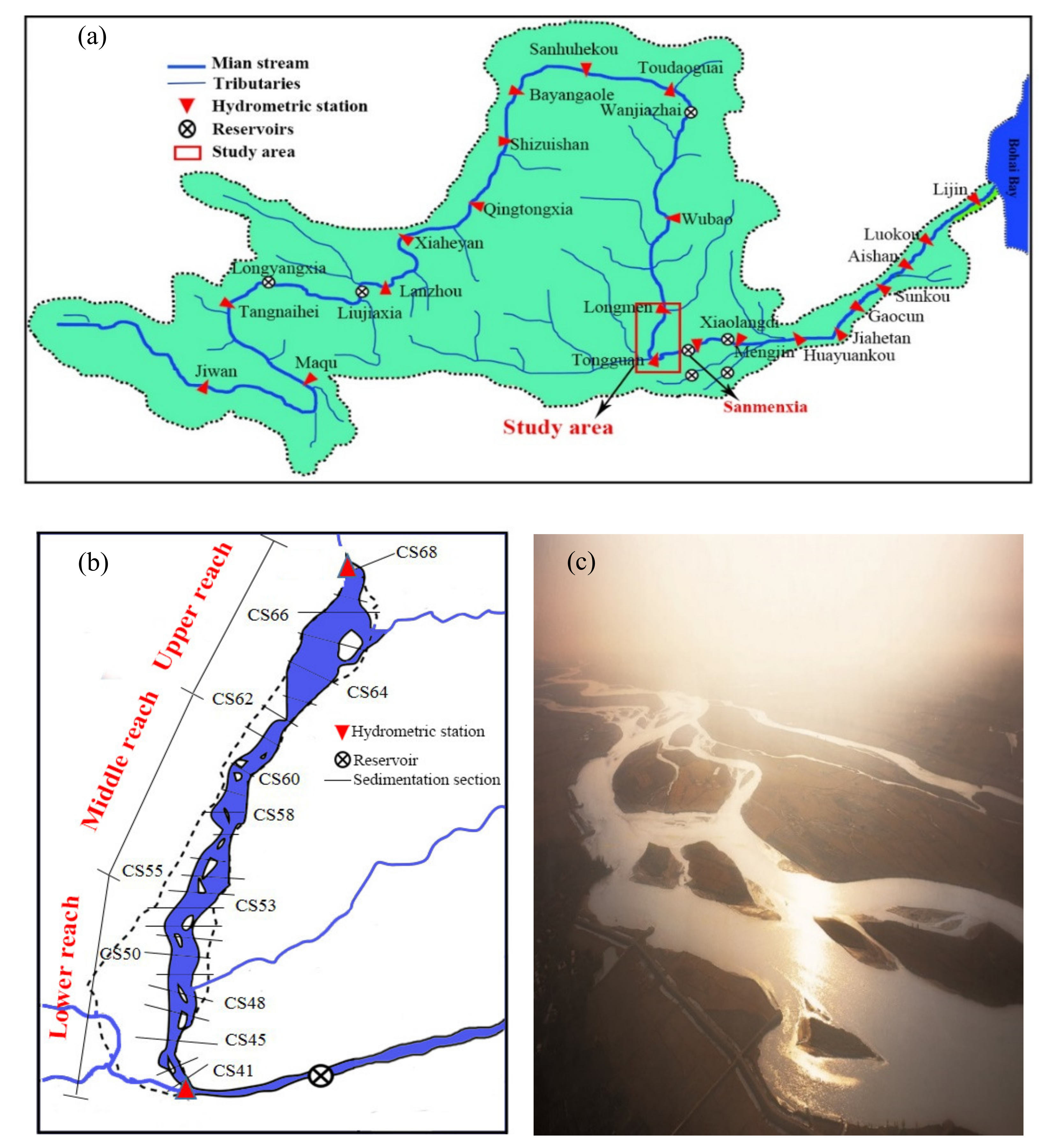
2. Study Area and Data Collection
2.1. Study Area
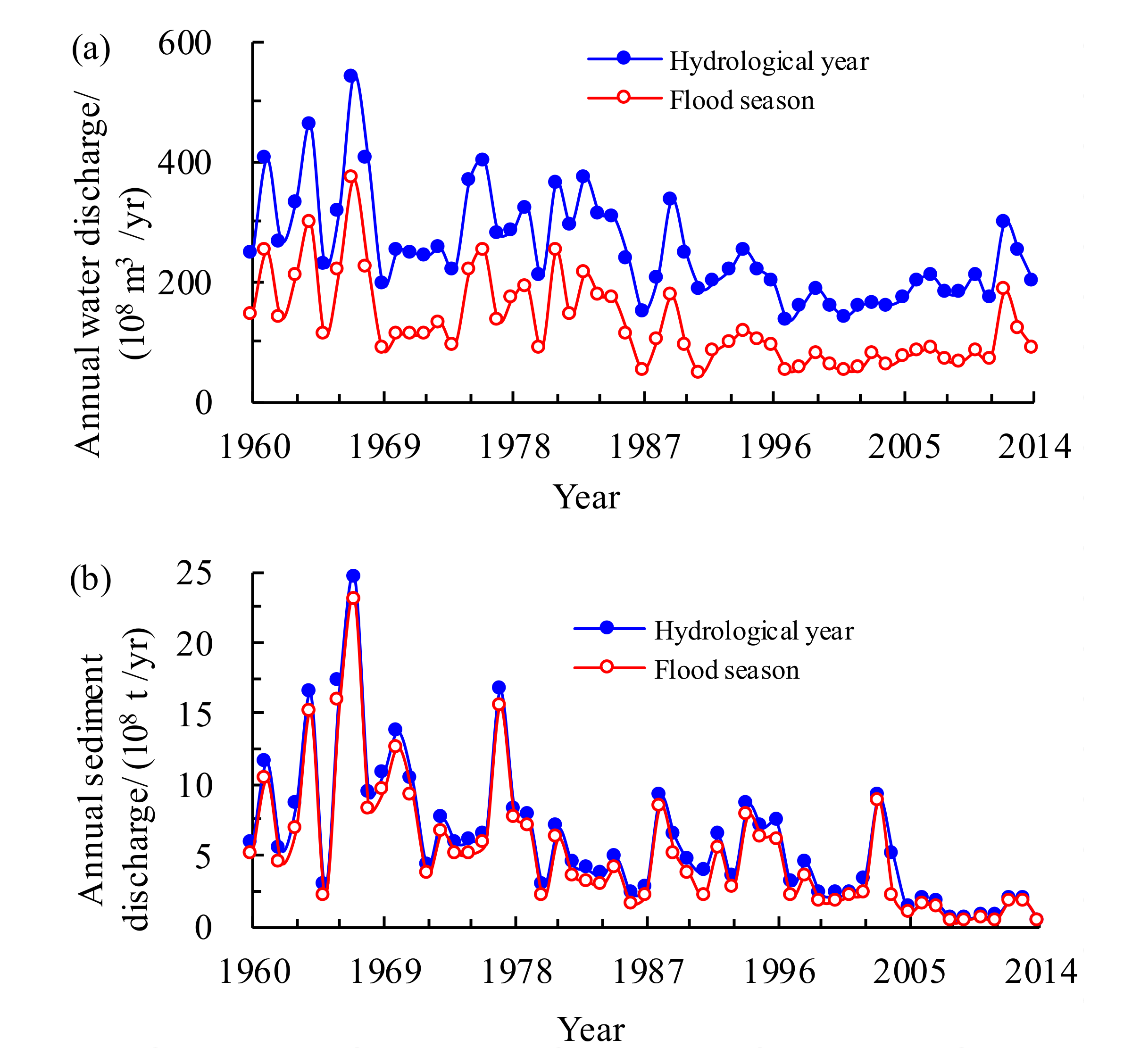
2.2. Data Collection
3. Methods
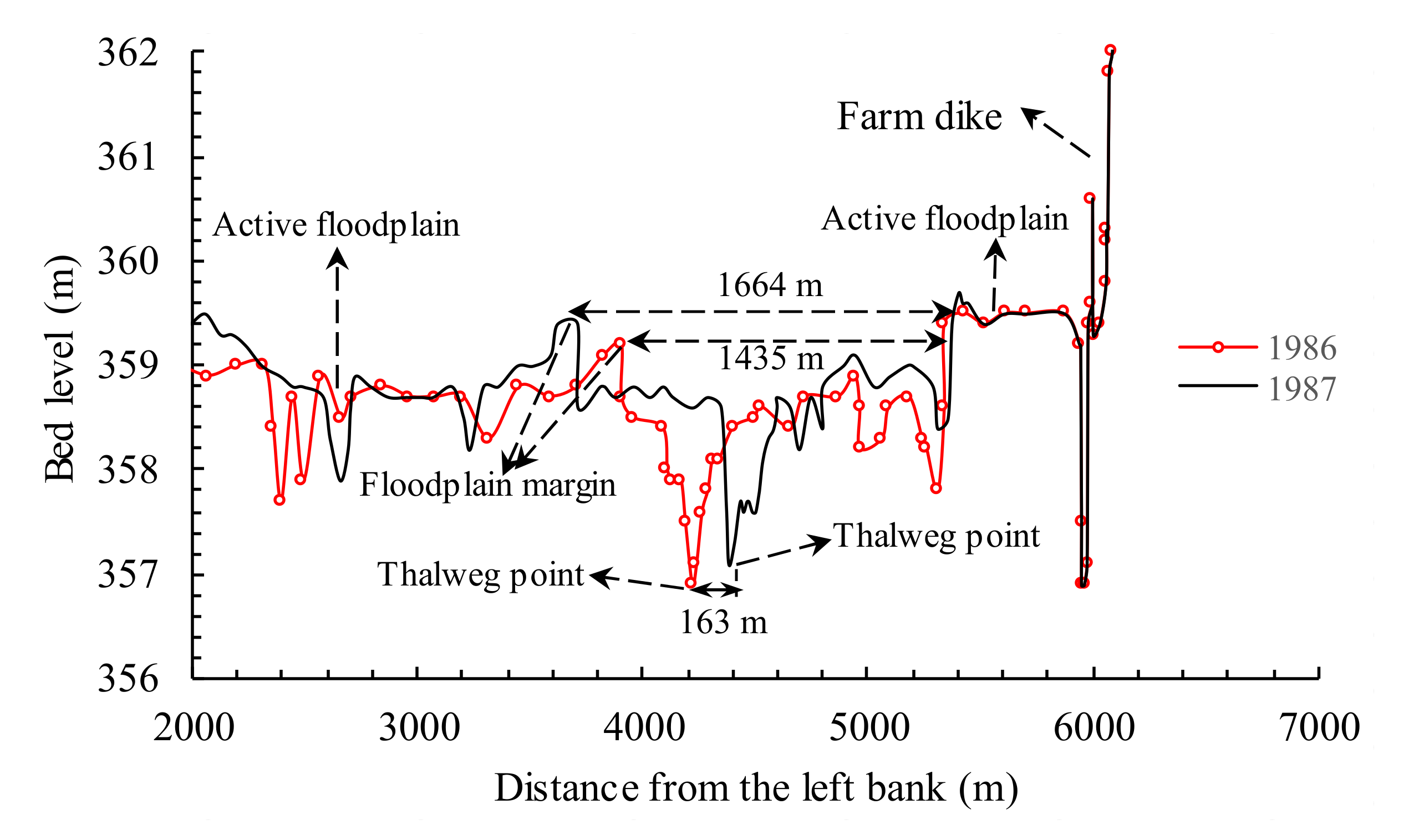
3.1. Determination of Parameters for Channel Lateral Migration
3.2. Determination of Different Boundary Conditions
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Variation in Channel Bankfull Width
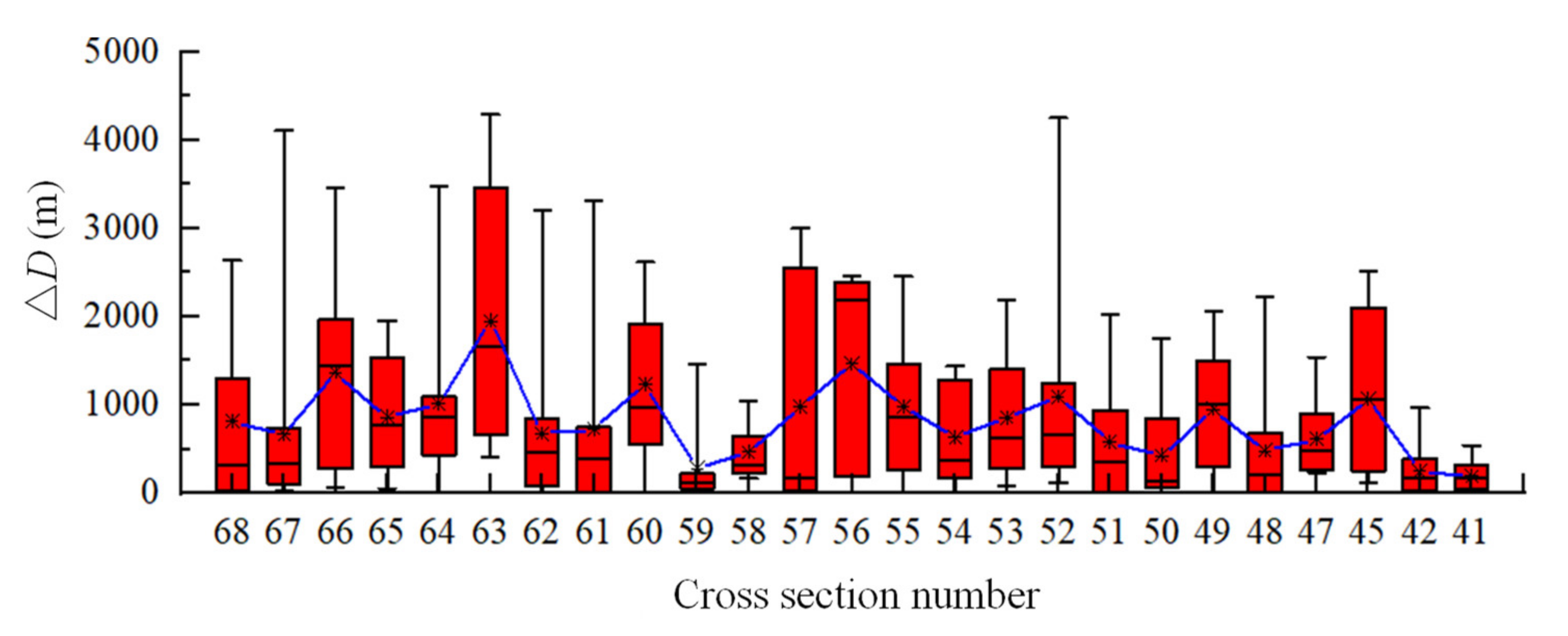
4.2. Variation in Thalweg Migration Distance
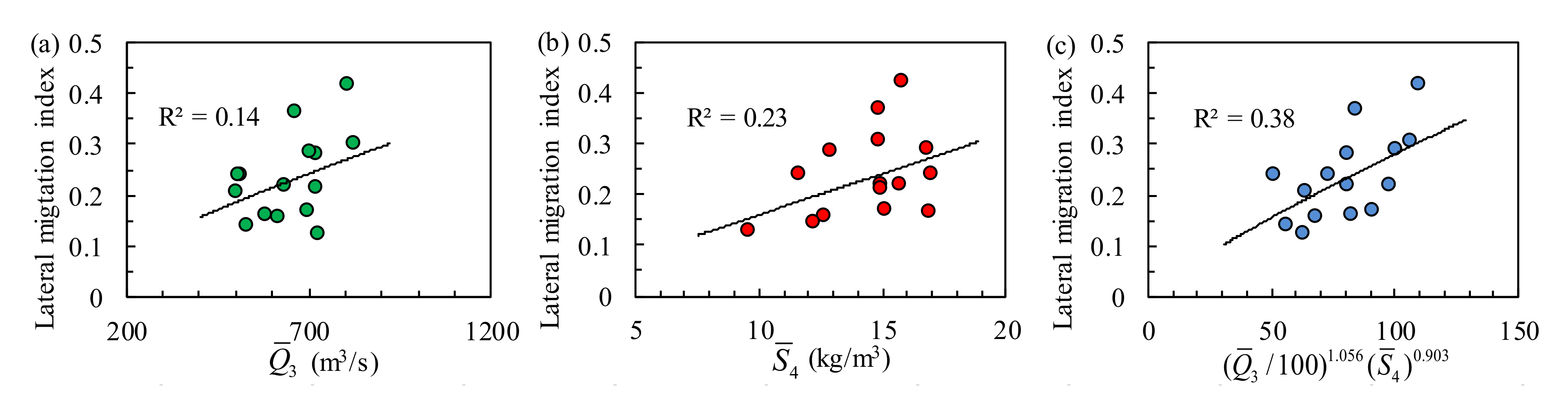
4.3. Effect of Upstream Boundary Conditions on Lateral Migration
4.4. Effect of Downstream Boundary Conditions on Lateral Migration
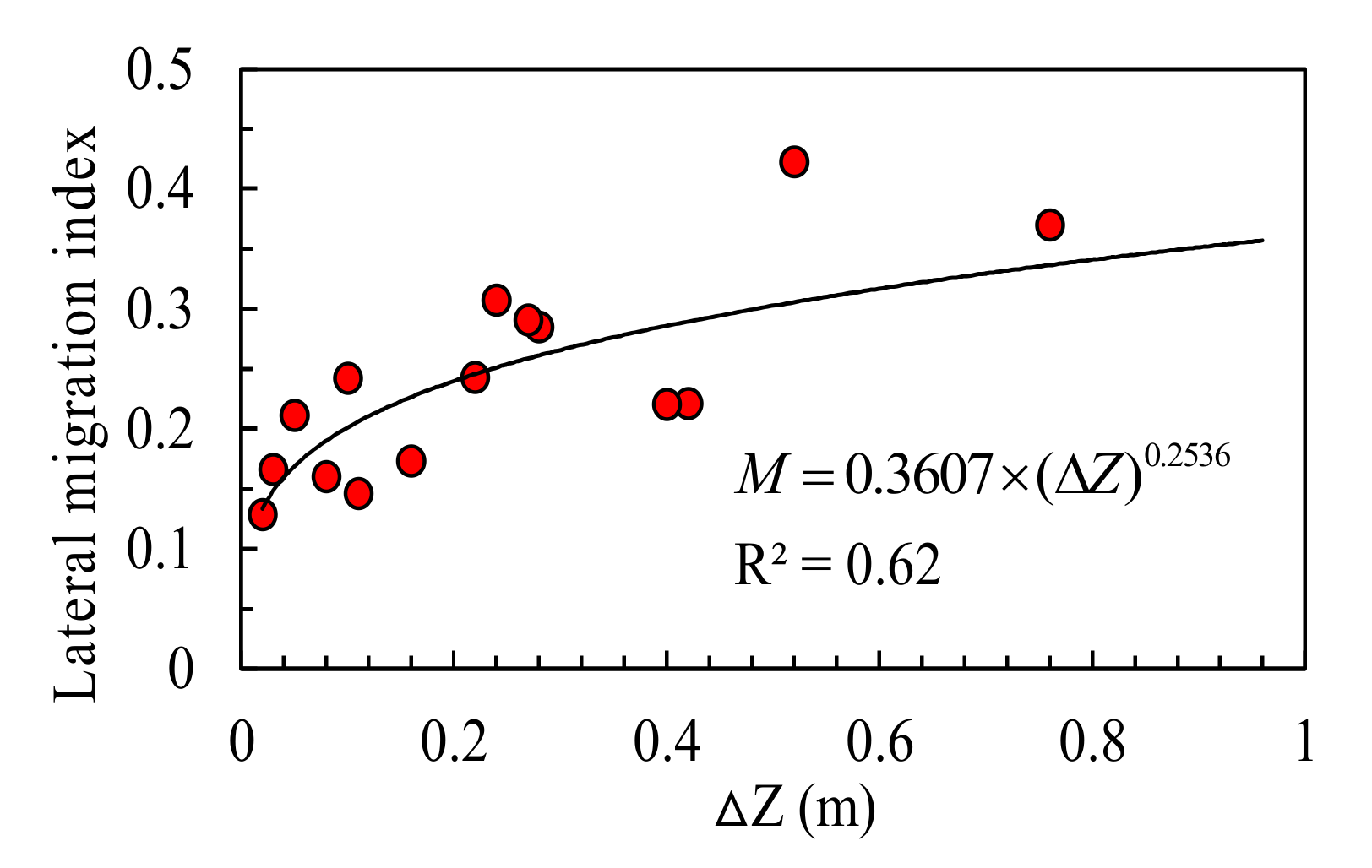
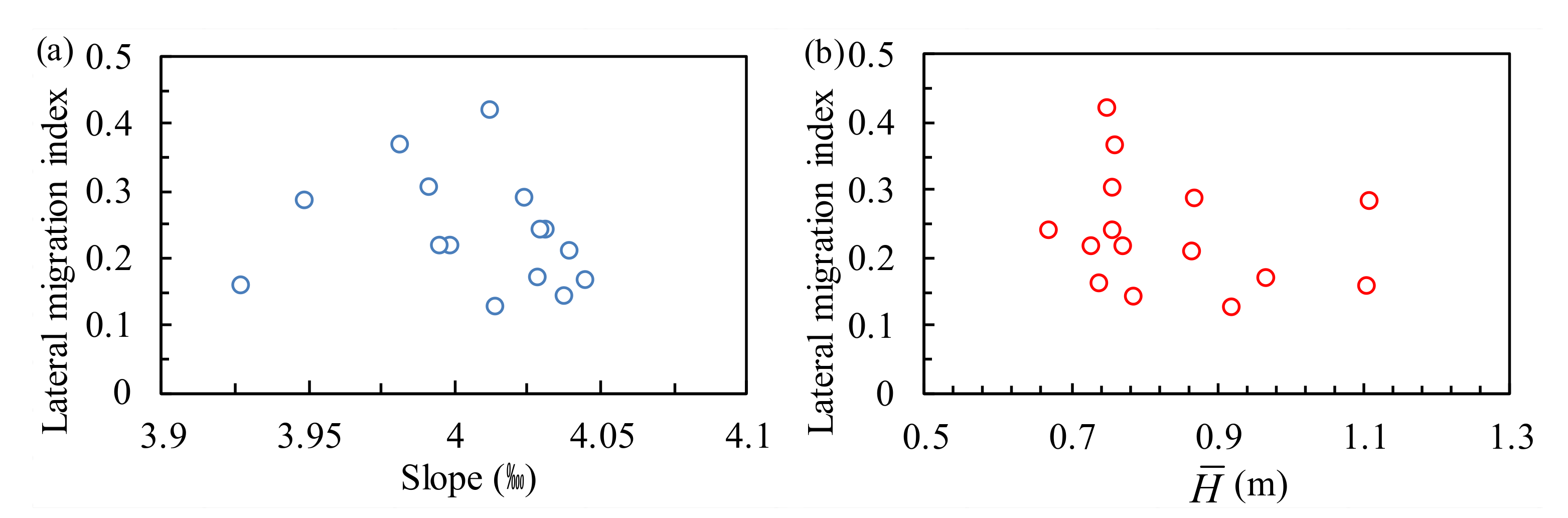
4.5. Effect of Other Boundary Conditions on Lateral Migration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooke, J.M. Magnitude and distribution of rates of river bank erosion. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 1980, 5, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, M.A. Global Geomorphology; Longman Scientific & Technical Harlow: White Plains, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, D.M. The measurement of river bank erosion and lateral channel change: A review. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 1993, 18, 777–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, J.; Das, N.; Ahmed, I.; Bhowmik, M. Channel migration and its impact on land use/land cover using RS and GIS: A study on Khowai River of Tripura, North-East India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2017, 20, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, J.Q.; Zhou, M.R.; Deng, S.; Zhang, X. Variation in reach-scale thalweg-migration intensity in a braided reach of the lower Yellow River in 1986–2015. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2017, 42, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, F.D., Jr.; Milhous, R.T. Sediment and aquatic habitat in river systems. Final report, American Society of Civil Engineers Task Committee on Sediment Transport and Aquatic Habitat. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1992, 118, 669–687. [Google Scholar]
- Bunn, S.E.; Arthington, A.H. Basic principles and ecological consequences of altered flow regimes for aquatic biodiversity. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florsheim, J.L.; Mount, J.F.; Chin, A. Bank erosion as a desirable attribute of rivers. BioScience 2008, 58, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, G.A.; Julien, P.Y.; Baird, D.C. Case Study: Modeling the Lateral Mobility of the Rio Grande below Cochiti Dam, New Mexico. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2005, 131, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.D.; Bangen, S.; Gillies, E.; Kramer, N.; Moir, H.; Wheaton, J. Let the river erode! Enabling lateral migration increases geomorphic unit diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, F.D., Jr.; Simon, A.; Steffen, L.J. Reservoir effects on downstream river channel migration. Environ. Conserv. 2000, 27, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, P.H.; Park, N.; Chang, K.A.; Briaud, L.J. Prediction of time-dependent channel meander migration based on large-scale laboratory experiments. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghinassi, M.; Nemec, W.; Aldinucci, M.; Nehyba, S.; Özaksoy, V.; Fidolini, F. Plan-form evolution of ancient meandering rivers reconstructed from longitudinal outcrop sections. Sedimentology 2014, 61, 952–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alber, A.; Piégay, H. Characterizing and modelling river channel migration rates at a regional scale: Case study of south-east France. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legg, N.T.; Olson, P.L. Channel Migration Processes and Patterns in Western Washington. A Synthesis for Floodplain Management and Restoration; Washington State Department of Ecology: Olympia, WA, USA, 2014.
- Xia, J.Q.; Li, J.; Carling, P.A.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, X. Dynamic adjustments in bankfull width of a braided reach. Proc. Inst. Civil Eng. Water Manag. 2019, 172, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, C.; Goswami, D.C. A Study on bank erosion and bank line migration pattern of the Subansiri river in Assam using remote sensing and GIS technology. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2013, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, N.C.; Erwin, S.O.; Schmidt, J.C. Spatial and temporal patterns in channel change on the Snake River downstream from Jackson Lake dam, Wyoming. Geomorphology 2013, 200, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lin, B.; Kuang, H. Numerical modelling of channel migration with application to laboratory rivers. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2015, 30, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A. River response to base level change: Implications for sequence stratigraphy. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.Y. River Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, D.M.; Grove, J.R.; Couperthwaite, J.S.; Leeks, G.J.L. Downstream change in river bank erosion rates in the Swale-Ouse system, Northern England. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Xia, J.Q.; Zhou, M.R.; Jiang, Q.R. Characteristics of main channel migration in the braided reach of the Lower Yellow River after the Xiaolangdi Reservoir operation. Adv. Water Sci. 2019, 30, 198–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Begin, Z.B.; Meyer, D.F.; Schumm, S.A. Development of longitudinal profiles of alluvial channels in response to base-level lowering. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1981, 6, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.L.; Keim, R.F.; Johnson, E.L.; Hupp, C.R.; Marre, S.; King, S.L. Geomorphic adjustment to hydrologic modifications along a meandering river: Implications for surface flooding on a floodplain. Geomorphology 2016, 269, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vachtman, D.; Laronne, J.B. Hydraulic geometry of cohesive channels undergoing base level drop. Geomorphology 2013, 197, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.F.; Xia, J.Q.; Zhou, M.R.; Deng, S. Morphodynamic evolution in a meandering reach of the Middle Yangtze River under upstream and downstream controls. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2019, 43, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.X.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Liu, X.F. River base level change in mouth channel evolution: The case of the Yellow River delta, China. Catena 2019, 183, 104193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odgaard, A.J. Streambank erosion along two rivers in Iowa. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, C.E.; Doyle, P.F. Comparison of bank erosion at vegetated and non-vegetated channel bends. Water Resour. Bull. 1995, 31, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanson, G.C.; Hickin, E.J. A statistical analysis of bank erosion and channel migration in western Canada. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1986, 97, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Hou, S.Z.; Wang, P. The relationship between changes of the main streamline and flow and sediment regime in Xiaobeiganliu reach of Yellow River. China Rural Water Hydropower 2018, 11, 98–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yellow River Xiaobeiganliu Shanxi Division. Xiaobeiganliu in Yellow River; The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brice, J.C. Stream Channel Stability Assessment, Final Report; Report FHWA/RD-82/021; Federal Highway Administration, US Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 1982.
- Xia, J.Q.; Li, X.J.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.L.; Zong, Q.L. Response of reach-scale bankfull channel geometry in the Lower Yellow River to the altered flow and sediment regime. Geomorphology 2014, 213, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.S.; Xia, J.Q.; Fu, X.D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G. Effect of altered flow regime on bankfull area of the lower Yellow River, China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 1585–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.S.; Zheng, S.; Thorne, C.R. A general framework for using the rate law to simulate morphological response to disturbance in the fluvial system. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 36, 575–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, A.P.; Fei, X.J. Sediment transport capacity of hyperconcentrated flow. Sci. China Ser. G Phys. Mech. Astron. 2008, 51, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maren, D.S.; Winterwerp, J.C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Pu, Q. Suspended sediment dynamics and morphodynamics in the Yellow River, China. Sedimentology 2009, 56, 785–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Qi, P.; Melching, C.S. Fluvial hydraulics of hyperconcentrated floods in Chinese rivers. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, J.Q.; Zhou, M.R.; Deng, S.; Wang, Z. Channel geometry adjustments in response to hyperconcentrated floods in a braided reach of the Lower Yellow River. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2018, 42, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.W.; Zheng, S.; Tan, G.M.; Shu, C.; Han, Q. Morphodynamic adjustments in the Yichang—Chenglingji Reach of the Middle Yangtze River since the operation of the Three Gorges Project. Catena 2019, 172, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wu, B.S. Simulation of sedimentation processes of the Xiaobeiganliu reach of the Yellow River and the lower Wei River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 45, 150–162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, W.W.; Wu, B.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, R.Y. Simulation of sedimentation processes in dry and wet seasons in the Xiaobeiganliu reach of the Yellow River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 880–892. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, L.R.; Legleiter, C.J.; Wydzga, M.A.; Dunne, T. Channel dynamics and habitat development in a meandering, gravel bed river. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.M.; Wang, W.H.; Xie, B.F.; Zhang, M. Fluvial processes of the downstream reaches of the reservoirs in the Lower Yellow River. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, C. Quantifying the connections between flow, bar deposition, and meander migration in large gravel-bed rivers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.S.; Wang, G.Q.; Ma, J.M.; Zhang, R. Case study: River training and its effects on fluvial processes in the Lower Yellow River, China. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | LM-MQ Reach | MQ-JMK Reach | JMK-TG Reach | Xiaobeiganliu Reach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1987 | 470 | 147 | 189 | 230 |
| 1988 | 536 | 225 | 281 | 319 |
| 1989 | 1082 | 930 | 292 | 586 |
| 1990 | 1603 | 350 | 347 | 543 |
| 1991 | 1393 | 625 | 485 | 707 |
| 1992 | 974 | 671 | 312 | 535 |
| 1993 | 270 | 508 | 324 | 347 |
| 1994 | 245 | 620 | 165 | 265 |
| 1995 | 592 | 127 | 424 | 337 |
| 1996 | 469 | 421 | 510 | 472 |
| 1997 | 441 | 360 | 172 | 276 |
| 1998 | 281 | 274 | 421 | 333 |
| 1999 | 375 | 287 | 275 | 304 |
| 2000 | 164 | 314 | 194 | 210 |
| 2001 | 276 | 235 | 389 | 307 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Q. Lateral Migration in a Wandering Reach of the Middle Yellow River in Response to Different Boundary Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5229. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155229
Li J, Zhang Y, Ji Q. Lateral Migration in a Wandering Reach of the Middle Yellow River in Response to Different Boundary Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(15):5229. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155229
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jie, Yi Zhang, and Qingfeng Ji. 2020. "Lateral Migration in a Wandering Reach of the Middle Yellow River in Response to Different Boundary Conditions" Applied Sciences 10, no. 15: 5229. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155229
APA StyleLi, J., Zhang, Y., & Ji, Q. (2020). Lateral Migration in a Wandering Reach of the Middle Yellow River in Response to Different Boundary Conditions. Applied Sciences, 10(15), 5229. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155229




