Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone (LHRH) Conjugated Magnetite Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents for Breast Cancer Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
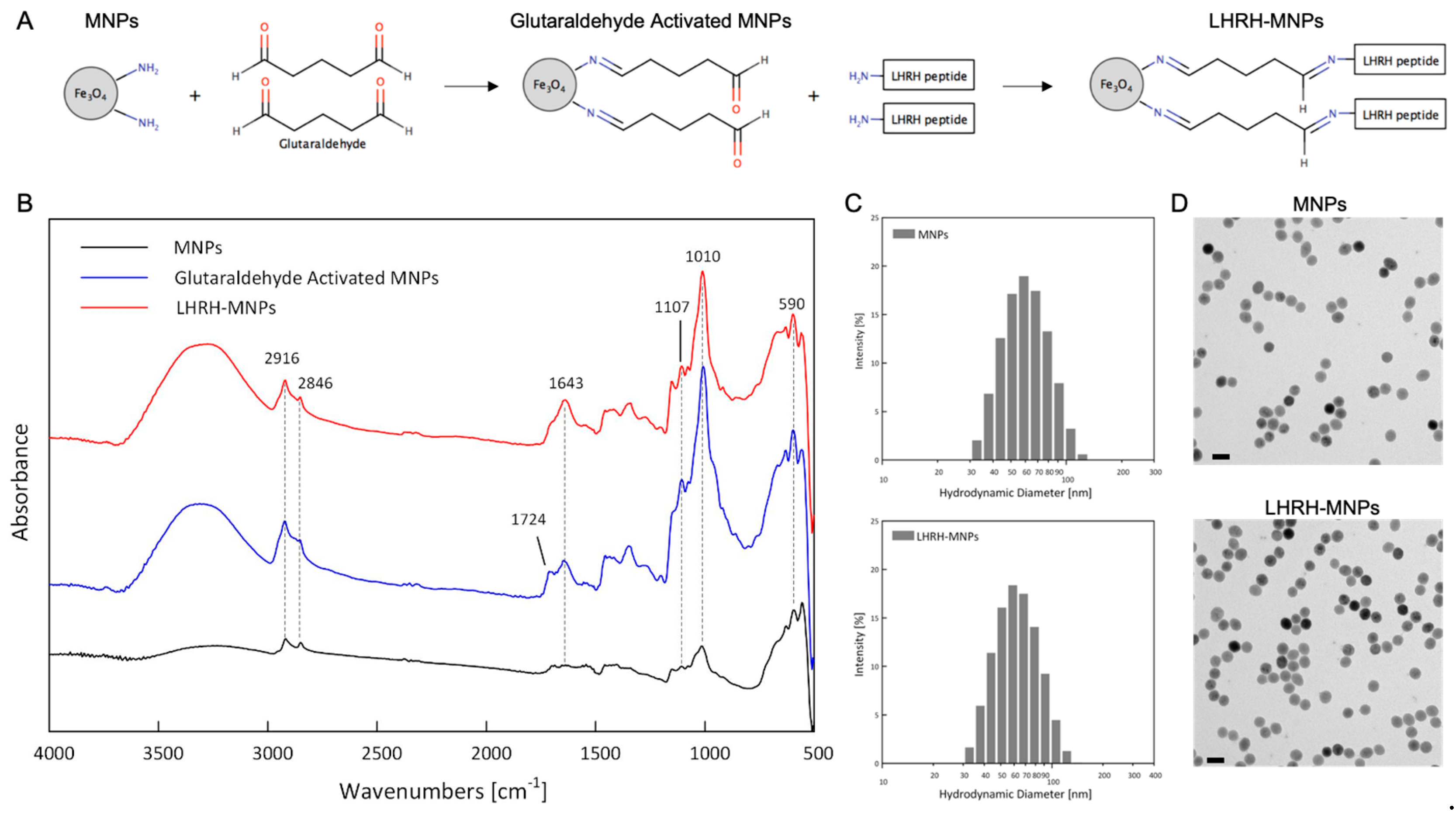
2.1. Conjugation of LHRH Peptides to MNPs
2.2. Characterization of MNPs and LHRH-MNPs
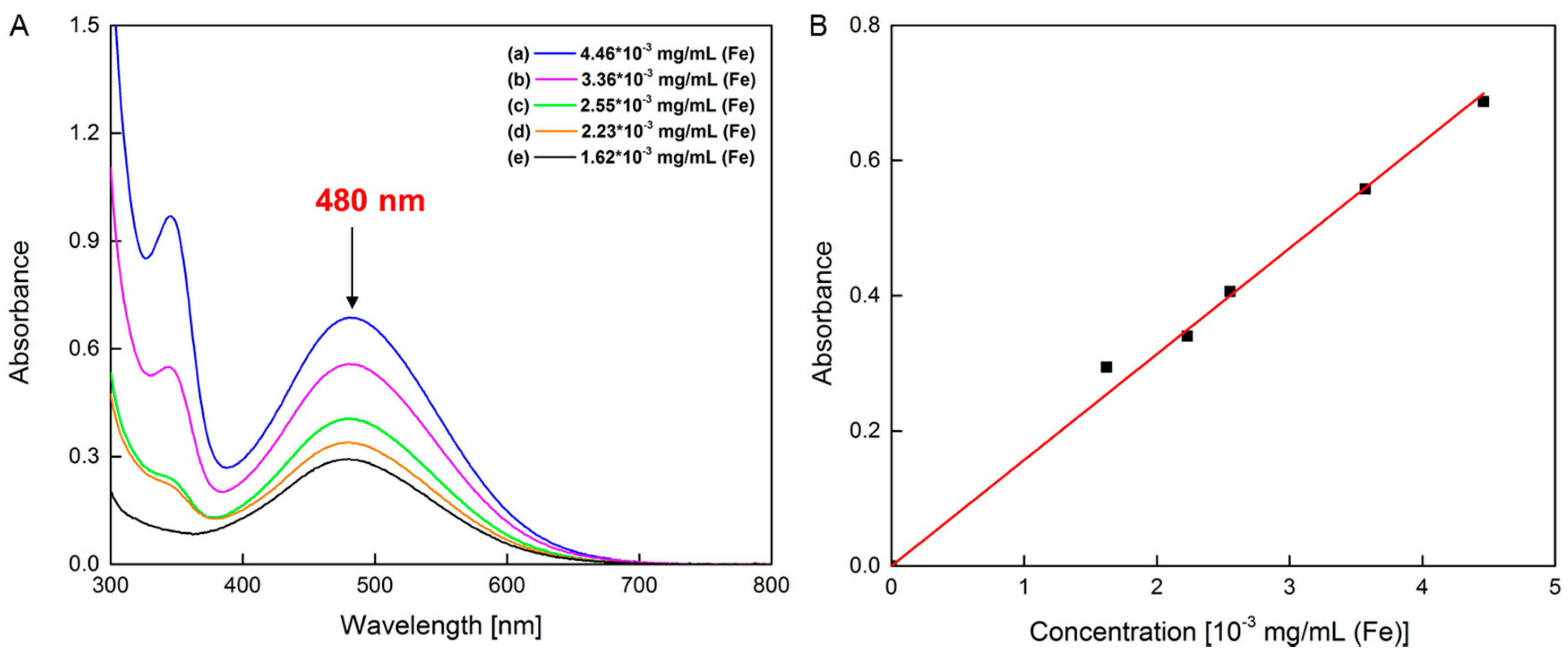
2.3. Iron Concentration Measurement
2.4. In Vitro MRI Scans
2.5. In Vivo MRI Study
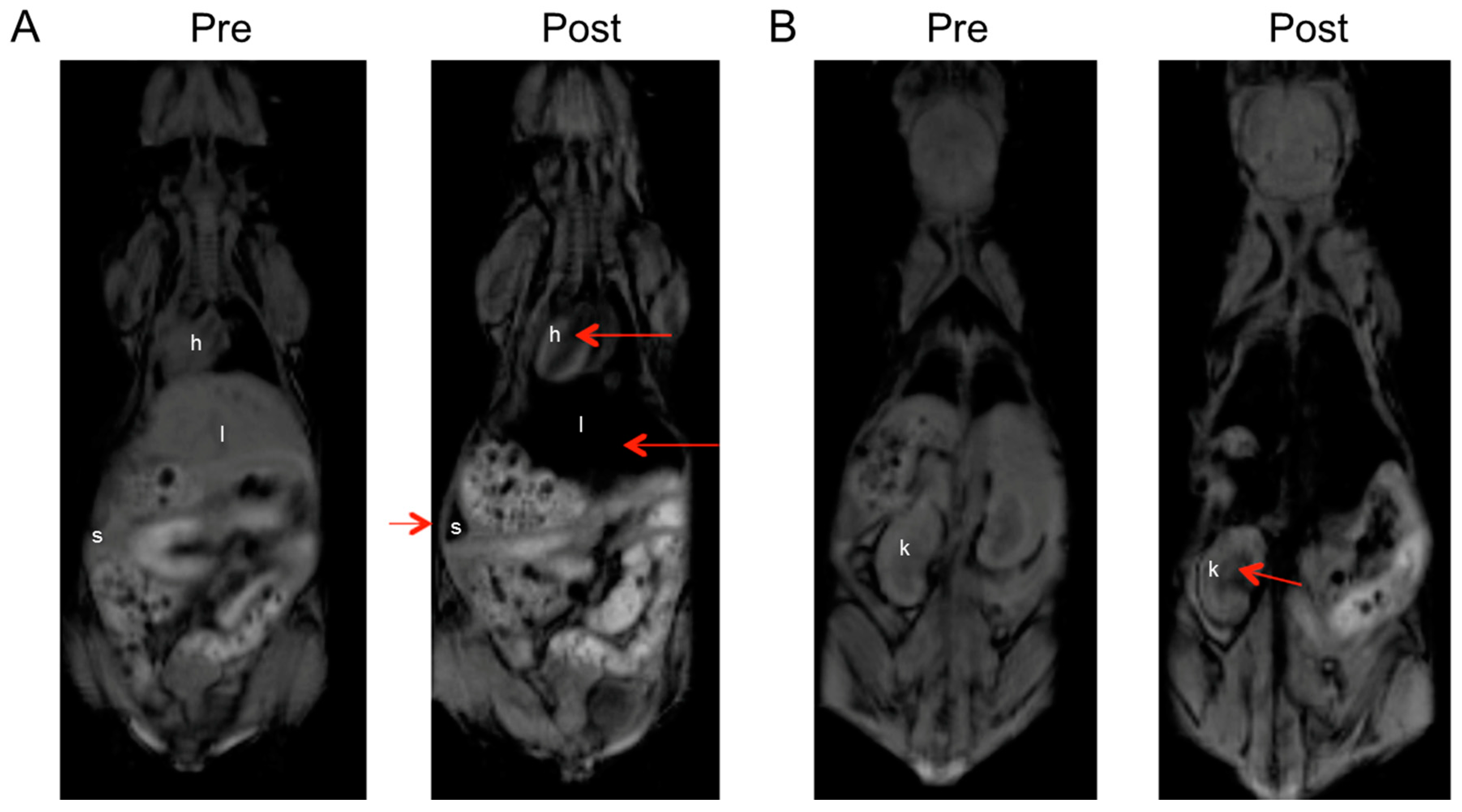
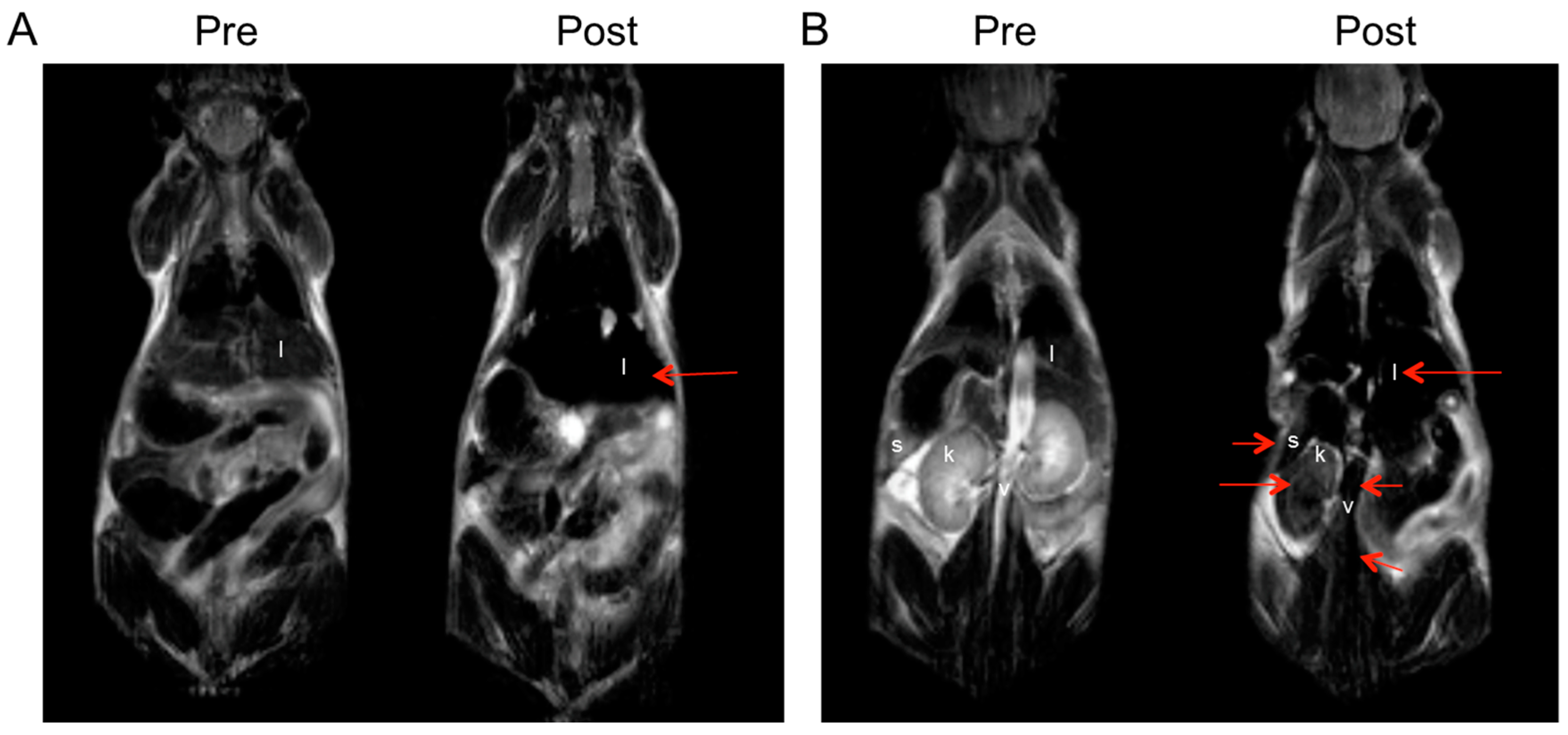
2.5.1. MR Imaging of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Non-Tumor-Bearing Mice
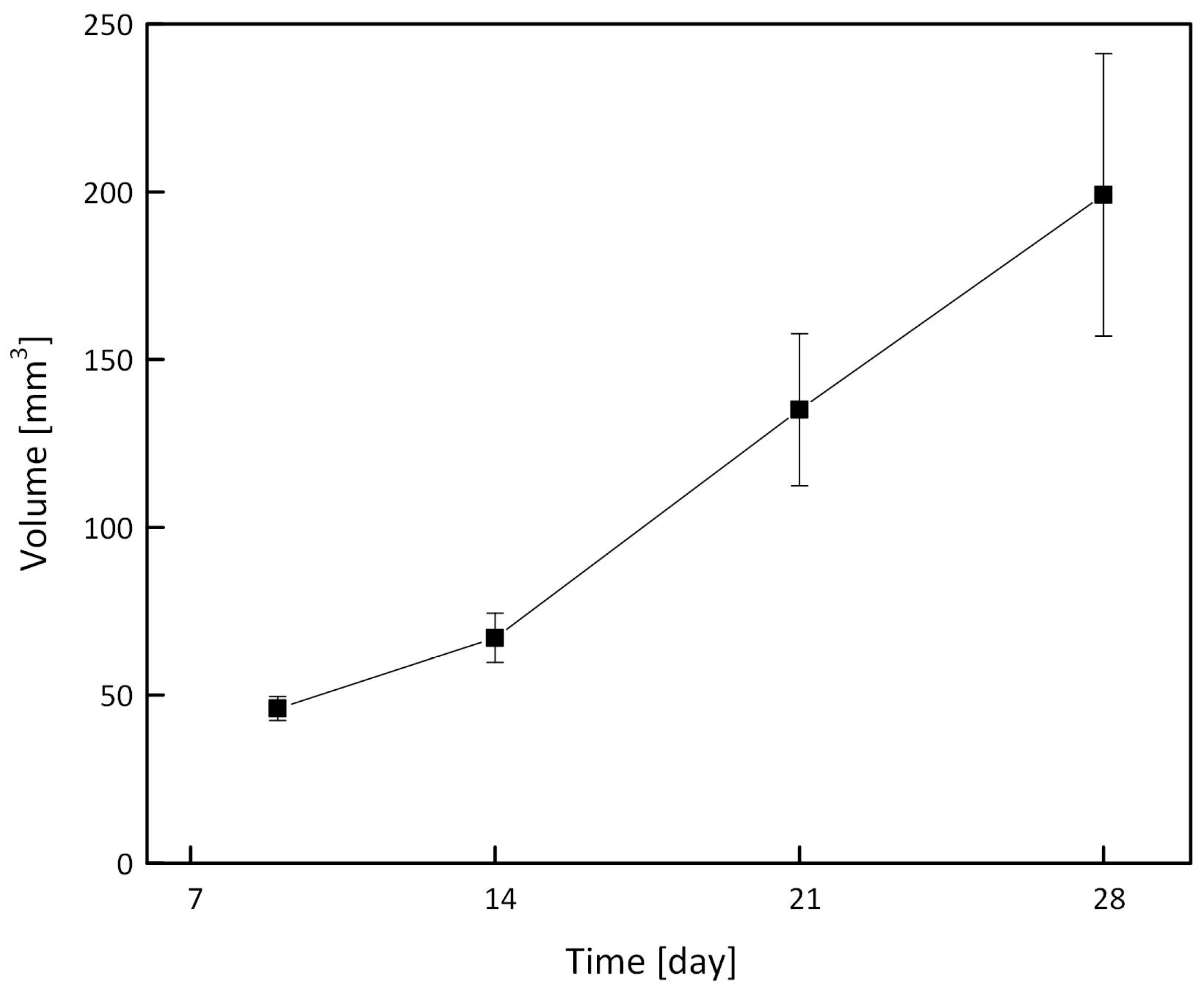
2.5.2. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Tumor Model
2.5.3. MR Imaging of Tumor-Bearing Mice through Intratumoral Injection
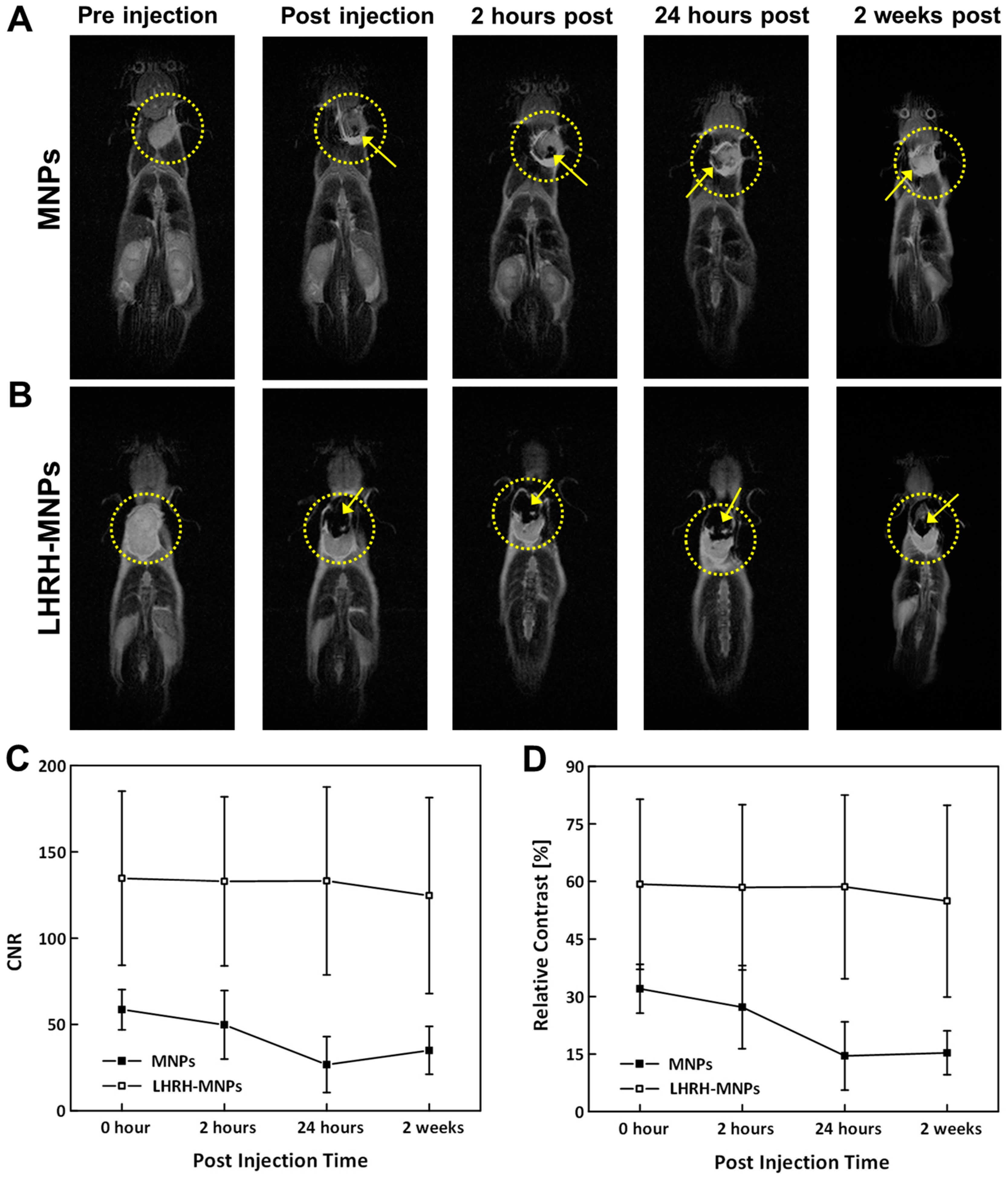
2.5.4. MR Imaging of Tumor-Bearing Mice through Intravenous Injection
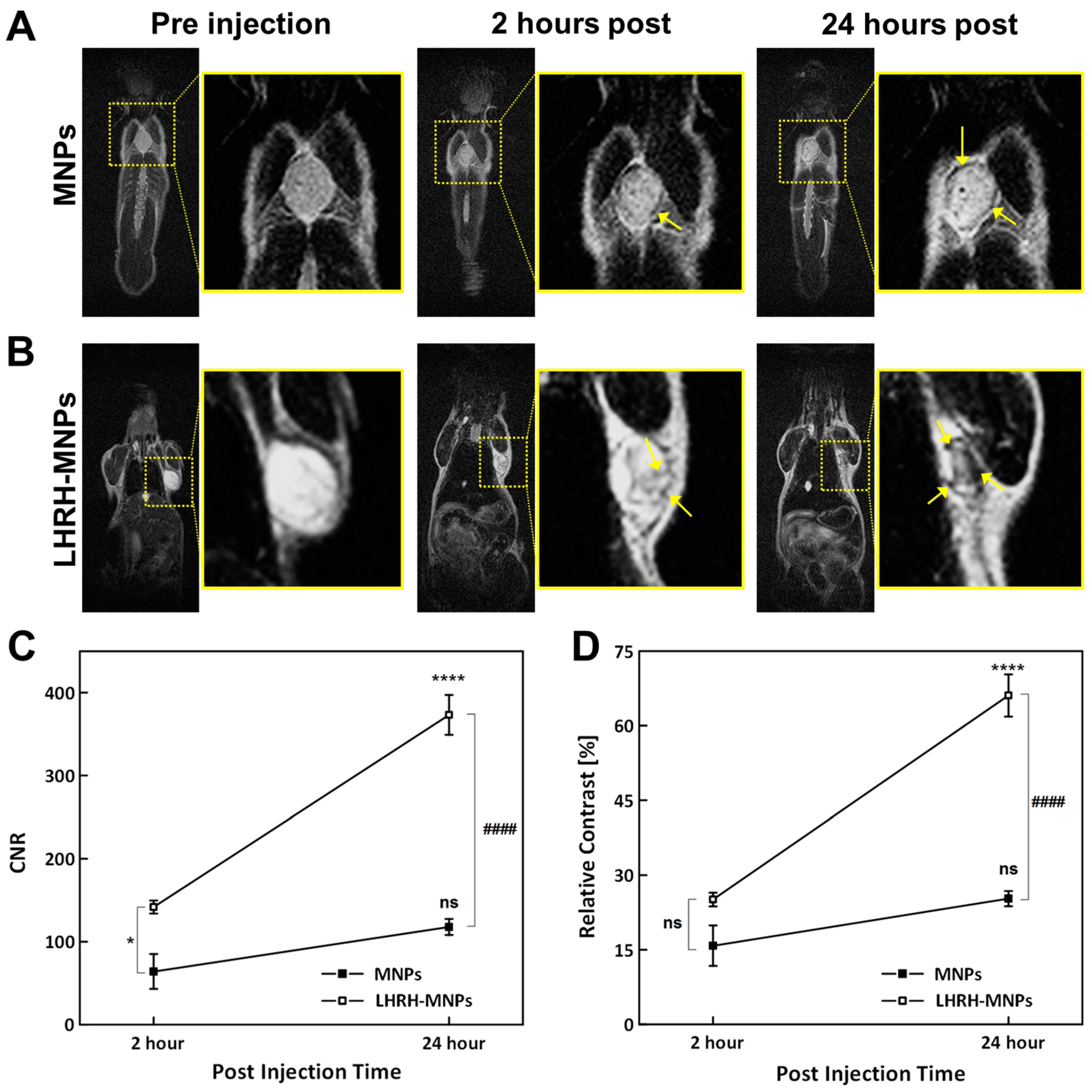
2.6. MR Image Analysis
2.7. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.8. Ethics Statement
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LHRH-MNP Conjugation
3.2. Nanoparticle Structure and Size Distribution
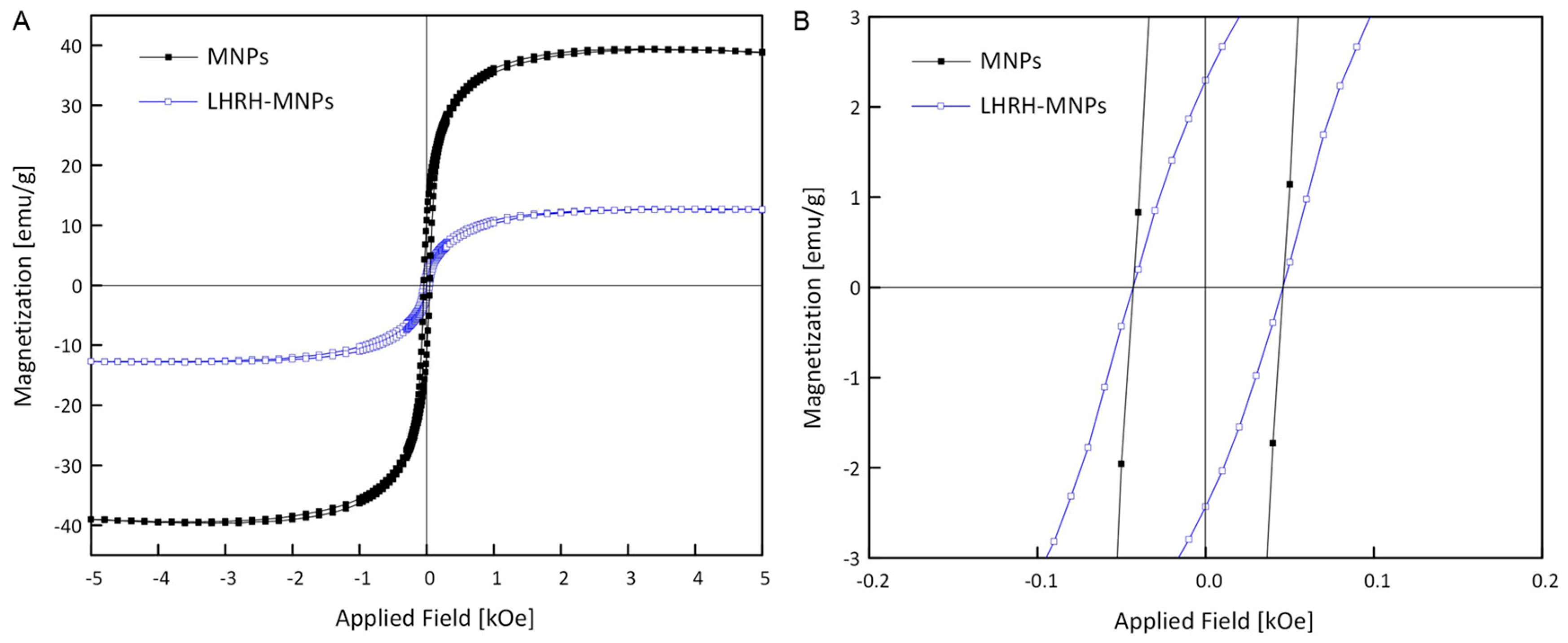
3.3. Magnetic Properties of MNPs and LHRH-MNPs
3.4. Nanoparticle Concentration Characterization
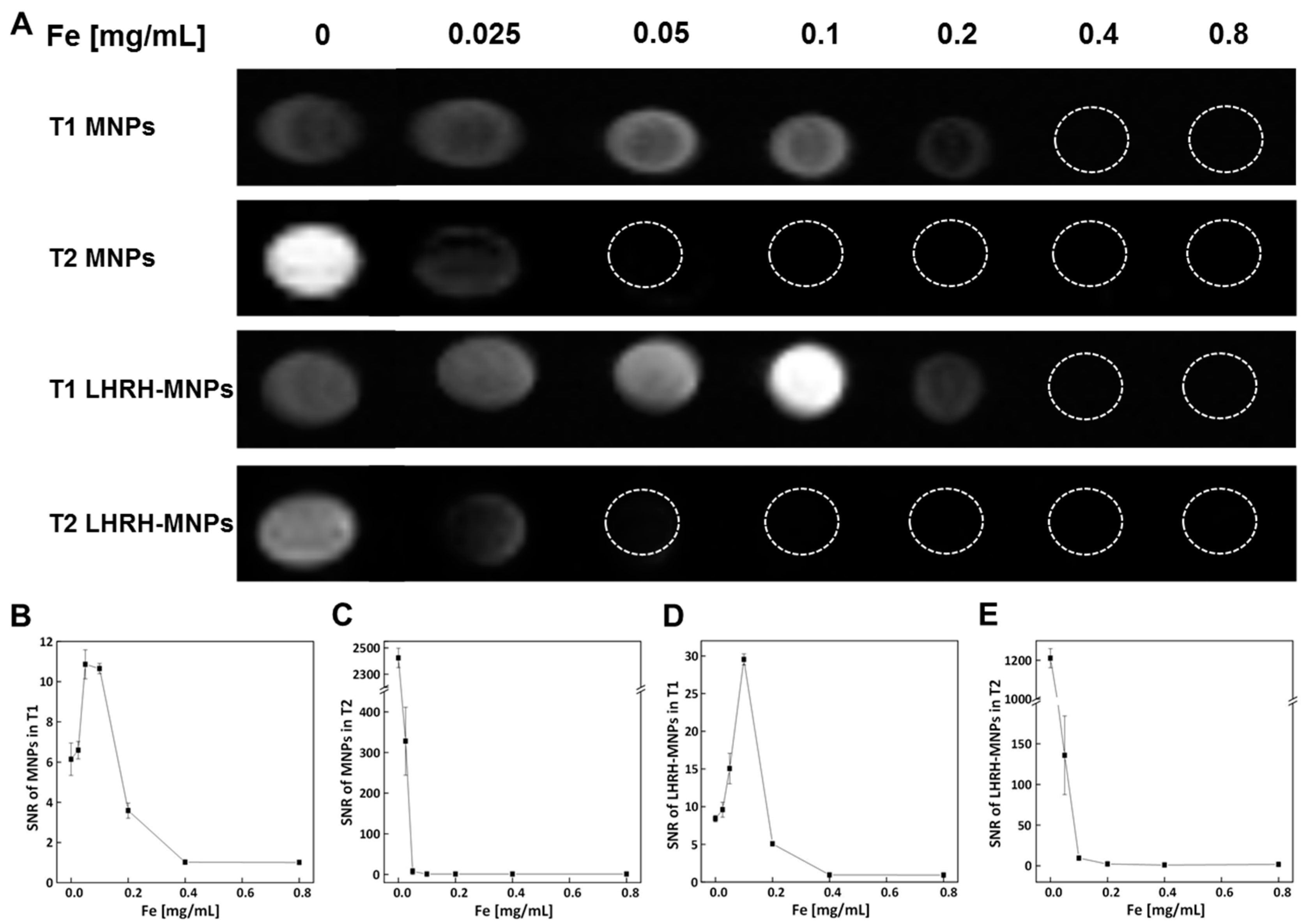
3.5. In Vitro MRI
3.6. In Vivo MRI of Non-Tumor-Bearing Mice
3.7. In Vivo MRI of Tumor-Bearing Mice through Intratumoral Injections
3.8. In Vivo MRI of Tumor-Bearing Mice through Intravenous Injections
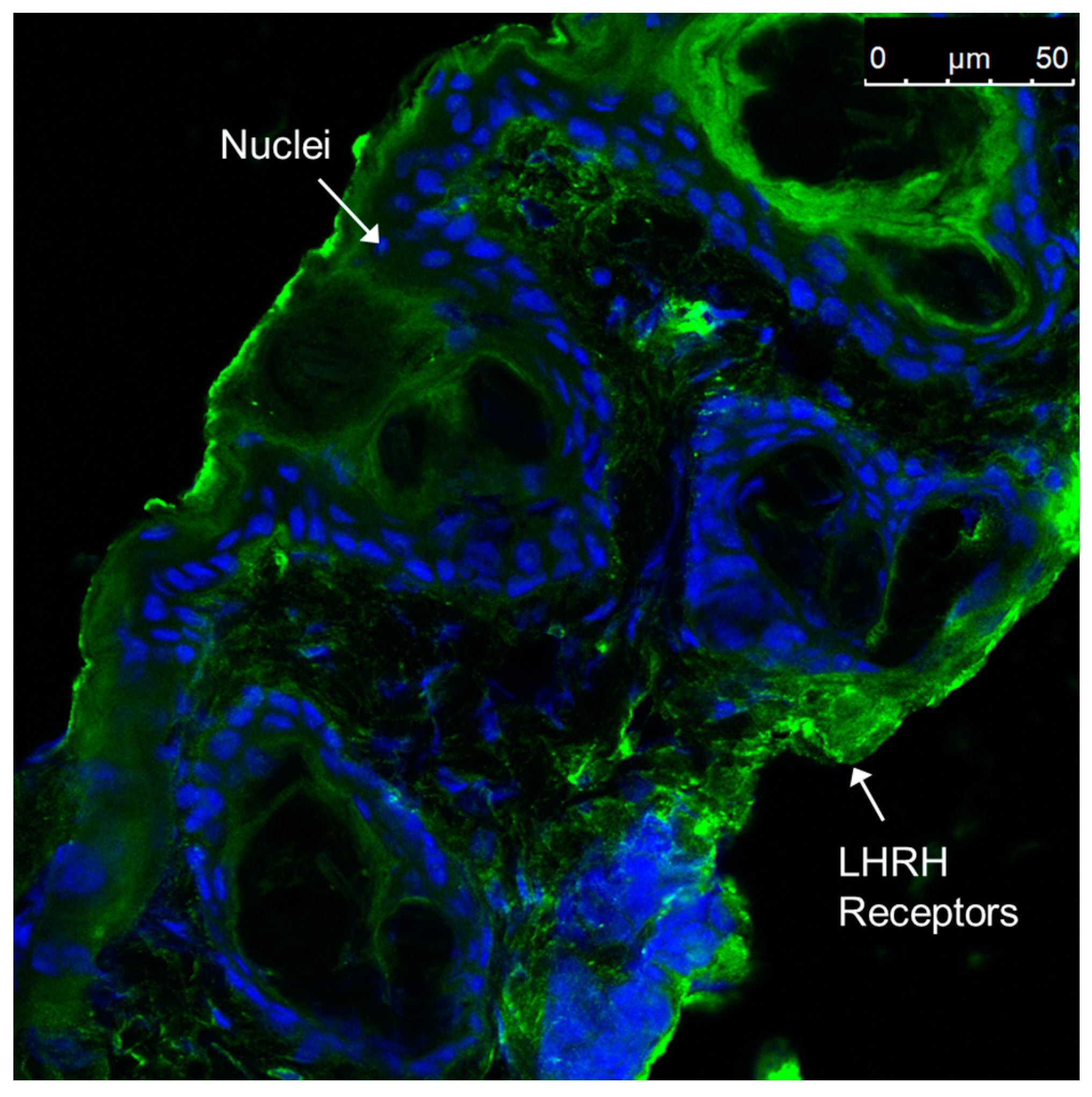
3.9. Immunohistochemical Staining of LHRH Receptors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Aggarwal, R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016, 293, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, C.L.; Recht, A. Side Effects of Adjuvant Treatment of Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broet, P.; Scholl, S.M.; de la Rochefordiere, A.; Fourquet, A.; Moreau, T.; De Rycke, Y.; Asselain, B.; Pouillart, P. Short and long-term effects on survival in breast cancer patients treated by primary chemotherapy: An updated analysis of a randomized trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1999, 58, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, C.; Carey, L.A. Understanding and treating triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology 2008, 22, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Tanja, O.; Snjezana, F.; Erika, M.; Barbara, M.; Simona, B. Triple negative breast cancer–prognostic factors and survival. Radiol. Oncol. 2011, 45, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laurentiis, M.; Cianniello, D.; Caputo, R.; Stanzione, B.; Arpino, G.; Cinieri, S.; Lorusso, V.; De Placido, S. Treatment of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): Current options and future perspectives. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2010, 36, S80–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, F.; Enright, K.; Dent, R.; Dranitsaris, G.; Myers, J.; Flynn, C.; Fralick, M.; Kumar, R.; Clemons, M. Survival Outcomes for Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Implications for Clinical Practice and Trial Design. Clin. Breast Cancer 2009, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisserie-Lacroix, M.; Mac Grogan, G.; Debled, M.; Ferron, S.; Asad-Syed, M.; Brouste, V.; Mathoulin-Pelissier, S.; Hurtevent-Labrot, G. Radiological features of triple-negative breast cancers (73 cases). Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2012, 93, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.-Y.; Lin, B.-R.; Huang, D.-P. Ultrasonographic findings of triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 10040–10043. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Obayemi, J.D.; Du, J.; Soboyejo, W.O. An investigation of the viscoelastic properties and the actin cytoskeletal structure of triple negative breast cancer cells. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, U.; Kopka, L.; Grabbe, E. Breast Carcinoma: Effect of Preoperative Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging on the Therapeutic Approach. Radiology 1999, 213, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esserman, L.; Hylton, N.; Yassa, L.; Barclay, J.; Frankel, S.; Sickles, E. Utility of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Management of Breast Cancer: Evidence for Improved Preoperative Staging. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, Z.R.; Kievit, F.M.; Zhang, M. Magnetite nanoparticles for medical MR imaging. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, R.R.; Hesselink, J.R.; Zlatkin, M.B.; Vrues, J.V. Clinical Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Elsevier Health Sciences: London, UK, 2005; p. 3824. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.-N.; Wei, C.; Zhu, Z.-Z.; Hou, Y.-L.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Xu, Z.-C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and surface coating techniques for biomedical applications. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 37503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Magnetite nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and treatment monitoring: Recent advances. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Sherwood, J.A.; Sun, Z. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as T1 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, Y.; Zou, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, C. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MR imaging of pancreatic cancer: Potential for early diagnosis through targeted strategies. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.-H.; Qian, X.; Mao, H.; Wang, A.Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Nie, S.; Shin, D.M. Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor imaging and therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.W.; Treeck, O.; Buchholz, S.; Seitz, S.; Ortmann, O.; Engel, J.B. Receptors for luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (GnRH) as therapeutic targets in triple negative breast cancers (TNBC). Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Reyes, M.; Maya-Núñez, G.; Pérez-Solis, M.A.; López-Muñoz, E.; Guillén, N.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C.; Aguilar-Rojas, A. Treatment of Breast Cancer With Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogs. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obayemi, J.D.; Salifu, A.A.; Eluu, S.C.; Uzonwanne, V.O.; Jusu, S.M.; Nwazojie, C.C.; Onyekanne, C.E.; Ojelabi, O.; Payne, L.; Moore, C.M.; et al. LHRH-Conjugated Drugs as Targeted Therapeutic Agents for the Specific Targeting and Localized Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Fan, J.; Galiana, G.; Branca, R.T.; Clasen, P.L.; Ma, S.; Zhou, J.; Leuschner, C.; Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Hormes, J.; et al. LHRH-functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for breast cancer targeting and contrast enhancement in MRI. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Biomim. Supramol. Syst. 2009, 29, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Obayemi, J.D.; Malatesta, K.; Kosmrlj, A.; Soboyejo, W.O. Enhanced cellular uptake of LHRH-conjugated PEG-coated magnetite nanoparticles for specific targeting of triple negative breast cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 88, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Youssefian, S.; Obayemi, J.; Malatesta, K.; Rahbar, N.; Soboyejo, W. Investigation of adhesive interactions in the specific targeting of Triptorelin-conjugated PEG-coated magnetite nanoparticles to breast cancer cells. Acta Biomater. 2018, 71, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayemi, J.D.; Hu, J.; Uzonwanne, V.O.; Odusanya, O.S.; Malatesta, K.; Anuku, N.; Soboyejo, W.O. Adhesion of ligand-conjugated biosynthesized magnetite nanoparticles to triple negative breast cancer cells. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 68, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Surface Effects and Properties Related to Biomedicine Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinikaridou, A.; Qiao, Y.; Giordano, N.; Hamilton, J.A. Detection of thrombus size and protein content by ex vivo magnetization transfer and diffusion weighted MRI. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2012, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maubon, A.J.; Ferru, J.-M.; Berger, V.; Soulage, M.C.; DeGraef, M.; Aubas, P.; Coupeau, P.; Dumont, E.; Rouanet, J.-P. Effect of Field Strength on MR Images: Comparison of the Same Subject at 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 T. Radiographics 1999, 19, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Sarkar, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mishra, R.; Kundu, P.P. Efficient oral insulin delivery by dendronized chitosan: In vitro and in vivo studies. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 43890–43902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Du, K.; Fang, C.; Bhattarai, N.; Veiseh, O.; Kievit, F.; Stephen, Z.; Lee, D.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Ratner, B.; et al. PEG-Mediated Synthesis of Highly Dispersive Multifunctional Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles: Their Physicochemical Properties and Function In Vivo. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutirman, Z.A.; Sanagi, M.M.; Abd Karim, K.J.; Wan Ibrahim, W.A. Preparation of methacrylamide-functionalized crosslinked chitosan by free radical polymerization for the removal of lead ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochelle, M.C.; Udo, S. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurences and Uses, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Boschstrabe, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Adolphi, N.L.; Butler, K.S.; Lovato, D.M.; Tessier, T.E.; Trujillo, J.E.; Hathaway, H.J.; Fegan, D.L.; Monson, T.C.; Stevens, T.E.; Huber, D.L.; et al. Imaging of Her2-targeted magnetic nanoparticles for breast cancer detection: Comparison of SQUID-detected magnetic relaxometry and MRI. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2012, 7, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Zheng, J. Clearance Pathways and Tumor Targeting of Imaging Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6655–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arami, H.; Khandhar, A.; Liggitt, D.; Krishnan, K.M. In vivo delivery, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles. ChSRv 2015, 44, 8576–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, K.; Huang, J.; Xiao, K. Uptake, distribution, clearance, and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different sizes and coatings. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, N.J.; Weng, X.; Siow, B.; Veiga, C.; Ashford, M.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Schätzlein, A.G.; Uchegbu, I.F. Clustering superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles produces organ-targeted high-contrast magnetic resonance images. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1135–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Y.; Sun, W.; Luo, Y.; Cai, H.; Pan, Y.; Shen, M.; Xia, J.; Shi, X. Hyaluronic acid-modified hydrothermally synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted tumor MR imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3666–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, H.H.; Holt-Casper, D.; Grainger, D.W.; Ghandehari, H. Nanoparticle uptake: The phagocyte problem. Nano Today 2015, 10, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründker, C.; Emons, G. The Role of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Schally, A.V. Targeting of Cytotoxic Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Analogs to Breast, Ovarian, Endometrial, and Prostate Cancers1. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaoning, L.; Oleh, T.; Olena, T.; Canan, S.; Tamara, M. LHRH-Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, C.; Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Hansel, W.; Soboyejo, W.; Zhou, J.; Hormes, J. LHRH-conjugated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for detection of breast cancer metastases. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 99, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharap, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Chandna, P.; Khandare, J.J.; Qiu, B.; Gunaseelan, S.; Sinko, P.J.; Stein, S.; Farmanfarmaian, A.; Minko, T. Tumor-specific targeting of an anticancer drug delivery system by LHRH peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12962–12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuschner, C.; Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Hansel, W.; Hormes, J. Targeting Breast Cancer Cells and Their Metastases Through Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone (LHRH) Receptors Using Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Biom. Nanotechnol. 2005, 1, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | T1 GRE | T2 FSE |
|---|---|---|
| Echo Time (TE) [ms] | 3.8 | 80 |
| Repetition Time (TR) [ms] | 15.4 | 4593.7 |
| Field of View (FOV) [mm] | 100 | 150 |
| Flip Angle [°] | 15 | 180 |
| Matrix Size | 256 × 256 | 256 × 256 |
| Number of Slices | 24 | 24 |
| Thickness [mm] | 1.3 | 1.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Obayemi, J.; Malatesta, K.; Yurkow, E.; Adler, D.; Soboyejo, W. Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone (LHRH) Conjugated Magnetite Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents for Breast Cancer Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155175
Hu J, Obayemi J, Malatesta K, Yurkow E, Adler D, Soboyejo W. Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone (LHRH) Conjugated Magnetite Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents for Breast Cancer Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(15):5175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155175
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jingjie, John Obayemi, Karen Malatesta, Edward Yurkow, Derek Adler, and Winston Soboyejo. 2020. "Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone (LHRH) Conjugated Magnetite Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents for Breast Cancer Imaging" Applied Sciences 10, no. 15: 5175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155175
APA StyleHu, J., Obayemi, J., Malatesta, K., Yurkow, E., Adler, D., & Soboyejo, W. (2020). Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone (LHRH) Conjugated Magnetite Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents for Breast Cancer Imaging. Applied Sciences, 10(15), 5175. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155175






