Auditory Device Voice Activity Detection Based on Statistical Likelihood-Ratio Order Statistics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Auditory Device VAD Implementation
3. Conventional Statistical LRT-Based VAD
4. Proposed VAD Based on LR Order Statistics
4.1. Signal Sparseness Model for LRT
4.2. VAD Based on LR Order Statistics
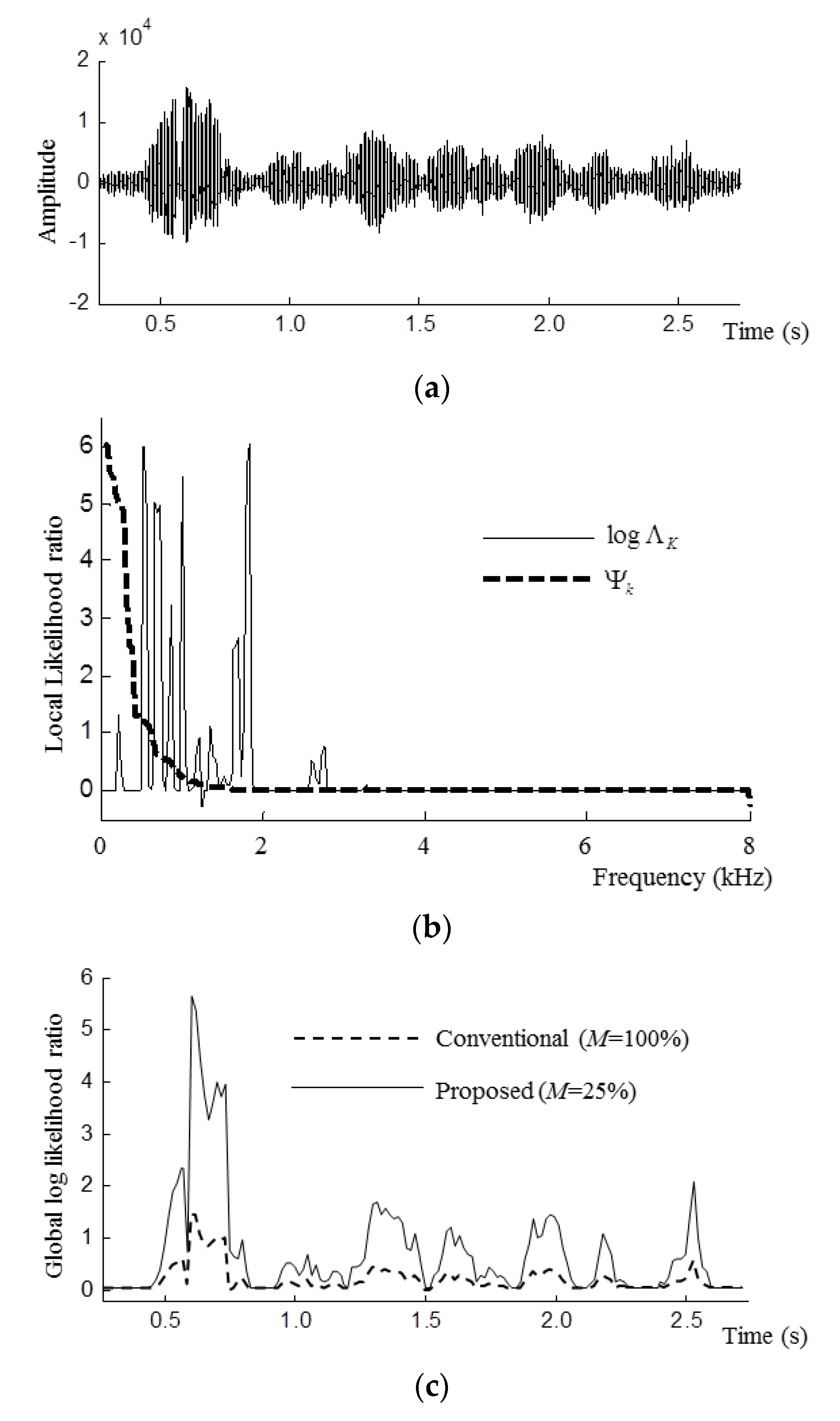
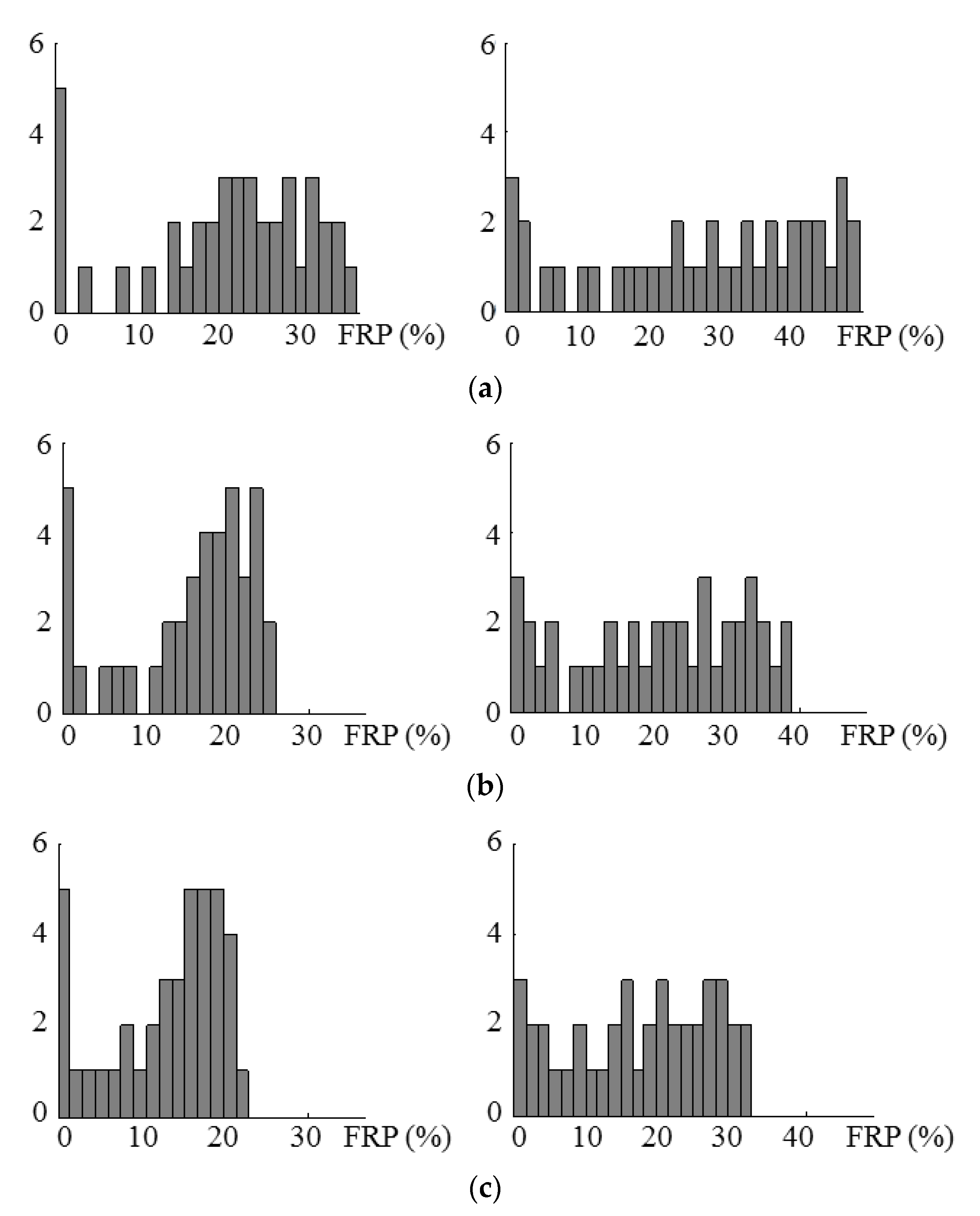
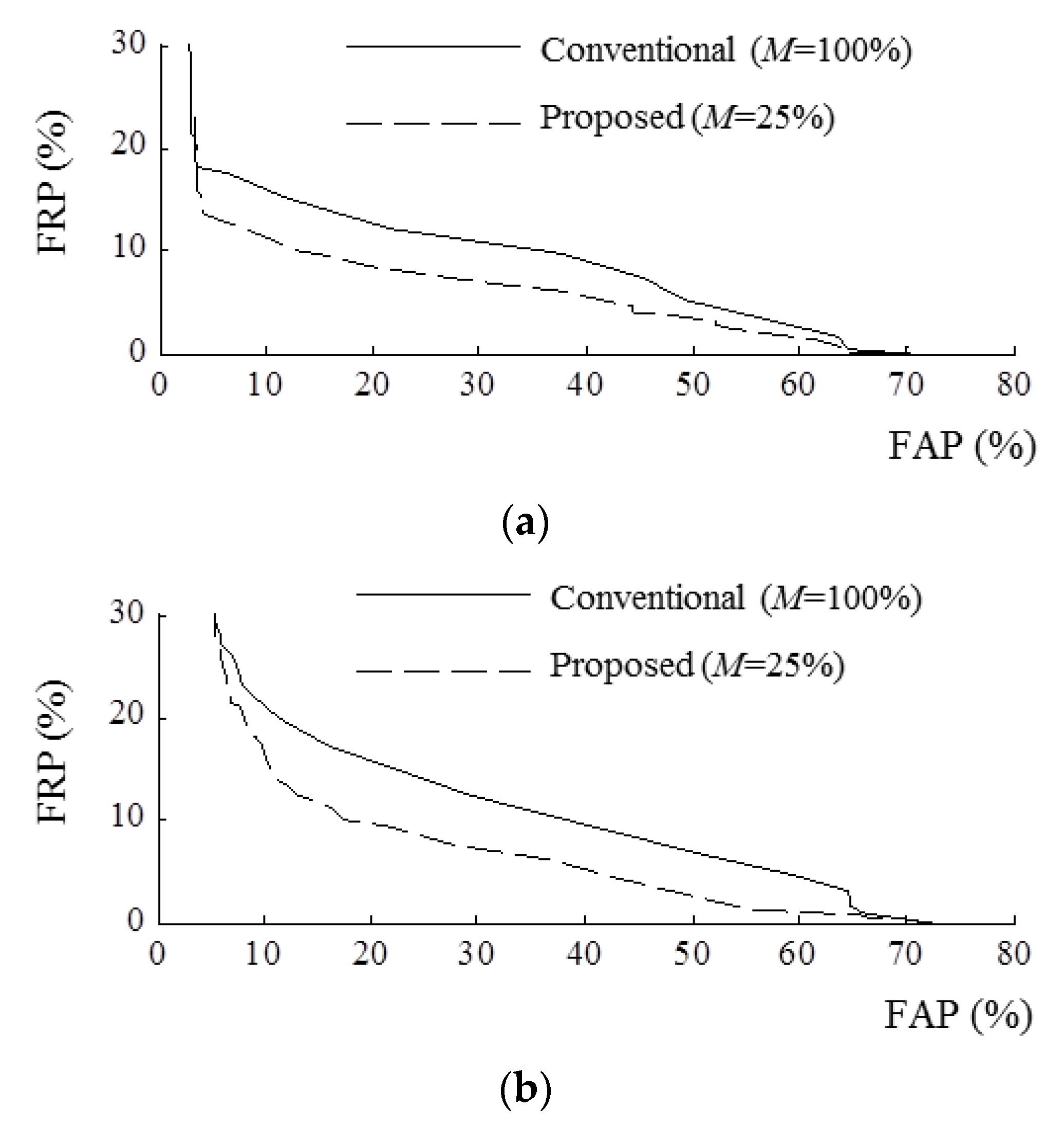
5. Experiments and Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benyassine, A.; Shlomot, E.; Su, H.Y.; Massaloux, D.; Lamblin, C.; Petit, J.P. ITU-T Recommendation G729 Annex B: A silence compression scheme for use with G729 optimized for V70 digital simultaneous voice and data applications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 1997, 35, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Makino, S.; Chen, J. Speech Enhancement; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ETSI Std. Speech Processing, Transmission and Quality Aspects (STQ); Distributed Speech Recognition; Advanced Front–End Feature Extraction Algorithm; Compression Algorithms; ETSI ES 202 050 V1.1.1 (2002–10); European Telecommunications Standards Institute: Valbonne, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, G.; Herzke, T.; Berg, D.; Hohmann, V. The master hearing aid: A PC based platform for algorithm development and evaluation. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2006, 92, 618–628. [Google Scholar]
- Kochkin, S. MarkeTrak VII: Why my hearing aids are in the drawer: The consumers’ perspective. Hear. J. 2000, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochkin, S. MarkeTrak VII: Obstacles to adult non-user adoption of hearing aids. Hear. J. 2007, 60, 24–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomp, R. Auditory handicap of hearing impairment and the limited benefit of hearing aids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 63, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, E.W.; Yoho, S.E.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. An algorithm to improve speech recognition in noise for hearing-impaired listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trawicki, M.B.; Johnson, M.T. Distributed multichannel speech enhancement with minimum mean-square error short-time spectral amplitude, log-spectral amplitude, and spectral phase estimation. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizou, P.C. Speech Enhancement: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Kang, B.O.; Jung, H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H.S. Statistical model-based noise reduction approach for car interior applications to speech recognition. ETRI J. 2010, 32, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.; Kim, N.S.; Sung, W. A statistical model–based voice activity detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1999, 6, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.D.; Kondoz, A. Analysis and improvement of a statistical model–based voice activity detector. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2001, 8, 276–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, J.; Puntonet, C.G.; Segura, J.C. Generalized LRT–based voice activity detector. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2006, 13, 636–639. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.W.; Kwon, H.J.; Jin, S.H.; Kim, N.S. Voice activity detection based on conditional MAP criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2008, 15, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.W.; Kim, H.K. Multi-Task Learning U-Net for Single-Channel Speech Enhancement and Mask-Based Voice Activity Detection. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, R.; Sainath, T.N.; Simko, G.; Parada, C. Feature learning with raw-waveform CLDNNs for voice activity detection. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Hahn, M. Vowel based voice activity detection with LSTM recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing Systems, Auckland, New Zealand, 21–24 November 2016; pp. 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Wang, D. Boosting contextual information for deep neural network based voice activity detection. IEEE/Acm Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 24, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, J.M. A real-time hearing-aid research platform (HARP): Realization, calibration, and evaluation. Acust. United Acust. 2013, 99, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Bleeck, S. An open development platform for auditory real-time signal processing. Speech Commun. 2018, 98, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäuml, R.W.; Sörgel, W. Uniform polyphase filter banks for use in hearing aids: Design and constraint. In Proceedings of the 16th European Signal Processing Conference, Lausanne, Switzerland, 25–29 August 2008; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Löllmann, H.; Vary, P. Low delay noise reduction and dereverberation for hearing aids. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. 2009, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M.A.; Moore, B.C. Tolerable hearing aid delays. III. Effects on speech production and perception of across-frequency variation in delay. Ear Hear. 2003, 24, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löllmann, H.W.; Vary, P. Uniform and warped low delay filter-banks for speech enhancement. Speech Commun. 2007, 49, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löllmann, H.W.; Vary, P. Low delay filter-banks for speech and audio processing. In Speech and Audio Processing in Adverse Environments; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 13–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.M. Hearing Aid Speech Enhancement Using Phase Difference-Controlled Dual-Microphone Generalized Sidelobe Canceller. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 2169–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofolo, J.; Lamel, L.F.; Fisher, W.M.; Fiscus, J.G.; Pallett, D.S.; Dahlgren, N.L.; Zue, V. TIMIT Acoustic–Phonetic Continuous Speech Corpus; Linguistic Data Consortium: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, A.; Steeneken, H.J.M. Assessment for automatic speech recognition: II. NOISEX-92: A database and an experiment to study the effect of additive noise on speech recognition systems. Speech Commun. 1993, 12, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Speech | Noise | |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Absent | |
| Present | ||
| Absent | ||
| Noise Types | SNR (dB) | RDER (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRP (%) | FAP (%) | FRP (%) | FAP (%) | |||
| White | 20 | 15.81 | 11.31 | 10.17 | 12.00 | 18.25 |
| 15 | 16.74 | 3.38 | 11.00 | 4.07 | 25.10 | |
| 10 | 16.92 | 6.28 | 12.25 | 4.55 | 27.59 | |
| 5 | 18.49 | 3.59 | 13.08 | 6.48 | 11.41 | |
| 0 | 19.79 | 8.76 | 15.90 | 12.00 | 2.28 | |
| Babble | 20 | 15.35 | 11.93 | 10.36 | 13.03 | 14.26 |
| 15 | 15.40 | 4.76 | 7.49 | 6.62 | 30.01 | |
| 10 | 14.89 | 11.10 | 8.41 | 9.66 | 30.47 | |
| 5 | 21.22 | 9.86 | 14.15 | 11.17 | 18.53 | |
| 0 | 24.60 | 15.45 | 20.99 | 14.48 | 11.44 | |
| Volvo | 20 | 14.93 | 11.52 | 8.88 | 13.38 | 15.84 |
| 15 | 14.75 | 4.07 | 8.60 | 7.03 | 16.95 | |
| 10 | 14.70 | 4.55 | 10.03 | 5.66 | 18.49 | |
| 5 | 14.89 | 4.83 | 9.85 | 6.14 | 18.91 | |
| 0 | 14.98 | 5.17 | 10.96 | 5.45 | 18.56 | |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.M. Auditory Device Voice Activity Detection Based on Statistical Likelihood-Ratio Order Statistics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155026
Kim SM. Auditory Device Voice Activity Detection Based on Statistical Likelihood-Ratio Order Statistics. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(15):5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155026
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seon Man. 2020. "Auditory Device Voice Activity Detection Based on Statistical Likelihood-Ratio Order Statistics" Applied Sciences 10, no. 15: 5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155026
APA StyleKim, S. M. (2020). Auditory Device Voice Activity Detection Based on Statistical Likelihood-Ratio Order Statistics. Applied Sciences, 10(15), 5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155026





