Laser Lens Size Measurement Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle and Systems
2.1. Principle of OCT
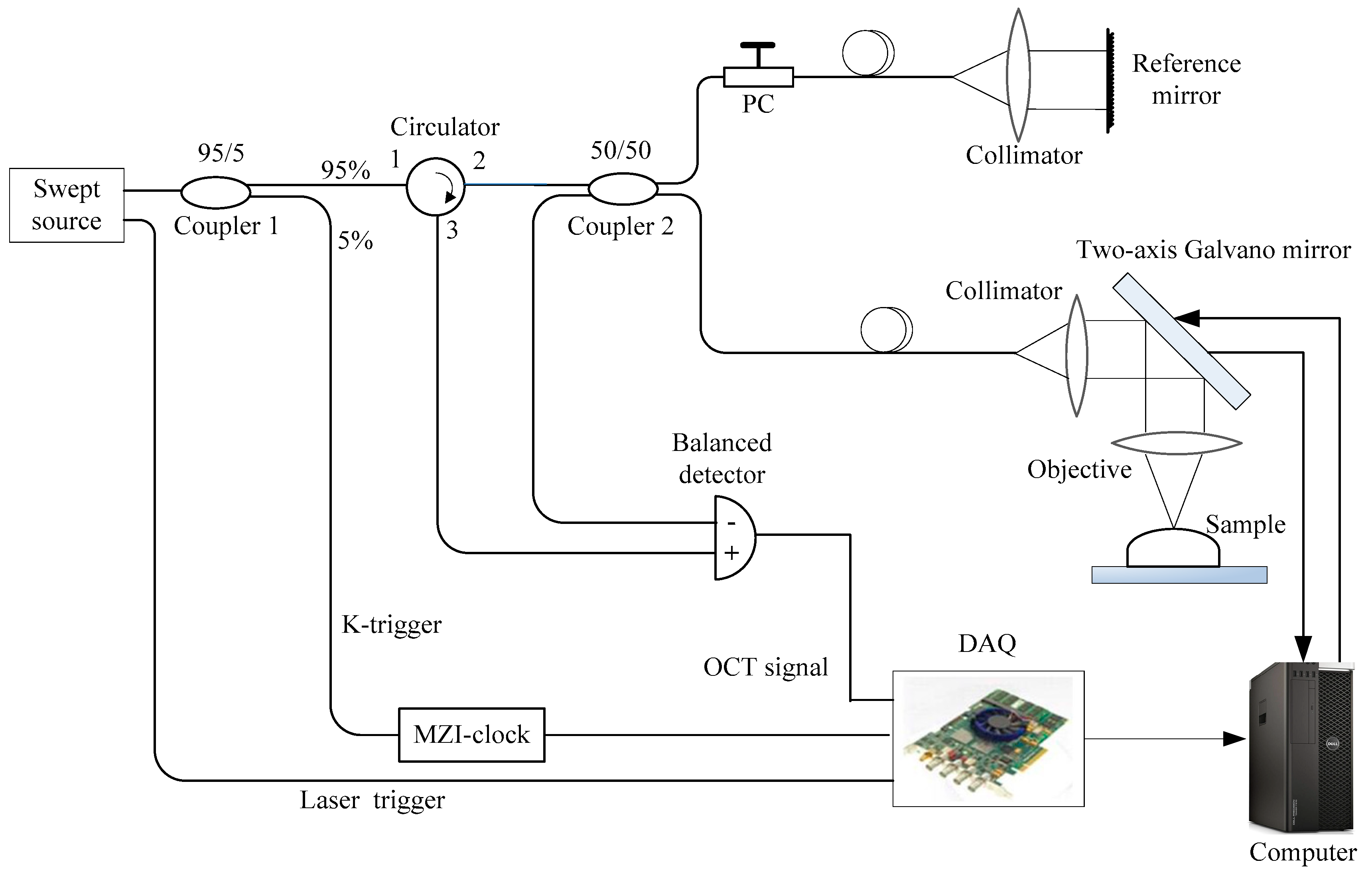
2.2. OCT System
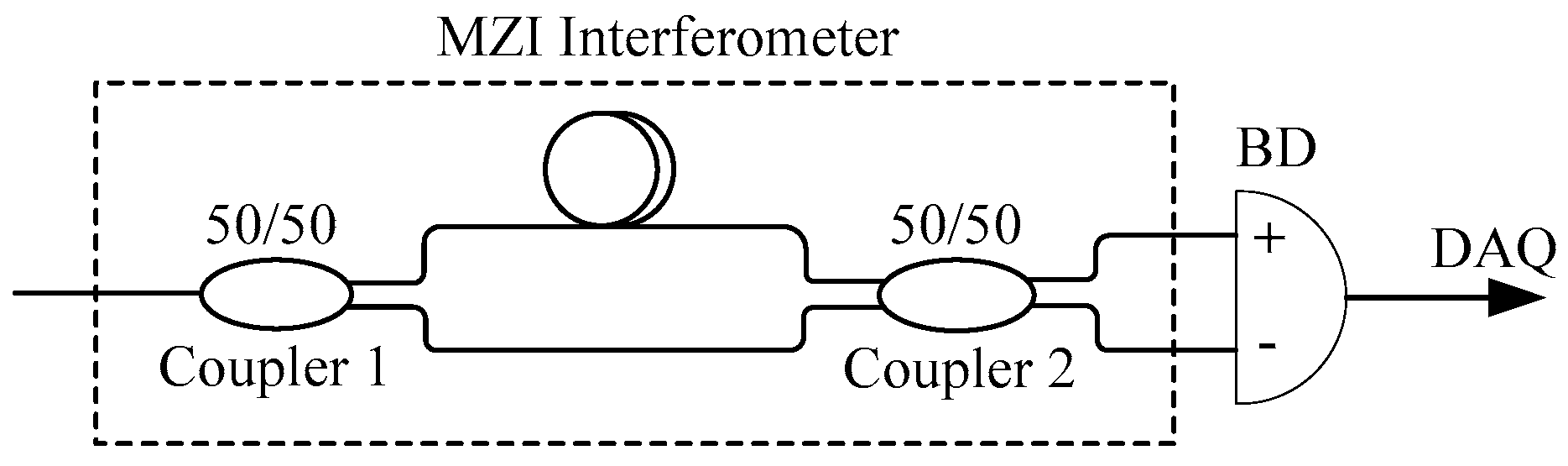
2.3. K-trigger
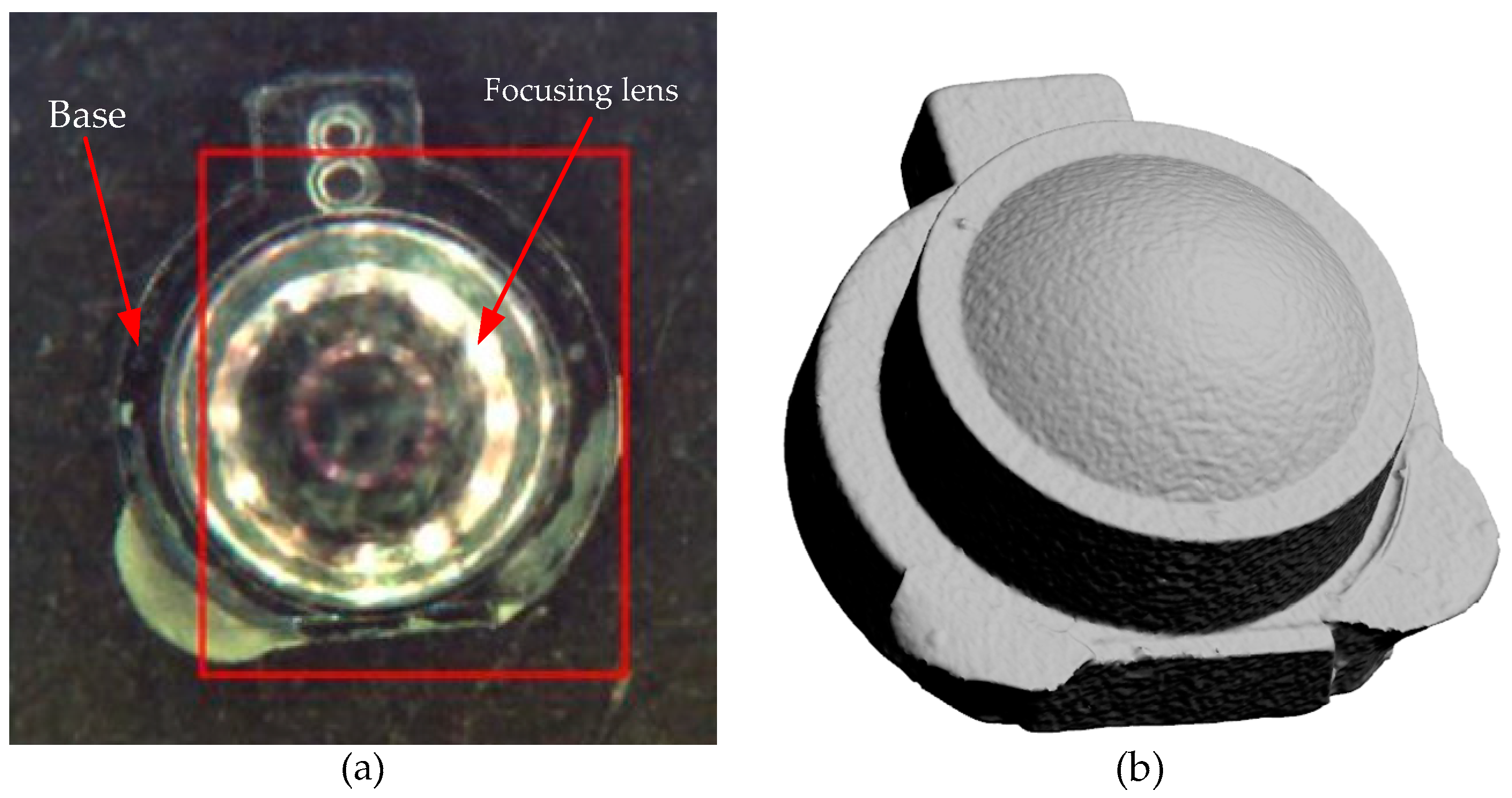
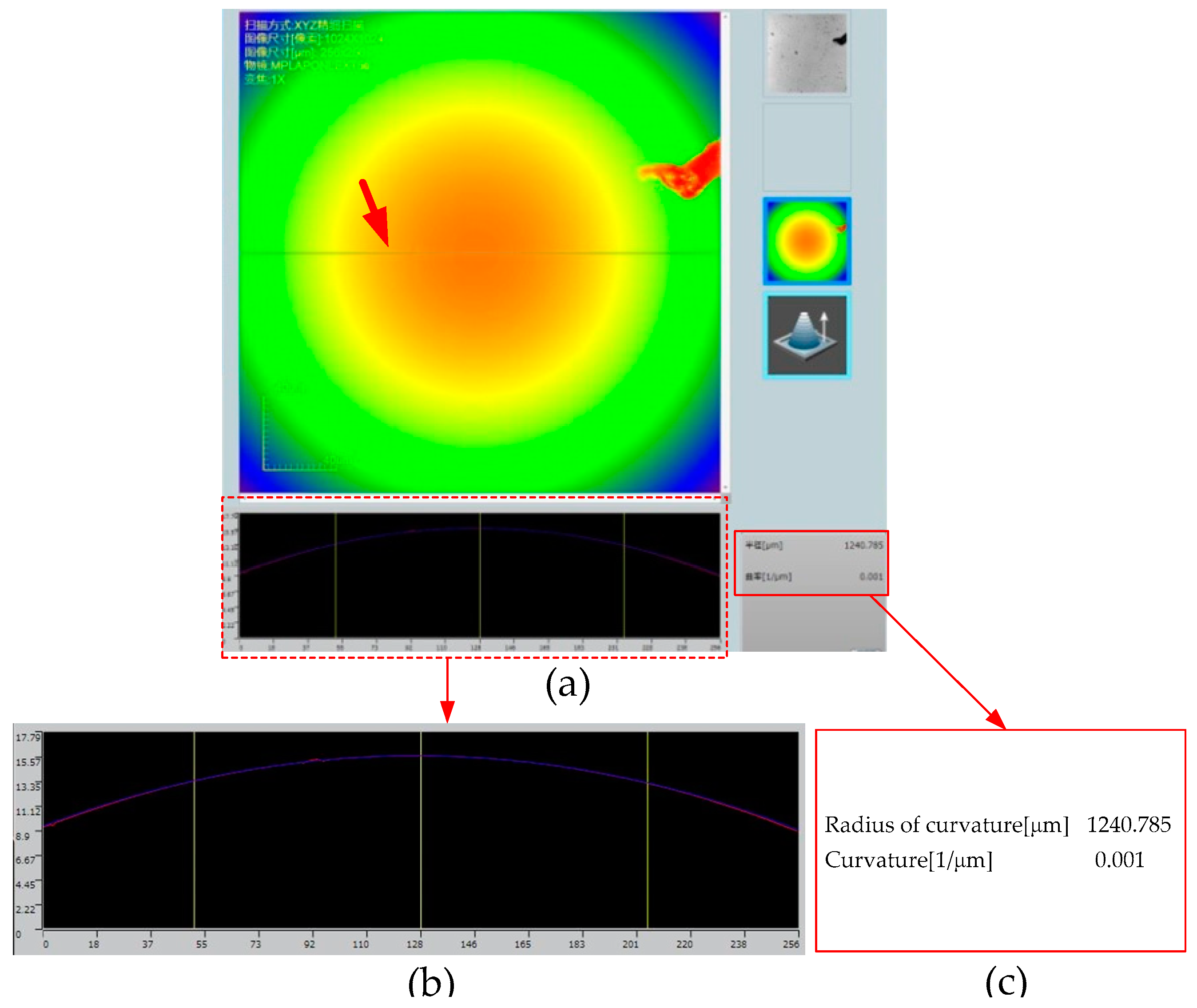
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malacara, D. Optical Shop Testing, 3rd ed.; A John Wiley & Sons, lnc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 820–823. [Google Scholar]
- Spiridonov, M.; Toebaert, D. Simple yet accurate noncontact device for measuring the radius of curvature of a spherical mirror. App. Opt. 2006, 45, 6805–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Chhaniwal, V.K. Measurement of parameters of simple lenses using digital holographic interferometry and a synthetic reference wave. App. Opt. 2007, 46, 2022–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.D.; Qiu, L.R.; Yang, J.M.; Zhao, W.Q. Laser differential confocal radius measurement system. App. Opt. 2012, 51, 6275–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawall, J.R. High resolution determination of radii of curvature using fabry-perot interferometry. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 45302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Qiu, L.R.; Ge, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.Q. Differential confocal self-collimation method for high-accuracy measurements of lens decentration. Opt. Express. 2020, 28, 12058–12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhong, S.C. Non-Contact Measurement of Small-Module Gears Using Optical Coherence Tomography. App. Sci. 2018, 8, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, T.K.; Pullafito, C.A.; et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science. 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cha, Y.M.; Han, J.H. High-Accuracy Retinal Layer Segmentation for Optical Coherence Tomography Using Tracking Kernels Based on Gaussian Mixture Model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Joe, J.; Ma, T.; Liang, S.; Zhang, J.; Dilbahar, M.; Aidan, R.; Sari, M.; Matthew, B.; et al. Integrated IVUS-OCT Imaging for Atherosclerotic Plaque Characterization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 7100108. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, E.D.; Mcleod, R.R. Phase-sensitive swept-source interferometry for absolute ranging with application to measurements of group refractive index and thickness. Opt. Express. 2011, 19, 8117–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sticker, M.; Pircher, M.; Götzinger, E.; Sattmann, H.; Fercher, A.F.; Hitzenberger, C.K. En face imaging of single cell layers by differential phase-contrast optical coherence microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkansky, M.; Iii, D.L.; Pujari, V. Subsurface detection and characterization of Hertzian cracks in Si3N4 balls using optical coherence tomography. NDT&E Int. 2001, 34, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Q.; Ge, X.; Bo, E.; Xie, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, S.; et al. Cellular resolution corneal imaging with extended imaging range. Opt. Express. 2019, 27, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, E.A.; Huang, D.; Lin, C.P.; Puliafito, C.A.; Hee, M.R.; Fujimoto, J.G. High-speed optical coherence domain reflectometry. Opt. Lett. 1992, 17, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, W.; Morgner, U.; Kärtner, F.X.; Pitris, C.; Boppart, S.A.; Li, X.D.; Ippen, E.P.; Fujimoto, J.G. In vivo ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lexer, F.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Fercher, A.F.; Kulhavy, M. Wavelength-tuning interferometry of intraocular distances. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 6548–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choma, M.A.; Sarunic, M.V.; Yang, C.; Izatt, J.A. Sensitivity advantage of swept source and fourier domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express. 2003, 11, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boer, J.F.D.; Cense, B.; Park, B.H.; Pierce, M.C.; Bouma, B.E. Improved signal-to-noise ratio in spectral-domain compared with time-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 2067–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Izatt, J.; Hee, M.; Owen, G.M.; Swanson, E.A.; Fujimoto, J.G. Optical coherence microscopy in scattering media. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 590–592. [Google Scholar]
- Leitgeb, R.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Fercher, A.F. Performance of fourier domain vs. time domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express. 2003, 11, 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Dorrer, C.; Belabas, N.; Likforman, J.P.; Joffre, M. Spectral resolution and sampling issues in fourier transform spectral interferometry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2013, 17, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.D.; Mao, Y.X.; Flueraru, C.; Sherif, S. Optical coherence tomography: Technology and Applications. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7156, 715606. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.M.; Choma, M.A.; Izatt, J.A. Heterodyne swept-source optical coherence tomography for complete complex conjugate ambiguity removal. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 064005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Gille, H.K.; Wu, J.; Yang, C. Ex vivo optical coherence tomography imaging of collector channels with a scanning endoscopic probe. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3921–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, R.; Wojtkowski, M.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Jiang, J.Y.; Cable, A.E. Three-dimensional and c-mode oct imaging with a compact, frequency swept laser source at 1300 nm. Opt. Express. 2006, 13, 10523–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xi, J.F.; Li, H.; Li, J.S.; Li, X.D. Generic real-time uniform K-space sampling method for high-speed swept-source optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express. 2010, 18, 9511–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Ding, Z.H.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.H. Spectral phase based k-domain interpolation for uniform sampling in swept-source optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express. 2011, 19, 18430–18439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
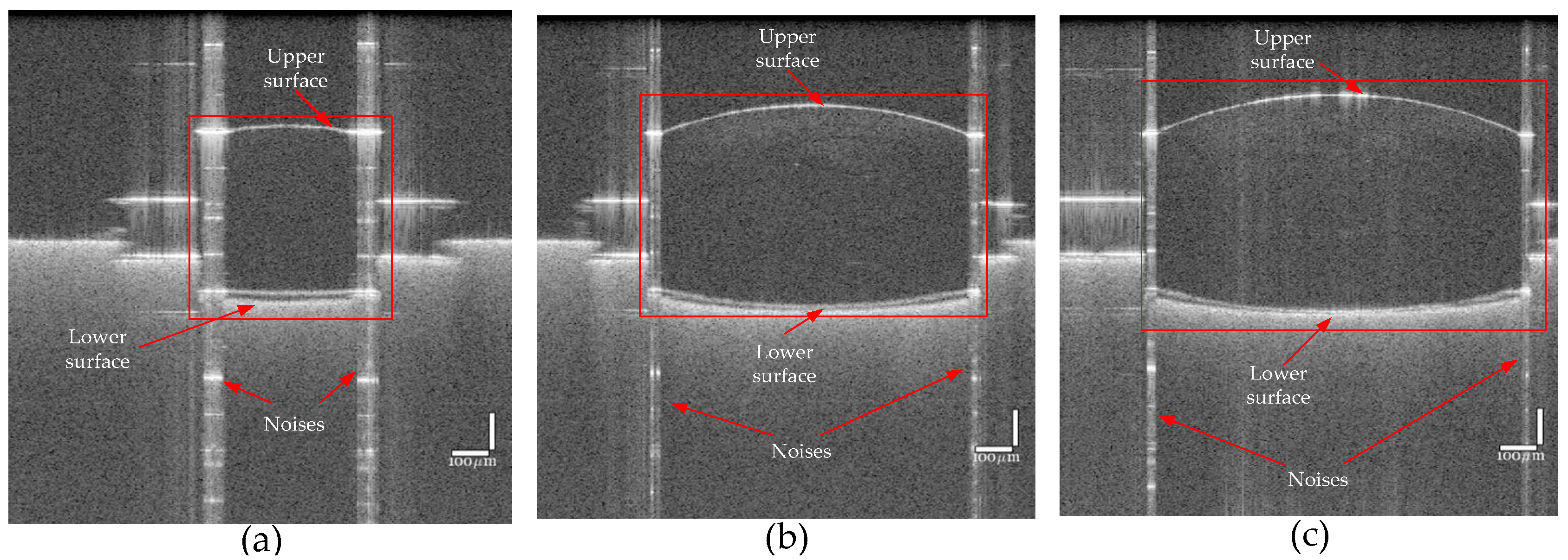
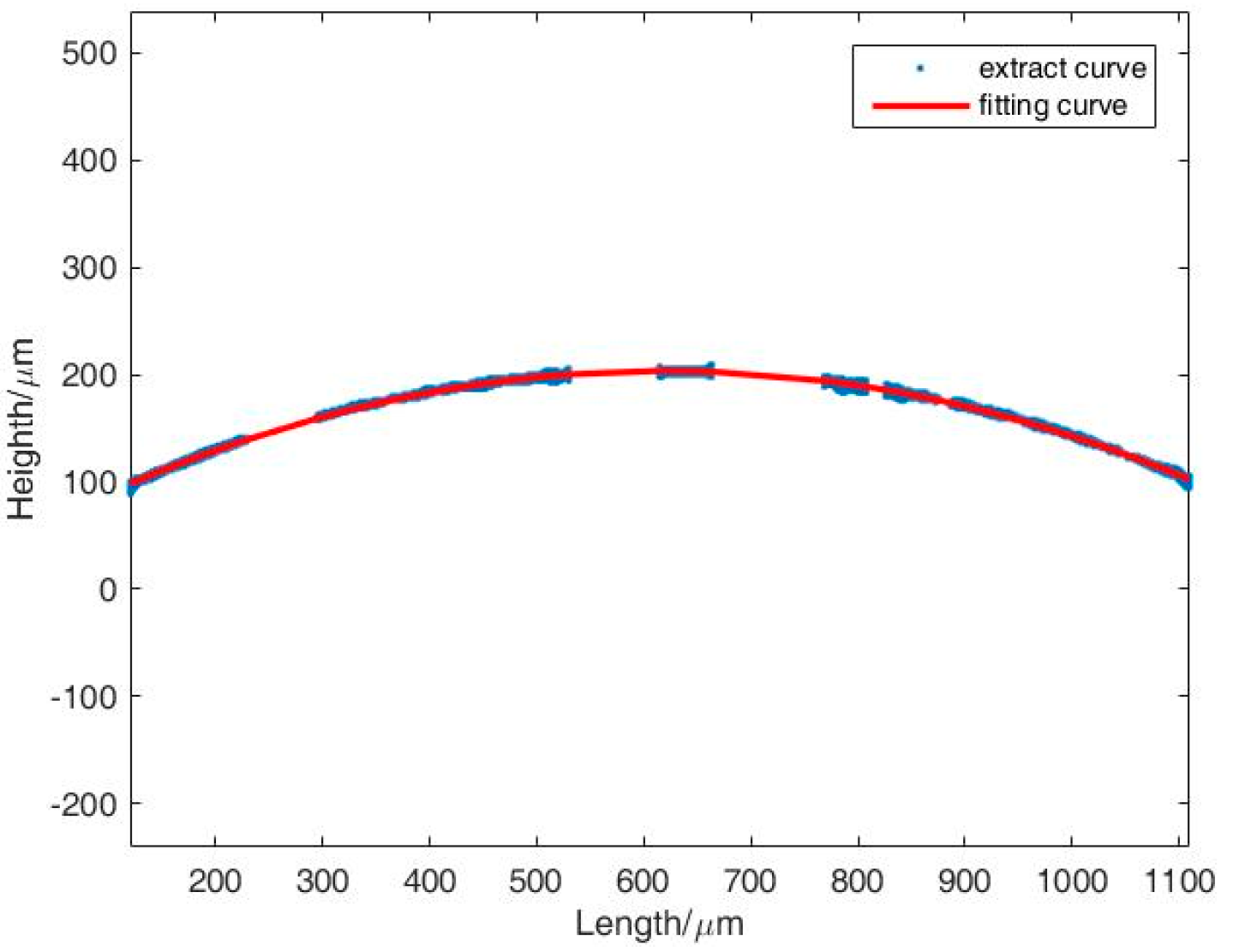
| Different Measurements | Measurement Value (mm) | Relative Error | Mean Value (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.2226 | −2.19% | 1.2479 | 0.0247 |
| 2 | 1.2863 | 2.9% | ||
| 3 | 1.2738 | 1.9% | ||
| 4 | 1.2256 | −1.95% | ||
| 5 | 1.2338 | −1.30% | ||
| 6 | 1.2665 | 1.32% | ||
| 7 | 1.2266 | −1.87% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, P.; Zhao, H.; Qin, Y. Laser Lens Size Measurement Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144936
Jia P, Zhao H, Qin Y. Laser Lens Size Measurement Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144936
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Pingping, Hong Zhao, and Yuwei Qin. 2020. "Laser Lens Size Measurement Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144936
APA StyleJia, P., Zhao, H., & Qin, Y. (2020). Laser Lens Size Measurement Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144936




