Train Speed Estimation from Track Structure Vibration Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Algorithm of Train Speed Estimation
3. Procedures for Train Speed Estimation
3.1. Train Speed Estimation from Acceleration Dynamic Response Signals
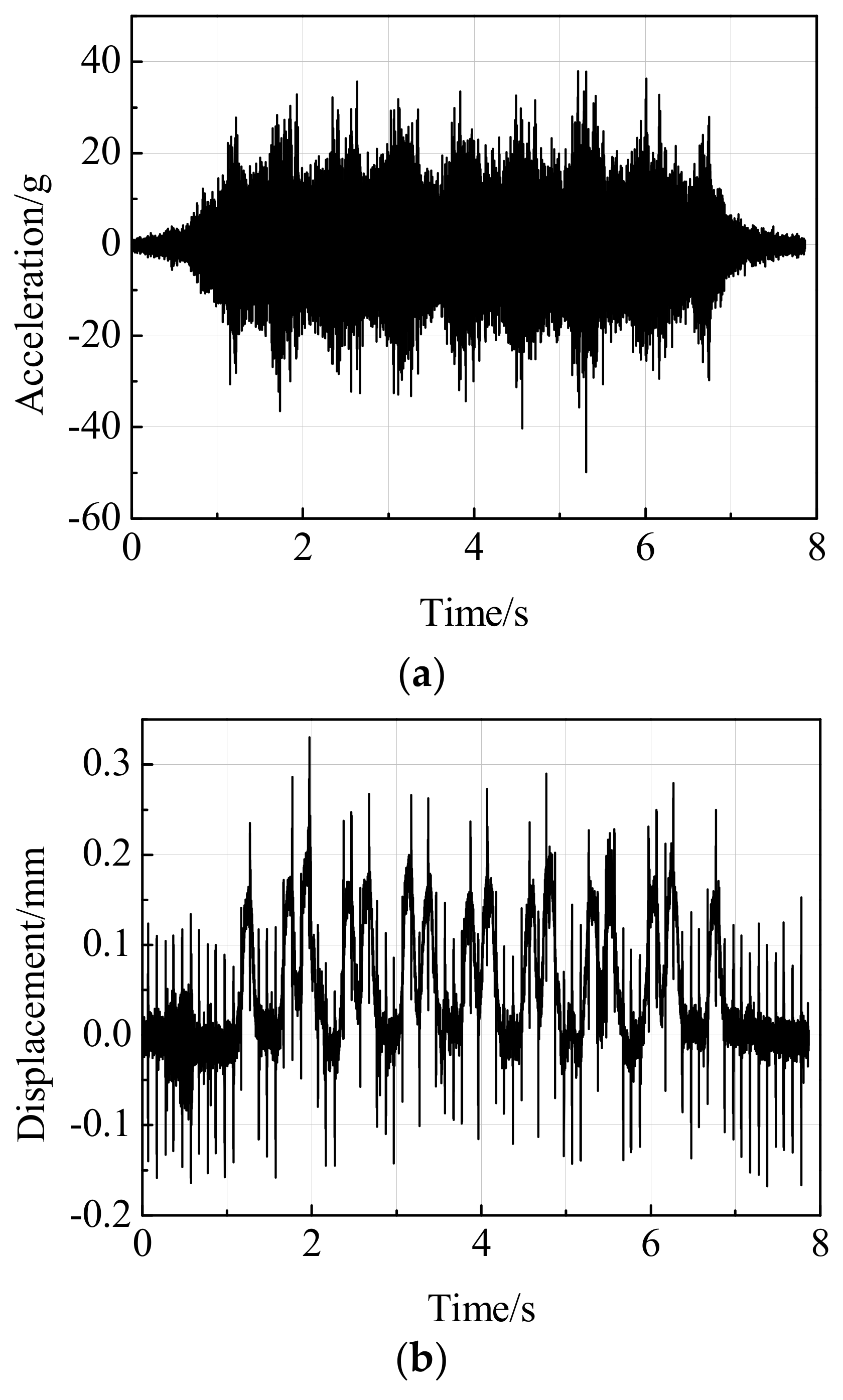
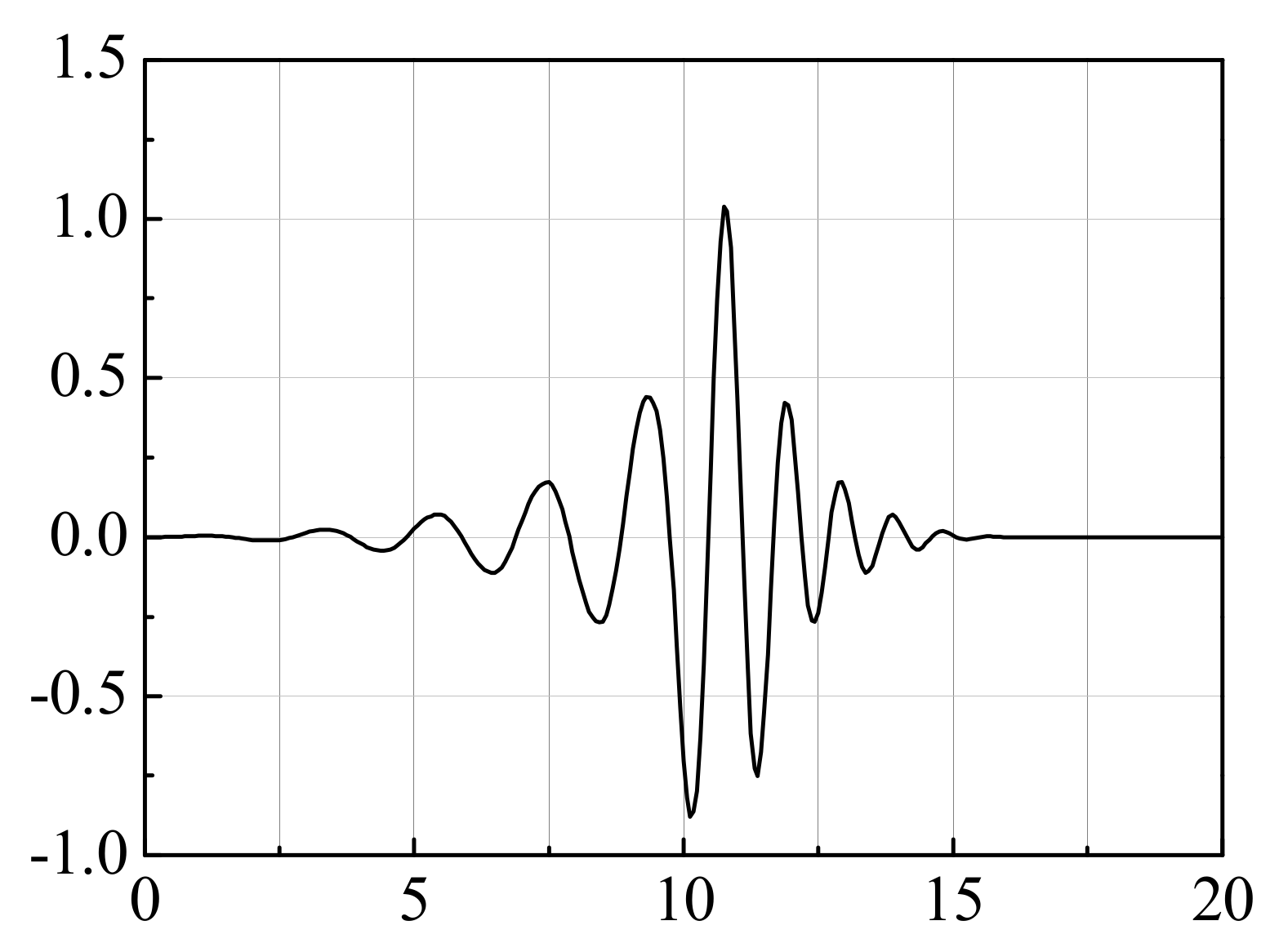
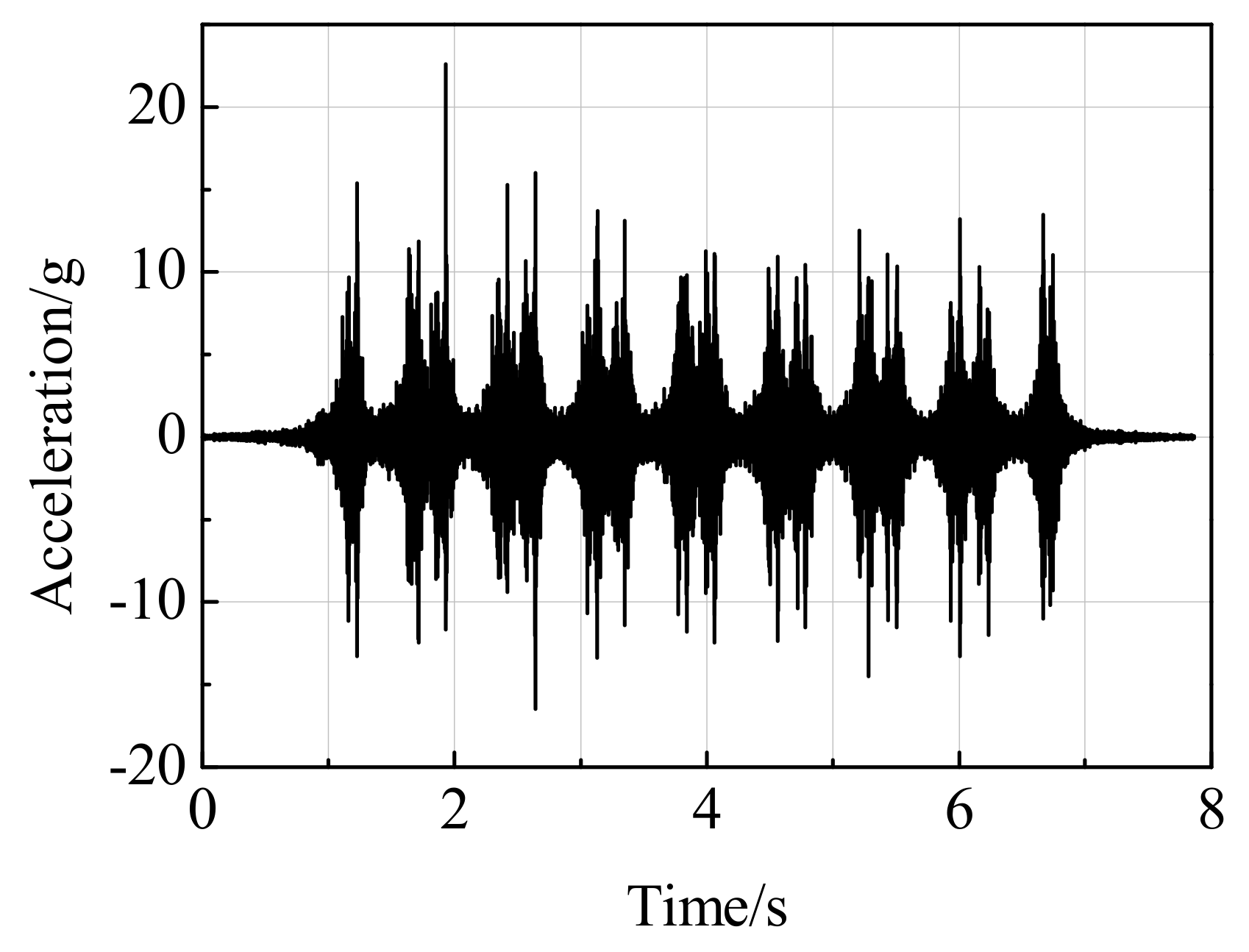
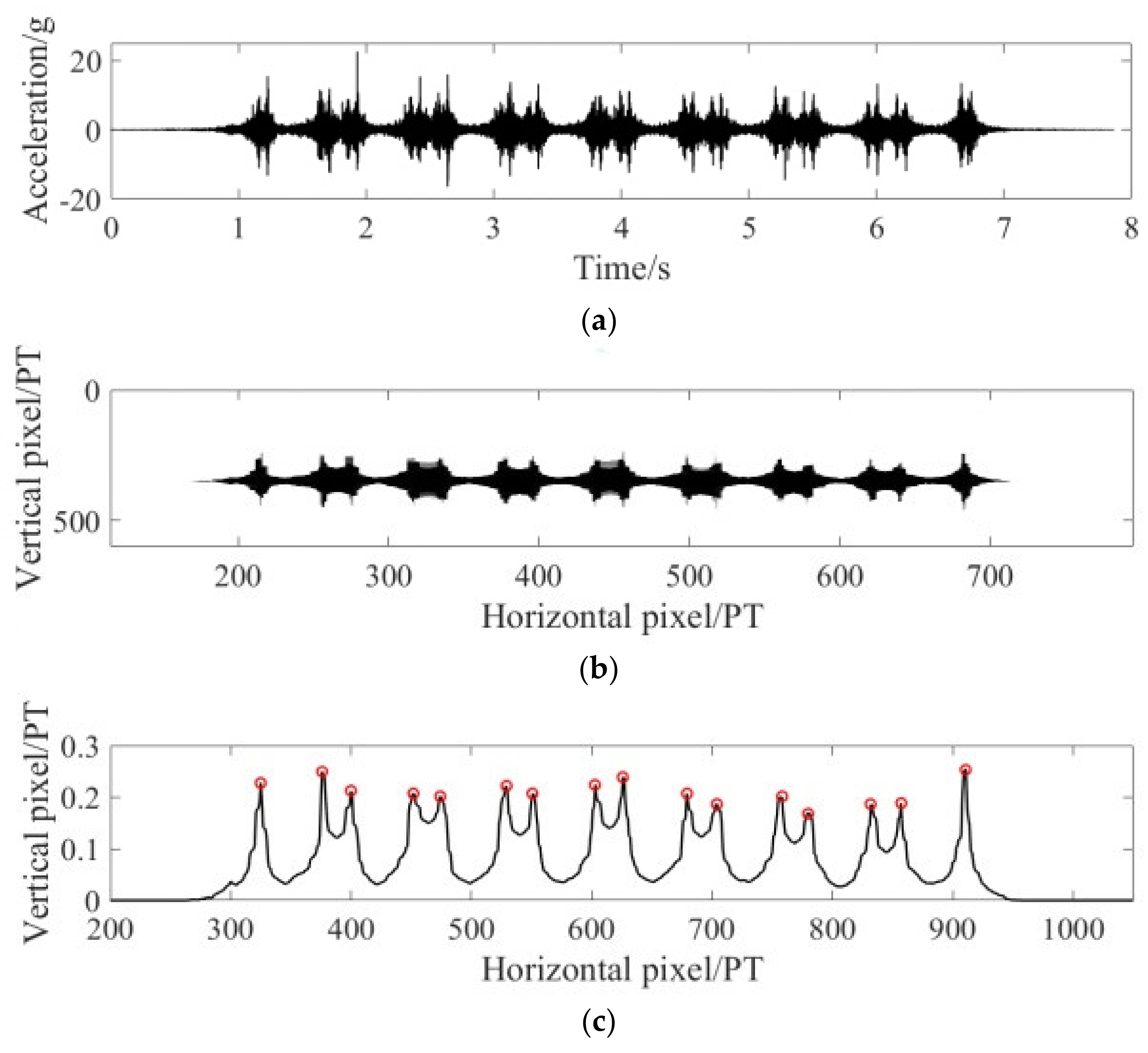
3.1.1. Signal Pretreatment
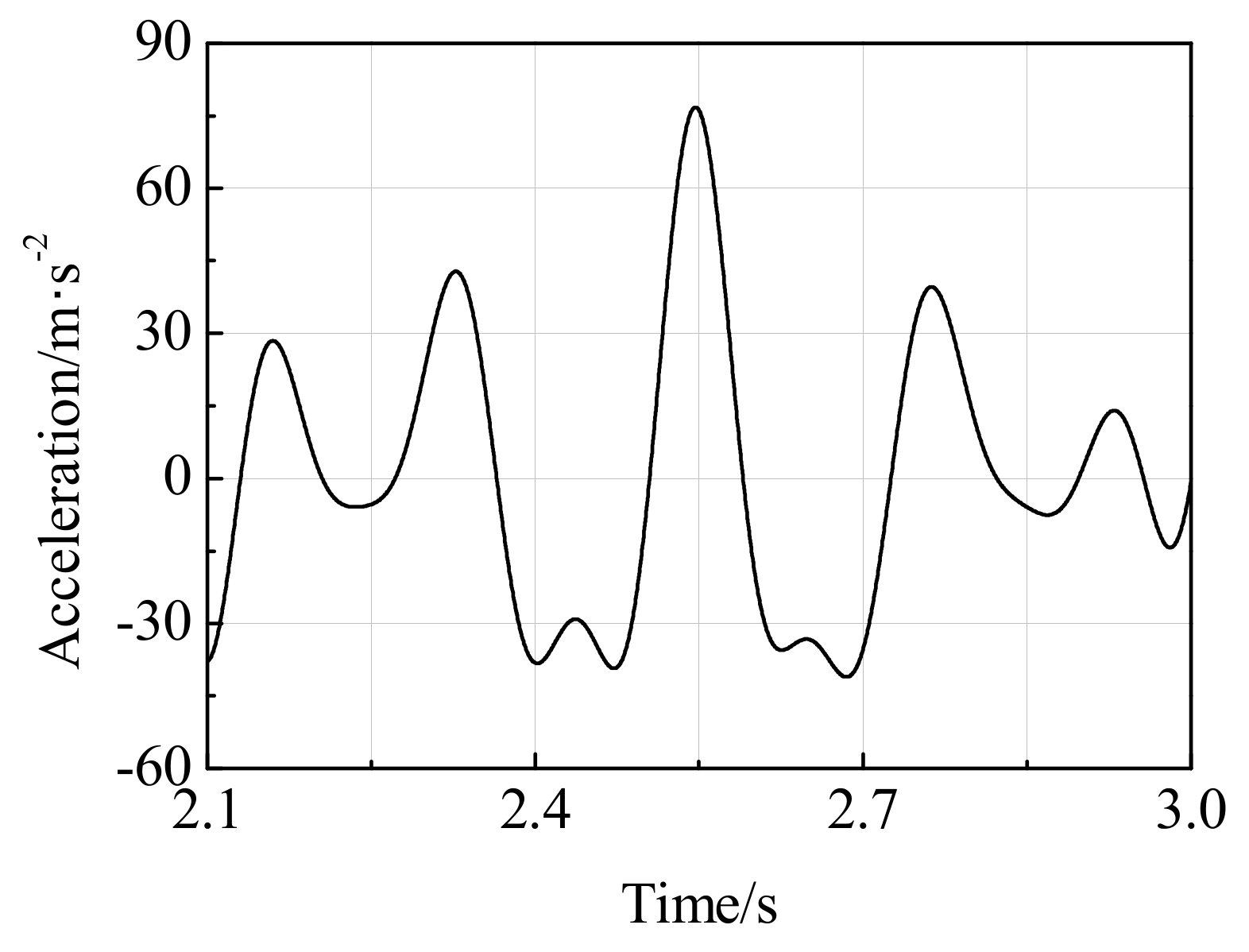
3.1.2. Signal Feature Extraction
3.1.3. Train Speed Calculation
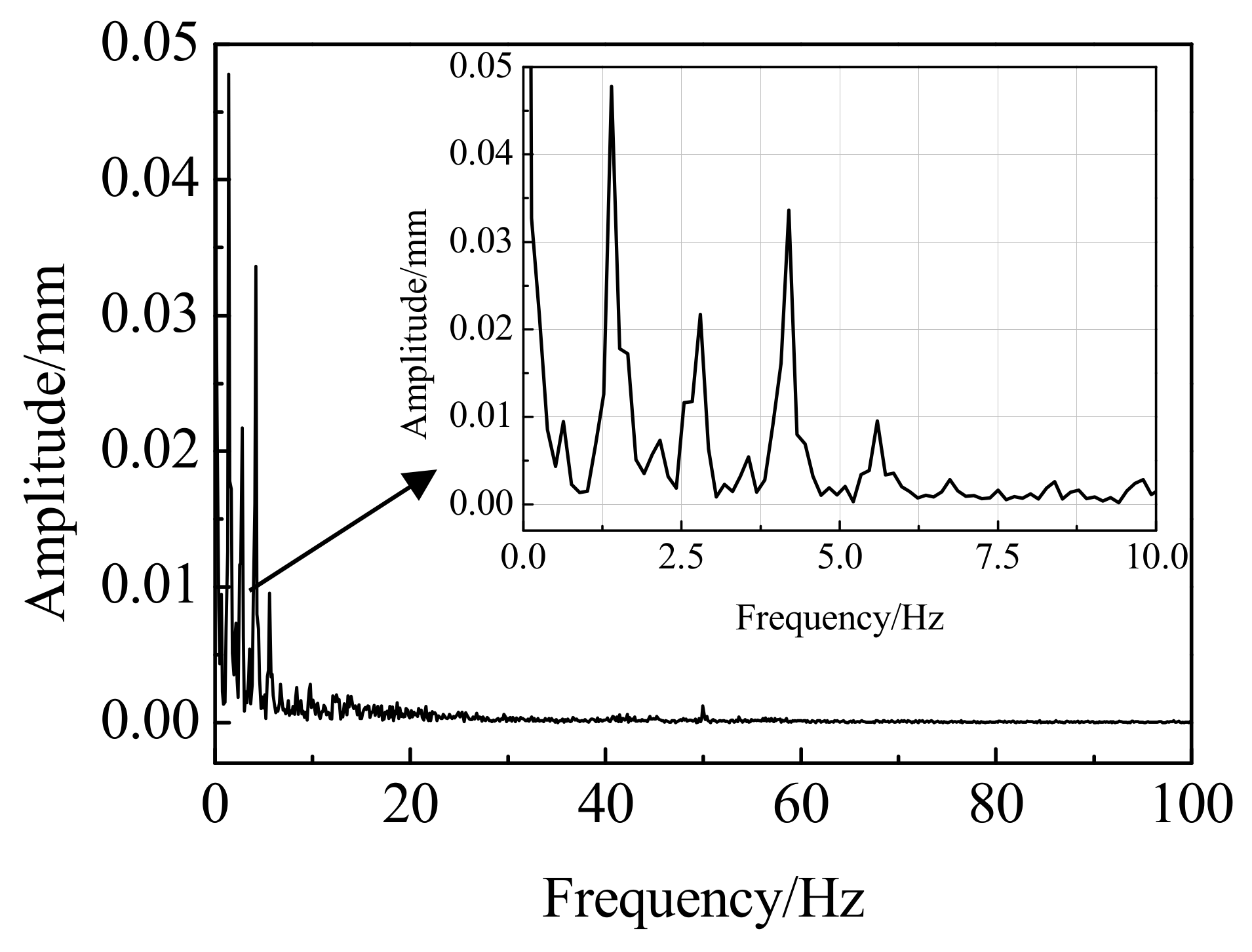
3.2. Train Speed Estimation from Displacement Dynamic Response Signals
4. Verification of the Train Speed Estimation Method
4.1. Test Overview
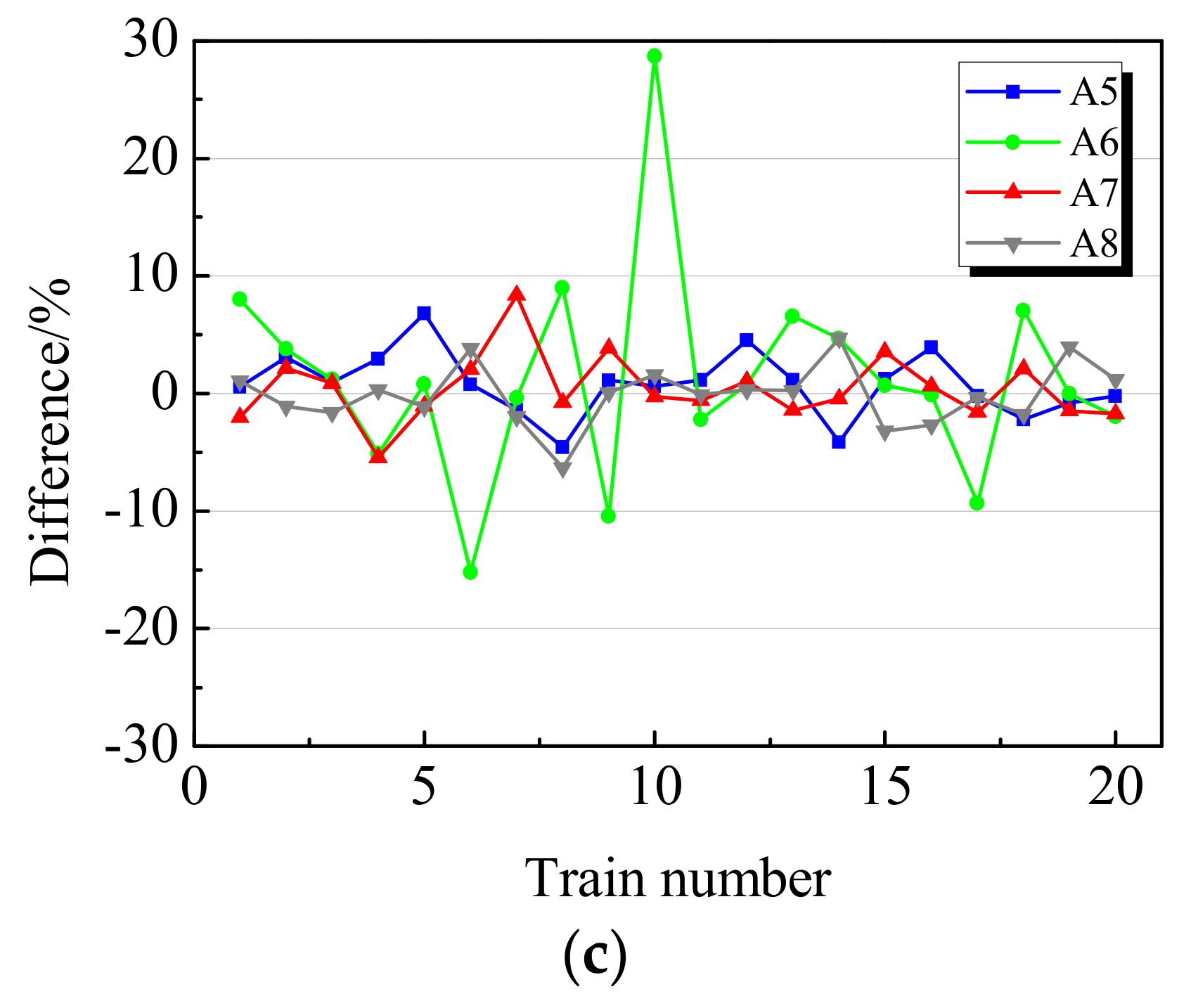
4.2. Train Speed Estimation Results
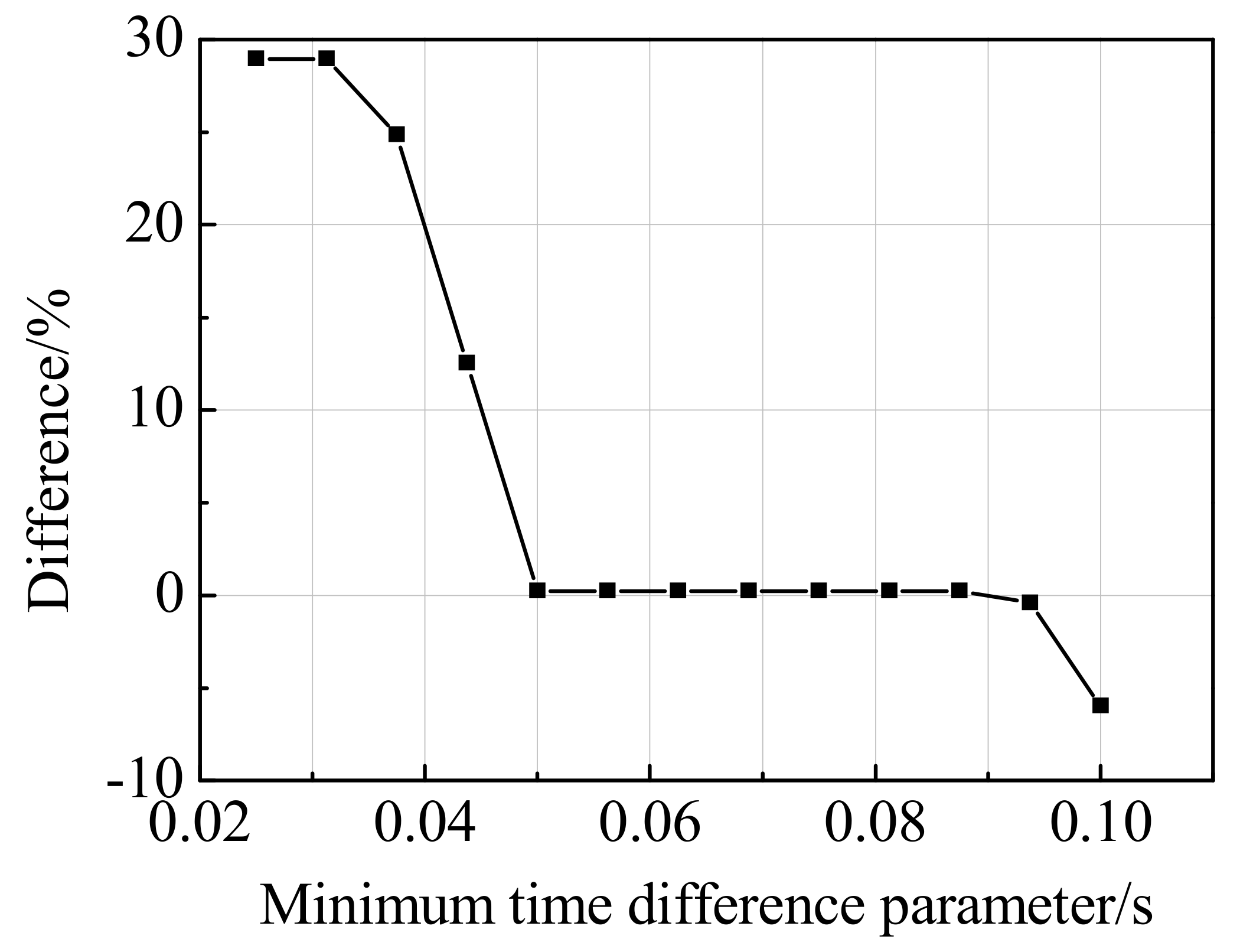
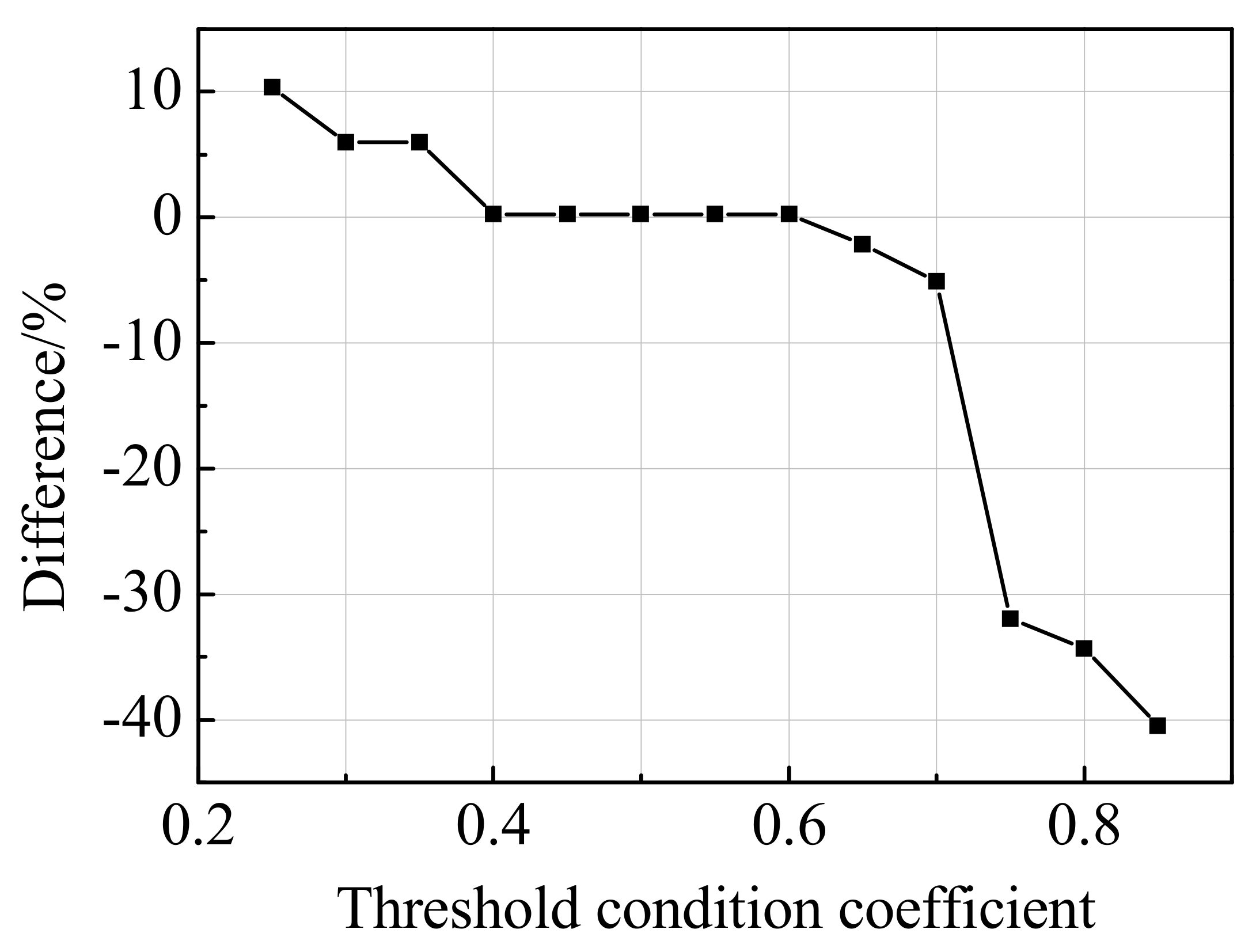
4.3. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Wei, T.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Gildas, M.A.; Zhao, L.; Guo, W. Experimental Study of the Influence of Extremely Repeated Thermal Loading on a Ballastless Slab Track-Bridge Structure. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, A.; Costa, P.A.; Calcada, R. A new strategy to estimate static loads for the dynamic weighing in motion of railway vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2019, 234, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, F.; Gautier, P.E.; Letourneaux, F. Noise sources for high speed trains: A review of results in the TGV case. In Noise and Vibration Mitigation for Rail Transportation Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kouroussis, G.; Connolly, D.; Verlinden, O. Railway-induced ground vibrations—A review of vehicle effects. Int. J. Rail Transp. 2014, 2, 69–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auersch, L. Theoretical and Experimental Excitation Force Spectra for Railway-Induced Ground Vibration: Vehicle-Track-Soil Interaction, Irregularities and Soil Measurements. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2010, 48, 235–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, G. Fatigue evaluation of steel bridge details integrating multi-scale dynamic analysis of coupled 0train-track-bridge system and fracture mechanics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, E.; Torralba, A.; Franquelo, L.G. ASIC implementation of a digital tachometer with high precision in a wide speed range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, G.; Vu, T.; Varshavsky, A.; Gruteser, M.; Martin, R.P.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Vehicular speed estimation using received signal strength from mobile phones. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 26–29 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, D.; Kouroussis, G.; Woodward, P.K.; Costa, P.A.; Verlinden, O.; Forde, M.C. Field testing and analysis of high speed rail vibrations. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2014, 67, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, M.; Hensel, S.; Strau, T. Eddy current sensor based velocity and distance estimation in rail vehicles. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2015, 9, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, B.; Ye, S. Train speed measurement system based on the scanning laser radar. China Railw. Sci. 2009, 30, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Auersch, L. Ground vibration due to railway traffic-the calculation of the effects of moving static loads and their experimental verification. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 293, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombaert, G.; Degrande, G. Ground-borne vibration due to static and dynamic axle loads of InterCity and high-speed trains. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 319, 1036–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Lo, K.F. An automatic procedure for train speed evaluation by the dominant frequency method. Comput. Geotech. 2011, 38, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouroussis, G.; Connolly, D.P.; Laghrouche, O.; Forde, M.C.; Woodward, P.K.; Verlinden, O. Robustness of railway rolling stock speed calculation using ground vibration measurements. In MATEC Web of Conferences; paper no. 20: 07002; EDP Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kouroussis, G.; Connolly, D.P.; Forde, M.C.; Verlinden, O. Train speed calculation using ground vibrations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2015, 229, 466–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, C.B.; Hashmi, M.F.; Bokde, N.D.; Geem, Z.W. Investigations of object detection in images/videos using various deep learning techniques and embedded platforms—A comprehensive review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.H.; Lin, H.T.; Huang, J.Y. Dominant frequencies of train-induced vibrations. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 319, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ling, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F. Dominant frequencies of train-induced vibrations in a seasonally frozen region. Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 2015, 116, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, D.A.; Ponce, J. Computer Vision A Modern Approach, 2nd ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, R.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Projection Metric Learning on Grassmann Manifold with Application to Video based Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vega, J.; Fraile, A.; Alarcon, E.; Hermanns, L. Dynamic response of underpasses for high-speed train lines. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 5125–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuguen, R.T.; Volante, E.J.P.; Causo, A.; Bayot, R.; Peren, G.; Macaraig, R.M.; Libatique, N.J.C.; Tangonan, G.L. Automated fish fry counting and schooling behavior analysis using computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Colloquium on Signal Processing & Its Applications, Malacca, Malaysia, 23–25 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, M.; Chen, M.; Quian, J.; Sun, C.; Du, S. Feature extraction and classification method of multi-pose pests using machine vision. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Zhang, T. A counter method for the image of blood cell. Comput. Appl. Softw. 2000, 17, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Han, M.; Li, C. Parking space and obstacle detection based on a vision sensor and checkerboard grid laser. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Song, R.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, J. Noise and vibration mitigation performance of damping pad under CRTS-III ballastless track in high speed rail viaduct. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 3525–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, P.; Romero, A.; Dominguez, J. Vibrations induced by HST passage on ballast and non-ballast tracks. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 30, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Liu, W.; Degrande, G.; Lombaert, G.; Liu, W. Prediction of vibrations induced by underground railway traffic in Beijing. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 310, 608–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, D.; Sakai, H.; Aikawa, A.; Tsuzuki, S.; Sakaguchi, H. Novel discrete element modeling coupled with finite element method for investigating ballasted railway track dynamics. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Qian, Y.; Huang, H.; Tutumluer, E. An integrated approach to dynamic analysis of railroad track transitions behavior. Transp. Geotech. 2014, 1, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Method | Test Location | Advantage | Shortcoming | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tachometers | On-board | No additional measurement | Using inside the train | ~5% |
| GPS | On-board | Cheap | Using inside the train | 5–10% |
| Optical sensors | Ground | Very accurate | Affected by weather especially rain and snow | <1% |
| Wheel counters | Ground | Very accurate | Stationary application | <1% |
| Eddy current sensors | Ground | Accurate | Affecting by rail structure state | ~1% |
| Laser radar system | Ground | Easy to use | Accuracy dependingon the position | 1–5% |
| Sensor | Location | Content | The Track Curve | Structure State |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Slab | Displacement | Inside | Healthy |
| D2 | Slab | Displacement | Inside | Layer gap |
| D3 | Slab | Displacement | Outside | Healthy |
| D4 | Slab | Displacement | Outside | Layer gap |
| A1 | Rail | Acceleration | Inside | Healthy |
| A2 | Rail | Acceleration | Inside | Layer gap |
| A3 | Rail | Acceleration | Outside | Healthy |
| A4 | Rail | Acceleration | Outside | Layer gap |
| A5 | Slab | Acceleration | Inside | Healthy |
| A6 | Slab | Acceleration | Inside | Layer gap |
| A7 | Slab | Acceleration | Outside | Healthy |
| A8 | Slab | Acceleration | Outside | Layer gap |
| Sensor | Absolute Average Differences/% | Sensor | Absolute Average Differences/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0.64 | A3 | 1.49 |
| D2 | 0.59 | A4 | 1.28 |
| D3 | 0.59 | A5 | 2.12 |
| D4 | 0.62 | A6 | 5.81 |
| A1 | 1.53 | A7 | 2.08 |
| A2 | 1.26 | A8 | 1.87 |
| Train Number | Sensor | Threshold Condition Coefficient | Minimum Time Difference Parameter/s | Estimated Train Speed/km·h−1 | Difference/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | A1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 124.7 | 0.1 |
| 9 | A1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 255.4 | 105.0 |
| 9 | A1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 125.4 | 0.6 |
| 9 | A1 | 0.3 | 0.05 | 149.0 | 19.6 |
| 9 | A1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 125.4 | 0.6 |
| 20 | A1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 228.8 | 0.7 |
| 20 | A1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 235.0 | 3.4 |
| 20 | A1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 228.8 | 0.7 |
| 20 | A1 | 0.3 | 0.05 | 228.3 | 0.5 |
| 20 | A1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 111.7 | −50.8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Han, B. Train Speed Estimation from Track Structure Vibration Measurements. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144742
Wang X, Shi X, Wang J, Yu X, Han B. Train Speed Estimation from Track Structure Vibration Measurements. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144742
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinyue, Xianfeng Shi, Jialiang Wang, Xun Yu, and Baoguo Han. 2020. "Train Speed Estimation from Track Structure Vibration Measurements" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144742
APA StyleWang, X., Shi, X., Wang, J., Yu, X., & Han, B. (2020). Train Speed Estimation from Track Structure Vibration Measurements. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144742







