Ion Current Rectification in Extra-Long Nanofunnels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
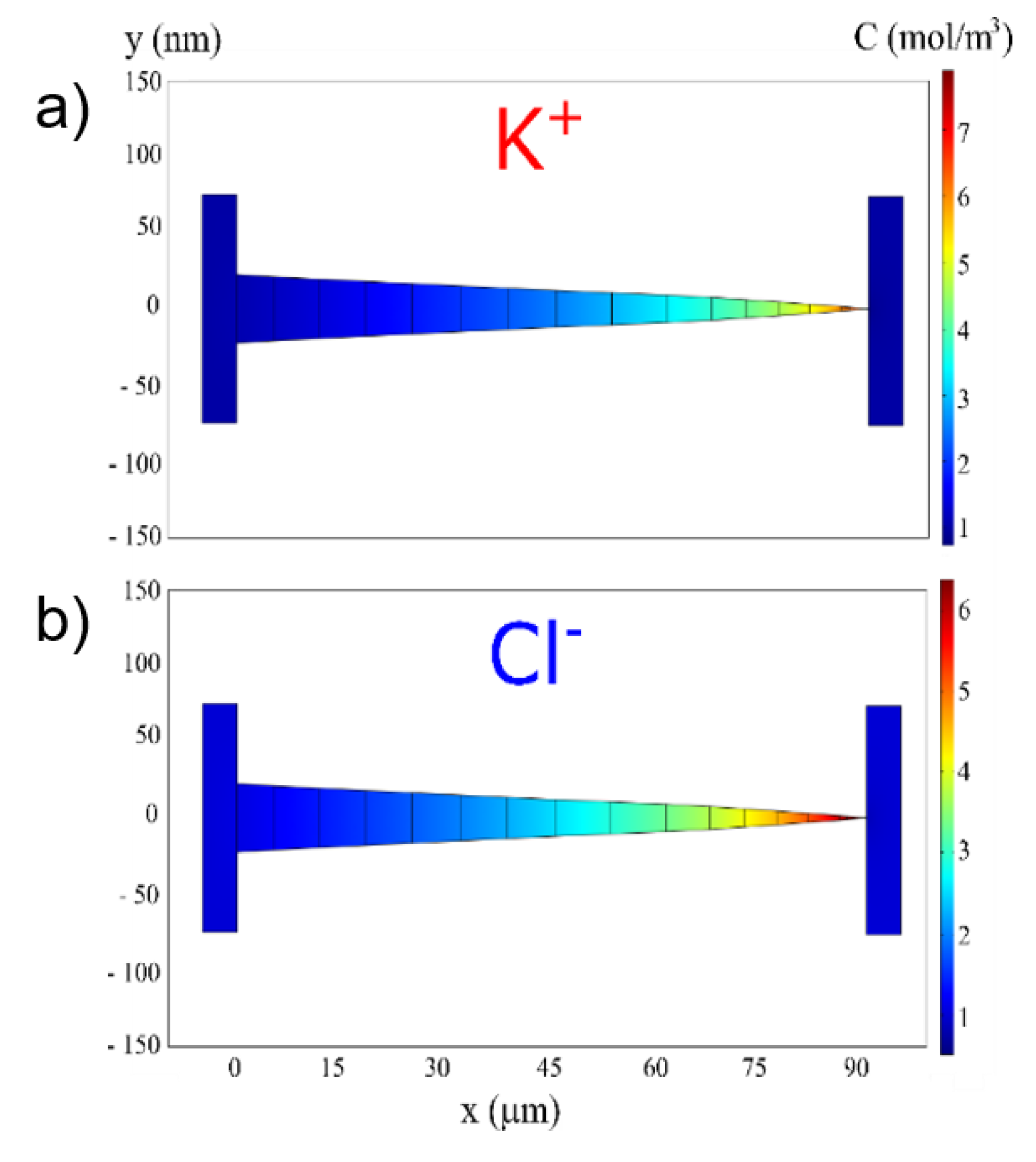
2.1. Funnel and Nanochannel Geometry
2.2. Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
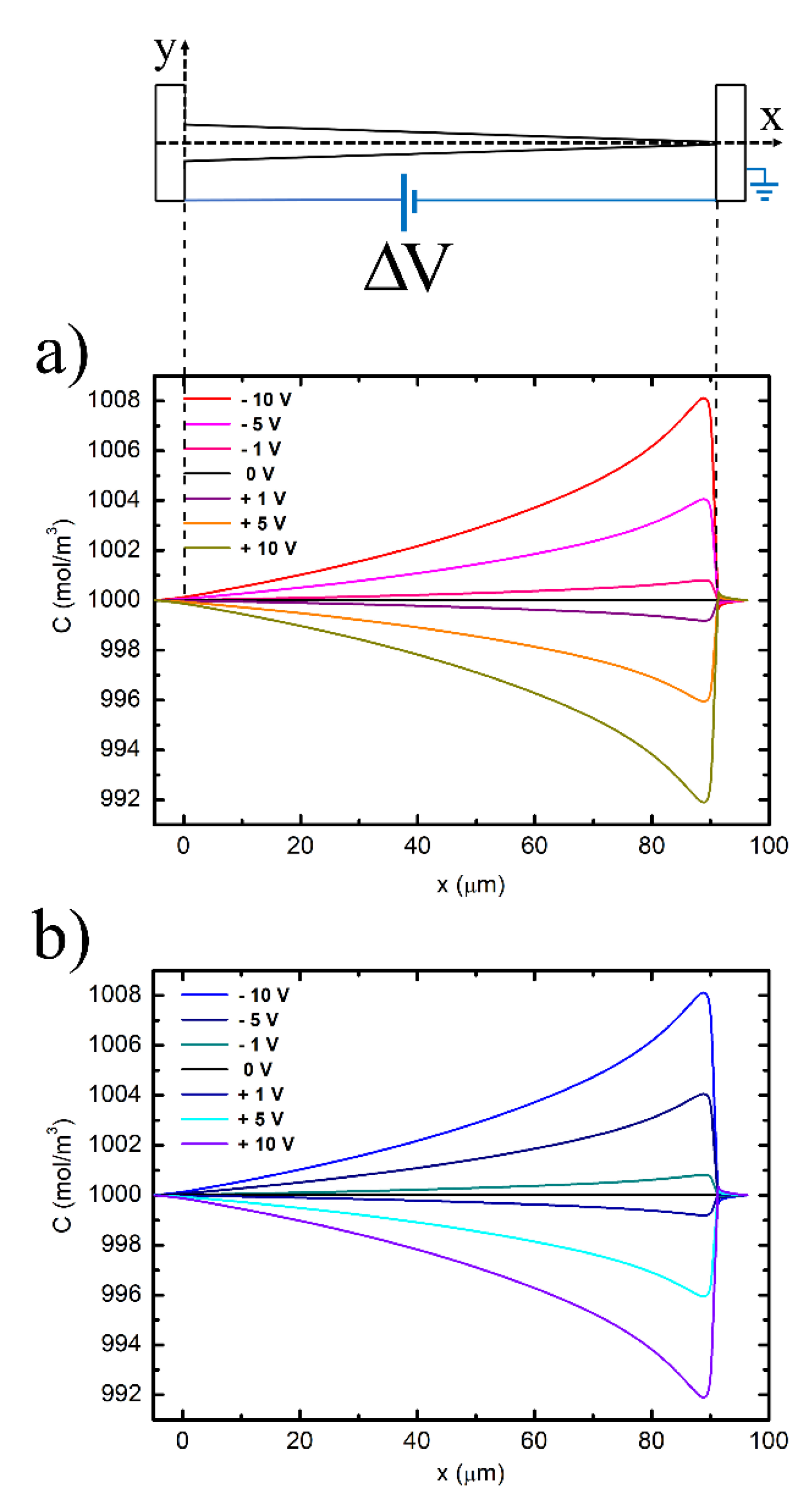
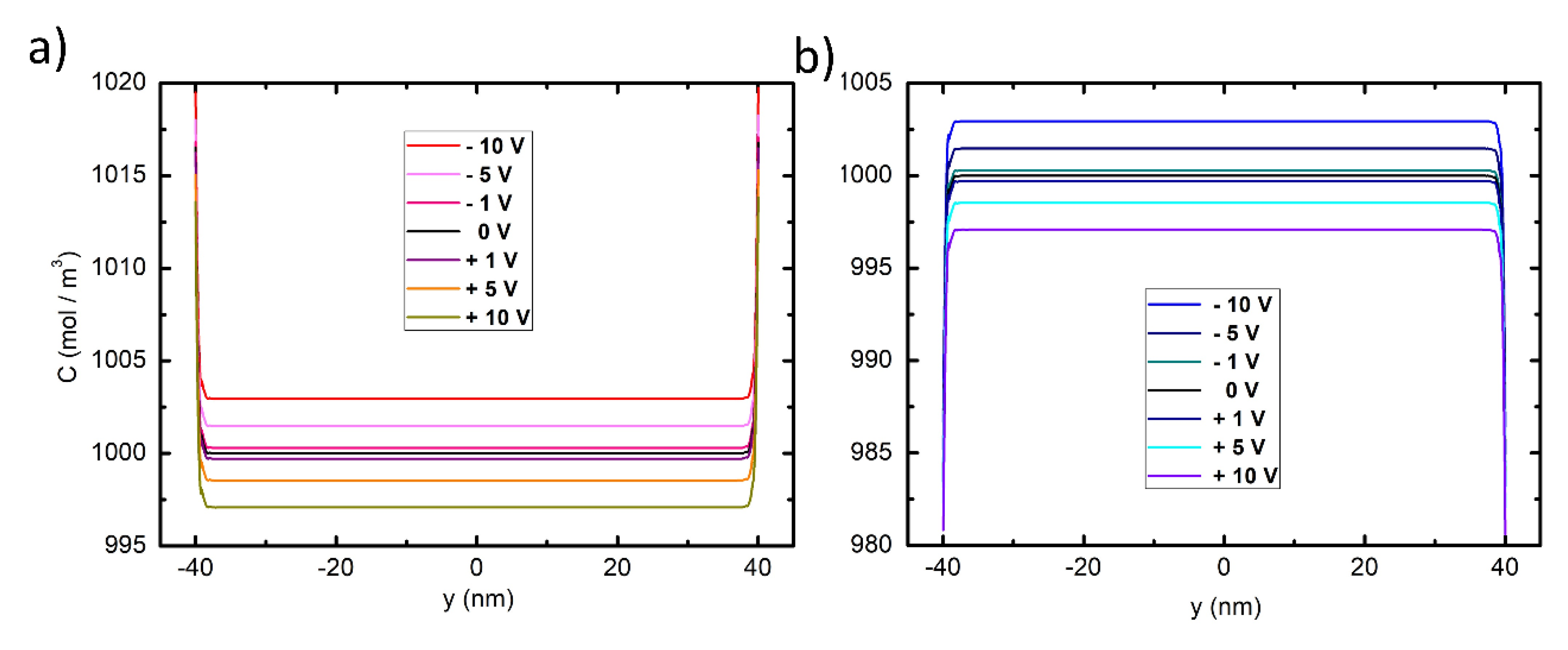
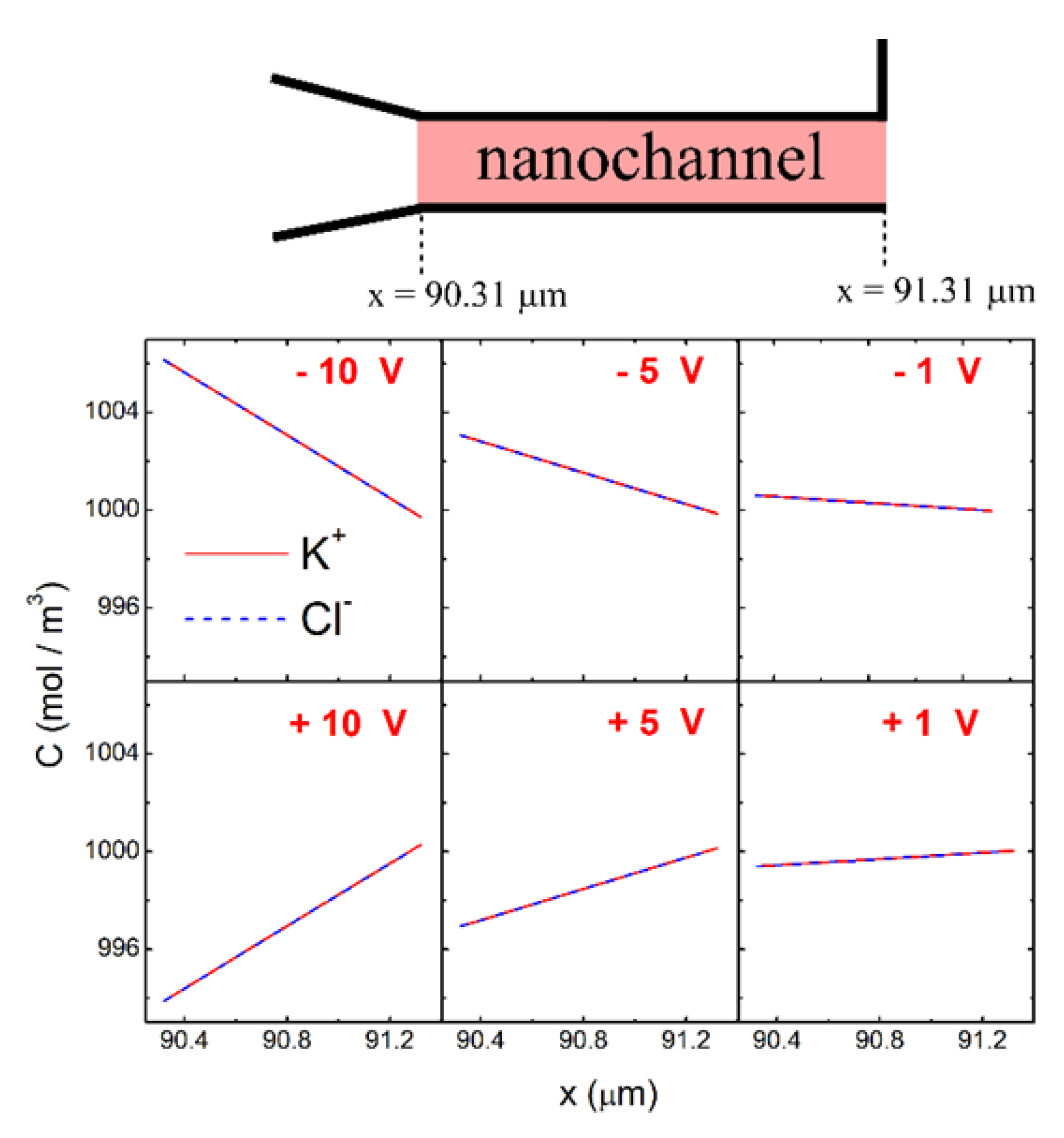
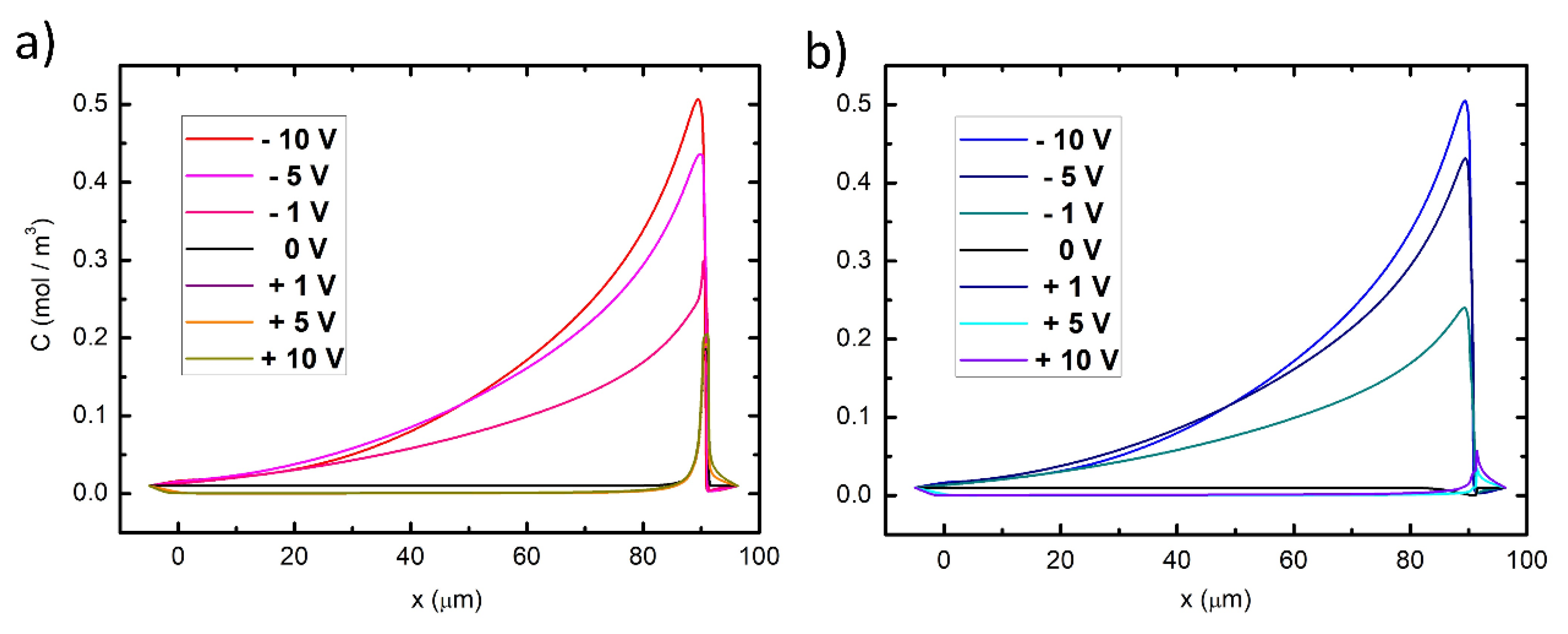
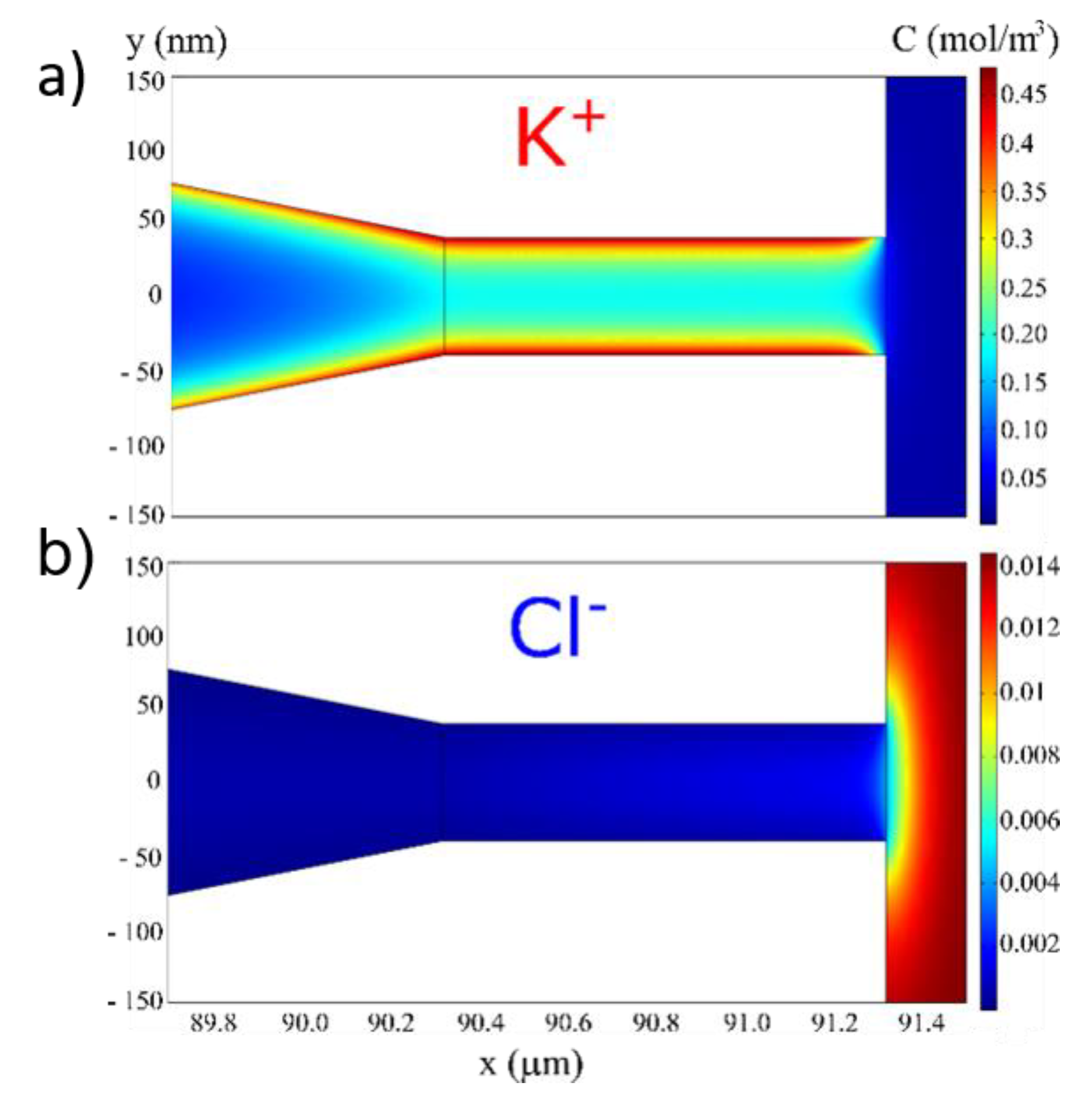
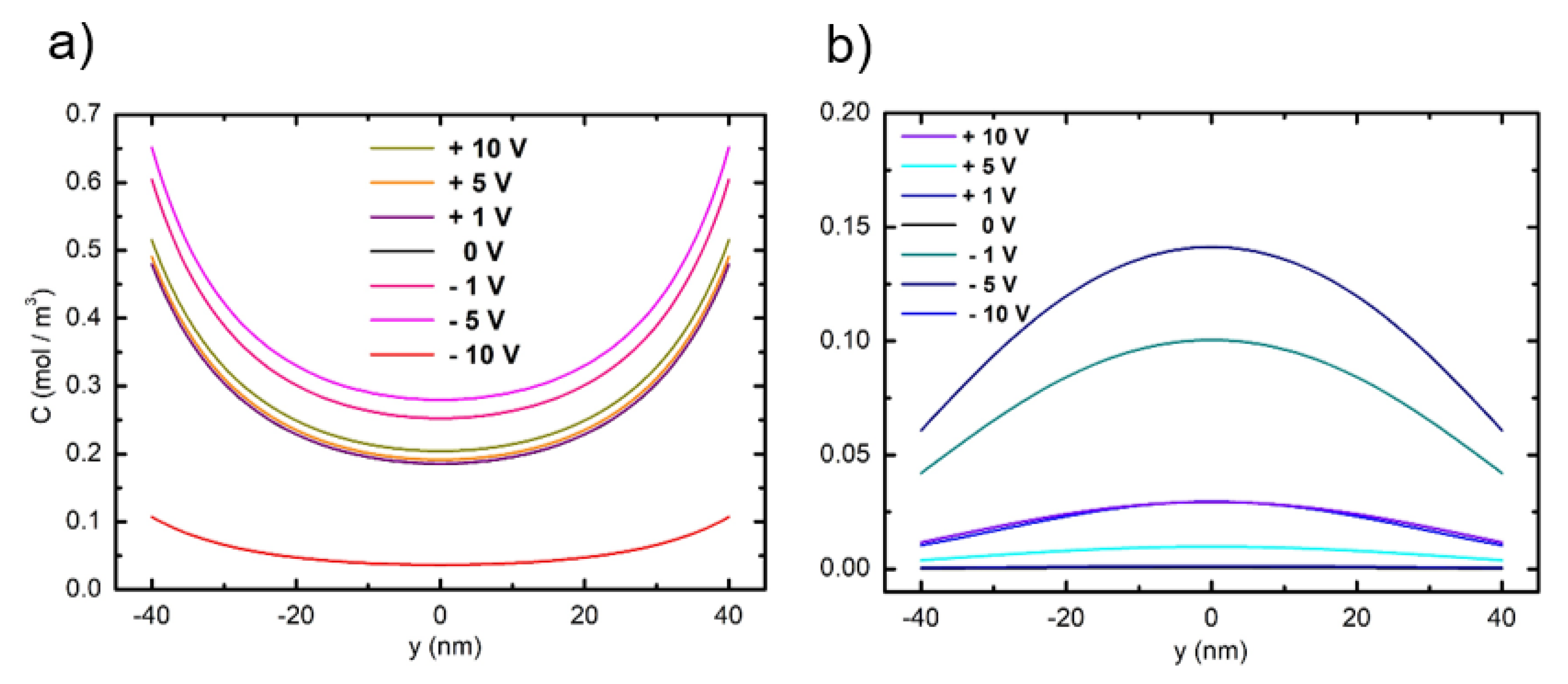
3.1. Accumulation
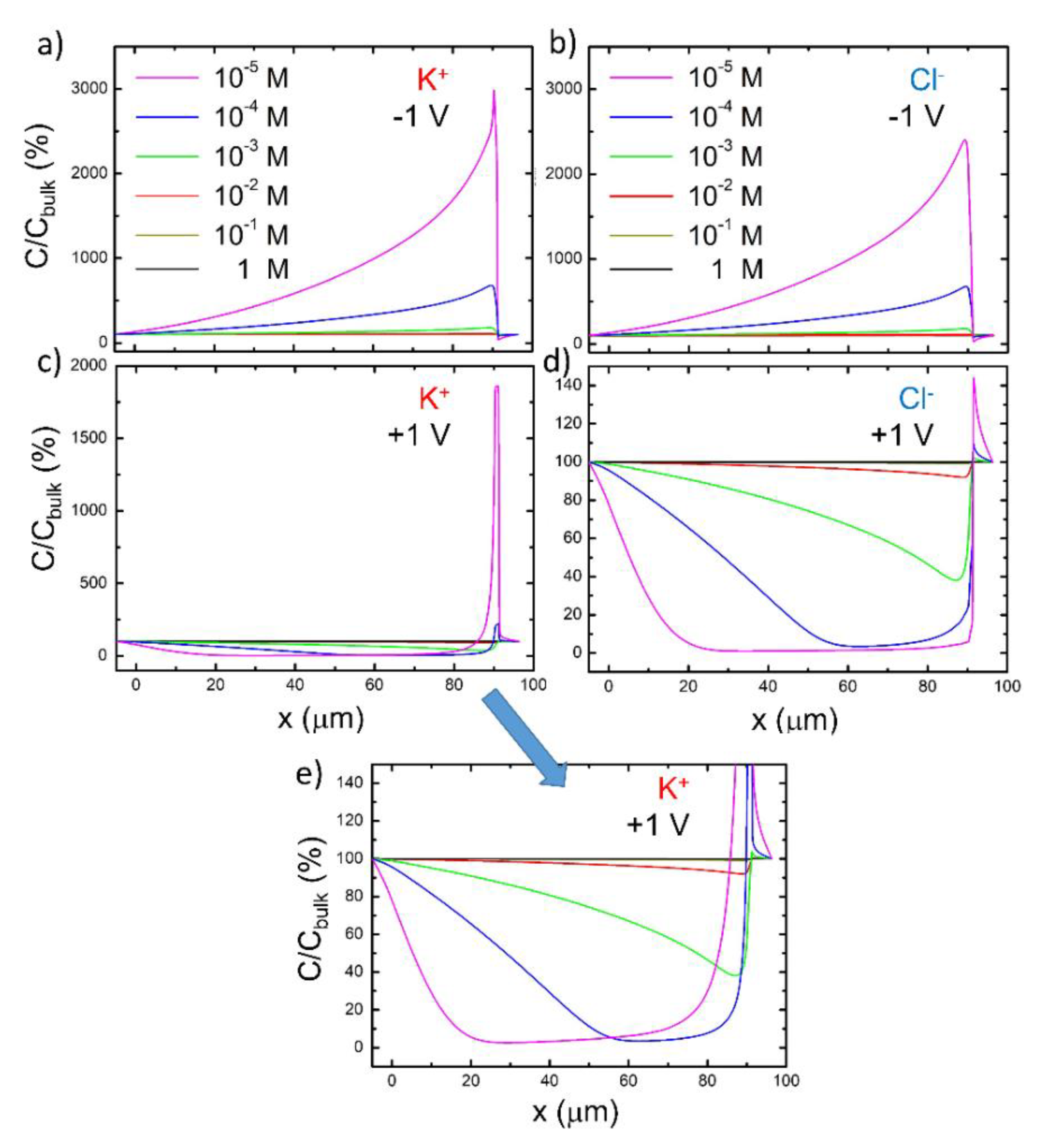
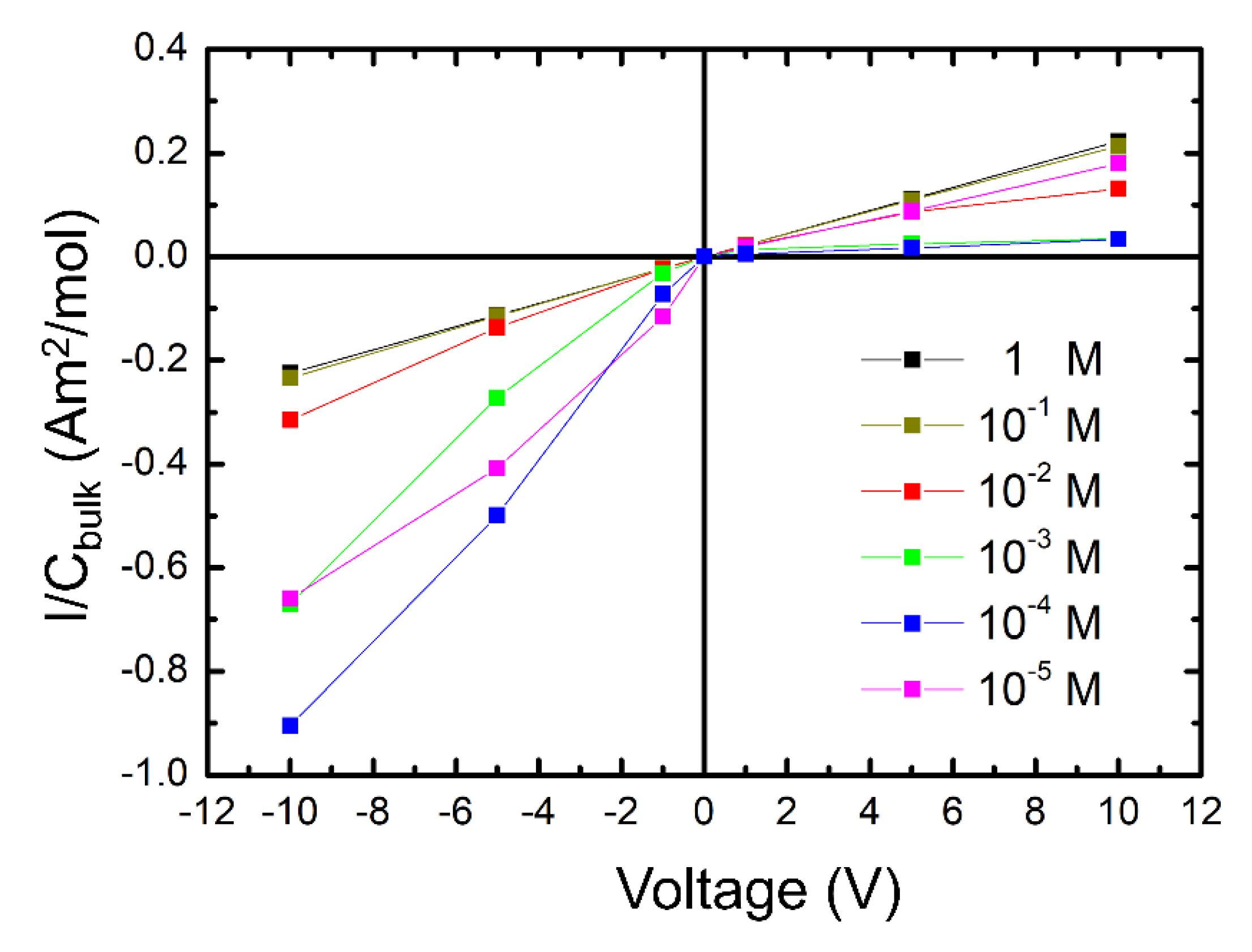
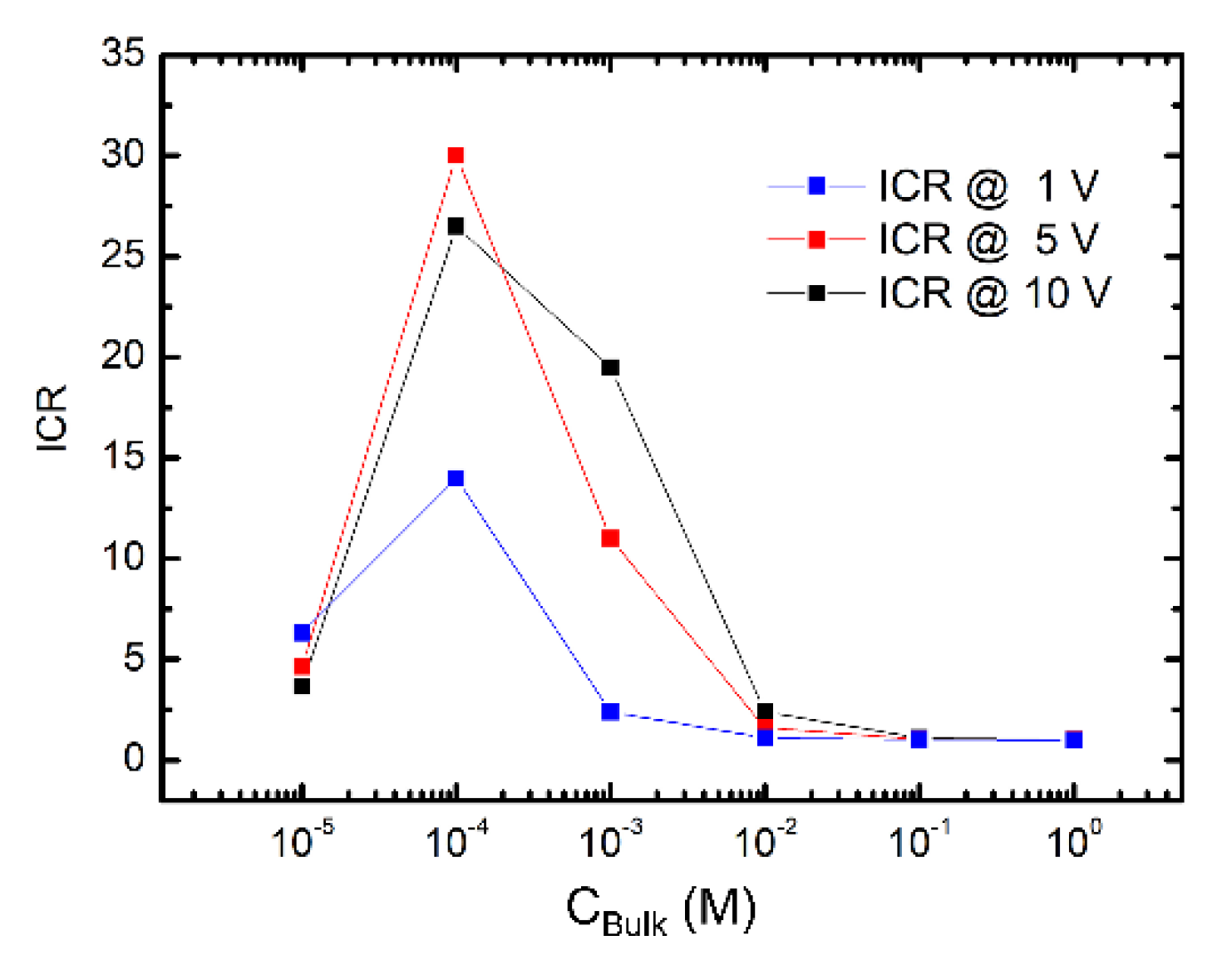
3.2. Rectification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abgrall, P.; Nguyen, N. Nanofluidic devices and their applications. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2326–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovarik, M.; Jacobson, S. Nanofluidics in Lab-on-a-Chip Devices. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7133–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocquet, L. Nanofluidics coming of age. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plecis, A.; Schoch, R.; Renaud, P. Ionic transport phenomena in nanofluidics: Experimental and theoretical study of the exclusion-enrichment effect on a chip. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoch, R.; Han, J.; Renaud, P. Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 839–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, C. Solid-state nanopores. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, M.; Eijkel, J.; Pennathur, S. Nanofluidic technology for biomolecule applications: A critical review. Lab A Chip 2010, 10, 957–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasianowicz, J.; Brandin, E.; Branton, D.; Deamer, D. Characterization of individual polynucleotide molecules using a membrane channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13770–13773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Ion/Molecule Transportation in Nanopores and Nanochannels: From Critical Principles to Diverse Functions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8658–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varongchayakul, N.; Song, J.; Meller, A.; Grinstaff, M. Single-molecule protein sensing in a nanopore: A tutorial. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8512–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanunu, M. Nanopores: A journey towards DNA sequencing. Phys. Life Rev. 2012, 9, 125–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Escosura-Muniz, A.; Merkoci, A. Nanochannels for electrical biosensing. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, Z.; Mogensen, K.; Nunes, P.; Zhou, K.; Hildenbrand, B.; Mitra, I.; Tan, Z.; Zlotnick, A.; Kutter, J.; Jacobson, S. Nanofluidic Devices with Two Pores in Series for Resistive-Pulse Sensing of Single Virus Capsids. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9573–9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, Z.; Haywood, D.; Kneller, A.; Selzer, L.; Zlotnick, A.; Jacobson, S. Single-Particle Electrophoresis in Nanochannels. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, G.; Darvish, A.; Kim, M. Use of solid-state nanopores for sensing co-translocational deformation of nano-liposomes. Analyst 2015, 140, 4865–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, H.C.; Chung, T.D. Ionic Circuits Based on Polyelectrolyte Diodes on a Microchip. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3830–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiguji, H.; Yang, P.; Majumdar, A. Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, R.; Duan, C.; Castelino, K.; Daiguji, H.; Majumdar, A. Rectification of ionic current in a nanofluidic diode. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshi, M.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z.; Duan, C. Geometrical control of ionic current rectification in a configurable nanofluidic diode. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 054102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwy, Z.; Fulinski, A. Fabrication of a synthetic nanopore ion pump. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 198103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schatz, G.C. Advantages of Conical Pores for Ion Pumps. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schatz, G.C. Conical Nanopores for Efficient Ion Pumping and Desalination. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 2842–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangle, T.A.; Mani, A.; Santiago, J.G. On the Propagation of Concentration Polarization from Microchannel-Nanochannel Interfaces Part II: Numerical and Experimental Study. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangle, T.A.; Mani, A.; Santiago, J.G. Theory and experiments of concentration polarization and ion focusing at microchannel and nanochannel interfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1014–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Ye, X.; Li, Z.; Hang, J. Deciphering ion concentration polarization-based electrokinetic molecular concentration at the micro-nanofluidic interface: Theoretical limits and scaling laws. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15187–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosentsvit, L.; Wang, W.; Schiffbauer, J.; Chang, H.C.; Yossifon, G. Ion current rectification in funnel-shaped nanochannels: Hysteresis and inversion effects. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, E.; Pezzuoli, D.; Repetto, D.; Guida, P.; Firpo, G.; Lo Savio, R.; Repetto, L.; Valbusa, U. Junction gap breakdown-based fabrication of PDMS ionic rectifiers. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2020, 30, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiguji, H. Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Anand, R.K. Recent advancements in ion concentration polarization. Analyst 2016, 141, 3496–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Song, Y.; Han, J. Nanofluidic concentration devices for biomolecules utilizing ion concentration polarization: Theory, fabrication, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwy, Z.; Howorka, S. Engineered voltage-responsive nanopores. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, D.; Kruithof, M.; Dekker, C. Surface-charge-governed ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 035901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oeffelen, L.; Van Roy, W.; Idrissi, H.; Charlier, D.; Lagae, L.; Borghs, G. Ion Current Rectification, Limiting and Overlimiting Conductances in Nanopores. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.; Zhou, K.; Harms, Z.; Jacobson, S. Ion Transport in Nanofluidic Funnels. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3897–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, J.F.; Wolfram, M.T.; Burger, M.; Trautmann, C.; Nguyen, G.; Pevarnik, M.; Bayer, V.; Siwy, Z. Rectification properties of conically shaped nanopores: Consequences of miniaturization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 16917–16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlushkou, D.; Perry, J.M.; Jacobson, S.C.; Tallarek, U. Propagating Concentration Polarization and Ionic Current Rectification in a Nanochannel-Nanofunnel Device. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, P.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Enhanced Stability and Controllability of an Ionic Diode Based on Funnel-Shaped Nanochannels with an Extended Critical Region. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3345–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiedt, B.; Healy, K.; Morrison, A.; Neumann, R.; Siwy, Z. Transport of ions and biomolecules through single asymmetric nanopores in polymer films. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2005, 236, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubeil, C.; Bund, A. The Role of Nanopore Geometry for the Rectification of Ionic Currents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7866–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwy, Z. Ion-current rectification in nanopores and nanotubes with broken symmetry. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.; Vlassiouk, I.; Siwy, Z. Comparison of bipolar and unipolar ionic diodes. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 265301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Joo, S.; Cheney, M.; Qian, S. Effects of Electroosmotic Flow on Ionic Current Rectification in Conical Nanopores. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 3883–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Ji, H.; Xue, J.; Ouyang, Q. Asymmetric properties of ion transport in a charged conical nanopore. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 051201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervera, J.; Schiedt, B.; Neumann, R.; Mafe, S.; Ramirez, P. Ionic conduction, rectification, and selectivity in single conical nanopores. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 104706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.M.; Hou, H.H.; Chiu, P.H.; Yang, R.J. Sample preconcentration from dilute solutions on micro/nanofluidic platforms: A review. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoitevin, M.; Ma, T.; Bechelany, M.; Janot, J.; Balme, S. Functionalization of single solid state nanopores to mimic biological ion channels: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 250, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassiouk, I.; Siwy, Z. Nanofluidic diode. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassiouk, I.; Kozel, T.; Siwy, Z. Biosensing with Nanofluidic Diodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8211–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xia, X. High-performance bioanalysis based on ion concentration polarization of micro-/nanofluidic devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4007–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Yossifon, G. Combining dielectrophoresis and concentration polarization-based preconcentration to enhance bead-based immunoassay sensitivity. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9436–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzuoli, D.; Angeli, E.; Repetto, D.; Ferrera, F.; Guida, P.; Firpo, G.; Repetto, L. Nanofluidic-Based Accumulation of Antigens for Miniaturized Immunoassay. Sensors 2020, 20, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuoli, D.; Angeli, E.; Repetto, D.; Guida, P.; Firpo, G.; Repetto, L. Increased Flexibility in Lab-on-Chip Design with a Polymer Patchwork Approach. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassiouk, I.; Smirnov, S.; Siwy, Z. Ionic selectivity of single nanochannels. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas, A.; Berardi, D.; Diez, F. Numerical investigation of the current transition regimes in nanochannels. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momotenko, D.; Girault, H.H. Scan-Rate-Dependent Ion Current Rectification and Rectification Inversion in Charged Conical Nanopores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14496–14499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.S.; Bund, A. Ion current rectification at nanopores in glass membranes. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarik, M.; Zhou, K.; Jacobson, S. Effect of Conical Nanopore Diameter on Ion Current Rectification. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15960–15966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, P.; Apel, P.; Cervera, J.; Mafe, S. Pore structure and function of synthetic nanopores with fixed charges: Tip shape and rectification properties. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 315707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Repetto, D.; Angeli, E.; Pezzuoli, D.; Guida, P.; Firpo, G.; Repetto, L. Ion Current Rectification in Extra-Long Nanofunnels. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113749
Repetto D, Angeli E, Pezzuoli D, Guida P, Firpo G, Repetto L. Ion Current Rectification in Extra-Long Nanofunnels. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113749
Chicago/Turabian StyleRepetto, Diego, Elena Angeli, Denise Pezzuoli, Patrizia Guida, Giuseppe Firpo, and Luca Repetto. 2020. "Ion Current Rectification in Extra-Long Nanofunnels" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113749
APA StyleRepetto, D., Angeli, E., Pezzuoli, D., Guida, P., Firpo, G., & Repetto, L. (2020). Ion Current Rectification in Extra-Long Nanofunnels. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113749




