Numerical Investigation on Handling Stability of a Heavy Tractor Semi-Trailer under Crosswind
Abstract
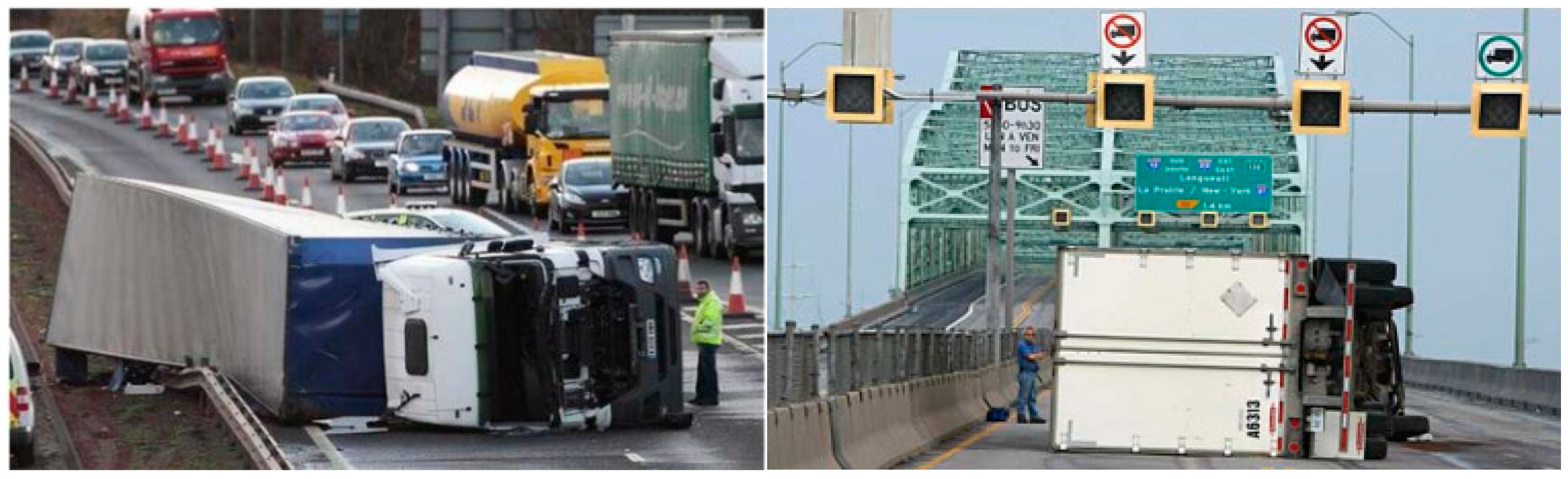
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Method and Validation
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Validation Case of Heavy Tractor Semi-Trailer Model
3. Computation of the Aerodynamic Characteristics
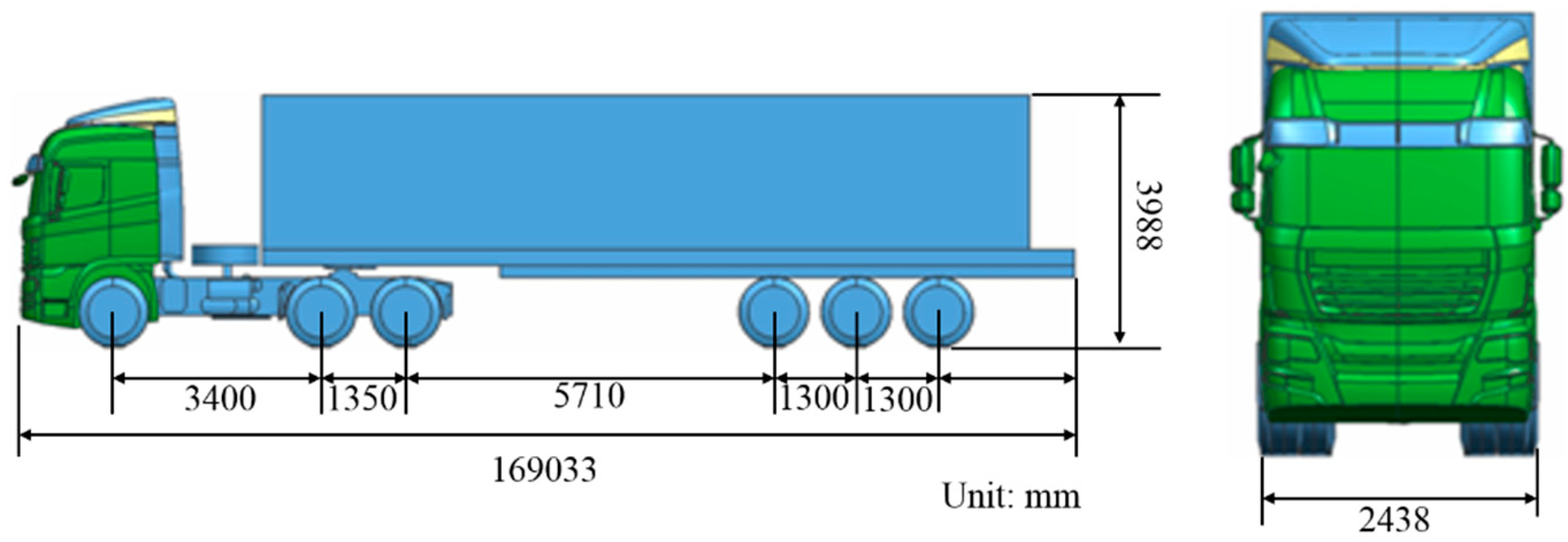
3.1. Detailed Study of Target Vehicle Model
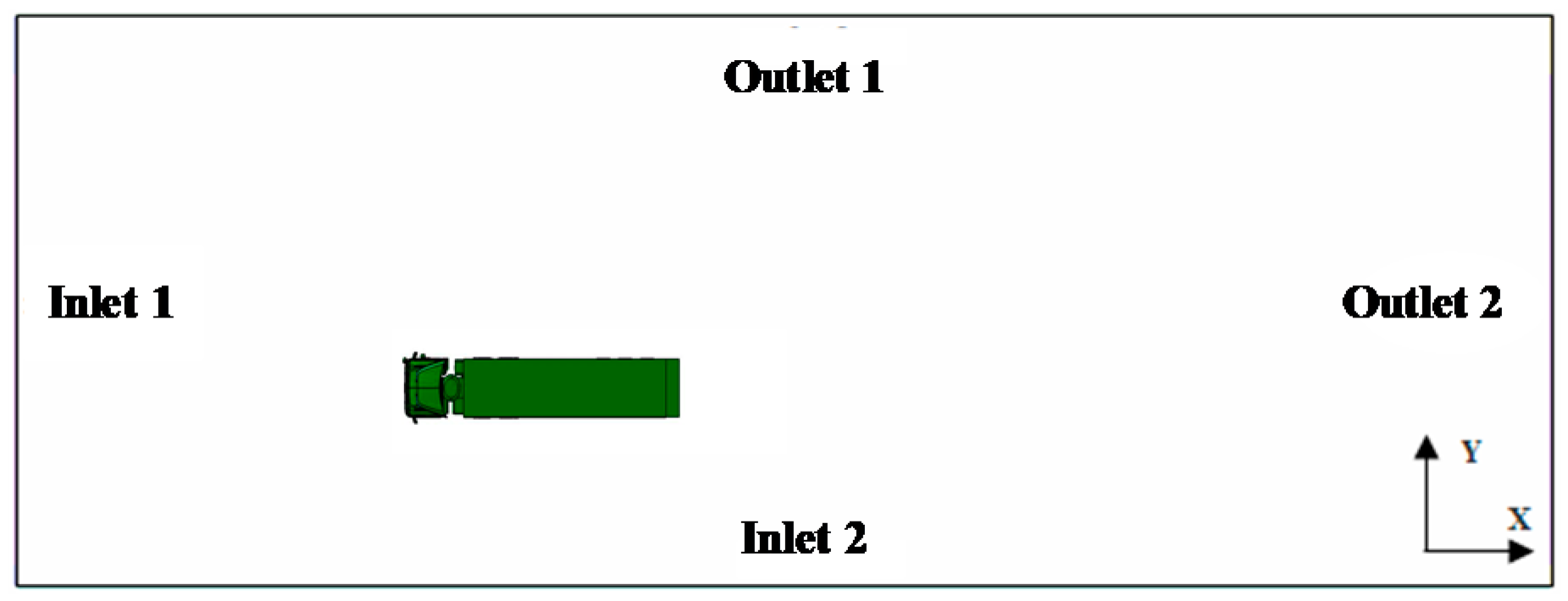
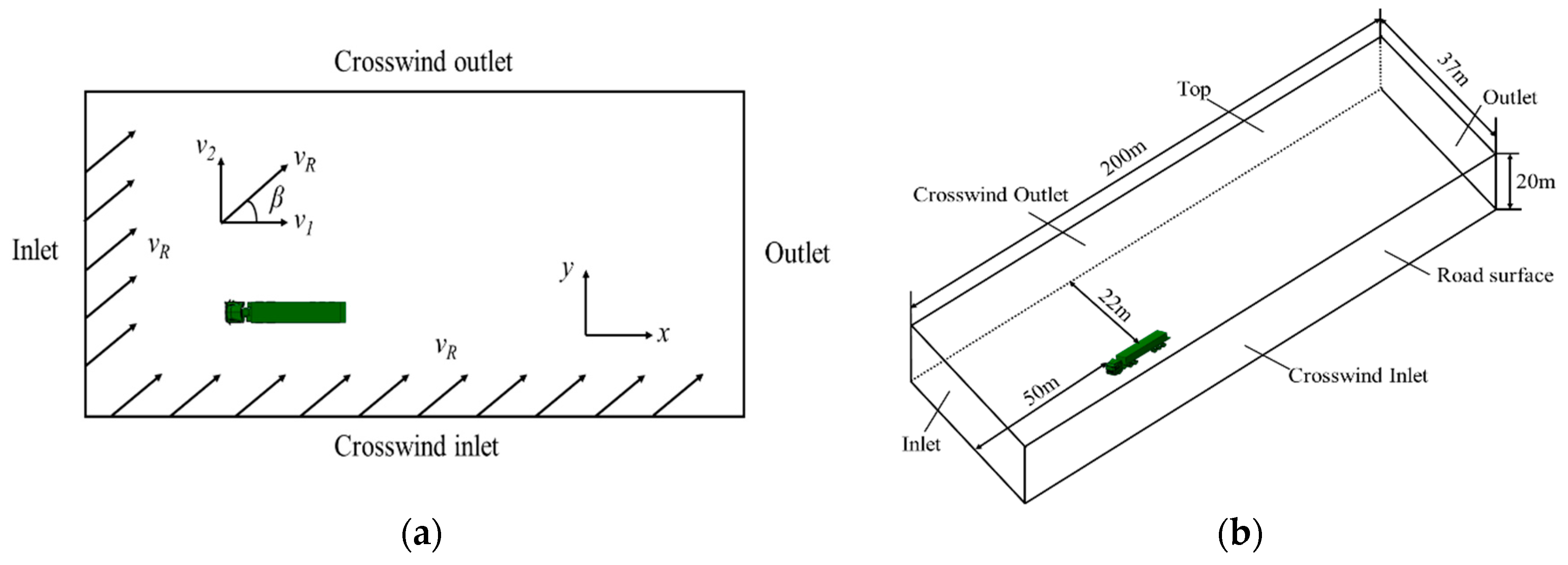
3.2. Computational Domain and Boundary Condition
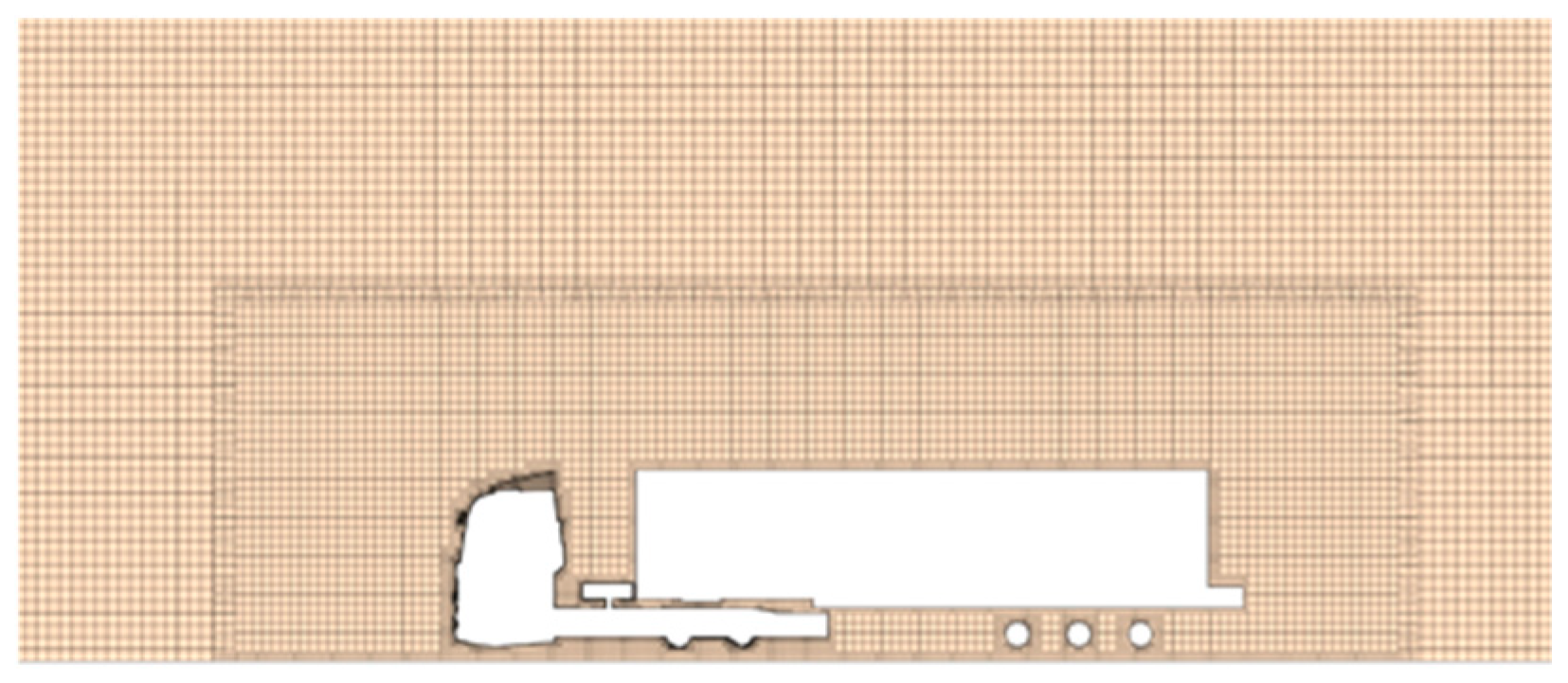
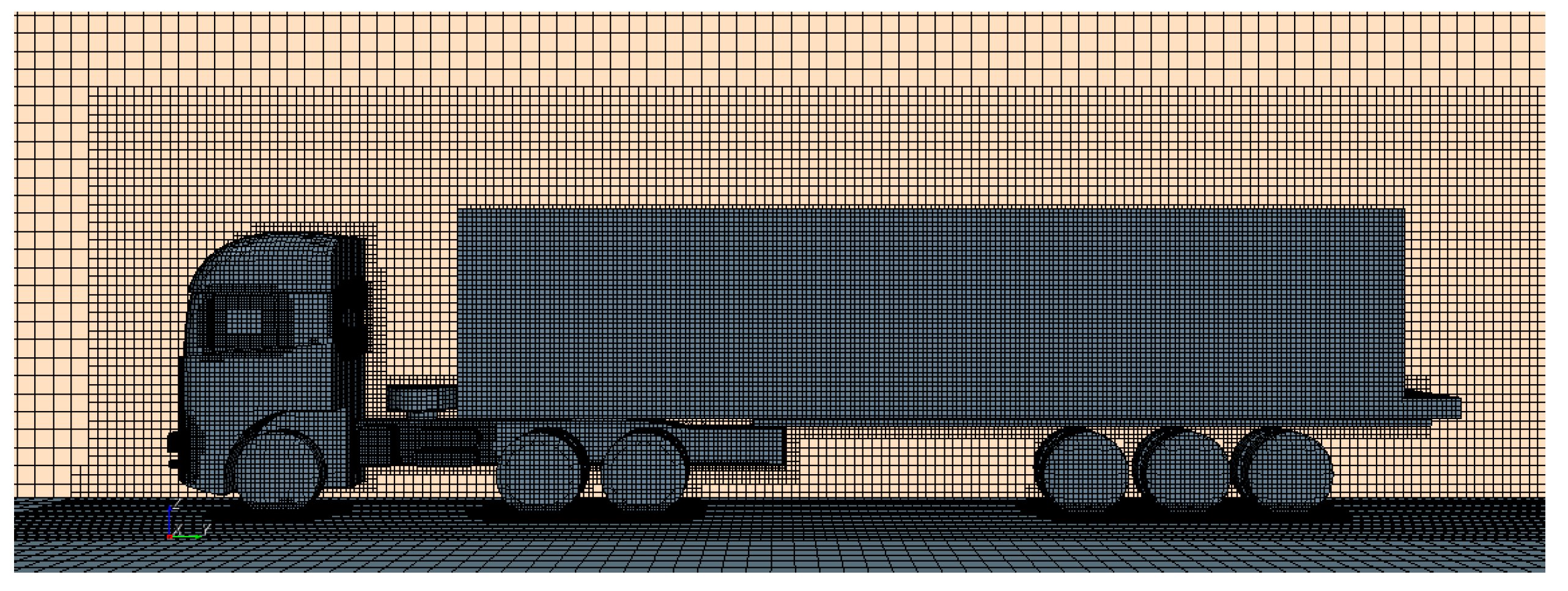
3.3. Computational Grid
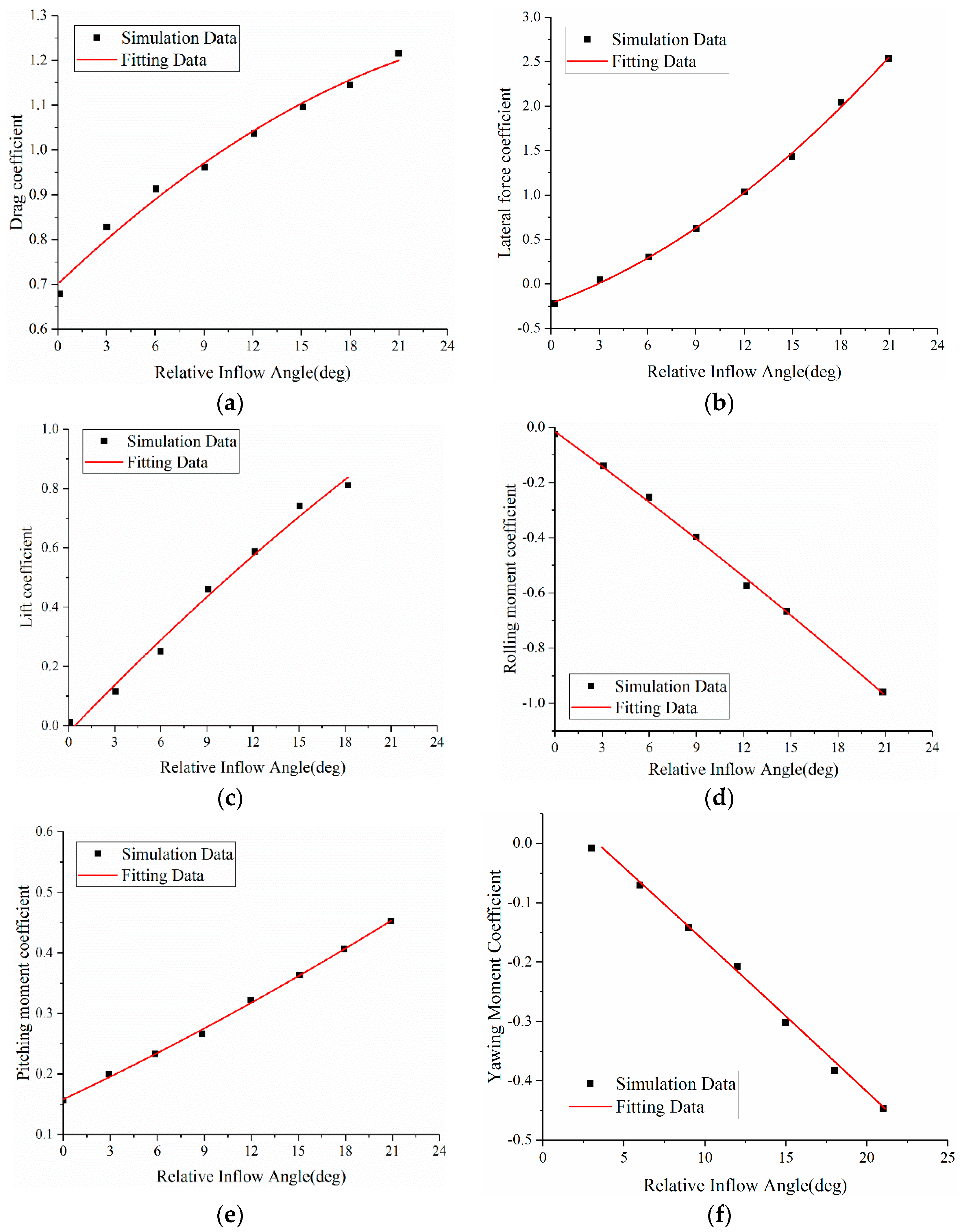
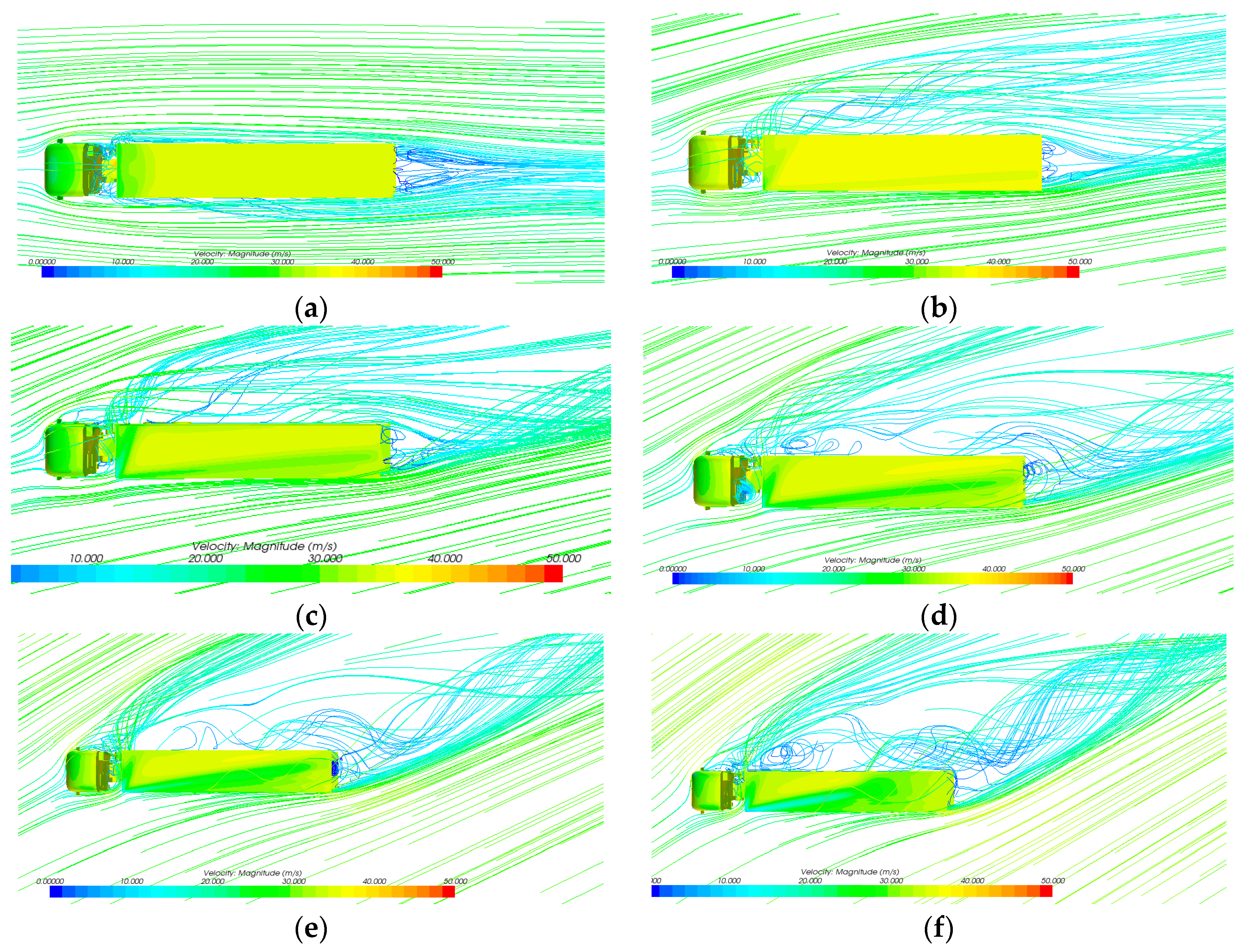
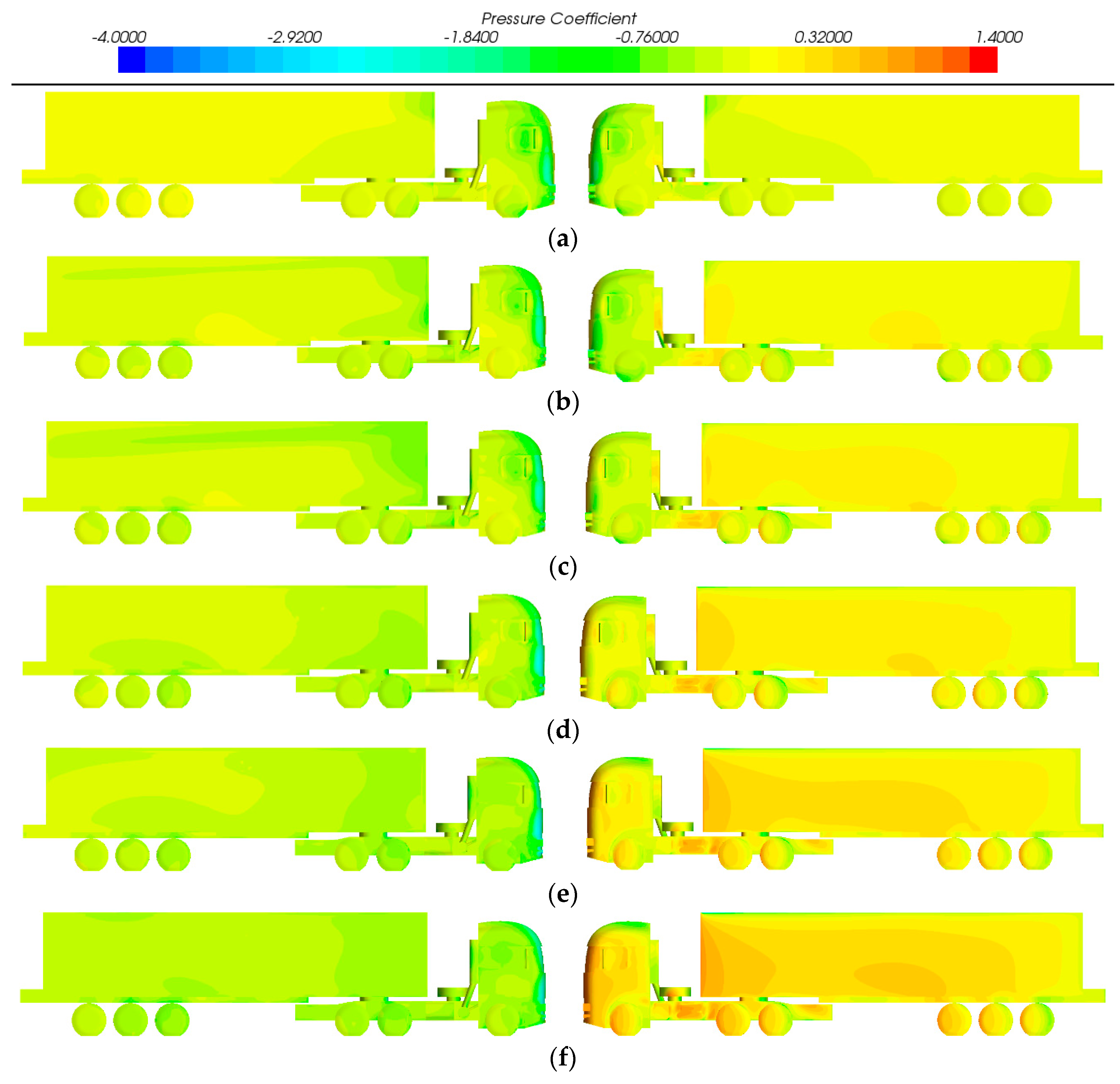
3.4. Results and Discussion
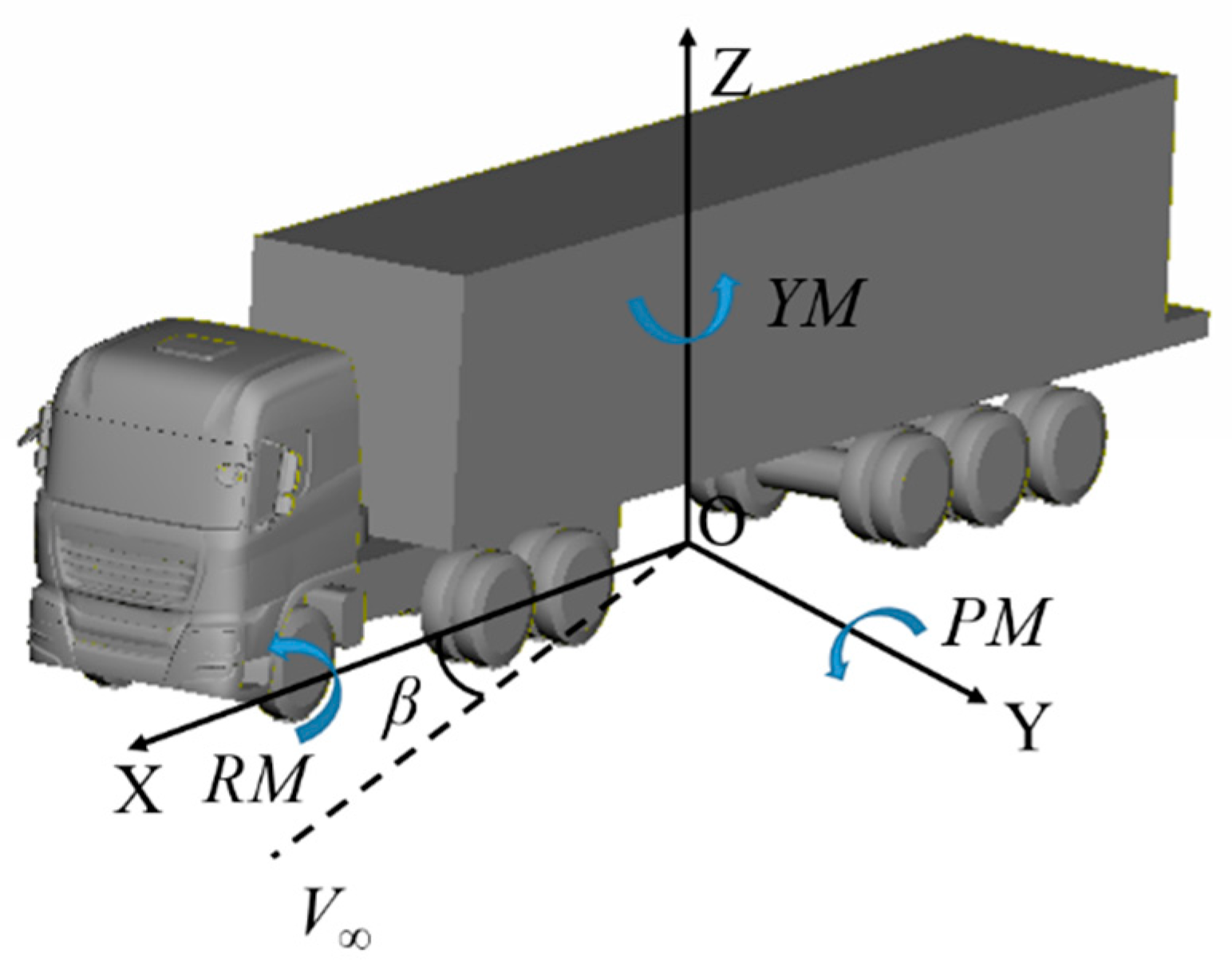
4. Multi-Body Dynamic Simulation
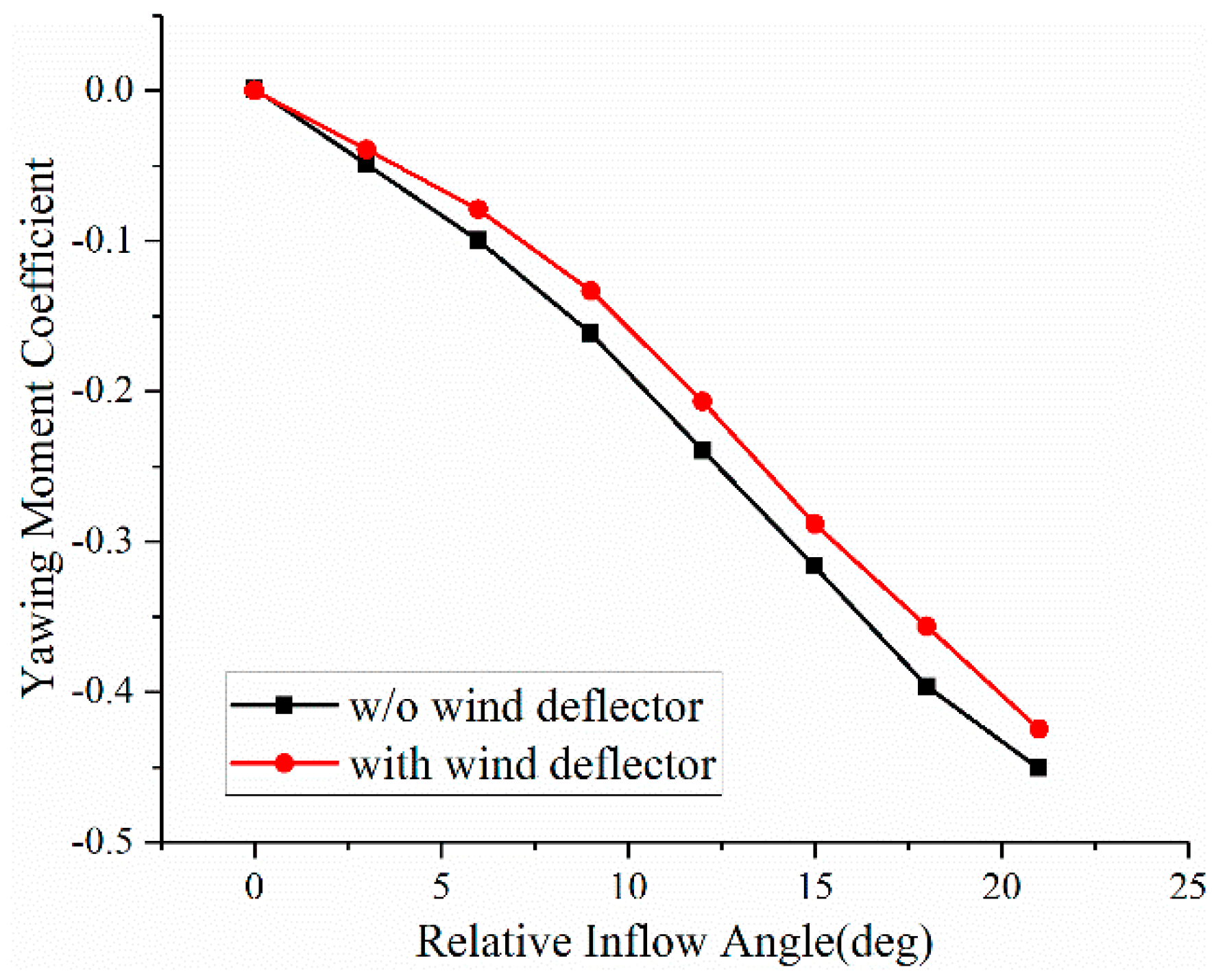
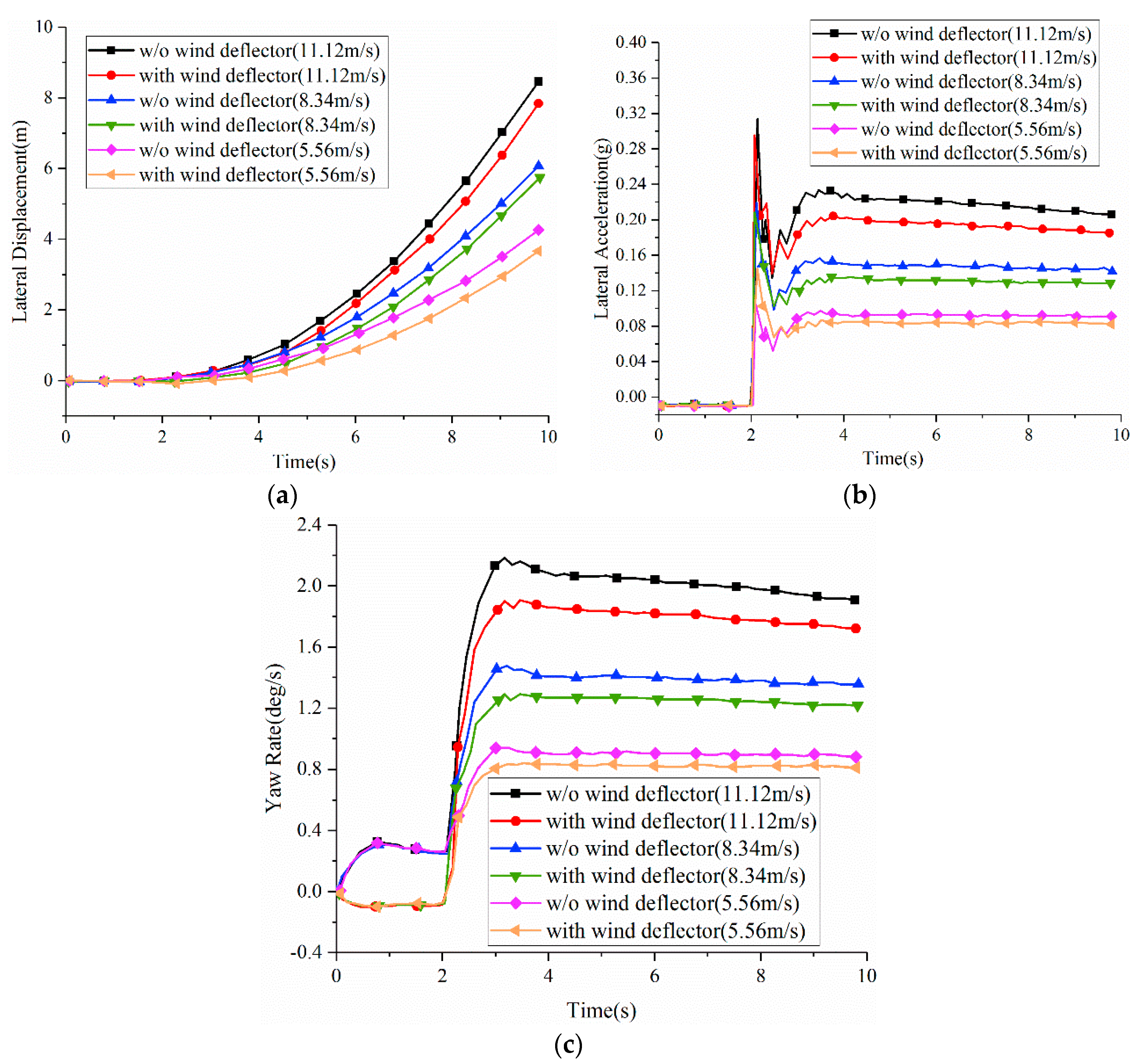
5. Effect of the Wind Deflector on Crosswind Stability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, C.; Chang, C.; Huang, C.; Wu, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, M. Windbreak protection for road vehicles against crosswind. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 116, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.; Watkins, S. The Unsteady Wind Environment of Road Vehicles. Part One: A Review of The on-Road Turbulent Wind Environment. SAE Paper 2007-01-1236. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2007-01-1236/ (accessed on 16 April 2017).
- Baker, C. Risk Analysis of Pedestrian and Vehicle Safety in Windy Environments. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 147, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.; Schrefl, M.; Demuth, R. On Various Aspects of the Unsteady Aerodynamic Effects on Cars Under Crosswind Conditions. SAE Paper 2007-01-1548. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2007-01-1548/ (accessed on 16 April 2017).
- Ferrand, V. Forces and Flow Structures on a Simplified Car Model Exposed to an Unsteady Harmonic Crosswind. J. Fluids Eng. 2014, 136, 011101–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hooge, A.; Rebbeck, L.; Palin, R.; Murphy, Q.; Gargoloff, J.; Duncan, B. Application of Real-World Wind Conditions for Assessing Aerodynamic Drag for On-Road Range Prediction. SAE Paper 2015-01-1551. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2015-01-1551/ (accessed on 14 April 2015).
- Tunay, T.; Firat, E.; Sahin, B. Experimental investigation of the flow around a simplified ground vehicle under effects of the steady crosswind. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 71, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajendra Singh, M.; Nagpurwala, Q.; Nassar, A.; Shankapal, S. Numerical Investigations on Crosswind Aerodynamics and Its Effect on the Stability of a Passenger Car. SAE Paper 2009-26-059. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2009-26-0059/ (accessed on 21 January 2009).
- Tsubokura, M.; Nakashima, T.; Ikenaga, T.; Onishi, K.; Kitoh, K.; Oshima, N.; Kobayashi, T. HPC-LES for the Prediction of Unsteady Aerodynamic Forces on a Vehicle in a Gusty Cross-Flow Condition. SAE Paper 2008-01-3001. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2008-01-3001/ (accessed on 2 December 2008).
- Cai, C.; Chen, S. Framework of Vehicle-Bridge-Wind Dynamic Analysis. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2004, 92, 579–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, J.; Rho, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, D. High Speed Driving Stability of Passenger Car Under Crosswind Effects. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2014, 15, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihashi, K.; Okumura, K. Analysis of Vehicle Stability in Crosswinds. SAE Paper 2000-05-0255. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2000-05-0255/?src=942507 (accessed on 12 June 2000).
- Nakashima, T.; Tsubokura, M.; Ikenaga, T.; Doi, Y. HPC-LES for Unsteady Aerodynamics of a Heavy Duty Truck in Wind Gust-2nd report: Coupled Analysis with Vehicle Motion. SAE Paper 2010-01-1021. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2010-01-1021/ (accessed on 12 April 2010).
- Juhlin, M.; Eriksson, P. A Vehicle Parameter Study on Crosswind Sensitivity of Buses. SAE Paper 2004-01-2612. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2004-01-2612/ (accessed on 26 October 2004).
- Schroeck, D.; Krantz, W.; Widdecke, N.; Wiedemann, J. Unsteady Aerodynamic Properties of a Vehicle Model and Their Effect on Driver and Vehicle under Side Wind Conditions. SAE Paper 2011-01-0154. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2011-01-0154/ (accessed on 12 April 2011).
- Tsubokura, M.; Takahashi, K.; Matsuuki, T.; Nakashima, T.; Ikenaga, T.; Kitoh, K. HPC-LES for Unsteady Aerodynamics of a Heavy Duty Truck in Wind Gust-1st report: Validation and Unsteady Flow Structures. SAE Paper 2010-01-1010. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2010-01-1010/ (accessed on 12 April 2010).
- Spalding, D.B. Chemical reaction in turbulent fluids. J. Phys. Chem. Hydrodyn. 1983, 4, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Karabelas, S.J.; Koumroglou, B.C.; Argyropoulos, C.D.; Markatos, N.C. High Reynolds number turbulent flow past a rotating cylinder. Appl. Math. Modell. 2012, 36, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. Mathematical Models of Turbulence; Academic Press: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, W.; Cebeci, T. Calculation of turbulent flows. In Ch. 5 in Turbulence. Part of the Topics in Applied Physics Book Series, 2nd ed.; Bradshaw, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1978; Volume 12, pp. 193–229. [Google Scholar]
- Badshaw, P. Introduction to turbulence. In Ch. 1 in Turbulence. Topics in Applied Physics, 2nd ed.; Bradshaw, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1978; Volume 12, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Launder, B.E.; Sharma, B.I. Application of the energy dissipation model of turbulence to the calculation of flow near a spinning disk, Lett. Heat Mass Transf. 1974, 1, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Equations of turbulent motion of an incompressible fluid. Izv Acad. Nauk SSSR Phys. 1942, 6, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, D.C. Reassessment of the scale-determining equation for advanced turbulence models. AIAA J. 1988, 26, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhot, V.; Orszag, S.A.; Thangam, S.; Gatski, T.B.; Speziale, C.G. Development of turbulence models for shear flows by a double expansion technique. Phys. Fluids Fluid Dyn. 1992, 4, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsourakis, N.; Bartzis, J.G.; Markatos, N.C. Evaluation of Reynolds stress, k–e and RNG k–e turbulence models in street canyon flows using various experimental datasets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2012, 12, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, C.D.; Sideris, G.M.; Christolis, M.N.; Nivolianitou, Z.; Markatos, N.C. Modelling pollutants dispersion and plume rise from large hydrocarbon tank fires in neutrally stratified atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Reitz, R.D. Reitz. Turbulence modeling of internal combustion engines using RNG κ-ε models. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1995, 106, 267–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Befrui, B.; Gosman, A.D. Assessment of variants of the k–ϵ turbulence model for engine flow applications. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 1989, 9, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Xie, X.; Deng, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, C. Performance evaluation of an automotive thermoelectric generator with inserted fins or dimpled-surface hot heat exchanger. Appl. Energy 2018, 218, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, X. Numerical investigation of the passive control of cavity flow oscillations by a dimpled non-smooth surface. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 111, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Gu, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, Y. Aerodynamic Shape Optimization of a Container-Truck’s Wind Deflector Using Approximate Model. SAE Paper 2010-01-2035. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2010-01-2035/ (accessed on 5 October 2010).
- Yang, Z.G.; Johnson, J.P.; Morley, J.B.; Unaune, S.; Sovani, S.D. Dynamic Moving Mesh CFD Study of Semi-truck Passing a Stationary Vehicle with Hood Open. SAE Paper 2007-01-0111. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2007-01-0111/ (accessed on 16 April 2007).
- Gong, X.; Gu, Z.Q.; Li, Z.L. A Study on the Numerical Simulation of Car Aerodynamic Characteristics Under Crosswind Conditions. Automot. Eng. 2010, 32, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lun, T.; Savas, O. Transient Aerodynamics of Vehicle Platoons during in-line Oscillations. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2001, 89, 1085–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Osth, J.; Krajnovic, S. A Study of the Aerodynamics of a Generic Container Freight Wagon using Large-Eddy Simulation. J. Fluids Struct. 2014, 44, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.; Muñoz-Paniagua, J.; Jiménez, A.; Migoya, E.; Crespo, A. Numerical Study of the Influence of Synthetic Turbulent Inflow Conditions on the Aerodynamics of a Train. J. Fluids Struct. 2015, 56, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Q. Wind Tunnel Investigations of Aerodynamic Coefficients of Road Vehicles on Bridge Deck. J. Fluids Struct. 2012, 30, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Ahmadian, M. Effects of Commercial Truck Configuration on Roll Stability in Roundabouts. SAE Paper 2015-01-2741. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2015-01-2741/ (accessed on 29 September 2015).






| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| m | Vehicle total mass (powered unit) | 7600 kg |
| ms | Vehicle sprung mass (powered unit) | 4455 kg |
| lf | Distance between c.g. and the 1-axis (powered unit) | 2.0 m |
| lr | Distance between c.g. and the 3-axis (powered unit) | 2.75 m |
| L | Vehicle length (powered unit) | 7.25 m |
| H | Vehicle height (powered unit) | 3.9 m |
| Ixx | Rolling moment of inertia (powered unit) | 2283.9 kg•m2 |
| Iyy | Pitching moment of inertia (powered unit) | 35,402.8 kg•m2 |
| Izz | Yawing moment of inertia (powered unit) | 34,802.6 kg•m2 |
| mt | Vehicle total mass (trailer unit) | 7570 kg |
| mts | Vehicle sprung mass (trailer unit) | 5500 kg |
| lft | Distance between c.g. and the 3-axis (trailer unit) | 3.3 m |
| lrt | Distance between c.g. and the 6-axis (trailer unit) | 5.01 m |
| Lt | Vehicle length (trailer unit) | 12.2 m |
| Ht | Vehicle height (trailer unit) | 4.2 m |
| Ixxt | Rolling moment of inertia (trailer unit) | 8997.1 kg•m2 |
| Iyyt | Pitching moment of inertia (trailer unit) | 150,000 kg•m2 |
| Izzt | Yawing moment of inertia (trailer unit) | 150,000 kg•m2 |
| Ksf | Upper vertical spring stiffness | 0.25 N/m |
| Ksr | Lower vertical spring stiffness | 0.7 N/m |
| Cf | Upper vertical damping | 15,000 Ns/m |
| Cr | Lower vertical damping | 30,000 Ns/m |
| Cαf | Cornering stiffness of one tyre (front) | 140,000 N/rad |
| Cαr | Cornering stiffness of one tyre (rear) | 140,000 N/rad |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Su, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y. Numerical Investigation on Handling Stability of a Heavy Tractor Semi-Trailer under Crosswind. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113672
Zhang Q, Su C, Zhou Y, Zhang C, Ding J, Wang Y. Numerical Investigation on Handling Stability of a Heavy Tractor Semi-Trailer under Crosswind. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113672
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qianwen, Chuqi Su, Yi Zhou, Chengcai Zhang, Jiuyang Ding, and Yiping Wang. 2020. "Numerical Investigation on Handling Stability of a Heavy Tractor Semi-Trailer under Crosswind" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113672
APA StyleZhang, Q., Su, C., Zhou, Y., Zhang, C., Ding, J., & Wang, Y. (2020). Numerical Investigation on Handling Stability of a Heavy Tractor Semi-Trailer under Crosswind. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113672




