Ultrasonic Technology Applied against Mosquito Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
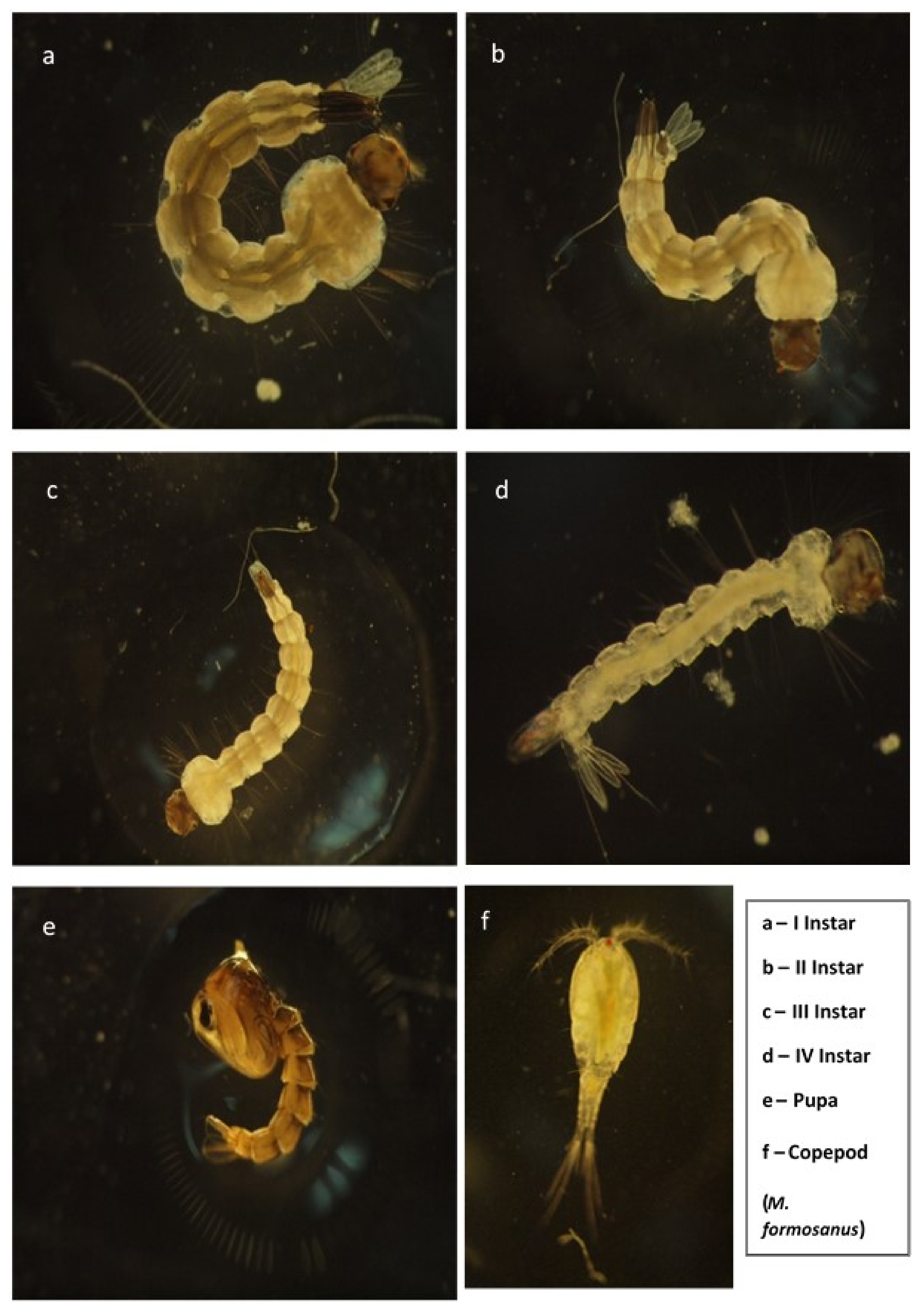
2.1. Mosquito Rearing
2.2. Copepod Culture
2.3. Efficacy of Ultrasonic Treatment at Laboratory Conditions
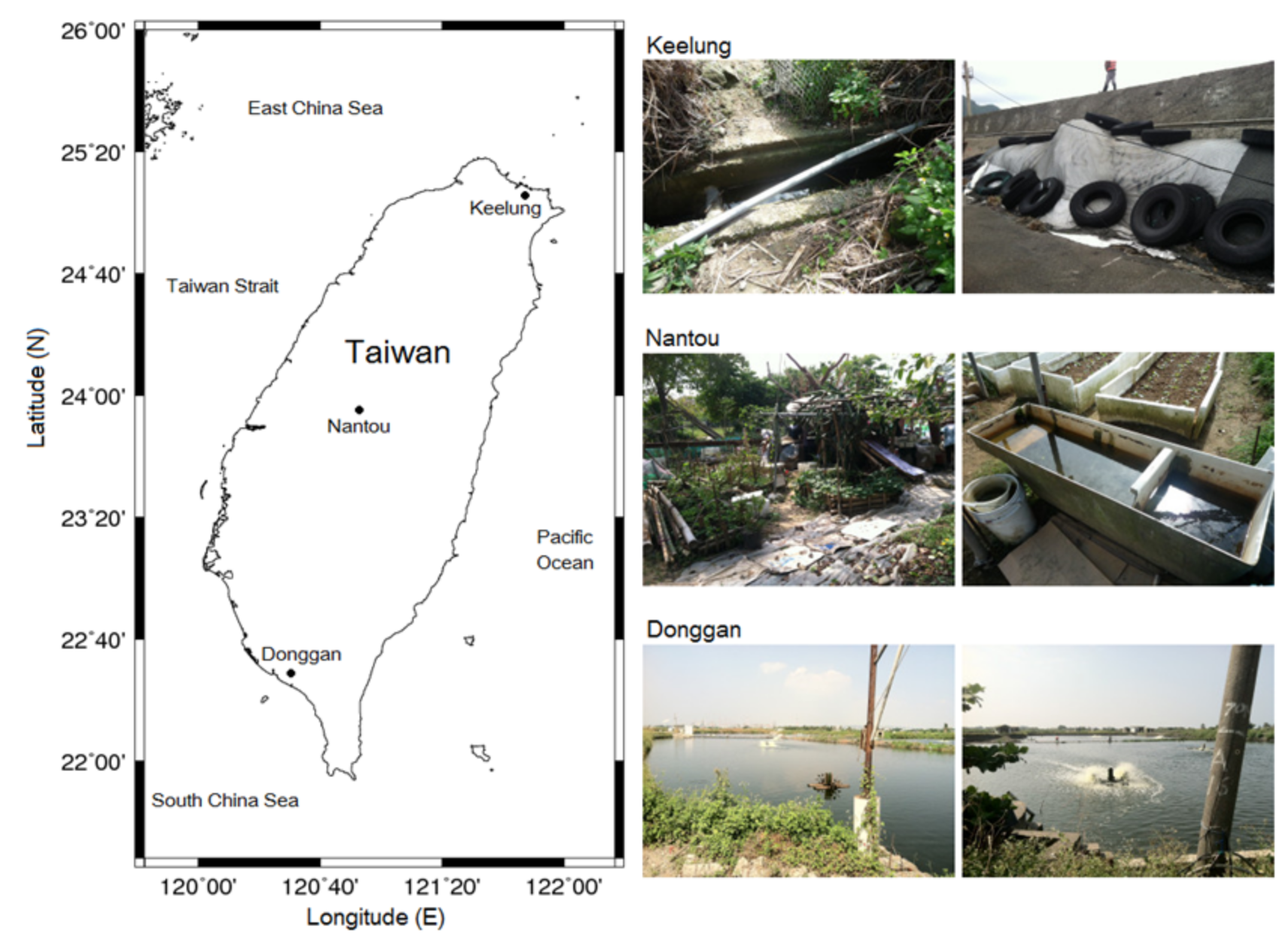
2.4. Efficacy of Ultrasonic Treatment in the Field
2.5. Statistical Analysis
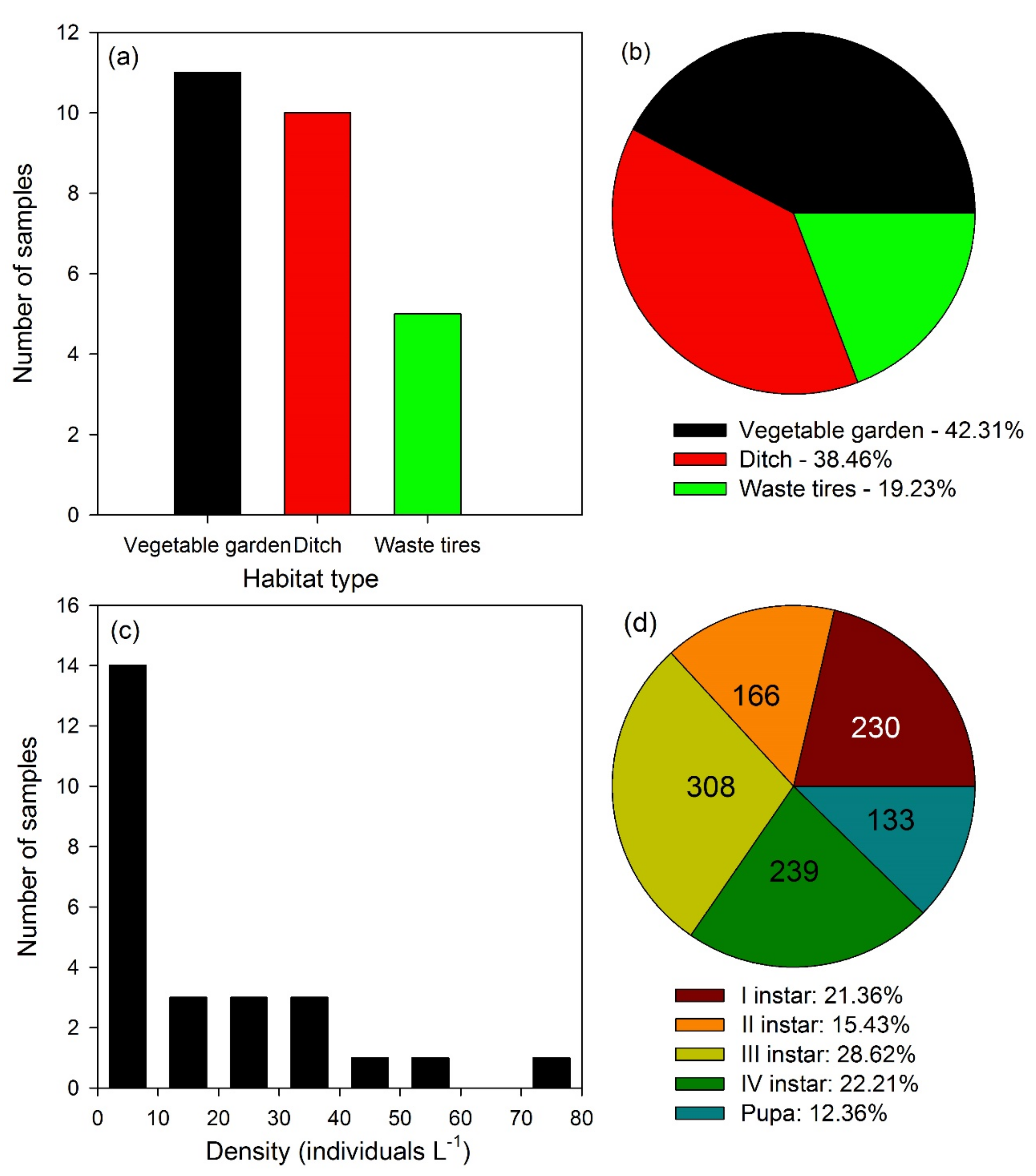
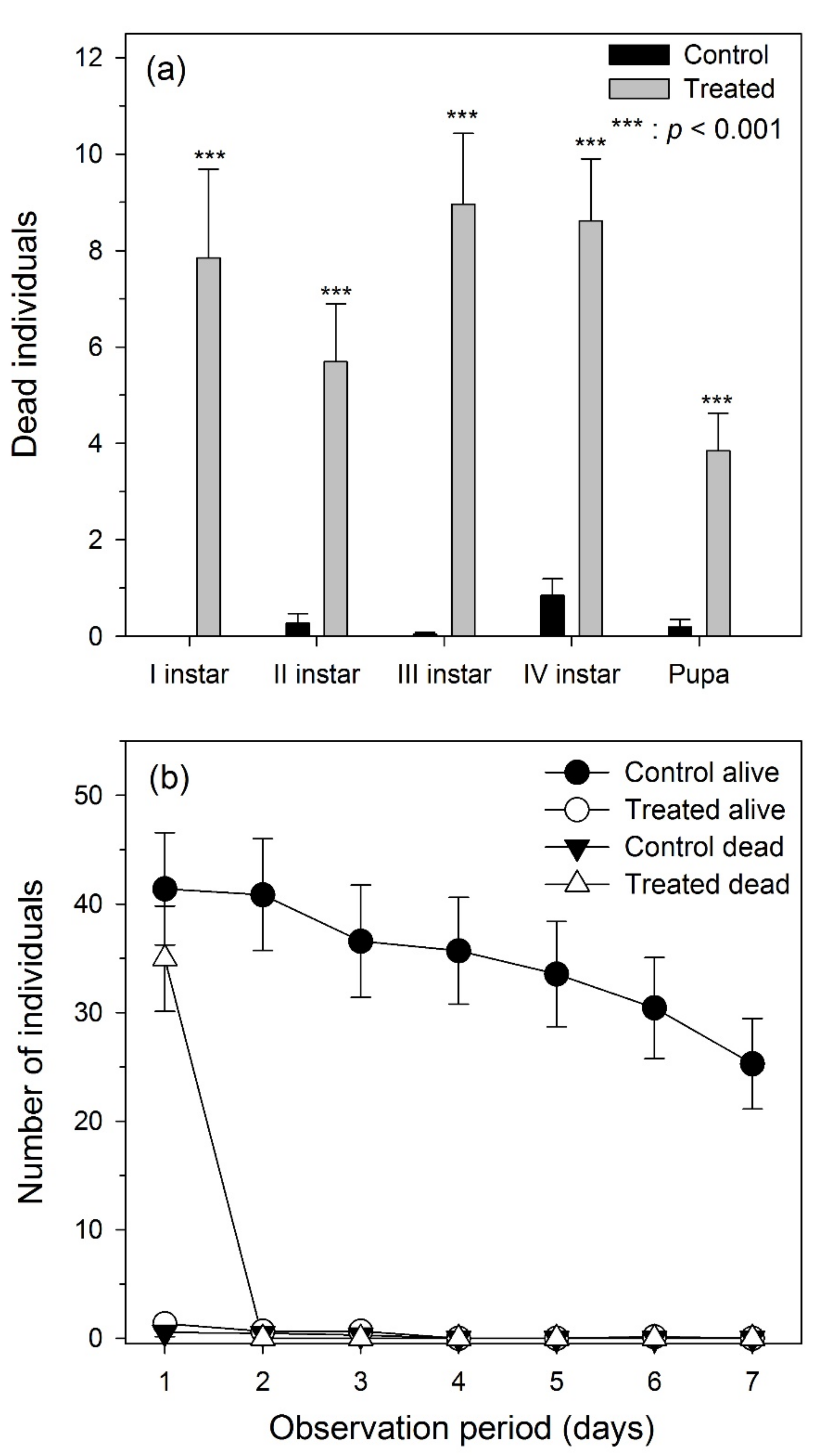
3. Results
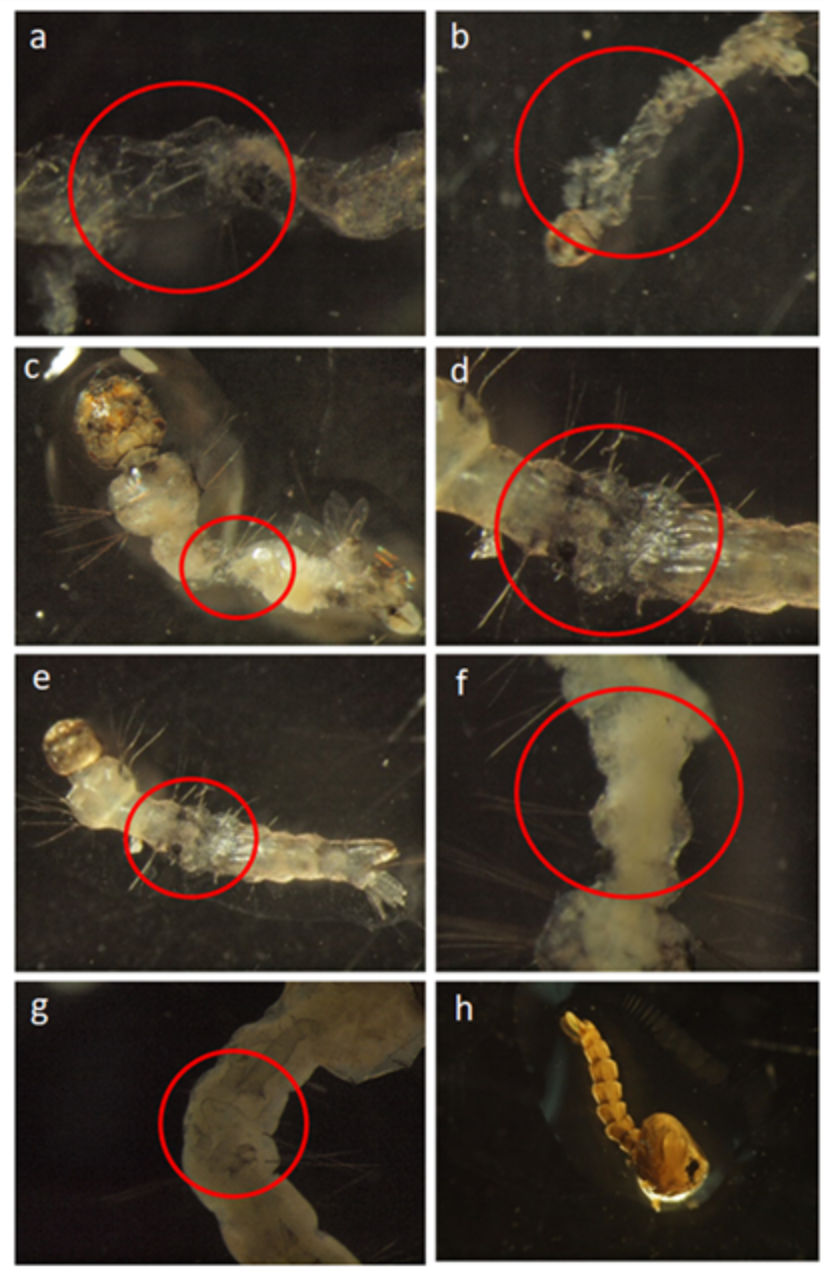
3.1. Laboratory Experiments
3.2. Field Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Challenges for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilpatrick, A.M.; Randolph, S.E. Drivers, dynamics, and control of emerging vector-borne zoonotic diseases. Lancet 2012, 380, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benelli, G.; Beier, J. Current vector control challenges in the fight against malaria. Acta Trop. 2017, 174, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, S.V.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. The emergence of arthropod-borne viral diseases: A global prospective on dengue, chikungunya, and Zika fevers. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G.; Lo Iacono, A.; Canale, A.; Mehlhorn, H. Mosquito vectors and the spread of cancer: An overlooked connection? Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nyberg, H.J.; Muto, K. Acoustic tracheal rupture provides insights into larval mosquito respiration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindhauser, M.K.; Allen, T.; Frank, V.; Santhana, R.S.; Dye, C. Zika: The origin and spread of a mosquito-borne virus. Bull. World Health Org. 2016, 94, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Laboratory and Field Testing of Mosquito Larvicides. 2005. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/69101 (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.C. Effects of oil-film layer and surfactant of the siphonal respiration and survivorship in the fourth instar larvae of Aedes togoi mosquito in laboratory conditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benelli, G. Research in mosquito control: Current challenges for a brighter future. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2801–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, K.; Aruna, P.; Panneerselvam, C.; Madhiyazhagan, P.; Paulpandi, M.; Subramaniam, J.; Rajaganesh, R.; Wei, H.; Alsalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; et al. Fighting arboviral diseases: Low toxicity on mammalian cells, dengue growth inhibition (in vitro) and mosquitocidal activity of Centroceras clavulatum-synthesized silver nanoparticles. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Fernandes, A.; Ceretti-Junior, W.; Wilke, A.B.B.; Marrelli, M.T. Mosquitoes in urban green spaces: Using an island biogeographic approach to identify drivers of species richness and composition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, S.R.; Stone, C.M.; Fonseca, D.M.; Fefferman, N.H. The importance of being urgent: The impact of surveillance target and scale on mosquito-borne disease control. Epidemics 2017, 23, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.W.; Paploski, I.A.; Kikuti, M.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Silva, M.M.; Campos, G.S.; Sardi, S.I.; Kitron, U.; Reis, M.G.; Ribeiro, G.S. Outbreak of exanthematous illness associated with Zika, chikungunya, and dengue viruses, Salvador, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2274–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G.; Mehlhorn, H. Declining malaria, rising dengue and Zika virus: Insights for mosquito vector control. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, S.; Calvez, E.; Chouin-Carneiro, T.; Diallo, D.; Failloux, A.B. An overview of mosquito vectors of zika virus. Microbes Infect. 2018, 20, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Health Ministry. Dengue. Bol. Epidem. 2016, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, J.N.; Moise, I.K.; Maranto, G.L.; Beier, J.C. Revamping mosquito-borne disease control to tackle future threats. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, B.; Sikulu-Lord, M.T.; Mayagaya, V.S.; Devine, G.; Dowell, F.; Churcher, T.S. Monitoring the age of mosquito populations using near-infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benelli, G. Plant-borne ovicides in the fight against mosquito vectors of medical and veterinary importance: A systematic review. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3201–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqqash, M.N.; Gökçe, A.; Bakhsh, A.; Salim, M. Insecticide resistance and its molecular basis in urban insect pests. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G. Plant-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles as an emerging tool against mosquitoes of medical and veterinary importance: A review. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela, R.; Benelli, G. Ethnobotanical knowledge on botanical repellents employed in the African region against mosquito vectors—A review. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 167, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, F.M.; Dabiré, R.K.; Sawadogo, S.P.; Torr, S.J.; Gibson, G. Exploiting Anopheles responses to thermal, odour and visual stimuli to improve surveillance and control of malaria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gina, L.; Elizabeth, H. Literature review of the effects of ultrasonic waves on cyanobacteria, other aquatic organisms, and water quality. Wisconsin DNR 2014, 195, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.L. The botanical effects of ultrasound: A review. Env. Exp. Bot. 1983, 23, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, P.; Fan, L.; Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A. Impact of sonication at 20 kHz on Microcystis aeruginosa, Anabaena circinalis, and Chlorella sp. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, L.A. Ultrasonic algae control literature review. AWPD 2010, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Madge, B.A.; Jensen, J.N. Disinfection of wastewater using a 20-kHz ultrasound unit. Water Env. Res. 2002, 74, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Olmedilla, D. Preventing the Growth of Barnacles by Using Ultrasonic Sound. Master Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, T.J. Large scale sonochemical processing: Aspiration and actuality. Ultrason. Sono. Chem. 2000, 7, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlein, D.; Rosner, F.; Brand, S.; Jenderka, K.V.; Wicke, M. Non-destructive estimation of the intramuscular fat content of the longissimus muscle of pigs by means of spectral analysis of ultrasound echo signals. Meat Sci. 2005, 69, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, F.; Ellis, M.; Miller, K.D.; Novakofski, J.; Wilson, E.R.; McKeith, F.K. Comparison of transverse and longitudinal real-time ultrasound scans for prediction of lean cut yields and fat-free lean content in live pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1996, 74, 2566–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleczek, K.; Wawro, K.; Wilkiewicz-Wawro, E.; Makowski, W.; Konstantynowicz, K. Relationships between breast muscle thickness measured by ultrasonography and meatiness and fatness in broiler chicken. Arch. Tierzucht. 2009, 52, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, A. Carcass characteristics of Peking ducks selected for greater breast muscle thickness using ultrasound scanning in response to dietary protein. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2009, 5, 731–739. [Google Scholar]
- Emenheiser, J.C.; Greiner, S.P.; Lewis, R.M.; Notter, D.R. Validation of live animal ultrasonic measurements of body composition in market lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stelzleni, A.M.; Perkins, T.L.; Brown AHJr Pohlman, F.W.; Johnson, Z.B.; Sandelin, B.A. Genetic parameter estimates of yearling live animal ultrasonic measurements in Brangus cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 3150–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosworth, B.G.; Holland, M.; Brazil, B.L. Evaluation of ultrasound imagery and body shape to predict carcass and fillet yield in farm-raised catfish. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, U.; Murugan, K.; Panneerselvam, C.; Rajaganesh, R.; Roni, M.; Aziz, A.T.; Al-Aoh, H.A.N.; Trivedi, S.; Rehman, H.; Kumar, S.; et al. Suaeda maritima-based herbal coils and green nanoparticles as potential biopesticides against the dengue vector Aedes aegypti and the tobacco cutworm Spodoptera litura. Physiol. Mol. Plant. Path. 2018, 101, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Frings, H. Pest control with sound waves; Ultrasonics as a possibility in the future of rodent and insect control. Pest. Control. 1948, 16, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Mankin, R.W. Applications of acoustics in insect pest management. CAB Rev. 2012, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohankumar, D. Ultrasound and Insects. 2010. Available online: http://www.electroschematics.com/3864/ultrasound-and-insects/ (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Fredregill, C.L.; Motl, G.C.; Dennett, J.A.; Bueno, R.; Debboun, M. Efficacy of two larvasonic units against Culex larvae and effects on common aquatic non-target organisms in Harris County, Texas. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 2015, 31, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, S.M.; Osmani, M.H.; Ahmad, H.S. Effect of ultrasonic waves on the hatching of Aedes aegypti eggs at a frequency of 0.5 mc./s. J. Econ. Entomol. 1963, 56, 668–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britch, S.C.; Nyberg, H.; Aldridge, R.L.; Swan, T.; Linthicum, K. Acoustic control of mosquito larvae in artificial drinking water containers. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 2016, 32, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, W.A.; Lutes, K.L. Tests of ultrasonic emissions on mosquito attraction to hosts in a flight chamber. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 1985, 1, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashush, H.; Rozenszajn, L.A.; Blass, M.; Barda-Saad, M.; Azimov, D.; Radnay, J.; Zipori, D.; Rosenschein, U. Apoptosis induction of human myeloid leukemic cell by ultrasound exposure. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lagneaux, L.; de Meulenaer, E.C.; Delforge, A.; Dejeneffe, M.; Massy, M.; Moerman, C.; Hannecart, B.; Canivet, Y.; Lepeltier, M.F.; Bron, D. Ultrasonic low-energy treatment: A novel approach to induce apoptosis in human leukemic cells. Exp. Hematol. 2002, 30, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.M.; Wan, M.X.; Lu, M.Z.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, L. The alteration of protein profile of Walker 256 carinosarcoma cells during the apoptotic process induced by ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2005, 31, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehier-Humbert, S.; Guy, R.H. Physical methods for gene transfer: Improving the kinetics of gene delivery into cells. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanker, R.; Kumar, R.; Hwang, J.S. How effective are Mesocyclops aspericornis (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) in controlling mosquito immatures in the environment with an application of phytochemicals? Hydrobiologia 2013, 716, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Wu, C.H.; Tsai, K.H.; King, C.-C.; Hwang, J.S. How does ambush predatory copepod Megacyclops formosanus (Harada 1931) capture mosquito larvae, Aedes aegypti? Zool. Stud. 2012, 51, 927–936. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Molinero, J.C.; Wu, C.-H.; Tsai, K.-H.; King, C.-C.; Hwang, J.-S. Behavioral changes in mosquito larvae induced by copepod predation. Hydrobiologia 2015, 749, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Wu, Q.Y.; Hao, H.W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M. Effect of 1.7 MHz ultrasound on a gas-vacuolate cyanobacterium and a gas-vacuole negative cyanobacterium. Coll. Surf. B Biointer. 2004, 36, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, B. Ultrasonic damages on cyanobacterial photosynthesis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2006, 13, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Chen, Y.; Hao, H.; Wu, M.; Wang, B.; Lv, H.; Zhang, G. Influence of ultrasonic field on microcystins produced by bloom-forming algae. Coll. Surf. B. 2005, 41, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donskoy, D.M.; Ludiyanskiy, M.L. Low frequency sound as a control measure for zebra mussel fouling. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Zebra Mussel and Other Aquatic Nuisance Organisms Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 14–21 February 1995; pp. 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sueur, J.; Mackie, D.; Windmill, J.F.C. So small, so loud: Extremely high sound pressure level from a pygmy aquatic insect (Corixidae, Micronectinae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uteshev, V.K.; Pashovkin, T.N.; Sevirov, A.N.; Mel′nikova, E.V.; Sadikova, D.G.; Karnaukhov, V.N.; Gakhova, E.N. The survival of amphibian embryos after continuous ultrasonic treatment. Biofizika 2006, 51, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Wu, C.H.; Hwang, J.S. Diving as an anti-predator behavior in mosquito pupae. Zool. Stud. 2012, 51, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar]
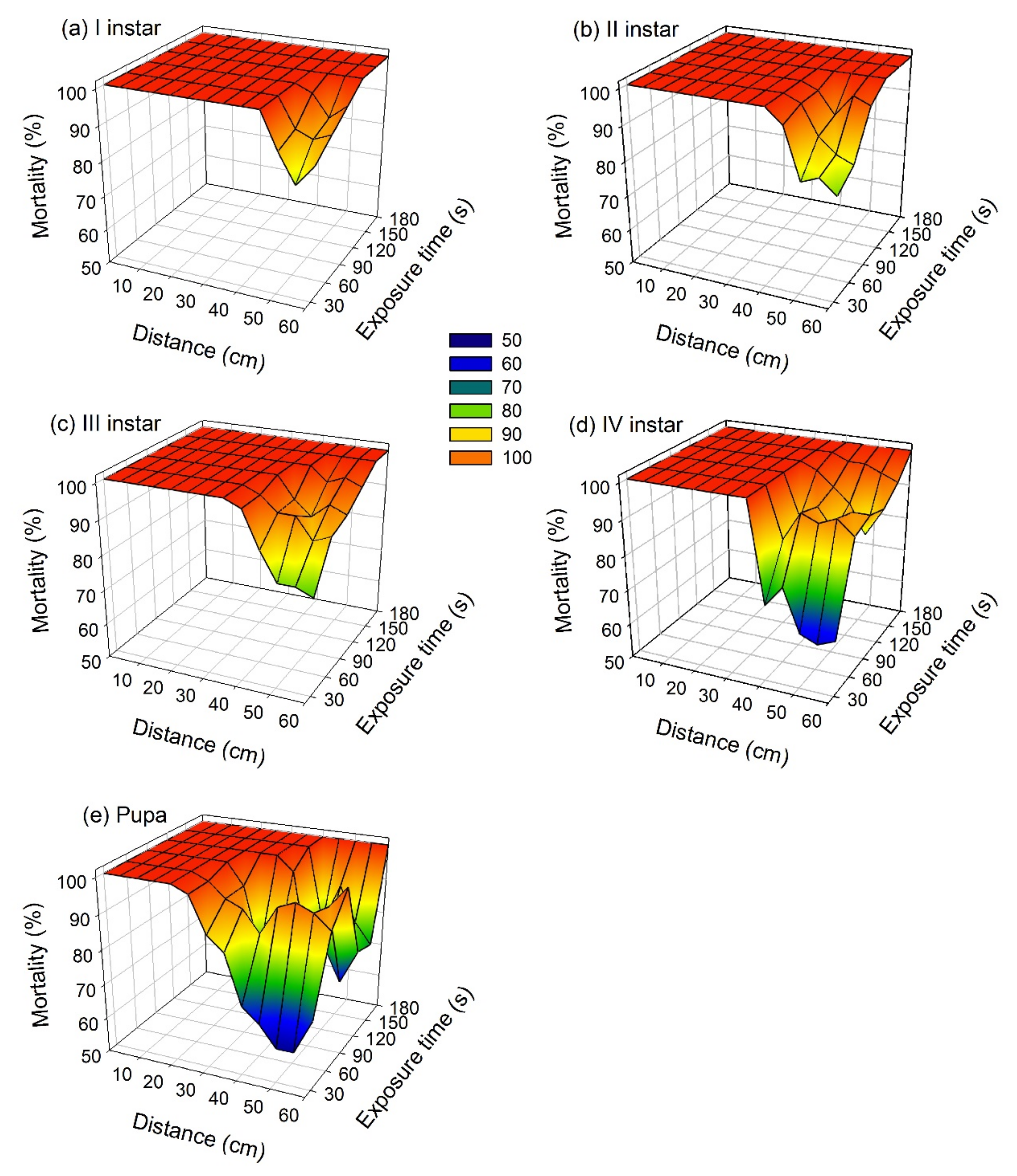
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | d.f. | Mean Square | F | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I instar larva | |||||
| Distance (cm) | 0.99 | 12 | 0.08 | 18.24 | <0.001 |
| Time (s) | 0.35 | 5 | 0.07 | 15.36 | <0.001 |
| Distance (cm) × Time (s) | 1.23 | 60 | 0.02 | 4.54 | <0.001 |
| Error | 1.41 | 312 | <0.01 | ||
| II instar larva | |||||
| Distance (cm) | 1.66 | 12 | 0.14 | 47.86 | <0.001 |
| Time (s) | 0.76 | 5 | 0.15 | 52.79 | <0.001 |
| Distance (cm) × Time (s) | 2.27 | 60 | 0.04 | 13.09 | <0.001 |
| Error | 0.90 | 312 | < 0.01 | ||
| III instar larva | |||||
| Distance (cm) | 2.29 | 12 | 0.19 | 37.74 | <0.001 |
| Time (s) | 0.98 | 5 | 0.20 | 38.81 | <0.001 |
| Distance (cm) × Time (s) | 2.16 | 60 | 0.04 | 7.15 | <0.001 |
| Error | 1.57 | 312 | 0.01 | ||
| IV instar larva | |||||
| Distance (cm) | 5.69 | 12 | 0.47 | 68.03 | <0.001 |
| Time (s) | 1.94 | 5 | 0.39 | 55.75 | <0.001 |
| Distance (cm) × Time (s) | 3.67 | 60 | 0.06 | 8.78 | <0.001 |
| Error | 2.17 | 312 | 0.01 | ||
| Pupa | |||||
| Distance (cm) | 9.06 | 12 | 0.76 | 24.30 | <0.001 |
| Time (s) | 3.21 | 5 | 0.64 | 20.64 | <0.001 |
| Distance (cm) × Time (s) | 6.11 | 60 | 0.10 | 3.27 | <0.001 |
| Error | 9.70 | 312 | 0.03 | ||
| Treatment Group and Fitted Model |
|---|
| I instar larva |
| ŷ = 98.95 − 0.074 (Dist.) + 0.021 (ET) |
| (0.53) (0.010) (0.004) |
| II instar larva |
| ŷ = 98.31 − 0.104 (Dist.) + 0.032 (ET) |
| (0.59) (0.011) (0.004) |
| III instar larva |
| ŷ = 98.01 − 0.129 (Dist.) + 0.037 (ET) |
| (0.62) (0.012) (0.004) |
| IV instar larva |
| ŷ = 96.46 − 0.235 (Dist.) + 0.063 (ET) |
| (1.00) (0.019) (0.007) |
| Pupa |
| ŷ = 96.60 − 0.377 (Dist.) + 0.070 (ET) |
| (2.08) (0.040) (0.015) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalimuthu, K.; Tseng, L.-C.; Murugan, K.; Panneerselvam, C.; Aziz, A.T.; Benelli, G.; Hwang, J.-S. Ultrasonic Technology Applied against Mosquito Larvae. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103546
Kalimuthu K, Tseng L-C, Murugan K, Panneerselvam C, Aziz AT, Benelli G, Hwang J-S. Ultrasonic Technology Applied against Mosquito Larvae. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103546
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalimuthu, Kandasamy, Li-Chun Tseng, Kadarkarai Murugan, Chellasamy Panneerselvam, Al Thabiani Aziz, Giovanni Benelli, and Jiang-Shiou Hwang. 2020. "Ultrasonic Technology Applied against Mosquito Larvae" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103546
APA StyleKalimuthu, K., Tseng, L.-C., Murugan, K., Panneerselvam, C., Aziz, A. T., Benelli, G., & Hwang, J.-S. (2020). Ultrasonic Technology Applied against Mosquito Larvae. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103546







