Neural Approximation Enhanced Predictive Tracking Control of a Novel Designed Four-Wheeled Rollator
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To facilitate close to the requirements of the elderly or disabled users for assisted walking, according to the Kano and QFD model, a four-wheeled rollator that meets the travel needs of the elderly are innovatively designed by TRIZ theory.
- At the same time, the radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) approximation-based trajectory tracking control system is created to realize the high safety conditions of the assistant elderly walker system.
- The comparative tracking performance using classical MPC and the proposed neural-based model predictive control (NMPC) method is discussed, presenting availability for the users to move carefully and stably.
2. Novel Industrial Design for the Rollator
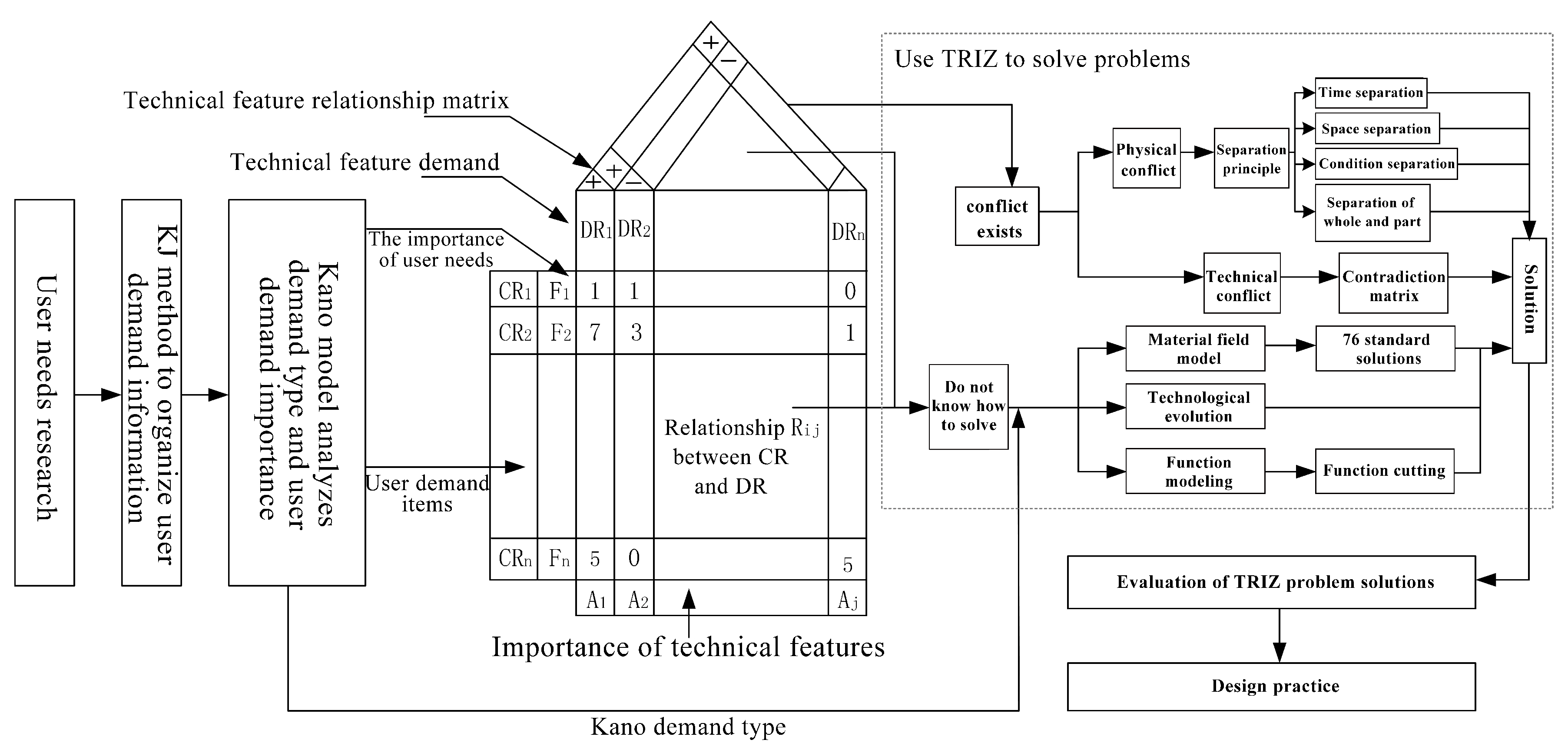
2.1. Product Innovation Model
- User interviews such as interviews and observations to conduct the needs research.
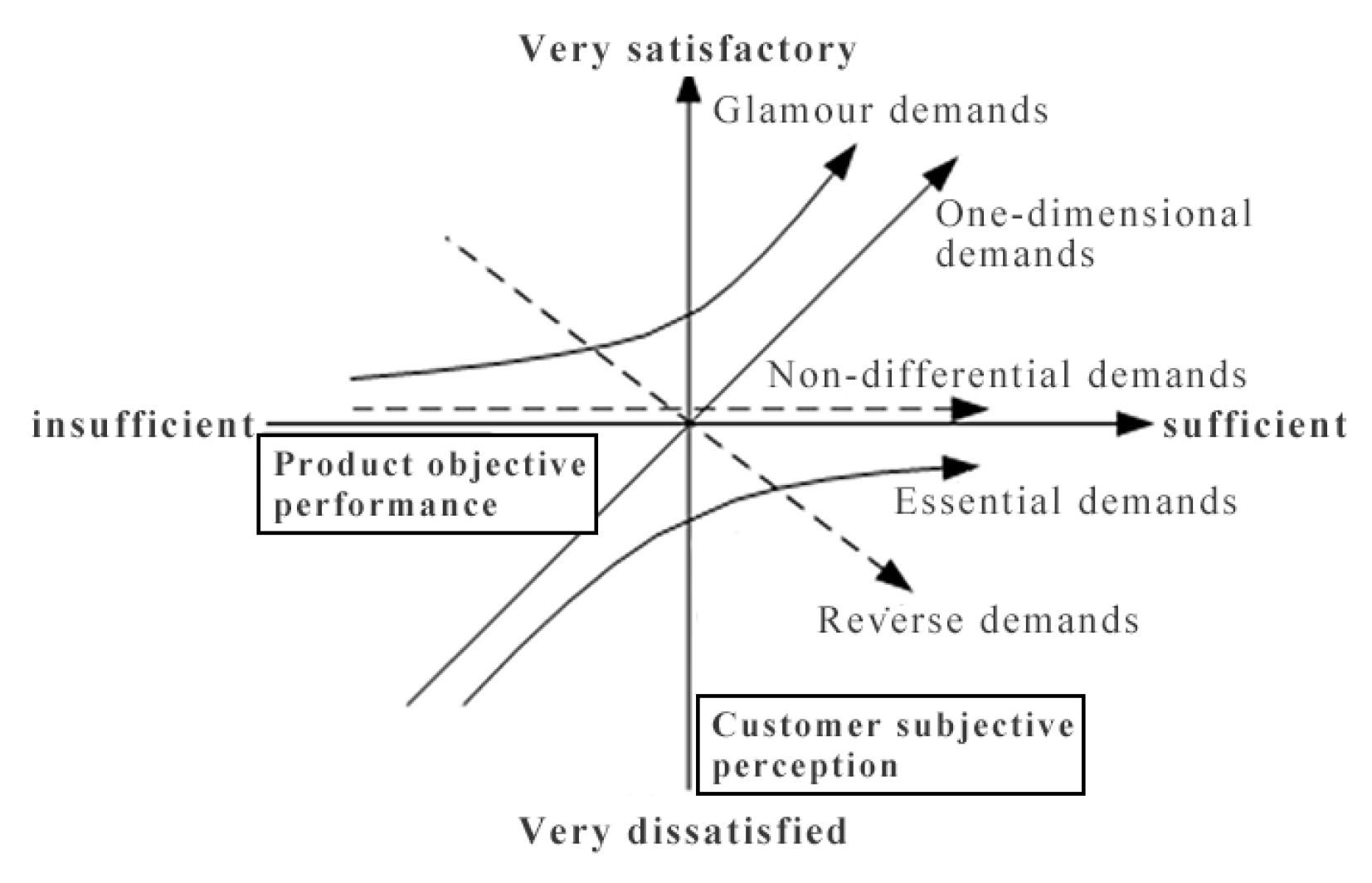
- The Kano model for user needs analysis.
- A quality house to convert user needs into technical features.
- TRIZ tool to solve product innovation.
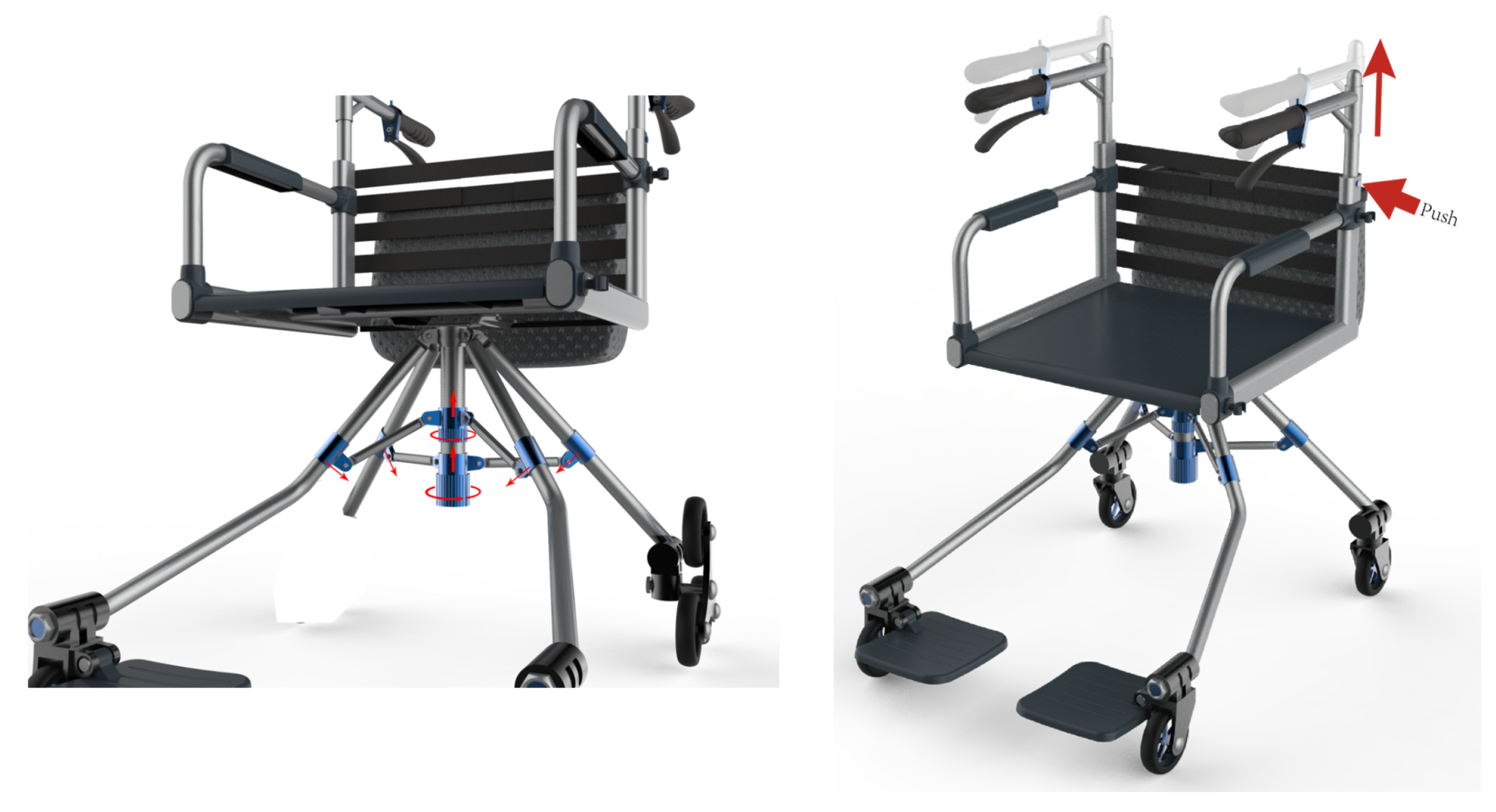
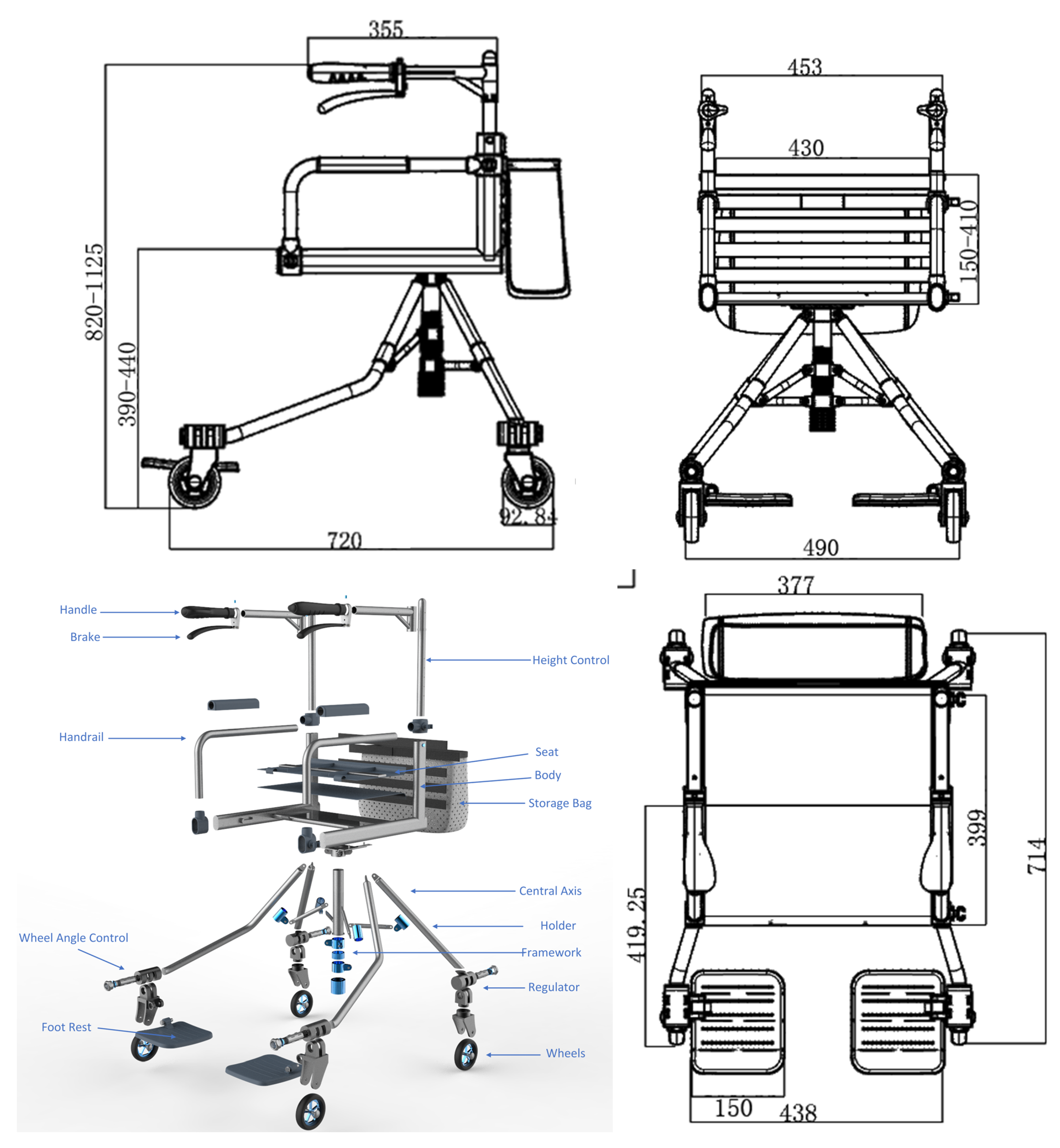
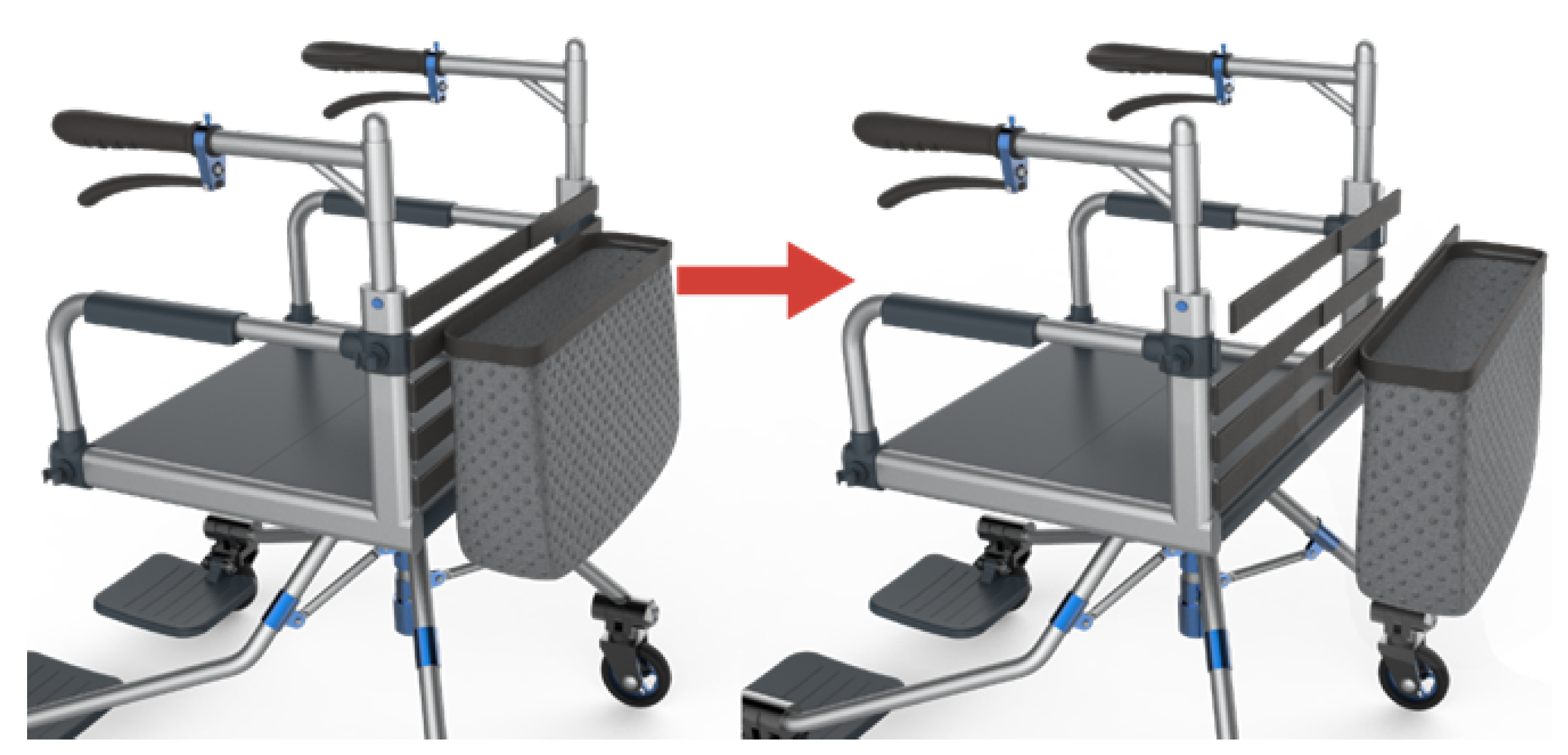
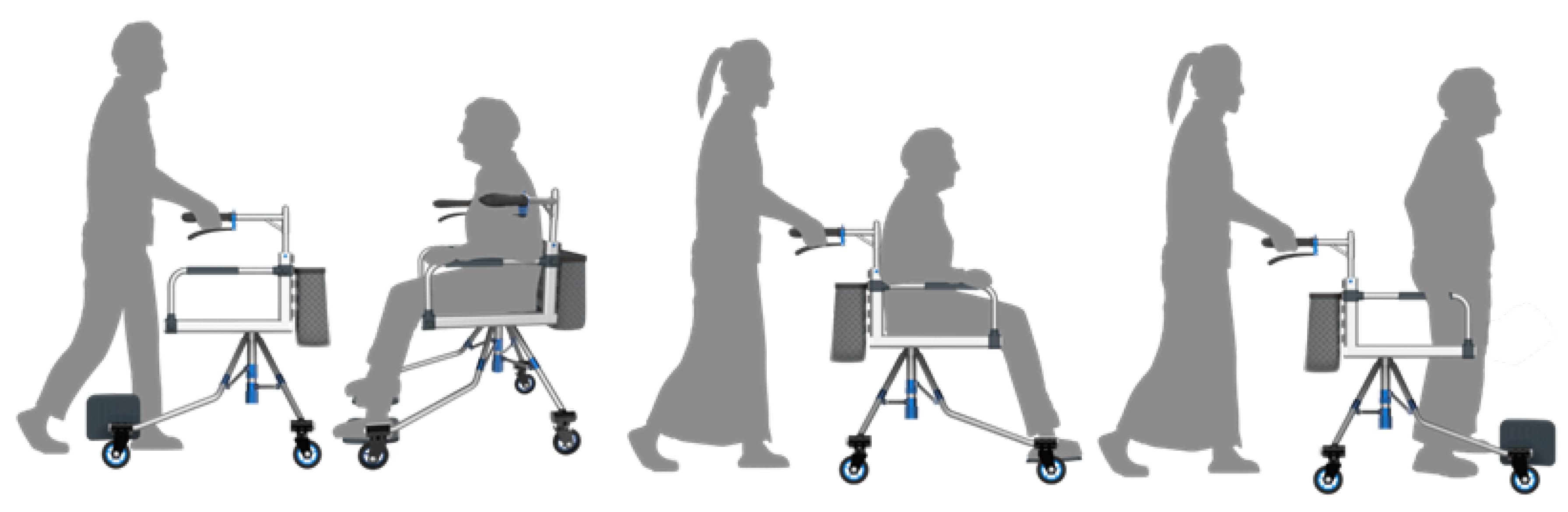
2.2. The Mechanical Design of Elderly Rollator Based on an Industrial Innovation Method
3. Predictive Controller Design of the Rollator Based on Neural Approximation
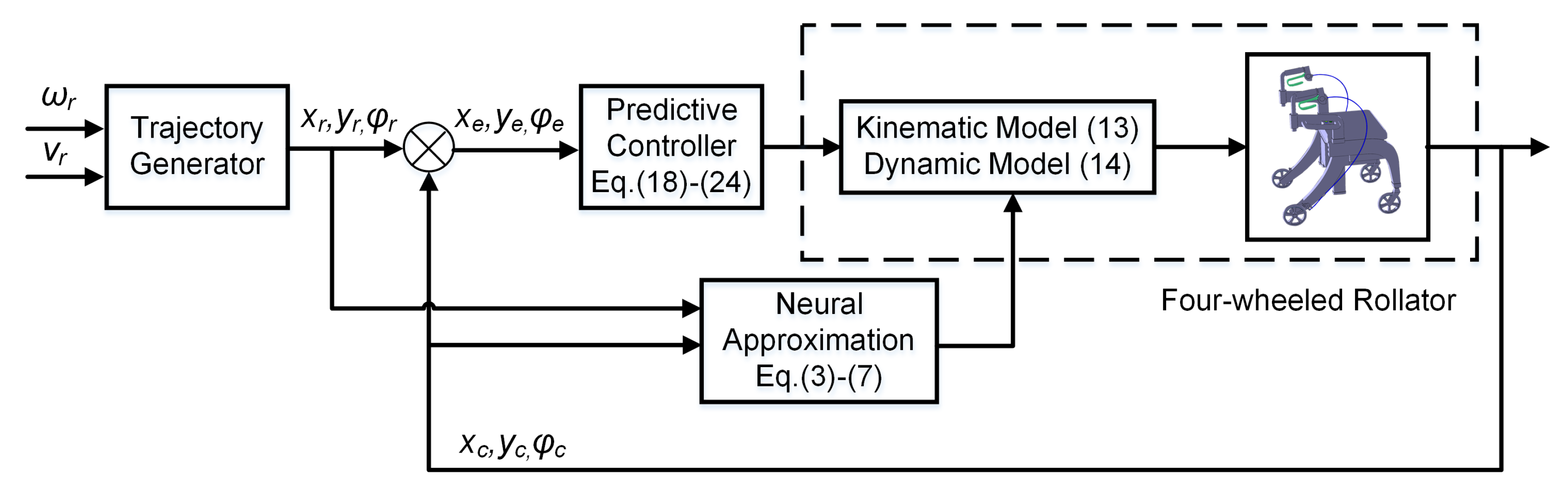
3.1. Neural Approximation
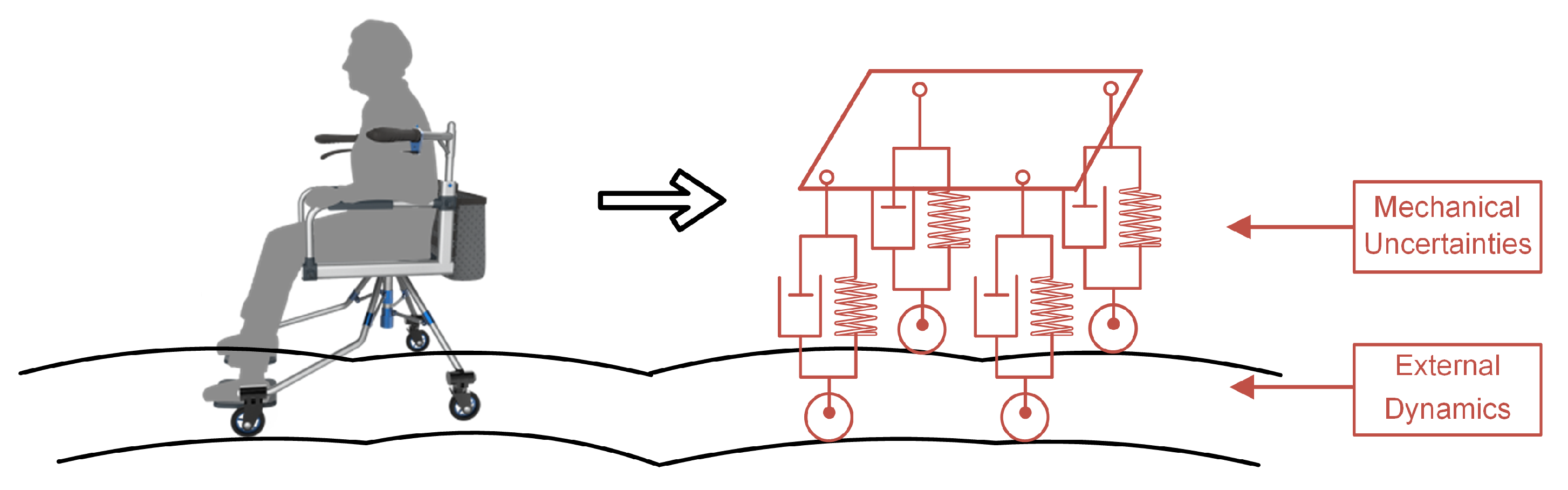
3.2. The State Model of the Elderly Rollator
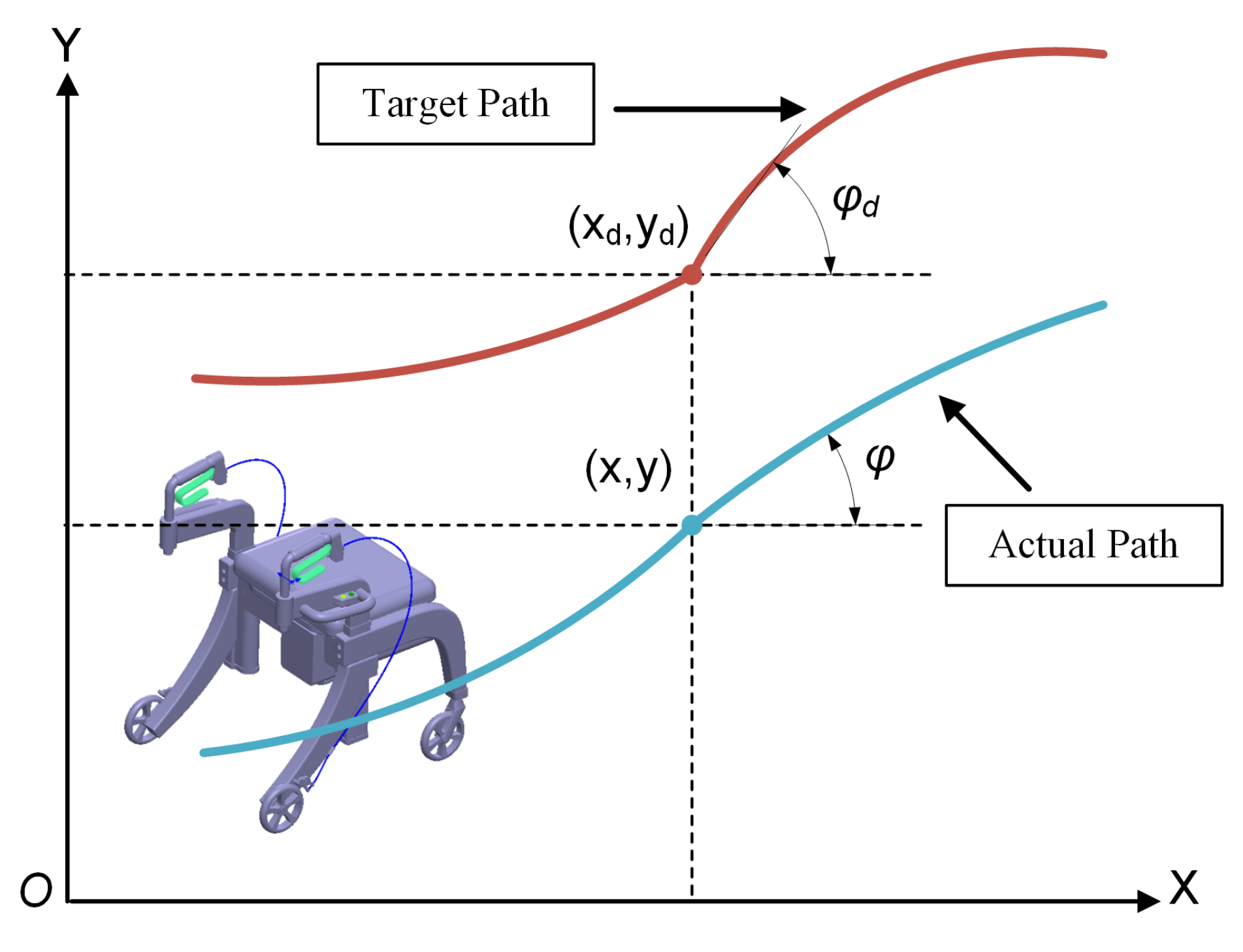
3.3. Predictive Controller Development
4. Results and Discussion
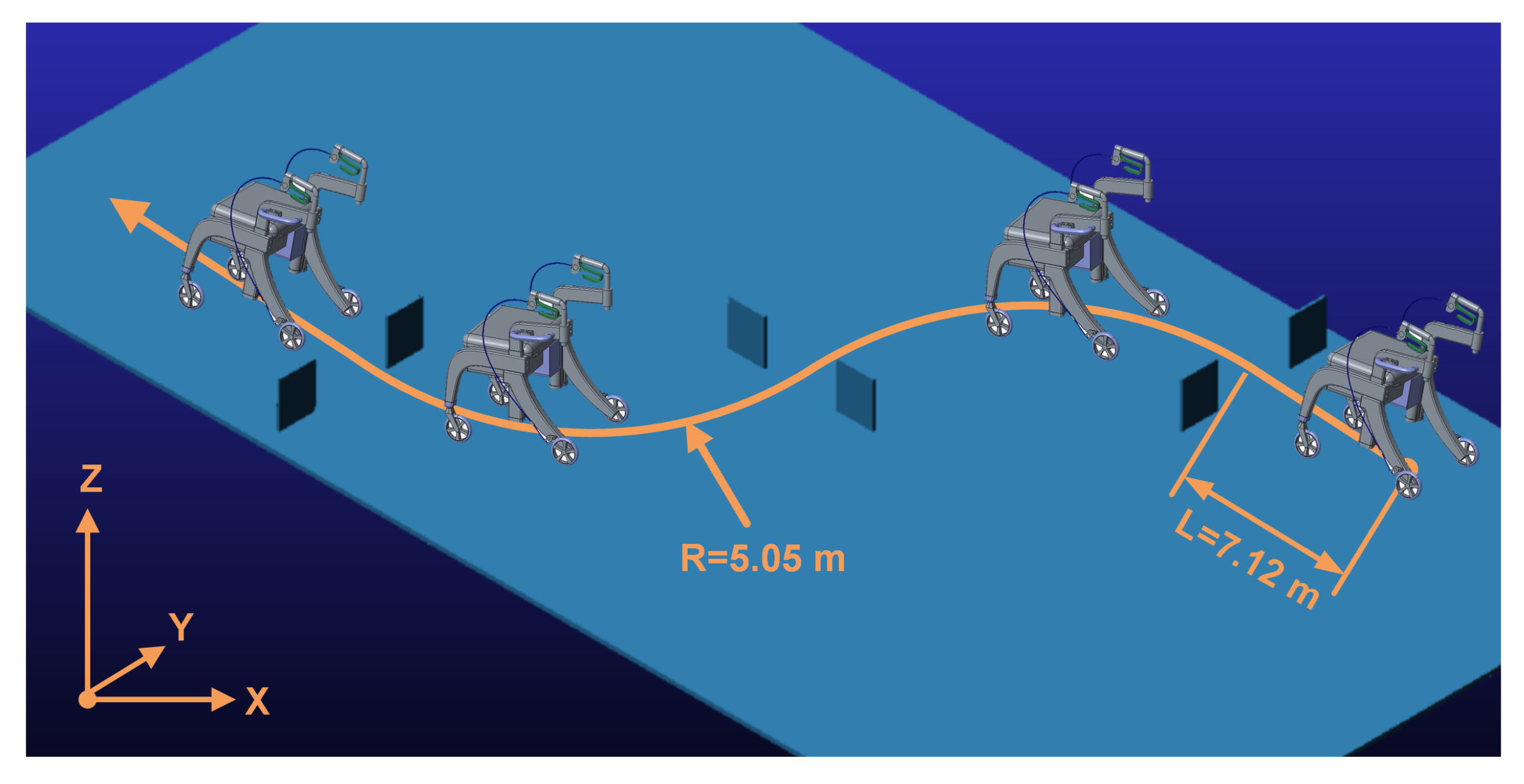
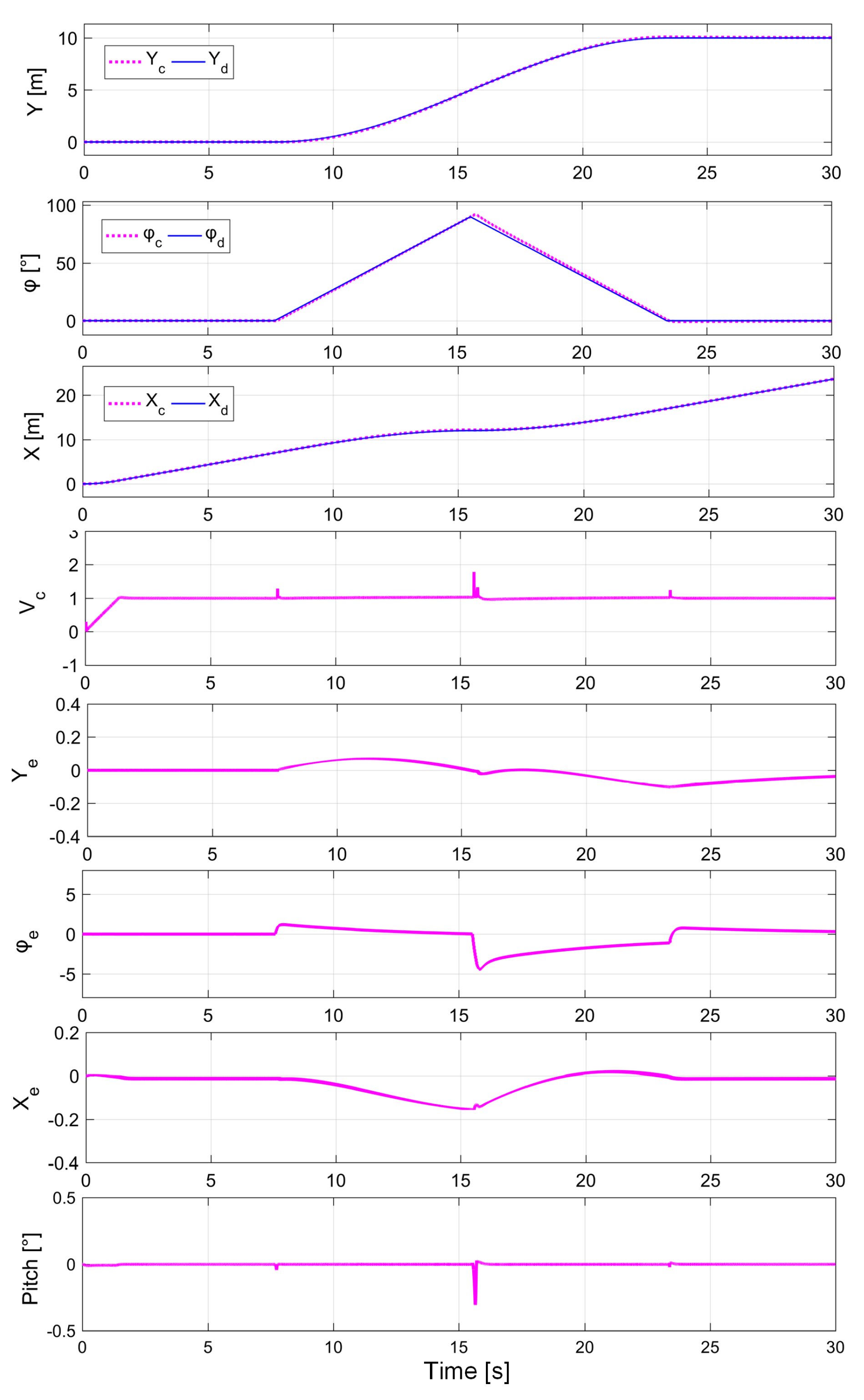
- Trajectory tracking co-simulation of the elderly rollator, including straight lines, curves, and obstacles, is intended to illustrate the position accuracy and robustness of the proposed NMPC algorithm.
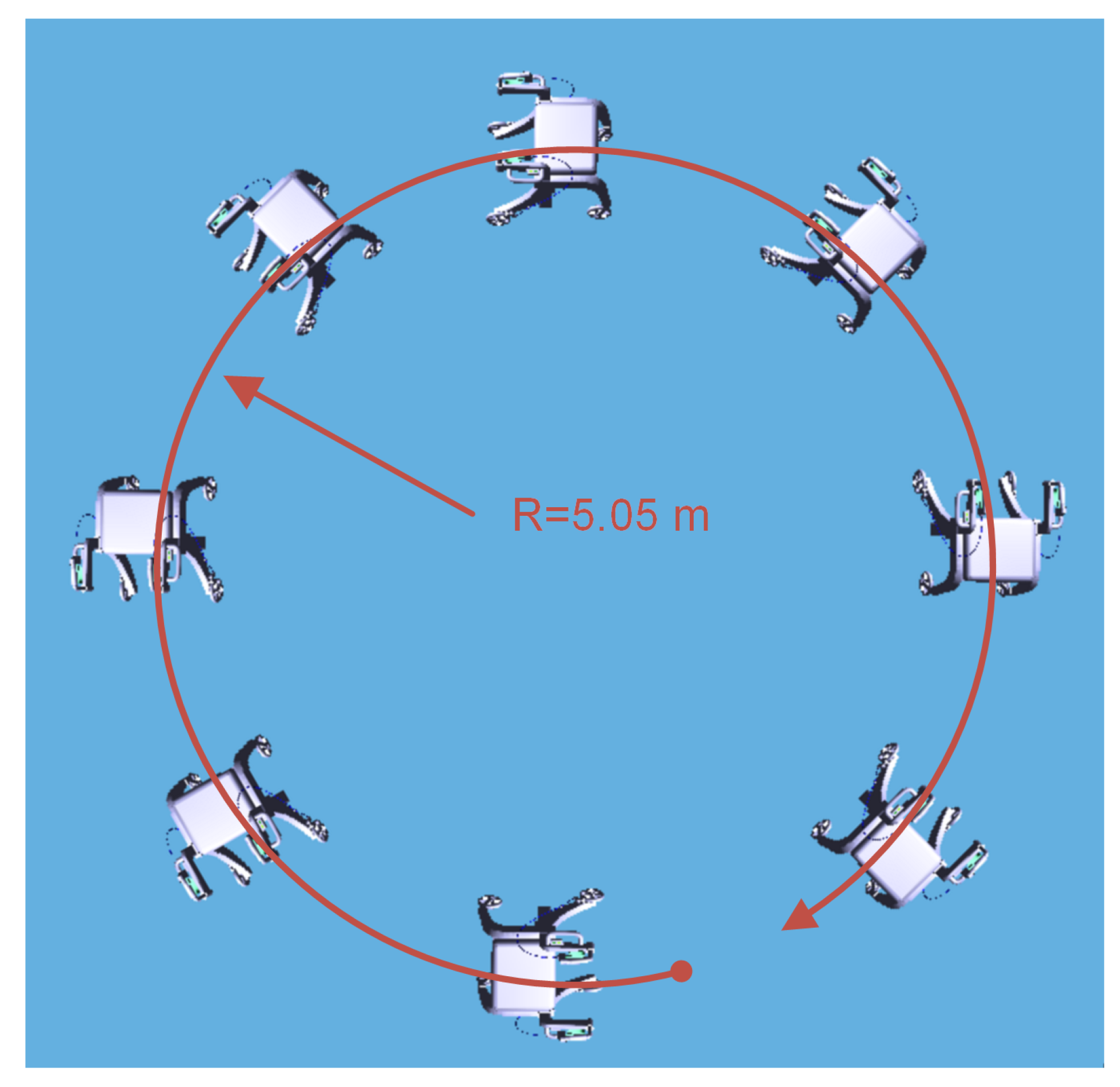
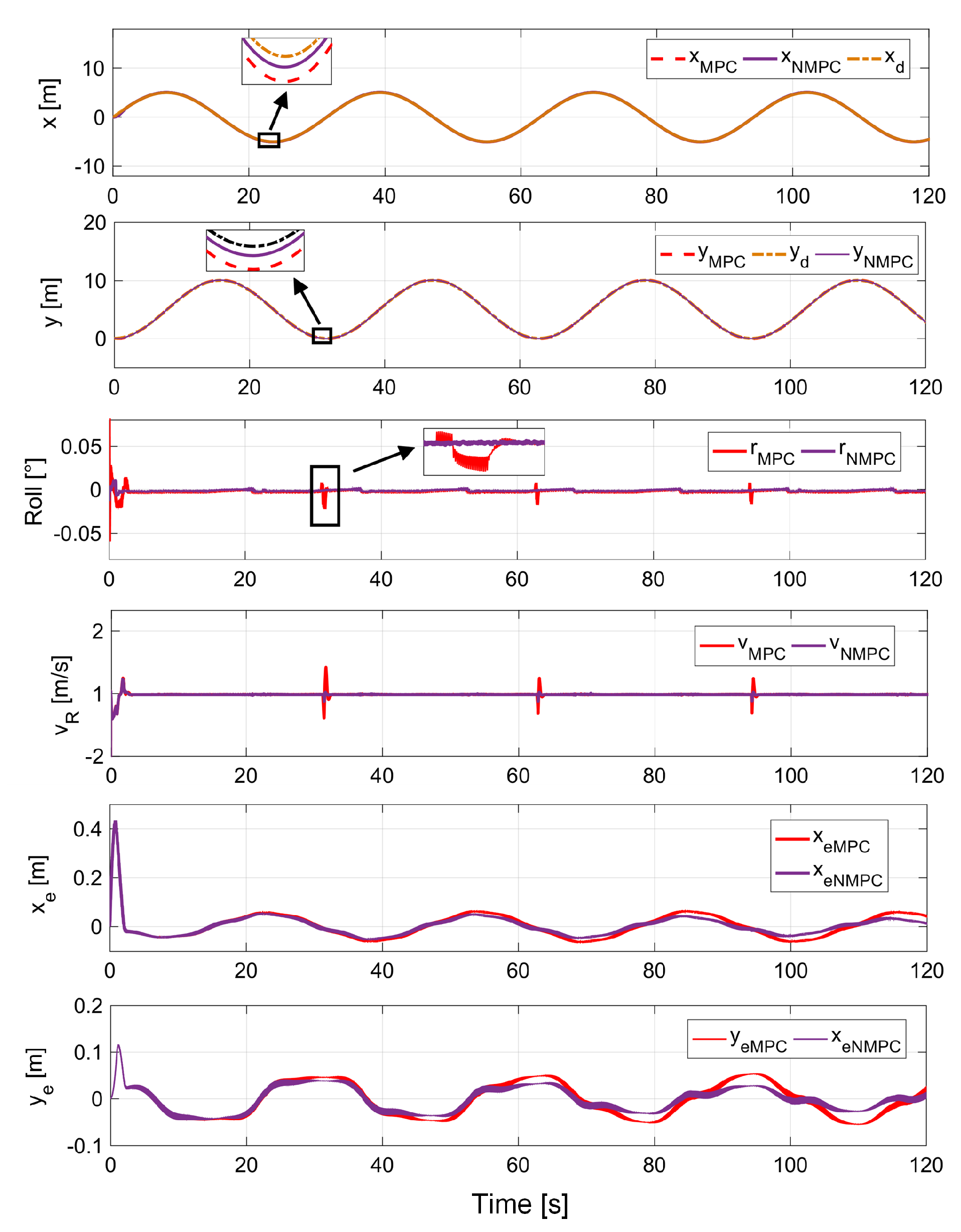
- To further demonstrate the advantage of NMPC in uncertain disturbances for the assistive elderly walker, including internal mechanical friction and external rollator and human interaction forces, a contrast experiment using NMPC and MPC related to previous work [35], is discussed for the circular path.
5. Conclusions
6. Points for Future Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| RBFNN | Radial Basis Function Neural Network |
| TRIZ | Theory of Inventive Problem Solving |
| QFD | Quality Function Deployment |
| HOQ | House of Quality |
| PID | Proportion Integration Differentiation |
References
- Li, Z.; Xiao, S.; Ge, S.S.; Su, H. Constrained multilegged robot system modeling and fuzzy control with uncertain kinematics and dynamics incorporating foot force optimization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2015, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, C.Y.; Li, G.; Su, H. Fuzzy approximation-based adaptive backstepping control of an exoskeleton for human upper limbs. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 23, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Q.; Yu, L.; Xu, W.; Li, F. Paralleling voltage oscillation forecast method of energy device based on hysteresis curve equation. J. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, C.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. Improved Human–Robot Collaborative Control of Redundant Robot for Teleoperated Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Ye, Z.; Deng, M.; Yang, C. Physical Human–Robot Interaction of a Robotic Exoskeleton By Admittance Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9614–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, C. EMG-Based neural network control of an upper-limb power-assist exoskeleton robot. In International Symposium on Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Sandoval, J.; Makhdoomi, M.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. Safety-enhanced human-robot interaction control of redundant robot for teleoperated minimally invasive surgery. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 6611–6616. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Guo, Z.; Johansson, K.H.; Shi, L. Causality countermeasures for anomaly detection in cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 63, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D. Hands on Systematic Innovation; Citeseer: Kyoto, Japan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Yang, K.; Taguchi, S. Enhancing robust design with the aid of TRIZ and axiomatic design (Part I). In TRIZ Journal, October; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Borgianni, Y.; Matt, D.T. Axiomatic Design and TRIZ: Deficiencies of their Integrated Use and Future Opportunities. Procedia CIRP 2015, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Trappey, A.J. Service design for intelligent parking based on theory of inventive problem solving and service blueprint. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinodh, S.; Kamala, V.; Jayakrishna, K. Integration of ECQFD, TRIZ, and AHP for innovative and sustainable product development. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 2758–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, S.; Barattin, D. Exploiting TRIZ tools in interaction design. Procedia Eng. 2015, 131, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, C.; Cruz, C.; Ramirez, Y.; Kraslawski, A. Adaptation of TRIZ contradiction matrix for solving problems in process engineering. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 103, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pelt, A.; Hey, J. Using TRIZ and human-centered design for consumer product development. Procedia Eng. 2011, 9, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.C.; Le, V.H.; Kim, J.; Choi, E.; Kang, B.; Park, J.O.; Kim, C.S. Untethered robotic motion and rotating blade mechanism for actively locomotive biopsy capsule endoscope. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93364–93374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Yuan, P.; Yang, C.; Song, R. Development of sensory-motor fusion-based manipulation and grasping control for a robotic hand-eye system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2016, 47, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z. Cooperative Manipulation of Wearable Dual-Arm Exoskeletons Using Force Communication Between Partners. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Su, H.; Li, Z.; Ao, D.; Song, R. Adaptive control with a fuzzy tuner for cable-based rehabilitation robot. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2016, 14, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, B.; Ajoudani, A.; Yang, C.; Su, C.Y.; Bicchi, A. Asymmetric bimanual control of dual-arm exoskeletons for human-cooperative manipulations. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 34, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qi, W.; Hu, Y.; Sandoval, J.; Zhang, L.; Schmirander, Y.; Chen, G.; Aliverti, A.; Knoll, A.; Ferrigno, G.; et al. Towards Model-Free Tool Dynamic Identification and Calibration Using Multi-Layer Neural Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Kan, Z.; Gao, H. Reference Trajectory Reshaping Optimization and Control of Robotic Exoskeletons for Human-Robot Co-Manipulation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Deshpande, S.; Dassau, E.; Doyle, F.J., III. Feedback control algorithms for automated glucose management in T1DM: the state of the art. In The Artificial Pancreas; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, L.; Su, W.; Zhao, K.; Xu, C.; Huang, J.; Pi, M. Hybrid brain/muscle signals powered wearable walking exoskeleton enhancing motor ability in climbing stairs activity. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Zong, G. Fuzzy-approximation-based asymptotic tracking control for a class of uncertain switched nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Su, H.; Ye, W. Development of multi-fingered dexterous hand for grasping manipulation. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2014, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Fu, W.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z. The lateral tracking control for the intelligent vehicle based on adaptive PID neural network. Sensors 2017, 17, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Ou, L. A simulation of vehicle lateral stability based on fuzzy PID control. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, Zhangjiajie, China, 11–12 April 2009; Volume 2, pp. 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Wang, R. An adaptive fuzzy-sliding lateral control strategy of automated vehicles based on vision navigation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2013, 51, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Lu, S. Vehicle lateral stability control based on sliding mode control. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Jinan, China, 18–21 August 2007; pp. 638–642. [Google Scholar]
- Grondin, S.L.; Li, Q. Intelligent control of a smart walker and its performance evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, J.Y.; Gage, W.H.; Poupart, P.; McIlroy, W.E. Upper limb contributions to frontal plane balance control in rollator-assisted walking. Assist. Technol. 2014, 26, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkjær, T.; Larsen, P.K.; Pedersen, G.; Nielsen, L.H.; Simonsen, E.B. Biomechanical analysis of rollator walking. Biomed. Eng. Online 2006, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Qi, W.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Su, H.; Ferrigno, G.; Momi, E.D. Novel Design and Lateral Stability Tracking Control of a Four-Wheeled Rollator. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Su, H.; Zhang, L.; Miao, S.; Chen, G.; Knoll, A. Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for Mobile Robot Using Varying-Parameter Convergent Differential Neural Network. Robotics 2019, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Nguyen, P.B.; Kang, B.; Choi, E.; Park, J.O.; Kim, C.S. A novel tip-positioning control of a magnetically steerable guidewire in sharply curved blood vessel for percutaneous coronary intervention. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 2069–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumpouros, Y.; Karavasili, A.; Efthimiou, E.; Fotinea, S.E.; Goulas, T.; Vacalopoulou, A. User Evaluation of the MOBOT rollator type robotic mobility assistive device. Technologies 2017, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, X.S.; Tzafestas, C.S.; Maragos, P.; Pavlakos, G.; Chalvatzaki, G.; Moustris, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Peer, A.; Stanczyk, B.; Fotinea, E.S.; et al. Advances in intelligent mobility assistance robot integrating multimodal sensory processing. In International Conference on Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 692–703. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, Y.; Kang, Y.; Chen, C.P. Adaptive neural control of a kinematically redundant exoskeleton robot using brain-machine interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yang, C.; Su, H.; Liu, C. A Robot Learning Method with Physiological Interface for Teleoperation Systems. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. Adaptive decoupling control of a serial redundant robot for teleoperated minimally invasive surgery. In IEEE ICRA Workshop on Supervised Autonomy in Surgical Robotics; IEEE: Brisbane, Australia, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Wei, Q.; Shi, C.; Su, C.Y. Human-Inspired Control of Dual-Arm Exoskeleton Robots With Force and Impedance Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotinea, S.E.; Efthimiou, E.; Koutsombogera, M.; Dimou, A.L.; Goulas, T.; Maragos, P.; Tzafestas, C. The MOBOT human-robot communication model. In Proceedings of the 2015 6th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (CogInfoCom), Gyor, Hungary, 19–21 October 2015; pp. 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Koumpouros, Y.; Toulias, T.L.; Koumpouros, N. The importance of patient engagement and the use of social media marketing in healthcare. Technol. Health Care 2015, 23, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Deng, C.; Zhao, K. Human Cooperative Control of a Wearable Walking Exoskeleton for Enhancing Climbing Stair Activities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Su, C.Y. Adaptive fuzzy control of operation space constrained exoskeletons under unmodelled dynamics. In Proceedings of the 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 29 June–4 July 2014; pp. 3277–3282. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Yang, C.; He, W.; Chen, C.P. Force sensorless admittance control with neural learning for robots with actuator saturation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, C. Adaptive neural network based variable stiffness control of uncertain robotic systems using disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Enayati, N.; Vantadori, L.; Spinoglio, A.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. Online human-like redundancy optimization for tele-operated anthropomorphic manipulators. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 15, 1729881418814695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.; Shi, D. Cooperative attitude control for a wheel-legged robot. In Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, J.; Su, H.; Vieyres, P.; Poisson, G.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. Collaborative framework for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery using a 7-DOF anthropomorphic robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 106, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, W. Model Predictive Control for Self-Driving Vehicles; Beijing Institute of Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L. Path tracking of automatic parking system based on sliding mode control. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 356–364. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Pan, Z.; Li, M.; Peng, H. A Lateral Control Method for Wheel-Footed Robot Based on Sliding Mode Control and Steering Prediction. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 58086–58095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Su, C.Y.; Deng, J.; Zhang, W. Vision-based model predictive control for steering of a nonholonomic mobile robot. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2015, 24, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.; Shi, D.; Huang, Y. Compound control for energy management of the hybrid ultracapacitor-battery electric drive systems. Energy 2019, 175, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiao, H.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y. Model Predictive Control of Nonholonomic Chained Systems Using General Projection Neural Networks Optimization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2015, 45, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Shi, Y.; Buckham, B. Trajectory Tracking Control of an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Using Lyapunov-Based Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5796–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S. Observer-based robust control of 6-DOF parallel electrical manipulator with fast friction estimation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Fan, K.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y. Neural Approximation Enhanced Predictive Tracking Control of a Novel Designed Four-Wheeled Rollator. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010125
Zhang X, Li J, Fan K, Chen Z, Hu Z, Yu Y. Neural Approximation Enhanced Predictive Tracking Control of a Novel Designed Four-Wheeled Rollator. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin, Jiehao Li, Ke Fan, Ziyang Chen, Zhenhuan Hu, and Yu Yu. 2020. "Neural Approximation Enhanced Predictive Tracking Control of a Novel Designed Four-Wheeled Rollator" Applied Sciences 10, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010125
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, J., Fan, K., Chen, Z., Hu, Z., & Yu, Y. (2020). Neural Approximation Enhanced Predictive Tracking Control of a Novel Designed Four-Wheeled Rollator. Applied Sciences, 10(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010125



